Fabrication of Thin-Film Composite Nanofiltration Membrane Employing Polyelectrolyte and Metal–Organic Framework (MOF) via Spin-Spray-Assisted Layer-by-Layer Assembly †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Polyelectrolyte Membrane (PEM) Thin-Film Composite (TFC) Fabrication
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.3.2. Hydrophilicity
2.3.3. Surface Charge
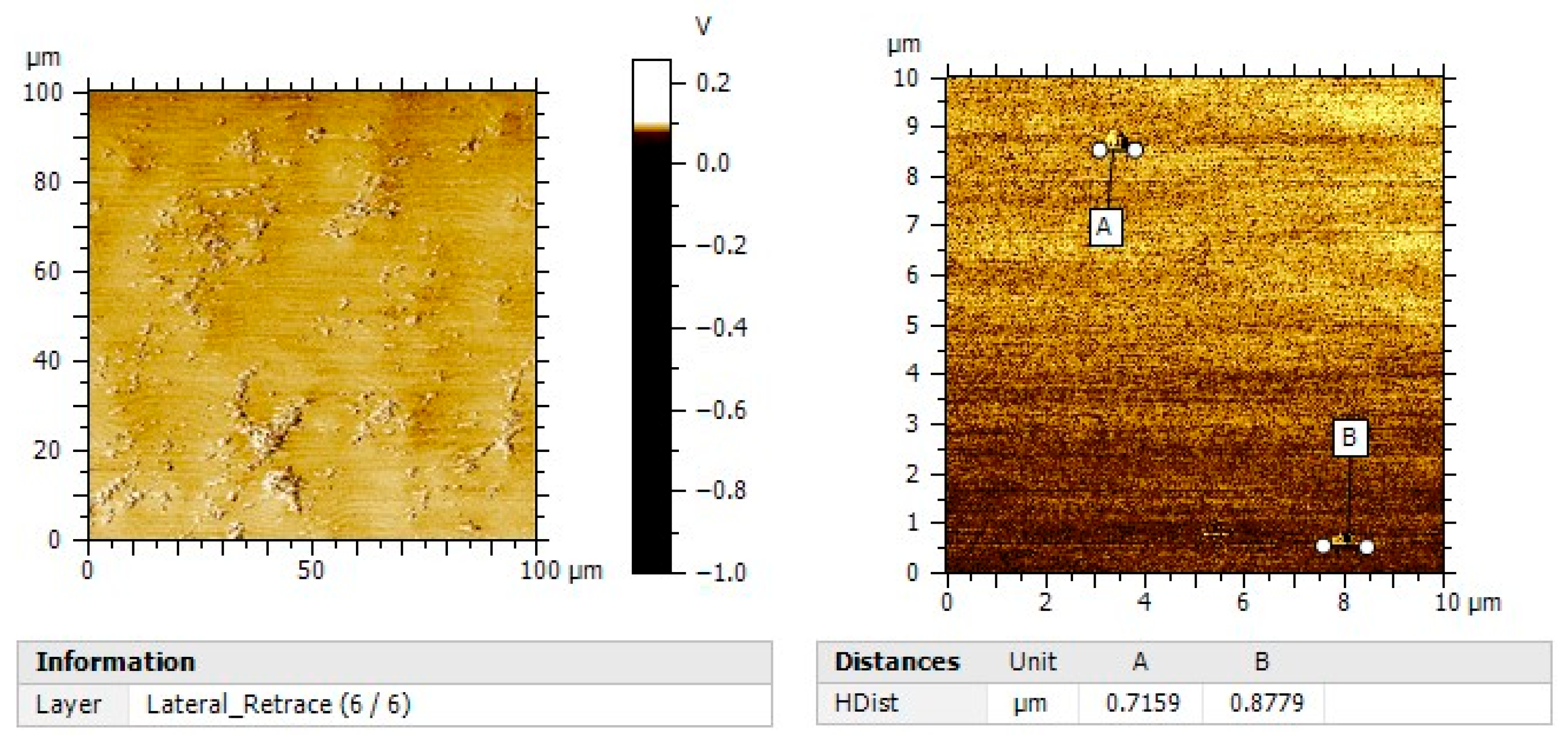
2.3.4. Atomic Force Microscopy
2.4. Membrane Performance Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. MOF303 Sonication
3.2. Performance of (PEI/PSS)10-MOF303 NF Membrane
3.3. Long-Term Permeation Test (BSA Fouling Test)
4. Conclusions and Future Work
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Macedo, A.T.Z.N.; Pulido, J.M.O.; Fragoso, R.; Duarte, E.d.C.N.F.D. The Use and Performance of Nanofiltration Membranes for Agro-Industria l Effluents Purification. In Nanofiltration; InTech: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tul Muntha, S.; Kausar, A.; Siddiq, M. Advances in Polymeric Nanofiltration Membrane: A Review. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 2017, 56, 841–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulyanti, R.; Susanto, H. Wastewater Treatment by Nanofiltration Membranes. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Sustainable Agriculture and Environment (4th ICSAE), Surakarta, Indonesia, 10–12 August 2017; IOP Publishing Ltd.: Bristol, UK, 2018; Volume 142, p. 012017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; He, Q.; Luo, J.; Wan, Y.; Darling, S.B. Sharpening Nanofiltration: Strategies for Enhanced Membrane Selectivity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 39948–39966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, D.; Karki, S.; Ingole, P.G. Current Advances and Opportunities in the Development of Nanofiltration (NF) Membranes in the Area of Wastewater Treatment, Water Desalination, Biotechnological and Pharmaceutical Applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.N.R.; Mohammad, A.W.; Mahmoudi, E.; Ang, W.L.; Leo, C.P.; Teow, Y.H. An Overview of the Modification Strategies in Developing Antifouling Nanofiltration Membranes. Membranes 2022, 12, 1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Fang, F.; Wu, J.; Zhang, K. The Anti-Biofouling Properties of Thin-Film Composite Nanofiltration Membranes Grafted with Biogenic Silver Nanoparticles. Desalination 2015, 375, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wan, Y.; Shi, Y.; Pan, G.; Yan, H.; Xu, J.; Guo, M.; Qin, L.; Liu, Y. Facile Modification of Thin-Film Composite Nanofiltration Membrane with Silver Nanoparticles for Anti-Biofouling. J. Polym. Res. 2016, 23, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, A.; Yasin, M.; Akhtar, F.; Gilani, M.; Almohamadi, H.; Younas, M.; Mushtaq, A.; Aslam, M.; Hassan, M.; Nawaz, R.; et al. Enhancing Water Purification by Integrating Titanium Dioxide Nanotubes into Polyethersulfone Membranes for Improved Hydrophilicity and Anti-Fouling Performance. Membranes 2024, 14, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purushothaman, M.; Arvind, V.; Saikia, K.; Vaidyanathan, V.K. Fabrication of Highly Permeable and Anti-Fouling Performance of Poly(Ether Ether Sulfone) Nanofiltration Membranes Modified with Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, S.; Mahmood, A.; Kim, S.