Abstract
This study focuses on the polyphenol levels and antioxidant activity in the water kefir beverage after 72 and 96 h of fermentation. The exopolysaccharides (dextran) were extracted from water kefir granules and characterized using Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). Increasing the fermentation time induced a significant increase both in polyphenol content, with more than 100% for each of the polyphenol classes investigated, and in antioxidant activity. The kefir grain accumulated higher levels of dextran. The tribiotic characteristics of water kefir, determined by the combination of prebiotics (polyphenols and polysaccharides) with probiotics and bioactive microbial metabolites, are enhanced after 96 h of fermentation.
1. Introduction
Water kefir is a homemade fermented drink that has started to receive attention in scientific research. This fermented drink is produced by immersing the grains with a specific symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY) in a 5–10% sucrose solution, along with various dried fruits and slices of lemon. Usually, this mixture of SCOBY, sucrose solution, dried fruits and slices of lemon is left to ferment for 1–2 days at a temperature of 25–30 °C [1]. The result of this fermentation process is a carbonated beverage with a pale yellow hue and a pleasant sour taste. Importantly, the resulting beverage contains relatively low levels of sugar and alcohol [2].
Water kefir includes a variety of compounds that may provide health benefits when consumed, including those with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial properties [3]. SCOBY produces a specific biofilm structure, that is the water kefir grains, which consist of a symbiotic matrix of various microorganisms, such as lactic acid bacteria (LAB) like Lactobacillus paracasei, Lactobacillus hilgardii, and Lactobacillus nagelii, as well as yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) and acetic acid bacteria [3,4]. These grains have a gelatinous texture and typically appear in shades of brown to translucent white [2,5]. Throughout the fermentation process, the microorganisms within the water kefir grains metabolize the sugars, resulting in the production of lactic acid, carbon dioxide, and small amounts of alcohol. These byproducts contribute to the distinct taste and carbonation found in water kefir [6]. As the fermentation progresses, some of the microorganisms may transfer into the liquid, enriching it with probiotics and other beneficial compounds. This process is known as “pitching” and transforms the sugar–water solution into the fermented beverage that is known as water kefir [5].
Furthermore, lactic acid bacteria are able to metabolize sucrose to produce two important types of polysaccharides: α-glucans and fructans. In the case of water kefir, the main α-glucan that is formed is dextran [7]. Depending on the fermentation substrates, water kefir drinks can be enriched with other valuable compounds such as polyphenols which have antioxidant activity (AOA). We have limited knowledge concerning the polyphenol content and AOA in water kefir and how the fermentation time influences these, in the absence of polyphenol-rich substrates. Also rather limited is the information about the production of polysaccharides after 3 days of fermentation.
The combination of prebiotics (polyphenols and polysaccharides) with probiotics and bioactive microbial metabolites is characteristic of tribiotic products [8,9,10]. Understanding the evolution of these components at the end of the fermentation is useful for the production of a beverage with enhanced tribiotic effect.
The main aim of this research was to evaluate the polyphenol content and antioxidant potential of water kefir after fermentation periods of 3 and 4 days. An additional goal was the extraction of dextran polysaccharides from water kefir granules at the end of the fermentation period.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The following substances were employed: 96% pharmaceutical ethanol, copper sulfate, potassium ferricyanide (from Chimopar Srl, Bucharest, Romania), Trolox with a purity of 97% (from Acros Organics, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Pittsburgh, PA, USA), gallic acid, 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl, and ascorbic acid (procured from Sigma-Aldrich, Merck Group, Darmstadt, Germany), Folin Ciocalteu’s phenol reagent, iron(III) chloride with a purity of 98%, 2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline with a purity of 98%, and 2,4,6-tri(2-pyridyl-1,3,5-triazine) with a purity of 98% (all from Alfa Aesar, Kandel, Germany), hydrochloric acid, acetic acid (from Chimopar Srl, Bucharest, Romania), sodium acetate, phenol (from Scharlau, Barcelona, Spain), chlorogenic acid (from Cayman Chemical, Ann Arbor, MI, USA), and quercetin dihydrate (from Sigma-Aldrich, Merck Group, Darmstadt, Germany). The water kefir granules were purchased from The Water Kefir Company, Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
2.2. Preparing Water Kefir Drink
Water kefir granules were introduced into a solution containing 5% (w/v) sugar, 1 L of sterilized water, and 50 g of lemon (equivalent to 2 slices). The container was covered with a sterile gauze and left to ferment for 4 days at a temperature of 21 °C, with occasional stirring during this period. Once the fermentation process was complete, the kefir grains were separated and kept aside for future use in a new fermentation cycle and for dextran extraction. The resulting beverage was then refrigerated at 4 °C and reserved for further analysis. A sample was aseptically collected after 3 days as well. The dried substance was determined by freeze-drying 1 mL of water kefir sample at 3 and 4 days of fermentation obtaining the following values: 0.053 g dry substance water kefir fermented for 3 days and 0.044 g dry substance water kefir fermented for 4 days.
