Can Health Improvements from a Community-Based Exercise and Lifestyle Program for Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Be Maintained? A Follow up Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Roland, G.; Hass, L.; Greent, W.; Ottoson, J.M. Fundamental Issues in Translational Research. In From Clinical Trials to Community: The Science of Translating Diabetes and Obesity Research; Natcher Conference Center, National Institutes of Health: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wethington, E.E.; Dunifon, R.E. Research for the Public Good: Applying the Methods of Translational Research to Improve Human Health and Well-Being; American Psychological Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, M.S.; Damschroder, L.; Hagedorn, H.; Smith, J.; Kilbourne, A.M. An introduction to implementation science for the non-specialist. BMC Psychol. 2015, 3, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas 2021—10th Edition. 2021. Available online: https://diabetesatlas.org/ (accessed on 14 October 2021).
- Kalyani, R.R.; Golden, S.H.; Cefalu, W.T. Diabetes and Aging: Unique Considerations and Goals of Care. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. Insufficient Physical Activity. Available online: https://www.aihw.gov.au/reports/risk-factors/insufficient-physical-activity/contents/insufficient-physical-activity (accessed on 1 April 2022).
- Kostić, R.; Uzunović, S.; Pantelić, S.; Đurašković, R. A comparative analysis of the indicators of the functional fitness of the elderly. Facta Univ. Ser. Phys. Educ. Sport 2011, 9, 161–171. [Google Scholar]
- Milanović, Z.; Pantelić, S.; Trajković, N.; Sporiš, G.; Kostić, R.; James, N. Age-related decrease in physical activity and functional fitness among elderly men and women. Clin. Interv. Aging 2013, 8, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riebe, D.; Blissmer, B.J.; Greaney, M.L.; Ewing Garber, C.; Lees, F.D.; Clark, P.G. The relationship between obesity, physical activity, and physical function in older adults. J. Aging Health 2009, 21, 1159–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuna, H.D.; Edeer, A.O.; Malkoc, M.; Aksakoglu, G. Effect of age and physical activity level on functional fitness in older adults. Eur. Rev. Aging Phys. Act. 2009, 6, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, W.L.; Ouyang, P.; Wu, A.W.; Barone, B.B.; Stewart, K.J. Fatness and fitness: How do they influence health-related quality of life in type 2 diabetes mellitus? Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2008, 6, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, R.T.; Yalla, S.V.; Fleischer, A.E.; Wu, S.C. A Growing Troubling Triad: Diabetes, Aging, and Falls. J. Aging Res. 2013, 2013, 342650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodama, S.; Saito, K.; Tanaka, S.; Maki, M.; Yachi, Y.; Asumi, M.; Sugawara, A.; Totsuka, K.; Shimano, H.; Ohashi, Y. Cardiorespiratory fitness as a quantitative predictor of all-cause mortality and cardiovascular events in healthy men and women: A meta-analysis. JAMA 2009, 301, 2024–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Norman, I.J.; While, A.E. Physical activity in older people: A systematic review. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirwan, M.; Chiu, C.L.; Hay, M.; Laing, T. Community-based exercise and lifestyle program improves health outcomes in older adults with type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 6147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, C.; Jarczok, M.N.; Litaker, D. Community-based efforts to promote physical activity: A systematic review of interventions considering mode of delivery, study quality and population subgroups. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2014, 17, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotnikoff, R.C.; Karunamuni, N.D.; Johnson, J.A.; Kotovych, M.; Svenson, L.W. Health-related behaviours in adults with diabetes: Associations with health care utilization and costs. Can. J. Public Health 2008, 99, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaneda, C.; Layne, J.E.; Munoz-Orians, L.; Gordon, P.L.; Walsmith, J.; Foldvari, M.; Roubenoff, R.; Tucker, K.L.; Nelson, M.E. A Randomized Controlled Trial of Resistance Exercise Training to Improve Glycemic Control in Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunstan, D.W.; Vulikh, E.; Owen, N.; Jolley, D.; Shaw, J.; Zimmet, P. Community Center–Based Resistance Training for the Maintenance of Glycemic Control in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gallé, F.; Di Onofrio, V.; Miele, A.; Belfiore, P.; Liguori, G. Effects of a community-based exercise and motivational intervention on physical fitness of subjects with type 2 diabetes. Eur. J. Public Health 2019, 29, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grelier, S.; Serresse, O.; Boudreau-Lariviere, C.; Zory, R. Effects of a three-month combined training program on the cardiopulmonary and muscle strength capacities of type 2 diabetic subjects. J. Sports Med. Phys. Fit. 2013, 53, 56–64. [Google Scholar]
