Liraglutide Increases Gastric Fundus Tonus and Reduces Food Intake in Type 2 Diabetic Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Drugs and Chemicals
2.2. Animals
2.3. In Vivo Studies
2.4. Functional Studies
2.4.1. Relaxation Induced by SNP or NA of Gastric Fundus Strips Isolated from Treated and Non-Treated Rats with Liraglutide
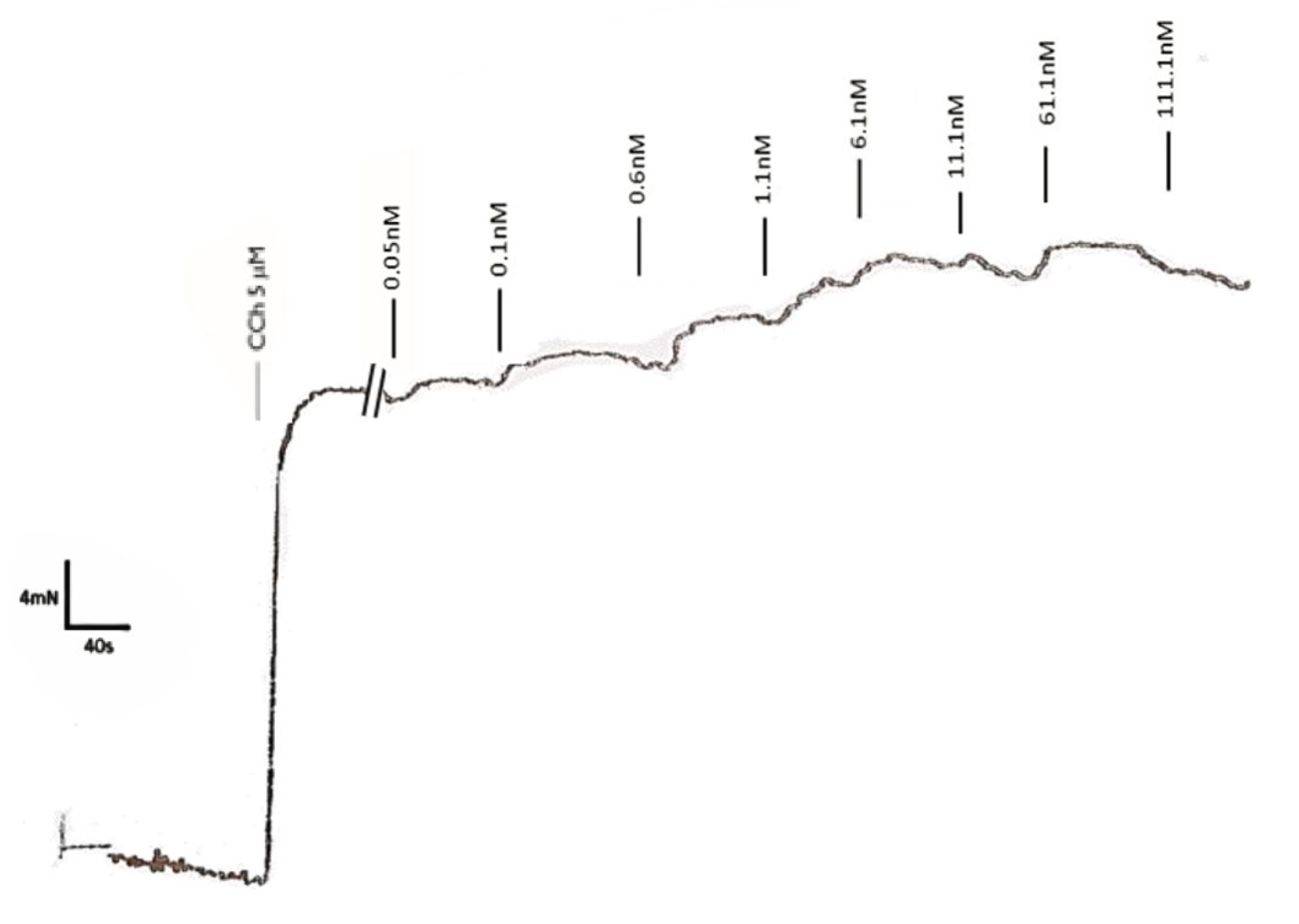
2.4.2. Responses to GLP1-RA of Pre-Contracted Gastric Fundus Strips Isolated from Non-Treated Rats
2.4.3. Analysis of Results
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
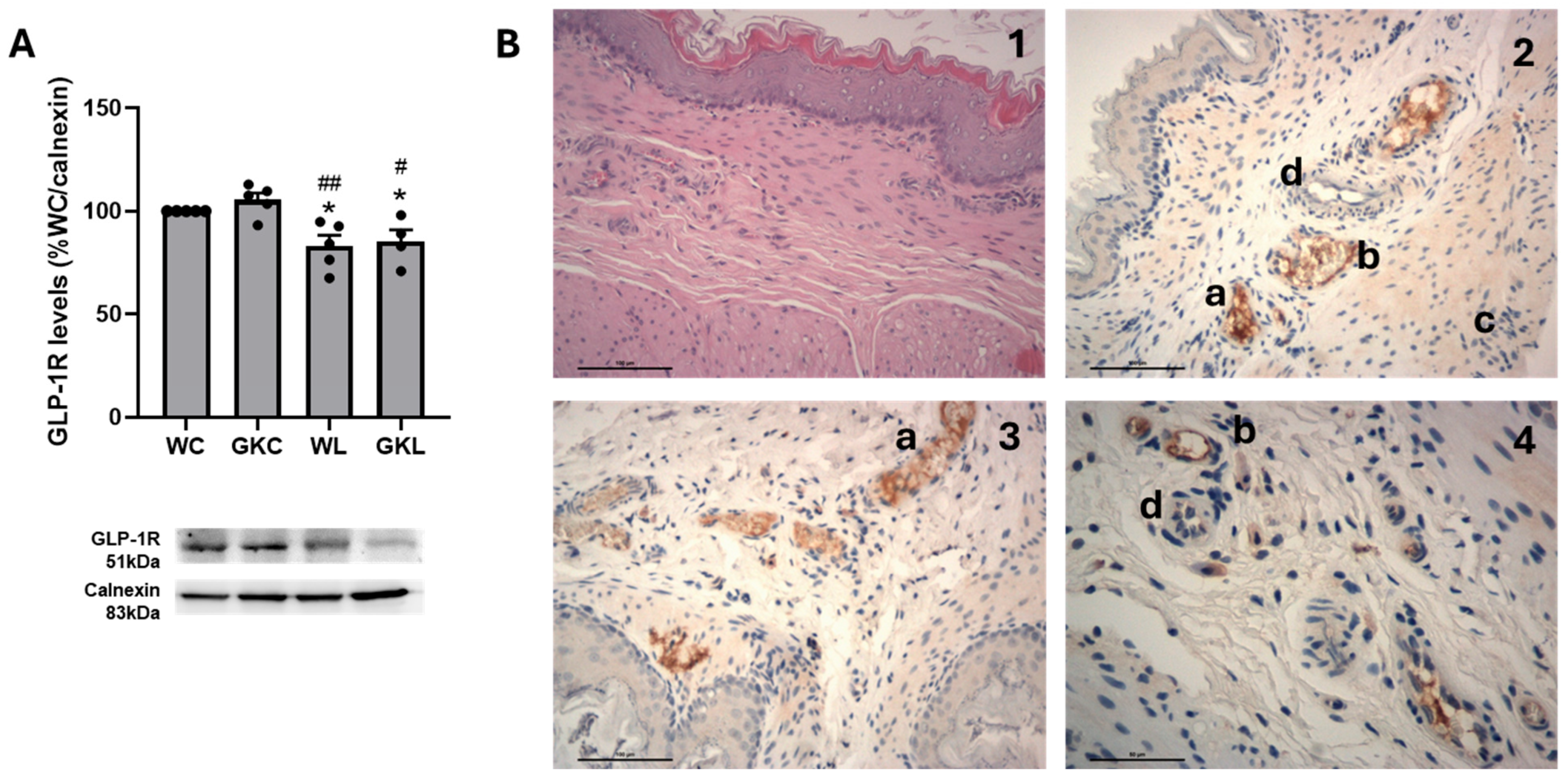
2.6. Immunohistochemistry
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
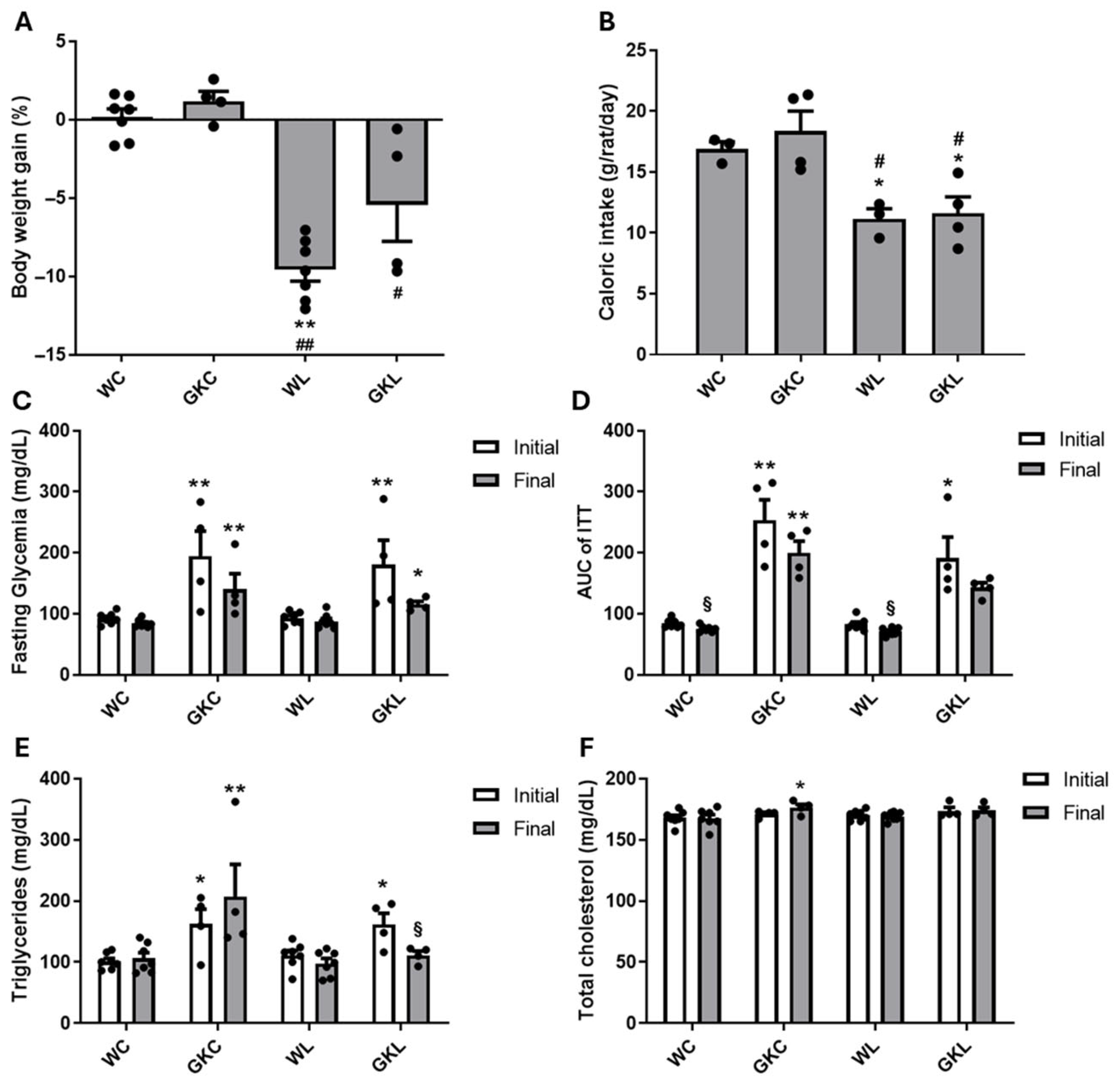
3.1. Liraglutide Improves Metabolic Profile in Diabetic GK Rats
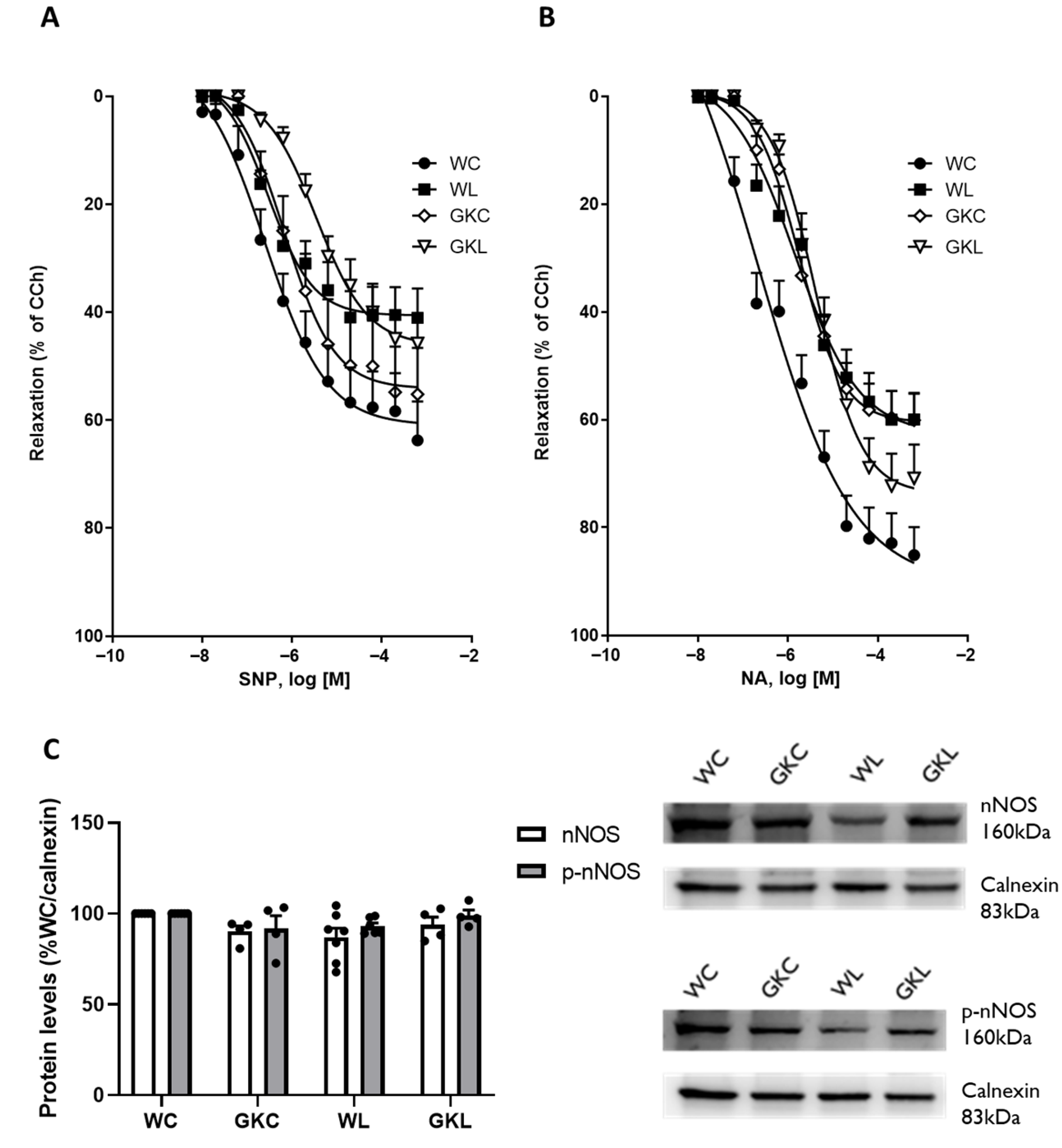
3.2. Liraglutide Treatment Reduces NO- and NA-Induced Relaxation of Gastric Fundus from Wistar and Diabetic GK Rats
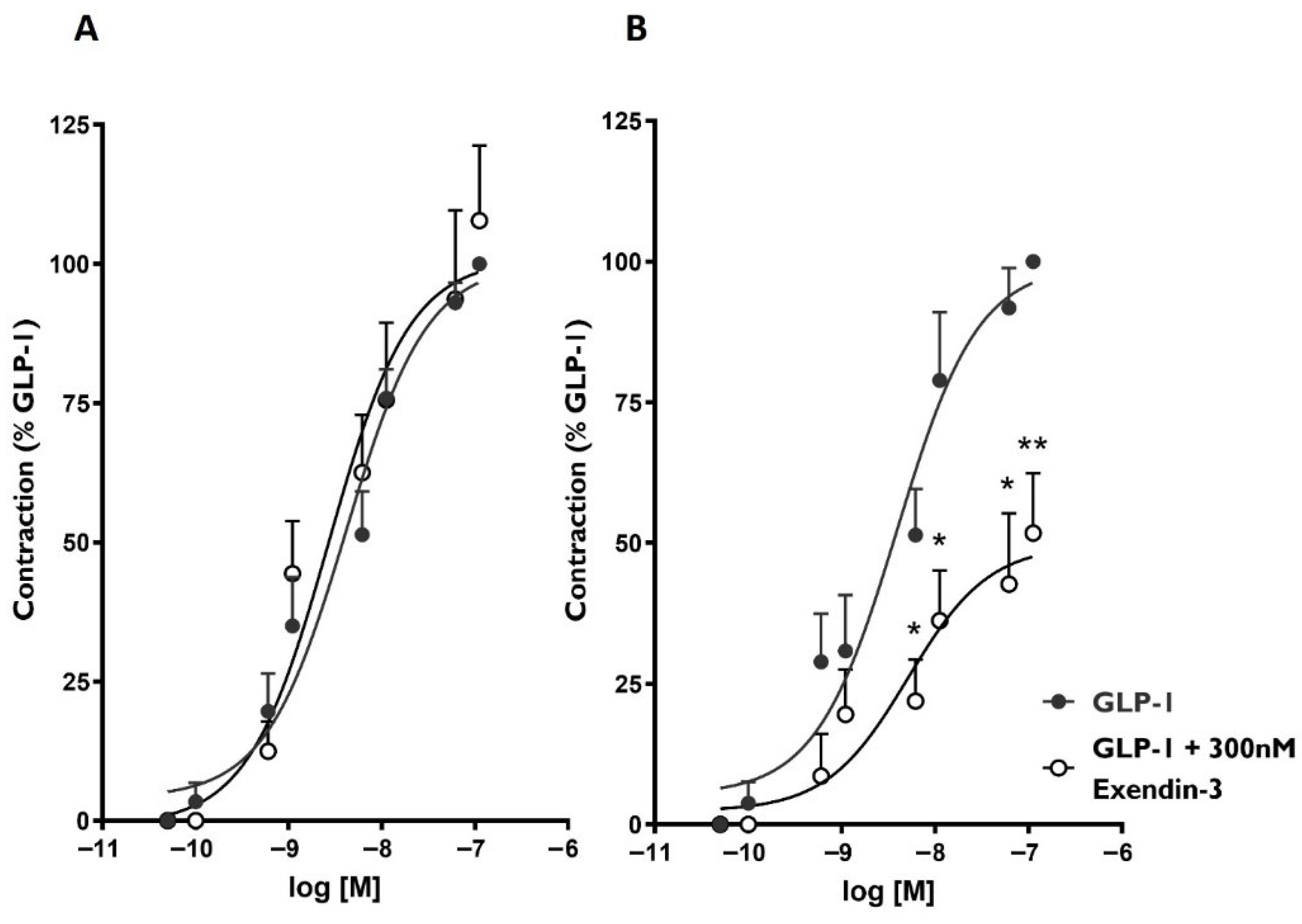
3.3. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists Induce Distinct Contractile Responses of Rat Gastric Fundus Through GLP-1R-Dependent and -Independent Pathways
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 11th ed.; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- ElSayed, N.A.; Aleppo, G.; Aroda, V.R.; Bannuru, R.R.; Brown, F.M.; Bruemmer, D.; Collins, B.S.; Hilliard, M.E.; Isaacs, D.; Johnson, E.L.; et al. 3. Prevention or Delay of Type 2 Diabetes and Associated Comorbidities: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2023. Diabetes Care 2023, 46 (Suppl. S1), S41–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasyurek, H.M.; Altunbas, H.A.; Balci, M.K.; Sanlioglu, S. Incretins: Their physiology and application in the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2014, 30, 354–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zheng, J.; Wang, S.; Lau, H.K.; Fathi, A.; Wang, Q. Cardiovascular Benefits of Native GLP-1 and its Metabolites: An Indicator for GLP-1-Therapy Strategies. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban, K.; Noyan-Ashraf, M.H.; Hoefer, J.; Bolz, S.S.; Drucker, D.J.; Husain, M. Cardioprotective and vasodilatory actions of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor are mediated through both glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor-dependent and -independent pathways. Circulation 2008, 117, 2340–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Meier, J.J. MANAGEMENT OF ENDOCRINE DISEASE: Are all GLP-1 agonists equal in the treatment of type 2 diabetes? Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 181, R211–R234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, L.V.; Flint, A.; Olsen, A.K.; Ingwersen, S.H. Liraglutide in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2016, 55, 657–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, L.B.; Lau, J. The Discovery and Development of Liraglutide and Semaglutide. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secher, A.; Jelsing, J.; Baquero, A.F.; Hecksher-Sorensen, J.; Cowley, M.A.; Dalboge, L.S.; Hansen, G.; Grove, K.L.; Pyke, C.; Raun, K.; et al. The arcuate nucleus mediates GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide-dependent weight loss. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 4473–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Bloemendaal, L.; Veltman, D.J.; Ten Kulve, J.S.; Groot, P.F.; Ruhe, H.G.; Barkhof, F.; Sloan, J.H.; Diamant, M.; Ijzerman, R.G. Brain reward-system activation in response to anticipation and consumption of palatable food is altered by glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor activation in humans. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2015, 17, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ard, J.; Fitch, A.; Fruh, S.; Herman, L. Weight Loss and Maintenance Related to the Mechanism of Action of Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists. Adv. Ther. 2021, 38, 2821–2839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Can, J.; Sloth, B.; Jensen, C.B.; Flint, A.; Blaak, E.E.; Saris, W.H. Effects of the once-daily GLP-1 analog liraglutide on gastric emptying, glycemic parameters, appetite and energy metabolism in obese, non-diabetic adults. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 38, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, L.L.; Young, A.A.; Parkes, D.G. Pharmacology of exenatide (synthetic exendin-4): A potential therapeutic for improved glycemic control of type 2 diabetes. Regul. Pept. 2004, 117, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, D.J. The biology of incretin hormones. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, A.; Lund, A.; Knop, F.K.; Vilsboll, T. Glucagon-like peptide 1 in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 390–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.E.; Drucker, D.J. Pharmacology, physiology, and mechanisms of incretin hormone action. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 819–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.; Rao, X.; Rajagopalan, S. An emerging role of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) beyond glucose control: Potential implications in cardiovascular disease. Atherosclerosis 2013, 226, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amato, A.; Cinci, L.; Rotondo, A.; Serio, R.; Faussone-Pellegrini, M.S.; Vannucchi, M.G.; Mule, F. Peripheral motor action of glucagon-like peptide-1 through enteric neuronal receptors. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2010, 22, 664–e203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, A.; Baldassano, S.; Liotta, R.; Serio, R.; Mule, F. Exogenous glucagon-like peptide 1 reduces contractions in human colon circular muscle. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 221, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marathe, C.S.; Rayner, C.K.; Jones, K.L.; Horowitz, M. Effects of GLP-1 and incretin-based therapies on gastrointestinal motor function. Exp. Diabetes Res. 2011, 2011, 279530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotondo, A.; Amato, A.; Lentini, L.; Baldassano, S.; Mule, F. Glucagon-like peptide-1 relaxes gastric antrum through nitric oxide in mice. Peptides 2011, 32, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirra, J.; Nicolaus, M.; Woerle, H.J.; Struckmeier, C.; Katschinski, M.; Goke, B. GLP-1 regulates gastroduodenal motility involving cholinergic pathways. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2009, 21, 609-e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyke, C.; Heller, R.S.; Kirk, R.K.; Orskov, C.; Reedtz-Runge, S.; Kaastrup, P.; Hvelplund, A.; Bardram, L.; Calatayud, D.; Knudsen, L.B. GLP-1 receptor localization in monkey and human tissue: Novel distribution revealed with extensively validated monoclonal antibody. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 1280–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturis, J.; Gotfredsen, C.F.; Romer, J.; Rolin, B.; Ribel, U.; Brand, C.L.; Wilken, M.; Wassermann, K.; Deacon, C.F.; Carr, R.D.; et al. GLP-1 derivative liraglutide in rats with beta-cell deficiencies: Influence of metabolic state on beta-cell mass dynamics. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 140, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagakubo, D.; Shirai, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Kaji, N.; Arisato, C.; Watanabe, S.; Takasugi, A.; Asai, F. Prophylactic effects of the glucagon-like Peptide-1 analog liraglutide on hyperglycemia in a rat model of type 2 diabetes mellitus associated with chronic pancreatitis and obesity. Comp. Med. 2014, 64, 121–127. [Google Scholar]
