Abstract
Sulfite liquor is the by-product of wood chips treatment. An alternative method for recovering the carbonaceous components from sulfite liquor was investigated. A 3% CS suspension surprisingly incorporated almost all the carbon–sulfite phase in an aerogel system rising up at the surface of a beige liquid phase. The resulting solid and liquid phases were analytically characterized usingTEM-EDX, XRD, FTIR, ICP-OES, and UV-Vis methods, respectively. The TEM-EDX analysis revealed nanoparticles and microneedles with high C, O, Na, and S contents ionotropically adsorbed by CS, with this new hybrid material appearing as a biopolymer–carbon–metal nanocomposite aerogel with potential adsorbent, catalytic, and/or semiconductive properties.
1. Introduction
The sulfite liquor which resulted during cellulose extraction contains sodium salts and hundreds of different organic molecules with many hydroxyl groups obtained from the thermo-chemical braking of α-O-4 and β-O-4 ether bonds between hemicellulose, syringyl, and guaiacyl monomers of lignin [1]. The energetic value of sulfite liquor is known, and thisis the main application; however, a higher degree of interest has emerged intothe separation and valorization of the diversity of biocomponents, including biodiesel, fertilizers, and adsorbents [1,2,3,4,5]. The proposed ionotropic adsorption of carbonaceous and metallic nano/micro-particles with activated chitosan [6,7], simultaneously with the separation of the two ionically interconnected nano-dispersed phases from the residual sulfite liquor, represents an innovative approach, with only a few studieshaving been conducted on this subject [3,8,9]. There are also documented studies in the literature on the adsorbent properties of chitosan for pollutants and metals in water [10,11]. Chitosan’sionic properties and polymeric structure also means that it is recommended for electrochemical, -sensor, and -capacitor applications [12,13,14,15], respectively, as well as (bio)catalytic applications [16,17,18,19]. Thus, using the proposed new method, both the separation of the carbon phase from the sulfite liquor and the production of a possible multi-functional biopolymer–carbon–metal nanocomposite aerogel with (bio)catalytic and electro-/semiconductive properties can be achieved.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Synthesis Method
Sulfite liquor (SL) provided by Pulp and Paper Factory (Combinatul de CelulozășiHârtie S.A., Drobeta-Turnu Severin, Romania) derives from beech and poplar, and the fraction used is a viscous, adhesive, homogeneous brown suspension with amean density of 1082 kg/m3. This research focused on the non-thermal separation of the carbonic phase from ligno-sulfonated mineral sulfite liquor using a homogeneous suspension of 1, 2, and 3% chitosan ionically activated with 1% acetic acid in avolume ratio of 1:1 (20 mL:20 mL) CS:SL. The 3% chitosan suspension (CS3) achieved the separation of the carbonic phase from the initial SL sulfite liquor while converting it into a floating aerogel on top of a clear solution with a pale beige–yellow aspect.
2.2. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis was performed with the help of a Rigaku diffractometer (Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) and SmartLab acquisition software (version 1.3.3.0) working in wide-angle X-ray diffraction (WAX) mode at 40 kV voltage and a 200 mA emission current, generating a CuKα1 (λ = 1.54059Å) radiation in the 2θ interval 5–60° with a 4°/min scan speed and 0.02° resolution. The PDXL software (version 2.7.2.0) was used for the smoothing of diffractograms, peak deconvolution and identification, and for evaluation of the crystallinity degree (Xc, %) as the ratio between the area of crystalline peaks and the total peaks area. OriginPro 2022b software (version 9.9.5, OriginLab Corporation, Northampton, MA, USA) was used for importing the PDXL generated “.csv” files for the graphical representation.
2.3. TEM and TEM-EDX Microscopy
Microscopic images of the chitosan–lignin microstructure in a scale of 20–2000 nm were obtained using a TECNAI F20 G2 TWIN Cryo-TEM transmission electron microscope from FEI Company, Wortham, TX, USA, working at 30 kV in LFD mode. Chitosan and sulfite liquor samples were placed on a holey carbon grid without staining due to thegood contrast of the samples. The elemental distribution was determined using the TEM-EDX detector X-MaxN 80T (Oxford Instruments, Abingdon, United Kingdom).
