Diabetes-Induced Osteoporosis: Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry Bone Quality Is Better than Bone Quantity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Pathophysiology of Diabetes-Induced Osteoporosis
3. Limitations of Conventional Assessment of Bone Health in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
4. Trabecular Bone Score (TBS) and Diabetes Mellitus
5. Hip Geometry and Diabetes Mellitus
6. Bone Strain Index (BSI) and Diabetes Mellitus
7. Other Diagnostic Technologies to Assess Bone Status in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
8. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGEs | Advanced glycation end products |
| BMD | Bone mineral density |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| BR | Buckling ratio |
| BSI | Bone Strain Index |
| CSA | Cross-sectional area |
| CSMI | Cross-sectional moment of inertia |
| CTX | C-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen |
| DKA | Diabetic ketoacidosis |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| DXA | Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry |
| eGFR | Estimated glomerular filtration rate |
| FEA | Finite Element Analysis |
| FEM | Finite Element Model |
| FRAX® | Fracture risk assessment tool |
| GAD | glutamic acid decarboxylase |
| HAL | Hip axis length |
| HDL | High-density lipoprotein |
| HR-pQCT | High-Resolution peripheral Quantitative Computed Tomography |
| HSA | Hip Structural Analysis |
| IA-2 | Islet tyrosine phosphatase 2 |
| IDF | International Diabetes Federation |
| IGF-I | Insulin-like growth factor-I |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| MAFLD | Metabolically associated fatty liver disease |
| microMRI | Micro Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| NHS | National Health Systems |
| NSA | Neck-shaft angle |
| NTX | N-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen |
| P1NP | Procollagen type I N-terminal propeptide |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| TBS | Trabecular Bone Score |
| TNFα | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| T1DM | Type 1 diabetes mellitus |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| Z | Section modulus |
| ZnT8 | Zinc transporter 8 |
References
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 2. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2025. Diabetes Care 2025, 48, S27–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prevention USCfDCa. National Diabetes Statistics Report. Estimates of Diabetes and Its Burden in the United States. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/php/data-research/index.html (accessed on 2 May 2025).
- Ziegler, A.G.; Rewers, M.; Simell, O.; Simell, T.; Lempainen, J.; Steck, A.; Winkler, C.; Ilonen, J.; Veijola, R.; Knip, M.; et al. Seroconversion to multiple islet autoantibodies and risk of progression to diabetes in children. JAMA 2013, 309, 2473–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diabetes Atlas, 11th ed.; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2025.
- Salmi, A.; di Filippo, L.; Ferrari, C.; Frara, S.; Giustina, A. Ultrasound and FibroScan((R)) Controlled Attenuation Parameter in patients with MAFLD: Head to head comparison in assessing liver steatosis. Endocrine 2022, 78, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorodeski Baskin, R.; Alfakara, D. Root Cause for Metabolic Syndrome and Type 2 Diabetes: Can Lifestyle and Nutrition Be the Answer for Remission. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2023, 52, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration; Sarwar, N.; Gao, P.; Seshasai, S.R.; Gobin, R.; Kaptoge, S.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Ingelsson, E.; Lawlor, D.A.; Selvin, E.; et al. Diabetes mellitus, fasting blood glucose concentration, and risk of vascular disease: A collaborative meta-analysis of 102 prospective studies. Lancet 2010, 375, 2215–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabala, A.; Darsalia, V.; Holzmann, M.J.; Franzen, S.; Svensson, A.M.; Eliasson, B.; Patrone, C.; Nystrom, T.; Jonsson, M. Risk of first stroke in people with type 2 diabetes and its relation to glycaemic control: A nationwide observational study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2020, 22, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, L.; Pontiroli, A.E. Role of obesity and hypertension in the incidence of atrial fibrillation, ischaemic heart disease and heart failure in patients with diabetes. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021, 20, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, M.; Woodward, M.; Peters, S.A.E. Diabetes, Glycated Hemoglobin, and the Risk of Myocardial Infarction in Women and Men: A Prospective Cohort Study of the UK Biobank. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 2050–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao Kondapally Seshasai, S.; Kaptoge, S.; Thompson, A.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Gao, P.; Sarwar, N.; Whincup, P.H.; Mukamal, K.J.; Gillum, R.F.; Holme, I.; et al. Diabetes mellitus, fasting glucose, and risk of cause-specific death. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 829–841. [Google Scholar]
