Abstract
Detrusor sphincter dyssynergia (DSD) is defined as an external urethral sphincter anomalous contraction concomitant to detrusor contraction during voiding, due to a neurological disease. It commonly occurs in suprasacral spinal cord-injured (SCI) patients and can be associated with autonomic dysreflexia. DSD generates risks to the urinary system and overall health; hence, it should be promptly diagnosed and managed. Bladder neck dyssynergia is a condition that should be integrated in DSD assessment. We reviewed the literature indexed in PubMed/Medline on the evaluation methods of DSD in SCI patients. Urodynamics is the mainstay evaluation method and has a prognostic value for the progression of upper urinary tract structural degradation and renal function decline. We found a lack of consensus on the optimal urodynamics configuration when evaluating DSD, especially in obtaining and measuring the signal from external urethral sphincter (EUS) activity. It appears that a combination of recordings of voiding cystourethrography and EUS electromyography, either with or without EUS pressure measurement, is the most accurate method available for evaluating DSD. While gathering articles, we came across an interesting approach in evaluating DSD in the past: urodynamics coupled with ultrasound imaging. Despite being considered valuable from a diagnostic standpoint by some prominent authors, it is no longer represented in the current literature. In addition to the instrumental diagnosis, health professionals should consider additional clinical features when evaluating and managing DSD in SCI patients, to design a customized plan to achieve the best compromise between quality of life and urinary system protection.
1. Introduction
Detrusor sphincter dyssynergia (DSD) is defined as a detrusor contraction concurrent with an involuntary contraction of the urethral and/or periurethral striated muscle []. The most recent International Continence Society (ICS) 2020 Standards [] define DSD as a dyscoordination between detrusor and rhabdosphincter function during voiding due to a neurological abnormality (i.e., detrusor contraction synchronous with the contraction of the urethral and/or periurethral striated muscle). This is a feature of neurological bladder voiding disorders. DSD generally occurs due to a lesion above the sacral level and below the pons []. According to these standards [], the classifications of DSD can be divided into two groups: intermittent (type 1), in patients with incomplete neurologic lesions; and continuous (type 2), which occurs more often in patients with complete lesions. In type 1 DSD (intermittent), there is a progressive increase in external urethral sphincter (EUS) contraction activity that peaks at maximal detrusor contraction, followed by sudden relaxation of the EUS as the detrusor pressure declines, allowing for urination. In type 2 DSD, there is a continuous EUS contraction throughout the entire detrusor contraction, resulting in a urinary obstruction or an inability to urinate (Figure 1 and Figure 2). DSD occurs when there is a disruption of spinobulbar pathways between the pontine micturition complex and Onuf’s nucleus, which results in high urethral closure pressures during a detrusor contraction [].
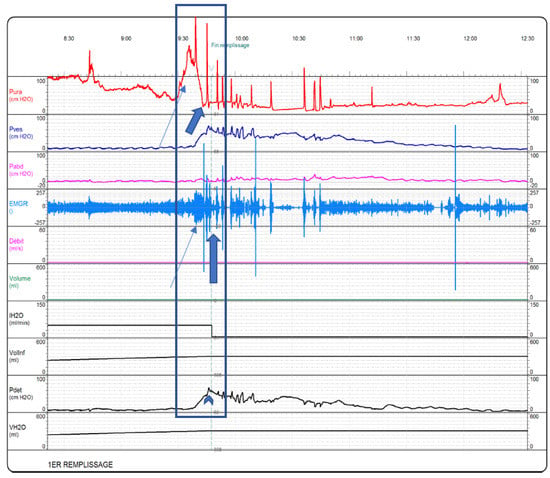
Figure 1.
Urodynamics of type 1 DSD according to ICS classification, with an increase in EUS activity (line arrows) following a sudden decrease (block arrows) in both EMG and EUS-pressure channels as the detrusor pressure peaks and starts to slowly decrease (arrowhead), source: UdEPP Rehazenter database.
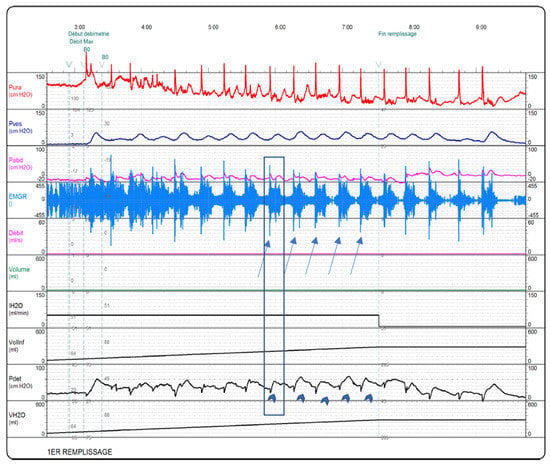
Figure 2.
