Development and Validation of a Method for the Determination of Caffeine in a Small Volume of Saliva Using SPE-LC-DAD
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Solvents
2.2. LC-DAD Conditions
2.3. Preparation of Quality Control (QC) and Standard Solutions
2.4. Collection of Blank Saliva Samples
2.5. Extraction of Caffeine from Saliva Samples
2.6. Preparation of Calibration and Quality Control Samples
2.7. Validation
2.7.1. Linearity
2.7.2. Intra- and Inter-Day Precision
2.7.3. Lower Limit of Quantification (LLOQ)
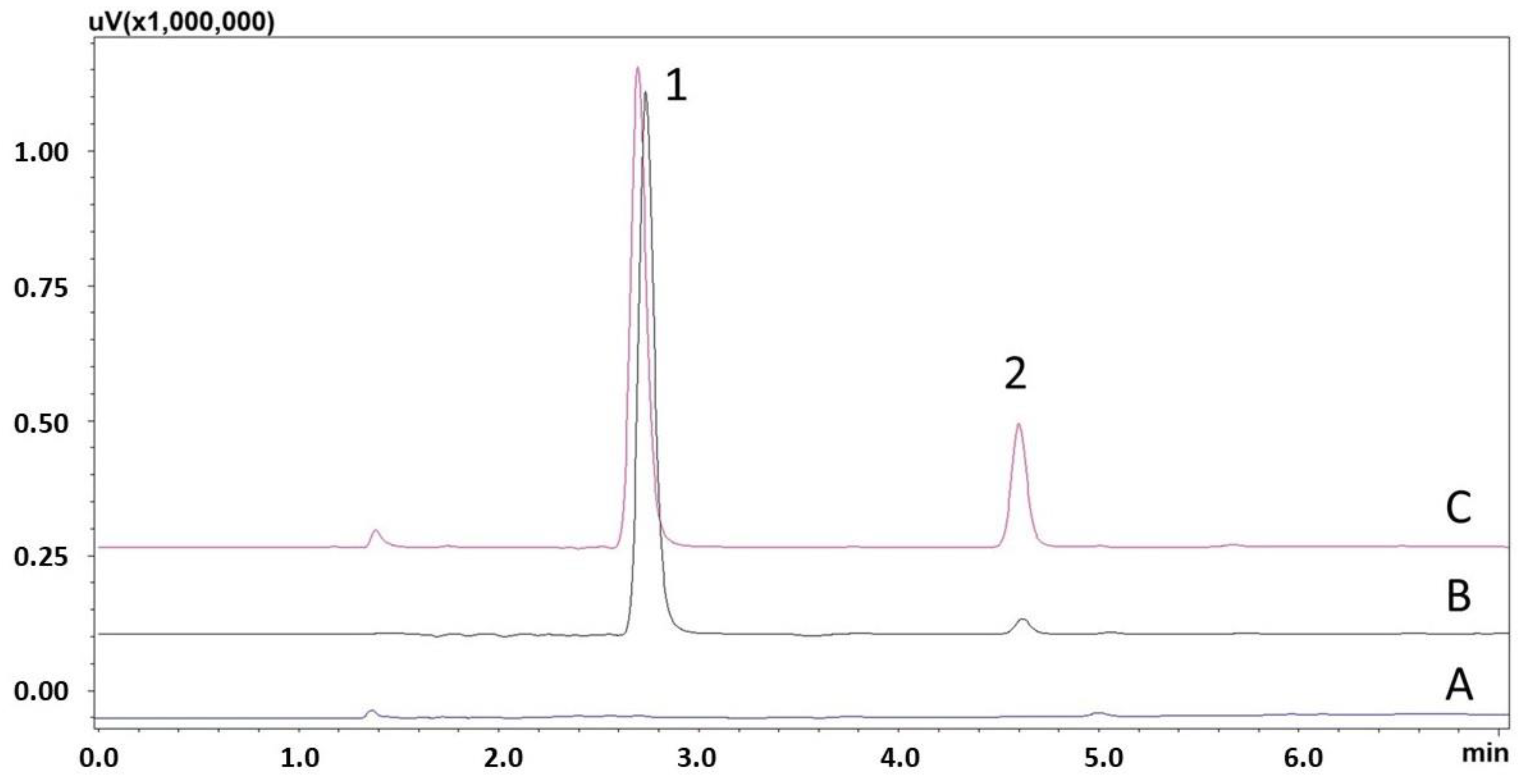
2.7.4. Selectivity
2.7.5. Extraction and Absolute Recovery
2.7.6. Stability
2.8. Application of the Analytical Method and Statistical Analysis of the Results
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
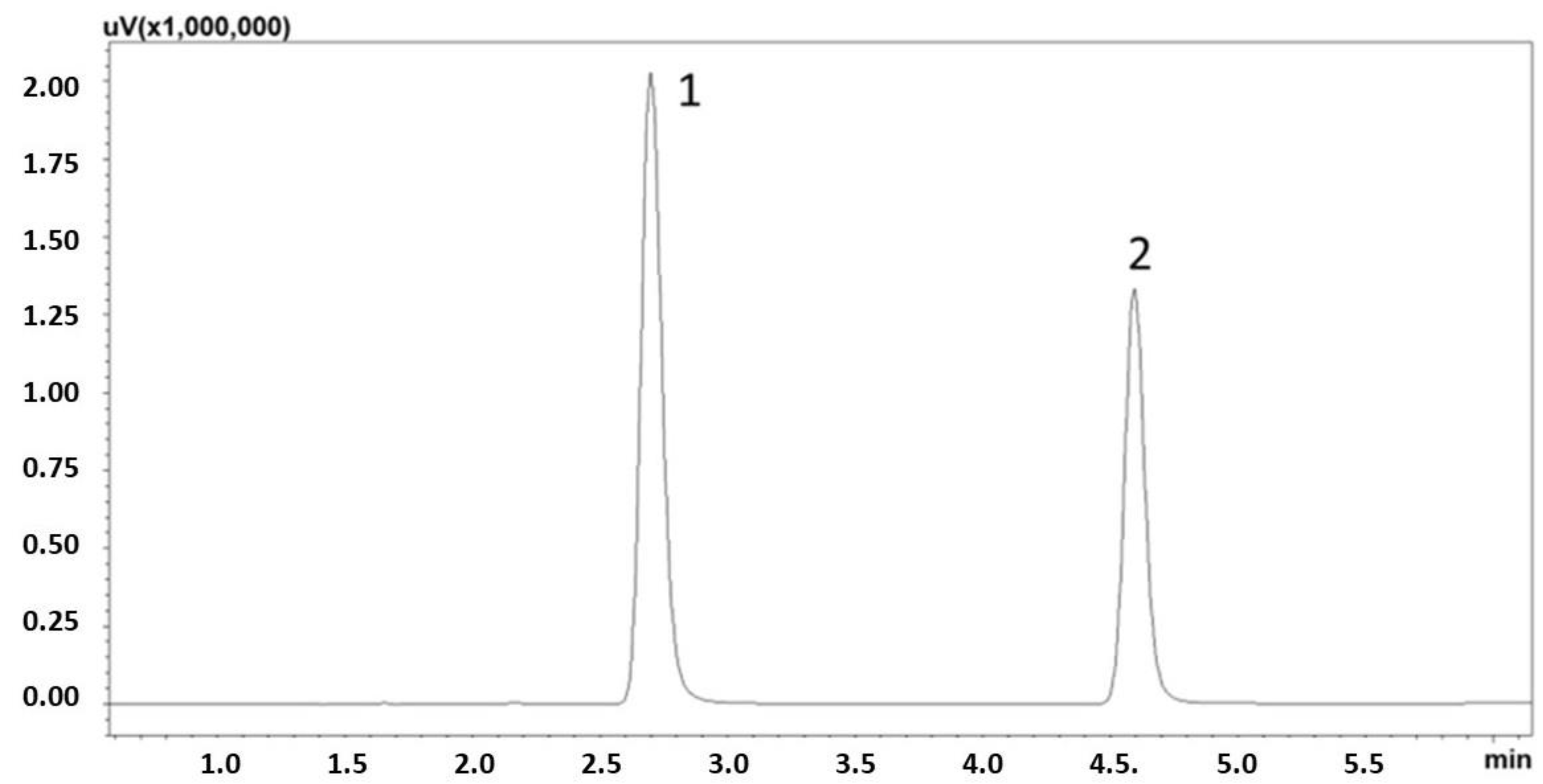
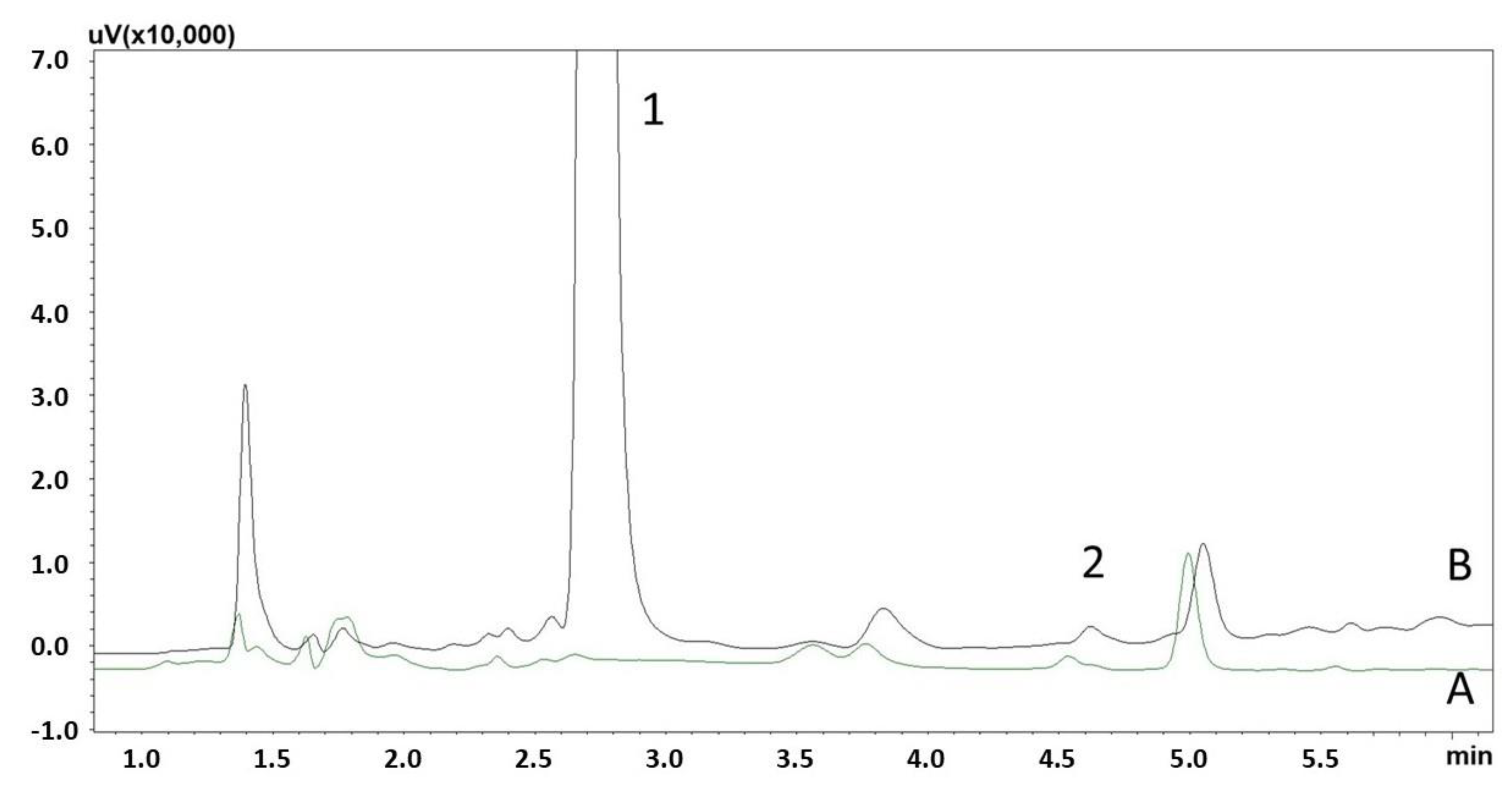
3.1. Optimization of the Separation and Extraction Processes
3.2. Method Validation
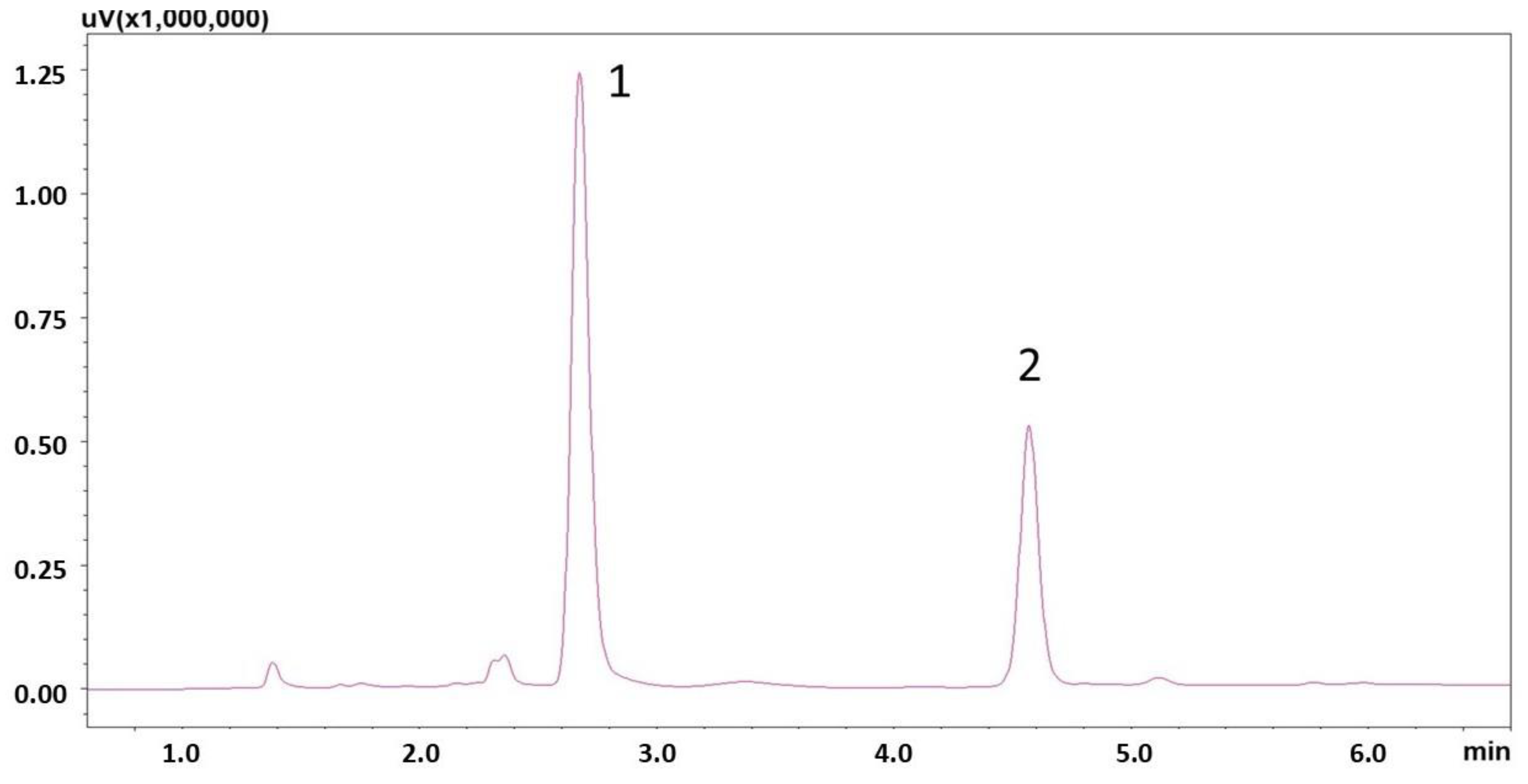
3.3. Application of the Method and Statistical Analysis of the Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CAF | caffeine |
| GABA-A | γ-aminobutyric acid type A |
| FDA | Food and Drug Administration |
| LC | liquid chromatography |
| GC | gas chromatography |
| LLE | liquid–liquid extraction |
| SPE | solid-phase extraction |
| SPME | solid phase microextraction |
| QC | quality control |
| IS | internal standard |
| EMA | European Medicines Agency |
| CV | coefficient of variation |
| LLOQ | lower limit of quantification |
| DAD | diode array detector |
| R2 | determination coefficient |
References
- Oliphant, E.A.; Hanning, S.M.; McKinlay, C.J.D.; Alsweiler, J.M. Caffeine for apnea and prevention of neurodevelopmental impairment in preterm infants: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Perinatol. 2024, 44, 785–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belayneh, A.; Molla, F. The Effect of Coffee on Pharmacokinetic Properties of Drugs: A Review. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 7909703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Lei, X.; Dong, W. Caffeine and bronchopulmonary dysplasia: Clinical benefits and the mechanisms involved. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2022, 57, 1392–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, R.B.; Diener, H.C.; Robbins, M.S.; Garas, S.Y.; Patel, K. Caffeine in the management of patients with headache. J. Headache Pain 2017, 18, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, N.R.; Liu, X.; Rhein, L.M.; Darnall, R.A.; Corwin, M.J.; McEntire, B.L.; Ward, R.M.; James, L.P.; Sherwin, C.M.T.; Heeren, T.C.; et al. Salivary caffeine concentrations are comparable to plasma concentrations in preterm infants receiving extended caffeine therapy. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 82, 754–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, V.S.; Shiva, S.; Manikantan, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Pharmacology of caffeine and its effects on the human body. Eur. J. Med. Chem. Rep. 2024, 10, 100138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Costa Silva, R.G.; Augusto, F. Sol–gel molecular imprinted ormosil for solid-phase extraction of methylxanthines. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1114, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Military Nutrition Research. Caffeine for the Sustainment of Mental Task Performance; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLellan, T.M.; Caldwell, J.A.; Lieberman, H.R. A review of caffeine’s effects on cognitive, physical and occupational performance. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2016, 71, 294–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willson, C. The clinical toxicology of caffeine: A review and case study. Toxicol. Rep. 2018, 5, 1140–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawrot, P.; Jordan, S.; Eastwood, J.; Rotstein, J.; Hugenholtz, A.; Feeley, M. Effects of caffeine on human health. Food Addit. Contam. 2003, 20, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrillo, J.A.; Benitez, J. Clinically significant pharmacokinetic interactions between dietary caffeine and medications. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2000, 39, 127–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.R.; Padowski, J.M.