Sarcopenia and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Sarcopenia: What Is the Problem?
2. Sarcopenia and Systemic Risks
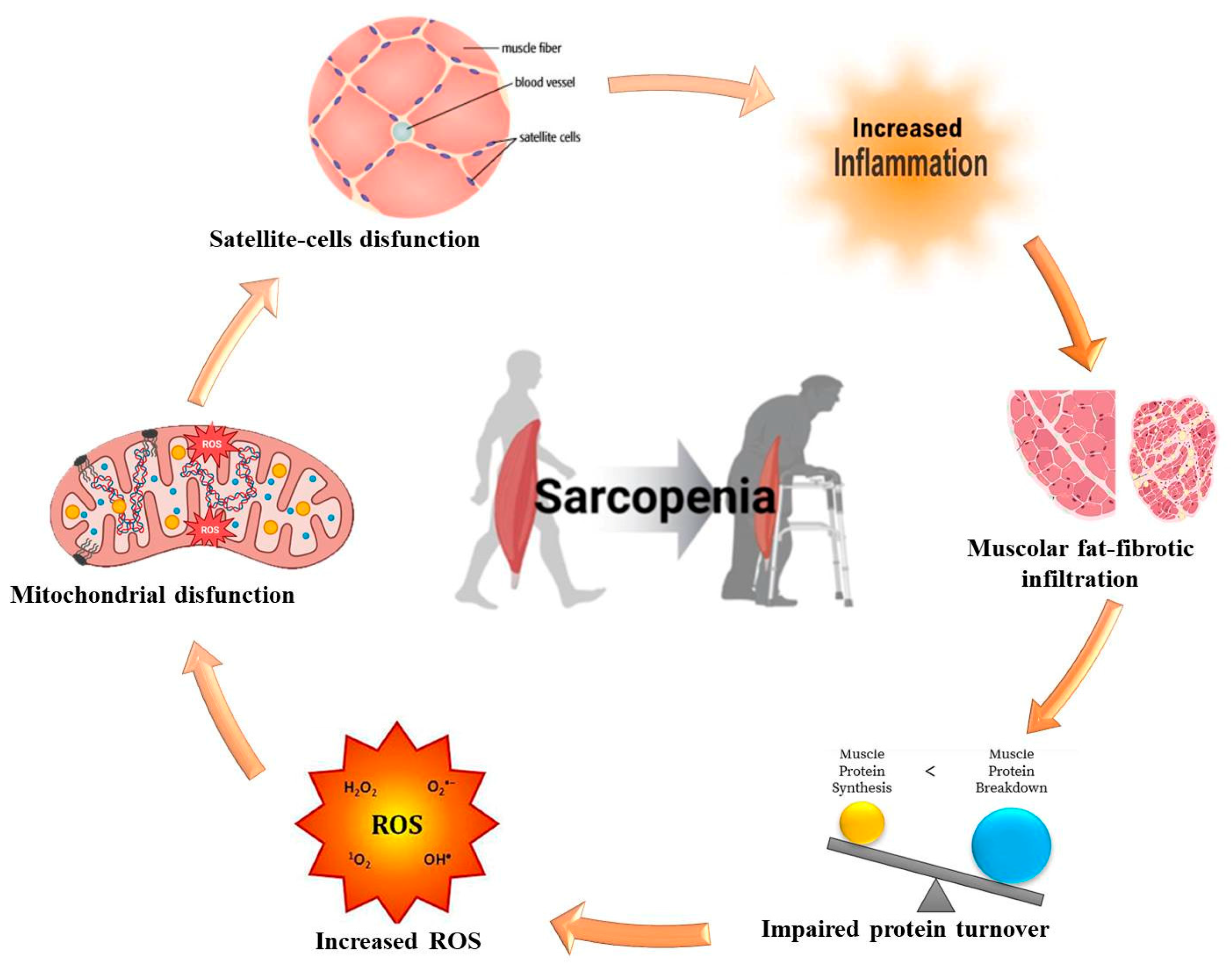
3. Molecular and Pathophysiological Mechanisms of Sarcopenia
4. Sarcopenia Classification and Diagnostic Models
5. MASLD and Sarcopenia: Shared Pathogenetic Mechanisms
6. Potential Treatments
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cruz-Jeentoft, A.J.; Baeyens, J.P.; Bauer, J.M.; Boirie, Y.; Cederholm, T.; Landi, F.; Martin, F.C.; Michel, J.P.; Rolland, Y.; Schneider, S.M.; et al. Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Report of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. Age Ageing 2010, 39, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United Nations. Department of Economic and Social Affairs 2023. World Social Report 2023: Leaving No One behind in an Ageing World. Available online: https://repository.gheli.harvard.edu/repository/12779/ (accessed on 30 June 2024).