2.3. Analysis of Total Phenolic Content
2.3.1. Total Polyphenol Content
The Folin–Ciocalteau method [11] was used to determine polyphenol content. A calibration curve was prepared using known concentrations of gallic acid. Results were expressed as μg of gallic acid equivalent per gram of dry mass (μg GAE/g).
2.3.2. Total Flavonoid Content
We used the sodium acetate colorimetric method [12]. Results were expressed as μg of quercetin equivalent per gram of dry mass (μg QE/g).
2.3.3. Total Hydroxycinnamic Acids
A modified method [13] involving HCl and NaOH was used to determine total hydroxycinnamic acid content. Results were expressed as μg of chlorogenic acid per gram of dry mass (μg Chae/g).
2.4. Analysis of Antioxidant Activity
The assessment of antioxidant activity was carried out through a series of experiments employing the DPPH assay [14], FRAP assay [15], CUPRAC assay [16], and PFRAP assay [17]. These methods utilized diverse standard solutions: Trolox was used for the DPPH, FRAP, and CUPRAC assays, while PFRAP employed ascorbic acid. The outcomes were presented as Trolox equivalents and ascorbic acid equivalents per gram of dry mass (μM TE/g and ascorbic acid equivalents/g).
2.5. Total Carbohydrates with H2SO4-Phenol Method
Total carbohydrates were determined using the H2SO4-Phenol method [18]. Glucose was used as a standard. Results were expressed as milligrams of glucose equivalent per gram of sample.
2.6. Dextran Extraction
Dextran was extracted from water kefir grains using a 10:1 water-to-grains ratio (w/v), hot water extraction, centrifugation, and ethanol precipitation. The resulting exopolysaccharides were freeze-dried [18].
2.7. FT-IR Analysis of Dextran
Fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR) spectra were acquired using a Perkin Elmer instrument located in Beaconsfield, UK. The measurements were conducted across a frequency range spanning from 4000 to 500 cm−1, employing a resolution of 4 cm−1.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
Statistical significance was evaluated through independent samples t-tests, employing the SPSS 26 statistical software (IBM SPSS Corp, Armonk, NY, USA). A significance level of p < 0.05 was adopted. The experiments were conducted in triplicate. The significance levels were denoted using the following symbols: p < 0.05 was indicated as “*”, p between 0.05 and 0.01 as “**”, and p between 0.01 and 0.001 as “***”. For highly significant results with p < 0.001, “****” was used.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of Total Phenolic Content
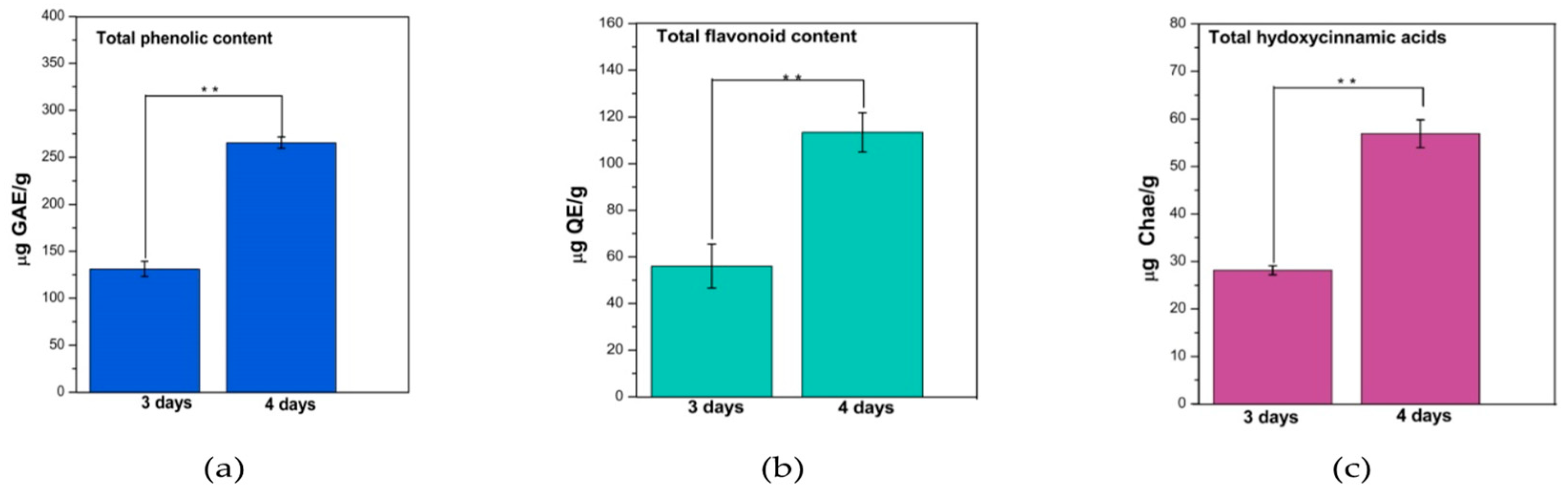
From Figure 1 it can be seen that the fermentation time significantly influenced (p < 0.001) the total polyphenol content (TPC), total flavonoid content (TFC), and total hydroxycinnamic acid content (HAT) in water kefir. Increasing the fermentation period from 3 to 4 days increased more than 2* the polyphenol content.