- Riazi-Farzad, B.; Nicholls, P.J.; Sewell, R.D. Sensitivity differences to 5-HT and carbachol in subsections of the isolated rat stomach fundus strip: An improved preparation. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 1996, 35, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vane, J.R. A sensitive method for the assay of 5-hydroxytryptamine. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 120 (Suppl. S4), 142–147; discussion 140–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, B.S.; Gago, B.; Barbosa, R.M.; Cavaleiro, C.; Laranjinha, J. Ethyl nitrite is produced in the human stomach from dietary nitrate and ethanol, releasing nitric oxide at physiological pH: Potential impact on gastric motility. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 82, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolessa, T.; Gutniak, M.; Holst, J.J.; Efendic, S.; Hellstrom, P.M. Glucagon-like peptide-1 retards gastric emptying and small bowel transit in the rat: Effect mediated through central or enteric nervous mechanisms. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1998, 43, 2284–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wettergren, A.; Wojdemann, M.; Holst, J.J. Glucagon-like peptide-1 inhibits gastropancreatic function by inhibiting central parasympathetic outflow. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 275, G984–G992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imeryuz, N.; Yegen, B.C.; Bozkurt, A.; Coskun, T.; Villanueva-Penacarrillo, M.L.; Ulusoy, N.B. Glucagon-like peptide-1 inhibits gastric emptying via vagal afferent-mediated central mechanisms. Am. J. Physiol. 