Narrative Review: Obesity, Type 2 DM and Obstructive Sleep Apnoea—Common Bedfellows
Abstract
1. Introduction
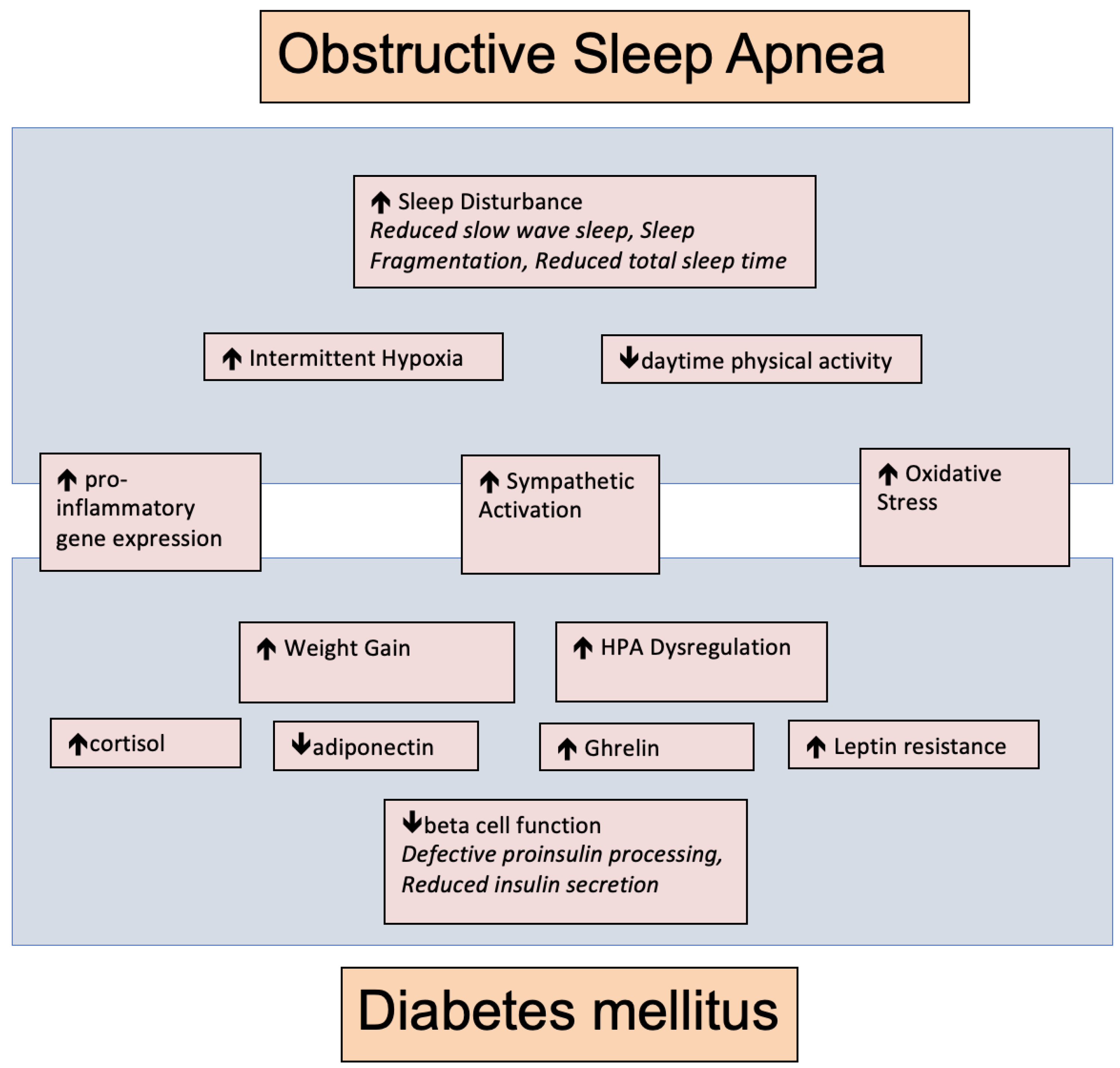
2. Potential Pathophysiological Links between T2DM and OSA
2.1. Inflammation
2.2. Autonomic Nervous System
2.3. Endocrinopathy
2.4. Pancreatic Effects of Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia
3. Sleep Loss and Fragmentation
4. Population Studies of Relationship between OSA and T2DM
5. Effect of CPAP on T2DM
6. Should All Patients with T2DM Be Screened for OSA?
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jennum, P.; Schultz-Larsen, K.; Christensen, N. Snoring, sympathetic activity and cardiovascular risk factors in a 70 year old population. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 1993, 9, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunstein, R.R.; Stenlof, K.; Hedner, J.; Sjostrom, L. Impact of obstructive sleep apnea and sleepiness on metabolic and cardiovascular risk factors in the Swedish Obese Subjects (SOS) Study. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1995, 19, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Enright, P.L.; Newman, A.B.; Wahl, P.W.; Manolio, T.A.; Haponik, E.F.; Boyle, P.J. Prevalence and correlates of snoring and observed apneas in 5201 older adults. Sleep 1996, 19, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes. Diabetes Care 2014, 37 (Suppl. 1), S81–S90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, M.; Fleming, T.; Robinson, M.; Thomson, B.; Graetz, N.; Margono, C.; Mullany, E.C.; Biryukov, S.; Abbafati, C.; Abera, S.F.; et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2014, 384, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.; Roux, F. The relationship of obesity and obstructive sleep apnea. Clin. Chest Med. 2009, 30, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoelson, S.E.; Lee, J.; Goldfine, A.B. Inflammation and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vgontzas, A.N.; Papanicolaou, D.A.; Bixler, E.O.; Kales, A.; Tyson, K.; Chrousos, G.P. Elevation of plasma cytokines in disorders of excessive daytime sleepiness: Role of sleep disturbance and obesity. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 1313–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vgontzas, A.N.; Papanicolaou, D.A.; Bixler, E.O.; Hopper, K.; Lotsikas, A.; Lin, H.M.; Kales, A.; Chrousos, G.P. Sleep apnea and daytime sleepiness and fatigue: Relation to visceral obesity, insulin resistance, and hypercytokinemia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciftci, T.U.; Kokturk, O.; Bukan, N.; Bilgihan, A. The relationship between serum cytokine levels with obesity and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Cytokine 2004, 28, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minoguchi, K.; Tazaki, T.; Yokoe, T.; Minoguchi, H.; Watanabe, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Adachi, M. Elevated production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha by monocytes in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Chest 2004, 126, 1473–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotamisligil, G.S.; Shargill, N.S.; Spiegelman, B.M. Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: Direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science 1993, 259, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Mechanisms of TNF-alpha-induced insulin resistance. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. DM 1999, 107, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trayhurn, P.; Wang, B.; Wood, I.S. Hypoxia in adipose tissue: A basis for the dysregulation of tissue function in obesity? Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 100, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavie, L. Intermittent hypoxia: The culprit of oxidative stress, vascular inflammation and dyslipidemia in obstructive sleep apnea. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2008, 2, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloch-Damti, A.; Bashan, N. Proposed mechanisms for the induction of insulin resistance by oxidative stress. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2005, 7, 1553–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, R.P. Oxidative stress and impaired insulin secretion in type 2 DM. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2006, 6, 615–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lurie, A. Metabolic disorders associated with obstructive sleep apnea in adults. Adv. Cardiol. 2011, 46, 67–138. [Google Scholar]
