Adipose Tissue Dysfunction and Hepatic Steatosis in New-Onset Diabetes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Trial Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Laboratory Assays
2.4. Imaging Assessment
2.5. Noninvasive Markers of MAFLD
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
- Cytokines and hepatic steatosis index
- Cytokines and hepatic fibrosis
- Comparison of areas under ROC curves (95% CI) for predictors of HS
- Predictors for hepatic steatosis by multivariate logistic regression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MAFLD | Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease |
| NAFLD | Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease |
| MASLD | Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver diseases |
| HDL | High-density lipoprotein |
| HS | Hepatic steatosis |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| IR | Insulin resistance |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| WC | Waist circumference |
| HipC | Hip circumference |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| TC | Total cholesterol |
| TG | Triglycerides |
| FPG | Fasting plasma glucose |
| FPI | Fasting plasma insulin |
| HbA1c | Glycated hemoglobin |
| GPT | Glutamate–pyruvate transaminase |
| GOT | Glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase |
| GGT | Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase |
| INR | International Normalized Ratio |
| HOMA-IR | Homeostasis Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance |
| SBP | Systolic blood pressure |
| DBP | Diastolic blood pressure |
| HIS | Hepatic steatosis index |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| FI | FornsFibrosis Index |
| AUROC | Area under the Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve |
| CIs | Confidence intervals |
| OR | Odds ratios |
| MetS | Metabolic syndrome |
| ACC | Acetyl-CoA carboxylase |
| FA | Fatty acid |
| WHR | Waist-to-hip ratio |
References
- Eslam, M.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Dufour, J.-F.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.E.; Koh, T.J.L.; Tang, A.S.P.; Quek, J.; Yong, J.N.; Tay, P.; Tan, D.J.H.; Lim, W.H.; Lin, S.Y.; Huang, D.; et al. Global prevalence and clinical characteristics of metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: A meta-analysis and systematic review of 10 739 607 individuals. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 2691–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Kalligeros, M.; Henry, L. Epidemiology of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2024, 31, S32–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Golabi, P.; Paik, J.M.; Henry, A.; Van Dongen, C.; Henry, L. The Global Epidemiology of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): A Systematic Review. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholongitas, E.; Pavlopoulou, I.; Papatheodoridi, M.; Markakis, G.E.; Bouras, E.; Haidich, A.B.; Papatheodoridis, G. Epidemiology of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Europe: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2021, 34, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL); European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD); European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO). EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). J. Hepatol. 2024, 81, 492–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portincasa, P.; Baffy, G. Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: Evolution of the final terminology. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2024, 124, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.; Golabi, P.; de Avila, L.; Paik, J.M.; Srishord, M.; Fukui, N.; Qiu, Y.; Burns, L.; Afendy, A.; Nader, F. The global epidemiology of NAFLD and NASH in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefan, N.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A. Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: Heterogeneous pathomechanisms and effectiveness of metabolism-based treatment. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2025, 13, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefan, N.; Targher, G. Clusters of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease for precision medicine. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2025, 22, 226–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldas, C.A.M.; Freire de Carvalho, J. Antiphospholipid syndrome and polyarteritis nodosa: A diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. Rheumatol. Int. 2013, 33, 2697–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusu, E.; Enache, G.; Jinga, M.; Dragut, R.; Raluca, N.; Parpala, C.; Popescu, H.; Homentcovschi, C.; Ateia, S.; Posea, M.; et al. Adiponectin in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Med. Surg. J. 2015, 119, 664–669. Available online: https://www.revmedchir.ro/index.php/revmedchir/issue/view/14 (accessed on 14 March 2025).