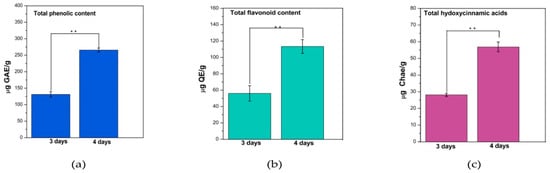
Figure 1.
Assessment of total polyphenols (a) (μg GAE/g dried mass sample), flavonoids (b) (μg QE/g dried mass sample) and hydroxycinnamic acids (c) (μg Chae/g dried mass sample). Bars are error bars. Statistical significance was assessed using independent samples t-tests. The sample size (p) for each group was 3. The significance level (p) was set at 0.05. p < 0.05 was indicated as “*”, p between 0.05 and 0.01 as “**”, and p between 0.01 and 0.001 as “***”. For highly significant results with p < 0.001, “****” was used.
3.2. Analysis of Antioxidant Activity
To assess the antioxidant activity of samples obtained from the two fermentation periods, several methods were used, such as DPPH for measuring radical scavenging activity, FRAP, PFRAP, and CUPRAC for evaluating reducing antioxidant power.
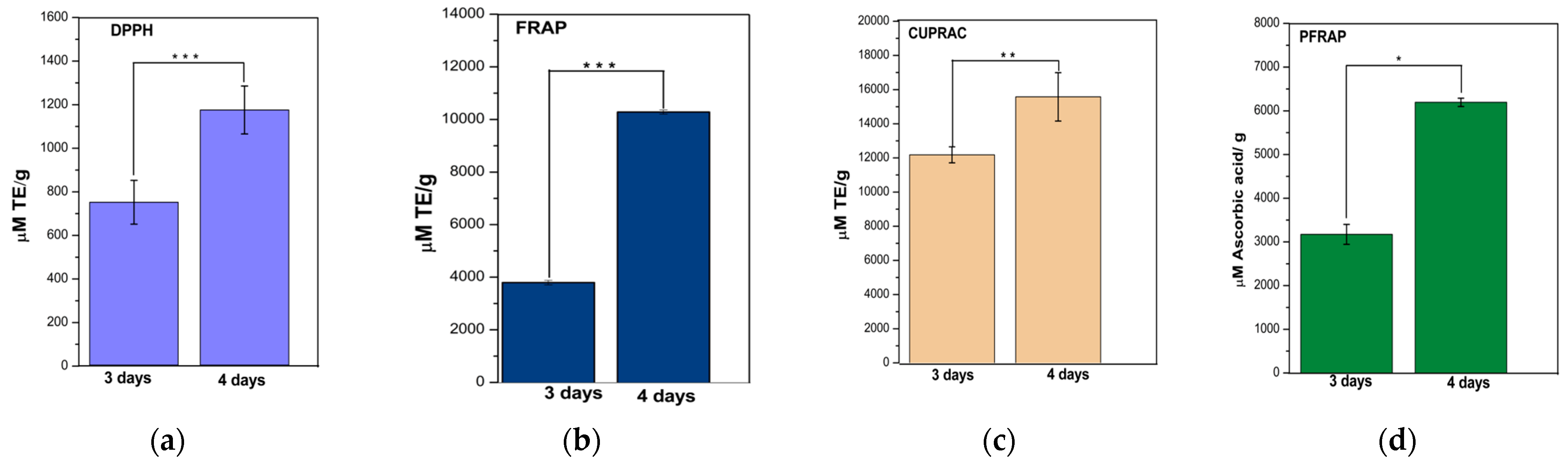
For the DPPH, FRAP and CUPRAC methods, the p values range from 0.004 to 0.001 (Figure 2a–c), indicating strong statistical evidence that fermentation time has a significant effect on the results. However, for the PFRAP method, the p value is 0.014 (Figure 2d), suggesting weaker statistical evidence for a significant impact, although there could still be a significant influence at a stricter level of significance. In conclusion, fermentation time seems to have a significant impact on the results for most methods (DPPH, FRAP and CUPRAC), whereas for the PFRAP method the influence of fermentation time is not statistically significant.