- Anjana, R.M.; Mohan, V.; Rangarajan, S.; Gerstein, H.C.; Venkatesan, U.; Sheridan, P.; Dagenais, G.R.; Lear, S.A.; Teo, K.; Karsidag, K.; et al. Contrasting Associations Between Diabetes and Cardiovascular Mortality Rates in Low-, Middle-, and High-Income Countries: Cohort Study Data From 143,567 Individuals in 21 Countries in the PURE Study. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 3094–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanazawa, I.; Takeno, A.; Tanaka, K.I.; Yamane, Y.; Sugimoto, T. Osteoporosis and vertebral fracture are associated with deterioration of activities of daily living and quality of life in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2019, 37, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilaca, T.; Schini, M.; Harnan, S.; Sutton, A.; Poku, E.; Allen, I.E.; Cummings, S.R.; Eastell, R. The risk of hip and non-vertebral fractures in type 1 and type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis update. Bone 2020, 137, 115457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofbauer, L.C.; Busse, B.; Eastell, R.; Ferrari, S.; Frost, M.; Muller, R.; Burden, A.M.; Rivadeneira, F.; Napoli, N.; Rauner, M. Bone fragility in diabetes: Novel concepts and clinical implications. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, V.N.; Shah, C.S.; Snell-Bergeon, J.K. Type 1 diabetes and risk of fracture: Meta-analysis and review of the literature. Diabet. Med. 2015, 32, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, D.R.; Haynes, K.; Leonard, M.B.; Willi, S.M.; Denburg, M.R. Type 1 diabetes is associated with an increased risk of fracture across the life span: A population-based cohort study using The Health Improvement Network (THIN). Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 1913–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossini, M.; Adami, S.; Bertoldo, F.; Diacinti, D.; Gatti, D.; Giannini, S.; Giusti, A.; Malavolta, N.; Minisola, S.; Osella, G.; et al. Guidelines for the diagnosis, prevention and management of osteoporosis. Reumatismo 2016, 68, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melton, L.J.; Chrischilles, E.A., 3rd; Cooper, C.; Lane, A.W.; Riggs, B.L. Perspective. How many women have osteoporosis? J. Bone Miner. Res. 1992, 7, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melton, L.J.; Atkinson, E.J., 3rd; O’Connor, M.K.; O’Fallon, W.M.; Riggs, B.L. Bone density and fracture risk in men. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1998, 13, 1915–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaborators, G.B.D.D. Global, regional, and national burden of diabetes from 1990 to 2021, with projections of prevalence to 2050: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2023, 402, 203–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tebe, C.; Martinez-Laguna, D.; Carbonell-Abella, C.; Reyes, C.; Moreno, V.; Diez-Perez, A.; Collins, G.S.; Prieto-Alhambra, D. The association between type 2 diabetes mellitus, hip fracture, and post-hip fracture mortality: A multi-state cohort analysis. Osteoporos. Int. 2019, 30, 2407–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoback, D.; Rosen, C.J.; Black, D.M.; Cheung, A.M.; Murad, M.H.; Eastell, R. Pharmacological Management of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women: An Endocrine Society Guideline Update. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, N.C.; Poole, K.E.; Ralston, S.H.; McCloskey, E.V.; Sangan, C.B.; Wiggins, L.; Jones, C.; Gittoes, N.; Compston, J.; Osteoporosis, R.O.S.; et al. Towards a cure for osteoporosis: The UK Royal Osteoporosis Society (ROS) Osteoporosis Research Roadmap. Arch. Osteoporos. 2022, 17, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggio, A.B.; Ferrari, S.; Kraenzlin, M.; Marchand, L.M.; Schwitzgebel, V.; Beghetti, M.; Rizzoli, R.; Farpour-Lambert, N.J. Decreased bone turnover in children and adolescents with well controlled type 1 diabetes. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 23, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vestergaard, P. Discrepancies in bone mineral density and fracture risk in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes—A meta-analysis. Osteoporos. Int. 2007, 18, 427–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napoli, N.; Chandran, M.; Pierroz, D.D.; Abrahamsen, B.; Schwartz, A.V.; Ferrari, S.L.; Bone, I.O.F.; Diabetes Working, G. Mechanisms of diabetes mellitus-induced bone fragility. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armas, L.A.; Akhter, M.P.; Drincic, A.; Recker, R.R. Trabecular bone histomorphometry in humans with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Bone 2012, 50, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, L.; He, X.; Farmer, P.; Boden, S.; Kozlowski, M.; Rubin, J.; Nanes, M.S. Inhibition of osteoblast differentiation by tumor-necrosis factor-alpha. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 3956–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glantschnig, H.; Fisher, J.E.; Wesolowski, G.; Rodan, G.A.; Reszka, A.A. M-CSF, TNFalpha and RANL ligand promote osteoclast survival by signaling through mTOR/S6 kinase. Cell Death Differ. 2003, 10, 1165–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyer, C.; Funahashi, T.; Tanaka, S.; Hotta, K.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Pratley, R.E.; Tataranni, P.A. Hypoadiponectinemia in obesity andt type 2 diabetes: Close association with insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 1930–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, A.V.; Garnero, P.; Hillier, T.A.; Sellmeyer, D.E.; Strotmeyer, E.S.; Feingold, K.R.; Resnick, H.E.; Tylavsky, F.A.; Black, D.M.; Cummings, S.R.; et al. Pentosidine and increased fracture risk in older adults with type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 2380–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiari, P.; Leo, S.; Zavan, B.; Vindigni, V.; Rimessi, A.; Bianchi, K.; Franzin, C.; Cortivo, R.; Rossato, M.; Vettor, R.; et al. High glucose induces adipogenic differentiation of muscle-derived stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 1226–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, J.S.; Ferreira, V.M.; Maquigussa, E.; Naves, M.A.; Boim, M.A. Effects of high glucose and high insulin concentrations on osteoblast function in vitro. Cell Tissue Res. 2014, 358, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frassetto, L.A.; Sebastian, A. How metabolic acidosis and oxidative stress alone and interacting may increase the risk of fracture in diabetic subjects. Med. Hypotheses 2012, 79, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thalassinos, N.C.; Hadjiyanni, P.; Tzanela, M.; Alevitaki, C.; Philokiprou, D. Calcium metabolism in diabetes mellitus: Effect of improved blood glucose control. Diabet. Med. 1993, 10, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Yamauchi, M.; Sugimoto, T. Elevated sclerostin levels are associated with vertebral fractures in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 4030–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazziotti, G.; Frara, S.; Giustina, A. Pituitary diseases and bone. Endocr. Rev. 2018, 39, 440–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, A.D.; Etcheverry, S.B.; Cortizo, A.M. Effect of advanced glycation endproducts on the secretion of insulin-like growth factor-I and its binding proteins: Role in osteoblast development. Acta Diabetol. 2001, 38, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terada, M.; Inaba, M.; Yano, Y.; Hasuma, T.; Nishizawa, Y.; Morii, H.; Otani, S. Growth-inhibitory effect of a high glucose concentration in osteoblast-like cells. Bone 1998, 22, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuche-Berenguer, B.; Portal-Núñez, S.; Moreno, P.; González, N.; Acitores, A.; López-Herrandón, A.; Esbrit, P.; Valverde, I.; Villanueva-Peñacarrillo, M.L. Presence of a functional receptor for GLP-1 in osteoblastic cells, independent of the cAMP-linked GLP-1 receptor. J. Cell. Physiol. 2010, 225, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, C.; Vázquez, P.; Blázquez, C.; Barrio, P.A.; Alvarez Mdel, M.; Blázquez, E. Signaling and biological effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 on the differenziation of mesenchymal stem cells from human bone marrow. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 298, E634–E643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufour, A.B.; Kiel, D.P.; Williams, S.A.; Weiss, R.J.; Samelson, E.J. Risk Factors for Incident Fracture in Older Adults With Type 2 Diabetes: The Framingham Heart Study. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 1547–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustina, A.; di Filippo, L.; Facciorusso, A.; Adler, R.A.; Binkley, N.; Bollerslev, J.; Bouillon, R.; Casanueva, F.F.; Cavestro, G.M.; Chakhtoura, M.; et al. Vitamin D status and supplementation before and after Bariatric Surgery: Recommendations based on a systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2023, 24, 1011–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, J.K.; Leutscher, P.; Sorensen, S. Gut Microbiota in Bone Health and Diabetes. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2021, 19, 462–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajivalizadeh, S.; Aazami, H.; Mansourzadeh, M.; Dehghanbanadaki, H. Mapping the Landscape of Trabecular Bone Score and Diabetes Mellitus: A Bibliometric Analysis of Authorship and Collaboration Trends Over a Decade. Clin. Transl. Metab. 2025, 23, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Peel, N.; Clowes, J.A.; McCloskey, E.V.; Eastell, R. Use of DXA-based structural engineering models of the proximal femur to discriminate hip fracture. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2009, 24, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourtada, F.A.; Beck, T.J.; Hauser, D.L.; Ruff, C.B.; Bao, G. Curved beam model of the proximal femur for estimating stress using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry derived structural geometry. J. Orthop. Res. 1996, 14, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peacock, M.; Turner, C.H.; Liu, G.; Manatunga, A.K.; Timmerman, L.; Johnston, C.C., Jr. Better discrimination of hip fracture using bone density, geometry and architecture. Osteoporos. Int. 1995, 5, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamari, J.; Ammarullah, M.I.; Saad, A.P.M.; Syahrom, A.; Uddin, M.; van der Heide, E.; Basri, H. The Effect of Bottom Profile Dimples on the Femoral Head on Wear in Metal-on-Metal Total Hip Arthroplasty. J. Funct. Biomater. 2021, 12, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milgrom, C.; Giladi, M.; Simkin, A.; Rand, N.; Kedem, R.; Kashtan, H.; Stein, M.; Gomori, M. The area moment of inertia of the tibia: A risk factor for stress fractures. J. Biomech. 1989, 22, 1243–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khennane, A. Introduction to Finite Element Analysis Using MATLAB® and Abaqus; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd, J.A.; Schousboe, J.T.; Broy, S.B.; Engelke, K.; Leslie, W.D. Executive Summary of the 2015 ISCD Position Development Conference on Advanced Measures From DXA and QCT: Fracture Prediction Beyond BMD. J. Clin. Densitom. 2015, 18, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammann, P.; Rizzoli, R. Bone strength and its determinants. Osteoporos. Int. 2003, 14 (Suppl. S3), 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulivieri, F.M.; Rinaudo, L. Beyond Bone Mineral Density: A New Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry Index of Bone Strength to Predict Fragility Fractures, the Bone Strain Index. Front. Med. 2020, 7, 590139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uygur, M.M.; Frara, S.; di Filippo, L.; Giustina, A. New tools for bone health assessment in secreting pituitary adenomas. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 34, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uygur, M.M.; di Filippo, L.; Frara, S.; Menotti, S.; Giustina, A. Pathophysiology and evaluation of bone health in adrenal diseases. Endocrine 2025, 89, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hough, F.S.; Pierroz, D.D.; Cooper, C.; Ferrari, S.L.; Bone, I.C.; Diabetes Working, G. Mechanisms in Endocrinology: Mechanisms and evaluation of bone fragility in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 174, R127–R138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdalrahaman, N.; McComb, C.; Foster, J.E.; McLean, J.; Lindsay, R.S.; McClure, J.; McMillan, M.; Drummond, R.; Gordon, D.; McKay, G.A.; et al. Deficits in Trabecular Bone Microarchitecture in Young Women with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2015, 30, 1386–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanbhogue, V.V.; Hansen, S.; Frost, M.; Jørgensen, N.R.; Hermann, A.P.; Henriksen, J.E.; Brixen, K. Bone Geometry, Volumetric Density, Microarchitecture, and Estimated Bone Strength Assessed by HR-pQCT in Adult Patients With Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2015, 30, 2188–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewing, L.; Potasso, L.; Baumann, S.; Schenk, D.; Gazozcu, F.; Lippuner, K.; Kraenzlin, M.; Zysset, P.; Meier, C. Bone Microarchitecture and Strength in Long-Standing Type 1 Diabetes. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2022, 37, 837–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilaca, T.; Paggiosi, M.; Walsh, J.S.; Selvarajah, D.; Eastell, R. The Effects of Type 1 Diabetes and Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy on the Musculoskeletal System: A Case-Control Study. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2021, 36, 1048–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, I.A.G.; Viggers, R.; Harslof, T.; Frost, M.; Vestergaard, P. Bone properties in persons with type 1 diabetes and healthy controls—A cross-sectional study. Bone 2025, 190, 117306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hygum, K.; Starup-Linde, J.; Harslof, T.; Vestergaard, P.; Langdahl, B.L. Mechanisms in Endocrinology: Diabetes mellitus, a state of low bone turnover—A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 176, R137–R157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giangregorio, L.M.; Leslie, W.D.; Lix, L.M.; Johansson, H.; Oden, A.; McCloskey, E.; Kanis, J.A. FRAX underestimates fracture risk in patients with diabetes. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2012, 27, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, A.V.; Vittinghoff, E.; Bauer, D.C.; Hillier, T.A.; Strotmeyer, E.S.; Ensrud, K.E.; Donaldson, M.G.; Cauley, J.A.; Harris, T.B.; Koster, A.; et al. Association of BMD and FRAX score with risk of fracture in older adults with type 2 diabetes. JAMA 2011, 305, 2184–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevroja, E.; Cafarelli, F.P.; Guglielmi, G.; Hans, D. DXA parameters, Trabecular Bone Score (TBS) and Bone Mineral Density (BMD), in fracture risk prediction in endocrine-mediated secondary osteoporosis. Endocrine 2021, 74, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, E.L.; Huang, W.N.; Chen, H.H.; Chen, J.P.; Chen, D.Y.; Hsieh, T.Y.; Hung, W.T.; Lai, K.L.; Lin, C.T.; Tang, K.T.; et al. Degraded microarchitecture by low trabecular bone score is associated with prevalent vertebral fractures in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arch. Osteoporos. 2020, 15, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hans, D.; Barthe, N.; Boutroy, S.; Pothuaud, L.; Winzenrieth, R.; Krieg, M.A. Correlations between trabecular bone score, measured using anteroposterior dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry acquisition, and 3-dimensional parameters of bone microarchitecture: An experimental study on human cadaver vertebrae. J. Clin. Densitom. 2011, 14, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothuaud, L.; Barthe, N.; Krieg, M.A.; Mehsen, N.; Carceller, P.; Hans, D. Evaluation of the potential use of trabecular bone score to complement bone mineral density in the diagnosis of osteoporosis: A preliminary spine BMD-matched, case-control study. J. Clin. Densitom. 2009, 12, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, H.; Binkley, N.; Hans, D.; Leslie, W.D. Fracture risk gradient assessed by categories of bone mineral density and trabecular bone score: The Manitoba BMD Registry. Arch. Osteoporos. 2023, 18, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, H.; Binkley, N.; Boggild, M.; Chan, W.P.; Leslie, W.D.; McCloskey, E.; Morgan, S.L.; Silva, B.C.; Cheung, A.M. Clinical Use of Trabecular Bone Score: The 2023 ISCD Official Positions. J. Clin. Densitom. 2024, 27, 101452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martineau, P.; Leslie, W.D.; Johansson, H.; Oden, A.; McCloskey, E.V.; Hans, D.; Kanis, J.A. Clinical Utility of Using Lumbar Spine Trabecular Bone Score to Adjust Fracture Probability: The Manitoba BMD Cohort. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2017, 32, 1568–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martineau, P.; Leslie, W.D.; Johansson, H.; Harvey, N.C.; McCloskey, E.V.; Hans, D.; Kanis, J.A. In which patients does lumbar spine trabecular bone score (TBS) have the largest effect? Bone 2018, 113, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leslie, W.D.; Aubry-Rozier, B.; Lamy, O.; Hans, D.; Manitoba Bone Density, P. TBS (trabecular bone score) and diabetes-related fracture risk. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubago-Guisado, E.; Moratalla-Aranda, E.; Gonzalez-Salvatierra, S.; Gil-Cosano, J.J.; Garcia-Fontana, B.; Garcia-Fontana, C.; Gracia-Marco, L.; Munoz-Torres, M. Do patients with type 2 diabetes have impaired hip bone microstructure? A study using 3D modeling of hip dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1069224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaccorsi, G.; Fila, E.; Messina, C.; Maietti, E.; Ulivieri, F.M.; Caudarella, R.; Greco, P.; Guglielmi, G. Comparison of trabecular bone score and hip structural analysis with FRAX((R)) in postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 29, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo, L.; Puigoriol, E.; Rodriguez, J.R.; Peris, P.; Kanterewicz, E. Usefulness of the Trabecular Bone Score for assessing the risk of osteoporotic fracture. Rev. Clin. Esp. 2018, 218, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri, A.; Shojaeefard, E.; Bakhshayeshkaram, M.; Dabbaghmanesh, M.M.; Heydari, S.T.; Talezadeh, P.; Farhadi, M.; Nikkhah, A.; Dabbaghmanesh, M.H. Hip structural analysis, trabecular bone score, and bone mineral density in post-menopausal women with type-2 diabetes mellitus: A multi-center cross-sectional study in the south of Iran. Arch. Osteoporos. 2023, 18, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baleanu, F.; Bergmann, P.; Hambye, A.S.; Dekelver, C.; Iconaru, L.; Cappelle, S.I.; Moreau, M.; Paesmans, M.; Karmali, R.; Body, J.J. Assessment of bone quality with trabecular bone score in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A study from the FRISBEE cohort. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2019, 73, e13347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holloway, K.L.; De Abreu, L.L.F.; Hans, D.; Kotowicz, M.A.; Sajjad, M.A.; Hyde, N.K.; Pasco, J.A. Trabecular Bone Score in Men and Women with Impaired Fasting Glucose and Diabetes. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2018, 102, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haeri, N.S.; Kotlarczyk, M.P.; Perera, S.; Greenspan, S.L. Diabetes Mellitus is Associated with Poor Bone Microarchitecture in Older Adults Residing in Long-Term Care Facilities. J. Osteoporos. 2022, 2022, 2522014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gani, L.U.; Saripalli, K.R.; Fernandes, K.; Leong, S.F.; Tsai, K.T.; Tan, P.T.; Chong, L.R.; King, T.F.J. Bone mineral density and trabecular bone score in elderly type 2 diabetes Southeast Asian patients with severe osteoporotic hip fractures. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho-Pham, L.T.; Tran, B.; Do, A.T.; Nguyen, T.V. Association between pre-diabetes, type 2 diabetes and trabecular bone score: The Vietnam Osteoporosis Study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 155, 107790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, T.L.; Chuang, M.H.; Wang, Y.F.; Koo, M. Comparison of Trabecular Bone Score-Adjusted Fracture Risk Assessment (TBS-FRAX) and FRAX Tools for Identification of High Fracture Risk among Taiwanese Adults Aged 50 to 90 Years with or without Prediabetes and Diabetes. Medicina 2022, 58, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Choi, H.J.; Ku, E.J.; Kim, K.M.; Kim, S.W.; Cho, N.H.; Shin, C.S. Trabecular bone score as an indicator for skeletal deterioration in diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Tang, J.; Xue, C.; Di, W.; Cheng, P. Age-related trends in trabecular bone scores and bone mineral density in Chinese men with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A cross-sectional study. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho-Pham, L.T.; Nguyen, T.V. Association between trabecular bone score and type 2 diabetes: A quantitative update of evidence. Osteoporos. Int. 2019, 30, 2079–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharibzadeh, S.; Goodarzi, G.; Tehrani, S.S.; Fahimfar, N.; Razi, F.; Sanjari, M.; Khalagi, K.; Shafiee, G.; Heshmat, R.; Amini, A.; et al. Bone mass and microarchitecture in T2DM patients and corticosteroids therapy: The Bushehr Elderly Health program. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2022, 21, 717–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, K.M.; Lim, S.; Kang, M.I.; Baek, K.H.; Min, Y.K. Efficacy of bisphosphonate therapy on postmenopausal osteoporotic women with and without diabetes: A prospective trial. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2022, 22, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vavanikunnel, J.; Charlier, S.; Becker, C.; Schneider, C.; Jick, S.S.; Meier, C.R.; Meier, C. Association Between Glycemic Control and Risk of Fracture in Diabetic Patients: A Nested Case-Control Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 1645–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayat, K.; Fang, Q.L.; Shi, B.M.; Qin, L.Q. Influence of glycemic control and hypoglycemia on the risk of fracture in patients with diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Osteoporos. Int. 2021, 32, 1693–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal, R.; Cibula, D.; Ghosh, C.; Weinstock, R.S.; Moses, A.M. Bone quality assessment in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Osteoporos. Int. 2014, 25, 1969–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.P.; Kuo, S.F.; Lin, Y.C.; Fan, C.M.; Chen, J.F. Status of bone strength and factors associated with vertebral fracture in postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes. Menopause 2019, 26, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordklint, A.K.; Almdal, T.P.; Vestergaard, P.; Lundby-Christensen, L.; Boesgaard, T.W.; Breum, L.; Gade-Rasmussen, B.; Sneppen, S.B.; Gluud, C.; Hemmingsen, B.; et al. The effect of metformin versus placebo in combination with insulin analogues on bone mineral density and trabecular bone score in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. Osteoporos. Int. 2018, 29, 2517–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trandafir, A.I.; Sima, O.C.; Gheorghe, A.M.; Ciuche, A.; Cucu, A.P.; Nistor, C.; Carsote, M. Trabecular Bone Score (TBS) in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Updated Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomo, T.; Dreyer, P.; Muszkat, P.; Weiler, F.G.; Bonansea, T.C.P.; Domingues, F.C.; Vieira, J.G.H.; Silva, B.C.; Brandao, C.M.A. Effect