Principles of Nutritional Management in Patients with Liver Dysfunction—A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Role of Nutrition in Alcoholic Liver Disease (ALD)
3.2. Role of Nutrition in Liver Cirrhosis
3.3. Malnutrition in Liver Cirrhosis
3.4. Micronutrient Deficiencies in Liver Cirrhosis
3.5. Role of Nutrition in Management of Malnutrition and Sarcopenia in Liver Cirrhosis
3.6. Role of Nutrition in Management of Obesity in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis
3.7. Role of Nutrition in Ascites
3.8. Role of Nutrition in Management of Hepatic Encephalopathy (HE) in End-Stage Liver Failure
3.9. Role of Nutrition in Liver Transplantation
3.10. Role of Nutrition in Gallbladder Diseases
3.11. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver (NAFLD)
3.12. Dietary Strategies in the Nutritional Management of (NAFLD)
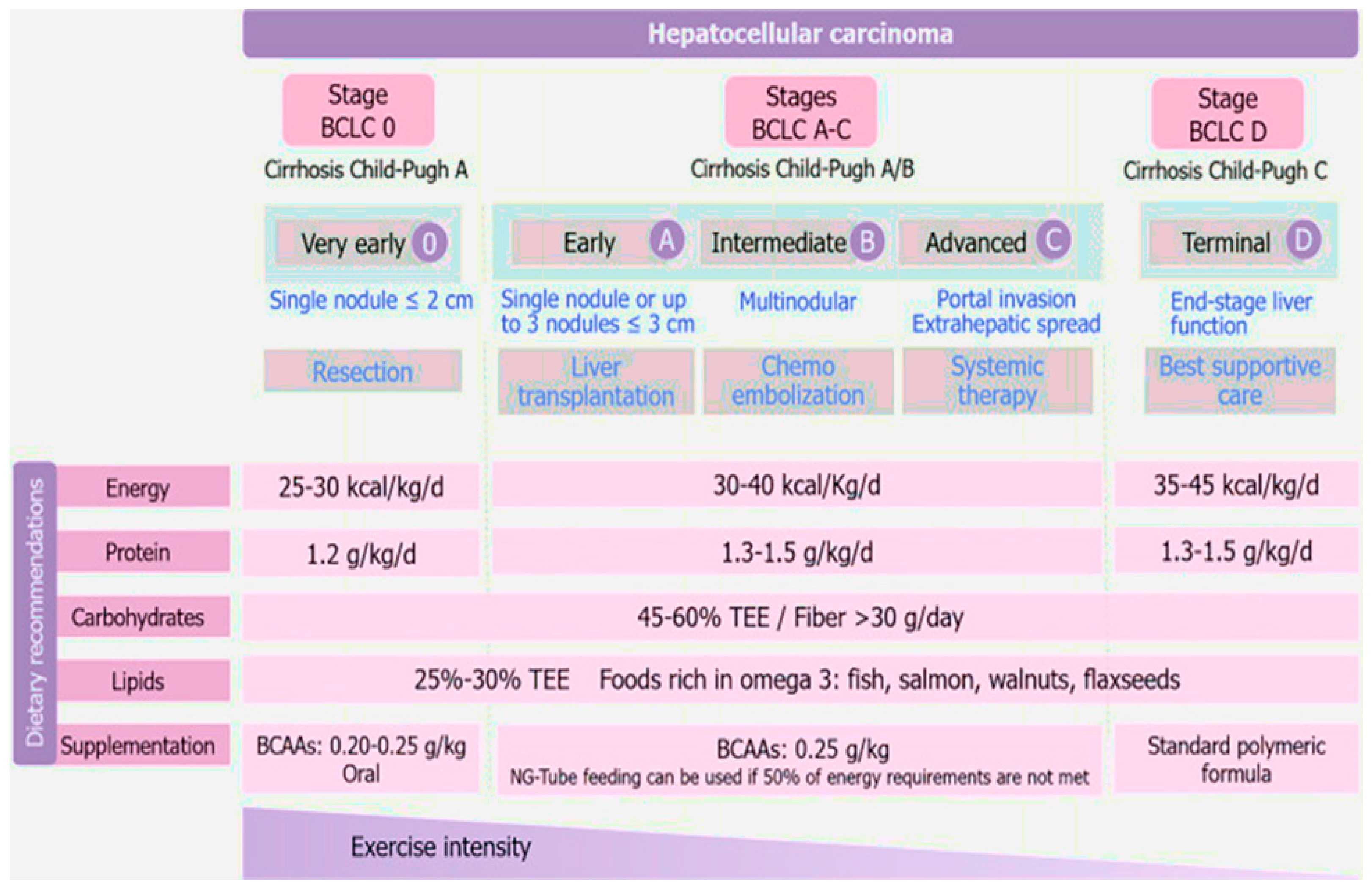
3.13. Nutritional Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
3.14. Hepatitis A Virus (HAV)
3.15. Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)
3.16. Nutritional Considerations to Prevent and Manage Viral Hepatitis A and B
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mandato, C.; Di Nuzzi, A.; Vajro, P. Nutrition and liver disease. Nutrients 2017, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.; Gomes, S.; Peixoto, A.; Torres-Ramalho, P.; Cardoso, H.; Azevedo, R.; Cunha, C.; Macedo, G. Nutrition in chronic liver disease. GE Port. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 22, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smart, K.M.; Alex, G.; Hardikar, W. Feeding the child with liver disease: A review and practical clinical guide. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 26, 810–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purnak, T.; Yilmaz, Y. Liver disease and malnutrition. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2013, 27, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shergill, R.; Syed, W.; Rizvi, S.A.; Singh, I. Nutritional support in chronic liver disease and cirrhotics. World J. Hepatol. 2018, 10, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.M.; Overgard, E.B.; Cohen, A.E.; DiBaise, J.K. Nutrition Assessment and Management in Advanced Liver Disease. Nutr. Clin. Pr. 2013, 28, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovici, P.; Moraru, E. Nutrition in cholestasis and long-term impact on trasnplant. Rev. Med.-Chir. A Soc. Med. Si Nat. Din Iasi 2010, 114, 726–730. [Google Scholar]