-J.; Lee, K.-H. Graphene Oxide Modified Polyamide Nanofiltration Membrane with Improved Flux and Antifouling Properties. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 2065–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.; Wu, C.; Yang, Z.; Tang, C.Y. Carbon Nanotube Interlayer Enhances Water Permeance and Antifouling Performance of Nanofiltration Membranes: Mechanisms and Experimental Evidence. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 2656–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarrabi, H.; Yekavalangi, M.E.; Vatanpour, V.; Shockravi, A.; Safarpour, M. Improvement in Desalination Performance of Thin Film Nanocomposite Nanofiltration Membrane Using Amine-Functionalized Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube. Desalination 2016, 394, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Li, M.; Yu, K.; Hu, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L. Sulfonated Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes Assisted Thin-Film Nanocomposite Membrane with Enhanced Water Flux and Anti-Fouling Property. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 524, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.-F.; Marand, E.; Martin, S.M. Novel Zwitterion Functionalized Carbon Nanotube Nanocomposite Membranes for Improved RO Performance and Surface Anti-Biofouling Resistance. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 509, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Chen, T.; Pan, X. Metal–Organic-Framework-Based Materials for Antimicrobial Applications. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 3808–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Nguyen, H.L.; Hanikel, N.; Li, K.K.-Y.; Zhou, Z.; Ma, T.; Yaghi, O.M. High-Yield, Green and Scalable Methods for Producing MOF-303 for Water Harvesting from Desert Air. Nat. Protoc. 2023, 18, 136–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, A.; Suresh, S.; Khan, A.; Kuo, L.H.; Chi, L.T.; Ganguly, A.; Kao, C.-Y.; Sharma, M.K.; Wang, T.-S.A.; Kang, D.-Y.; et al. Metal-Organic Frameworks as Thermocatalysts for Hydrogen Peroxide Generation and Environmental Antibacterial Applications. Sci. Adv. 2025, 11, eads4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, S.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Kapteijn, F.; Liu, X. Highly Water-Permeable Metal–Organic Framework MOF-303 Membranes for Desalination. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 20055–20058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, A.M. Fast and Versatile Pathway in Fabrication of Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Nanofiltration Membrane with Tunable Properties. J. Chem. 2021, 2021, 9978596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siahkamari, L.; Bakhtiari, O. Preparation of Post-Synthetized MOF-303@ Graphene Oxide (GO) Composite Membrane for Pervaporative Dehydration of Ethanol. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 359, 130564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Su, P.; Fan, H.; Liu, J.; Xin, B.; Chen, T.; Zhong, G.; Xie, J.; Li, J.; Deng, J.; et al. Regulating Positively Charged MOF-303 Membranes for Enhanced Ion Selectivity. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 517, 164373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshof, M.G.; De Vos, W.M.; De Grooth, J.; Benes, N.E. On the Long-Term pH Stability of Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Nanofiltration Membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 615, 118532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junker, M.A.; Regenspurg, J.A.; Valdes Rivera, C.I.; Brinke, E.T.; De Vos, W.M. Effects of Feed Solution pH on Polyelectrolyte Multilayer Nanofiltration Membranes. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, Y. Fouling of Reverse Osmosis (RO) and Nanofiltration (NF) Membranes by Low Molecular Weight Organic Compounds (LMWOCs), Part 1: Fundamentals and Mechanism. Membranes 2024, 14, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y. Fouling of Nanofiltration and Reverse Osmosis Membranes by Organic Macromolecules and Their Mixtures. Ph.D. Dissertation, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore, 2011. [Google Scholar]




| Time, min | Particle Size, nm | |
|---|---|---|
| Bath Sonication | Probe Sonication 1 | |
| 5 | - | 1053.6 ± 163.31 |
| 10 | 2502 ± 450.36 | 961.8 ± 126.96 |
| 15 | - | 969.8 ± 135.77 |
| 20 | 1477.4 ± 217.12 | 913.0 ± 127.82 |
| 30 | 1251.2 ± 137.63 | 826.5 ± 99.18 |
| 40 | 1406.5 ± 196.84 | 995.5 ± 129.42 |
| Surface Properties | (PEI/PSS)5 | (PEI/PSS)5-MOF303 |
|---|---|---|
| Surface charge, mV | 2.43 | 18.7 |
| Contact angle, ° | 17.88 ± 0.61 | 25.60 ± 2.61 |
| Performance * | (PEI/PSS)5 | (PEI/PSS)5-MOF303 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MOF303 size, nm | 1251.2 (dispersed by bath sonicator) | 826.0 (dispersed by probe sonicator) | |
| Rejection rate, % | 42.61 ± 2.58 | 18.94 ± 1.58 | 47.01 ± 0.63 |
| Permeability, L/m2·h·bar | 9.46 ± 0.46 | 0.91 ± 0.13 | 8.33 ± 0.11 |
| Membrane | Method | Testing Condition | Result (Rejection; Permeability) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (PDAC/PSS)8 | Dip LbL | 5 mM NaCl (292.5 ppm); 5 bar | 40%; 12 L/h·m2·bar | [23] |
| (PAA/PSS)6 | Dip LbL | 5 mM NaCl (292.5 ppm); 25 °C 5 bar | 38%; 10 L/h·m2·bar | [24] |
| (PEI/PSS)5-MOF303 | SSA-LbL | 2000 ppm NaCl; 25 °C; 10 bar | 47%, 8.3 L/h·m2·bar | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fadhillah, F. Fabrication of Thin-Film Composite Nanofiltration Membrane Employing Polyelectrolyte and Metal–Organic Framework (MOF) via Spin-Spray-Assisted Layer-by-Layer Assembly. Eng. Proc. 2025, 105, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025105003
Fadhillah F. Fabrication of Thin-Film Composite Nanofiltration Membrane Employing Polyelectrolyte and Metal–Organic Framework (MOF) via Spin-Spray-Assisted Layer-by-Layer Assembly. Engineering Proceedings. 2025; 105(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025105003
Chicago/Turabian StyleFadhillah, Farid. 2025. "Fabrication of Thin-Film Composite Nanofiltration Membrane Employing Polyelectrolyte and Metal–Organic Framework (MOF) via Spin-Spray-Assisted Layer-by-Layer Assembly" Engineering Proceedings 105, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025105003
APA StyleFadhillah, F. (2025). Fabrication of Thin-Film Composite Nanofiltration Membrane Employing Polyelectrolyte and Metal–Organic Framework (MOF) via Spin-Spray-Assisted Layer-by-Layer Assembly. Engineering Proceedings, 105(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/engproc2025105003






