Metabolic Syndrome, Hepatic Steatosis and Testosterone: A Matter of Sex
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Hepatic Steatosis
1.2. Metabolic Syndrome
2. Metabolic Syndrome and Hepatic Steatosis: Gender Differences
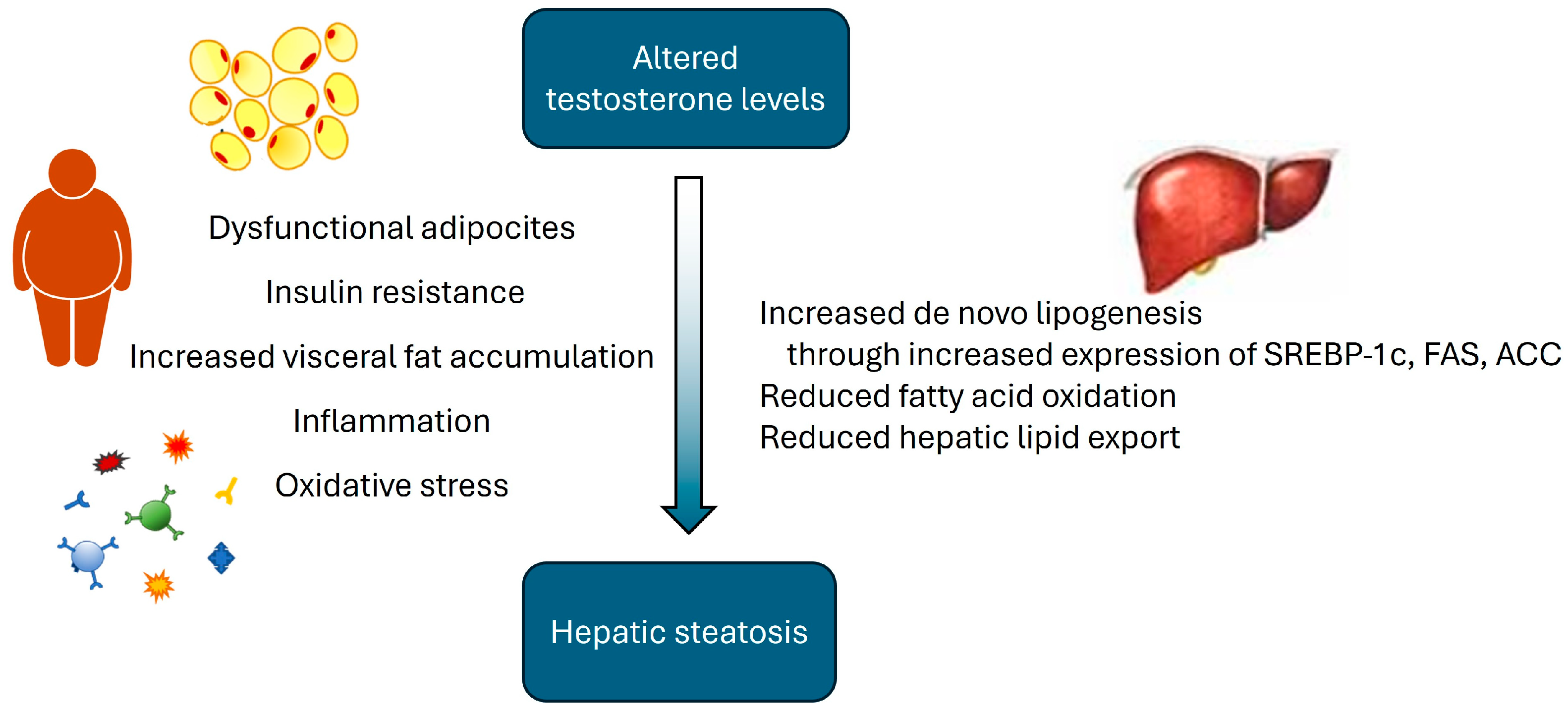
2.1. Metabolic Syndrome, Hepatic Steatosis and Androgens in Male Hypogonadism
2.2. Metabolic Syndrome, Hepatic Steatosis and Androgens in Female Hyperandrogenism
3. The Role of Estrogens: Hypogonadism in Females
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boutari, C.; Mantzoros, C.S. A 2022 update on the epidemiology of obesity and a call to action: As its twin COVID-19 pandemic appears to be receding, the obesity and dysmetabolism pandemic continues to rage on. Metabolism 2022, 133, 155217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, K.L.; Stafford, L.K.; McLaughlin, S.A.; Boyko, E.J.; Vollset, S.E.; Smith, A.E.; Dalton, B.E.; Duprey, J.; Cruz, J.A.; Hagins, H.; et al. Global, regional, and national burden of diabetes from 1990 to 2021, with projections of prevalence to 2050: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2023, 402, 203–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Golabi, P.; Paik, J.M.; Henry, A.; Van Dongen, C.; Henry, L. The global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): A systematic review. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslam, M.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Dufour, J.-F.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacke, F.; Horn, P.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Ratziu, V.; Bugianesi, E.; Francque, S.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Valenti, L.; Roden, M.; Schick, F.; et al. EASL–EASD–EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). J. Hepatol. 2024, 81, 492–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanni, E.; Bugianesi, E.; Kotronen, A.; De Minicis, S.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; Svegliati-Baroni, G. From the metabolic syndrome to NAFLD or vice versa? Dig. Liver Dis. 2010, 42, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Day, C.P. Progression of NAFLD to diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease or cirrhosis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yki-Järvinen, H. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease as a cause and a consequence of metabolic syndrome. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonardo, A.; Ballestri, S.; Marchesini, G.; Angulo, P.; Loria, P. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A precursor of the metabolic syndrome. Dig. Liver Dis. 2015, 47, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease—Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quek, J.; Chan, K.E.; Wong, Z.Y.; Tan, C.; Tan, B.; Lim, W.H.; Tan, D.J.H.; Tang, A.S.P.; Tay, P.; Xiao, J.; et al. Global prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in the overweight and obese population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Stepanova, M.; Ong, J.; Trimble, G.; AlQahtani, S.; Younossi, I.; Ahmed, A.; Racila, A.; Henry, L. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Is the Most Rapidly Increasing Indication for Liver Transplantation in the United States. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 19, 580–589.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; LaVine, J.E.; Charlton, M.; Cusi, K.; Rinella, M.; Harrison, S.A.; Brunt, E.M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 67, 328–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowman, J.; Tomlinson, J.; Newsome, P. Pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. QJM Int. J. Med. 2010, 103, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A. Hepatic Lipotoxicity and the Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: The Central Role of Nontriglyceride Fatty Acid Metabolites. Hepatology 2010, 52, 774–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonardo, A.; Carani, C.; Carulli, N.; Loria, P. ‘Endocrine NAFLD’ a hormonocentric perspective of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease pathogenesis. J. Hepatol. 2006, 44, 1196–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzzetti, E.; Pinzani, M.; Tsochatzis, E.A. The multiple-hit pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Metabolism 2016, 65, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; Sanyal, A.J.; George, J.; Panel, I.C. MAFLD: A Consensus-Driven Proposed Nomenclature for Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1999–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, S.; Loomba, R. Review article: Emerging role of the gut microbiome in the progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and potential therapeutic implications. Aliment. Pharmacol Ther. 2019, 50, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangitano, E.; Corradini, S.G.; Lubrano, C.; Gnessi, L. La Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, una patologia epatica di interesse endocrinologico. L’Endocrinologo 2021, 5, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirpich, I.A.; Marsano, L.S.; McClain, C.J. Gut-liver axis, nutrition, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Biochem. 