Adaptive IoT-Based Platform for CO2 Forecasting Using Generative Adversarial Networks: Enhancing Indoor Air Quality Management with Minimal Data †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Hardware Architecture and Data Acquisition
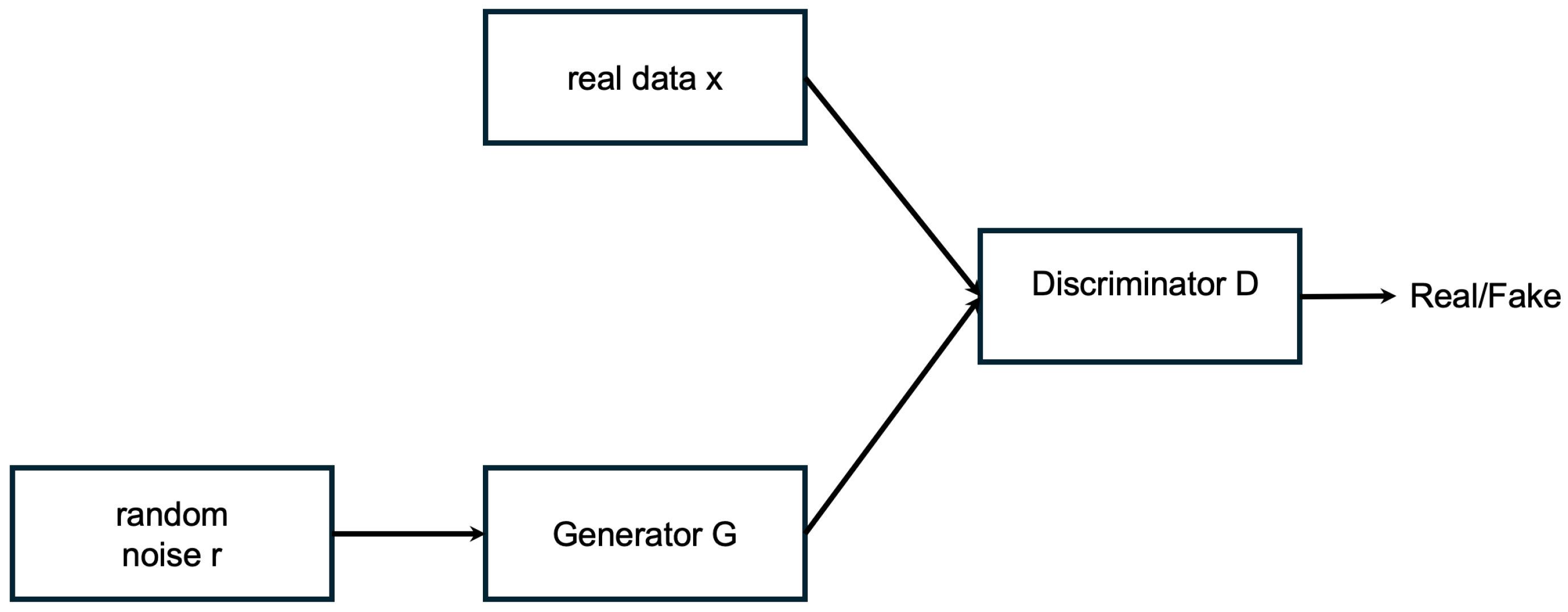
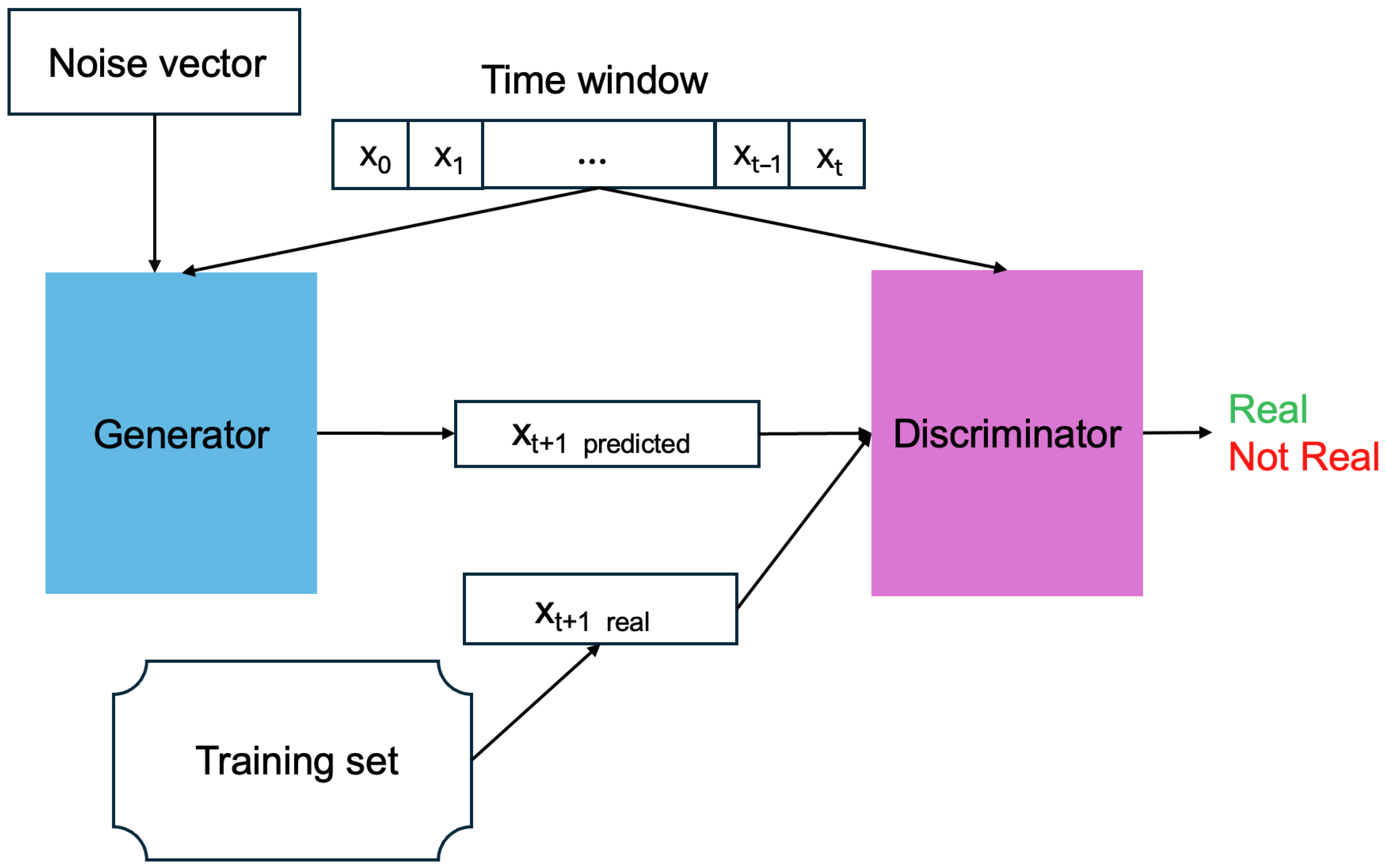
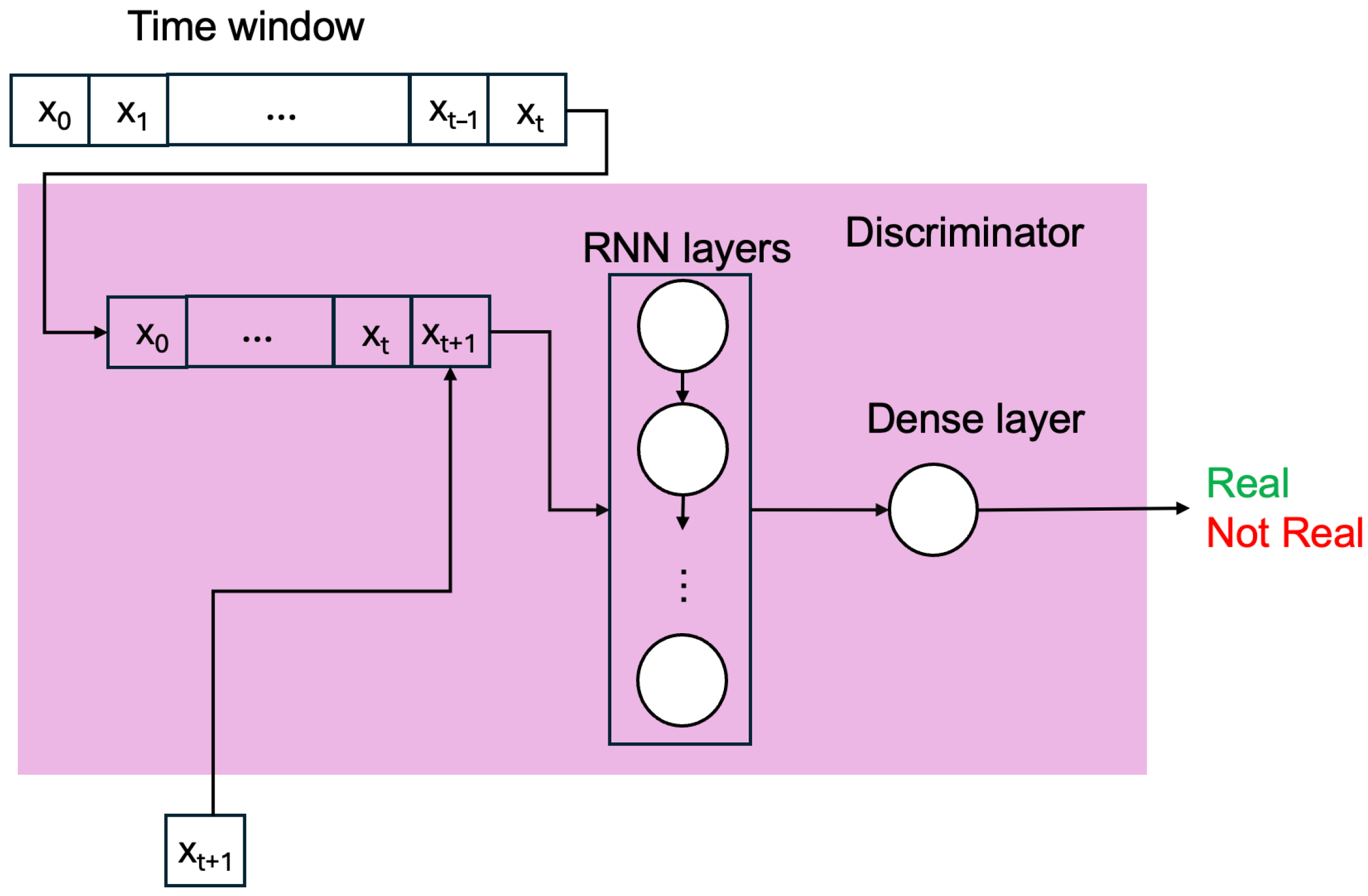
2.2. Methodology
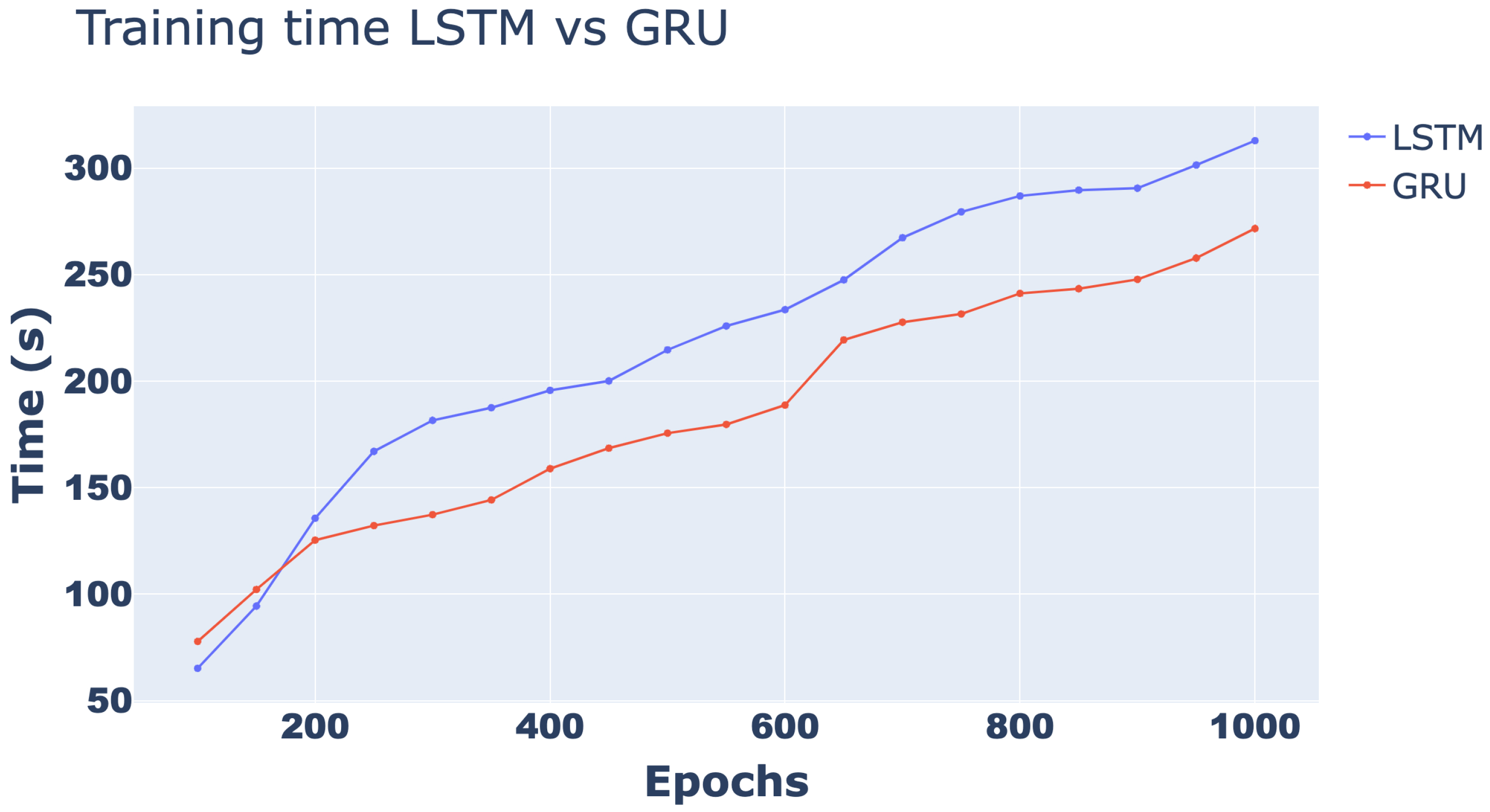
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marć, M.; Tobiszewski, M.; Zabiegała, B.; de la Guardia, M.; Namieśnik, J. Current air quality analytics and monitoring: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 853, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wu, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, X. Influence of PM1 exposure on total and cause-specific respiratory diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 15117–15126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chen, Y.; Lu, F.; Chen, L.; Dong, Z. The Association between