Abstract
Background: This study examined differences in body composition, dietary intake, and exercise habits between people with type 1 diabetes (T1DM) and those without diabetes (NDM). We also sought to clarify the clinical and lifestyle characteristics of overweight people with T1DM. Methods: This controlled cross-sectional study was conducted at a single center, and included 45 people with T1DM and 50 NDM individuals. Body composition, nutrient intake, and exercise habits were evaluated, and exercise habits were compared between people with a T1DM onset before 20 years of age and those with an onset at or after 20 years of age, in relation to the NDM group. Overweight was defined using a BMI of 25.0 kg/m2 as the cutoff. Results: The T1DM group had significantly higher BMI and body fat than the NDM group, but no significant difference in muscle mass, and consumed a higher percentage of carbohydrates and a lower percentage of fat. The early-onset T1DM group had significantly lower exercise habits during their school years and in their current life than the NDM group. Individuals in the overweight T1DM group had a lower time in range on a continuous glucose monitor and a higher carbohydrate intake than those in the non-overweight T1DM group. Conclusions: The study suggested that the T1DM group had a significantly higher body fat percentage and carbohydrate intake, and significantly reduced exercise habits as students, compared to the NDM group.
1. Introduction
With recent improvements in the prognosis of people with type 1 diabetes (T1DM), the extension of healthy life expectancy has become a prominent concern [1,2]. However, it is necessary to prevent diabetes-related complications to extend the healthy life expectancy among people with diabetes. Common complications of diabetes include microvascular (neuropathy, retinopathy, and nephropathy) and macrovascular disorders. The determination of appropriate interventions for sarcopenia and other age-related syndromes in older people with diabetes has recently garnered attention [3,4]. Historically, people with T1DM were thought to be characterized primarily by having leaner bodily characteristics than those with type 2 diabetes. Recently, however, the Japan Diabetes Clinical Data Management Study (JDDM), a multicenter study in Japan, has reported a trend of increased body mass index (BMI) among people with T1DM [5]. Previous studies have reported that approximately half of the people with T1DM in other countries are obese, compared to approximately a quarter in Japan [6,7]. The complications of obesity and metabolic syndrome have generally been identified as risk factors for microvascular and macrovascular diseases [8,9,10]. In a study on T1DM and metabolic syndrome, the odds ratios for macrovascular complications in those with T1DM were 5.9 (95% confidence interval [CI], 2.1–16.4) for those <40 years of age, 2.7 (95% CI, 1.7–4.2) for those 40–60 years of age, and 1.7 (95% CI, 1.1–2.7) for those >60 years of age, with the difference being greater at younger ages [10]. Therefore, interventions to improve dietary and exercise habits are expected to be effective for treating people with T1DM complicated by obesity.
Previous studies on intake of nutrients and other components among people with T1DM in other countries have reported that although total energy and protein intake are in line with current recommendations, carbohydrate and fat intake are lower [11,12,13]. Additionally, the intake of micronutrients (vitamins and minerals, which are only required in small amounts, but are essential for proper growth and metabolic functions) has been shown to fall below the standard values or guidelines established by various countries [14,15,16]. It has also been reported that physical activity and exercise habits, which are considered risk factors for overweight and the progression of sarcopenia in the future, tend to be lower in people with childhood-onset T1DM, due to fear of hypoglycemia [17,18,19,20]. These lifestyle habits persist in adulthood, and may therefore have an impact on body composition. Previous studies have reported on dietary intake and exercise in patients with T1DM, but studies that comprehensively assess body composition and diet and exercise habits are limited. In addition, obesity in T1DM has been reported to increase the risk of microvascular and macrovascular complications, but the underlying dietary and exercise habits are not fully understood.
In this study, we compared body composition, dietary habits, and exercise habits between people with T1DM and those without (NDM). We also investigated the clinical profile and lifestyle habits of people with T1DM complicated by overweight, which has become an issue of increased concern in recent years.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
This controlled cross-sectional study was conducted at a single center. The primary endpoints were body composition, dietary intake, and past and current exercise habits in the T1DM and NDM groups. Secondary endpoints were clinical data, body composition, dietary intake, and exercise habits in the overweight T1DM and non-overweight T1DM groups. Each participant was given a verbal explanation of the study, and their written consent was obtained.