- Jiménez-Cortegana, C.; García-Galey, A.; Tami, M.; Del Pino, P.; Carmona, I.; López, S.; Alba, G.; Sánchez-Margalet, V. Role of Leptin in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Braunersreuther, V.; Viviani, G.L.; Mach, F.; Montecucco, F. Role of cytokines and chemokines in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 727–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearce, S.G.; Thosani, N.C.; Pan, J.J. Noninvasive biomarkers for the diagnosis of steatohepatitis and advanced fibrosis in NAFLD. Biomark. Res. 2013, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Kountouras, J.; Mantzoros, C.S. Adipokines in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Metabolism 2016, 65, 1062–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, A.; Asal, A.; Seidkhani-Nahal, A.; Noori-Zadeh, A. A systematic review and meta-analysis of serum resistin level and its relation to HOMA-IR score using meta-regression in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients. Mediterr. J. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 14, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Obesity: Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic: Report of a World Health Organization Consultation; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Matthews, D.R.; Hosker, J.P.; Rudenski, A.S.; Naylor, B.A.; Treacher, D.F.; Turner, R.C. Homeostasis model assessment: Insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985, 28, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, S62–S69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, K.G.; Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Cleeman, J.I.; Donato, K.A.; Fruchart, J.C.; James, W.P.; Loria, C.M.; Smith, S.C., Jr.; et al. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: A joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation 2009, 120, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, J.R.; Mohanty, S.R. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A review and update. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2010, 55, 560–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong-Hoon, L.; Donghee, K.; Hwa Jung, K.; Chang-Hoon, L.; Jong In, Y.; Won, K.; Yoon Jun, K.; Jung-Hwan, Y.; Sang-Heon, C.; Myung-Whun, S.; et al. Hepatic steatosis index: A simple screening tool reflecting nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig. Liver Dis. 2010, 42, 503–508. [Google Scholar]