- Mendes, R.; Sousa, N.; Themudo-Barata, J.; Reis, V. Impact of a community-based exercise programme on physical fitness in middle-aged and older patients with type 2 diabetes. Gac. Sanit. 2016, 30, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallè, F.; Krakauer, J.C.; Krakauer, N.Y.; Valerio, G.; Liguori, G. Can an Exercise-Based Educational and Motivational Intervention be Durably Effective in Changing Compliance to Physical Activity and Anthropometric Risk in People with Type 2 Diabetes? A Follow-Up Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathieu, M.E.; Brochu, M.; Béliveau, L. DiabetAction: Changes in physical activity practice, fitness, and metabolic syndrome in type 2 diabetic and at-risk individuals. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2008, 18, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australian Bureau of Statistics. Socio-Economic Indexs for Areas (SEIFA) 2016. Available online: https://www.abs.gov.au/ausstats/abs@.nsf/mf/2033.0.55.001 (accessed on 14 October 2021).
- Rikli, R.E.; Jones, C.J. Development and validation of criterion-referenced clinically relevant fitness standards for maintaining physical independence in later years. Gerontologist 2013, 53, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royal Australian College of General Practitioners. The Red Book: 7.2 Overweight; Royal Australian College of General Practitioners: Melbourne, Australia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organisation. BMI: Body Mass Index. Available online: http://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/disease-prevention/nutrition/a-healthy-lifestyle/body-mass-index-bmi (accessed on 14 October 2021).
- Plotnikoff, R.C.; Costigan, S.A.; Karunamuni, N.D.; Lubans, D.R. Community-based physical activity interventions for treatment of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2013, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trikkalinou, A.; Papazafiropoulou, A.K.; Melidonis, A. Type 2 diabetes and quality of life. World J. Diabetes 2017, 8, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payette, H.; Gueye, N.R.; Gaudreau, P.; Morais, J.A.; Shatenstein, B.; Gray-Donald, K. Trajectories of physical function decline and psychological functioning: The Quebec longitudinal study on nutrition and successful aging (NuAge). J. Gerontol. B Psychol. Sci. Soc. Sci. 2011, 66 (Suppl. S1), i82–i90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, K.K.; Hilliard, M.; Piatt, G.; Ievers-Landis, C.E. Effective strategies for encouraging behavior change in people with diabetes. Diabetes Manag. 2015, 5, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.Q.M.; Chin, Y.H.; Ng, C.H.; Liow, Y.; Devi, M.K.; Khoo, C.M.; Goh, L.H. Multidisciplinary team approach to diabetes. An outlook on providers’ and patients’ perspectives. Prim. Care Diabetes 2020, 14, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deloitte Access Economics. Summary Report—Value of Accredited Exercise Physiologists in Australia. Available online: https://www.essa.org.au/wp-content/uploads/2015/10/Deloitte-Report-2015_Value-of-AEPs-in-Australia_Summary.pdf (accessed on 15 May 2022).
- Craike, M.; Britt, H.; Parker, A.; Harrison, C. General practitioner referrals to exercise physiologists during routine practice: A prospective study. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2019, 22, 478–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurynski, Y.; Smith, C.; Siette, J.; Nic Giolla Easpaig, B.; Simons, M.; Knaggs, G.T. Identifying enablers and barriers to referral, uptake and completion of lifestyle modification programmes: A rapid literature review. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e045094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, K.L.; Harrison, E.L.; Reeder, B.A.; Sari, N.; Chad, K.E. Is Self-Reported Physical Activity Participation Associated with Lower Health Services Utilization among Older Adults? Cross-Sectional Evidence from the Canadian Community Health Survey. J. Aging Res. 2015, 2015, 425354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, N.; Laing, T. Measuring the Social Return on Investment (SROI) for Beat It. Available online: https://www.diabetesqualified.com.au/measuring-the-social-return-on-investment-sroi-for-beat-it/ (accessed on 1 December 2021).