Urodynamics of type 2 (continuous) DSD according to ICS classification, where there is a continuous EUS contraction throughout the entire detrusor contraction. This case is better defined by type 2 according to the Blaivas et al. classification []: clonic EUS contractions in EMG channel (line arrows) and EUS pressure channel (red graph) interspersed through detrusor contractions (arrowheads), source: UdEPP Rehazenter database.
Although this is a straightforward definition, there are still some controversies on this topic:
- (a)
- There were previous DSD classifications considering three groups by Blaivas [] and three dysfunctions by Yalla [], according to sphincter electromyographic (EMG) activity during urodynamics.
- (b)
- In contrast with the above definition [] that considers DSD as being striated urethral sphincter overactivity during voiding, detrusor–internal sphincter dyssynergia or bladder neck dyssynergia (BND) is a failure of the smooth muscle of the bladder neck and proximal urethra to relax during detrusor contraction in the voiding phase [,]. BND might have implications in the evaluation and management methods of DSD [];
- (c)
- DSD may also occur in non-neurological pathologies [,].
The prevalence of DSD in suprasacral spinal cord-injured (SCI) patients after the spinal shock phase is high [], and ranges between 70 and 100% [,].
In clinical practice, a neurogenic bladder in SCI leading to high vesical pressures, such as any type of DSD, is associated with the risk of rapidly developing irreversible pathophysiological and structural modifications, such as bladder wall thickening and trabeculations, vesicoureteral reflux, uretero-hydronephrosis, in addition to infectious and lithiasis complications in the bladder, ureters, and kidneys leading to renal failure, and a risk of neoplasia [,,,]. Additionally, in SCI patients with lesions above T6, namely those with complete lesions, DSD is also associated with frequent episodes of autonomic dysreflexia [].
Hence, DSD is prevalent in the SCI population, and is threatening to the urinary system and overall health status, which means that its diagnosis must be established as soon as possible. Although urodynamics is the cornerstone of DSD assessment, other aspects should also be evaluated in SCI patients. One may ask, should the clinician evaluating two different SCI patients with the same urodynamics criteria for DSD severity consider other clinical parameters to establish a follow-up and therapeutic intervention plan?
Different therapeutic interventions for DSD are discussed elsewhere in the literature. The treatment plan should be patient centered. EUS botulinum toxin injection and a bladder drainage strategy, preferably with clean intermittent catheterization, are the mainstay when managing DSD in SCI patients. Other therapeutic options include oral drugs (alpha-blockers), EUS stents, and EUS sphincterotomy [].
In this review, we aim to audit the literature, focusing on the evaluation methods of DSD in SCI patients, including urodynamics settings and the assessment of other clinical dimensions. The International Classification of Function and Disability and Health [] provides the framework of reasoning.
2. Methods
We performed a review of the biomedical literature in PubMed/Medline database, according to the PRISMA checklist (Figure 3), applying the keywords: “detrusor sphincter dyssynergia”, “bladder sphincter dyssynergia”, “neurogenic bladder spinal cord”, “detrusor sphincter dyssynergia”, “dyssynergie vésico-sphinctérienne”, and filtered for articles with an abstract in English, French, Portuguese, and Spanish from 1976 to 2022.
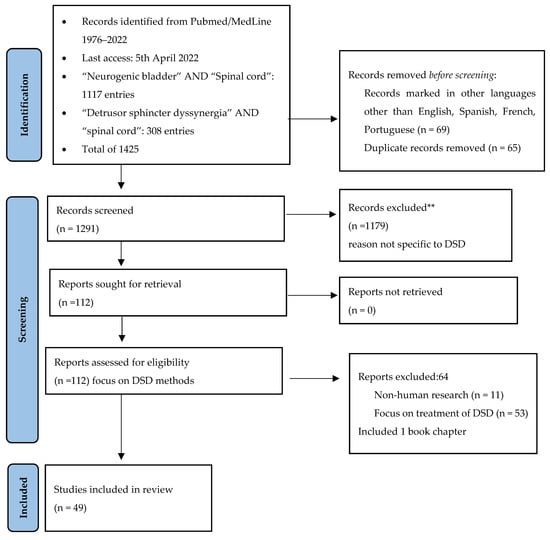
Figure 3.
Literature review according to PRISMA flow chart.
Employing the above-mentioned criteria, the search for “Detrusor sphincter dyssynergia” resulted in 851 heterogeneous results. Similarly, combining “neurogenic bladder” and “spinal cord” resulted in a broader sample of 1007 disparate papers. This led us to narrow the search, combining keywords as following: “spinal cord” and “detrusor sphincter dyssynergia”, thereby resulting in 295 articles. We further used cross-referencing to identify meaningful studies in this subject. The sampled articles were then sorted according to the following principles: describing at least one method for evaluating DSD, and with human clinical pertinence.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Urodynamics Evaluation of DSD in SCI Patients
Urodynamics investigation is the mainstay in evaluating neurogenic bladders, including DSD, in SCI patients. We should keep in mind that the presence of DSD criteria in the urodynamic testing of a patient with unknown spinal cord pathology should address further investigation of spinal cord involvement [,]. At the same time, the examiner should be aware that, during urodynamics, a neurologically intact subject may voluntarily contract the external sphincter during detrusor contractions [].