2.4. ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy
The Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectra of raw and processed materials were recorded on an IRTracer-100 FTIR (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan) in attenuated total reflectance (ATR) mode by taking the average of the 45 spectra at a resolution of 4 cm−1 in wavenumbers ranging from 4000 to 400 cm−1. Commercial chitosan from crab shells (highly viscous) and alkali lignin low-sulfonated (both from Merck-SigmaAldrich, St. Louis, MI, USA) were used as the FTIR standards. The exported “.txt” files were graphically overlaid using the OriginPro 2022b. software, version 9.9.5, from OriginLab Corporation (Northampton, MA, USA).
2.5. Inductively Coupled Plasma–Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES)
The concentration of Na, K, P, Ca, Mg, Fe, Si, and Cr was determined viaICP-OES using Optima 2100 DV Perkin Elmer equipment (Perkin Elmer, Waltham, MA, USA).
2.6. Ultraviolet–Visible (UV-Vis) Spectrometry
UV-Vis electronic absorption spectrometry analyzes were performed in the wavelength range of λ 200–1000 nm using theClarioStar BMG Labtech plate reader (Ortenberg, Germany).
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Aerogel Macroscopic Aspect and X-ray Diffraction
The homogeneous 3% cationic chitosan suspension showed a remarkable property of the physical adsorption of carbon nano/microparticles from the residual ligno-sulfonated sulfite liquor in 99% yield, with the resulting liquid phase after filtration being a clear, pale beige–yellow solution, as can be seen in Figure 1a. Chitosan suspensions of concentrations lower than 3% become ionically supersaturated by the multitude of carbonic and ionic compounds in the sulfite liquor that lost their polymeric interconnections, dispersing homogeneously, without phase separation. The carbonaceous aerogel which resulted after the initial SL sulfite liquor made contact with a homogeneous 3% chitosan suspension in a volumetric ratio of 1:1wasanalyzed using X-ray diffraction (XRD), as shown in Figure 1b, and was compared with the initial SL and SLCS hydrogel, together with initial chitosan and lignin as the standard commercial materials.
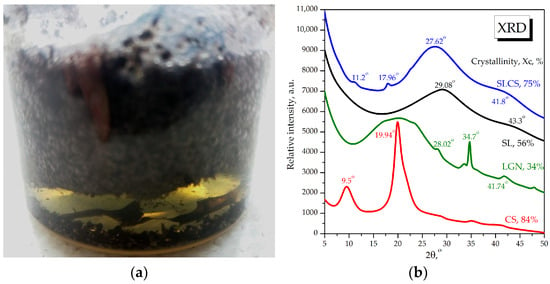
Figure 1.
(a) Photography of ionotropic phases separation and aerogel SLCS aspect. (b) X-ray diffraction analysis of initial sulfite liquor (SL), the resulting aerogel SLCS, commercial alkali lignin (LGN), and chitosan (CS).
The XRD analyses revealed the diffractometric features of the initial and obtained materials. Chitosan is a semi-crystalline biopolymer (83% crystallinity) with two characteristic diffraction peaks at 2θ angles of 9.6° and 19.9°, respectively, with an amorphous peak at 21.1°. The initial dry SL sulfite liquor is mainly amorphous (56% crystallinity) with three broad peaks at 2θ angles of 28.5°, 33° (amorphous), and 43.4°. By mixing the homogeneous CS3% suspension with sulfite liquor, itself a homogeneous carbonic–mineral nanosuspension, a phenomenon of the ionotropic adsorption of carbonic–mineral components into the polymeric structure of the cationic chitosan was produced. It is worth noting that CS suspensions in lower concentrations of 1% and 2% did not cause the separation phenomenon; this was the result of the chitosan dispersing in the sulfite liquor without achieving phase separation. The hypothesis of the separation phenomenon is that at a higher concentration, chitosan predominantly retains its polymeric structure, to which it adsorbs through hydrophobic interactions the carbonaceous nano/microparticle, and through ionic interactions, it adsorbs mineral salts. From Figure 1, it can be seen that the chitosan-specific signal is almost completely lost after interaction with SL sulfite liquor, with the new solid phase SLCS having a sulfite liquor-like diffractogram, with the main peaks being by 2° to the left, yielding 26.5° and 41.2°, respectively. In addition, SLCS shows two low-intensity peaks at 11.2° and 17.9°, which could correspond to a new conformation of chitosan interconnected with carbonaceous structures in sulfite liquor. Also, the SLCS crystallinity of 76% represents an intermediate value between the crystallinity of chitosan—83%—and that of sulfite liquor—56%. Therefore, the X-ray diffraction analysis revealed the adsorption of the carbonic phase of sulfite liquor in the polymeric structure of chitosan and the strong influence of the carbonic phase in denaturing the diffractogram of chitosan and preserving the amorphous character of sulfite liquor.