Short-Term Exposure to PM1 and Daily Hospital Admission and Related Expenditures in Beijing. Toxics 2024, 12, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, S.; Iwamatsu, T.; Miura, T.; Tsutsumi, F.; Tanaka, N. Investigation of Indoor Air Quality in Residential Buildings by Measuring CO2 Concentration and a Questionnaire Survey. Sensors 2022, 22, 7331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azuma, K.; Kagi, N.; Yanagi, U.; Osawa, H. Effects of low-level inhalation exposure to carbon dioxide in indoor environments: A short review on human health and psychomotor performance. Environ. Int. 2018, 121, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apte, M.G.; Fisk, W.J.; Daisey, J.M. Association between indoor CO2 concentrations and Sick Building Syndrome in U.S. office buildings: An analysis of the 1994–1996 base study data. Indoor Air 2000, 10, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baudet, A.; Baurès, E.; Blanchard, O.; Le Cann, P.; Gangneux, J.P.; Florentin, A. Indoor Carbon Dioxide, Fine Particulate Matter and Total Volatile Organic Compounds in Private Healthcare and Elderly Care Facilities. Toxics 2022, 10, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folk, A.L.; Wagner, B.E.; Hahn, S.L.; Larson, N.; Barr-Anderson, D.J.; Neumark-Sztainer, D. Changes to Physical Activity during a Global Pandemic: A Mixed Methods Analysis among a Diverse Population-Based Sample of Emerging Adults in the US. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persily, A.; de Jonge, L. Carbon dioxide generation rates for building occupants. Indoor Air 2017, 27, 868–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Ramalho, O.; Malingre, L.; Sivanantham, S.; Little, J.C.; Mandin, C. Machine learning and statistical models for predicting indoor air quality. Indoor Air 2019, 29, 704–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candanedo, L.M.; Feldheim, V. Accurate occupancy detection of an office room from light, temperature, humidity and CO2 measurements using