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, G.; Luo, S.; Lazarus, P.; Layton, M.E.; McPherson, S. Pharmacokinetic analysis and comparison of caffeine administered rapidly or slowly in coffee chilled or hot versus chilled energy drink in healthy young adults. Clin. Toxicol. 2016, 54, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, N.Y.; Mimpen, J.Y.; van den Bogaard, W.J.M.; Flesch, F.M.; van de Meent, M.H.M.; Torano, J.S. Analysis of caffeine and paraxanthine in human saliva with ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography for CYP1A2 phenotyping. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2015, 995–996, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georga, K.A.; Samanidou, V.F.; Papadoyannis, I.N. Use of novel solid-phase extraction sorbent materials for high-performance liquid chromatography quantitation of caffeine metabolism products methylxanthines and methyluric acids in samples of biological origin. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 2001, 759, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georga, K.A.; Samanidou, V.F.; Papadoyannis, I.N. Improved micro-method for HPLC analysis of caffeine and its demethylated metabolites in human biological fluids after SPE. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2000, 23, 1523–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehlig, A.; Daval, J.-L.; Debry, G. Caffeine and the central nervous system: Mechanisms of action, biochemical, metabolic and psychostimulant effects. Brain Res. Rev. 1992, 17, 139–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikoff, D.; Welsh, B.T.; Henderson, R.; Brorby, G.P.; Britt, J.; Myers, E.; Goldberger, J.; Lieberman, H.R.; O’Brien, C.; Peck, J.; et al. Systematic review of the potential adverse effects of caffeine consumption in healthy adults, pregnant women, adolescents, and children. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 109, 585–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panel, E.; Nda, A. Scientific Opinion on the safety of caffeine. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowaczewska, M.; Wiciński, M.; Kaźmierczak, W. The Ambiguous Role of Caffeine in Migraine Headache: From Trigger to Treatment. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabrizi, R.; Saneei, P.; Lankarani, K.B.; Akbari, M.; Kolahdooz, F.; Esmaillzadeh, A.; Nadi-Ravandi, S.; Mazoochi, M.; Asemi, Z. The effects of caffeine intake on weight loss: A systematic review and dos-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 2688–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zylber-Katz, E.; Granit, L.; Levy, M. Relationship between caffeine concentrations in plasma and saliva. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1984, 36, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ptolemy, A.S.; Tzioumis, E.; Thomke, A.; Rifai, S.; Kellogg, M. Quantification of theobromine and caffeine in saliva, plasma and urine via liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: A single analytical protocol applicable to cocoa intervention studies. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2010, 878, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendriss, E.K.; Markoglou, N.; Wainer, I.W. Liquid chromatographic method for the simultaneous determination of caffeine and fourteen caffeine metabolites in urine. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 2000, 746, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, V.; Gross, A.S.; Xu, H.; McLachlan, A.J. Pharmacokinetics of caffeine in plasma and saliva, and the influence of caffeine abstinence on CYP1A2 metrics. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 63, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sager, M.; Jedamzik, P.; Merdivan, S.; Grimm, M.; Schneider, F.; Kromrey, M.L.; Hasan, M.; Oswald, S.; Kühn, J.; Koziolek, M.; et al. Low dose caffeine as a salivary tracer for the determination of gastric water emptying in fed and fasted state: A MRI validation study. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2018, 127, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce-Rodríguez, H.D.; García-Robles, A.A.; Sáenz-González, P.; Verdú-Andrés, J.; Campíns-Falcó, P. On-line in-tube solid phase microextraction coupled to capillary liquid chromatography-diode array detection for the analysis of caffeine and its metabolites in small amounts of biological samples. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 178, 112914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napierała, M.; Florek, E. Qualitative and quantitative determination of caffeine in saliva by high performance liquid chromatography. Prz. Lek. 2016, 73, 777–780. [Google Scholar]
- Leodori, G.; De Bartolo, M.I.; Belvisi, D.; Ciogli, A.; Fabbrini, A.; Costanzo, M.; Manetto, S.; Conte, A.; Villani, C.; Fabbrini, G.; et al. Salivary caffeine in Parkinson’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liguori, A.; Hughes, J.R.; Grass, J.A. Absorption and subjective effects of caffeine from coffee, cola and capsules. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1997, 58, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzakri, T.; Rehenbrock, L.; Senekowitsch, S.; Rump, A.; Schick, P.; Krause, J.; Kromrey, M.-L.; Grimm, M.; Weitschies, W. Determination of gastric water emptying in fasted and fed state conditions using a compression-coated tablet and salivary caffeine kinetics. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, V.; Gross, A.S.; McLachlan, A.J. Caffeine and paraxanthine HPLC assay for CYP1A2 phenotype assessment using saliva and plasma. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2010, 24, 1136–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begas, E.; Kouvaras, E.; Tsakalof, A.K.; Bounitsi, M.; Asprodini, E.K. Development and validation of a reversed-phase HPLC method for CYP1A2 phenotyping by use of a caffeine metabolite ratio in saliva. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2015, 29, 1657–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plonka, J. Methods of biological fluids sample preparation—Biogenic amines, methylxanthines, water-soluble vitamins. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2015, 29, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Medicines Agency. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en (accessed on 19 August 2025).