3.2. TEM-EDX Microscopy
TEM revealed nano- and micro-carbon formations of varying sizes, both needle-like and irregular. The elemental composition determined by X-ray scattering (EDX) showed a high content of Na, the third most abundant element after C and O, followed by S, Ca, Cl, and Si. The resulting carbonaceous particle sizes of chitosan 3% and lignin (SLCS) are predominantly micron-sized (0.5–2 µm), compared to those observed in the 50% diluted sulfite liquor (SLd), which are predominantly nanometric (20–100 nm, Figure 2a,b). Na and S from Na2SO3 are found in both samples in various amounts, being higher in SLCS.
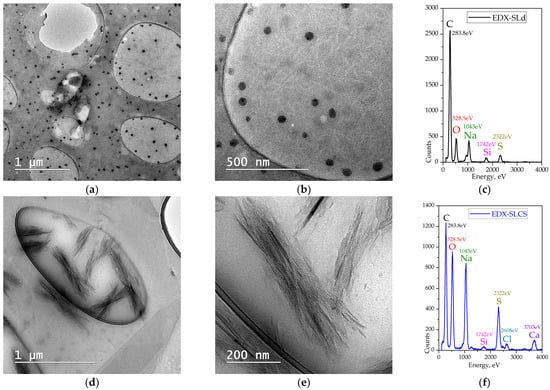
Figure 2.
TEM and TEM-EDX microscopy: (a,b) TEM of SLd; (c) TEM-EDX of SLd; (d,e) TEM of SLCS; (f) TEM-EDX of SLCS.
TEM-EDX microscopy analyses revealed needle-like nano- and micro-carbon formations or irregular shapes representing carbon–metal nanocomposites grafted onto chitosan. The elemental composition determined viaX-ray scattering (EDX) confirms the ionotropic adsorption of some compounds in sulfite liquor with high Na and S contents, but also small amounts of Ca, Cl, and Si.
3.3. ATR-FTIR Spectroscopy
Infrared spectroscopy has proved to be relevant for highlighting absorption bands specific to ligno-sulphonic materials subjected to various physico-thermo-chemical experiments, and is therefore used for spectral comparison with the new chitosan–sulfite liquor aerogel in Figure 3. Chitosan (CS) shows IR absorption bands characteristic of O-H and N-H hydrogen bond vibrations in the wavenumber region of 3500–3000 cm−1, C-H in the region of 3000–2800 cm−1, -OH and -NH in the molecular fingerprint range of 1650–1550 cm−1, amine and amide bands in the region of 1450–1250 cm−1, and bands characteristic of C-O and C-O-C bonds in polysaccharides in the region of 1200–850 cm−1, respectively.
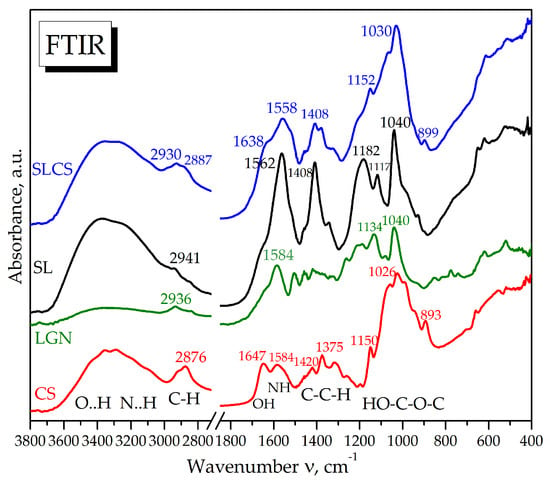
Figure 3.
FTIR spectroscopy of the initial sulfite liquor (SL), the resulting aerogel SLCS, commercial alkali lignin (LGN), and chitosan (CS).
The FTIR spectrum of the SLCS sample, i.e., the chitosan–lignosulphonate system, can be visualized as a convolution of the chitosan spectra with the carbon phase from sulfite liquor. The hydroxyl and amine bands of chitosan, at 1650 cm−1 and 1550 cm−1, respectively, are significantly involved in the fixation of carbonaceous materials in the sulfite liquor via hydrogen bonding and ionic bonding with the cationic groups of activated chitosan -NH3+. Also, the amide III band at 1420 ± 50 cm−1 increases in intensity relative to the similar region of chitosan, evidencing that it binds carboxylated compounds from sulfite liquor that have absorption bands at 1408 ± 50 cm−1 in SL. The C-O-C polysaccharide band at 1026 ± 75 cm−1 also increases in intensity and width, suggesting the binding of novel compounds to the -C-OH, -OH, and -NH3+ side groups of the pyridine aromatic rings of chitosan.