statistical learning models. Energy Build 2016, 112, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaei, B.; Shiehbeigi, A.; Kani, A.H.M.A. Modeling indoor air carbon dioxide concentration using artificial neural network. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 16, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.; Shin, D.; Kim, K.; Yang, J. Indoor air quality analysis using deep learning with sensor data. Sensors 2017, 17, 2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallio, J.; Tervonen, J.; Räsänen, P.; Mäkynen, R.; Koivusaari, J.; Peltola, J. Forecasting office indoor CO2 concentration using machine learning with a one-year dataset. Build. Environ. 2021, 187, 107409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putra, J.C.P.; Safrilah; Ihsan, M. The prediction of indoor air quality in office room using artificial neural network. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Engineering, Technology, and Industrial Application (ICETIA), Surakarta, Indonesia, 13–14 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Segala, G.; Doriguzzi-Corin, R.; Peroni, C.; Gazzini, T.; Siracusa, D. A Practical and Adaptive Approach to Predicting Indoor CO2. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rescio, G.; Manni, A.; Caroppo, A.; Carluccio, A.M.; Siciliano, P.; Leone, A. Multi-Sensor Platform for Predictive Air Quality Monitoring. Sensors 2023, 23, 5139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upsens, QuAir. Available online: https://www.upsens.com/quair (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- SMARTEX. Available online: https://www.smartex.it/ (accessed on 11 September 2025).
- Leone, A.; Rescio, G.; Diraco, G.; Manni, A.; Siciliano, P.; Caroppo, A. Ambient and Wearable Sensor Technologies for Energy Expenditure Quantification of Ageing Adults. Sensors 2022, 22, 4893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, A.; Rescio, G.; Caroppo, A.; Siciliano, P.; Manni, A. Human Postures Recognition by Accelerometer Sensor