2015, 48, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Kesika, P.; Suganthy, N.; Chaiyasut, C. A Review on Role of Microbiome in Obesity and Antiobesity Properties of Probiotic Supplements. Hindawi BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 3291367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nor, M.H.M.; Ayob, N.; Mokhtar, N.M.; Ali, R.A.R.; Tan, G.C.; Wong, Z.; Shafiee, N.H.; Wong, Y.P.; Mustangin, M.; Nawawi, K.N.M. The Effect of Probiotics (MCP® BCMC® Strains) on Hepatic Steatosis, Small Intestinal Mucosal Immune Function, and Intestinal Barrier in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpi, R.Z.; Barbalho, S.M.; Sloan, K.P.; Laurindo, L.F.; Gonzaga, H.F.; Grippa, P.C.; Zutin, T.L.M.; Girio, R.J.S.; Repetti, C.S.F.; Detregiachi, C.R.P.; et al. The Effects of Probiotics, Prebiotics and Synbiotics in Non-Alcoholic Fat Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spooner, H.C.; Derrick, S.A.; Maj, M.; Manjarín, R.; Hernandez, G.V.; Tailor, D.S.; Bastani, P.S.; Fanter, R.K.; Fiorotto, M.L.; Burrin, D.G.; et al. High-Fructose, High-Fat Diet Alters Muscle Composition and Fuel Utilization in a Juvenile Iberian Pig Model of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marjot, T.; Tomlinson, J.W.; Hodson, L.; Ray, D.W. Timing of energy intake and the therapeutic potential of intermittent fasting and time-restricted eating in NAFLD. Gut 2023, 72, 1607–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Lin, B.; Huang, Y.; Yang, S.; Huang, C.; Shi, L.; Liu, D.; Zhang, P.; Lin, J.; Xu, B.; et al. Effects of Time-Restricted Eating on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e233513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.-J.; He, J.; Pan, L.-L.; Ma, Z.-M.; Han, C.-K.; Chen, C.-S.; Chen, Z.; Han, H.-W.; Chen, S.; Sun, Q.; et al. Effects of Moderate and Vigorous Exercise on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. JAMA Intern. Med. 2016, 176, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Pan, L.; Ma, Z.; Chen, Z.; Huang, Z.; Sun, Q.; Lu, Y.; Han, C.; Lin, M.; Li, X.; et al. Long-term effect of exercise on improving fatty liver and cardiovascular risk factors in obese adults: A 1-year follow-up study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahed, G.; Aoun, L.; Bou Zerdan, M.; Allam, S.; Bou Zerdan, M.; Bouferraa, Y.; Assi, H.I. Metabolic Syndrome: Updates on Pathophysiology and Management in 2021. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, J.L.S.; Barbalho, S.M.; de Araujo, R.R.; Bechara, M.D.; Sloan, K.P.; Sloan, L.A. Metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular diseases: Going beyond traditional risk factors. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2022, 38, e3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galassi, A.; Reynolds, K.; He, J. Metabolic Syndrome and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Med. 2006, 119, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tune, J.D.; Goodwill, A.G.; Sassoon, D.J.; Mather, K.J. Cardiovascular consequences of metabolic syndrome. Transl. Res. 2017, 183, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duell, P.B.; Welty, F.K.; Miller, M.; Chait, A.; Hammond, G.; Ahmad, Z.; Cohen, D.E.; Horton, J.D.; Pressman, G.S.; Toth, P.P.; et al. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Cardiovascular Risk: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2022, 42, E168–E185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzurović, E.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Mantzoros, C. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome and their association with vascular risk. Metabolism 2021, 119, 154770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeren, J.; Scheja, L. Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease and lipoprotein metabolism. Mol. Metab. 2021, 50, 101238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangitano, E.; Gnessi, L.; Lenzi, A.; Ray, D. Chronobiology and Metabolism: Is Ketogenic Diet Able to Influence Circadian Rhythm? Front. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 756970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecora, G.; Sciarra, F.; Gangitano, E.; Venneri, M.A. How Food Choices Impact on Male Fertility. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2023, 12, 864–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangitano, E.; Baxter, M.; Voronkov, M.; Lenzi, A.; Gnessi, L.; Ray, D. The interplay between macronutrients and sleep: Focus on circadian and homeostatic processes. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1166699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangitano, E.; Tozzi, R.; Mariani, S.; Lenzi, A.; Gnessi, L.; Lubrano, C. Ketogenic Diet for Obese COVID-19 Patients: Is Respiratory Disease a Contraindication? A Narrative Review of the Literature on Ketogenic Diet and Respiratory Function. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 771047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangitano, E.; Tozzi, R.; Gandini, O.; Watanabe, M.; Basciani, S.; Mariani, S.; Lenzi, A.; Gnessi, L.; Lubrano, C. Ketogenic diet as a preventive and supportive care for COVID-19 patients. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangitano, E.; Martinez-Sanchez, N.; Bellini, M.I.; Urciuoli, I.; Monterisi, S.; Mariani, S.; Ray, D.; Gnessi, L. Weight Loss and Sleep, Current Evidence in Animal Models and Humans. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangitano, E.; Gnessi, L.; Merli, M. Protein Catabolism and the Dysregulation of Energy Intake-Related Hormones May Play a Major Role in the Worsening of Malnutrition in Hospitalized Cirrhotic Patients. Livers 2022, 2, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masi, D.; Gangitano, E.; Criniti, A.; Ballesio, L.; Anzuini, A.; Marino, L.; Gnessi, L.; Angeloni, A.; Gandini, O.; Lubrano, C. Obesity-Associated Hepatic Steatosis, Somatotropic Axis Impairment, and Ferritin Levels Are Strong Predictors of COVID-19 Severity. Viruses 2023, 15, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risi, R.; Masieri, S.; Poggiogalle, E.; Watanabe, M.; Caputi, A.; Tozzi, R.; Gangitano, E.; Masi, D.; Mariani, S.; Gnessi, L.; et al. Nickel sensitivity is associated with gh-igf1 axis impairment and pituitary abnormalities on mri in overweight and obese subjects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauvais-Jarvis, F. Sex differences in energy metabolism: Natural selection, mechanisms and consequences. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2024, 20, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.N.; O’Sullivan, A.J. Sex differences in energy metabolism need to be considered with lifestyle modifications in humans. J. Nutr. Metab. 2011, 2011, 391809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tramunt, B.; Smati, S.; Grandgeorge, N.; Lenfant, F.; Arnal, J.-F.; Montagner, A.; Gourdy, P. Sex differences in metabolic regulation and diabetes susceptibility. Diabetologia 2019, 63, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wei, Y.; Huang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, K.; Yang, W.; Chen, J.; Chen, J. Important Hormones Regulating Lipid Metabolism. Molecules 2022, 27, 7052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwyer, A.A.; Quinton, R. The metabolic syndrome in central hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism. Front. Horm. Res. 2018, 49, 156–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaruvongvanich, V.; Sanguankeo, A.; Riangwiwat, T.; Upala, S. Testosterone, sex hormone-binding globulin and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Hepatol. 2017, 16, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escobar-Morreale, H.F.; Álvarez-Blasco, F.; Botella-Carretero, J.I.; Luque-Ramírez, M. The striking similarities in the metabolic associations of female Androgen excess and male Androgen deficiency. Hum. Reprod. 2014, 29, 2083–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lonardo, A.; Nascimbeni, F.; Ballestri, S.; Fairweather, D.; Win, S.; Than, T.A.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Suzuki, A. Sex differences in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease state of the art and identification of research gaps. Hepatology 2019, 70, 1457–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolaou, N.; Gathercole, L.L.; Marchand, L.; Althari, S.; Dempster, N.J.; Green, C.J.; van de Bunt, M.; McNeil, C.; Arvaniti, A.; Hughes, B.A.; et al. AKR1D1 is a novel regulator of metabolic phenotype in human hepatocytes and is dysregulated in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Metabolism 2019, 99, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnard, L.; Nikolaou, N.; Louw, C.; Schiffer, L.; Gibson, H.; Gilligan, L.C.; Gangitano, E.; Snoep, J.; Arlt, W.; Tomlinson, J.W.; et al. The A-ring reduction of 11-ketotestosterone is efficiently catalysed by AKR1D1 and SRD5A2 but not SRD5A1. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 202, 105724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appanna, N.; Gibson, H.; Gangitano, E.; Dempster, N.J.; Morris, K.; George, S.; Arvaniti, A.; Gathercole, L.L.; Keevil, B.; Penning, T.M.; et al. Differential activity and expression of human 5β-reductase (Akr1d1) splice variants. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2021, 66, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pivonello, R.; Menafra, D.; Riccio, E.; Garifalos, F.; Mazzella, M.; de Angelis, C.; Colao, A. Metabolic disorders and male hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhasin, S.; Brito, J.P.; Cunningham, G.R.; Hayes, F.J.; Hodis, H.N.; Matsumoto, A.M.; Snyder, P.J.; Swerdloff, R.S.; Wu, F.C.; Yialamas, M.A. Testosterone Therapy in Men with Hypogonadism: An Endocrine Society. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 1715–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isidori, A.M.; Aversa, A.; Calogero, A.; Ferlin, A.; Francavilla, S.; Lanfranco, F.; Pivonello, R.; Rochira, V.; Corona, G.; Maggi, M. Adult- and late-onset male hypogonadism: The clinical practice guidelines of the Italian Society of Andrology and Sexual Medicine (SIAMS) and the Italian Society of Endocrinology (SIE). J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2022, 45, 2385–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, G.; Mannucci, E.; Fisher, A.D.; Lotti, F.; Petrone, L.; Balercia, G.; Bandini, E.; Forti, G.; Maggi, M. Low levels of androgens in men with erectile dysfunction and obesity. J. Sex. Med. 2008, 5, 2454–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.; Kim, Y.-S.; Son, E.S.; Kim, K.-N.; Kim, B.-T.; Lee, D.-J.; Kim, K.-M. Total testosterone and sex hormone-binding globulin are associated with metabolic syndrome independent of age and body mass index in Korean men. Maturitas 2013, 74, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupelian, V.; Page, S.T.; Araujo, A.B.; Travison, T.G.; Bremner, W.J.; McKinlay, J.B. Low sex hormone-binding globulin, total testosterone, and symptomatic androgen deficiency are associated with development of the metabolic syndrome in nonobese men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- E Laaksonen, D.; Niskanen, L.; Punnonen, K.; Nyyssönen, K.; Tuomainen, T.-P.; Salonen, R.; Rauramaa, R.; Salonen, J.T. Sex hormones, inflammation and the metabolic syndrome: A population-based study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2003, 149, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laaksonen, D.E.; Niskanen, L.; Punnonen, K.; Nyyssönen, K.; Tuomainen, T.-P.; Valkonen, V.-P.; Salonen, J.T. The metabolic syndrome and smoking in relation to hypogonadism in middle-aged men: A prospective cohort study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 712–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, C.J.; Chacko, E.C.; Pappachan, J.M. Male Obesity-related Secondary Hypogonadism—Pathophysiology, Clinical Implications and Management. Eur. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, E.M.; Huhtaniemi, I.T.; O’Neill, T.W.; Finn, J.D.; Pye, S.R.; Lee, D.M.; Tajar, A.; Bartfai, G.; Boonen, S.; Casanueva, F.F.; et al. Age-associated changes in hypothalamic-pituitary-testicular function in middle-aged and older men are modified by weight change and lifestyle factors: Longitudinal results from the European Male Ageing Study. Eur. J. Endocrinol./Eur. Fed. Endocr. Soc. 2013, 168, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corona, G.; Rastrelli, G.; Monami, M.; Saad, F.; Luconi, M.; Lucchese, M.; Facchiano, E.; Sforza, A.; Forti, G.; Mannucci, E.; et al. Body weight loss reverts obesity-associated hypogonadotropic hypogonadism: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 168, 829–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, P.G. The hypogonadal–obesity cycle: Role of aromatase in modulating the testosterone–estradiol shunt–a major factor in the genesis of morbid obesity. Med. Hypotheses 1999, 52, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aftab, S.A.S.; Kumar, S.; Barber, T.M. The role of obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus in the development of male obesity-associated secondary hypogonadism. Clin. Endocrinol. 2013, 78, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitteloud, N.; Dwyer, A.A.; DeCruz, S.; Lee, H.; Boepple, P.A.; Crowley, W.F.; Hayes, F.J. Inhibition of Luteinizing Hormone Secretion by Testosterone in Men Requires Aromatization for Its Pituitary but Not Its Hypothalamic Effects: Evidence from the Tandem Study of Normal and Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone-Deficient Men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, T.; Kennedy, R. Cytokines and hypothalamic-pituitary function. Cytokine 1993, 5, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Poll, T.; Romijn, J.A.; Endert, E.; Sauerwein, H.P. Effects of tumor necrosis factor on the hypothalamic-pituitary-testicular axis in healthy men. Metabolism 1993, 42, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, S.H.; Small, C.J.; Stanley, S.A.; Franks, S.; Ghatei, M.A.; Bloom, S.R. The In Vitro Role of Tumour Necrosis Factor-Alpha and Interleukin-6 in the Hypothalamic-Pituitary Gonadal Axis. J. Neuroendocr. 