of soft tissue noise on trabecular bone score in postmenopausal women with diabetes: A cross-sectional study. Bone 2022, 157, 116339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, T.; Shah, R.; Pal, R.; Rastogi, A.; Singla, V.; Bhadada, S.K. Trabecular Bone Score in Asian-Indian Post-menopausal Women Across the Spectrum of Hyperglycaemia: Insights from a Cross-Sectional Study. Indian. J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2025, 29, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballato, E.; Deepika, F.N.U.; Russo, V.; Fleires-Gutierrez, A.; Colleluori, G.; Fuenmayor, V.; Chen, R.; Villareal, D.T.; Qualls, C.; Armamento-Villareal, R. One-Year Mean A1c of > 7% is Associated with Poor Bone Microarchitecture and Strength in Men with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2022, 111, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackuliak, P.; Kuzma, M.; Killinger, Z.; Payer, J. Good long-term glycemic compensation is associated with better trabecular bone score in postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes. Physiol. Res. 2019, 68, S149–S156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Araujo, I.M.; Salmon, C.E.G.; de Paula, F.J.A. Ectopic fat in muscle and poor glycemic control are negatively associated with trabecular bone score in type 2 diabetes. Clinics 2024, 79, 100430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depczynski, B.; Liew, P.Y.; White, C. Association of glycaemic variables with trabecular bone score in post-menopausal women with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabet. Med. 2020, 37, 1545–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamacchia, O.; Sorrentino, M.R.; Berti, G.; Paradiso, M.; Corrado, A.; Cantatore, F.P.; De Cosmo, S. Glomerular filtration rate is associated with trabecular bone score in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 164, 108164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, H.J.; Ryoo, S.R.; Kim, J.E.; Choi, Y.J.; Park, I.; Shin, G.T.; Kim, H.; Jeong, J.C. Trabecular bone score may indicate chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorder (CKD-MBD) phenotypes in hemodialysis patients: A prospective observational study. BMC Nephrol. 2020, 21, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maamar El Asri, M.; Pariente Rodrigo, E.; Diaz-Salazar de la Flor, S.; Pini Valdivieso, S.; Ramos Barron, M.C.; Olmos Martinez, J.M.; Hernandez Hernandez, J.L. Trabecular bone score and 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels in microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Med. Clin. 2022, 158, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dule, S.; Barchetta, I.; Cimini, F.A.; Passarella, G.; Dellanno, A.; Filardi, T.; Venditti, V.; Bleve, E.; Bailetti, D.; Romagnoli, E.; et al. Reduced High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Is an Independent Determinant of Altered Bone Quality in Women with Type 2 Diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, C.W.; Fang, W.H.; Chen, W.L. Clinical relevance of the relationship between Trabecular Bone Score and metabolic syndrome. J. Investig. Med. 2022, 70, 967–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romagnoli, E.; Lubrano, C.; Carnevale, V.; Costantini, D.; Nieddu, L.; Morano, S.; Migliaccio, S.; Gnessi, L.; Lenzi, A. Assessment of trabecular bone score (TBS) in overweight/obese men: Effect of metabolic and anthropometric factors. Endocrine 2016, 54, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, B.C.; Broy, S.B.; Boutroy, S.; Schousboe, J.T.; Shepherd, J.A.; Leslie, W.D. Fracture Risk Prediction by Non-BMD DXA Measures: The 2015 ISCD Official Positions Part 2: Trabecular Bone Score. J. Clin. Densitom. 2015, 18, 309–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazullina, O.N.; Korbut, A.I.; Klimontov, V.V. Factors associated with trabecular bone score in postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes and normal bone mineral density. World J. Diabetes 2022, 13, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pechmann, L.M.; Petterle, R.R.; Moreira, C.A.; Borba, V.Z.C. Osteosarcopenia and trabecular bone score in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 65, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, S.; Akesson, K.E.; Al-Daghri, N.; Biver, E.; Chandran, M.; Chevalley, T.; Josse, R.G.; Kendler, D.L.; Lane, N.E.; Makras, P.; et al. Bone microstructure and TBS in diabetes: What have we learned? A narrative review. Osteoporos. Int. 2025, 36, 1115–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merugu, C.; Sahoo, J.; Kamalanathan, S.; Ramkumar, G.; Reddy, S.V.B.; Kar, S.S.; Naik, D.; Roy, A.; Narayanan, N.; Patel, D.; et al. Effect of a single dose of zoledronic acid on bone mineral density and trabecular bone score in Indian postmenopausal osteoporotic women with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus—A prospective cohort pilot study. Endocrine 2023, 82, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, S.; Betah, D.; Feldman, R.G.; Langdahl, B.L.; Oates, M.; Timoshanko, J.; Wang, Z.; Dhaliwal, R. Romosozumab Improves Tissue Thickness-Adjusted Trabecular Bone Score in Women With Osteoporosis and Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Refaie, A.; Baldassini, L.; Mondillo, C.; Ceccarelli, E.; Tarquini, R.; Gennari, L.; Gonnelli, S.; Caffarelli, C. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists and Diabetic Osteopathy: Another Positive Effect of Incretines? A 12 Months Longitudinal Study. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2024, 115, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, T.; Lodes, S.; Kastner, B.; Lehmann, T.; Hans, D.; Lamy, O.; Muller, U.A.; Wolf, G.; Samann, A. Trabecular bone score in type 1 diabetes--a cross-sectional study. Osteoporos. Int. 2016, 27, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleksova, J.; Ebeling, P.R.; Milat, F.; Elder, G.J. DXA-derived advanced hip analysis and the trabecular bone score in end-stage kidney disease secondary to type 1 diabetes. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2022, 187, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Trabecular bone score in type 1 diabetes: A meta-analysis of cross-sectional studies. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2023, 18, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Nagendra, L.; Chandran, M.; Kapoor, N.; Patil, P.; Dutta, D.; Kalra, S. Trabecular bone score in adults with type 1 diabetes: A meta-analysis. Osteoporos. Int. 2024, 35, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, C.; Piodi, L.P.; Grossi, E.; Eller-Vainicher, C.; Bianchi, M.L.; Ortolani, S.; Di Stefano, M.; Rinaudo, L.; Sconfienza, L.M.; Ulivieri, F.M. Artificial neural network analysis of bone quality DXA parameters response to teriparatide in fractured osteoporotic patients. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulivieri, F.M.; Rinaudo, L.; Messina, C.; Piodi, L.P.; Capra, D.; Lupi, B.; Meneguzzo, C.; Sconfienza, L.M.; Sardanelli, F.; Giustina, A.; et al. Bone Strain Index predicts fragility fracture in osteoporotic women: An artificial intelligence-based study. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2021, 5, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulivieri, F.M.; Rinaudo, L.; Piodi, L.P.; Barbieri, V.; Marotta, G.; Sciume, M.; Grifoni, F.I.; Cesana, B.M. Usefulness of Dual X-ray Absorptiometry-Derived Bone Geometry and Structural Indexes in Mastocytosis. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2020, 107, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizza, I.C.; Bongiorno, A.; Pedulla, M.; Albano, D.; Sconfienza, L.M.; Messina, C. DXA: New Concepts and Tools Beyond Bone Mineral Density. Semin. Musculoskelet. Radiol. 2024, 28, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaCroix, A.Z.; Beck, T.J.; Cauley, J.A.; Lewis, C.E.; Bassford, T.; Jackson, R.; Wu, G.; Chen, Z. Hip structural geometry and incidence of hip fracture in postmenopausal women: What does it add to conventional bone mineral density? Osteoporos. Int. 2010, 21, 919–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broy, S.B.; Cauley, J.A.; Lewiecki, M.E.; Schousboe, J.T.; Shepherd, J.A.; Leslie, W.D. Fracture Risk Prediction by Non-BMD DXA Measures: The 2015 ISCD Official Positions Part 1: Hip Geometry. J. Clin. Densitom. 2015, 18, 287–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, S.; Aston, C.E.; Chadwick, J.; Gulati, S.; Wang, H.; Sisson, S.B.; Misra, M.; Chernausek, S.D. Collagen glycosylation, hip structural analysis, and trabecular bone score in adolescents with type 1 diabetes: A cross-sectional study. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2025, 17, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schileo, E.; Taddei, F. Finite Element Assessment of Bone Fragility from Clinical Images. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2021, 19, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammarullah, M.I.; Afif, I.Y.; Maula, M.I.; Winarni, T.I.; Tauviqirrahman, M.; Akbar, I.; Basri, H.; van der Heide, E.; Jamari, J. Tresca Stress Simulation of Metal-on-Metal Total Hip Arthroplasty during Normal Walking Activity. Materials 2021, 14, 7554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choisne, J.; Valiadis, J.M.; Travert, C.; Kolta, S.; Roux, C.; Skalli, W. Vertebral strength prediction from Bi-Planar dual energy x-ray absorptiometry under anterior compressive force using a finite element model: An in vitro study. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 87, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, C.; Libonati, F.; Rinaudo, L.; Bellazzi, M.; Ulivieri, F.M.; Vergani, L. A new finite element based parameter to predict bone fracture. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulivieri, F.M.; Rinaudo, L. The Bone Strain Index: An Innovative Dual X-ray Absorptiometry Bone Strength Index and Its Helpfulness in Clinical Medicine. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Palermo, L.; Black, D.M.; Eastell, R. Prediction of incident hip fracture with the estimated femoral strength by finite element analysis of DXA Scans in the study of osteoporotic fractures. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2014, 29, 2594–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, E.F.; Bayraktar, H.H.; Keaveny, T.M. Trabecular bone modulus-density relationships depend on anatomic site. J. Biomech. 2003, 36, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, K.S.; Rohlmann, A.; Zander, T.; Taylor, W.R. Lumbar spinal loads vary with body height and weight. Med. Eng. Phys. 2013, 35, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaccorsi, G.; Sciavicco, G.; Rinaudo, L.; Brigato, A.; Fiorella, G.; Carnevale, A.; Ulivieri, F.M.; Messina, C. Usefulness of DXA-based bone strain index in postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arch. Osteoporos. 2024, 19, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, W.H.; Hung, V.W.; Cheuk, K.Y.; Chau, W.W.; Tsoi, K.K.; Wong, R.M.; Chow, S.K.; Lam, T.P.; Yung, P.S.; Law, S.W.; et al. Best performance parameters of HR-pQCT to predict fragility fracture: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2021, 36, 2381–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samelson, E.J.; Demissie, S.; Cupples, L.A.; Zhang, X.; Xu, H.; Liu, C.T.; Boyd, S.K.; McLean, R.R.; Broe, K.E.; Kiel, D.P.; et al. Diabetes and Deficits in Cortical Bone Density, Microarchitecture, and Bone Size: Framingham HR-pQCT Study. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2018, 33, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanbhogue, V.V.; Hansen, S.; Frost, M.; Jorgensen, N.R.; Hermann, A.P.; Henriksen, J.E.; Brixen, K. Compromised cortical bone compartment in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with microvascular disease. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 174, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walle, M.; Whittier, D.E.; Frost, M.; Muller, R.; Collins, C.J. Meta-analysis of Diabetes Mellitus-Associated Differences in Bone Structure Assessed by High-Resolution Peripheral Quantitative Computed Tomography. Curr. Osteoporos. Rep. 2022, 20, 398–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilmeier, U.; Joseph, G.B.; Pasco, C.; Dinh, N.; Torabi, S.; Darakananda, K.; Youm, J.; Carballido-Gamio, J.; Burghardt, A.J.; Link, T.M.; et al. Longitudinal Evolution of Bone Microarchitecture and Bone Strength in Type 2 Diabetic Postmenopausal Women With and Without History of Fragility Fractures-A 5-Year Follow-Up Study Using High Resolution Peripheral Quantitative Computed Tomography. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 599316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loffler, M.T.; Wu, P.H.; Kazakia, G.J. MR-based techniques for intracortical vessel visualization and characterization: Understanding the impact of microvascular disease on skeletal health. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2023, 30, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walle, M.; Duseja, A.; Whittier, D.E.; Vilaca, T.; Paggiosi, M.; Eastell, R.; Müller, R.; Collins, C.J. Bone remodeling and responsiveness to mechanical stimuli in individuals with type 1 diabetes mellitus. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2024, 39, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuggle, N.R.; Reginster, Y.; Al-Daghr, N.; Bruyere, O.; Burlet, N.; Campusano, C.; Cooper, C.; Diez Perez, A.; Halbout, P.; Ghi, T.; et al. Radiofrequency echographic multi spectrometry (REMS) in the diagnosis and management of osteoporosis: State of the art. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2024, 36, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caffarelli, C.; Toma Pitinca, M.D.; Al Refaie, A.; Ceccarell, E.; Gonnelli, S. Ability of radiofrequency echographic multispectometry to identify osteoporosis status in elderly women with type 2 diabetes. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2022, 34, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonnelli, S.; Al Refaie, A.; Baldassini, L.; De Vita, M.; Caffarelli, C. Ultrasound-based techniques in diabetic bone disease: State of the art and future perspectives. Indian. J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 26, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizu, H.; Shizimu, T.; Sakamoto, Y.; Toyama, F.; Kitahara, K.; Takayama, H.; Miyamoto, M.; Iwasaki, N. Radiofrequency echographic Multispectrometry (REMS) can overcome the effects of structural Internal Artifacts and evaluate bone fragility accurately. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2024, 114, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Gao, L.; Liu, C.; Bao, X.; Tian, Y.; Li, Y. Denosumab Improves Glycaemic Parameters in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis Patients with Combined Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Cell Mol. Biol. 2023, 69, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, R.; Ikenoue, T.; Ishii, R.; Niihata, K.; Aita, T.; Okuda, T.; Shimizu, S.; Taguri, M.; Kurita, N. Comparative cardiovascular safety of romosozumab versus bisphosphonates in Japanese patients with osteoporosis: A new-user, active comparator design with instrumental variable analyses. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Liu, Z.; Lu, M.; Zhang, Y. The combination of linagliptin and metformin rescues bone loss in type 2 diabetic osteoporosis. J. Drug Target. 2023, 31, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, T.; Mazziotti, G.; Doga, M.; Carpinteri, R.; Simetovic, N.; Vescovi, P.P.; Giustina, A. Vertebral fractures in males with type 2 diabetes treated with rosiglitazone. Bone 2009, 45, 784–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
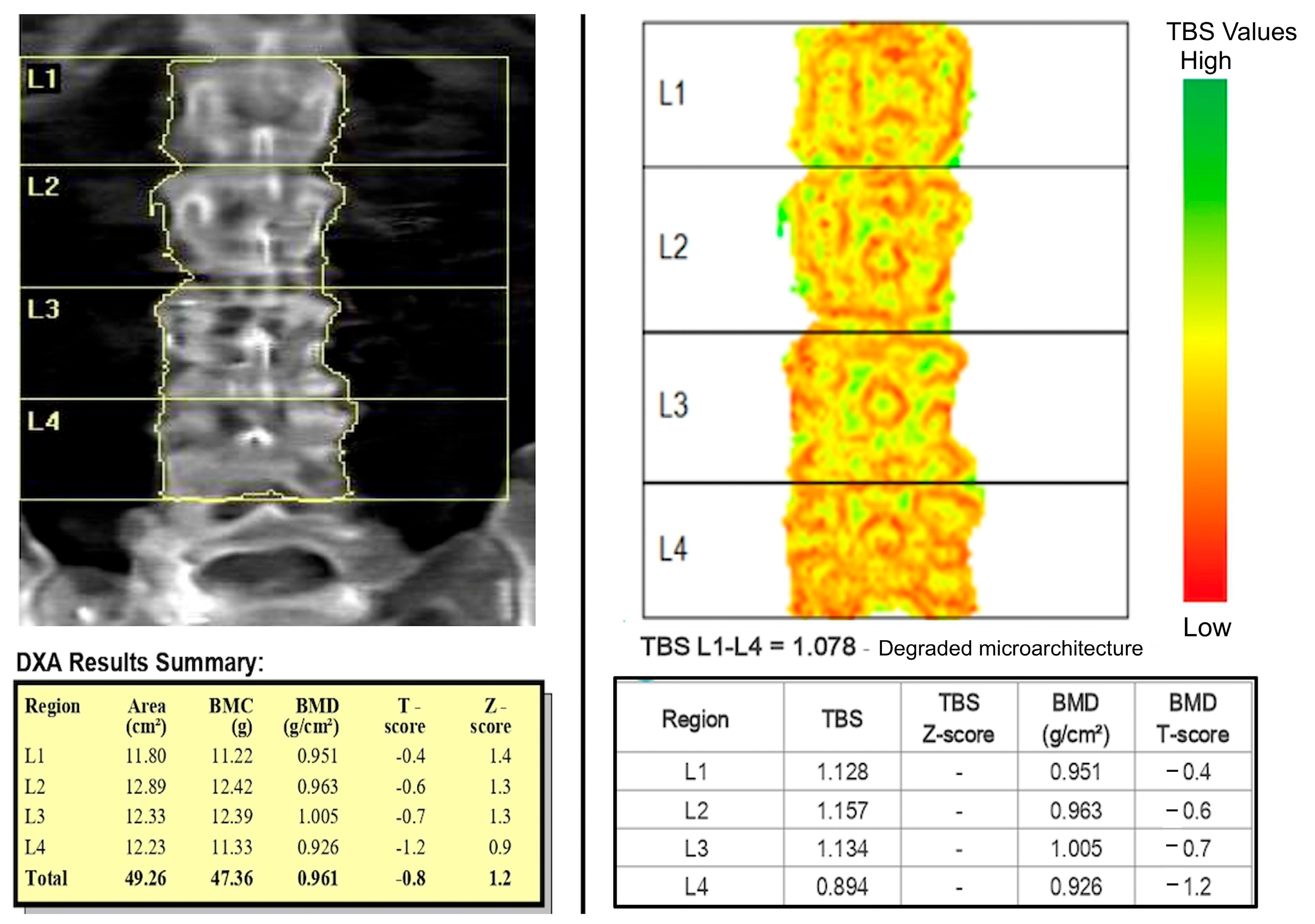

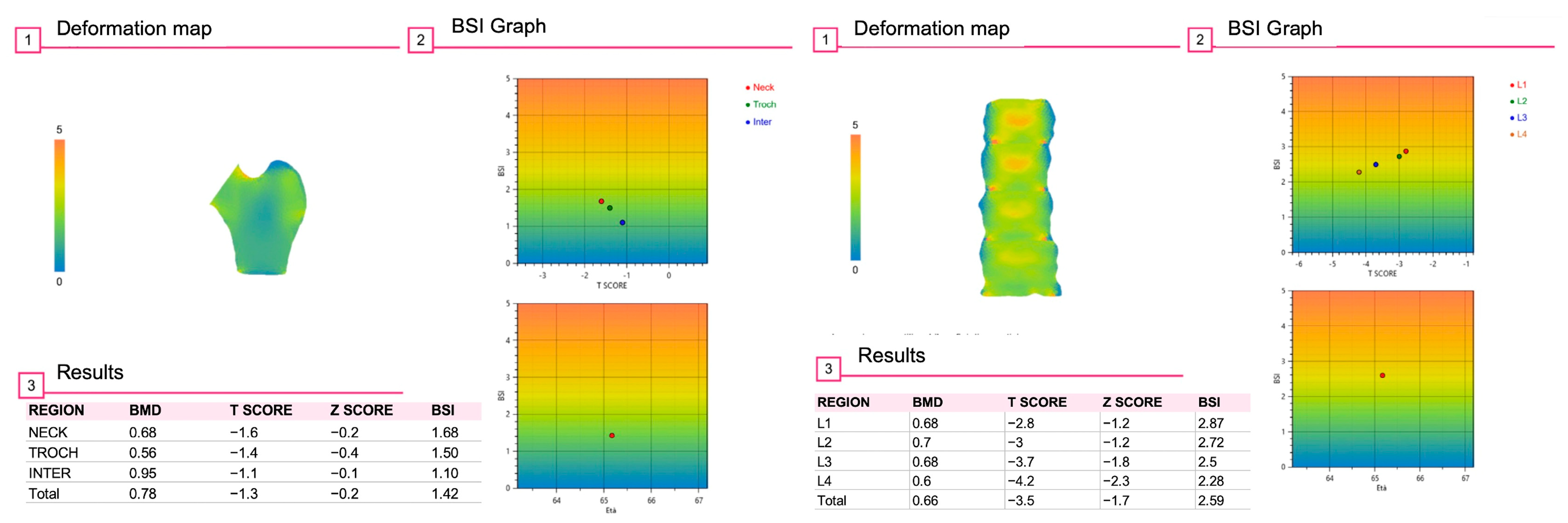
| Technique | Principle | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| DXA-BMD | Measurements of areal bone mineral density (g/cm2) |
|
|
| TBS | Texture analysis of lumbar DXA to indirectly estimate trabecular microarchitecture |
|
|
| BSI | Finite Element Analysis applied to DXA images to estimate bone strength |
|
|
| HSA | Geometric analysis of the proximal femur |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Frara, S.; Messina, C.; Ulivieri, F.M. Diabetes-Induced Osteoporosis: Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry Bone Quality Is Better than Bone Quantity. Diabetology 2025, 6, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6090095
Frara S, Messina C, Ulivieri FM. Diabetes-Induced Osteoporosis: Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry Bone Quality Is Better than Bone Quantity. Diabetology. 2025; 6(9):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6090095
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrara, Stefano, Carmelo Messina, and Fabio Massimo Ulivieri. 2025. "Diabetes-Induced Osteoporosis: Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry Bone Quality Is Better than Bone Quantity" Diabetology 6, no. 9: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6090095
APA StyleFrara, S., Messina, C., & Ulivieri, F. M. (2025). Diabetes-Induced Osteoporosis: Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry Bone Quality Is Better than Bone Quantity. Diabetology, 6(9), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6090095