and ML Architecture Integrated in Embedded Platforms: Benchmarking and Performance Evaluation. Sensors 2023, 23, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, T.; KS, U.R.; Naik, S.M.; Panja, M.; Manvitha, B. Ten years of generative adversarial nets (GANs): A survey of the state-of-the-art. Mach. Learn. Sci. Technol. 2024, 5, 011001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, D.; Cao, J. Generative adversarial networks (GANs survey): Challenges, solutions, and future directions. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2005.00065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Yu, X.; Cheng, T. Multi-task Semantic Segmentation for Apolloscape based on CGAN. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1550, 032071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Liu, K.; Wang, S.; Lei, Y.; Li, J. CWM-CGAN Method for Renewable Energy Scenario Generation Based on Weather Label Multi-Factor Definition. Processes 2022, 10, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.; Horne, B.G.; Tino, P.; Giles, C.L. Learning long-term dependencies in NARX recurrent neural networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1996, 7, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


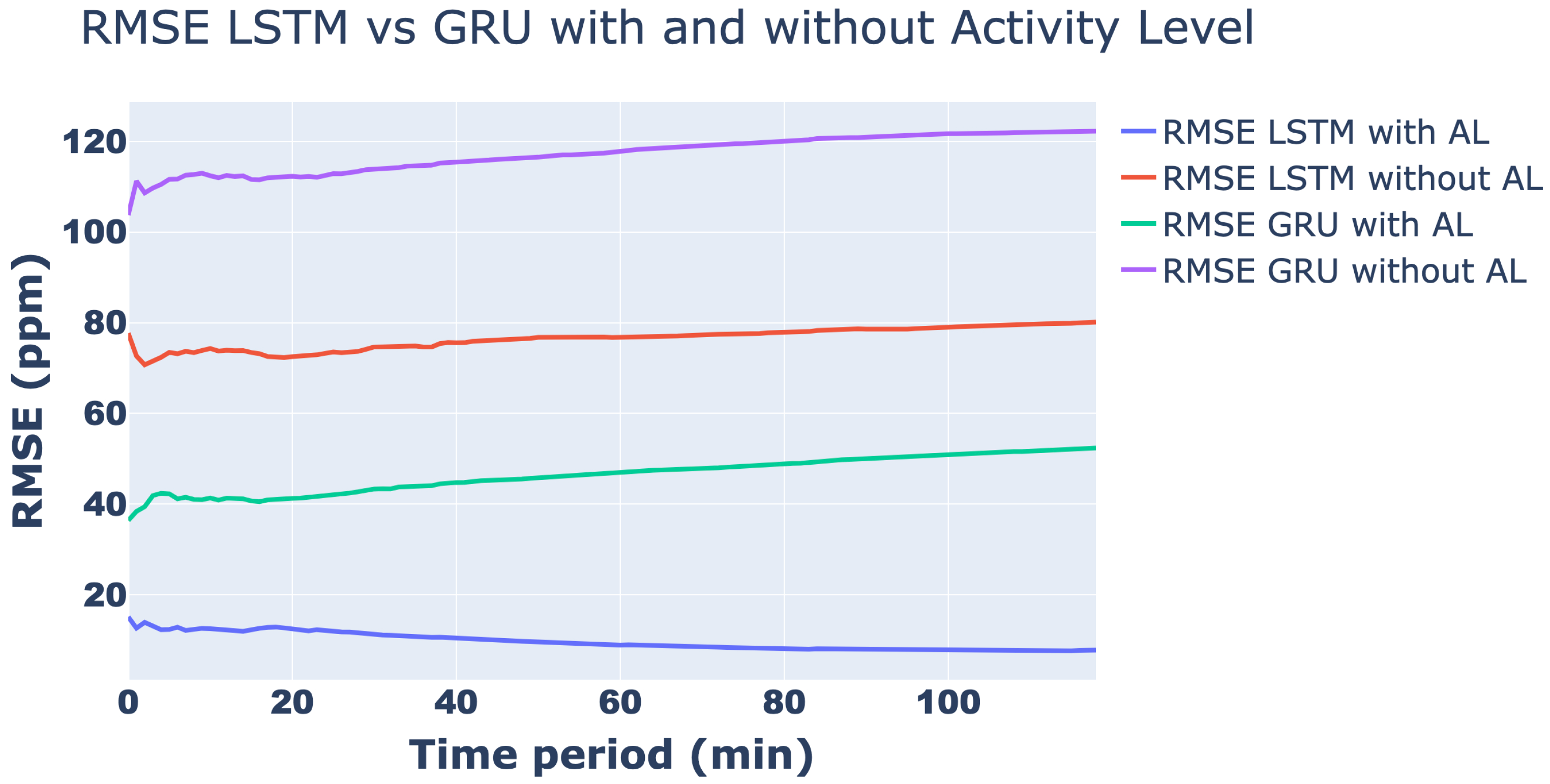
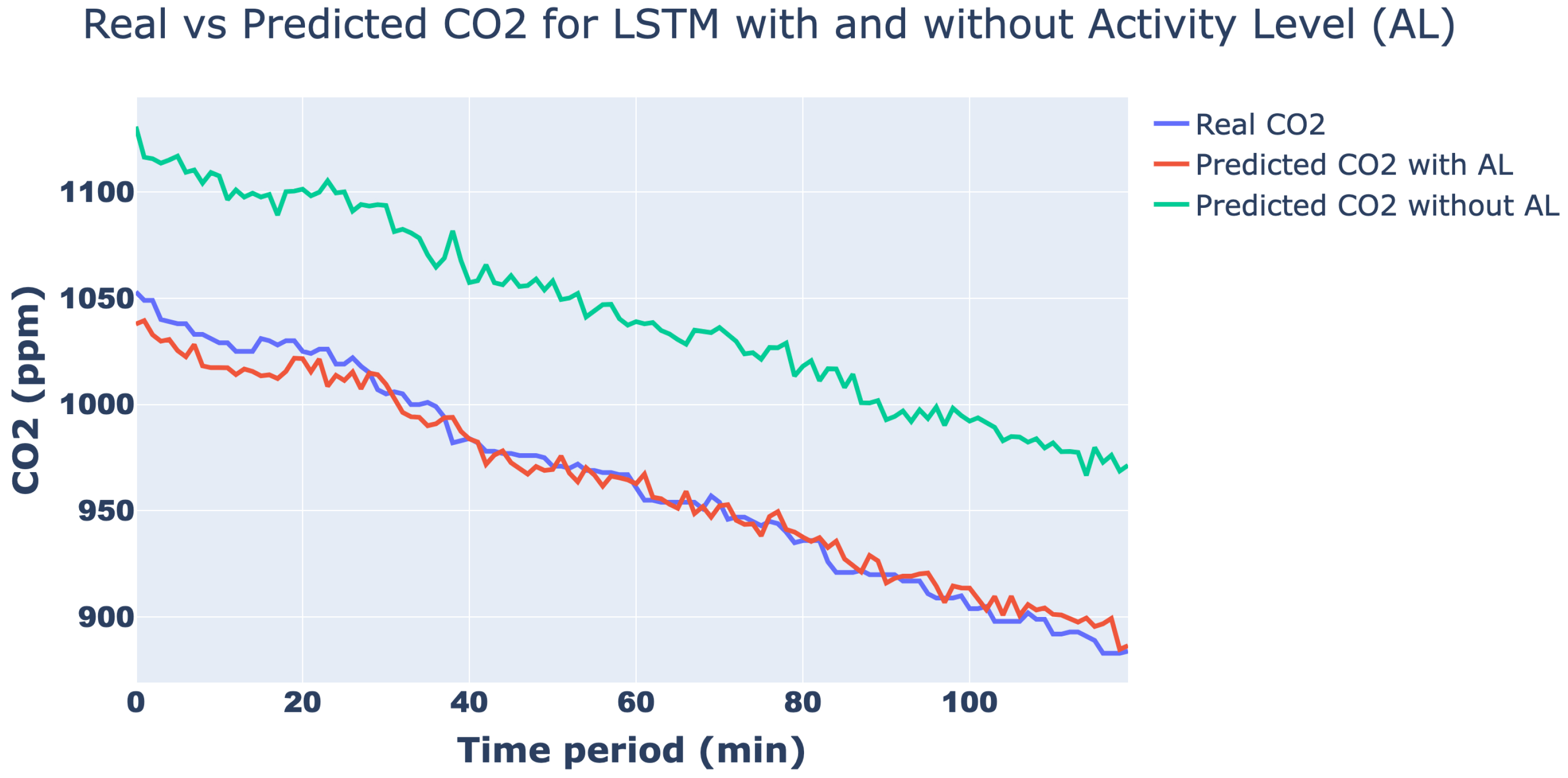
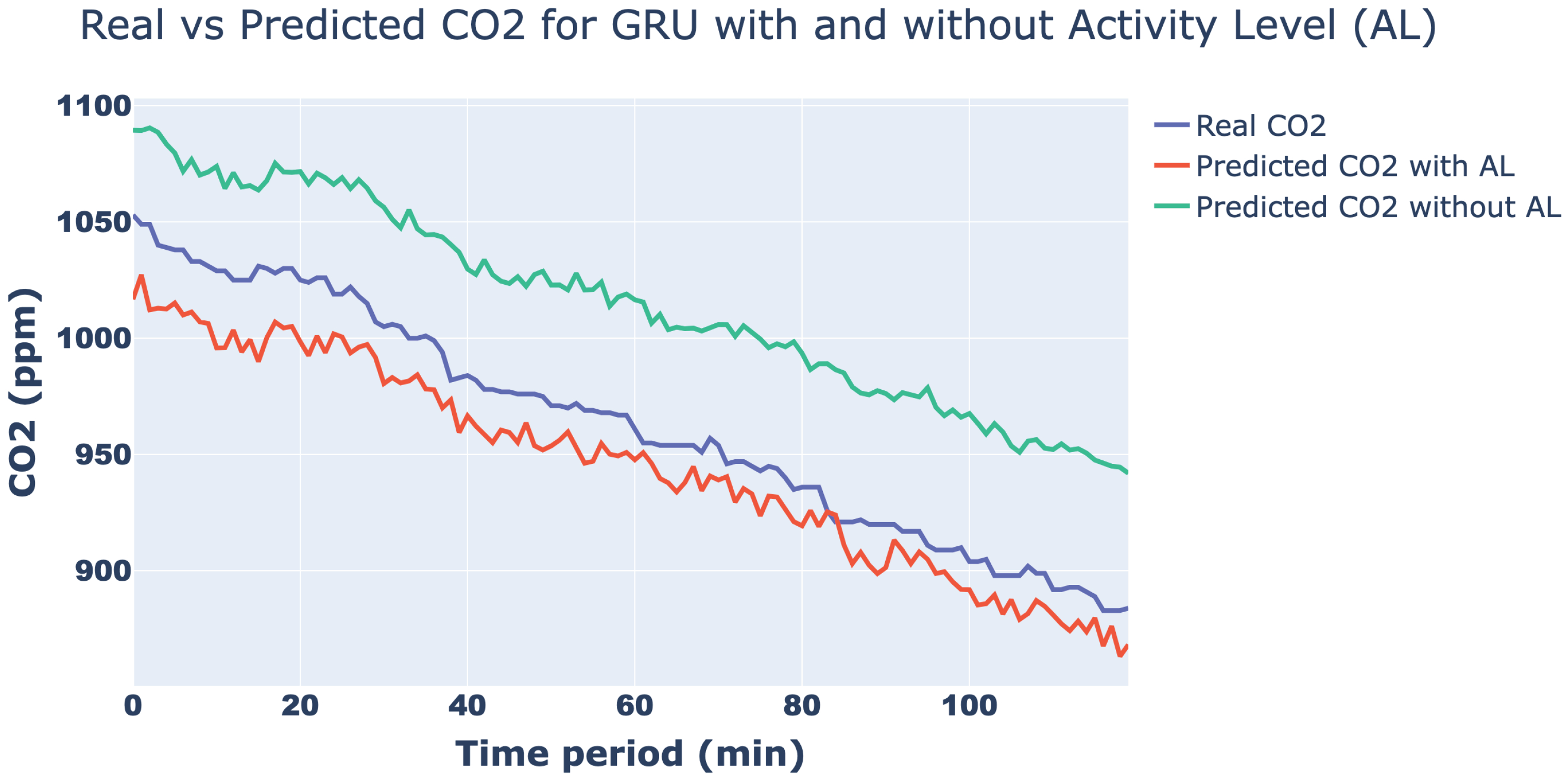
| Hyperparameter | RNN Variant | |
|---|---|---|
| LSTM | GRU | |
| # cells in G | 64 | 8 |
| # cells in D | 128 | 32 |
| Size of noise vector | 4 | 16 |
| Size of time window | 4 | 4 |
| # training iteration for D | 4 | 2 |
| Cell Type | RMSE (ppm) | |
|---|---|---|
| With Activity Level | Without Activity Level | |
| LSTM | 7.78 | 80.22 |
| GRU | 52.41 | 122.28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leone, A.; Manni, A.; Caroppo, A.; Rescio, G. Adaptive IoT-Based Platform for CO2 Forecasting Using Generative Adversarial Networks: Enhancing Indoor Air Quality Management with Minimal Data. Eng. Proc. 2025, 110, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025110003
Leone A, Manni A, Caroppo A, Rescio G. Adaptive IoT-Based Platform for CO2 Forecasting Using Generative Adversarial Networks: Enhancing Indoor Air Quality Management with Minimal Data. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 110(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025110003
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeone, Alessandro, Andrea Manni, Andrea Caroppo, and Gabriele Rescio. 2025. "Adaptive IoT-Based Platform for CO2 Forecasting Using Generative Adversarial Networks: Enhancing Indoor Air Quality Management with Minimal Data" Engineering Proceedings 110, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025110003
APA StyleLeone, A., Manni, A., Caroppo, A., & Rescio, G. (2025). Adaptive IoT-Based Platform for CO2 Forecasting Using Generative Adversarial Networks: Enhancing Indoor Air Quality Management with Minimal Data. Engineering Proceedings, 110(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025110003