- Banke-Thomas, A.O.; Madaj, B.; Charles, A.; van den Broek, N. Social Return on Investment (SROI) methodology to account for value for money of public health interventions: A systematic review. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
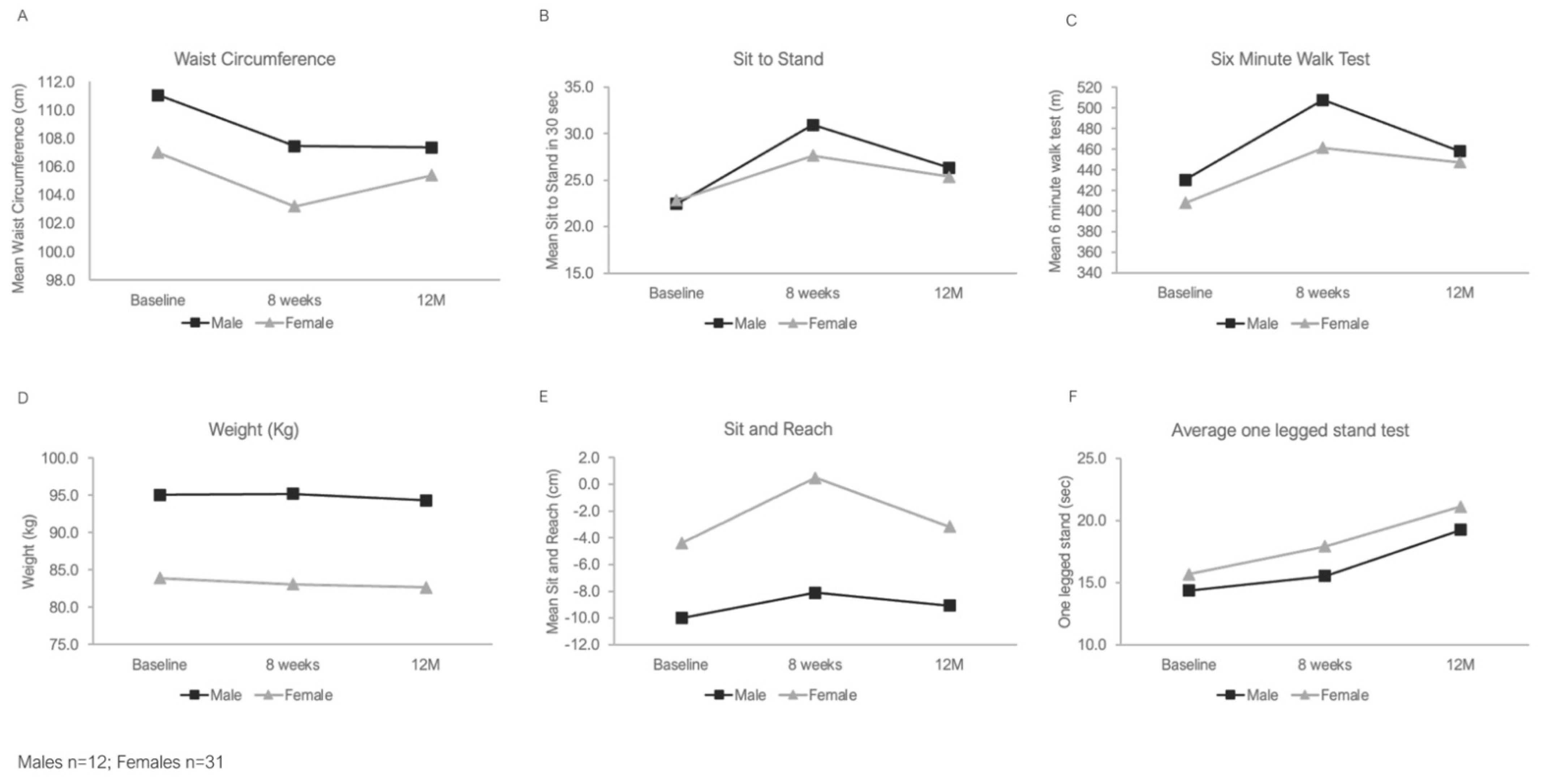
| Male (n = 12) | Female (n = 31) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline Mean (SD) | 8 Weeks Mean (SD) | 12 Month Mean (SD) | Baseline Mean (SD) | 8 Weeks Mean (SD) | 12 Month Mean (SD) | |
| Weight (kg) | 95.1 (23.1) | 95.2 (23.1) | 94.3 (21.6) | 83.9 (18.3) | 83.1 (17.5) | 82.6 (17) |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 111.1 (16.7) | 107.5 (16.5) | 107.4 (14.3) | 107 (15.2) | 103.2 (13.8) | 105.4 (15.1) |
| Chair sit and reach (cm) | −10 (7.5) | −8.1 (7.7) | −9.1 (9.4) | −4.4 (9) | 0.5 (8.1) | −3.2 (9.1) |
| Sit to Stand in 30 s | 22.4 (9.8) | 30.9 (14.6) | 26.3 (10.5) | 22.8 (7.5) | 27.6 (7) | 25.4 (7) |
| Six-minute Walk test (m) | 430.3 (213.2) | 507.6 (208.5) | 458.2 (145.2) | 408 (83.3) | 461.3 (79.8) | 447.3 (90.5) |
| Balance (seconds) *,# | 14.4 (9.6) | 15.5 (9.3) | 19.3 (17.8) | 15.7 (13.8) | 17.9 (11.7) | 21.1 (16.8) |
| Males n (%) | Female n (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 8 Weeks | 12 Months | Baseline | 8 Weeks | 12 Months | |
| Waist circumference (cm) # | 3 (25%) | 3 (25%) | 2 (16.7%) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| BMI (kg/m2) * | 3 (25%) | 3 (25%) | 2 (16.7%) | 4 (13.3%) | 5 (16.1%) | 4 (13.3%) |
| Chair sit and reach (cm) | 4 (33.3%) | 6 (50.0%) | 6 (50%) | 16 (51.6% | 20 (64.5%) | 16 (51.6%) |
