Efficient LC-MS/MS for Routine Fungicide Residue Analysis in Complex Matrices †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Apparatus and Reagents
2.2. Samples and Sample Pretreatment
2.3. Preparation of Blank, Matrix-Matched Calibration Standards and Solution for Recovery
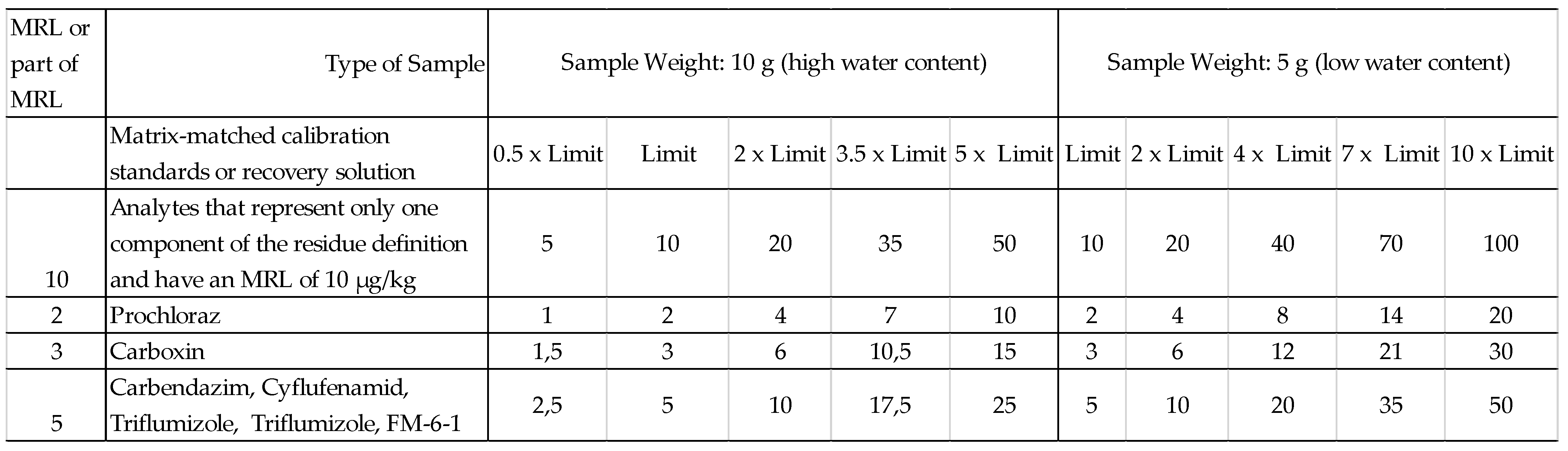
3. Results
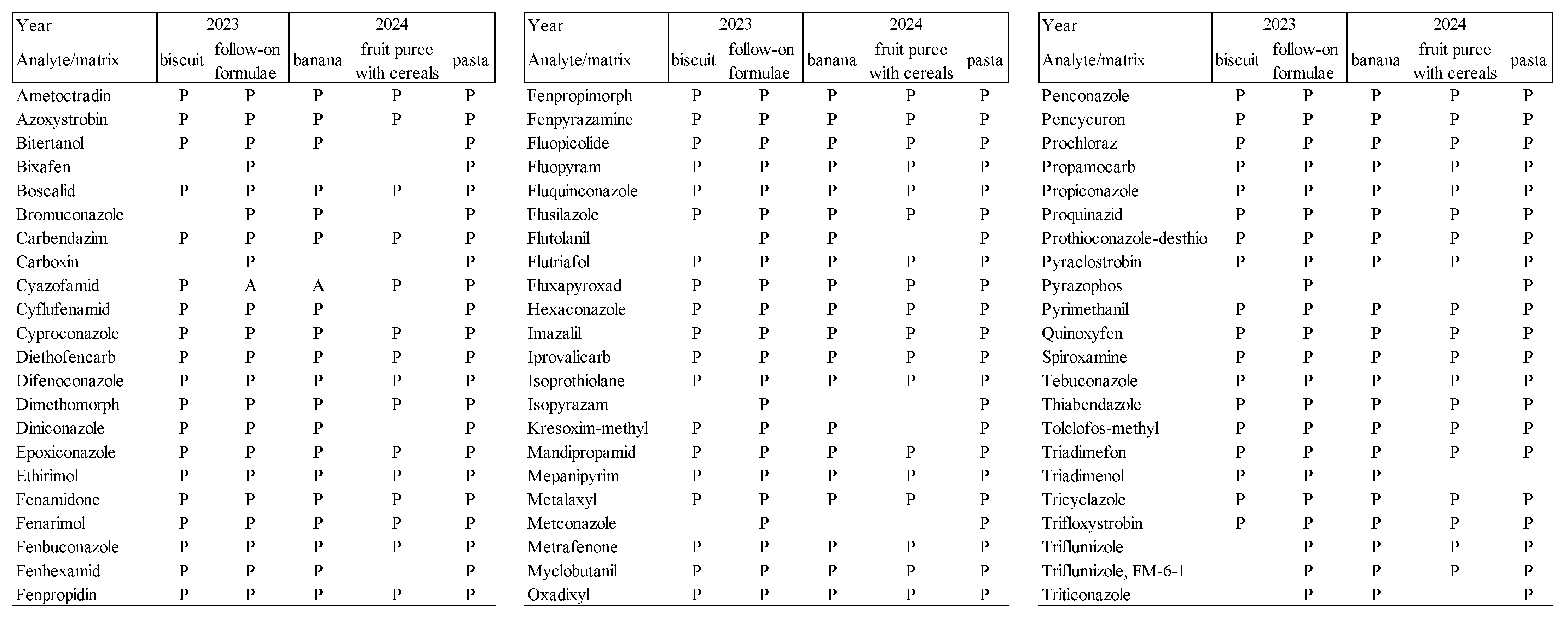
3.1. LOQ and Analyte Limits

3.2. Evaluation of Linearity, Selectivity, Specificity, and Accuracy
3.3. Tables for Optimized LC and MS/MS Conditions
| LC Conditions | |
|---|---|
| Column: | Kinetex® 2.6 μm Polar C18 100 Å, 100 × 2.1 mm |
| Column temperature: | 30 °C |
| Injection volume: | 4 μL |
| Autosampler temperature: | 15 °C |
| Mobile phase A: | 0.1% Formic acid in deionized water |
| Mobile phase B: | 0.1% Formic acid in Methanol |
| Run time: | 22 min |
| Flow rate: | 0.25 mL/min |
| Time (min) | Mobile Phase A (%) | Mobile Phase B (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 5 | 95 |
| 2 | 5 | 95 |
| 5.2 | 45 | 55 |
| 10.7 | 95 | 5 |
| 11.7 | 95 | 5 |
| 11.8 | 100 | 0 |
| 15 | 100 | 0 |
| 15.1 | 5 | 95 |
| 22 | 5 | 95 |
| MS/MS Conditions | |
|---|---|
| Scan type: | Scheduled MRM |
| Target cycle time: | 1 s |
| Ion source: | ESI |
| Curtain gas (CUR): | 40 psi |
| Collision gas (CAD): | Medium |
| Ion Spray Voltage (IS): | 5500 V |
| Temperature (TEM): | 400 °C |
| Ion source Gas 1 (GS1): | 50 psi |
| Ion source Gas 2 (GS2): | 50 psi |
| Entrance Potencial (EP): | 10 V |
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- QuEChERS. Available online: http://quechers.cvua-stuttgart.de/ (accessed on 30 September 2025).