2001, 13, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, P.M.; Kelly, D.M.; Jones, T.H. Testosterone and insulin resistance in the metabolic syndrome and T2DM in men. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2013, 9, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isidori, A.M.; Caprio, M.; Strollo, F.; Moretti, C.; Frajese, G.; Isidori, A.; Fabbri, A. Leptin and androgens in male obesity: Evidence for leptin contribution to reduced androgen levels. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 84, 3673–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Völzke, H.; Aumann, N.; Krebs, A.; Nauck, M.; Steveling, A.; Lerch, M.M.; Rosskopf, D.; Wallaschofski, H. Hepatic steatosis is associated with low serum testosterone and high serum DHEAS levels in men. Int. J. Androl. 2010, 33, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kwon, H.; Park, J.-H.; Cho, B.; Kim, D.; Oh, S.-W.; Lee, C.M.; Choi, H.-C. A low level of serum total testosterone is independently associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazo, M.; Zeb, I.; Nasir, K.; Tracy, R.P.; Budoff, M.J.; Ouyang, P.; Vaidya, D. Association Between Endogenous Sex Hormones and Liver Fat in a Multiethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 1686–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gild, P.; Cole, A.P.; Krasnova, A.; Dickerman, B.A.; von Landenberg, N.; Sun, M.; Mucci, L.A.; Lipsitz, S.R.; Chun, F.K.-H.; Nguyen, P.L.; et al. Liver Disease in Men Undergoing Androgen Deprivation Therapy for Prostate Cancer. J. Urol. 2018, 200, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbonetti, A.; Vassallo, M.R.C.; Cotugno, M.; Felzani, G.; Francavilla, S.; Francavilla, F. Low testosterone and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Evidence for their independent association in men with chronic spinal cord injury. J. Spinal Cord. Med. 2016, 39, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, N.K.; Koo, H.S.; Haam, J.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Park, K.; Park, K.; Kim, Y. Prediction of prevalent but not incident non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by levels of serum testosterone. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 30, 1211–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggio, M.; Basaria, S.; Ble, A.; Lauretani, F.; Bandinelli, S.; Ceda, G.P.; Valenti, G.; Ling, S.M.; Ferrucci, L. Correlation between testosterone and the inflammatory marker soluble interleukin-6 receptor in older men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 345–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupelian, V.; Chiu, G.R.; Araujo, A.B.; Williams, R.E.; Clark, R.V.; McKinlay, J.B. Association of sex hormones and C-reactive protein levels in men. Clin. Endocrinol. 2010, 72, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaenko, L.; Jia, Y.; Wang, C.; Diaz-Arjonilla, M.; Yee, J.K.; French, S.W.; Liu, P.Y.; Laurel, S.; Chong, C.; Lee, K.; et al. Testosterone replacement ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in castrated male rats. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yassin, A.A.; Alwani, M.; Talib, R.; Almehmadi, Y.; Nettleship, J.E.; Alrumaihi, K.; Albaba, B.; Kelly, D.M.; Saad, F. Long-term testosterone therapy improves liver parameters and steatosis in hypogonadal men: A prospective controlled registry study. Aging Male 2020, 23, 1553–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qudimat, A.; Al-Zoubi, R.M.; Yassin, A.A.; Alwani, M.; Aboumarzouk, O.M.; AlRumaihi, K.; Talib, R.; Al Ansari, A. Testosterone treatment improves liver function and reduces cardiovascular risk: A long-term prospective study. Arab. J. Urol. 2021, 19, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, F.; Doros, G.; Haider, K.S.; Haider, A. Differential effects of 11 years of long-term injectable testosterone undecanoate therapy on anthropometric and metabolic parameters in hypogonadal men with normal weight, overweight and obesity in comparison with untreated controls: Real-world data from a controlled registry study. Int. J. Obes. 2020, 44, 1264–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolov, R.; Gianatti, E.; Wong, D.; Kutaiba, N.; Gow, P.; Grossmann, M.; Sinclair, M. Testosterone therapy reduces hepatic steatosis in men with type 2 diabetes and low serum testosterone concentrations. World J. Hepatol. 2022, 14, 754–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traish, A.M.; Haider, A.; Haider, K.S.; Doros, G.; Saad, F. Long-Term Testosterone Therapy Improves Cardiometabolic Function and Reduces Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Men with Hypogonadism. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 22, 414–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyos, C.M.; Yee, B.J.; Phillips, C.L.; Machan, E.A.; Grunstein, R.R.; Liu, P.Y. Body compositional and cardiometabolic effects of testosterone therapy in obese men with severe obstructive sleep apnoea: A randomised placebo-controlled trial. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 167, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Bhasin, S.; Tang, E.R.; Aakil, A.; Anderson, S.W.; Jara, H.; Davda, M.; Travison, T.G.; Basaria, S. Effect of Testosterone Administration on Liver Fat in Older Men with Mobility Limitation: Results From a Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Gerontol. 2013, 68, 954–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.S.; Han, S.H.; Swerdloff, R.; Pak, Y.; Budoff, M.; Wang, C. The Effect of Testosterone Replacement Therapy on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Older Hypogonadal Men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 109, e757–e764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, M.; Wierman, M.E.; Angus, P.; Handelsman, D.J. Reproductive Endocrinology of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Endocr. Rev. 2019, 40, 417–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirschberg, A.L. Hyperandrogenism and Cardiometabolic Risk in Pre- and Postmenopausal Women—What Is the Evidence? Endocr. Soc. 2024, 109, 1202–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffer, L.; Kempegowda, P.; Arlt, W.; O’Reilly, M.W.; O’Reilly, M.W.; O’Reilly, M.W. The sexually dimorphic role of androgens in human metabolic disease. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 177, R125–R143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotterdam ESHRE/ASRM-Sponsored PCOS Consensus Workshop Group. Revised 2003 consensus on diagnostic criteria and long-term health risks related to polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Hum. Reprod. 2004, 19, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anagnostis, P.; Tarlatzis, B.C.; Kauffman, R.P. Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS): Long-term metabolic consequences. Metabolism 2018, 86, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonardo, A.; Mantovani, A.; Lugari, S.; Targher, G. NAFLD in some common endocrine diseases: Prevalence, pathophysiology, and principles of diagnosis and management. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, A.L.L.; Faria, L.C.; Guimarães, T.C.M.; Moreira, G.V.; Cândido, A.L.; Couto, C.A.; Reis, F.M. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2017, 40, 1279–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petta, S.; Ciresi, A.; Bianco, J.; Geraci, V.; Boemi, R.; Galvano, L.; Magliozzo, F.; Merlino, G.; Craxì, A.; Giordano, C. Insulin resistance and hyperandrogenism drive steatosis and fibrosis risk in young females with PCOS. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, H.; Sprung, V.S.; Pugh, C.J.A.; Daousi, C.; Irwin, A.; Aziz, C.; Adams, V.L.; Thomas, E.L.; Bell, J.D.; Kemp, G.J.; et al. Polycystic ovary syndrome with hyperandrogenism is characterized by an increased risk of hepatic steatosis compared to nonhyperandrogenic PCOS phenotypes and healthy controls, independent of obesity and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 3709–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumarendran, B.; O’Reilly, M.W.; Manolopoulos, K.N.; Toulis, K.A.; Gokhale, K.M.; Sitch, A.J.; Wijeyaratne, C.N.; Coomarasamy, A.; Arlt, W.; Nirantharakumar, K. Polycystic ovary syndrome, androgen excess, and the risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in women: A longitudinal study based on a United Kingdom primary care database. PLoS Med. 2018, 15, e1002542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, M.; Wellons, M.; I Cedars, M.; VanWagner, L.; Gunderson, E.P.; Ajmera, V.; Torchen, L.; Siscovick, D.; Carr, J.J.; Terry, J.G.; et al. Testosterone Levels in Pre-Menopausal Women are Associated with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Midlife. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 112, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borzan, V.; Lerchbaum, E.; Missbrenner, C.; Heijboer, A.C.; Goschnik, M.; Trummer, C.; Theiler-Schwetz, V.; Haudum, C.; Gumpold, R.; Schweighofer, N.; et al. Risk of insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome in women with hyperandrogenemia: A comparison between pcos phenotypes and beyond. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Zheng, J.; Li, S.; Tao, T.; Ma, J.; Liu, W. Characteristics and contributions of hyperandrogenism to insulin resistance and other metabolic profiles in polycystic ovary syndrome. Acta Obs. Gynecol. Scand. 2015, 94, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Medeiros, S.F.; Rodgers, R.J.; Norman, R.J. Adipocyte and steroidogenic cell cross-talk in polycystic ovary syndrome. Hum. Reprod. Updat. 2021, 27, 771–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armeni, E.; Stamatelopoulos, K.; Rizos, D.; Georgiopoulos, G.; Kazani, M.; Kazani, A.; Kolyviras, A.; Stellos, K.; Panoulis, K.; Alexandrou, A.; et al. Arterial stiffness is increased in asymptomatic nondiabetic postmenopausal women with a polycystic ovary syndrome phenotype. J. Hypertens. 