- McPherson, S.; Stewart, S.F.; Henderson, E.; Burt, A.D.; Day, C.P. Simple non-invasive fibrosis scoring systems can reliably exclude advanced fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Gut 2010, 59, 1265–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forns, X.; Ampurdanès, S.; Llovet, J.M.; Aponte, J.; Quintó, L.; Martínez-Bauer, E.; Bruguera, M.; Sánchez-Tapias, J.M.; Rodés, J. Identification of chronic hepatitis C patients without hepatic fibrosis by a simple predictive model. Hepatology 2002, 36, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotronen, A.; Juurinen, L.; Hakkarainen, A.; Westerbacka, J.; Cornér, A.; Bergholm, R.; Yki-Järvinen, H. Liver fat is increased in type 2 diabetic patients and underestimated by serum alanine aminotransferase compared with equally obese nondiabetic subjects. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.; Sorokin, E.P.; Thomas, E.L.; Sattar, N.; Cule, M.; Bell, J.D.; Yaghootkar, H. Estimating the Effect of Liver and Pancreas Volume and Fat Content on Risk of Diabetes: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Cule, M.; Bell, D.; Sattar, N.; Yaghootkar, H. Differing genetic variants associated with liver fat and their contrasting relationships with cardiovascular diseases and cancer. J. Hepatol. 2024, 81, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, N.; Schick, F.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Häring, H.-U.; White, M.F. The role of hepatokines in NAFLD. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 236–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdullah, M.; AlQwaidi, S.; Alshehri, A.; Alamry, F.; Alamri, R.; Alsolbi, Z.; Alqurashi, B.; Aldandan, Y.; Alrashidi, A.; Aljumaie, M. Obesity-Induced Inflammation and Its Role in the Development of Insulin Resistance. J. Healthc. Sci. 2024, 4, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Talbot, C.; Chaurasia, B. Ceramides in Adipose Tissue. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saponaro, C.; Sabatini, S.; Gaggini, M.; Carli, F.; Rosso, C.; Positano, V.; Armandi, A.; Caviglia, G.P.; Faletti, R.; Bugianesi, E.; et al. Adipose tissue dysfunction and visceral fat are associated with hepatic insulin resistance and severity of NASH even in lean individuals. Liver Int. 2022, 42, 2418–2427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vesković, M.; Šutulović, N.; Hrnčić, D.; Stanojlović, O.; Macut, D.; Mladenović, D. The Interconnection between Hepatic Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease—The Transition from an Adipocentric to Liver-Centric Approach. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 9084–9102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, E.M.; Abd Al Aziz, R.A.; Sabry, D.; Badary, H.A.; Gaber, Y.; Yosry, A.; Zakaria, Z. The association of adiponectin gene polymorphisms with susceptibility and progression of NAFLD in a cohort of Egyptian patients. Egypt. Liver J. 2021, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinou, E.; Pericleous, M.; Stefanova, I.; Kaur, V.; Angelidi, A.M. Diagnostic Modalities of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: From Biochemical Biomarkers to Multi-Omics Non-Invasive Approaches. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franczyk, M.P.; He, M.; Yoshino, J. Removal of Epididymal Visceral Adipose Tissue Prevents Obesity-Induced Multi-organ Insulin Resistance in Male Mice. J. Endocr. Soc. 2021, 5, bvab024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Lam, K.S.; Xu, A. Protective roles of adiponectin in obesity-related fatty liver diseases: Mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Arq. Bras. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 53, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Kountouras, J.; Mantzoros, C.S. Leptin in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A narrative review. Metabolism 2015, 64, 60–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotundo, L.; Persaud, A.; Feurdean, M.; Ahlawat, S.; Kim, H.-S. The Association of leptin with severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A population-based study. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2018, 24, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrescu, M.; Vlaicu, S.I.; Ciumărnean, L.; Milaciu, M.V.; Mărginean, C.; Florea, M.; Vesa, Ș.C.; Popa, M. Chronic Inflammation—A Link between Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Dysfunctional Adipose Tissue. Medicina 2022, 58, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramignoli, R.; Ranade, A.R.; Venkataramanan, R.; Strom, S.C. Effects of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines on Hepatic Metabolism in Primary Human Hepatocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.A.; Bakir, A.S.; Shabana, S.S. Serum TGF-β, Serum MMP-1, and HOMA-IR as noninvasive predictors of fibrosis in Egyptian patients with NAFLD. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokota, T.; Oritani, K.; Takahashi, I.; Ishikawa, J.; Matsuyama, A.; Ouchi, N.; Kihara, S.; Funahashi, T.; Tenner, A.J.; Tomiyama, Y.; et al. Adiponectin, a new member of the family of soluble defense collagens, negatively regulates the growth of myelomonocytic progenitors and the functions of macrophages. Blood 2000, 96, 1723–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steppan, C.M.; Wang, J.; Whiteman, E.L.; Birnbaum, M.J.; Lazar, M.A. Activation of SOCS-3 by resistin. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 1569–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radonjić, T.; Dukić, M.; Jovanović, I.; Zdravković, M.; Mandić, O.; Popadić, V.; Popović, M.; Nikolić, N.; Klašnja, S.; Divac, A.; et al. Aging of Liver in Its Different Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| HS- (n = 37) | HS+ (n = 118) | Total (n = 155) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Median | Mean | SD | Median | Mean | SD | Median | p 1 | |