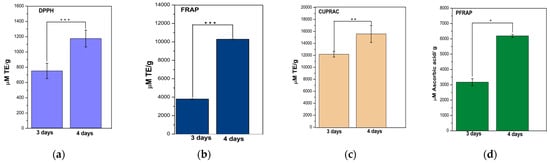
Figure 2.
Antioxidant activity assays using the DPPH (a), FRAP (b), CUPRAC (c) and PFRAP (d) methods. Results were expressed as TE (μM Trolox equivalent/g sample mass) or ascorbic acid equivalents (for PFRAP) at 3 and 4 days. Bars are error bars. Statistical significance was assessed using independent samples t-tests. p < 0.05 was indicated as “*”, p between 0.05 and 0.01 as “**”, and p between 0.01 and 0.001 as “***”. For highly significant results with p < 0.001, “****” was used. The significance level (p) was set at 0.05. p was between 0.004 and 0.0001 for DPPH, FRAP and CUPRAC; p was 0.014 for PFRAP.
In fermented beverages like water kefir, several microorganisms, including Lactobacillus, Lactococcus, Leuconostoc, and Streptococcus species, play a crucial role [19]. During the fermentation process, these microorganisms facilitate enzymatic hydrolysis, breaking down the cell wall structure and metabolizing the bioactive compounds present. This could explain the increase in antioxidant activities and phenolic compound content with the increase in fermentation time. Lemons are especially known for their high content in citric and ascorbic acid, but they also contain polyphenols with proven health benefits [20,21,22,23], the release of which is probably enhanced by fermentation. The observed increase in antioxidant activity after 4 days of fermentation suggests that