Comparative Studies of Various NNRTIs in the Active Site of Different HIV-1RT Receptors †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Software
2.2. Molecular Modelling Studies
2.2.1. Protein Preparation
2.2.2. Ligand Preparation
2.2.3. Receptor Grid Generation
2.2.4. Docking Protocol Validation
3. Results and Discussions
There Are Many HIV-1 Protein Crystal Structures Available in the Literature
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Turner, B.G.; Summers, M.F. Structural biology of HIV 1 1Edited by P. E. Wright. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 285, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Gupta, S.; Singh, J.; Arsi, T. Azoles as non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs): Mini review. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2017, 8, 29. [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq, E. New approaches toward anti-HIV chemotherapy. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 1297–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Clercq, E. The design of drugs for HIV and HCV. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 1001–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Lee, D.; Park, C.; So, W.; Jo, M.; Ok, T.; Kwon, J.; Kong, S.; Jo, S.; Kim, Y.; et al. Discovery of Phenylaminopyridine Derivatives as Novel HIV-1 Non-nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 678–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Milton, J.; Weaver, K.L.; Short, S.A.; Stuart, D.I.; Stammers, D.K. Structural Basis for the Resilience of Efavirenz (DMP-266) to Drug Resistance Mutations in HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase. Structure 2000, 8, 1089–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marongiu, M.E.; Pani, A.; Artico, M.; Massa, S.; Mai, A.; La Colla, P. Selective inhibition of HIV-1 replication by a novel series of 2-substituted 6-benzyl-pyrimidines. In Proceedings of the VIII International Conference on AIDS, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 19–24 July 1992; pp. 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Marongiu, M.E.; Pani, A.; Musiu, C.; LA COLLA, P.; Mai, A.; Sbardella, G.; Artico, M. 3,4-Dihydro-2-Alkoxy-6-Benzyl-Oxopyrimidines [DABOs]: Development of a Potent Class of Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2001, 65–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, O.S.; Pedersen, E.B. Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors: The NNRTI Boom. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 1999, 10, 285–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artico, M. Selected non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs): The DABOs family. Drugs Future 2002, 27, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchen, D.B.; Decornez, H.; Furr, J.R.; Bajorath, J. Docking and scoring in virtual screening for drug discovery: Methods and applications. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 935–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostashari-Rad, T.; Arian, R.; Sadri, H.; Mehridehnavi, A.; Mokhtari, M.; Ghasemi, F.; Fassihi, A. Study of CXCR4 chemokine receptor inhibitors using QSPR and molecular docking methodologies. J. Comput. Chem. 2019, 18, 1950018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.; Lewi, P.J.; Hughes, S.H.; Arnold, E. Crystallography and the design of anti-AIDS drugs: Conformational flexibility and positional adaptability are important in the design of non-nucleoside HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2005, 88, 209–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindstrom, W.; Morris, G.M.; Weber, C.; Huey, R. AutoDock 4; The Scripps Research Institute, Molecular Graphics Laboratory: La Jolla, CA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- The Research Collaboratory for Structural Bioinformatics (RCSB). Protein Data Bank. Available online: http://www.rcsb.org/pdb (accessed on 1 May 2012).
- Prodrg 2 Server. Available online: http://prodrg1.dyndns.org/ (accessed on 15 August 2020).