- Zavyalova, A.N.; Novikova, V.P.; Ignatova, P.D. Axis «microbiota-muscle». Exp. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2022, 11, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manickam, R.; Duszka, K.; Wahli, W. PPARs and Microbiota in Skeletal Muscle Health and Wasting. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kim, H.J. Normal Aging Induces Changes in the Brain and Neurodegeneration Progress: Review of the Structural, Biochemical, Metabolic, Cellular, and Molecular Changes. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 931536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Shen, J.; Gao, Y.; Wang, X.X.; Jia, Q.Y.; Li, M. Nutritional status of the older adults in nursing homes: A cross-sectional study. J. Clin. Nurs. 2024, 33, 2640–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livshits, G.; Kalinkovich, A. Restoration of epigenetic impairment in the skeletal muscle and chronic inflammation resolution as a therapeutic approach in sarcopenia. Ageing Res. Rev. 2024, 96, 102267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokrysheva, N.G.; Krupinova, J.A.; Volodicheva, V.L.; Mirnaya, S.S.; Melnichenko, G.A. A view at sarcopenia by endocrinologist. Obes. Metab. 2018, 15, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perna, S.; Spadaccini, D.; Rondanelli, M. Sarcopenic Obesity: Time to target the phenotypes. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2019, 10, 710–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velarde, M.C. Mitochondrial and sex steroid hormone crosstalk during aging. Longev. Healthspan 2014, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.M. Sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2016, 31, 1054–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkins, J.L.; Whincup, P.H.; Morris, R.W.; Lennon, L.T.; Papacosta, O.; Wannamethee, S.G. Sarcopenic obesity and risk of cardiovascular disease and mortality: A populationbased cohort study of older men. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2014, 62, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axelrod, C.L.; Dantas, W.S.; Kirwan, J.P. Sarcopenic obesity: Emerging mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Metabolism 2023, 146, 155639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, T.; Green, A.E.; Kim, Y.A.; Bae, S.J.; Ha, K.T.; Gariani, K.; Lee, M.R.; Menzies, K.J.; Ryu, D. Sarcopenia and Muscle Aging: A Brief Overview. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 35, 716–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picca, A.; Calvani, R.; Cesari, M.; Landi, F.; Bernabei, R.; Coelho- Júnior, H.J.; Marzetti, E. Biomarkers of Physical Frailty and Sarcopenia: Coming up to the Place? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morley, J.E. Sarcopenia: Diagnosis and treatment. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2008, 12, 452–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paddon-Jones, D.; Short, K.R.; Campbell, W.W.; Volpi, E.; Wolfe, R.R. Role of dietary protein in the sarcopenia of aging. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 1562S–1566S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ticinesi, A.; Nouvenne, A.; Cerundolo, N.; Catania, P.; Prati, B.; Tana, C.; Meschi, T. Gut Microbiota, Muscle Mass and Function in Aging: A Focus on Physical Frailty and Sarcopenia. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sire, R.; Rizzatti, G.; Ingravalle, F.; Pizzoferrato, M.; Petito, V.; Lopetuso, L.; Graziani, C.; de Sire, A.; Mentella, M.C.; Mele, M.C.; et al. Skeletal muscle-gut axis: Emerging mechanisms of sarcopenia for intestinal and extra intestinal diseases. Minerva Gastroenterol. Dietol. 2018, 64, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narici, M.V.; Maffulli, N. Sarcopenia: Characteristics, mechanisms and functional significance. Br. Med. Bull. 2010, 95, 139–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzke, B.; Neubauer, O.; Cameron-Smith, D.; Wagner, K.H. Dietary protein, muscle and physical function in the very old. Nutrients 2018, 10, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, V.; Singh, R.; Acharya, S.K. Predictive value of arterial ammonia for complications and outcome in acute liver failure. Gut 2006, 55, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalimar Sheikh, M.F.; Mookerjee, R.P.; Agarwal, B.; Acharya, S.K.; Jalan, R. Prognostic Role of Ammonia in Patients with Cirrhosis. Hepatology 2019, 70, 982–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodpaster, B.H.; Park, S.W.; Harris, T.B.