Synthesis and Molecular Docking of N,N′-[succinylbis(oxy)]dibenzamides as Inhibitors of Cathepsin S and Cathepsin K †
Abstract
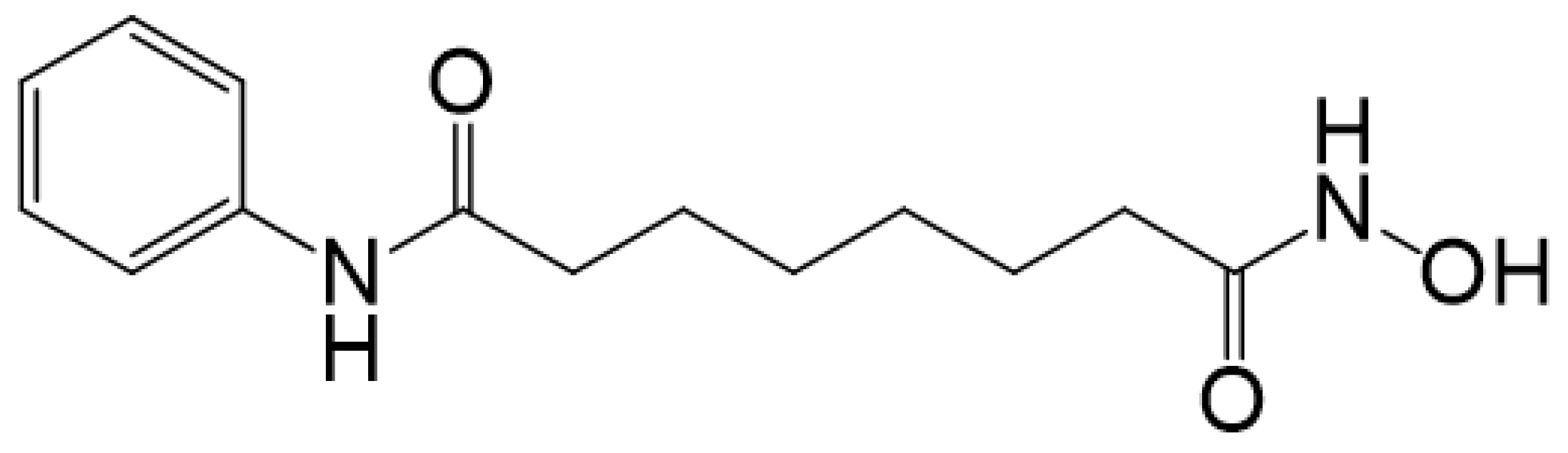
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Experimental Section
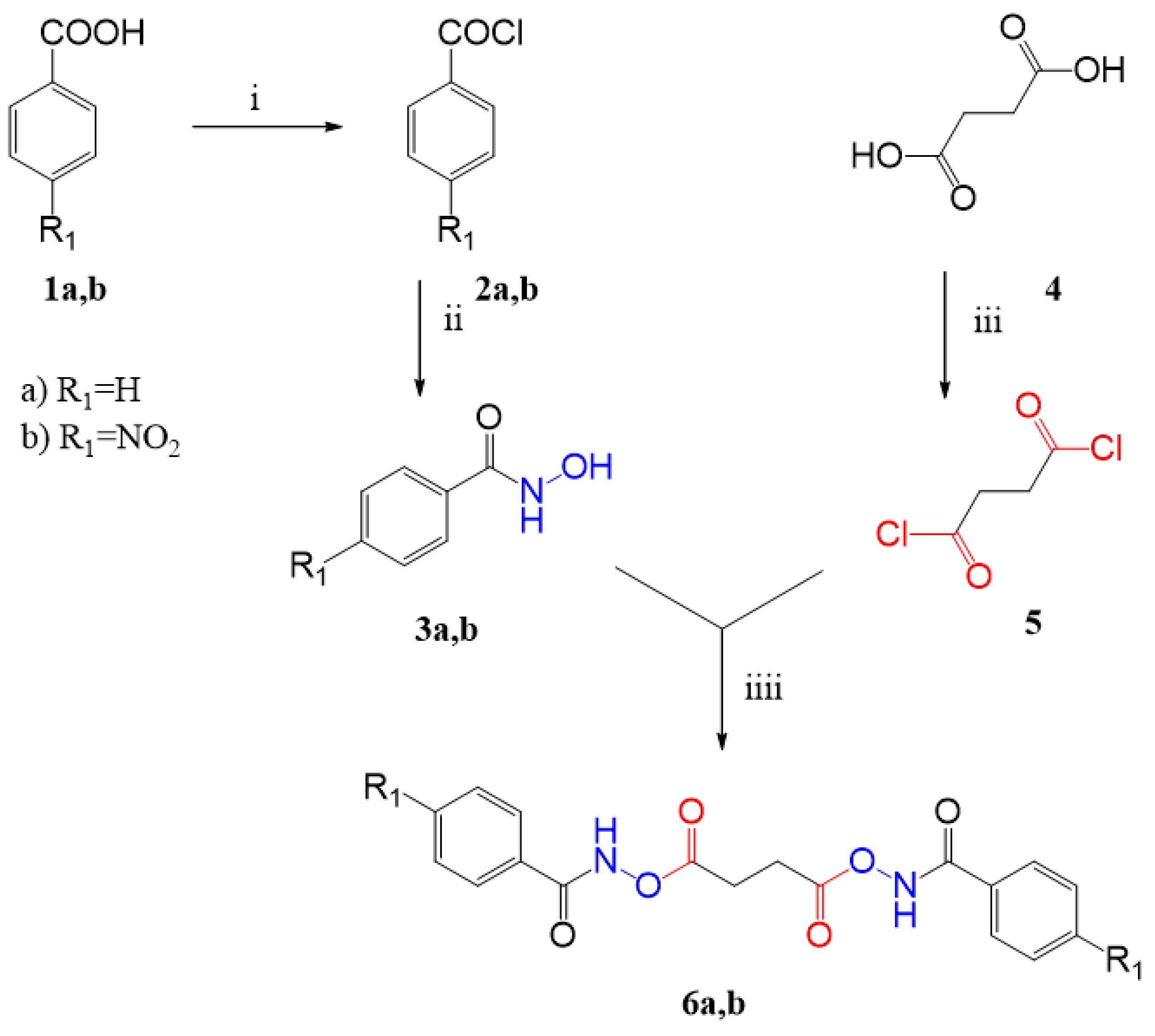
3.1. Synthesis
3.1.1. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Benzoyl Chlorides 2a,b
3.1.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Benzhydroxamic Acids 3a,b
3.1.3. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Succinyl Chloride 5
3.1.4. General Procedure for the Synthesis of N,N′-[succinylbis(oxy)]dibenzamides 6a,b
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bauer, L.; Exner, O. The Chemistry of Hydroxamic Acids and N-Hydroxyimides. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1974, 13, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van’t Riet, B.; Wampler, G.L. Synthesis of hydroxy- and aminosubstituted benzohydroxamic acids: Inhibition of ribonucleotide reductase and antitumor activity. J. Med. Chem. 1979, 22, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Arthur, B.P. Suberoylanilide Hydroxamic Acid as a Potential Therapeutic Agent for Human Breast Cancer Treatment. Mol. Med. 2003, 58, 1283–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Faiyz, Y.S.S.; Clark, A.J.; Filik, R.P.; Peacock, J.L.; Thomas, G.H. Rearrangements of activated O-acyl hydroxamic acid derivatives. Tetrahedron Lett. 1998, 39, 1269–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, V.; Kos, J.; Turk, B. Cysteine Cathepsins (proteases)—On the main stage of cancer? Cancer Cell 2004, 5, 409–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilkinson, R.D.A.; Williams, R.; Scott, C.J.; Burden, R.E. Cathepsin S: Therapeutic, diagnostic, and prognostic potential. Biol. Chem. 2015, 396, 867–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brömme, D.; Lecaille, F. Cathepsin K inhibitors for osteoporosis and potential off-target effects. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2009, 18, 585–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

