In Silico Studies for the Identification of Potential Inhibitors of the QACE Protein Against Antibiotic-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Molecular Target Selection Criteria
2.2. Virtual Screening Workflow
2.3. In Silico ADMET Evaluation
2.4. Molecular Docking Protocol
2.4.1. Ligand Preparation
2.4.2. Receptor Preparation
2.4.3. Docking Calculations
3. Results and Discussion
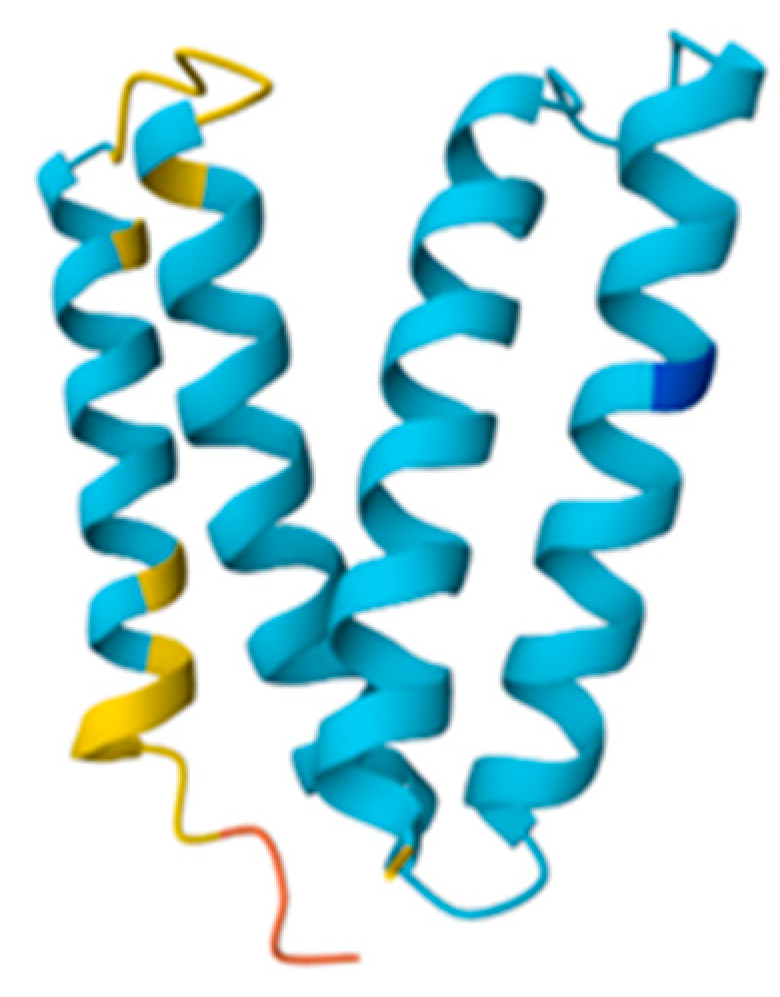
3.1. Molecular Target Selection
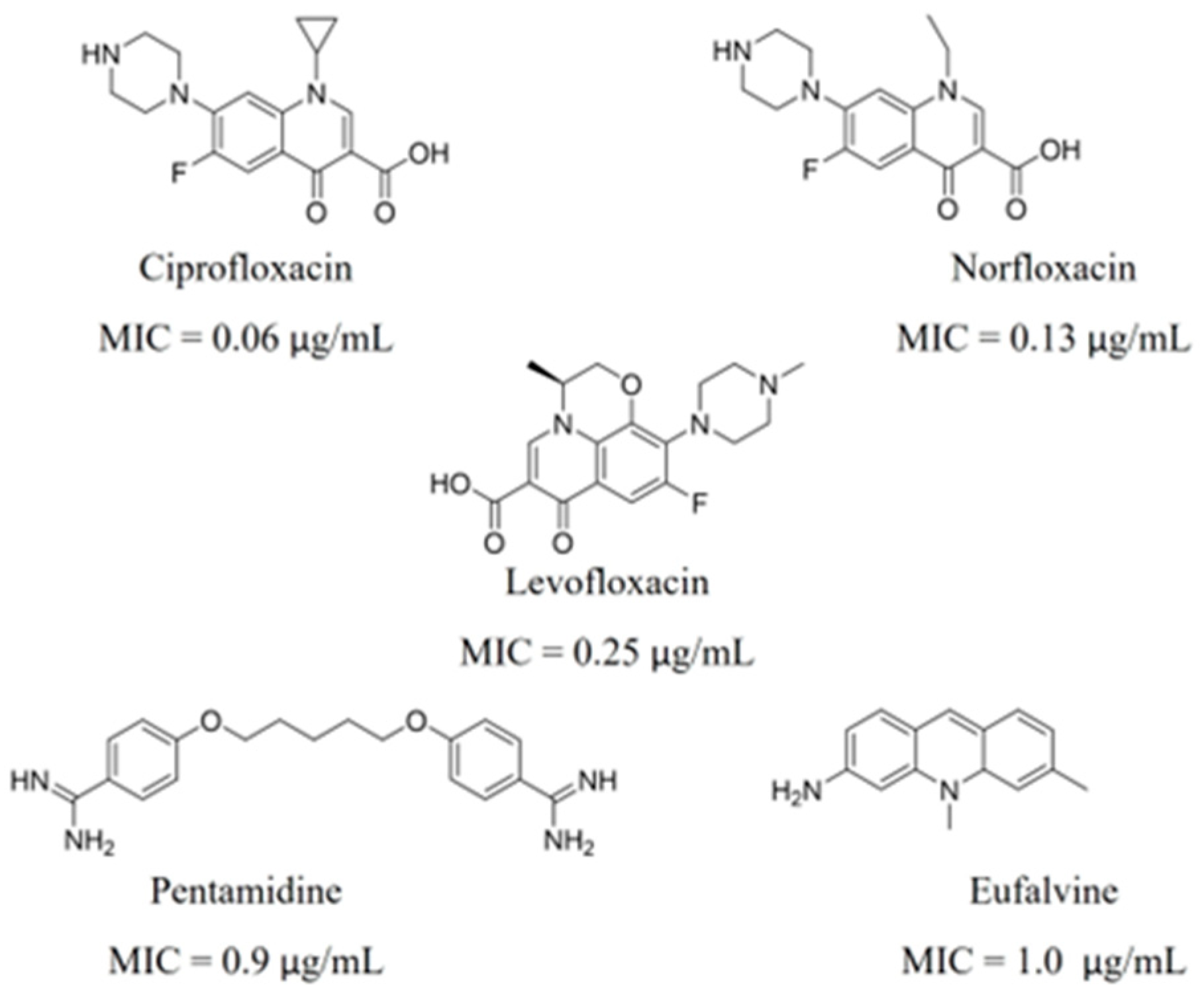
3.2. Virtual Screening
3.3. Prediction of Pharmacokinetic Properties
3.4. Molecular Docking Studies
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADME | Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion |
| CDC | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention |
| ChEMBL | Chemical database of bioactive drug-like molecules |
| CYP3A4 | Cytochrome P450 3A4 |
| hERG | human Ether-à-go-go-Related Gene |
| ki | Inhibition constant |
| LogP | Octanol–water partition coefficient |
| MDL | Molecular Design Limited (chemical file format) |
| MIC | Minimum Inhibitory Concentration |
| MMFF | Merck Molecular Force Field |
| NMR | Nuclear Magnetic Resonance |
| PDBQT | Protein Data Bank, Quaternion, Torsional degrees of freedom |
| QAC | Quaternary Ammonium Compound-resistance protein |
| QACE | Quaternary Ammonium Compound-resistance Efflux protein |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- Naghavi, M.; Vollset, S.E.; Ikuta, K.S.; Swetschinski, L.R.; Gray, A.P.; Wool, E.E.; Aguilar, G.R.; Mestrovic, T.; Smith, G.; Han, C.; et al. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance a systematic analysis with forecasts to 2050. Lancet 2024, 404, 1199–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reardon, S. WHO warns against ‘post-antibiotic’ era. Nature 2014, 15, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, J. An audience with Jim O’Neill. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Fuente-Nunez, C.; Cesaro, A.; Hancock, R.E.W. Antibiotic failure: Beyond antimicrobial resistance. Drug Resist. Updates 2023, 71, 101012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, F.; Wang, B.; Xie, L.; Chen, W. New FDA drug approvals for 2024: Synthesis and clinical application. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2025, 285, 117241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chellat, M.F.; Raguž, L.; Riedl, R. Targeting Antibiotic Resistance. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 6600–6626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, T.; Page, J.E.; Walker, S. Uncovering the activities, biological roles, and regulation of bacterial cell wall hydrolases and tailoring enzymes. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 3347–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, P.; Hernando-Amado, S.; Reales-Calderon, J.A.; Corona, F.; Lira, F.; Alcalde-Rico, M.; Bernardini, A.; Sanchez, M.B.; Martinez, J.L. Bacterial Multidrug Efflux Pumps: Much More Than Antibiotic Resistance Determinants. Microorganisms 2016, 4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, W.R.; Arias, C.A. ESKAPE pathogens: Antimicrobial resistance, epidemiology, clinical impact and therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 598–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshad, N.; Azzam, W.; Zilberberg, M.D.; Shorr, A.F. Acinetobacter baumannii Complex Infections: New Treatment Options in the Antibiotic Pipeline. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.; Lakhanpal, D. Acinetobacter baumannii: A comprehensive review of global epidemiology, clinical implications, host interactions, mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance and mitigation strategies. Microb. Pathog. 