1997, 273, G920–G927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, P.J.; Fledelius, C.; Knudsen, L.B.; Tang-Christensen, M. Systemic administration of the long-acting GLP-1 derivative NN2211 induces lasting and reversible weight loss in both normal and obese rats. Diabetes 2001, 50, 2530–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagyanszki, M.; Bodi, N. Diabetes-related alterations in the enteric nervous system and its microenvironment. World J. Diabetes 2012, 3, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cellek, S. Point of NO return for nitrergic nerves in diabetes: A new insight into diabetic complications. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2004, 10, 3683–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.L.; Huang, X.; Wu, Y.S.; Zhang, C.M.; Meng, X.M.; Liu, D.H.; Kim, Y.C.; Xu, W.X. Gastric nNOS reduction accompanied by natriuretic peptides signaling pathway upregulation in diabetic mice. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 4626–4635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eickhoff, H.; Louro, T.M.; Matafome, P.N.; Vasconcelos, F.; Seica, R.M.; Castro, E.S.F. Amelioration of glycemic control by sleeve gastrectomy and gastric bypass in a lean animal model of type 2 diabetes: Restoration of gut hormone profile. Obes. Surg. 2015, 25, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broide, E.; Bloch, O.; Ben-Yehudah, G.; Cantrell, D.; Shirin, H.; Rapoport, M.J. Reduced GLP-1R expression in gastric glands of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E1691–E1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, T.; Obata, A.; Shimoda, M.; Okauchi, S.; Hirukawa, H.; Kohara, K.; Kinoshita, T.; Nogami, Y.; Nakanishi, S.; Mune, T.; et al. Decreased glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor expression in endothelial and smooth muscle cells in diabetic db/db mice: TCF7L2 is a possible regulator of the vascular glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2017, 14, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanada, J.; Obata, A.; Obata, Y.; Fushimi, Y.; Shimoda, M.; Kohara, K.; Nakanishi, S.; Mune, T.; Kaku, K.; Kaneto, H. Dulaglutide exerts beneficial anti atherosclerotic effects in ApoE knockout mice with diabetes: The earlier, the better. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Mamillapalli, R.; Zhu, W.; Chan, O. Long-Term Use of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists Alter GLP-1 Receptor mRNA Expression in Hindbrain Pathways That Regulate Gastric Motility in Mice. Diabetes 2018, 67 (Suppl. S1), 1088–P. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, M.B.; Al Batran, R.; Ussher, J.R. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor action in the vasculature. Peptides 2019, 111, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloch, O.; Broide, E.; Ben-Yehudah, G.; Cantrell, D.; Shirin, H.; Rapoport, M.J. Nutrient induced type 2 and chemical induced type 1 experimental diabetes differently modulate gastric GLP-1 receptor expression. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 2015, 561353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Schirra, J.; Nicolaus, M.; Roggel, R.; Katschinski, M.; Storr, M.; Woerle, H.J.; Goke, B. Endogenous glucagon-like peptide 1 controls endocrine pancreatic secretion and antro-pyloro-duodenal motility in humans. Gut 2006, 55, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodier, G.; Magous, R.; Mochizuki, T.; Martinez, J.; Nguyen, D.L.; Bali, J.P.; Bataille, D.; Jarrousse, C. Effect of glicentin, oxyntomodulin and related peptides on isolated gastric smooth muscle cells. Pflug. Arch. 1997, 434, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, P.; Vanden Berghe, P.; Verschueren, S.; Lehmann, A.; Depoortere, I.; Tack, J. Review article: The role of gastric motility in the control of food intake. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 33, 880–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sodium Nitroprusside (SNP) | Noradrenaline (NA) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emax (%CCh) | pEC50 | s/n | Emax (%CCh) | pEC50 | s/n | |