| Procedure | SPE Sorbent | Sample Handling Procedure | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Strata–X | Collect the solution after adding 500 μL of redistilled water | ||
| Washing solvent | Drying time | Elution solvent | ||
| 2. | Strata–X–CW | 1. 100 mM K2HPO4 solution 2. Methanol | 5 min | 5% formic acid in methanol |
| 3. | EVOLUTE® EXPRESS ABN | 1. 0.1 M HCl 2. Methanol | 5 min | 5% ammonium in methanol |
| 4. | EVOLUTE® EXPRESS ABN | 1. 0.1 M HCl 2. Methanol: water (10:90, v/v) | 5 min | 5% ammonium in methanol |
| Calibration Curve y = ax + b (n = 4) | |
|---|---|
| Range (ng/mL) | 10–10,000 |
| Determination coefficient (R2) | 0.995 ± 0.0051 |
| Slope a ± Δa | 0.00006 ± 0.000004 |
| Intercept b ± Δb | −0.0006625 ± 0.0067 |
| LLOQ (ng/mL) | 10.0 |
| QC (ng/mL) | Intra-Day (CV%) | Inter-Day (CV%) | Extraction Recovery (%) | Absolute Recovery (%) | Stability (Difference %) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 °C | −21 °C | |||||
| 30 | 1.52 | 8.63 | 93.86 | 83.77 | −3.03 | −1.24 |
| 4000 | 3.01 | 9.79 | 97.37 | 90.58 | −1.99 | −0.69 |
| 8000 | 2.83 | 12.11 | 90.53 | 86.16 | −1.03 | −1.09 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alghanem, S.; Dziurkowska, E. Development and Validation of a Method for the Determination of Caffeine in a Small Volume of Saliva Using SPE-LC-DAD. Analytica 2025, 6, 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica6040040
Alghanem S, Dziurkowska E. Development and Validation of a Method for the Determination of Caffeine in a Small Volume of Saliva Using SPE-LC-DAD. Analytica. 2025; 6(4):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica6040040
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlghanem, Suhail, and Ewelina Dziurkowska. 2025. "Development and Validation of a Method for the Determination of Caffeine in a Small Volume of Saliva Using SPE-LC-DAD" Analytica 6, no. 4: 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica6040040
APA StyleAlghanem, S., & Dziurkowska, E. (2025). Development and Validation of a Method for the Determination of Caffeine in a Small Volume of Saliva Using SPE-LC-DAD. Analytica, 6(4), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/analytica6040040