- Vgontzas, A.N.; Zoumakis, E.; Lin, H.M.; Bixler, E.O.; Trakada, G.; Chrousos, G.P. Marked decrease in sleepiness in patients with sleep apnea by etanercept, a tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonist. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 4409–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornalley, P.J.; Battah, S.; Ahmed, N.; Karachalias, N.; Agalou, S.; Babaei-Jadidi, R.; Dawnay, A. Quantitative screening of advanced glycation endproducts in cellular and extracellular proteins by tandem mass spectrometry. Biochem. J. 2003, 375, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.C.; Chow, W.S.; Lam, J.C.; Lam, B.; Bucala, R.; Betteridge, J.; M Ip, M.S. Advanced glycation endproducts in nondiabetic patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep 2006, 29, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Friedman, E.A. Advanced glycosylated end products and hyperglycemia in the pathogenesis of diabetic complications. Diabetes Care 1999, 22 (Suppl. 2), B65–B71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lam, J.C.; Tan, K.C.; Lai, A.Y.; Lam, D.C.; Ip, M.S. Increased serum levels of advanced glycation end-products is associated with severity of sleep disordered breathing but not insulin sensitivity in non-diabetic men with obstructive sleep apnoea. Sleep Med. 2012, 13, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cizza, G.; Piaggi, P.; Lucassen, E.A.; de Jonge, L.; Walter, M.; Mattingly, M.S.; Kalish, H.; Csako, G.; Rother, K.I.; Study Group, S.E. Obstructive sleep apnea is a predictor of abnormal glucose metabolism in chronically sleep deprived obese adults. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65400. [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldsen, S.E.; Rostrup, M.; Moan, A.; Mundal, H.H.; Gjesdal, K.; Eide, I.K. The sympathetic nervous system may modulate the metabolic cardiovascular syndrome in essential hypertension. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1992, 20 (Suppl. 8), S32–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimsdale, J.E.; Coy, T.; Ziegler, M.G.; Ancoli-Israel, S.; Clausen, J. The effect of sleep apnea on plasma and urinary catecholamines. Sleep 1995, 18, 377–381. [Google Scholar]
- Kruszynska, Y.T.; Worrall, D.S.; Ofrecio, J.; Frias, J.P.; Macaraeg, G.; Olefsky, J.M. Fatty acid-induced insulin resistance: Decreased muscle PI3K activation but unchanged Akt phosphorylation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polotsky, V.Y.; Li, J.; Punjabi, N.M.; Rubin, A.E.; Smith, P.L.; Schwartz, A.R.; O’Donnell, C.P. Intermittent hypoxia increases insulin resistance in genetically obese mice. J. Physiol. 2003, 552, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iiyori, N.; Alonso, L.C.; Li, J.; Sanders, M.H.; Garcia-Ocana, A.; O’Doherty, R.M.; Polotsky, V.Y.; O’Donnell, C.P. Intermittent hypoxia causes insulin resistance in lean mice independent of autonomic activity. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 175, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasali, E.; Leproult, R.; Ehrmann, D.A.; Van Cauter, E. Slow-wave sleep and the risk of type 2 diabetes in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 1044–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, H.; Tamaki, S.; Itaya-Hironaka, A.; Yamauchi, A.; Sakuramoto-Tsuchida, S.; Morioka, T.; Takasawa, S.; Kimura, H. Attenuation of glucose-induced insulin secretion by intermittent hypoxia via down-regulation of CD38. Life Sci. 2012, 90, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, N.H.; Han, M.K.; Um, C.; Park, B.H.; Park, B.J.