- Anastassiades, M.; Lehotay, S.J.; Štajnbaher, D.; Schenck, F.J. Fast and Easy Multiresidue Method Employing Acetonitrile Extraction/Partitioning and “Dispersive Solid-Phase Extraction” for the Determination of Pesticide Residues in Produce. J. AOAC Int. 2003, 86, 412–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maximum Residue Levels. Available online: https://food.ec.europa.eu/plants/pesticides/maximum-residue-levels/guidelines-maximum-residue-levels_en (accessed on 30 September 2025).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions, and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions, or products referred to in the content. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuzniarová, M.; Micháliková, M.; Dömötörová, M. Efficient LC-MS/MS for Routine Fungicide Residue Analysis in Complex Matrices. Chem. Proc. 2025, 18, 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-29-26677
Kuzniarová M, Micháliková M, Dömötörová M. Efficient LC-MS/MS for Routine Fungicide Residue Analysis in Complex Matrices. Chemistry Proceedings. 2025; 18(1):88. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-29-26677
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuzniarová, Miroslava, Martina Micháliková, and Milena Dömötörová. 2025. "Efficient LC-MS/MS for Routine Fungicide Residue Analysis in Complex Matrices" Chemistry Proceedings 18, no. 1: 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-29-26677
APA StyleKuzniarová, M., Micháliková, M., & Dömötörová, M. (2025). Efficient LC-MS/MS for Routine Fungicide Residue Analysis in Complex Matrices. Chemistry Proceedings, 18(1), 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-29-26677