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Nevitt, M.; Schwartz, A.V.; Simonsick, E.M.; Tylavsky, F.A.; Visser, M.; Newman, A.B. The loss of skeletal muscle strength, mass, and quality in older adults: The health, aging and body composition study. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2006, 61, 1059–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.J.; Kim, D.J. An Overview of the Molecular Mechanisms Contributing to Musculoskeletal Disorders in Chronic Liver Disease: Osteoporosis, Sarcopenia, and Osteoporotic Sarcopenia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giudice, J.; Taylor, J.M. Muscle as a paracrine and endocrine organ. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2017, 34, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paltsyn, A.A. Myokines. Patol. Fiziol. 2020, 64, 135–141. [Google Scholar]
- Severinsen, M.C.K.; Pedersen, B.K. Muscle-Organ Crosstalk: The Emerging Roles of Myokines. Endocr. Rev. 2020, 41, 594–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancinelli, R.; Checcaglini, F.; Coscia, F.; Gigliotti, P.; Fulle, S.; Fanò- Illic, G. Biological Aspects of Selected Myokines in Skeletal Muscle: Focus on Aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suriano, F.; Van Hul, M.; Cani, P.D. Gut microbiota and regulation of myokine- adipokine function. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2020, 52, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahiri, S.; Kim, H.; Garcia-Perez, I.; Reza, M.M.; Martin, K.A.; Kundu, P.; Cox, L.M.; Selkrig, J.; Posma, J.M.; Zhang, H.; et al. The gut microbiota influences skeletal muscle mass and function in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaan5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosicki, G.J.; Fielding, R.A.; Lustgarten, M.S. Gut Microbiota Contribute to Age- Related Changes in Skeletal Muscle Size, Composition, and Function: Biological Basis for a Gut- Muscle Axis. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2018, 102, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spychala, M.S.; Venna, V.R.; Jandzinski, M.; Doran, S.J.; Durgan, D.J.; Ganesh, B.P.; Ajami, N.J.; Putluri, N.; Graf, J.; Bryan, R.M.; et al. Age-related changes in the gut microbiota influence systemic inflammation and stroke outcome. Ann. Neurol. 2018, 84, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gizard, F.; Fernandez, A.; De Vadder, F. Interactions between gut microbiota and skeletal muscle. Nutr. Metab. Insights 2020, 13, 1178638820980490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erokhina, A.S.; Golovanova, E.D. The relationship between comorbidity and sarcopenia: Impact on mortality and survival. Doctor 2021, 6, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lera, L.; Angel, B.; Marquez, C.; Saguez, R.; Albala, C. Besides Sarcopenia, Pre-Sarcopenia Also Predicts All-Cause Mortality in Older Chileans. Clin. Interv. Aging 2021, 16, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmstrom, T.K.; Morley, J.E. SARC-F: A Simple Questionnaire to Rapidly Diagnose Sarcopenia. JAMDA 2013, 14, 531–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issa, D.; Alkhouri, N.; Tsien, C.; Shah, S.; Lopez, R.; McCullough, A.; Dasarathy, S. Presence of sarcopenia (muscle wasting) in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2014, 60, 428–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bredella, M.A.; Ghomi, R.H.; Thomas, B.J.; Torriani, M.; Brick, D.J.; Gerweck, A.V.; Misra, M.; Klibanski, A.; Milleret, K.K. Comparison of DXA and CT in the assessment of body composition in premenopausal women with obesity and anorexia nervosa. Obesity 2010, 18, 2227–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grinevich, V.B.; Sas, E.I. The role of sarcopenia in the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2020, 183, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, F.