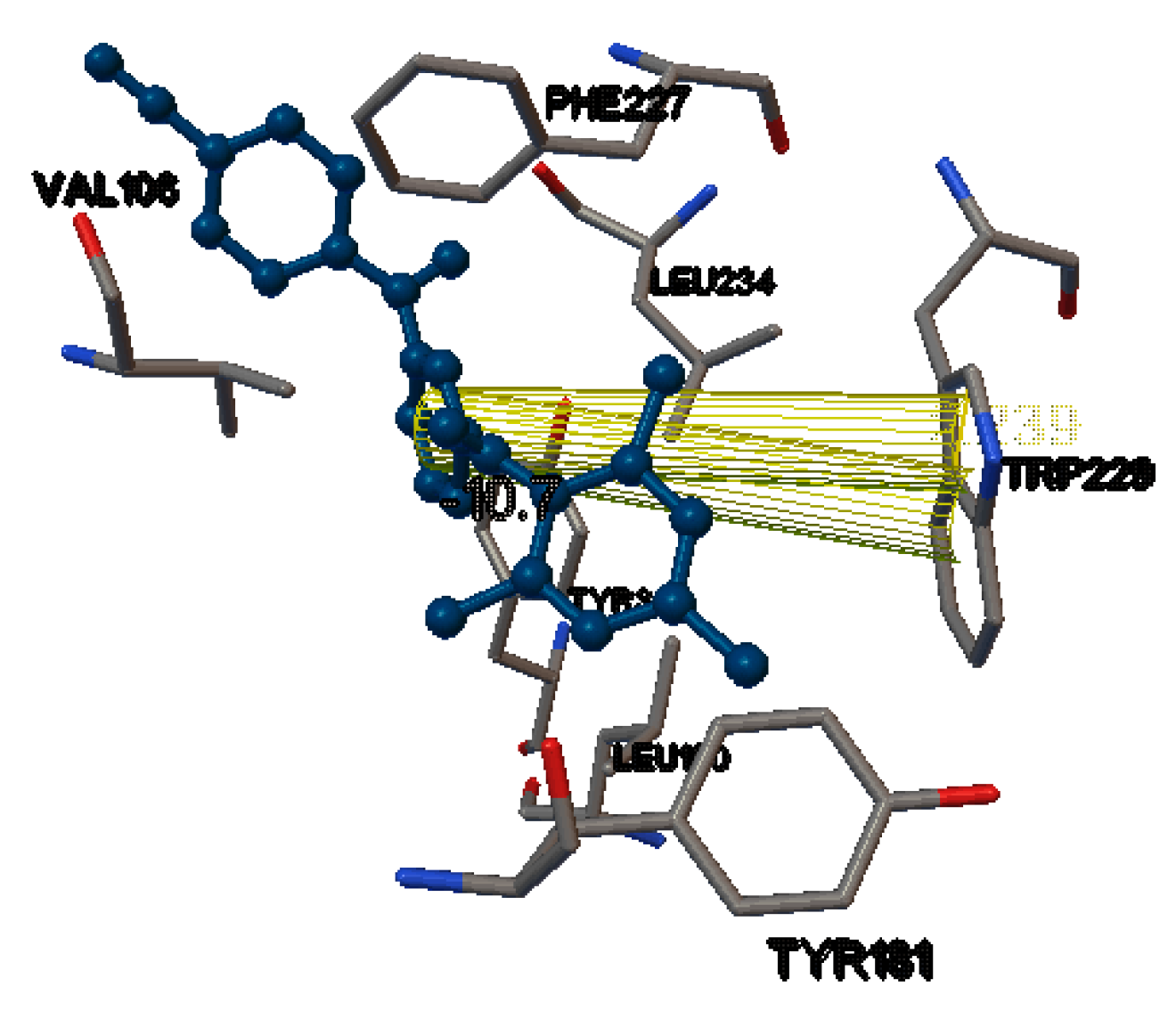

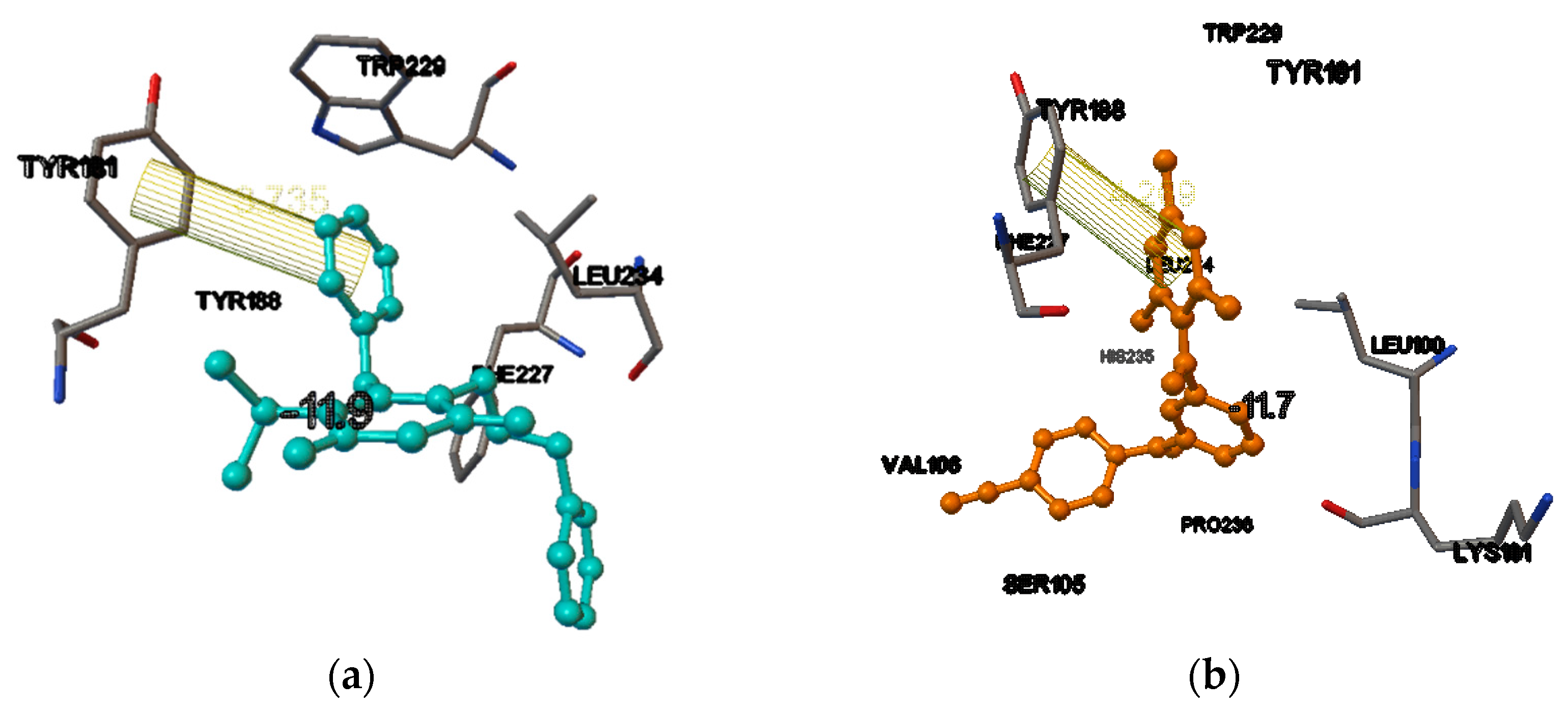
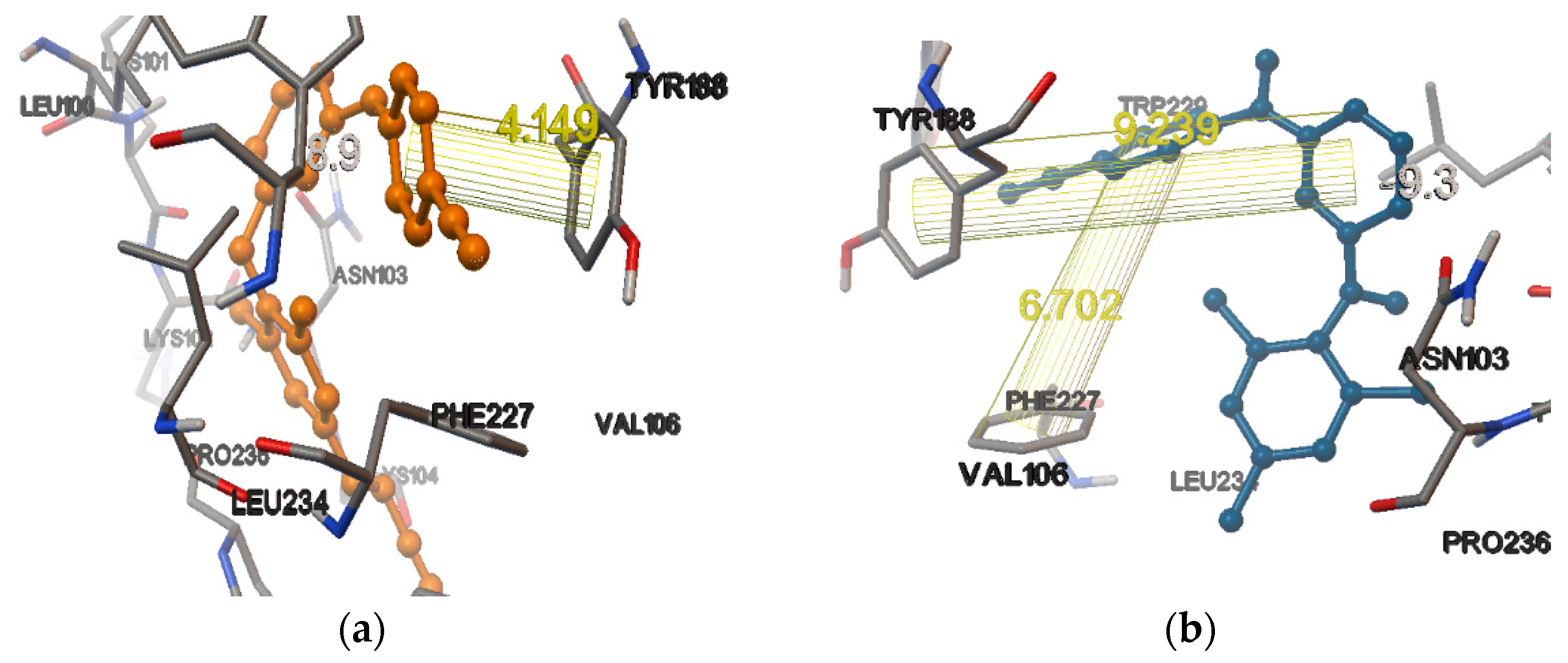
| Compound | Docking Scores On | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1KLM | 1JLB | 1RT2 | 3BGR | |
| Nevirapine | −10.2 | −9.7 | −9.5 | −9.5 |
| Efavirenz | −7.6 | −9.4 | −9.4 | −9.3 |
| Delaviridine | −9.5 | −6.9 | −8.5 | −6.8 |
| Rilpivirine | −9.9 | −8.4 | −9.2 | −8.7 |
| Doravirine | −8.6 | −9.7 | −11.2 | −7.1 |
| Etravirine | −8.8 | −6.9 | −9.6 | −6.9 |
| Lersivirine | −6.5 | −8.3 | −6.5 | −8.3 |
| Dapivirine | −10.7 | −8.9 | −11.7 | −9.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chandra, P.; Ganguly, S.; Karmakar, S. Comparative Studies of Various NNRTIs in the Active Site of Different HIV-1RT Receptors. Chem. Proc. 2021, 3, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-24-08313
Chandra P, Ganguly S, Karmakar S. Comparative Studies of Various NNRTIs in the Active Site of Different HIV-1RT Receptors. Chemistry Proceedings. 2021; 3(1):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-24-08313
Chicago/Turabian StyleChandra, Priyanka, Swastika Ganguly, and Soikata Karmakar. 2021. "Comparative Studies of Various NNRTIs in the Active Site of Different HIV-1RT Receptors" Chemistry Proceedings 3, no. 1: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-24-08313
APA StyleChandra, P., Ganguly, S., & Karmakar, S. (2021). Comparative Studies of Various NNRTIs in the Active Site of Different HIV-1RT Receptors. Chemistry Proceedings, 3(1), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-24-08313