3.1.1. Filling Cystometry/Pressure-Flow Study/Urethral Pressure
Cystometry evaluates the filling and storage phases of detrusor function by measuring changes in the intravesical pressure that occur with increases in bladder volume. The normal adult bladder capacity is around 400–750 mL, with bladder pressure not exceeding 15 cm·H2O during the filling phase. During cystometry, the leak-point pressure (the pressure value at which voiding occurs) is also measured. Whenever this is higher than 40 cm·H2O, which is common in DSD, it indicates a risk of subsequent renal damage [,]. Other abnormal cystometry findings in DSD patients include decreased bladder compliance, which is hazardous for the kidneys [,].
In the literature about DSD assessment in SCI subjects, we found a diversity of invasive urodynamic setups either with or without a pressure-flow study. While there is unanimity in the measuring method of intravesical pressure [,,], the disagreement was due mainly to the different techniques employed to obtain and measure the signal to study EUS behavior, either with or without bladder neck involvement.
Indirect Assessment of EUS Activity
DSD cannot be diagnosed or evaluated via filling cystometry alone, without any trace of EUS activity either from image or EMG, as Versi et al. confirmed []. Nevertheless, Geirsson et al. [] showed that, in 76 patients (56 men and 20 women) with suspected DSD, an ice water test during urodynamics could replace the burden of EUS EMG. In their study, the absence of leakage, despite a sustained reflex detrusor contraction, after a rapid instillation of 100 mL of sterile ice-water correlated with DSD, also defined by EUS EMG activity.
In an urodynamics study comprising filling cystometry and a pressure-flow study, without any direct recording(s) of EUS activity, Schaefer et al. [] described that in the presence of a constant detrusor contractility, changes in outflow resistance will lead to changes in flow rate, which, in the absence of artifacts, may be an indication of DSD.
Voiding Cystourethrography (VCUG) and EUS EMG
VCUG [], either with or without EUS EMG monitoring, is preconized by the 2020 ICS standards for the diagnosis of DSD []. Normal EUS EMG findings include an increment in the EMG activity of the EUS during bladder filling, secondary to an increased recruitment of motor units. Secondly, before voiding, and prior to detrusor contraction, diminished EMG activity in the EUS is expected. Conversely, in DSD, when a decrease in the EMG activity would be physiologically expected, there is an abnormal pattern of EUS EMG, with the markedly increased EMG activity of the EUS being a hallmark of DSD [].
Blaivas et al., in 1981 [], defined DSD as an increased EUS EMG activity during an involuntary detrusor contraction and, described DSD by VCUG as a dilated posterior urethra obstructed by the contracted EUS. Although Blaivas used and recommended VCUG in combination with EMG when studying DSD, recognizing an additional diagnostic value, he did not evaluate the relationship between the two.
Interestingly, while assessing DSD in SCI patients, some authors found some discordance of diagnostic value between VCUG and EUS EMG. This is intuitive, as De et al. [] explained: in some patients who might present BND, the closed bladder neck on VCUG prevents the visualization of the EUS. The De et al. article summarizes the controversies on this topic very well, including the diversity of EUS EMG recording methods. They reviewed 49 urodynamics studies from patients diagnosed with DSD (gender distribution not mentioned): 10 patients with DSD criteria by VCUG lacked EMG abnormality; 11 patients with DSD by EMG had a closed bladder neck in VCUG result, and therefore did not have the criteria of DSD by VCUG. They found only 60% agreement (28 urodynamic studies) between wire needle EUS EMG and VCUG in diagnosing DSD. Thus, they suggested that a combination of EUS EMG and VCUG may identify more cases of DSD than either modality alone. Moreover, in two different studies, using skin patch EMG electrodes, Miller et al. [] and Spettel et al. [] also found disparate findings from VCUG coupled with EUS EMG versus EMG and VCUG used alone in identifying DSD. In addition, they suggested a combined used of EUS EMG monitoring and VCUG in urodynamics to avoid underdiagnosing DSD.
From a methodological standpoint, we did not find any research, for this literature review, comparing placement and/or type of EMG electrodes (skin patch/wire/concentric/coaxial needle) while monitoring EUS EMG in urodynamics.
EUS Pressure Measurement
The role of urethral pressure measurement and profilometry in the diagnosis of DSD is controversial and is considered by the ICS to be investigational []. In the literature. it is commonly used to appreciate DSD treatment outcome, such as in EUS botulinum toxin injection [], where a decrease in EUS pressure is expected.
In our review, we found a lack of consensus concerning the use of this measure in invasive urodynamics while evaluating DSD patients.
Specifically for investigating DSD, recorded urethral pressure in the internal and external sphincter regions was used by Schurch et al. [], and coupled with EMG recording in periurethral striated muscles by Yalla et al. []. Stoffel et al. routinely used urethral pressures as a complementary measurement for diagnosing DSD. [].