longer fermentation periods are beneficial for improving the nutritional quality of water kefir. It is important to note that the antioxidant activity observed in fermented water kefir may vary depending on factors such as the composition of the kefir grains, fermentation conditions, and specific nutrients present in the beverage [6,16].
3.3. Total Carbohydrate Content (TCC)
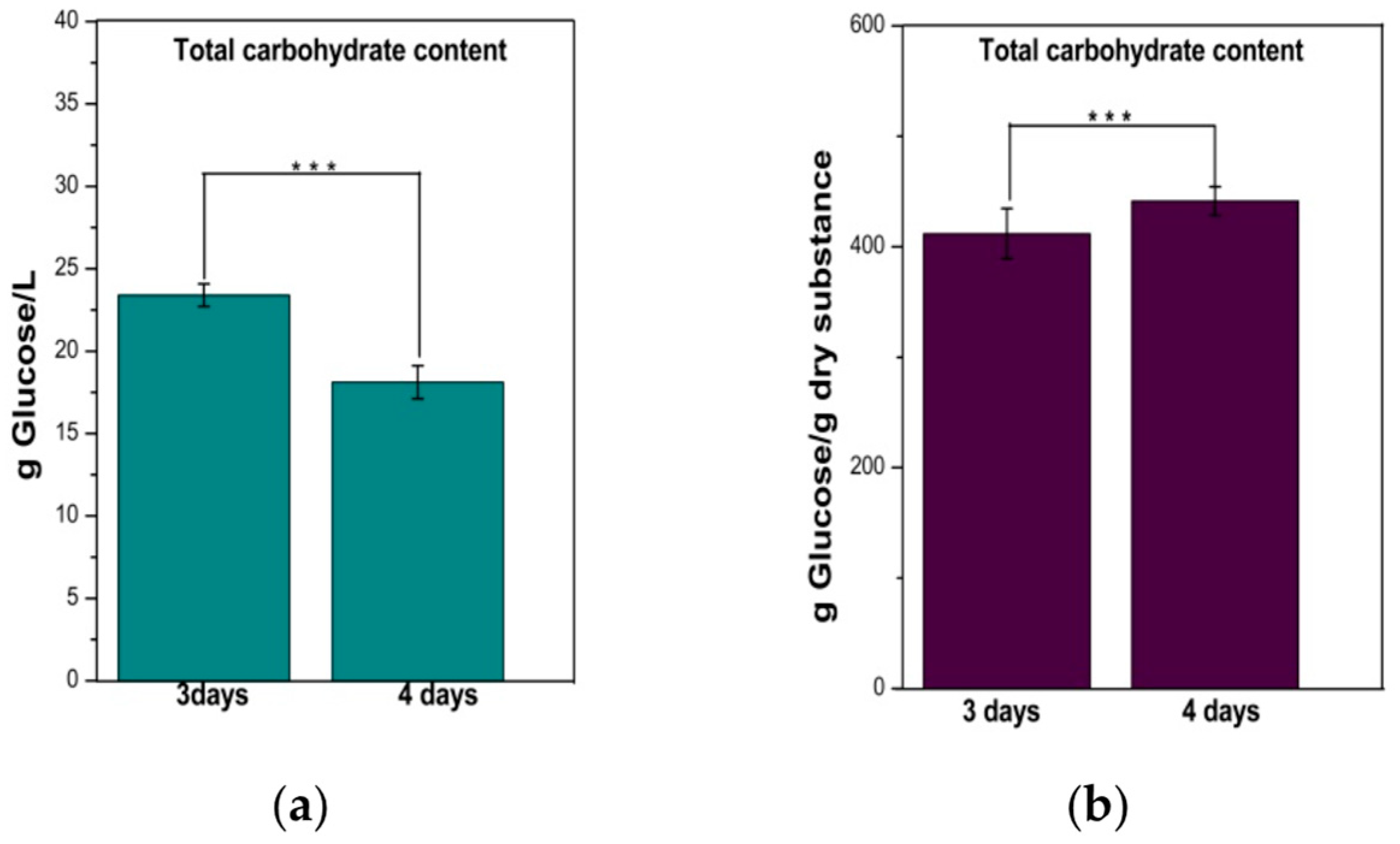
From Figure 3a one can observe that the left TCC is approx. 23 g/L from the 50 g/L (5%) initial sugar concentration after 3 days of fermentation; i.e., a significant proportion of initial saccharides were metabolized by the SCOBY consortium. After 4 days of fermentation the concentration decreases to 18 g/L. The TCC was also expressed per gram of dry substance, with the results indicating that almost 45% of the dry substance is represented by carbohydrates (Figure 3b).
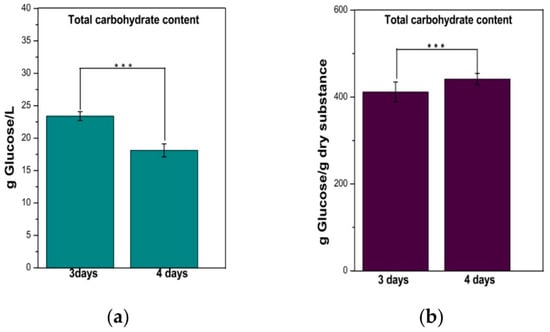
Figure 3.
The total carbohydrate content (TCC) of the water kefir beverage: (a) per liter of beverage; (b) per gram of dry substance. Bars are error bars. Statistical significance was assessed using independent samples t-tests. The significance level (p) was set at 0.05. The sample size (n) for each group was 3. p < 0.05 was indicated as “*”, p between 0.05 and 0.01 as “**”, and p between 0.01 and 0.001 as “***”. For highly significant results with p < 0.001, “****” was used. p was <0.001 for TCC.