2013, 31, 1998–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, D.; Kilic, I.D.; Sevgican, C.I.; Kilic, O.; Alatas, E.; Arslan, M.; Avci, E.; Guler, T. Arterial stiffness measured by cardio-ankle vascular index is greater in non-obese young women with polycystic ovarian syndrome. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2021, 47, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berbrier, D.E.; Leone, C.A.; Adler, T.E.; Bender, J.R.; Taylor, H.S.; Stachenfeld, N.S.; Usselman, C.W. Effects of androgen excess and body mass index on endothelial function in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. J. Appl. Physiol. 2023, 134, 868–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque-Ramírez, M.; Mendieta-Azcona, C.; Álvarez-Blasco, F.; Escobar-Morreale, H.F. Androgen excess is associated with the increased carotid intima-media thickness observed in young women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Hum. Reprod. 2007, 22, 3197–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempegowda, P.; Melson, E.; Manolopoulos, K.N.; Arlt, W.; O’Reilly, M.W. Implicating androgen excess in propagating metabolic disease in polycystic ovary syndrome. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 11, 204201882093431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shorakae, S.; Ranasinha, S.; Abell, S.; Lambert, G.; Lambert, E.; de Courten, B.; Teede, H. Inter-related effects of insulin resistance, hyperandrogenism, sympathetic dysfunction and chronic inflammation in PCOS. Clin. Endocrinol. 2018, 89, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, G.; Allard, C.; Morford, J.J.; Xu, W.; Liu, S.; Molinas, A.J.; Butcher, S.M.; Fine, N.H.; Blandino-Rosano, M.; Sure, V.N.; et al. Androgen excess in pancreatic β cells and neurons predisposes female mice to type 2 diabetes. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e98607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespo, R.P.; Bachega, T.A.S.S.; Mendonça, B.B.; Gomes, L.G. An update of genetic basis of PCOS pathogenesis. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 62, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, T.; Crespo, R.P.; Yance, V.V.R.; A Hayashida, S.; Baracat, E.C.; Carvalho, F.; Domenice, S.; Mendonca, B.B.; Gomes, L.G. Persistent poor metabolic profile in postmenopausal women with ovarian hyperandrogenism after testosterone level normalization. J. Endocr. Soc. 2019, 3, 1087–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torchen, L.C.; Tsai, J.N.; Jasti, P.; Macaya, R.; Sisk, R.; Dapas, M.L.; Hayes, M.G.; Urbanek, M.; Dunaif, A. Hyperandrogenemia is Common in Asymptomatic Women and is Associated with Increased Metabolic Risk. Obesity 2020, 28, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, H.; He, B. Effect of Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin on Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Mechanisms, Manifestations, Genetics, and Treatment. Int. J. Womens Health 2022, 14, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, S.Z.; Wagner, R.; Fritsche, L.; Peter, A.; Rettig, I.; Willmann, C.; Fehlert, E.; Martus, P.; Todenhöfer, T.; Stefan, N.; et al. Sex-specific associations of testosterone with metabolic traits. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klisic, A.; Kavaric, N.; Jovanovic, M.; Soldatovic, I.; Gligorovic-Barhanovic, N.; Kotur-Stevuljevic, J. Bioavailable testosterone is independently associated with Fatty Liver Index in postmenopausal women. Arch. Med. Sci. 2017, 5, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Kountouras, J.; Tsatsoulis, A.; Zafeiriadou, E.; Katsiki, E.; Patsiaoura, K.; Zavos, C.; Anastasiadou, V.V.; Slavakis, A. Sex steroids and sex hormone-binding globulin in postmenopausal women with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hormones 2013, 12, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, G.; Allard, C.; Xu, W.; Mauvais-Jarvis, F. The role of androgens in metabolism, obesity, and diabetes in males and females. Obesity 2015, 23, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupte, A.A.; Pownall, H.J.; Hamilton, D.J. Estrogen: An Emerging Regulator of Insulin Action and Mitochondrial Function. J. Diabetes Res. 2015, 2015, 916585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; López, M. Central regulation of energy metabolism by estrogens. Mol. Metab. 2018, 15, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galmés-Pascual, B.M.; Martínez-Cignoni, M.R.; Morán-Costoya, A.; Bauza-Thorbrügge, M.; Sbert-Roig, M.; Valle, A.; Proenza, A.M.; Lladó, I.; Gianotti, M. 17β-estradiol ameliorates lipotoxicity-induced hepatic mitochondrial oxidative stress and insulin resistance. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 150, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.J.; Eckert, A.; Lai, K.; Adelman, S.J.; Harnish, D.C. Reciprocal Antagonism Between Estrogen Receptor and NF-κB Activity In Vivo. Circ. Res. 2001, 89, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, H.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Inhibition of JNK suppresses autophagy and attenuates insulin resistance in a rat model of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Win, S.; Min, R.W.; Chen, C.Q.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, M.; Suzuki, A.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Wang, Y.; Aghajan, M.; et al. Expression of mitochondrial membrane-linked SAB determines severity of sex-dependent acute liver injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 5278–5293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, E.; Wang, Y. Protective Effects of Estrogen on Cardiovascular Disease Mediated by Oxidative Stress. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 5523516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelekanou, V.; Kampa, M.; Kiagiadaki, F.; Deli, A.; Theodoropoulos, P.; Agrogiannis, G.; Patsouris, E.; Tsapis, A.; Castanas, E.; Notas, G. Estrogen anti-inflammatory activity on human monocytes is mediated through cross-talk between estrogen receptor ERα36 and GPR30/GPER1. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 99, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-L.; Bajpai, A.; Hawthorne, E.A.; Bae, Y.; Castagnino, P.; Monslow, J.; Puré, E.; Spiller, K.L.; Assoian, R.K. Cardiovascular protection in females linked to estrogen-dependent inhibition of arterial stiffening and macrophage MMP12. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e122742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somani, Y.B.; Pawelczyk, J.A.; De Souza, M.J.; Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Proctor, D.N. Aging women and their endothelium: Probing the relative role of estrogen on vasodilator function. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2019, 317, H395–H404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadimitriou, K.; Mousiolis, A.C.; Mintziori, G.; Tarenidou, C.; Polyzos, S.A.; Goulis, D.G. Hypogonadism and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Endocrine 2024, 86, 28–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, C.M.; Ackerman, K.E.; Berga, S.L.; Kaplan, J.R.; Mastorakos, G.; Misra, M.; Murad, M.H.; Santoro, N.F.; Warren, M.P. Functional hypothalamic amenorrhea: An endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 1413–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.-J.; Kim, K.M.; An, J.H.; Lee, D.B.; Shim, J.H.; Lim, Y.-S.; Lee, H.C.; Lee, Y.S.; Ahn, J.-H.; Jung, K.H.; et al. Clinical significance of fatty liver disease induced by tamoxifen and toremifene in breast cancer patients. Breast 2016, 28, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanska, A.; Bergmann, K.; Sypniewska, G. Metabolic Syndrome and Menopause: Pathophysiology, Clinical and Diagnostic Significance. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2015, 72, 1–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovre, D.; Lindsey, S.H.; Mauvais-Jarvis, F. Effect of menopausal hormone therapy on components of the metabolic syndrome. Ther. Adv. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 11, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahmand, M.; Tehrani, F.R.; Khomami, M.B.; Noroozzadeh, M.; Azizi, F. Surgical menopause versus natural menopause and cardio-metabolic disturbances: A 12-year population-based cohort study. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2015, 38, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paoli, M.; Zakharia, A.; Werstuck, G.H. The Role of Estrogen in Insulin Resistance: A Review of Clinical and Preclinical Data. Am. J. Pathol. 2021, 191, 1490–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gangitano, E.; Scannapieco, F.; Lubrano, C.; Gnessi, L. Metabolic Syndrome, Hepatic Steatosis and Testosterone: A Matter of Sex. Livers 2024, 4, 534-549. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers4040038
Gangitano E, Scannapieco F, Lubrano C, Gnessi L. Metabolic Syndrome, Hepatic Steatosis and Testosterone: A Matter of Sex. Livers. 2024; 4(4):534-549. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers4040038
Chicago/Turabian StyleGangitano, Elena, Francesca Scannapieco, Carla Lubrano, and Lucio Gnessi. 2024. "Metabolic Syndrome, Hepatic Steatosis and Testosterone: A Matter of Sex" Livers 4, no. 4: 534-549. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers4040038
APA StyleGangitano, E., Scannapieco, F., Lubrano, C., & Gnessi, L. (2024). Metabolic Syndrome, Hepatic Steatosis and Testosterone: A Matter of Sex. Livers, 4(4), 534-549. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers4040038