In a series of 42 male suprasacral SCI patients, Bary et al. [] found an add-value of intraurethral pressure measurement to characterize DSD, even in those patients who underwent sphincterotomy to treat DSD. They mentioned that, apparently, the combined recordings of detrusor pressure, EUS EMG, and VCUG, along with intraurethral dynamic pressure measurement, would be the best available method in assessing DSD in SCI patients. However, in the article by Suzuki et al. [], out of 72 patients (36 men, 36 women) diagnosed with DSD using the VCUG and EUS EMG setting, only 6 patients were diagnosed with DSD when only EUS pressure was considered. Their cutoff for EUS pressure variation to diagnose DSD was defined as any increase, maintenance, or decrease < 10 cm·H2O during the voiding phase. They concluded that the EUS sphincter pressure measurement alone is inaccurate and cannot replace the combined pelvic floor EMG and VCUG method to assess DSD. Conversely, in a more recent study, Corona et al. [] described a protocol for using urethral pressure during urodynamics for identifying patients with DSD. In their retrospective analysis of a database of 72 patients (42 men, 30 women) diagnosed with SCI or multiple sclerosis and urodynamic evidence of DSD based in VCUG or EUS EMG findings, EMG alone diagnosed DSD in 79%, VCUG alone in 63%, and a rise in urethral pressure > 20 cm·H2O as a single indicator of DSD occurred in 86%. The 20 cm·H2O cutoff is relatively specific to DSD patients, since only 8.7% (2 of 23) of the control neurogenic bladder patients with detrusor overactivity without DSD had a urethral pressure amplitude > 20 cm·H2O during detrusor contraction. This threshold of 20 cm·H2O rise in urethral pressure is also defined by Stoffel et al. [], who obtained similar outcomes in their series. The conflicting results on this topic [,,], which could be explained by different methodologies and defined pressure cutoffs, claim the need for further investigation.
3.1.2. DSD and BND
Urodynamics with VCUG can evaluate BND [,,]. Yalla et al. [] considered that internal sphincter dyssynergia alone in SCI patients is rarely seen. In Schurch et al.’s [] research, 44 urodynamics studies from 34 out of spinal shock SCI patients (28 men, 6 women) with upper motor neuron bladders were evaluated. Interestingly they were able to investigate BND and DSD, since their urodynamics framework included pressure transducers in the bladder, bladder neck, and membranous/bulbar urethra. They found BND and DSD were both present in almost all patients with complete SCI above T12, and that paraplegics with incomplete lesions had DSD without BND. Furthermore, all tetraplegics, either complete or incomplete, presented with BND associated with autonomic dysreflexia. According to Schurch, active BND was independent of EUS action. BND would occur when there was a disruption of the inhibitory influence of the parasympathetic system on the sympathetic control in the bladder neck. These findings should raise questions when considering treatment options in patients with complete SCI above T12, where interventions aiming only the EUS might fail. Soler et al. [] retrospectively studied the outcome predictors of EUS botulinum toxin injection as a therapeutic intervention in 99 adults male suprasacral SCI patients with DSD, and they determined that the presence of a BND in VCUG was a predictor of failure for this intervention.
3.1.3. Ultrasound and Urodynamics
In 1986, when diagnostic ultra-sound technology was in its early stages, Perkash et al. used combined urodynamics and transrectal sonography, which they found instrumental in their understanding of neurogenic voiding dysfunction, as well as the role that DSD plays []. In our PubMed/Medline search, we found only three other articles, all dating back to the 1980s, related to the simultaneous use of urodynamics and transrectal ultrasound [,,]. Shapeero et al. [] explored the bladder neck and urethra functions of 32 men with suspected bladder neuromuscular dysfunction using transrectal sonography, urodynamic studies, and VCUG. There were 27 coupled transrectal voiding sonography and urodynamic studies with recordings of periurethral EMG, VCUG, and urethral pressure. Shabsigh et al. [] performed 31 combined transrectal ultrasonographic and urodynamic studies in 24 suprasacral SCI male patients to study specifically DSD. A variety of urodynamic measurements, including bladder pressure, rectal pressure (obtained from the water-filled condom around the ultrasound probe), detrusor (subtraction) pressure, uroflow, and EUS EMG activity were recorded, and this technique was considered useful in evaluating DSD. Both authors [,] found a superiority in diagnostic accuracy of sonography when compared with VCUG, with an advantage/drawback trade-off favoring the ultrasound (an absence of irradiation exposure to the patient and examiner, the potential of imaging the periurethral and bladder soft tissue, and a longer duration of image acquisition). Given the paucity of research results found on urodynamics combined with ultrasound imaging techniques, whose technology has improved exponentially, we searched the literature for other possibilities in this field that might be of interest for the instrumental evaluation of DSD in SCI individuals. Contrast-enhanced voiding urosonography (ceVUS) is a well-established ultrasound method used in children for detecting and grading vesicoureteral reflux, as well as for urethral imaging [,]. Notwithstanding, since we did not find any publication on contrast-enhanced voiding urosonography coupled with urodynamics, it seems logical that, at least conceptually, this possibility merits dedicated research in evaluating DSD in SCI patients, especially when electronic pressure sensors will be widely available in urodynamics.