| Sit to Stand in 30 s | 10 (83.3%) | 11 (91.7%) | 10 (83.3%) | 25 (80.6%) | 30 (96.8%) | 30 (96.8%) |
| Six-minute Walk test (m) | 2 (16.7%) | 4 (33.3%) | 5 (41.7%) | 3 (9.7%) | 9 (29.0%) | 6 (19.4%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kirwan, M.; Gwynne, K.; Laing, T.; Hay, M.; Chowdhury, N.; Chiu, C.L. Can Health Improvements from a Community-Based Exercise and Lifestyle Program for Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Be Maintained? A Follow up Study. Diabetology 2022, 3, 348-354. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology3020025
Kirwan M, Gwynne K, Laing T, Hay M, Chowdhury N, Chiu CL. Can Health Improvements from a Community-Based Exercise and Lifestyle Program for Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Be Maintained? A Follow up Study. Diabetology. 2022; 3(2):348-354. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology3020025
Chicago/Turabian StyleKirwan, Morwenna, Kylie Gwynne, Thomas Laing, Mellissa Hay, Noureen Chowdhury, and Christine L. Chiu. 2022. "Can Health Improvements from a Community-Based Exercise and Lifestyle Program for Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Be Maintained? A Follow up Study" Diabetology 3, no. 2: 348-354. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology3020025
APA StyleKirwan, M., Gwynne, K., Laing, T., Hay, M., Chowdhury, N., & Chiu, C. L. (2022). Can Health Improvements from a Community-Based Exercise and Lifestyle Program for Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Be Maintained? A Follow up Study. Diabetology, 3(2), 348-354. https://doi.org/10.3390/diabetology3020025