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, U.H. Significance of ecto-cyclase activity of CD38 in insulin secretion of mouse pancreatic islet cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 282, 781–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, T.A.; Ouchi, N.; Shibata, R.; Walsh, K. Adiponectin actions in the cardiovascular system. Cardiovasc. Res. 2007, 74, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, J.; Gao, Z.; Yin, J.; He, Q. Hypoxia is a potential risk factor for chronic inflammation and adiponectin reduction in adipose tissue of ob/ob and dietary obese mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 293, E1118–E1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jequier, E. Leptin signaling, adiposity, and energy balance. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2002, 967, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paracchini, V.; Pedotti, P.; Taioli, E. Genetics of leptin and obesity: A HuGE review. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2005, 162, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, B.O.; Haznedaroglu, I.C. Rethinking leptin and insulin action: Therapeutic opportunities for diabetes. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 2006, 38, 820–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Considine, R.V.; Sinha, M.K.; Heiman, M.L.; Kriauciunas, A.; Stephens, T.W.; Nyce, M.R.; Ohannesian, J.P.; Marco, C.C.; McKee, L.J.; Bauer, T.L.; et al. Serum immunoreactive-leptin concentrations in normal-weight and obese humans. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, H.; Oh, I.S.; Okada, S.; Mori, M. Leptin resistance and obesity. Endocr. J. 2007, 54, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, C.P.; Schaub, C.D.; Haines, A.S.; Berkowitz, D.E.; Tankersley, C.G.; Schwartz, A.R.; Smith, P.L. Leptin prevents respiratory depression in obesity. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 159, 1477–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, C.P.; Tankersley, C.G.; Polotsky, V.P.; Schwartz, A.R.; Smith, P.L. Leptin, obesity, and respiratory function. Respir. Physiol. 2000, 119, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, B.J.; Cheung, J.; Phipps, P.; Banerjee, D.; Piper, A.J.; Grunstein, R.R. Treatment of obesity hypoventilation syndrome and serum leptin. Respiration 2006, 73, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redolfi, S.; Corda, L.; La Piana, G.; Spandrio, S.; Prometti, P.; Tantucci, C. Long-term non-invasive ventilation increases chemosensitivity and leptin in obesity-hypoventilation syndrome. Respir. Med. 2007, 101, 1191–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, A.; Fruhbeck, G.; Zulueta, J.J.; Iriarte, J.; Seijo, L.M.; Alcaide, A.B.; Galdiz, J.B.; Salvador, J. Hyperleptinaemia, respiratory drive and hypercapnic response in obese patients. Eur. Respir. J. 2007, 30, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, Z.Z. Effects of continuous positive airway pressure therapy on glycaemic control, insulin sensitivity and body mass index in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea and type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. NPJ Prim. Care Respir. Med. 2015, 25, 15005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, K.; Shimizu, K.; Nakamura, T.; Narai, N.; Masuzaki, H.; Ogawa, Y.; Mishima, N.; Nakamura, T.; Nakao, K.; Ohi, O. Changes in intra-abdominal visceral fat and serum leptin levels in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome following nasal continuous positive airway pressure therapy. Circulation 1999, 100, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanner, B.M.; Kollhosser, P.; Buechner, N.; Zidek, W.; Tepel, M. Influence of treatment on leptin levels in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea. Eur. Respir. J. 2004, 23, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapsimalis, F.; Varouchakis, G.; Manousaki, A.; Daskas, S.; Nikita, D.; Kryger, M.; Gourgoulianis, K. Association