| Age (years) | 49.22 | 6.41 | 49.00 | 54.07 | 8.12 | 55.50 | 52.91 | 8.00 | 54.00 | <0.0001 |
| Weight (kg) | 72.01 | 15.09 | 70.00 | 86.58 | 16.55 | 88.00 | 83.10 | 17.32 | 85.70 | <0.0001 |
| WC (cm) | 82.51 | 12.43 | 82.00 | 99.14 | 14.08 | 99.50 | 95.17 | 15.40 | 97.00 | <0.0001 |
| BMI (kg/mp) | 24.99 | 3.79 | 24.57 | 30.33 | 5.27 | 30.21 | 29.05 | 5.45 | 28.81 | <0.0001 |
| HipC (cm) | 89.97 | 7.08 | 89.00 | 99.97 | 9.73 | 103.00 | 97.58 | 10.09 | 97.00 | <0.0001 |
| HSI | 33.38 | 3.54 | 33.40 | 39.59 | 5.94 | 39.19 | 38.11 | 6.07 | 37.94 | <0.0001 |
| Forns Index | 5.25 | 1.07 | 5.07 | 5.89 | 1.34 | 5.97 | 5.74 | 1.31 | 5.7 | 0.007 |
| FIB-4 | 0.33 | 0.47 | 0.2 | 0.89 | 1.23 | 0.43 | 0.76 | 1.23 | 0.34 | 0.016 |
| AST (UI/L) | 41.51 | 22.31 | 38.00 | 62.51 | 35.33 | 57.50 | 57.49 | 33.84 | 53.00 | 0.010 |
| ALT (UI/L) | 56.05 | 31.01 | 53.00 | 74.29 | 47.36 | 64.00 | 69.93 | 44.60 | 58.00 | 0.030 |
| GGT (UI/L) | 64.92 | 54.93 | 52.00 | 79.24 | 53.88 | 75.00 | 75.82 | 54.30 | 71.00 | 0.016 |
| FPG (mg/dL) | 102.50 | 29.30 | 94.00 | 112.13 | 33.56 | 99.00 | 109.83 | 32.76 | 97.00 | 0.119 |
| FPI (uUI/mL) | 9.76 | 3.60 | 10.15 | 14.27 | 7.97 | 13.00 | 13.19 | 7.41 | 11.90 | 0.001 |
| HOMA-IR | 2.56 | 0.82 | 2.73 | 4.33 | 3.02 | 3.99 | 3.91 | 2.77 | 3.18 | 0.002 |
| HbA1c (%) | 6.7 | 1.12 | 6.1 | 6.9 | 1.36 | 6.5 | 6.94 | 1.3 | 6.5 | 0.362 |
| Adiponectin (ng/mL) | 5.23 | 2.06 | 5.17 | 4.39 | 2.20 | 4.11 | 4.59 | 2.19 | 4.30 | 0.041 |
| Leptin (ng/mL) | 17.56 | 6.55 | 16.88 | 20.41 | 11.11 | 18.58 | 19.73 | 10.26 | 18.40 | 0.041 |
| Resistin (ng/mL) | 19.70 | 11.20 | 17.80 | 23.47 | 14.68 | 19.75 | 22.57 | 13.98 | 19.70 | 0.045 |
| TNF-α (pg/mL) | 14.89 | 4.14 | 15.41 | 16.22 | 6.72 | 15.22 | 15.90 | 6.21 | 15.24 | 0.026 |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 15.50 | 3.76 | 15.60 | 18.61 | 9.64 | 16.86 | 17.87 | 8.70 | 16.20 | 0.037 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 216.27 | 52.97 | 203.00 | 208.60 | 47.35 | 197.00 | 210.43 | 48.69 | 199.00 | 0.405 |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 140.86 | 54.36 | 136.00 | 177.54 | 76.76 | 170.00 | 168.79 | 73.58 | 163.00 | 0.008 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 43.31 | 10.26 | 40.30 | 38.87 | 9.44 | 36.95 | 39.93 | 9.79 | 37.70 | 0.015 |
| HS- | HS+ | Total | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolic WC | 37.8% (n = 14) | 81.4% (n = 96) | 71% (n =110) | <0.0001 |
| HypoHDL-C | 67.6% (n = 25) | 73.7% (n = 87) | 73.2% (n = 112) | 0.465 |
| Hypertension | 48.6% (n = 18) | 63.6% (n = 75) | 60% (n = 93) | 0.0106 |
| TG > 150 mg/dL | 35.1% (n = 13) | 58.5% (n = 69) | 52.9% (n = 82) | 0.013 |
| Without Obesity (n = 92) | With Obesity (n = 63) | Total (n = 155) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Median | Mean | SD | Median | Mean | SD | Median | p 1 | |