3.4. FTIR Analysis of the Extract from Water Kefir Granules
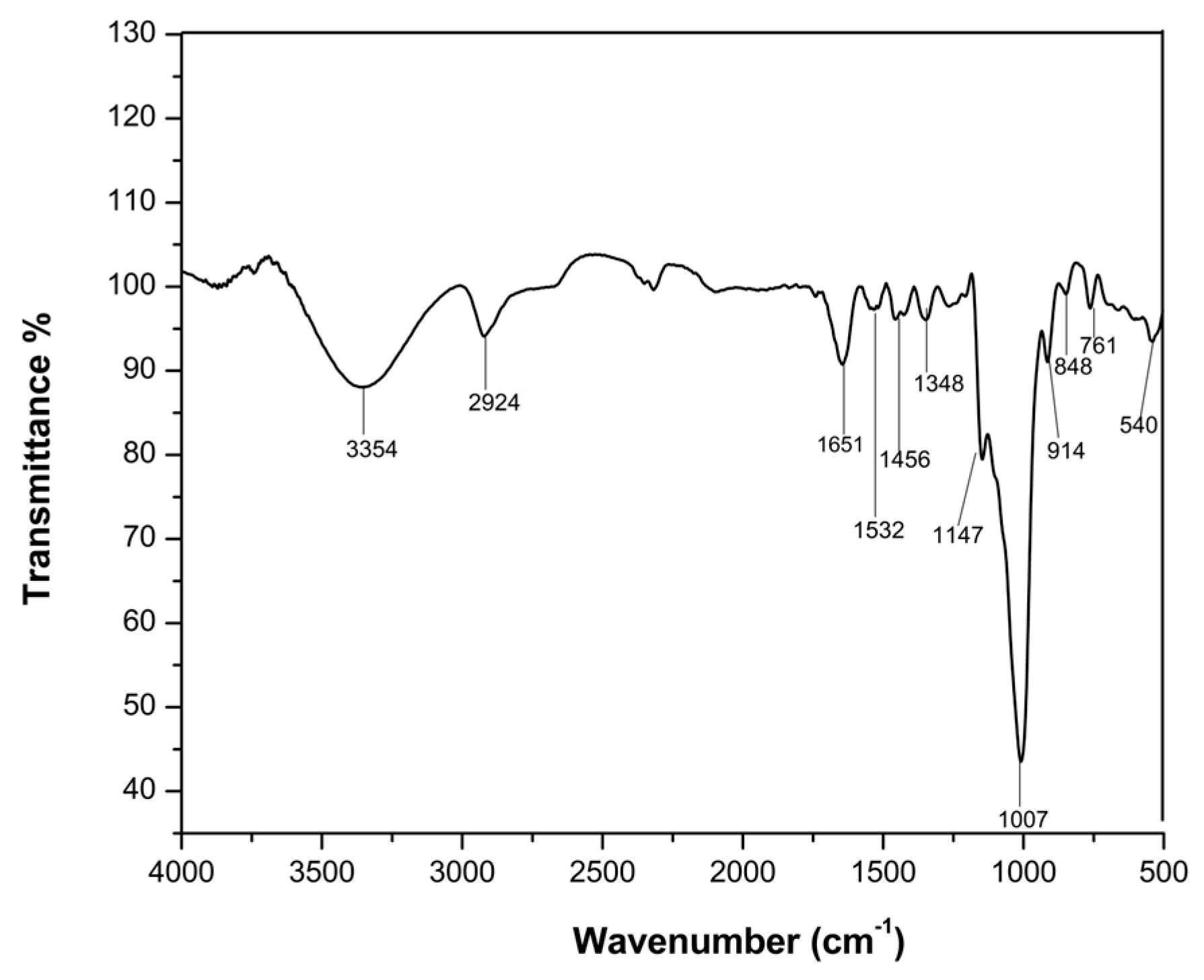
The main component of water kefir grains is dextran, which is a polysaccharide metabolized by lactic acid bacteria (LAB) such as Lactobacillus casei, Leuconostoc mesenteroides, Lactobacillus hordei and Lactobacillus hilgardii. Dextran is a high-molecular-weight homopolysaccharide composed of glucose molecules linked by 1–6 glycosidic bonds. Branching in the dextran structure occurs at the 2-, 3- or 4-positions [24], with the structure ascertained by a FT-IR analysis of the dextran sample. Figure 4 presents the FTIR spectrum of the extract from the water kefir grains after 4 days of fermentation, with several bands characteristic of stretching and deformation vibrations of chemical bonds in polysaccharides.
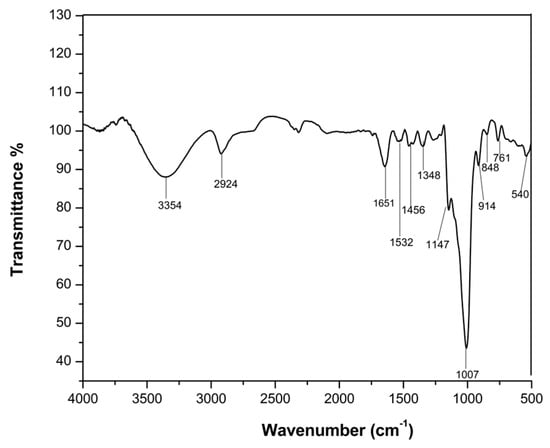
Figure 4.
ATR-FTIR spectrum of the extract from water kefir granules.
The band at 3221 cm−1 represents the stretching vibrations of the OH groups involved in hydrogen bonds. The band at 2924 cm−1 shows the stretching vibrations of C-H bonds (sp3 hybridization). The band at 1651 cm−1 is given by -OH groups of adsorbed water [25,26,27], but it can also show the contribution of amide I from proteins possibly extracted from the SCOBY biofilm. The band at 1532 cm−1 is usually attributed to amide II in proteins. The band at 1348 cm−1 is characteristic of the deformation band of the C-H bond [28].