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Liperoti, R.; Russo, A.; Giovannini, S.; Tosato, M.; Capoluongo, E.; Bernabei, R.; Onder, G. Sarcopenia and mortality risk in frail older persons aged 80 years and older: Results from ilSIRENTE study. Age Ageing 2013, 42, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigorieva, I.I.; Raskina, T.A.; Letaeva, M.V.; Malyshenko, O.S.; Averkieva, Y.V.; Masenko, V.L.; Kokov, A.N. Sarcopenia: Pathogenesis and diagnosis. Fundam. Clin. Med. 2019, 4, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erokhina, A.S.; Golovanova, E.D.; Miloserdov, M.A. Ultrasound assessment of muscle mass in the diagnosis of sarcopenia in cardiovascular patients. Cardiovasc. Ther. Prev. 2021, 20, 2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ido, A.; Nakayama, Y.; Ishii, K.; Iemitsu, M.; Sato, K.; Fujimoto, M.; Kurihara, T.; Hamaoka, T.; Satoh-Asahara, N.; Sanadaet, K. Ultrasound-derived abdominal muscle thickness better detects metabolic syndrome risk in obese patients than skeletal muscle index measured by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 0143858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanada, K.; Kuchiki, T.; Miyachi, M.; McGrath, K.; Higuchi, M.; Ebashi, H. Effects of age on ventilator threshold and peak oxygen uptake normalized for regional skeletal muscle mass in Japanese men and women aged 20–80 years. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 99, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijholt, W.; Scafoglieri, A.; Jager-Wittenaar, H.; Van der Schans, C.P. The reliability and validity of ultrasound to quantify muscles in older adults: A systematic review. J. Cachexia Sarkopenia Muscle 2017, 8, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenholm, S.; Harris, T.B.; Rantanen, T.; Visser, M.; Kritchevsky, S.B.; Ferrucci, L. Sarcopenic obesity: Definition, cause and consequences. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2008, 11, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Correa, C.H.; Pineda-Zuluaga, M.C.; Marulanda-Mejía, F. Skeletal Muscle Mass by Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis and Calf Circumference for Sarcopenia Diagnosis. J. Electr. Bioimpedance 2020, 11, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Kan, G.A.; Rolland, Y.; Andrieu, S.; Bauer, J.; Beauchet, O.; Bonnefoy, M.; Cesari, M.; Donini, L.M.; Gillette-Guyonnet, S.; Inzitari, M.; et al. Gait speed at usual pace as a predictor of adverse outcomes in community-dwelling older people an International Academy on Nutrition and Aging (IANA) Task Force. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2009, 13, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sas, E.I.; Barnakova, V.A. Skeletal muscle hormone activity and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Med. Alph. 2020, 17, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL); European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD); European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO). EASL–EASD–EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). J. Hepatol. 2024, 81, 492–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL); European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD); European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO). Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1388–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, A.; García-Lozano, M.R.; Gil-Gómez, A.; Romero-Gómez, M.; Ampuero, J. Glutaminolysis-ammonia-urea Cycle Axis, Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Progression and Development of Novel Therapies. J. Clin. Trans. Hepatol. 2022, 10, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishina, E.E.; Mayorov, A.Y.; Bogomolov, P.O.; Matsievich, M.V.; Kokina, K.Y.; Bogolyubova, A.V. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Cause or consequence of insulin resistance? Diabetes Mellit. 