| WC | 64.64 ± 7.06 | 6.26 ± 0.16 | 14/4 | 85.38 ± 5.21 | 6.12 ± 0.09 | 16/4 |
| WL | 43.60 ± 4.92 | 6.12 ± 0.12 | 15/4 | 61.63 ± 5.22 * | 5.7 ± 0.15 * | 16/4 |
| GKC | 55.75 ± 8.61 | 5.85 ± 0.10 | 15/4 | 60.44 ± 4.86 * | 5.62 ± 0.06 ** | 14/4 |
| GKL | 47.42 ± 5.12 | 5.22 ± 0.09 **** ### | 16/4 | 72.20 ± 6.10 | 5.27 ± 0.07 *** | 16/4 |
| Emax (mN) | pEC50 | s/n | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wistar | GK | Wistar | GK | Wistar | GK | |
| GLP-1 | 5.61 ± 0.69 | 9.09 ± 1.44 * | 8.33 ± 0.16 | 8.58 ± 0.16 | 16/4 | 12/4 |
| Exenatide | 11.67 ± 1.08 #### | 10.37 ± 1.99 | 8.78 ± 0.16 | 8.92 ± 0.21 | 11/3 | 12/3 |
| Liraglutide | 4.69 ± 0.81 §§§§ | 3.76 ± 1.01 # §§ | 9.62 ± 0.24 #### § | 9.06 ± 0.51 | 13/4 | 5/3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carrêlo, A.C.; Martins, B.; Seiça, R.; Fontes-Ribeiro, C.; Matafome, P.; Silva, S. Liraglutide Increases Gastric Fundus Tonus and Reduces Food Intake in Type 2 Diabetic Rats. Diabetology 2025, 6, 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6090096
Carrêlo AC, Martins B, Seiça R, Fontes-Ribeiro C, Matafome P, Silva S. Liraglutide Increases Gastric Fundus Tonus and Reduces Food Intake in Type 2 Diabetic Rats. Diabetology. 2025; 6(9):96. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6090096
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarrêlo, Ana Catarina, Beatriz Martins, Raquel Seiça, Carlos Fontes-Ribeiro, Paulo Matafome, and Sónia Silva. 2025. "Liraglutide Increases Gastric Fundus Tonus and Reduces Food Intake in Type 2 Diabetic Rats" Diabetology 6, no. 9: 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6090096
APA StyleCarrêlo, A. C., Martins, B., Seiça, R., Fontes-Ribeiro, C., Matafome, P., & Silva, S. (2025). Liraglutide Increases Gastric Fundus Tonus and Reduces Food Intake in Type 2 Diabetic Rats. Diabetology, 6(9), 96. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6090096