2025, 204, 107605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, A.; Islam, S.; Tankhilevich, E.; Sternberg, M.J.E. The AlphaFold Database of Protein Structures: A Biologist’s Guide. J. Mol. Biol. 2022, 434, 167336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaulton, A.; Hersey, A.; Nowotka, M.; Bento, A.P.; Chambers, J.; Mendez, D.; Mutowo, P.; Atkinson, F.; Bellis, L.J.; Cibrián-Uhalte, E.; et al. The ChEMBL database in 2017. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, T.; Freyss, J.; von Korff, M.; Rufener, C. DataWarrior: An Open-Source Program For Chemistry Aware Data Visualization And Analysis. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2015, 55, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Urrutia, F.; Medina-Franco, J.L. BIOMX-DB: A web application for the BIOFACQUIM natural product database. Mol. Inform. 2024, 43, e202400060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milne, G.W.A. Software Review of ChemBioDraw 12.0. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2010, 50, 2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hehre, W.J.; Huang, W.W. Chemistry with Computation: An Introduction to SPARTAN; Wavefunction, Inc.: Irvine, CA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Pacheco, A.B.; Hpc, L. Introduction to AutoDock and AutoDock Tools; Louisiana State University: Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, G.M.; Goodsell, D.S.; Halliday, R.S.; Huey, R.; Hart, W.E.; Belew, R.K.; Olson, A.J. Automated docking using a Lamarckian genetic algorithm and an empirical binding free energy function. J. Comput. Chem. 1998, 19, 1639–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jejurikar, B.L.; Rohane, S.H. Drug designing in discovery studio. Asian J. Res. Chem. 2021, 14, 135–138. [Google Scholar]
- Pearl, S.; Anbarasu, A. Genomic landscape of nosocomial Acinetobacter baumannii: A comprehensive analysis of the resistome, virulome, and mobilome. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 18203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The UniProt Consortium. UniProt: A hub for protein information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D204–D212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