| Age (years) | 52.20 | 8.09 | 52.00 | 53.95 | 7.817 | 56.00 | 52.91 | 8.00 | 54.00 | 0.113 |
| Weight (kg) | 73.85 | 13.12 | 71.50 | 96.60 | 13.43 | 94.80 | 83.10 | 17.32 | 85.70 | <0.001 |
| WC (cm) | 86.57 | 12.27 | 87.50 | 107.73 | 9.88 | 106.00 | 95.17 | 15.40 | 97.00 | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/mp) | 25.56 | 3.15 | 25.86 | 34.14 | 3.83 | 33.26 | 29.05 | 5.45 | 28.81 | <0.001 |
| HipC (cm) | 91.42 | 7.30 | 90.40 | 106.58 | 6.01 | 106.00 | 97.58 | 10.09 | 97.00 | <0.001 |
| HSI | 34.54 | 3.82 | 34.55 | 43.31 | 4.857 | 42.11 | 38.11 | 6.07 | 37.94 | <0.001 |
| Forns Index | 5.55 | 1.39 | 5.58 | 5.97 | 1.10 | 5.97 | 5.74 | 1.31 | 5.7 | 0.118 |
| FIB-4 | 0.76 | 1.5 | 0.29 | 0.76 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.76 | 1.23 | 0.34 | 0.517 |
| AST (UI/L) | 53.44 | 37.91 | 46.50 | 63.42 | 25.95 | 62.00 | 57.49 | 33.84 | 53.00 | 0.035 |
| ALT (UI/L) | 65.61 | 48.05 | 53.50 | 76.25 | 38.53 | 73.00 | 69.93 | 44.60 | 58.00 | 0.074 |
| GGT (UI/L) | 74.45 | 62.77 | 60.00 | 77.83 | 39.16 | 76.00 | 75.82 | 54.30 | 71.00 | 0.252 |
| FPG (mg/dL) | 111.46 | 38.01 | 96.00 | 107.44 | 23.13 | 98.00 | 109.83 | 32.76 | 97.00 | 0.913 |
| FPI (uUI/mL) | 12.616 | 7.64 | 11.100 | 14.036 | 7.03 | 13.200 | 13.19 | 7.41 | 11.90 | 0.05 |
| HOMA-IR | 3.69 | 2.89 | 2.97 | 4.21 | 2.57 | 3.73 | 3.91 | 2.77 | 3.18 | 0.023 |
| HbA1c (%) | 7.00 | 1.37 | 6.50 | 6.84 | 1.21 | 6.50 | 6.94 | 1.3 | 6.5 | 0.609 |
| Adiponectin (ng/mL) | 5.33 | 2.00 | 5.34 | 3.51 | 2.00 | 3.30 | 4.59 | 2.19 | 4.30 | <0.001 |
| Leptin (ng/mL) | 17.63 | 6.88 | 16.88 | 22.79 | 13.25 | 21.30 | 19.73 | 10.26 | 18.40 | 0.001 |
| Resistin (ng/mL) | 21.20 | 12.78 | 19.10 | 24.55 | 15.46 | 21.60 | 22.57 | 13.98 | 19.70 | 0.047 |
| TNF-α (pg/mL) | 15.19 | 5.74 | 15.02 | 16.93 | 6.75 | 15.27 | 15.90 | 6.21 | 15.24 | 0.041 |
| IL-6 (pg/mL) | 17.34 | 9.37 | 15.84 | 18.64 | 7.60 | 17.50 | 17.87 | 8.70 | 16.20 | 0.197 |
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 205.02 | 47.37 | 196.50 | 218.32 | 49.87 | 208.00 | 210.43 | 48.69 | 199.00 | 0.189 |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 148.94 | 57.78 | 154.00 | 197.77 | 84.30 | 182.00 | 168.79 | 73.58 | 163.00 | <0.001 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 41.980 | 10.91 | 38.000 | 36.93 | 6.92 | 36.000 | 39.93 | 9.79 | 37.70 | 0.001 |
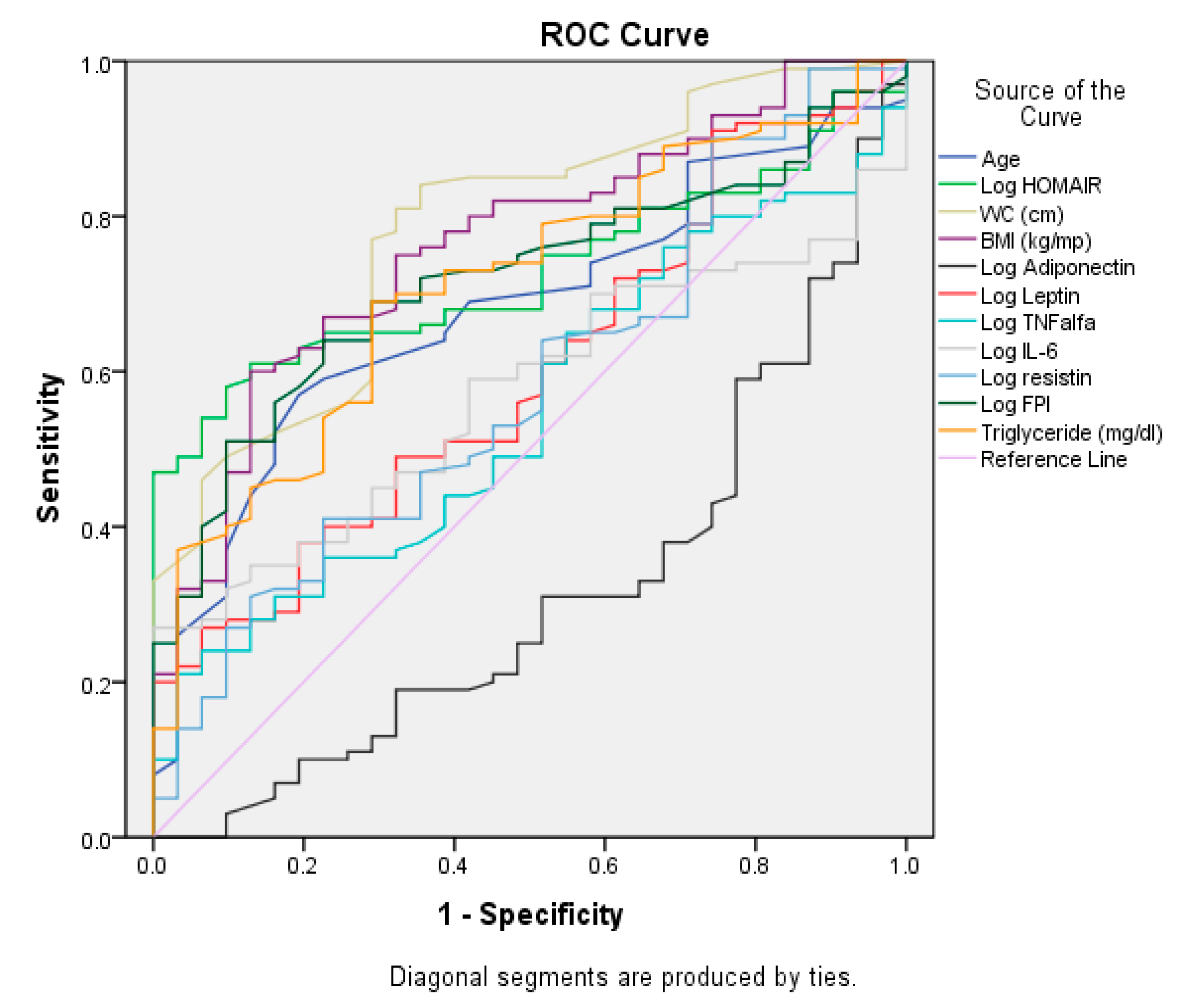
| Test Result Variables | AUROC | Std. Error | p | 95%CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | ||||
| Age (years) | 0.680 | 0.050 | 0.003 | 0.583 | 0.777 |
| Log HOMA-IR | 0.729 | 0.043 | <0.001 | 0.645 | 0.812 |
| WC (cm) | 0.786 | 0.044 | <0.001 | 0.699 | 0.872 |
| BMI (kg/mp) | 0.765 | 0.046 | <0.001 | 0.675 | 0.854 |