3.1.4. Uroflowmetry, Post Void Residual Volume (PVR) and Bladder Diary
While not specific to DSD, the measurement of the urinary flow rate in an SCI patient with DSD should confirm the presence of bladder outlet obstruction []. An intermittent or low flow and the presence of significant PVR in uroflowmetry in a SCI subject is highly suggestive of DSD []. In clinical practice, uroflowmetry or important PVR measured by ultrasound, indicating bladder outlet obstruction in an SCI patient, is a noninvasive procedure that should alert the clinician of the likelihood of DSD, fostering further urodynamics investigation. The same argument applies when there is evidence of urine retention in the data from a patient’s bladder or voiding diary, i.e., a daily record of the patient’s bladder functioning which provides an objective documentation of voiding pattern, sensation, volumes (including PVR), incontinence episodes, and events that might lead to an incontinent episode, or urine retention evidence []. PVR can also be used as an outcome to appreciate efficacy in DSD treatment [,].
3.2. Other Clinical Dimension in Evaluation of DSD in SCI Patients
3.2.1. Anamnesis
In SCI patients with DSD, anamnesis should ascertain comorbidities, past medical history, prior surgeries, bowel and sexual function, previous and present management of DSD, bladder emptying method, parenting desire, and factors implied in DSD management, such as prostate enlargement and post-obstetric urethral hypermobility [,]. Usual medication must be considered, with special attention paid to the anticholinergic burden, especially when dealing with older SCI patients presenting cognitive impairment either with or without glaucoma [,]. Clinicians should inquire for the availability of support, home and work circumstances, lifestyle factors, motivation for treatment, and risk for irritative conditions such as pressure ulcers. []. Special attention should be paid to clues of early clinical degradation, such as an aggravation of autonomic dysreflexia clinical pattern (episodes symptoms, duration, frequency, unknown trigger), recurrent urinary tract infections, and worsening signs of urinary retention. These should be kept in view in the therapeutic plan or while evaluating treatment outcomes [,]. Quality of life measures are common indicators of therapeutic success for DSD in SCI patients in the literature [] and are encouraged to be used in clinical practice [].
3.2.2. Physical Exam
SCI patients should have routine physical examination, including general neurologic examination, establishing SCI severity with a validated system such as the American Spinal Cord Injury (ASIA) score, (neurologic level and completeness of injury), verifying emergence from spinal shock by disclosure of the sacral metameric reflexes, which coincides with appearance of DSD, and searching for spasticity which is associated with DSD [,]. Physical exam should include a perineal examination, voluntary pelvic floor contractions, anal sphincter voluntary contraction and tone, sensation of the sacral dermatomes and testing the sacral reflexes (anocutaneous and respectively the bulbocavernosus and bulboanal in male or the clitoridocavernous, and clitoridoanal in female patients). An evaluation of the prostate is also important in men. Hand function should also be appreciated, expressly to assess the patient’s ability to practice clean intermittent bladder self-catheterization as a voiding method whether indicated; for this purpose, the pencil and paper test could be used [].
3.2.3. Complementary Diagnostic and Follow-Up
There are no one-size-fits-all surveillance workup protocols for these patients, but undoubtedly, a clinical frequent follow-up (annually for Corcos et al. []) is advised for this population of patients, and should include [,,] the assessment of:
- renal function:
- ○
- routine: plasma concentration of electrolytes, urea, creatinine (or cystatin C), 24 h creatinine clearance.
- ○
- optional or with special indication: kidney scintigraphy.
- upper and lower urinary tract structural changes:
- ○
- routine: upper and lower tract transabdominal ultrasound examination with morphometric measures and PVR estimation, screening for lithiasis, bladder trabeculation, and diverticula.
- ○
- optional or with special indication: VCUG, urethro-cystoscopy, transrectal ultrasound for prostate assessment, long term screening of neoplasms.
- screening for lower urinary tract bacterial colonization. Asymptomatic bacteriuria in these population should not be treated with antibiotics.
3.2.4. Autonomic Dysreflexia and DSD
Autonomic dysreflexia is an abnormal autonomic reflex responding to nociceptive stimuli below the level of injury, which develops in patients with high-level SCI (usually above T6) and is commonly associated with DSD []. A remarkable rise in blood pressure during an autonomic dysreflexia episode sometimes leads to serious complications, such as intracranial hemorrhage and lethal arrhythmias [,]. Physicians should remove the causes of the stimuli as soon as possible, and deal with the hypertensive crisis. When DSD is suspected in a patient undergoing invasive urodynamics, an infusion debit of 20 mL/min during cystometry is advised. Furthermore, symptoms and blood pressure should be carefully monitored during examinations that require bladder filling (urodynamics [], cystoscopy []). In SCI with DSD, an aggravation of autonomic dysreflexia should prompt for more DSD aggressive treatment [].