2.2. Participants
The T1DM group included 45 patients (mean age, 43.3 years; men, 47%) attending our diabetic outpatient clinic (Midori Clinic, Nagasaki, Japan) from July to December 2023. Participants were recruited through research referrals from attending physicians. The NDM group included 50 individuals (mean age, 43.6 years; men, 48%), age- (±2 years) and sex-matched to the T1DM group and living in the same area throughout the survey period from April to June 2024. The NDM participants were recruited through snowball sampling and poster solicitation. The exclusion criteria for the T1DM group were as follows: inability to maintain a standing position, pacemaker use, paralysis as a sequalae of cerebral infarction, steroid use, and diabetic nephropathy stage 4 or higher (estimated glomerular filtration rate [eGFR] < 30). The exclusion criteria for the NDM group were as follows: diagnosis of diabetes, pacemaker use, and paralysis of the dominant hand as a sequalae of stroke. In this study, patients were divided into overweight (BMI ≥ 25.0 kg/m2) and non-overweight (BMI < 25.0 kg/m2) groups.
2.3. Clinical Data
The following data were collected from patient medical records: duration of disease, age of onset, treatment status (multiple daily injection [MDI], continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion [CSII], hybrid closed loop [HCL]), complications (neuropathy, nephropathy, retinopathy), hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c; %), casual blood glucose (CBG; mg/dL), eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2), creatinine (Cr; mg/dL), triglyceride (TG; mg/dL), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and time in range (TIR; %) on a continuous glucose monitor (CGM).
2.4. Body Composition
Body weight (kg), BMI (kg/m2), muscle mass (kg), skeletal muscle mass index (SMI; kg/m2), body fat mass (kg), and body fat percentage (%) were measured using a bioelectrical impedance body composition analyzer (T1DM: Inbody270, Inbody Japan Inc., Tokyo, Japan; NDM: Inbody770, Inbody Japan Inc., Tokyo, Japan).
2.5. Nutrient and Food Group Intake
Dietary surveys were conducted using a brief self-administered diet history questionnaire (BDHQ) comprising 80 items. Participants were asked to answer these questions while recalling their eating habits over the month prior. The DHQ Support Center (Gender Medical Research Inc., Tokyo, Japan) was utilized for the calculation and processing of the intake of each nutrient. Energy-adjusted values were calculated for each nutrient using the density method (calculation of nutrient intake/1000 kcal) or as % energy (%E; nutrients as a percentage of total energy intake). The BDHQ has been previously validated [21,22].
2.6. Exercise Habit Survey
Exercise habits were surveyed to determine whether the participant’s current exercise routine was performed for at least 30 continuous min per session at least twice a week, and whether they walked for at least 1 h/day, as a measure of their physical activity level. Statistical analyses of past exercise habits were conducted based on the age of T1DM onset to evaluate exercise habits through elementary, middle, and high school years. We categorized those with an onset age < 20 years as the juvenile-onset T1DM (JOT1DM) group and those with an onset age ≥ 20 years as the non-juvenile-onset T1DM (N-JOT1DM) group. Age- and sex-matching were also confirmed between each NDM group [young control (AC) group or older control (OC) group] and the JOT1DM and N-JOT1DM groups.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Continuous variables were compared using the t-test, while categorical variables were analyzed using the χ2-test. Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS Statistics Ver. 28® (Ver.28, IBM, Stats Guild Inc., Chiba, Japan), with a statistical significance level of 5%.
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
The NDM group matched to the T1DM group had no significant difference in age or sex (age: 43.3 ± 15.7 vs. 43.6 ± 15.0, p = 0.923, men: 47% vs. 49%, p = 0.897). The mean duration of disease was 21.4 ± 12.2 years, and 78% of the participants were treated with MDI (Table 1).

Table 1.
Clinical characteristics of the T1DM group and comparison with the NDM group.