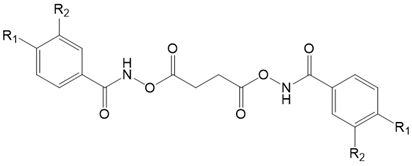 | ||||
| Сompound Number | R1 | R2 | Affinity with Cathepsin K | Affinity with Cathepsin S |
| 6a | -H | -H | −9.6 | −8.3 |
| 6b | -NO2 | -H | −8.7 | −7.6 |
| 6c | -H | -NO2 | −9.1 | −7.8 |
| 6d | -Me | -H | −10.3 | −8.6 |
| 6e | -H | -Me | −10.0 | −8.5 |
| 6f | -F | -H | −10.0 | −8.2 |
| 6g | -H | -F | −8.4 | −8.7 |
| 6h | -Cl | -H | −9.6 | −7.9 |
| 6i | -H | -Сl | −9.9 | −8.3 |
| 6j | -Br | -H | −9.8 | −8.3 |
| 6k | -H | -Br | −8.7 | −7.7 |
| 6l | -I | -H | −9.7 | −7.5 |
| 6m | -H | -I | −9.0 | −8.1 |
| 6n | -CN | -H | −9.2 | −8.0 |
| 6o | -H | -CN | −9.6 | −8.2 |
| Сompound Number | R1 | R2 | Charge on the Nitrogen Atom | Charge on the Oxygen Atom |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6d | -Me | -H | −0.187 | −0.244 |
| 6e | -H | -Me | −0.191 | −0.243 |
| 6f | -F | -H | −0.317 | −0.171 |
| 6g | -H | -F | −0.315 | −0.170 |
| 6i | -H | -Сl | −0.316 | −0.171 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trukhanova, Y.A.; Lalaev, B.Y.; Vakhnina, A.A. Synthesis and Molecular Docking of N,N′-[succinylbis(oxy)]dibenzamides as Inhibitors of Cathepsin S and Cathepsin K. Chem. Proc. 2022, 8, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-25-11637
Trukhanova YA, Lalaev BY, Vakhnina AA. Synthesis and Molecular Docking of N,N′-[succinylbis(oxy)]dibenzamides as Inhibitors of Cathepsin S and Cathepsin K. Chemistry Proceedings. 2022; 8(1):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-25-11637
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrukhanova, Yulia A., Boris Y. Lalaev, and Anna A. Vakhnina. 2022. "Synthesis and Molecular Docking of N,N′-[succinylbis(oxy)]dibenzamides as Inhibitors of Cathepsin S and Cathepsin K" Chemistry Proceedings 8, no. 1: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-25-11637
APA StyleTrukhanova, Y. A., Lalaev, B. Y., & Vakhnina, A. A. (2022). Synthesis and Molecular Docking of N,N′-[succinylbis(oxy)]dibenzamides as Inhibitors of Cathepsin S and Cathepsin K. Chemistry Proceedings, 8(1), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-25-11637