of sleep apnea severity and obesity with insulin resistance, C-reactive protein, and leptin levels in male patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Lung 2008, 186, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.R.; Palmer, L.J.; Larkin, E.K.; Jenny, N.S.; White, D.P.; Redline, S. Relationship between obstructive sleep apnea and diurnal leptin rhythms. Sleep 2004, 27, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsumi, K.; Kasahara, Y.; Kurosu, K.; Tanabe, N.; Takiguchi, Y.; Kuriyama, T. Sleep oxygen desaturation and circulating leptin in obstructive sleep apnea-hypopnea syndrome. Chest 2005, 127, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarugi, P.; Fiaschi, T. Adiponectin in health and diseases: From metabolic syndrome to tissue regeneration. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2010, 14, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, B.J.; Scalia, R.G.; Ma, X.L. Protective vascular and myocardial effects of adiponectin. Nat. Clin. Pract. Cardiovasc. Med. 2009, 6, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawano, J.; Arora, R. The role of adiponectin in obesity, DM, and cardiovascular disease. J. Cardiometabolic Syndr. 2009, 4, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.K.; Kumpawat, S.; Goel, A.; Banga, A.; Ramakrishnan, L.; Chaturvedi, P. Obesity, and not obstructive sleep apnea, is responsible for metabolic abnormalities in a cohort with sleep-disordered breathing. Sleep Med. 2007, 8, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokuda, F.; Sando, Y.; Matsui, H.; Koike, H.; Yokoyama, T. Serum levels of adipocytokines, adiponectin and leptin, in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Intern. Med. 2008, 47, 1843–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Harsch, I.A.; Bergmann, T.; Koebnick, C.; Wiedmann, R.; Ruderich, F.; Hahn, E.G.; Konturek, P.C. Adiponectin, resistin and subclinical inflammation—The metabolic burden in Launois Bensaude Syndrome, a rare form of obesity. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2007, 58 (Suppl. 1), 65–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- West, S.D.; Nicoll, D.J.; Wallace, T.M.; Matthews, D.R.; Stradling, J.R. Effect of CPAP on insulin resistance and HbA1c in men with obstructive sleep apnoea and type 2 diabetes. Thorax 2007, 62, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprung, V.S.; Kemp, G.J.; Wilding, J.P.; Adams, V.; Murphy, K.; Burgess, M.; Emegbo, S.; Thomas, M.; Needham, A.J.; Weimken, A.; et al. Randomised, cOntrolled Multicentre trial of 26 weeks subcutaneous liraglutide (a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor Agonist), with or without contiNuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and obstructive sleep apnoEa (OSA) (ROMANCE): Study protocol assessing the effects of weight loss on the apnea-hypnoea index (AHI). BMJ Open 2020, 10, e038856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackman, A.; Foster, G.D.; Zammit, G.; Rosenberg, R.; Aronne, L.; Wadden, T.; Claudius, B.; Jensen, C.B.; Mignot, E. Effect of liraglutide 3.0 mg in individuals with obesity and moderate or severe obstructive sleep apnea: The SCALE Sleep Apnea randomized clinical trial. Int. J. Obes. 2016, 40, 1310–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Khan, S.A.; Prabhakar, N.R.; Nanduri, J. Impairment of pancreatic beta-cell function by chronic intermittent hypoxia. Exp. Physiol. 2013, 98, 1376–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherwani, S.I.; Aldana, C.; Usmani, S.; Adin, C.; Kotha, S.; Khan, M.; Eubank, T.; Scherer, P.E.; Parinandi, N.; Magalang, U.J. Intermittent hypoxia exacerbates pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction in a mouse model of diabetes mellitus. Sleep 2013, 36, 1849–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polak, J.; Shimoda, L.A.; Drager, L.F.; Undem, C.; McHugh, H.; Polotsky, V.Y.; Punjabi, N.M. Intermittent hypoxia impairs glucose homeostasis in C57BL6/J mice: Partial improvement with cessation of the exposure. Sleep 2013, 36, 1483–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiegel, K.; Tasali, E.; Leproult, R.; Van Cauter, E. Effects of poor and short sleep on glucose metabolism and obesity risk. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2009, 5, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappuccio, F.P.; D’Elia, L.; Strazzullo, P.; Miller, M.A. Quantity and quality of sleep and incidence of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Song, Y.; Hollenbeck, A.; Blair, A.; Schatzkin, A.; Chen, H. Day napping and short night sleeping are associated with higher risk of diabetes in older adults. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayas, N.T.; White, D.P.; Al-Delaimy, W.K.; Manson, J.E.; Stampfer, M.J.; Speizer, F.E.; Patel, S.; Hu, F.B. A prospective study of self-reported sleep duration and incident diabetes in women. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallon, L.; Broman, J.E.; Hetta, J. High incidence of diabetes in men with sleep complaints or short sleep duration: A 12-year follow-up study of a middle-aged population. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 2762–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiegel, K.; Knutson, K.; Leproult, R.; Tasali, E.; Van Cauter, E. Sleep loss: A novel risk factor for insulin resistance and Type 2 diabetes. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 99, 2008–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharib, S.A.; Khalyfa, A.; Abdelkarim, A.; Bhushan, B.; Gozal, D. Integrative miRNA-mRNA profiling of adipose tissue unravels transcriptional circuits induced by sleep fragmentation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37669. [Google Scholar]
- Fendri, S.; Rose, D.; Myambu, S.; Jeanne, S.; Lalau, J.D. Nocturnal hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes with sleep apnoea syndrome. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2011, 91, e21–e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.Y.; Wu, J.S.; Yang, Y.C.; Shih, C.C.; Wang, R.H.; Lu, F.H.; Chang, C.J. Sleep duration is a potential risk factor for newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 2011, 60, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koren, D.; Levitt Katz, L.E.; Brar, P.C.; Gallagher, P.R.; Berkowitz, R.I.; Brooks, L.J. Sleep architecture and glucose and insulin homeostasis in obese adolescents. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 2442–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakker, J.P.; Weng, J.; Wang, R.; Redline, S.; Punjabi, N.M.; Patel, S.R. Associations between Obstructive Sleep Apnea, Sleep Duration, and Abnormal Fasting Glucose. The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 192, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einhorn, D.; Stewart, D.A.; Erman, M.K.; Gordon, N.; Philis-Tsimikas, A.; Casal, E. Prevalence of sleep apnea in a population of adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocr. Pract. 2007, 13, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Laaban, J.P.; Daenen, S.; Leger, D.; Pascal, S.; Bayon, V.; Slama, G.; Elgrably, F. Prevalence and predictive factors of sleep apnoea syndrome in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Metab. 2009, 35, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punjabi, N.M.; Shahar, E.; Redline, S.; Gottlieb, D.J.; Givelber, R.; Resnick, H.E. Sleep-disordered breathing, glucose intolerance, and insulin resistance: The Sleep Heart Health Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2004, 160, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seicean, S.; Kirchner, H.L.; Gottlieb, D.J.; Punjabi, N.M.; Resnick, H.; Sanders, M.; Budhiraja, R.; Singer, M.; Redline, S. Sleep-disordered breathing and impaired glucose metabolism in normal-weight and overweight/obese individuals: The Sleep Heart Health Study. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 1001–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichmuth, K.J.; Austin, D.; Skatrud, J.B.; Young, T. Association of sleep apnea and type II diabetes: A population-based study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2005, 172, 1590–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, N.S.; Wong, K.K.; Phillips, C.L.; Liu, P.Y.; Knuiman, M.W.; Grunstein, R.R. Is sleep apnea an independent risk factor for prevalent and incident diabetes in the Busselton Health Study? J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2009, 5, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamidi, S.; Wroblewski, K.; Broussard, J.; Day, A.; Hanlon, E.C.; Abraham, V.; Tasali, E. Obstructive sleep apnea in young lean men: Impact on insulin sensitivity and secretion. Diabetes Care 2012, 35, 2384–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulcun, E.; Ekici, M.; Ekici, A. Disorders of glucose metabolism and insulin resistance in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2012, 66, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredheim, J.M.; Rollheim, J.; Omland, T.; Hofso, D.; Roislien, J.; Vegsgaard, K.; Hjelmesæth, J. Type 2 diabetes and pre-diabetes are associated with obstructive sleep apnea in extremely obese subjects: A cross-sectional study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2011, 10, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, B.D.; Grote, L.; Ryan, S.; Pepin, J.L.; Bonsignore, M.R.; Tkacova, R.; Saaresranta, T.; Verbraecken, J.; Lévy, P.; Hedner, J.; et al. Diabetes mellitus prevalence and control in sleep-disordered breathing: The European Sleep Apnea Cohort (ESADA) study. Chest 2014, 146, 982–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Tan, J.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, Q. Obstructive sleep apnea, prediabetes and progression of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Diabetes Investig. 2022, 13, 1396–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuna, S.T.; Reboussin, D.M.; Strotmeyer, E.S.; Millman, R.P.; Zammit, G.; Walkup, M.P.; Wadden, T.A.; Wing, R.R.; Pi-Sunyer, F.X.; Spira, A.P.; et al. Effects of Weight Loss on Obstructive Sleep Apnea Severity. Ten-Year Results of the Sleep AHEAD Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 203, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carneiro-Barrera, A.; Diaz-Roman, A.; Guillen-Riquelme, A.; Buela-Casal, G. Weight loss and lifestyle interventions for obstructive sleep apnoea in adults: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2019, 20, 750–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babu, A.R.; Herdegen, J.; Fogelfeld, L.; Shott, S.; Mazzone, T. Type 2 diabetes, glycemic control, and continuous positive airway pressure in obstructive sleep apnea. Arch. Intern. Med. 2005, 165, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harsch, I.A.; Schahin, S.P.; Radespiel-Troger, M.; Weintz, O.; Jahreiss, H.; Fuchs, F.S.; Wiest, G.H.; Hahn, E.G.; Lohmann, T.; Konturek, P.C.; et al. Continuous positive airway pressure treatment rapidly improves insulin sensitivity in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 169, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassaballa, H.A.; Tulaimat, A.; Herdegen, J.J.; Mokhlesi, B. The effect of continuous positive airway pressure on glucose control in diabetic patients with severe obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath. 2005, 9, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, A.; Abel, S.L.; Loving, R.T.; Dailey, G.; Shadan, F.F.; Cronin, J.W.; Kripke, D.F.; Kline, L.E. CPAP therapy of obstructive sleep apnea in type 2 diabetics improves glycemic control during sleep. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2008, 4, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oktay, B.; Akbal, E.; Firat, H.; Ardic, S.; Kizilgun, M. CPAP treatment in the coexistence of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome and metabolic syndrome, results of one year follow up. Acta Clin. Belg. 2009, 64, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, S.P.; Ayappa, I.A.; Caples, S.M.; Kimoff, R.J.; Patel, S.R.; Harrod, C.G. Treatment of Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea With Positive Airway Pressure: An American Academy of Sleep Medicine Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and GRADE Assessment. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2019, 15, 301–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guest, J.F.; Panca, M.; Sladkevicius, E.; Taheri, S.; Stradling, J. Clinical outcomes and cost-effectiveness of continuous positive airway pressure to manage obstructive sleep apnea in patients with type 2 diabetes in the U.K. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G.; Han, D. Benefits of continuous positive airway pressure on glycaemic control and insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes and obstructive sleep apnoea: A meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, T.E.; Sawyer, A.M. Adherence to continuous positive airway pressure treatment for obstructive sleep apnoea: Implications for future interventions. Indian J. Med. Res. 2010, 131, 245–258. [Google Scholar]
- Pepin, J.L.; Viot-Blanc, V.; Escourrou, P.; Racineux, J.L.; Sapene, M.; Levy, P.; Dervaux, B.; Lenne, X.; Mallart, A. Prevalence of residual excessive sleepiness in CPAP-treated sleep apnoea patients: The French multicentre study. Eur. Respir. J. 2009, 33, 1062–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiropoulos, P.; Papanas, N.; Nena, E.; Tsara, V.; Fitili, C.; Tzouvelekis, A.; Christaki, P.; Maltezos, E.; Bouros, D. Markers of glycemic control and insulin resistance in non-diabetic patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Hypopnea Syndrome: Does adherence to CPAP treatment improve glycemic control? Sleep Med. 2009, 10, 887–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patruno, V.; Aiolfi, S.; Costantino, G.; Murgia, R.; Selmi, C.; Malliani, A.; Montano, N. Fixed and autoadjusting continuous positive airway pressure treatments are not similar in reducing cardiovascular risk factors in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Chest 2007, 131, 1393–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamidi, S.; Wroblewski, K.; Stepien, M.; Sharif-Sidi, K.; Kilkus, J.; Whitmore, H.; Tasali, E. Eight Hours of Nightly Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Improves Glucose Metabolism in Patients with Prediabetes. A Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 192, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckert, D.J. Phenotypic approaches to obstructive sleep apnoea—New pathways for targeted therapy. Sleep Med. Rev. 2018, 37, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Z.; Fan, J.; Nie, S.; Wei, Y. Effect of continuous positive airway pressure on long-term cardiovascular outcomes in patients with coronary artery disease and obstructive sleep apnea: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Respir. Res. 2018, 19, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, J.C.M.; Lai, A.Y.K.; Tam, T.C.C.; Yuen, M.M.A.; Lam, K.S.L.; Ip, M.S.M. CPAP therapy for patients with sleep apnea and type 2 diabetes mellitus improves control of blood pressure. Sleep Breath. 2017, 21, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEvoy, R.D.; Antic, N.A.; Heeley, E.; Luo, Y.; Ou, Q.; Zhang, X.; Mediano, O.; Chen, R.; Drager, L.F.; Liu, Z.; et al. CPAP for Prevention of Cardiovascular Events in Obstructive Sleep Apnea. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 919–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gervès-Pinquié, C.; Bailly, S.; Goupil, F.; Pigeanne, T.; Launois, S.; Leclair-Visonneau, L.; Masson, P.; Bizieux-Thaminy, A.; Blanchard, M.; Sabil, A.; et al. Positive Airway Pressure Adherence, Mortality and Cardio-Vascular Events in Sleep Apnea Patients. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2022, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janovsky, C.C.; Rolim, L.C.; de Sa, J.R.; Poyares, D.; Tufik, S.; Silva, A.B.; Dib, S.A. Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy contributes to sleep apnea in young and lean type 1 diabetes mellitus patients. Front. Endocrinol. 2014, 5, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, P.; Goyal, A.; Pakhare, A.; Goel, S.K.; Kumar, A.; Reddy, M.A.; Anoohya, V. Metabolic syndrome in non-obese patients with OSA: Learning points of a cross-sectional study from a tertiary care hospital in Central India. Sleep Breath. 2022, 26, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farabi, S.S. Type 1 diabetes and Sleep. Diabetes Spectr. 2016, 29, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jauch-Chara, K.; Schmid, S.M.; Hallschmid, M.; Born, J.; Schultes, B. Altered neuroendocrine sleep architecture in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 1183–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, M.P.; Multari, G.; Montesano, M.; Pagani, J.; Cervoni, M.; Midulla, F.; Cerone, E.; Ronchetti, R. Sleep apnoea in children with diabetes mellitus: Effect of glycaemic control. Diabetologia 2000, 43, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Borel, A.L.; Benhamou, P.Y.; Baguet, J.P.; Halimi, S.; Levy, P.; Mallion, J.M.; Pepin, J.L. High prevalence of obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome in a Type 1 diabetic adult population: A pilot study. Diabet Med. 2010, 27, 1328–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai-Coetzer, C.L.; Antic, N.A.; Rowland, L.S.; Catcheside, P.G.; Esterman, A.; Reed, R.L.; Williams, H.; Dunn, S.; McEvoy, R.D. A simplified model of screening questionnaire and home monitoring for obstructive sleep apnoea in primary care. Thorax 2011, 66, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai-Coetzer, C.L.; Antic, N.A.; Rowland, L.S.; Reed, R.L.; Esterman, A.; Catcheside, P.G.; Eckermann, S.; Vowles, N.; Williams, H.; Dunn, S. Primary care vs specialist sleep center management of obstructive sleep apnea and daytime sleepiness and quality of life: A randomized trial. JAMA 2013, 309, 997–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, H.Y.; Chen, P.Y.; Chuang, L.P.; Chen, N.H.; Tu, Y.K.; Hsieh, Y.J.; Wang, Y.C.; Guilleminault, C. Diagnostic accuracy of the Berlin questionnaire, STOP-BANG, STOP, and Epworth sleepiness scale in detecting obstructive sleep apnea: A bivariate meta-analysis. Sleep Med. Rev. 2017, 36, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kee, K.; Dixon, J.; Shaw, J.; Vulikh, E.; Schlaich, M.; Kaye, D.M.; Zimmet, P.; Naughton, M.T. Comparison of Commonly Used Questionnaires to Identify Obstructive Sleep Apnea in a High-Risk Population. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2018, 14, 2057–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senaratna, C.V.; Perret, J.L.; Lowe, A.; Bowatte, G.; Abramson, M.J.; Thompson, B.; Lodge, C.; Russell, M.; Hamilton, G.S.; Dharmage, S.C. Detecting sleep apnoea syndrome in primary care with screening questionnaires and the Epworth sleepiness scale. Med. J. Aust. 2019, 211, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sajkov, D.; Mupunga, B.; Bowden, J.J.; Langton, C.; Petrovsky, N. Narrative Review: Obesity, Type 2 DM and Obstructive Sleep Apnoea—Common Bedfellows. Diabetology 2022, 3, 447-459. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology3030033
Sajkov D, Mupunga B, Bowden JJ, Langton C, Petrovsky N. Narrative Review: Obesity, Type 2 DM and Obstructive Sleep Apnoea—Common Bedfellows. Diabetology. 2022; 3(3):447-459. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology3030033
Chicago/Turabian StyleSajkov, Dimitar, Bliegh Mupunga, Jeffrey J. Bowden, Christopher Langton, and Nikolai Petrovsky. 2022. "Narrative Review: Obesity, Type 2 DM and Obstructive Sleep Apnoea—Common Bedfellows" Diabetology 3, no. 3: 447-459. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology3030033
APA StyleSajkov, D., Mupunga, B., Bowden, J. J., Langton, C., & Petrovsky, N. (2022). Narrative Review: Obesity, Type 2 DM and Obstructive Sleep Apnoea—Common Bedfellows. Diabetology, 3(3), 447-459. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology3030033