3.2. Primary Endpoint: Body Composition, Nutrients, and Exercise Habits in T1DM and NDM Groups
The histogram of the BMI distribution between the T1DM and NDM groups showed that the T1DM group was shifted toward a higher BMI category (Figure 1a,b). Also, significant differences in BMI were observed in the T1DM and NDM groups (24.8 ± 4.6 vs. 23.1 ± 3.1, p = 0.040) (Table 1). The T1DM group had a significantly higher body fat mass and body fat percentage than the NDM group (body fat mass: 20.8 ± 7.4 vs. 16.1 ± 5.7, p < 0.001, body fat percentage: 31.9 ± 8.3 vs. 25.7 ± 8.1, p = 0.002) (Figure 2). There were no significant differences in muscle mass or SMI (Figure 2).
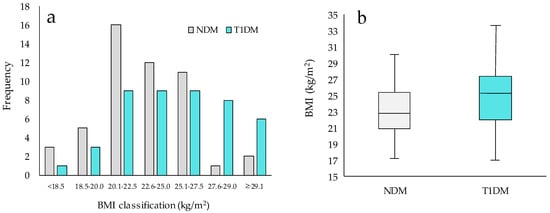
Figure 1.
BMI distribution in NDM and T1DM groups. T1DM: people with type 1 diabetes, NDM: people without diabetes, BMI: body mass index. NDM: n = 50, T1DM: n = 45. (a) Histogram of T1DM and NDM groups. (b) Box-and-whisker plot of BMI in T1DM and NDM Groups. Statistical analysis used t-tests.
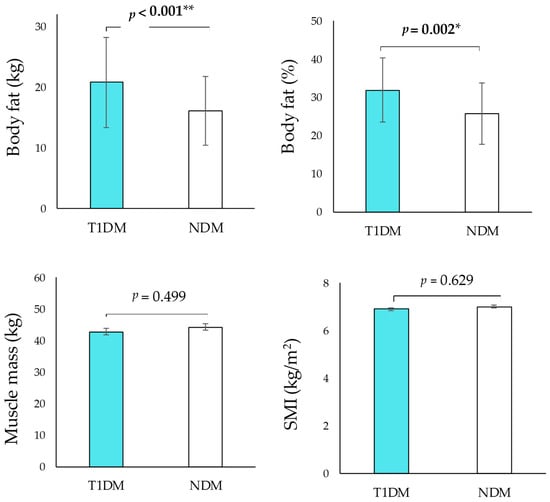
Figure 2.
Comparison of anthropometric and body composition in T1DM and NDM groups. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.
A comparison of the dietary intake between the T1DM and NDM groups showed no difference in total energy intake; however, the carbohydrate energy ratio (C%E) was significantly higher and the fat energy ratio (F%E) was significantly lower in the T1DM group. Furthermore, the T1DM group had a significantly lower intake of vitamins B1, B6, and C than the NDM group (Table 2).

Table 2.
Comparison of nutrient intakes in T1DM group and NDM group.
We found no statistically significant differences in age or sex between the JOT1DM group and the YC group by age of onset when comparing exercise habits (JOT1DM vs. YC: age, 35.3 ± 13.2 vs. 36.2 ± 12.6, p = 0.796, men, 50% vs. 52%, p = 0.898/N-JOT1DM vs. OC: age, 54.4 ± 11.7 vs. 54.0 ± 11.7, p = 0.911, men, 42% vs. 43%, p = 0.962, Table 3).

Table 3.
Comparison of age and gender with YC and OC groups.
There were significant differences in exercise habits by age of onset between the JOT1DM and YC groups for elementary, middle, high school, and current exercise habits (Table 4). In contrast, a comparison of the N-JOT1DM and OC groups showed significant differences in high school exercise habits, but not for elementary or middle school exercise habits, current exercise habits, or current physical activity (Table 4).

Table 4.
Comparison of past and current exercise habits between JOT1DM, N-JOT1DM, and each NDM group.
3.3. Secondary Endpoints: Parameters in Overweight and Non-Overweight T1DM Groups
There was no significant difference in age between the overweight and non-overweight T1DM groups (Table 5). The proportion of men was significantly higher in the non-overweight compared to the overweight T1DM group (70% vs. 23%, p = 0.002). Additionally, the proportion of individuals using sodium–glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors (SGLT2is) was significantly higher in the overweight T1DM group (9% vs. 43%, p = 0.009).