The region 1200–900 cm−1 is characteristic of polysaccharides with a pyranosic structure, that could be given by the monomeric units of glucose present in dextran [29]. The band at 1147 cm−1 corresponds to the stretching vibrations of the C-O bond from the carboxylic group. The band at 1007 cm−1 is characteristic of the stretching vibrations of the ether bond C-O-C, in glycosidic position α-1→6 or α-1→. The peak at 917 cm−1 comes from the vibrations of the pyranosic ring, and the bands under 900 cm−1 could be attributed to C-H bonds. Mainly the stretching vibrations of lateral groups (C-OH, C-C, C-H) can be found in this region.
The FTIR spectrum confirms the predominant polysaccharide character of the extract and suggests the possible presence of proteins.
4. Conclusions
Based on our preliminary findings, it can be observed that longer fermentation times result in the formation of a beverage that is both richer in bioactive compounds with antioxidant properties and also a significant source of dextran. This indicates that extended fermentation is useful in enhancing the nutritional and functional attributes of the final water kefir product.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.O.; methodology, E.-A.C.; validation, D.C.-A. and F.O.; formal analysis, E.-A.C.; investigation, E.-A.C. and I.P.-T.; resources, F.O.; data curation, E.-A.C.; writing—original draft preparation, E.-A.C.; writing—review and editing, D.C.-A.; visualization, F.M. and D.C.-A.; supervision, F.M. and D.C.-A.; project administration, D.C.-A. and F.O.; funding acquisition, F.O. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by project POC-A1-A1.2.3-G-2015-P_40_352-SECVENT, Sequential processes to close bioeconomy side stream and innovative bioproducts resulted from these, contract 81/2016, SMIS 105684, funded by Cohesion Funds of the European Union, subsidiary project 1391/2022-FructiRan. The APC was funded by the same project.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data are found within this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Gulitz, A.; Stadie, J.; Wenning, M.; Ehrmann, M.A.; Vogel, R.F. The microbial diversity of water kefir. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 151, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishzadeh, P.; Orsat, V.; Martinez, J.L. Process optimization for development of a novel water kefir drink with high antioxidant activity and potential probiotic properties from Russian olive fruit (Elaeagnus angustifolia). Food Bioprocess Technol. 2021, 14, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, A.F.; Moure, M.C.; Quiñoy, F.; Esposito, F.; Simonelli, N.; Medrano, M.; León-Peláez, Á. Water kefir, a fermented beverage containing probiotic microorganisms: From ancient and artisanal manufacture to industrialized and regulated commercialization. Future Foods 2022, 5, 100123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laureys, D.; Van Jean, A.; Dumont, J.; De Vuyst, L. Investigation of the instability and low water kefir grain growth during an industrial water kefir fermentation process. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 2811–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verce, M.; De Vuyst, L.; Weckx, S. Shotgun metagenomics of a water kefir fermentation ecosystem reveals a novel Oenococcus species. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Sounderrajan, A.; Serventi, L. Water kefir: A review of its microbiological profile, antioxidant potential and sensory quality. Acta Sci. Nutr. Health 2020, 4, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fels, L.; Jakob, F.; Vogel, R.F.; Wefers, D. Structural characterization of the exopolysaccharides from water kefir. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 189, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uțoiu, E.; Matei, F.; Toma, A.; Diguță, C.F.; Ștefan, L.M.; Mănoiu, S.; Vrăjmașu, V.V.; Moraru, I.; Oancea, A.; Israel-Roming, F. Bee collected pollen with enhanced health benefits, produced by fermentation with a Kombucha Consortium. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotârleţ, M.; Vasile, A.M.; Gaspar-Pintiliescu, A.; Oancea, A.; Bahrim, G.E. Tribiotication strategy for the functionalization of bovine colostrum through the biochemical activities of artisanal and selected starter cultures. CyTA-J. Food 2020, 18, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera-Barjas, G.; Banerjee, A.; Valdes, O.; Moncada, M.; Sirajunnisa, A.R.; Surendhiran, D.; Ramakrishnan, G.; Rani, N.S.; Hamidi, M.; Kozani, P.S. Food biotechnology: Innovations and challenges. In Future Foods; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 697–719. [Google Scholar]