FTIR infrared spectroscopy, therefore, revealed the involvement of the hydroxyl and amine bands of chitosan in the binding of carbonaceous materials in sulfite liquor through hydrogen bonding and ionic bonding with the cationic groups of activated chitosan -NH3+. Also, the increase in the intensity of the C-O-C polysaccharide band suggests the binding of novel compounds to the -C-OH, -OH, and -NH3+ side groups of the pyridine aromatic rings of chitosan, including through hydrophobic aromatic interactions.
3.4. Inductively Coupled Plasma–Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES)
Inductively coupled plasma–optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) analysis was used to determine the element content (Na, K, P, Ca, Mg, Fe, Si, Cr). The concentrations of the elements in the analyzed samples are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Elemental composition of liquid samples LSLd and LSLCS.
ICP-OES elemental analysis showed significant decrease inmetal ions by ionotropic adsorption in 3% chitosan suspension. Compared to the initial SLd diluted solution, Na decreases 3-fold, from 3.09% to 0.958%; also, K, Mg, P, and Si decrease 3-4-fold, and Fe decreases 77-fold, from 643 to 8.33 mg/Kg.
3.5. UV-Vis Spectroscopy
UV-Vis electron absorption spectrometry analyses were performed to obtain compositional information based on the signals produced by the electronic transitions of molecules from the ground state to an electronically excited state under the influence of light of a specific wavelength, frequency, and energy. The new liquid phase obtained by ionotropic separation is further compared with the diluted sample for the presence of sulfur and mercaptan compounds. Sulfides show specific n→σ* transition bands at wavelengths of λ 210 nm for (CH3)2S, 215 nm for (C2H5)2S, 235–240 nm for R2S, and 250 nm for RSSR disulfides, respectively, while RSH mercaptans show transition bands at λ 200 with shoulder at 225–230 nm [20]. Most sulfur compounds are found in lower concentrations in the new liquid phase compared to the initial liquid phase, suggesting that ionotropic adsorption with chitosan retains mostly carbon nano/microparticles in the sulfite liquor, but also several types of other sulfur compounds.
4. Conclusions
A general conclusion for the ionotropic separation with cationic chitosan of homogeneous lignosulfonate sulfite liquor nanosuspension is that this method can achieve both the separation of the carbonic phase from the sulfite liquor together with the synthesis of a multi-functional biopolymer–carbon–metal nanocomposite aerogel with potential adsorbent, catalytic, and/or semiconductive properties.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Ș.-O.D. and F.O.; methodology, Ș.-O.D., N.T. and B.T.; validation, Ș.-O.D. and F.O.; formal analysis, Ș.-O.D. and N.T.; investigation,Ș.-O.D., N.T., L.C. and B.T.; resources, M.S. and F.O.; data curation, Ș.-O.D.; writing—original draft preparation, Ș.-O.D.; writing—review and editing, F.O.; visualization, Ș.-O.D. and B.T.; supervision, F.O.; project administration, F.O and M.S.; funding acquisition, M.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by project POC-A1-A1.2.3-G-2015-P_40_352-SECVENT, Sequential processes to close bioeconomy side stream and innovative bioproducts resulted from these, contract 81/2016, SMIS 105684, funded by Cohesion Funds of the European Union, subsidiary projects 382/2020 BioBleach and 383/2020 LignoChar.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All the data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of the data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Lappalainen, J.; Baudouin, D.; Hornung, U.; Schuler, J.; Melin, K.; Bjelić, S.; Vogel, F.; Konttinen, J.; Joronen, T. Sub- and Supercritical Water Liquefaction of Kraft Lignin and Black Liquor Derived Lignin. Energies 2020, 13, 3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, W.M.; Viotti, P.V.; Vieira, M.G.A.; Baptista, C.; Scaliante, M.; Gimenes, M.L. Hydrothermal synthesis of biobased carbonaceous composite from a blend of kraft black liquor and tannin and its application to aspirin and paracetamol removal. Colloids Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2021, 608, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amriani, F.; Bani, O.; Muryanto, M.; Sari, A.A.; Sudiyani, Y. The enhancement of black liquor treatment by applying a natural flocculant and converting its sludge to a high-benefit product. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2019, 97, 1077–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Q.; Li, Y.; Meng, Y.; Lu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Tao, Y.A.; Wang, H.S. Pulping black liquor-based polymer hydrogel as water retention material and slow-release fertilizer. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 165, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Song, J.L.; Yan, M.Y.; Li, J.; Yang, J.M.; Huang, M.H.; Zhang, R.Y. Waste lignin-based cationic flocculants treating dyeing wastewater: Fabrication, and mechanism. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 874, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravishankar, K.; Venkatesan, M.; Desingh, R.P.; Mahalingam, A.; Sadhasivam, B.; Subramaniyam, R.; Dhamodharan, R. Biocompatible hydrogels of chitosan-alkali lignin for potential wound healing applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 102, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henao, E.; Delgado, E.; Contreras, H.; Quintana, G. Polyelectrolyte Complexation versus Ionotropic Gelation for Chitosan-Based Hydrogels with Carboxymethylcellulose, Carboxymethyl Starch, and Alginic Acid. Int. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganjidoust, H.; Tatsumi, K.; Yamagishi, T.; Gholian, R.N. Effect of synthetic and natural coagulant on lignin removal from pulp and paper wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 35, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, V.T.; Le, T.M.; Trinh, T.T.N.; Tran, C.L.; Duong, Y.H.P.; Huynh, V.Q.; Le, D.T.; Le, P.K. Development of Facile and Green Fabrication of Cellulose-Chitosan Composite Aerogel and Lignin/Silica Hybrid from Agro-wastes. Fibers Polym. 2023, 24, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.Q.; Peng, B.; Ji, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, D.Q. Chitosan(Chitin)/Cellulose Composite Biosorbents Prepared Using Ionic Liquid for Heavy Metal Ions Adsorption. Aiche J. 2009, 55, 2062–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Chatterjee, B.P.; Guha, A.K. Adsorptive removal of congo red, a carcinogenic textile dye by chitosan hydrobeads: Binding mechanism, equilibrium and kinetics. Colloids Surf. A-Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 299, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethi, S.; Medha; Singh, G.; Sharma, R.; Kaith, B.S.; Sharma, N.; Khullar, S. Fluorescent hydrogel of chitosan and gelatin cross-linked with maleic acid for optical detection of heavy metals. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, S.; Parshi, N.; Prodhan, C.; Chaudhuri, K.; Ganguly, J. Characterization of a fluorescent hydrogel synthesized using chitosan, polyvinyl alcohol and 9-anthraldehyde for the selective detection and discrimination of trace Fe3+ and Fe2+ in water for live-cell imaging. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 193, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.W.; Papaioannou, N.; David, N.M.; Luo, H.; Gao, H.; Tanase, L.C.; Degousee, T.; Samori, P.; Sapelkin, A.; Fenwick, O.; et al. Photoelectrochemical response of carbon dots (CDs) derived from chitosan and their use in electrochemical imaging. Mater. Horiz. 2018, 5, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahya, M.Z.A.; Arof, A.K. Studies on lithium acetate doped chitosan conducting polymer system. Eur. Polym. J. 2002, 38, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkabli, J.; Rizk, M.A.; Elshaarawy, R.F.M.; El-Sayed, W.N. Ionic chitosan Schiff bases supported Pd(II) and Ru(II) complexes; production, characterization, and catalytic performance in Suzuki cross-coupling reactions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 184, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, M.; Meysami, S.S.; Ferrero, G.A.; Xie, F.; Meng, H.; Grobert, N.; Titirici, M.M. Low-Cost Chitosan-Derived N-Doped Carbons Boost Electrocatalytic Activity of Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.J.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.L.; Han, H.W.; Yang, G. Double network bacterial cellulose hydrogel to build a biology-device interface. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 970–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preuss, K.; Kannuchamy, V.K.; Marinovic, A.; Isaacs, M.; Wilson, K.; Abrahams, I.; Titirici, M.M. Bio-inspired carbon electro-catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction. J. Energy Chem. 2016, 25, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaban, A.T.; Banciu, M.; Pogany, I.I. Aplicatii ale Metodelor Fizice in Chimica Organica-RO (Applications of Physical Methods in Organic Chemistry); Editura Stiintifica si Enciclopedica: Bucuresti, Romania, 1983; p. 288. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).