Table 5.
Comparison of anthropometric and body composition in non-overweight T1DM and overweight T1DM group.
In the evaluation of body composition, the overweight T1DM group had a significantly higher body weight, BMI, and body fat percentage than the non-overweight T1DM group. The SMI was also significantly higher in the overweight T1DM group. Clinical laboratory values showed that the overweight T1DM group had significantly higher HbA1c levels than the non-overweight T1DM group. When evaluating metabolic syndrome-related markers, the TG and HDL-C levels were significantly higher and lower in the overweight T1DM group, respectively.
In the dietary survey, the overweight group consumed more carbohydrates and less fat than the non-overweight group. There were no significant differences in any of the exercise habits and physical activity.
4. Discussion
The BMI distribution between the T1DM and NDM groups showed that the T1DM group shifted to a higher BMI category compared to the NDM group. Furthermore, a bioelectrical impedance analysis of body composition showed that the T1DM group had a significantly higher body fat mass and body fat percentage than the NDM group, while no significant differences were observed in muscle mass or SMI. While type 1 diabetes has traditionally been associated with a lean clinical phenotype, changes in lifestyle factors such as diet, nutrition, and physical activity in recent decades have led to an increasing prevalence of overweight and obesity among people with T1DM, particularly in the United States and Europe [23,24]. In Japanese people with T1DM, recent studies indicate an increasing prevalence of overweight and metabolic syndrome in Japanese people with T1DM [5,6,7]. On the other hand, sarcopenia associated with low body weight is prevalent in the elderly with type 1 diabetes [25,26]. Thus, age-dependent obesity-related complications have been reported in some Japanese people with T1DM, and this study also provides further evidence of overweight in this population. There are two possible patterns behind the development of overweight and sarcopenia in patients with T1DM: lifestyle factors characteristic of T1DM (e.g., nutritional supplementation for hypoglycemia) and general lifestyle factors (westernized diet and reduced physical activity) [27,28].
In the dietary context of increased overweight and obesity in people with T1DM, the T1DM group had higher C%E and lower F%E than the NDM group (examples of supplementary foods used to address low blood glucose are rice, fruit, and sweet drinks; these foods are high in C%E and %E). However, F%E and C%E were within the appropriate range when the intake ratios of the three macronutrients (carbohydrate, fat, and protein) in the T1DM group were compared with the Japanese Dietary Reference Intakes [29].
For physical activity, past and current exercise habits showed that the JOT1DM group had significantly reduced exercise habits than the YC group across all school years. Previous studies have suggested that lifestyle factors characteristic of T1DM are associated with limitations in physical activity due to fear of hypoglycemia and increased carbohydrate intake before or during exercise [30,31,32]. If there is a risk of hypoglycemia, appropriate measures should be taken, including blood glucose monitoring before exercise, adequate intake of carbohydrate supplements, and a reduction in insulin dose. For exercise interventions targeting sarcopenia in older people with T1DM, healthcare professionals should be fully aware of these precautions and ensure that the exercise interventions are properly implemented. However, these results should be interpreted with caution, as past physical activity habits may be subject to recall bias. Future research using prospective study designs, especially in pediatric populations, is warranted.
In our analysis, the T1DM group was associated with a higher C%E and less frequent exercise habits compared to the NDM group. This distinctive lifestyle, characterized by high C%E and low exercise frequency, may have influenced individuals’ BMI and body fat composition, underscoring its potential impact on these parameters. To investigate the clinical profile and lifestyle habits of people with T1DM complicated by overweight, we further analyzed the data to compare the overweight T1DM group with the non-overweight T1DM group.
Firstly, the overweight T1DM group had a longer disease duration and a higher proportion of men. In addition, this group had a significantly higher C%E and lower F%E compared to the non-overweight T1DM group. These findings highlight the importance of prioritizing weight management, especially in individuals with a longer disease duration.