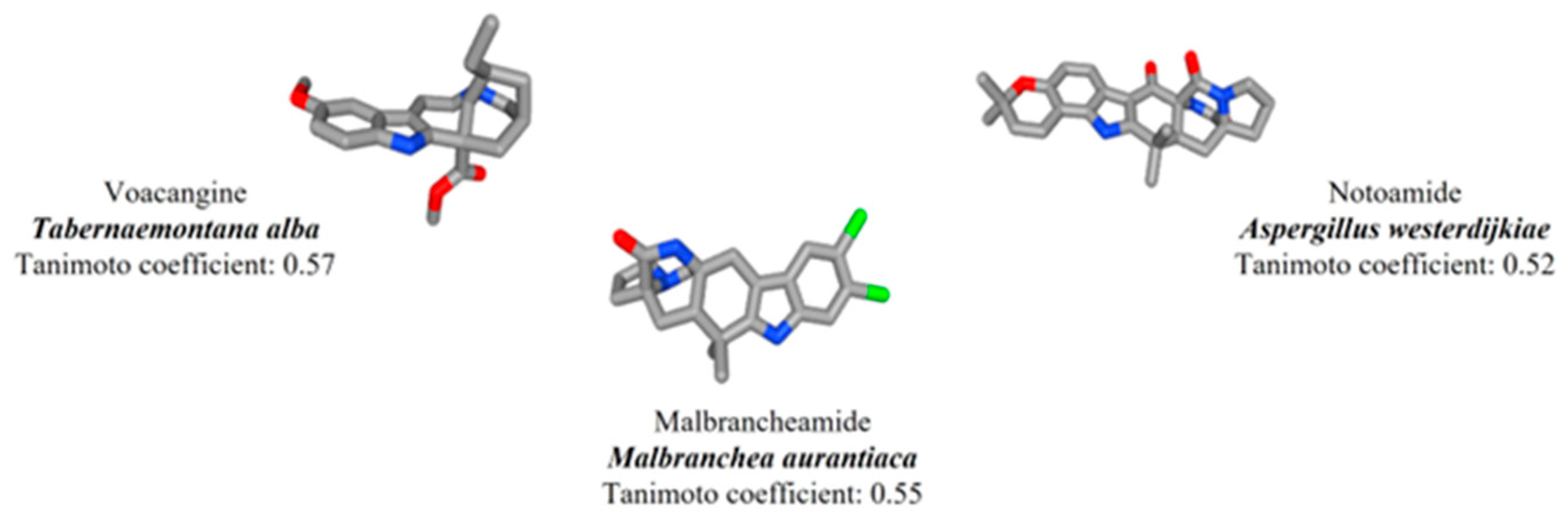

| Compound | Physicochemical Properties | Absorption | Distribution | Metabolism | Excretion | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular Weight (g/mol) | LogP | Permeability Caco-2 | Estimated Distribution Volume | Metabolism by CYP3A4 | Cleareance (mL/min) | |
| Voacangine | 368.47 | 3.30 | −4.913 | 3.26 | + | 9.83 |
| Malbrancheamide | 403.12 | 3.54 | −4.946 | 1.705 | +++ | 5.86 |
| Notoamide | 447.22 | 2.23 | −5.221 | 2.48 | +++ | 4.28 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Suárez-Castro, A.; Sánchez-Mejorada, G.F.; Rosales-López, F. In Silico Studies for the Identification of Potential Inhibitors of the QACE Protein Against Antibiotic-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Chem. Proc. 2025, 18, 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-29-26879
Suárez-Castro A, Sánchez-Mejorada GF, Rosales-López F. In Silico Studies for the Identification of Potential Inhibitors of the QACE Protein Against Antibiotic-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Chemistry Proceedings. 2025; 18(1):72. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-29-26879
Chicago/Turabian StyleSuárez-Castro, Abel, Genaro F. Sánchez-Mejorada, and Fernando Rosales-López. 2025. "In Silico Studies for the Identification of Potential Inhibitors of the QACE Protein Against Antibiotic-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii" Chemistry Proceedings 18, no. 1: 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-29-26879
APA StyleSuárez-Castro, A., Sánchez-Mejorada, G. F., & Rosales-López, F. (2025). In Silico Studies for the Identification of Potential Inhibitors of the QACE Protein Against Antibiotic-Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii. Chemistry Proceedings, 18(1), 72. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-29-26879






