Aldehyde Phenylamino-Pyrimidine as Key Precursor for the Synthesis of Imatinib Analogs and In Silico Studies of Their Intermediates †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Section
2.2. Synthesis of N-(2-methyl-5-(1H-pyrrol-1-yl)phenyl)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)pyrimidin-2-amine (2)
2.3. Synthesis of N-(5-azido-2-methylphenyl)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)pyrimidin-2-amine (7)
2.4. Synthesis of (1-(4-methyl-3-((4-(pyridin-3-yl)pyrimidin-2-yl)amino)phenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methanol (9)
2.5. Synthesis of 1-(4-methyl-3-((4-(pyridin-3-yl)pyrimidin-2-yl)amino)phenyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazole-4-carbaldehyde (3)
2.6. Computational Details
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nicolaou, C.A.; Humblet, C.; Hu, H.; Martin, E.M.; Dorsey, F.C.; Castle, T.M.; Burton, K.I.; Hu, H.; Hendle, J.; Hickey, M.J.; et al. Idea2Data: Toward a new paradigm for drug discovery. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, J.P.; Rees, S.; Kalindjian, S.B.; Philpott, K.L. Principles of early drug discovery. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 162, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleicher, K.H.; Bohm, H.J.; Muller, K.; Alanine, A.I. Hit and lead generation: Beyond high-throughput screening. Nature 2003, 2, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, N. Scaffold Hopping in Medicinal Chemistry, 1st ed.; Editorial Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dörwald, F.Z. Lead Optimization for Medicinal Chemist, 1st ed.; Editorial Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, J.; Ganellin, C.R. Analogue-Based Drug Discovery II, 2nd ed.; Editorial Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Raju, T.N.K. The Nobel Chronicles. Lancet 2000, 355, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Feunang, Y.D.; Guo, A.C.; Lo, E.J.; Marcu, A.; Grant, J.R.; Sajed, T.; Johnson, D.; Li, C.; Sayeeda, Z.; et al. DrugBank 5.0: A major update to the DrugBank database for 2018. Nucleic. Acids. Res. 2018, 46, D1074–D1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capdeville, R.; Buchdunger, E.; Zimmermann, J.; Matter, A. Glivec (STI571, imatinib), a rationally developed, targeted anticancer drug. Nat. Rev. 2002, 1, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, C.; Pimentel, L.; Canzian, H.; Oliveira, A.; Junior, F.; Dantas, R.; Hoelz, L.; Marinho, D.; Cunha, A.; Bastos, M.; et al. Hybrids of Imatinib with Quinoline: Synthesis, Antimyeloproliferative Activity Evaluation, and Molecular Docking. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 309–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LL Oliveira, A.; Moura, S.; Pimentel, L.; Neto, J.; Dantas, R.; Silva, F., Jr.; Bastos, M.; Boechat, N. New Imatinib Derivatives with Antiproliferative Activity against A549 and K562 Cancer Cells. Molecules 2022, 27, 750–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, F.; Chen, X.; He, Y.; You, Q.; Zhou, H. Identification of Type II Inhibitors Targeting BRAF Using Privileged Pharmacophores. Chem. Biol. Drug. Des. 2014, 83, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desogus, A.; Schenone, S.; Brullo, C.; Tintori, C.; Musumeci, F. Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase inhibitors: A patent review. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2015, 25, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Guo, Z. Medicinal chemistry strategies in follow-on drug discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2009, 14, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jourdan, J.P.; Since, M.; Kihel, L.E.; Lecoutey, C.; Corvaisier, S.; Legay, R.; de Oliveira Santos, J.S.; Cresteil, T.; Malzert-Fréon, A.; Rochais, C.; et al. Novel benzylidenephenylpyrrolizinones with pleiotropic activities potentially useful in Alzheimer’s disease treatment. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 114, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servín-García, G.; Chacon-García, L.; Islas-Jacome, A.; Gomez-Hurtado, M.A.; Rodríguez-García, G.; del Río, R.E.; Cortés-García, C.J. Late-stage functionalization of Vouacapane derivatives from Caesalpinia platyloba by a Groebke-Blackburn-Bienaymé reaction. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2023, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iranpoor, N.; Panahi, F.; Erfan, S.; Roozbin, F. Selective and Efficient Formylation of Indoles (C3) and Pyrroles (C2) Using 2,4,6-Trichloro-1,3,5-Triazine/Dimethylformamide (TCT/DMF) Mixed Reagent. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2017, 54, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Morales, C.M.; Araujo-Huitrado, J.G.; López-Hernández, Y.; Contreras-Celedón, C.; Islas-Jácome, A.; Granados-López, A.J.; Solorio-Alvarado, C.R.; López, J.A.; Chacón-García, L.; Cortés-García, C.J. A One-Pot Six-Component Reaction for the Synthesis of 1,5-Disubstituted Tetrazol-1,2,3-Triazole Hybrids and Their Cytotoxic Activity against the MCF-7 Cell Line. Molecules 2021, 26, 6104–6117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


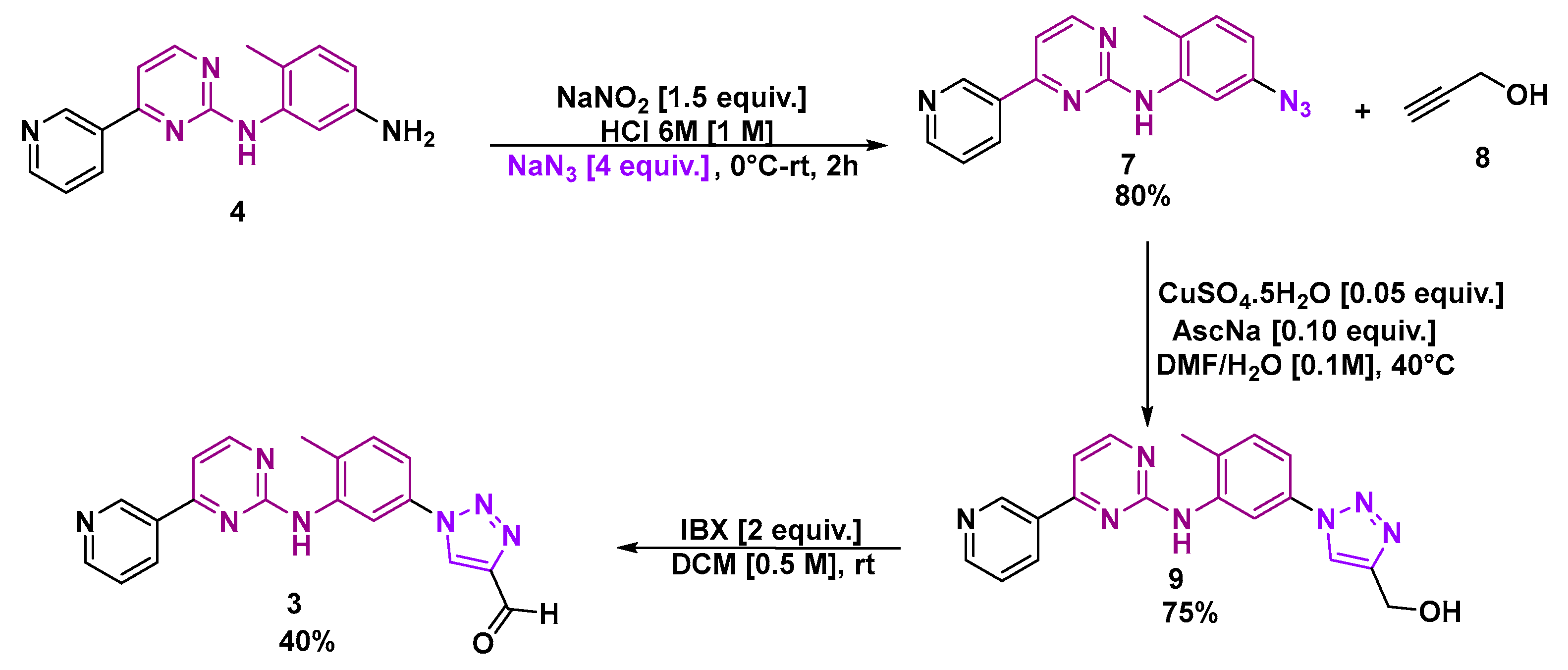

| Compounds | Receptor | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4WTP | 2HZI | |||
| ΔG (kcal/mol) | ki (nM) | ΔG (kcal/mol) | ki (nM) | |
| 2 | −9.32 | 147.95 | −9.51 | 107.06 |
| 9 | −9.7 | 77.39 | −8.89 | 304.09 |
| 10a | −10.69 | 14.51 | −10.82 | 11.78 |
| 10b | −9.39 | 131.87 | −8.55 | 536.54 |
| 10c | −10.54 | 18.67 | −11.39 | 4.46 |
| 10d | −10.5 | 20.27 | −8.88 | 309.21 |
| 10e | −9.82 | 63.43 | −9.75 | 71.42 |
| 10f | −12.04 | 1.49 | −9.09 | 215.89 |
| 10g | −9.62 | 89.23 | −10.78 | 12.51 |
| 10h | −10.41 | 23.34 | −10.45 | 21.89 |
| 10i | −11.56 | 3.38 | −9.54 | 101.34 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tierrablanca-Arias, L.E.; Cervantes-Valencia, H.; Piña-Gordillo, M.N.; Chacón-García, L.; Suárez-Castro, A.; Cortes-García, C.J. Aldehyde Phenylamino-Pyrimidine as Key Precursor for the Synthesis of Imatinib Analogs and In Silico Studies of Their Intermediates. Chem. Proc. 2023, 14, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-27-16108
Tierrablanca-Arias LE, Cervantes-Valencia H, Piña-Gordillo MN, Chacón-García L, Suárez-Castro A, Cortes-García CJ. Aldehyde Phenylamino-Pyrimidine as Key Precursor for the Synthesis of Imatinib Analogs and In Silico Studies of Their Intermediates. Chemistry Proceedings. 2023; 14(1):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-27-16108
Chicago/Turabian StyleTierrablanca-Arias, Luz E., Hugo Cervantes-Valencia, Mitzi N. Piña-Gordillo, Luis Chacón-García, Abel Suárez-Castro, and Carlos J. Cortes-García. 2023. "Aldehyde Phenylamino-Pyrimidine as Key Precursor for the Synthesis of Imatinib Analogs and In Silico Studies of Their Intermediates" Chemistry Proceedings 14, no. 1: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-27-16108
APA StyleTierrablanca-Arias, L. E., Cervantes-Valencia, H., Piña-Gordillo, M. N., Chacón-García, L., Suárez-Castro, A., & Cortes-García, C. J. (2023). Aldehyde Phenylamino-Pyrimidine as Key Precursor for the Synthesis of Imatinib Analogs and In Silico Studies of Their Intermediates. Chemistry Proceedings, 14(1), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecsoc-27-16108