Second, the use of SGLT2is was significantly higher in the overweight T1DM group than in the non-overweight T1DM group. In Japan, SGLT2is have been used clinically in T1DM [33], with studies showing that their use is more prevalent in men [34]. The present study also showed a higher proportion of SGLT2i users and men in the overweight group compared with the non-overweight group, confirming the findings of previous studies. These findings suggest the importance of prioritizing weight management, particularly for men. In addition, in people with T1DM complicated by overweight or obesity, it is important to adopt an approach that considers energy regulation for weight control and the risk of hypoglycemia.
Finally, the overweight T1DM group had significantly higher TG levels and lower HDL-C levels, both of which are associated with metabolic syndrome. Previous studies have suggested that obesity-related complications in T1DM increase the risk of developing microvascular and macrovascular disease [8,9,10]. However, previous studies have reported that only slightly more than half of overweight or obese people with T1DM received advice from health professionals regarding physical activity and nutrient intake [35]. Thus, it is suggested that overweight T1DM cases require interventions focused on the prevention of metabolic syndrome and atherosclerotic disease, in addition to careful attention to factors characteristic of T1DM. In addition, previous studies have suggested that insulin therapy may contribute to increases in body weight and fat mass [36,37]. In T1DM with obesity, blood glucose monitoring by CGM and appropriate review of insulin dosage are essential for T1DM, and lifestyle management using the Personal Health Record may also be important.
This study did have several limitations. First, it was a single-center study. Therefore, the generalizability of the results to all Japanese people with type 1 diabetes is limited. In addition, the control group was recruited from a specific region, which should be considered a potential limitation. Furthermore, future studies should increase the sample size to obtain more reliable findings for subgroup comparisons. A second limitation was the matching of cases and controls. In this study, we recruited people with T1DM, as well as those who lived in the same area and had not been diagnosed with diabetes. However, their backgrounds, such as their occupational and economic status, were not always perfectly matched. These factors may have influenced their diet and exercise habits. Third, all the participants in this study were relatively young; older people may have different body compositions, dietary intake, and exercise habits. Fourth, instead of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA), which is considered the gold standard for body composition measurement, bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) was used in this study. This should be recognized as one of the study’s limitations.
5. Conclusions
We suggested that the T1DM group had a significantly higher body fat percentage and carbohydrate intake ratio, and significantly reduced exercise habits as students, compared to the NDM group. These characteristic eating and exercise habits may be more pronounced in overweight individuals with T1DM.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, N.S. and N.A.; methodology, N.S. and N.A.; investigation, I.H., R.H., N.A. and N.S.; data curation, I.H.; writing—original draft preparation, I.H., R.H., N.A. and N.S.; writing—review and editing, N.S.; project administration. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Institutional Review Board Statement: The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of the University of Nagasaki (protocol code.: r5004, approval date: 19 March 2022).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We express our deep appreciation to the staff of Midori Clinic for their cooperation in conducting this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Otani, T.; Kasahara, T.; Miura, J.; Uchigata, Y.; Babazono, T. Clinical background of Japanese patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus who have received insulin therapy for 50 years or longer. Diabetol. Int. 2019, 10, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ikegami, H.; Hiromine, Y.; Noso, S. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in older adults: Current status and future prospects. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2022, 22, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen, L.K.; Liu, L.K.; Woo, J.; Assantachai, P.; Auyeung, T.W.; Bahyah, K.S.; Chou, M.Y.; Chen, L.Y.; Hsu, P.S.; Krairit, O.; et al. Sarcopenia in Asia: Consensus report of the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2014, 15, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Gao, Q.; Hu, K.; Wu, M.; Wang, Z.; Chen, F.; Mei, F.; Zhao, L.; Ma, B. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Sarcopenia in Patients with Diabetes: A Meta-analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 1470–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Japan Diabetes Clinical Data Management Study Group. Available online: http://jddm.jp/public-information/index-2022/ (accessed on 22 August 2024).