4. Conclusions
In SCI patients, anamnesis, symptoms, and signs related to neurogenic bladder, including DSD, may correlate poorly with urodynamics severity parameters. Still, careful history taking, clinical presentation, and bladder diary data have valuable information for urodynamics interpretation and should be coherent with urodynamics findings. Moreover, irritative conditions, such as pressure ulcers and anorectal problems, medication that influences DSD, and autonomic dysreflexia manifestations should be considered when analyzing urodynamics results. On the other hand, in SCI with DSD, urodynamics severity parallels with progression to deterioration of the upper renal tract and kidneys and is the basis of diagnosis and of the management plan in these patients.
Although this literature review sheds a light on the lack of consensus in the instrumental evaluation methods of DSD in SCI, which are a synonym of ongoing progress in this discipline, it also highlights the valuable effort being realized in urodynamics standardization. From our literature review, it emerges that urodynamics with coupled EUS EMG and VCUG, either with or without EUS pressure measurement, adds accuracy in diagnosing DSD in SCI individuals. In any case, since DSD is very prevalent in suprasacral SCI patients out of spinal shock phase, clinicians should have a high suspicion of its diagnosis in that context. When dealing with SCI patients with DSD, other clinical parameters, as well as urodynamics, are worthy when tailoring the management and treatment strategy.
Finally, more important than distinguishing the type of DSD, clinicians taking care of SCI patients must be aware of the evolutive natural history of DSD if left untreated, as well as its menacing consequences. Similar to other forms of neurogenic bladder, the goal in managing DSD in SCI patients is to define a follow-up and therapeutic intervention plans conducive to attain the best compromise between, on the one hand, quality of life, and social participation, and, on the other hand, protection of the urinary system.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.A.P.; methodology, J.A.P.; software, J.A.P.; validation, J.A.P. and T.D.; formal analysis, J.A.P.; investigation, J.A.P.; resources, J.A.P. and T.D.; data curation, J.A.P. and T.D.; writing—original draft preparation, J.A.P.; writing—review and editing, J.A.P. and T.D.; visualization, J.A.P. and T.D.; supervision, T.D.; project administration, J.A.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Jean-François Wilmart M.D. and Sylvie Foucret, for their careful reading and valuable remarks.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| BND | Bladder Neck Dyssynergia |
| DSD | Detrusor External Sphincter Dyssynergia |
| EMG | Electromyography |
| EUS | External Urethral Sphincter |
| ICS | International Continence Society |
| PVR | Post Void Residual Volume |
| SCI | Spinal Cord Injury |
| VCUG | Voiding cystourethrography |
References
- Abrams, P.; Cardozo, L.; Fall, M.; Griffiths, D.; Rosier, P.; Ulmsten, U.; Van Kerrebroeck, P.; Victor, A.; Wein, A.; Standardisation Sub-committee of the International Continence Society. The standardisation of terminology of lower urinary tract function: Report from the standardisation sub-committee of the International Continence Society. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2002, 21, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Ancona, C.; Haylen, B.; Oelke, M.; Abranches-Monteiro, L.; Arnold, E.; Goldman, H.; Hamid, R.; Homma, Y.; Marcelissen, T.; Rademakers, K.; et al. The International Continence Society (ICS) report on the terminology for adult male lower urinary tract and pelvic floor symptoms and dysfunction. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2019, 38, 433–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siroky, M.B.; Krane, R.J. Neurologic Aspects of Detrusor-sphincter Dyssynergia, with Reference to the Guarding Reflex. J. Urol. 1982, 127, 953–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoffel, J.T. Detrusor sphincter dyssynergia: A review of physiology, diagnosis, and treatment strategies. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2016, 5, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaivas, J.G.; Sinha, H.P.; Zayed, A.A.; Labib, K.B. Detrusor-external Sphincter Dyssynergia: A Detailed Electromyographic Study. J. Urol. 1981, 125, 545–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yalla, S.V.; Blunt, K.J.; Fam, B.A.; Constantinople, N.L.; Gutes, R.F. Detrusor-Urethral Sphincter Dyssynergia. J. Urol. 1977, 118, 1026–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schurch, B.; Yasuda, K.; Rossier, A.B. Detrusor Bladder Neck Dyssynergia Revisited. J. Urol. 1994, 152 Pt 1, 2066–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarenco, G.; Ismael, S.S.; Soler, J.M. The dyssynergic sphincter. In Textbook of the Neurogenic Bladder; Corcos, J., Ginsberg, D., Karsenty, G., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 133–137. [Google Scholar]