- Mahdavi, R.; Nikniaz, Z.; Rafraf, M.; Jouyban, A. Determination and comparison of total polyphenol and Vitamin C Contents of Natural Fresh and Commercial Fruit Juices. Pak. J. Nutr. 2010, 9, 968–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shraim, A.M.; Ahmed, T.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Hijji, Y.M. Determination of total flavonoid content by aluminum chloride assay: A critical evaluation. LWT 2021, 150, 111932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Štefan, M.B.; Vuković Rodríguez, J.; Blažeković, B.; Kindl, M.; Vladimir-Knežević, S. Total hydroxycinnamic acids assay: Prevalidation and application on Lamiaceae species. Food Anal. Methods 2014, 7, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, S.; Joshi, A.; Arora, B.; Bhowmik, A.; Sharma, R.; Kumar, P. Significance of FRAP, DPPH, and CUPRAC assays for antioxidant activity determination in apple fruit extracts. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2020, 246, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzie, I.F.; Strain, J. [2] Ferric reducing/antioxidant power assay: Direct measure of total antioxidant activity of biological fluids and modified version for simultaneous measurement of total antioxidant power and ascorbic acid concentration. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1999; Volume 299, pp. 15–27. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitriu, L.; Constantinescu-Aruxandei, D.; Preda, D.; Nichițean, A.-L.; Nicolae, C.-A.; Faraon, V.A.; Ghiurea, M.; Ganciarov, M.; Băbeanu, N.E.; Oancea, F. Honey and Its Biomimetic Deep Eutectic Solvent Modulate the Antioxidant Activity of Polyphenols. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Xu, T.; Lu, B.; Liu, R. Guidelines for antioxidant assays for food components. Food Front. 2020, 1, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasheminya, S.-M.; Dehghannya, J. Novel ultrasound-assisted extraction of kefiran biomaterial, a prebiotic exopolysaccharide, and investigation of its physicochemical, antioxidant and antimicrobial properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 243, 122645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorda, F.A.; de Melo Pereira, G.V.; Thomaz-Soccol, V.; Rakshit, S.K.; Pagnoncelli, M.G.B.; de Souza Vandenberghe, L.P.; Soccol, C.R. Microbiological, biochemical, and functional aspects of sugary kefir fermentation-A review. Food Microbiol. 2017, 66, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Salas, P.; Gómez-Caravaca, A.M.; Arráez-Román, D.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Guerra-Hernández, E.; García-Villanova, B.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, A. Influence of technological processes on phenolic compounds, organic acids, furanic derivatives, and antioxidant activity of whole-lemon powder. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, C.; Wakita, Y.; Inoue, T.; Hiramitsu, M.; Okada, M.; Mitani, Y.; Segawa, S.; Tsuchiya, Y.; Nabeshima, T. Effects of lifelong intake of lemon polyphenols on aging and intestinal microbiome in the senescence-accelerated mouse prone 1 (SAMP1). Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuchi, Y.; Hiramitsu, M.; Okada, M.; Hayashi, S.; Nabeno, Y.; Osawa, T.; Naito, M. Lemon Polyphenols Suppress Diet-induced Obesity by Up-Regulation of mRNA Levels of the Enzymes Involved in β-Oxidation in Mouse White Adipose Tissue. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2008, 43, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, D.; Vilas-Boas, A.A.; Teixeira, P.; Pintado, M. Functional Ingredients and Additives from Lemon by-Products and Their Applications in Food Preservation: A Review. Foods 2023, 12, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidović, S.Z.; Miljković, M.G.; Antonović, D.G.; Rajilić-Stojanović, M.D.; Dimitrijević-Branković, S.I. Water Kefir grain as a source of potent dextran producing lactic acid bacteria. Hem. Ind. 2015, 69, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidović, S.; Miljković, M.; Lazić, V.; Jović, D.; Jokić, B.; Dimitrijević, S.; Radetić, M. Impregnation of cotton fabric with silver nanoparticles synthesized by dextran isolated from bacterial species Leuconostoc mesenteroides T3. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 131, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.; Li, G.; Wang, C.; Ling, B.; Yang, R.; Huang, S. Extraction and characterization of dextran from Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides YB-2 isolated from mango juice. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 207, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coma, M.E.; Peltzer, M.A.; Delgado, J.F.; Salvay, A.G. Water kefir grains as an innovative source of materials: Study of plasticiser content on film properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 120, 109234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucena, M.d.A.; Ramos, I.F.d.S.; Geronço, M.S.; de Araújo, R.; da Silva Filho, F.L.; da Silva, L.M.L.R.; de Sousa, R.W.R.; Ferreira, P.M.P.; Osajima, J.A.; Silva-Filho, E.C. Biopolymer from Water Kefir as a Potential Clean-Label Ingredient for Health Applications: Evaluation of New Properties. Molecules 2022, 27, 3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Araújo, C.; Macedo, L.L.; Teixeira, L.J.Q. Use of mid-infrared spectroscopy to predict the content of bioactive compounds of a new non-dairy beverage fermented with water kefir. LWT 2023, 176, 114514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).