2017, 20, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, P.; Kleiner, D.E.; Dam-Larsen, S.; Adams, L.A.; Bjornsson, E.S.; Charatcharoenwitthaya, P.; Mills, P.R.; Keach, J.C.; Lafferty, H.D.; Stahler, A.; et al. Liver fibrosis, but no other histologic features, is associated with long-term outcomes of patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; Lavine, J.E.; Charlton, M.; Cusi, K.; Rinella, M.; Harrison, S.A.; Brunt, E.M.; Arun, S.J. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 67, 328–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chitturi, S.; Wong, V.W.S.; Chan, W.K.; Wong, G.L.H.; Wong, S.K.H.; Sollano, J.; Ni, Y.H.; Liu, C.J.; Lin, Y.C.; Lesmana, L.A.; et al. The Asia–Pacific Working Party on Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease guidelines 2017—Part 2: Management and special groups. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 33, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelakkot, C.; Ghim, J.; Ryu, S.H. Mechanisms regulating intestinal barrier integrity and its pathological implications. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Kim, J.H.; Yoon, J.W.; Kang, S.M.; Choi, S.H.; Park, Y.J.; Kim, K.W.; Lim, J.Y.; Park, K.S.; Jang, H.C. Sarcopenic obesity: Prevalence and association with metabolic syndrome in the Korean Longitudinal Study on Health and Aging (KLoSHA). Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1652–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.W.; Jung, H.W. Which one is associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease? Small muscle mass or large fat mass. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; McFarlane, C.; Lokireddy, S.; Bonala, X.G.; Masuda, S.; Gluckman, P.D.; Sharma, M.; Kambadur, R. Myostatin-deficient mice exhibit reduced insulin resistance through activating the AMP-activated protein kinase signalling pathway. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 1491–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasarathy, S.; Muc, S.; Runkana, A.; Mullen, K.D. Alteration in body composition in the portacaval anastamosis rat is mediated by increased expression of myostatin. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2011, 301, G731–G738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seldin, M.M.; Peterson, J.M.; Byerly, M.S.; Wei, Z.; Wong, G.W. Myonectin (CTRP15), a novel myokine that links skeletal muscle to systemic lipid homeostasis. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 11968–11980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, J.; Tsien, C.; Thapalaya, S.; Narayanan, A.; Weihl, C.C.; Ching, J.K.; Eghtesad, B.; Singh, K.; Fu, X.; Dubyak, G.; et al. Hyperammonemia-mediated autophagy in skeletal muscle contributes to sarcopenia of cirrhosis. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 303, E983–E993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.H.; Jung, K.S.; Kim, S.U.; Yoon, H.J.; Yun, Y.J.; Lee, B.W.; Kang, E.S.; Han, K.H.; Lee, H.C.; Cha, B.S. Sarcopaenia is associated with NAFLD independently of obesity and insulin resistance: Nationwide surveys (KNHANES 2008–2011). J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whillier, S. Exercise and Insulin Resistance. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1228, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zykina, E.J.; Simonova, Z.G. Hyperammonemia in patients with stable angina pectoris and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease at the steatosis stage. Exp. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2023, 8, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazebnik, L.B.; Golovanova, E.V.; Alekseenko, S.A.; Bueverov, A.O.; Plotnikova, E.Y.; Dolgushina, A.I.; Ilchenko, L.Y.; Ermolova, T.V.; Tarasova, L.V.; Lee, E.D.; et al. Russian Consensus “Hyperammonemia in Adults” (Version 2021). Exp. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2021, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.N.; Park, M.S.; Yang, S.J.; Yoo, H.J.; Kang, H.J.; Song, W.; Seo, J.A.; Kim, S.G.; Kim, N.H.; Baik, S.H.; et al. Prevalence and determinant factors of sarcopenia in patients with type 2 diabetes: The Korean Sarcopenic Obesity Study (KSOS). Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 1497–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasarathy, S.; Merli, M. Sarcopenia from mechanism to diagnosis and treatment in liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 1232–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Sayer, A.A. Sarcopenia. Lancet 2019, 393, 2636–2646, Erratum in Lancet 2019, 393, 2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reijnierse, E.M.; Verlaan, S.; Pham, V.K.; Lim, W.K.; Meskers, C.G.M.; Maier, A.B. Lower Skeletal Muscle Mass at Admission Independently Predicts Falls and Mortality 3 Months Post-discharge in Hospitalized Older Patients. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2019, 74, 1650–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goates, S.; Du, K.; Arensberg, M.B.; Gaillard, T.; Guralnik, J.; Pereira, S.L. Economic Impact of Hospitalizations in US Adults with Sarcopenia. J. Frailty Aging 2019, 8, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gale, C.R.; Martyn, C.N.; Cooper, C.; Sayer, A.A. Grip strength, body composition, and mortality. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2007, 36, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pichon, C.; Nachit, M.; Gillard, J.; Velde, G.V.; Lanthier, N.; Leclercq, I.A. Impact of L-ornithine L-aspartate on non-alcoholic steatohepatitis-associated hyperammonemia and muscle alterations. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1051157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasarathy, S.; Muc, S.; Hisamuddin, K.; Edmison, J.M.; Dodig, M.; McCullough, A.J.; Kalhan, S.C. Altered expression of genes regulating skeletal muscle mass in the portacaval anastomosis rat. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2007, 292, G1105–G1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.M.; Bevan, C.; Gollapudi, B.; Klaunig, J.E. Evaluation of the carcinogenicity of carbon tetrachloride. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 2023, 26, 342–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demura, S.; Yamada, T.; Yamaji, S.; Komatsu, M.; Morishita, K. The effect of L-ornithine hydrochloride ingestion on performance during incremental exhaustive ergometer bicycle exercise and ammonia metabolism during and after exercise. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 1166–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butterworth, R.F.; Canbay, A. Hepatoprotection by L-Ornithine L-Aspartate in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Dig. Dis. 2019, 37, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.X.; Wang, M.Y.; Yang, R.X.; Zhao, Z.H.; Xin, F.Z.; Li, Y.; Ren, T.Y.; Fan, J.G. Ammonia Scavenger Restores Liver and Muscle Injury in a Mouse Model of Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis With Sarcopenic Obesity. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 808497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterworth, R.F. L-Ornithine L-Aspartate for the Treatment of Sarcopenia in Chronic Liver Disease: The Taming of a Vicious Cycle. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 2019, 8182195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Davuluri, G.; Silva, R.N.E.; Engelen, M.P.K.J.; Ten, H.; Gabrie, A.M.; Prayson, R.; Deutz, N.E.P.; Dasarathy, S. Ammonia lowering reverses sarcopenia of cirrhosis by restoring skeletal muscle proteostasis. Hepatology 2017, 65, 2045–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butterworth, R.F.; Kircheis, G.; Hilger, N.; McPhail, M.J.W. Efficacy of l-ornithine l-aspartate for the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy and hyperammonemia in cirrhosis: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2018, 8, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canbay, A.; Sowa, J.P. L-ornithine L-aspartate (LOLA) as a novel approach for therapy of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Drugs 2019, 79, S39–S44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gairing, S.J.; Müller, L.; Kloeckner, R.; Galle, P.R.; Labenz, C. Review article: Post-TIPSS hepatic encephalopathy-current knowledge and future perspectives. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 55, 1265–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.; Sharma, B.C.; Mahajan, B.; Srivastava, S.; Kumar, A.; Sachdeva, S.; Sonika, U.; Dalal, A. L-ornithine L-aspartate in acute treatment of severe hepatic encephalopathy: A double-blind randomized controlled trial. Hepatology 2022, 75, 1194–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butterworth, R.F. L-Ornithine L-Aspartate: Multimodal Therapeutic Agent for Hyperammonemia and Hepatic Encephalopathy in Cirrhosis. J. Pharmacol. Pharm. Res. 2019, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kamimura, H.; Sato, T.; Natsui, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Yoshida, T.; Kamimura, K.; Tsuchiya, A.; Murayama, T.; Yokoyama, J.; Kawai, H.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms and Treatment of Sarcopenia in Liver Disease: A Review of Current Knowledge. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abenavoli, L.; Gambardella, M.L.; Scarlata, G.G.M.; Lenci, I.; Baiocchi, L.; Luzza, F. The Many Faces of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease Treatment: From the Mediterranean Diet to Fecal Microbiota Transplantation. Medicina 2024, 60, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colaci, C.; Gambardella, M.L.; Scarlata, G.G.M.; Boccuto, L.; Colica, C.; Luzza, F.; Scarpellini, E.; Mendez-Sanchez, N.; Abenavoli, L. Dysmetabolic comorbidities and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A stairway to metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Hepatoma Res. 2024, 10, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abenavoli, L.; Spagnuolo, R.; Scarlata, G.G.M.; Gambardella, M.L.; Boccuto, L.; Méndez-Sánchez, N.; Luzza, F. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Pilot Study. Life 2024, 14, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Topic | Details | References |
|---|---|---|
| Ammonia-lowering strategies | Long-term reduction is needed, as temporary reductions are ineffective. | [71] |
| Role of ammonia in sarcopenia | Ammonia is a key factor in muscle damage and sarcopenia, especially in cirrhotic patients. It triggers myostatin and autophagy, worsening muscle metabolism. | [72,73] |
| Cycle of muscle damage | Hyperammonemia causes muscle damage, reducing the muscle’s ability to detoxify ammonia, worsening sarcopenia, quality of life, and risk of mortality. | [26,74,75] |
| Pre-clinical findings | Reducing ammonia mitigates sarcopenia in liver disease models. Hyperammonemia disrupts muscle protein synthesis. | [76,77,78] |
| Physical exercise | Reduces MASLD likelihood (46% vs. 55%); improves mitochondrial function, addressing metabolic disorders. | [51] |
| LOLA therapy | Improves muscle mass and cognitive function, and reduces hospital stays in NAFLD and cirrhotic patients. Increases lean body mass in rodent MASH models. | [80,81,82] |
| Clinical evidence of LOLA | Reduces ammonia, sarcopenia, and mortality in cirrhotic patients, improving protein synthesis and cognitive function. | [26,82,86,87,88] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abenavoli, L.; Statsenko, M.; Scarlata, G.G.M.; Morano, D.; Myazin, R.; Emelyanov, D. Sarcopenia and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Narrative Review. Livers 2024, 4, 495-506. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers4040035
Abenavoli L, Statsenko M, Scarlata GGM, Morano D, Myazin R, Emelyanov D. Sarcopenia and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Narrative Review. Livers. 2024; 4(4):495-506. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers4040035
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbenavoli, Ludovico, Michael Statsenko, Giuseppe Guido Maria Scarlata, Domenico Morano, Roman Myazin, and Dmitriy Emelyanov. 2024. "Sarcopenia and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Narrative Review" Livers 4, no. 4: 495-506. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers4040035
APA StyleAbenavoli, L., Statsenko, M., Scarlata, G. G. M., Morano, D., Myazin, R., & Emelyanov, D. (2024). Sarcopenia and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Narrative Review. Livers, 4(4), 495-506. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers4040035