- Gross, O.; Leitner, L.; Rasenack, M.; Schubert, M.; Kessler, T.M. Detrusor sphincter dyssynergia: Can a more specific definition distinguish between patients with and without an underlying neurological disorder? Spinal Cord 2021, 59, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Deng, H.; Li, X.; Liao, L. The Video-Urodynamic and Electrophysiological Characteristics in Patients with Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury. Int. Neurourol. J. 2021, 25, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, J.H.; Choi, W.J.; Lee, K.Y.; Jung, T.Y.; Lee, J.K.; Park, W.H.; Shim, H.B. Complications of the upper urinary tract in patients with spinal cord injury: A long-term follow-up study. Urol. Res. 2005, 33, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Danforth, T.; Ginsberg, D.A. Urologic Management and Complications in Spinal Cord Injury Patients: A 40- to 50-year Follow-up Study. Urology 2017, 104, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackler, R.H. A 25-Year Prospective Mortality Study in the Spinal Cord Injured Patient: Comparison with the Long-Term Living Paraplegic. J. Urol. 1977, 117, 486–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.Q.; Franco, I. Management of vesicoureteral reflux in neurogenic bladder. Investig. Clin. Urol. 2017, 58 (Suppl. 1), S54–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkash, I. Autonomic dysreflexia and detrusor-sphincter dyssynergia in spinal cord injury patients. J. Spinal Cord Med. 1997, 20, 365–370. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. International Classification of Functioning, Disability, and Health: ICF; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, H.A.; Nettleton, J.; Blain, C.; Dalton, C.; Farhan, B.; Fernandes, A.; Georgopoulos, P.; Klepsch, S.; Lavelle, J.; Martinelli, E.; et al. Assessment of patients with lower urinary tract symptoms where an undiagnosed neurological disease is suspected: A report from an International Continence Society consensus working group. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2020, 39, 2535–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.U.; Shergill, I.S.; Arya, M.; Shah, P.J.R. Management of detrusor–external sphincter dyssynergia. Nat. Clin. Pract. Urol. 2006, 3, 368–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekido, N.; Igawa, Y.; Kakizaki, H.; Kitta, T.; Sengoku, A.; Takahashi, S.; Takahashi, R.; Tanaka, K.; Namima, T.; Honda, M.; et al. Clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of lower urinary tract dysfunction in patients with spinal cord injury. Int. J. Urol. 2020, 27, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosier, P.F.; Schaefer, W.; Lose, G.; Goldman, H.B.; Guralnick, M.; Eustice, S.; Dickinson, T.; Hashim, H. International Continence Society Good Urodynamic Practices and Terms 2016: Urodynamics, uroflowmetry, cystometry, and pressure-flow study. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2016, 36, 1243–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, W.; Abrams, P.; Liao, L.; Mattiasson, A.; Pesce, F.; Spangberg, A.; Sterling, A.M.; Zinner, N.R.; van Kerrebroeck, P.; International Continence Society. Good urodynamic practices: Uroflowmetry, filling cystometry, and pressure-flow studies. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2002, 21, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamorro, M.V.; Casado, J.S.; Zurbano, J.M.A.; del Pino, F.T.; Alba, D.V. Evidence-based medicine. Usefulness of isolated cystomanometry for the diagnosis of periurethral detrusor-sphincter dyssynergia in patients with suprasacral lesion. Arch. Esp. Urol. 1999, 52, 1073–1078. (In Spanish) [Google Scholar]
- Geirsson, G.; Fall, M. The Ice-Water Test in the Diagnosis of Detrusor-External Sphincter Dyssynergia. Scand. J. Urol. Nephrol. 1995, 29, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chancellor, M.B.; Kaplan, S.A.; Blaivas, J.G. Detrusor-external sphincter dyssynergia. Ciba Found. Symp. 1990, 151, 195–206. [Google Scholar]
- De, E.J.; Patel, C.Y.; Tharian, B.; Westney, O.L.; Graves, D.E.; Hairston, J.C. Diagnostic discordance of electromyography (EMG) versus voiding cystourethrogram (VCUG) for detrusor-external sphincter dyssynergy (DESD). Neurourol. Urodyn. 2005, 24, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, B.D.; Tallman, C.T.; Boone, T.B.; Khavari, R. Low Interrater Reliability of Videourodynamic Diagnosis of Detrusor External Sphincter Dyssynergia. Female Pelvic Med. Reconstr. Surg. 2021, 27, 297–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spettel, S.; Kalorin, C.; De, E. Combined Diagnostic Modalities Improve Detection of Detrusor External Sphincter Dyssynergia. ISRN Obstet. Gynecol. 2011, 2011, 323421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lose, G.; Griffiths, D.; Hosker, G.; Kulseng-Hanssen, S.; Perucchini, D.; Schäfer, W.; Thind, P.; Versi, E.; Standardization Sub-Committee; International Continence Society. Standardisation of urethral pressure measurement: Report from the standardisation sub-committee of the International Continence Society. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2002, 21, 258–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykstra, D.D.; Sidi, A.A.; Scott, A.B.; Pagel, J.M.; Goldish, G.D. Effects of Botulinum a Toxin on Detrusor-Sphincter Dyssynergia in Spinal Cord Injury Patients. J. Urol. 1988, 139, 919–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bary, P.R.; Day, G.; Lewis, P.; Chawla, J.; Evans, C.; Stephenson, T.P. Dynamic Urethral Function in the Assessment of Spinal Injury Patients. Br. J. Urol. 1982, 54, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellucci, C.; Wöllner, J.; Gregorini, F.; Birnböck, D.; Kozomara, M.; Mehnert, U.; Kessler, T.M. External Urethral Sphincter Pressure Measurement: An Accurate Method for the Diagnosis of Detrusor External Sphincter Dyssynergia? PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e37996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Corona, L.E.; Cameron, A.P.; Clemens, J.Q.; Qin, Y.; Stoffel, J.T. Urethral Pressure Measurement as a Tool for the Urodynamic Diagnosis of Detrusor Sphincter Dyssynergia. Int. Neurourol. J. 2018, 22, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soler, J.M.; Previnaire, J.G.; Hadiji, N. Predictors of outcome for urethral injection of botulinum toxin to treat detrusor sphincter dyssynergia in men with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 2016, 54, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkash, I. Physical medicine and rehabilitation: Sonographic urodynamics. West. J. Med. 1986, 144, 736. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Perkash, I.; Friedland, G.W. Catheter-induced hyperreflexia in spinal cord injury patients: Diagnosis by sonographic voiding cystourethrography. Radiology 1986, 159, 453–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapeero, L.; Friedland, G.; Perkash, I. Transrectal sonographic voiding cystourethrography: Studies in neuromuscular bladder dysfunction. Am. J. Roentgenol. 1983, 141, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabsigh, R.; Fishman, I.; Krebs, M. Combined Transrectal Ultrasonography and Urodynamics in the Evaluation of Detrusor-sphincter Dyssynergia. Br. J. Urol. 1988, 62, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ntoulia, A.; Pascual, E.A.; Back, S.J.; Bellah, R.D.; Salazar, V.P.B.; Chan, P.K.J.; Chow, J.S.; Robinot, D.C.; Darge, K.; Duran, C.; et al. Contrast-enhanced voiding urosonography, part 1: Vesicoureteral reflux evaluation. Pediatr. Radiol. 2021, 51, 2351–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnewolt, C.E.; Acharya, P.T.; Pascual, E.A.; Back, S.J.; Salazar, V.P.B.; Chan, P.K.J.; Chow, J.S.; Robinot, D.C.; Darge, K.; Duran, C.; et al. Contrast-enhanced voiding urosonography part 2: Urethral imaging. Pediatr. Radiol. 2021, 51, 2368–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarenco, G.; Ismaël, S.S.; Chesnel, C.; Charlanes, A.; Breton, F.L.E. Diagnosis and clinical evaluation of neurogenic bladder. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2017, 53, 975–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Liao, C.-H.; Kuo, H.-C. Therapeutic effects of detrusor botulinum toxin A injection on neurogenic detrusor overactivity in patients with different levels of spinal cord injury and types of detrusor sphincter dyssynergia. Spinal Cord 2011, 49, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habchi, H.; Galaup, J.-P.; Morel-Journel, N.; Ruffion, A. Toxine botulique A et dyssynergie vésico-sphinctérienne: Étude rétrospective portant sur 47 patients. Prog. Urol. 2014, 24, 234–239. (In French) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, M.J.; Apostolidis, A.; Cocci, A.; Emmanuel, A.; Gajewski, J.B.J.B.; Harrison, S.C.W.S.C.; Heesakkers, J.P.F.J.P.; Lemack, G.G.E.; Madersbacher, H.; Panicker, J.N.J.N.; et al. Neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction: Clinical management recommendations of the Neurologic Incontinence committee of the fifth International Consultation on Incontinence 2013. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2016, 35, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, C.; Gallacher, K.; Nakham, A.; Cruickshank, M.; Newlands, R.; Bond, C.; Myint, P.K.; Bhattacharya, D.; Mair, F.S. Barriers and facilitators to reducing anticholinergic burden: A qualitative systematic review. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2021, 43, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amarenco, G.; Guinet, A.; Jousse, M.; Verollet, D.; Ismael, S.S. Pencil and Paper Test: A New Tool to Predict the Ability of Neurological Patients to Practice Clean Intermittent Self-Catheterization. J. Urol. 2011, 185, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahfouz, W.; Corcos, J. Management of detrusor external sphincter dyssynergia in neurogenic bladder. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2011, 47, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-I.; Tan, C.O. Alterations in autonomic cerebrovascular control after spinal cord injury. Auton. Neurosci. 2018, 209, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.; Rabchevsky, A.G. Autonomic Consequences of Spinal Cord Injury. Compr. Physiol. 2014, 4, 1419–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, C.H.; Khonsari, F.; Vaziri, N.D.; Byrne, C.; Gordon, S.; Friis, R. The Effect of Modified Transurethral Sphincterotomy on Autonomic Dysreflexia. J. Urol. 1986, 135, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).