- Renard, E.; Ikegami, H.; Daher Vianna, A.G.; Pozzilli, P.; Brette, S.; Bosnyak, Z.; Lauand, F.; Peters, A.; Pilorget, V.; Jurišić-Eržen, D.; et al. The SAGE study: Global observational analysis of glycaemic control, hypoglycaemia and diabetes management in T1DM. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2021, 37, e3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Nishimura, R.; Shimada, A.; Abiru, N.; Matsuhisa, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Ikegami, H. Association between glycemic control and patient-reported outcomes in adults with type 1 diabetes in Japan: The SAGE study subanalysis. Diabetol. Int. 2023, 15, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Polsky, S.; Ellis, S.L. Obesity, insulin resistance, and type 1 diabetes mellitus. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2015, 22, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinhas-Hamiel, O.; Levek-Motola, N.; Kaidar, K.; Boyko, V.; Tisch, E.; Mazor-Aronovitch, K.; Graf-Barel, C.; Landau, Z.; Lerner-Geva, L.; Frumkin Ben-David, R.; et al. Prevalence of overweight, obesity and metabolic syndrome components in children, adolescents and young adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2015, 31, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.S.; Twigg, S.M.; Flack, J.R. Metabolic syndrome in type 1 diabetes and its association with diabetes complications. Diabet. Med. 2021, 38, e14376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faulkner, M.S.; Chao, W.H.; Kamath, S.K.; Quinn, L.; Fritschi, C.; Maggiore, J.A.; Williams, R.H.; Reynolds, R.D. Total homocysteine, diet, and lipid profiles in type 1 and type 2 diabetic and nondiabetic adolescents. J. Cardiovasc. Nurs. 2006, 21, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central][Green Version]
- Ewers, B.; Trolle, E.; Jacobsen, S.S.; Vististen, D.; Almdal, T.P.; Vilsbøll, T.; Bruun, J.M. Dietary habits and adherence to dietary recommendations in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes compared with the general population in Denmark. Nutrition 2019, 61, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smart, C.E.; Annan, F.; Higgins, L.A.; Jelleryd, E.; Lopez, M.; Acerini, C.L. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2018: Nutritional management in children and adolescents with diabetes. Pediatr. Diabetes 2018, 19, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, M.M.; Shenkin, A.; Schweinlin, A.; Amrein, K.; Augsburger, M.; Biesalski, H.K.; Bischoff, S.C.; Casaer, M.P.; Gundogan, K.; Lepp, H.L.; et al. ESPEN micronutrient guideline. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 1357–1424. Erratum in: Clin. Nutr. 2024, 43, 1024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2024.03.004. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giorgini, M.; Vitale, M.; Bozzetto, L.; Ciano, O.; Giacco, A.; Rivieccio, A.; Calabrese, I.; Riccardi, G.; Rivellese, A.A.; Annuzzi, G. Micronutrient Intake in a Cohort of Italian Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: Adherence to Dietary Recommendations. J. Diabetes Res. 2017, 2017, 2682319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ahola, A.J.; Mikkilä, V.; Mäkimattila, S.; Forsblom, C.; Freese, R.; Groop, P.H. Energy and nutrient intakes and adherence to dietary guidelines among Finnish adults with type 1 diabetes. Ann. Med. 2012, 44, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steffl, M.; Bohannon, R.W.; Sontakova, L.; Tufano, J.J.; Shiells, K.; Holmerova, I. Relationship between sarcopenia and physical activity in older people: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Interv. Aging 2017, 12, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Dent, E.; Morley, J.E.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Arai, H.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Guralnik, J.; Bauer, J.M.; Pahor, M.; Clark, B.C.; Cesari, M.; et al. International Clinical Practice Guidelines for Sarcopenia (ICFSR): Screening, Diagnosis and Management. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2018, 22, 1148–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppert, J.M.; Bellicha, A.; van Baak, M.A.; Battista, F.; Beaulieu, K.; Blundell, J.E.; Carraça, E.V.; Encantado, J.; Ermolao, A.; Pramono, A.; et al. Exercise training in the management of overweight and obesity in adults: Synthesis of the evidence and recommendations from the European Association for the Study of Obesity Physical Activity Working Group. Obes. Rev. 2021, 22, e13273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Brazeau, A.S.; Rabasa-Lhoret, R.; Strychar, I.; Mircescu, H. Barriers to physical activity among patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 2108–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kobayashi, S.; Honda, S.; Murakami, K.; Sasaki, S.; Okubo, H.; Hirota, N.; Notsu, A.; Fukui, M.; Date, C. Both comprehensive and brief self-administered diet history questionnaires satisfactorily rank nutrient intakes in Japanese adults. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 22, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kobayashi, S.; Murakami, K.; Sasaki, S.; Okubo, H.; Hirota, N.; Notsu, A.; Fukui, M.; Date, C. Comparison of relative validity of food group intakes estimated by comprehensive and brief-type self-administered diet history questionnaires against 16 d dietary records in Japanese adults. Public Health Nutr. 2011, 14, 1200–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manyanga, T.; Sellers, E.A.; Wicklow, B.A.; Doupe, M.; Fransoo, R. Not as skinny as we used to think: Body mass index in children and adolescents at diagnosis of type 1 diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2016, 30, 292–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- March, C.A.; Becker, D.J.; Libman, I.M. Nutrition and Obesity in the Pathogenesis of Youth-Onset Type 1 Diabetes and Its Complications. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 22, 622901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, H.; Kuroda, A.; Yoshida, S.; Yasuda, T.; Umayahara, Y.; Shimizu, S.; Ryomoto, K.; Yoshiuchi, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Matsuoka, T.A.; et al. High prevalence and clinical impact of dynapenia and sarcopenia in Japanese patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes: Findings from the Impact of Diabetes Mellitus on Dynapenia study. J. Diabetes Investig. 2021, 12, 1050–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tanabe, H.; Hirai, H.; Saito, H.; Tanaka, K.; Masuzaki, H.; Kazama, J.J.; Shimabukuro, M. Detecting Sarcopenia Risk by Diabetes Clustering: A Japanese Prospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 2729–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente-Suárez, V.J.; Beltrán-Velasco, A.I.; Redondo-Flórez, L.; Martín-Rodríguez, A.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F. Global Impacts of Western Diet and Its Effects on Metabolism and Health: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ladabaum, U.; Mannalithara, A.; Myer, P.A.; Singh, G. Obesity, abdominal obesity, physical activity, and caloric intake in US adults: 1988 to 2010. Am. J. Med. 2014, 127, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare: Dietary Reference Intakes for the Japanese (2020version). Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/stf/seisakunitsuite/bunya/kenkou_iryou/kenkou/eiyou/syokuji_kijyun.html (accessed on 22 August 2024).
- Van der Schueren, B.; Ellis, D.; Faradji, R.N.; Al-Ozairi, E.; Rosen, J.; Mathieu, C. Obesity in people living with type 1 diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alderisio, A.; Bozzetto, L.; Franco, L.; Riccardi, G.; Rivellese, A.A.; Annuzzi, G. Long-term body weight trajectories and metabolic control in type 1 diabetes patients on insulin pump or multiple daily injections: A 10-year retrospective controlled study. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2019, 29, 1110–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilarrasa, N.; San Jose, P.; Rubio, M.Á.; Lecube, A. Obesity in patients with type 1 diabetes: Links, risks and management challenges. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2021, 14, 2807–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Committee on the Proper Use of SGLT2 Inhibitors. Recommendations on the Proper Use of SGLT2 Inhibitors. J. Diabetes Investig. 2020, 11, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Abiru, N.; Shoji, S.; Kosakai, Y.; Snijder, R.; Asakawa, K.; Rokuda, M. Demographic and clinical characteristics of patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus initiating sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in Japan: A real-world administrative database analysis. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 190, 109973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, M.; Jeon, Y.; Echouffo-Tcheugui, J.B.; Selvin, E. Prevalence and Management of Obesity in U.S. Adults with Type 1 Diabetes. Ann. Intern. Med. 2023, 176, 427–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Russell-Jones, D.; Khan, R. Insulin-associated weight gain in diabetes--causes, effects and coping strategies. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2007, 9, 799–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. Influence of intensive diabetes treatment on body weight and composition of adults with type 1 diabetes in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial. Diabetes Care 2001, 24, 1711–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).