| Log Adiponectin | 0.314 | 0.055 | 0.002 | 0.207 | 0.421 |
| Log Leptin | 0.600 | 0.055 | 0.095 | 0.492 | 0.707 |
| Log TNFalfa | 0.549 | 0.055 | 0.414 | 0.442 | 0.656 |
| Log IL-6 | 0.572 | 0.050 | 0.229 | 0.474 | 0.670 |
| Log resistin | 0.583 | 0.057 | 0.163 | 0.471 | 0.695 |
| Log FPI | 0.719 | 0.046 | <0.001 | 0.629 | 0.808 |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 0.714 | 0.049 | <0.001 | 0.619 | 0.809 |
| HS | HIS | |
|---|---|---|
| HSI | 0.473 ** | 1 |
| Gender | 0.127 | 0.016 |
| Age | 0.278 ** | 0.237 ** |
| WC | 0.453 ** | 0.800 ** |
| BMI | 0.432 ** | 0.913 ** |
| WHR | 0.31 ** | 0.513 ** |
| HOMA-IR # | 0.337 ** | 0.464 ** |
| FPI # | 0.284 ** | 0.278 ** |
| FPG # | 0.177 * | 0.336 ** |
| HbA1c | 0.092 | 0.276 ** |
| Adiponectin # | −0.181 * | −0.438 ** |
| Leptin # | 0.105 | 0.243 ** |
| TNF-α # | 0.04 | 0.187 * |
| IL-6 # | 0.113 | 0.265 ** |
| Resistin # | 0.099 | 0.211 ** |
| Triglyceride | 0.233 ** | 0.379 ** |
| HDL-C | −0.215 ** | −0.355 ** |
| AST | 0.301 ** | 0.412 ** |
| ALT | 0.176 * | 0.255 ** |
| GGT | 0.175 * | 0.330 ** |
| Model 1 (Adjusted for WHR) | Model 2 (Adjusted for WC) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | OR (95% CI) | p * | OR (95% CI) | p ** |
| Age > 52.8 years | 4.941 (1.94–12.54) | <0.001 | 3.93 (1.51–10.27) | 0.005 |
| Smoking | 3.379 (1.28–8.85) | 0.013 | 2.76 (1–7.58) | 0.049 |
| Adiponectin < 7.2 ng/mL † | 3.258 (1.21–8.73) | 0.019 | 3.10 (1.15–8.36) | 0.026 |
| HOMA-IR > 2.85 † | 3.482 (1.38–8.74) | 0.008 | - | |
| WC (cm) | - | - | 5.15 (2–13.33) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rusu, E.; Jinga, M.; Cursaru, R.; Enache, G.; Costache, A.; Verde, I.; Nica, A.; Alionescu, A.; Rusu, F.; Radulian, G. Adipose Tissue Dysfunction and Hepatic Steatosis in New-Onset Diabetes. Diabetology 2025, 6, 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6070070
Rusu E, Jinga M, Cursaru R, Enache G, Costache A, Verde I, Nica A, Alionescu A, Rusu F, Radulian G. Adipose Tissue Dysfunction and Hepatic Steatosis in New-Onset Diabetes. Diabetology. 2025; 6(7):70. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6070070
Chicago/Turabian StyleRusu, Emilia, Mariana Jinga, Raluca Cursaru, Georgiana Enache, Adrian Costache, Ioana Verde, Andra Nica, Anca Alionescu, Florin Rusu, and Gabriela Radulian. 2025. "Adipose Tissue Dysfunction and Hepatic Steatosis in New-Onset Diabetes" Diabetology 6, no. 7: 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6070070
APA StyleRusu, E., Jinga, M., Cursaru, R., Enache, G., Costache, A., Verde, I., Nica, A., Alionescu, A., Rusu, F., & Radulian, G. (2025). Adipose Tissue Dysfunction and Hepatic Steatosis in New-Onset Diabetes. Diabetology, 6(7), 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology6070070