- Periyalwar, P.; Dasarathy, S. Malnutrition in Cirrhosis: Contribution and Consequences of Sarcopenia on Metabolic and Clinical Responses. Clin. Liver Dis. 2012, 16, 95–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, C.M.; Schenker, S. The Role of Nutritional Therapy in Alcoholic Liver Disease. Alcohol Res. Health 2006, 29, 296–306. [Google Scholar]
- Mendenhall, C.L.; Anderson, S.; Weesner, R.E.; Goldberg, S.J.; Crolic, K.A. Protein-calorie malnutrition associated with alcoholic hepatitis: Veterans administration cooperative study group on alcoholic hepatitis. Am. J. Med. 1984, 76, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezey, E. Interaction Between Alcohol and Nutrition in the Pathogenesis of Alcoholic Liver Disease. Semin. Liver Dis. 1991, 11, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, J.; Norenberg, M.D. Glutamine: A Trojan horse in ammonia neurotoxicity. Hepatology 2006, 44, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, M.C.; Aday, A.W. Food for Thought: Importance of Nutrition in Alcoholic Hepatitis. Pract. Gastroenterol. 2018, 31, 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, P.J.; Adcock, I.M. Glucocorticoid resistance in inflammatory diseases. Lancet 2009, 373, 1905–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thursz, M.R.; Richardson, P.; Allison, M.; Austin, A.; Bowers, M.; Day, C.P.; Downs, N.; Gleeson, D.; Macgilchrist, A.; Grant, A.; et al. Prednisolone or Pentoxifylline for Alcoholic Hepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1619–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singal, A.K.; Walia, I.; Singal, A.; Soloway, R.D. Corticosteroids and pentoxifylline for the treatment of alcoholic hepatitis: Current status. World J. Hepatol. 2011, 3, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendenhall, C.L.; Moritz, T.E.; Roselle, G.A.; Morgan, T.R.; Nemchausky, B.A.; Tamburro, C.H.; Schiff, E.R.; McClain, C.J.; Marsano, L.S.; Allen, J.I.; et al. Protein Energy Malnutrition in Severe Alcoholic Hepatitis: Diagnosis and Response to Treatment. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 1995, 19, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendenhall, C.; Bongiovanni, G.; Goldberg, S.; Miller, B.; Moore, J.; Rouster, S.; Schneider, D.; Tamburro, C.; Tosch, T.; Weesner, R.; et al. VA Cooperative Study on Alcoholic Hepatitis III: Changes in Protein-Calorie Malnutrition Associated with 30 Days of Hospitalization with and without Enteral Nutritional Therapy. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 1985, 9, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucey, M.R.; Mathurin, P.; Morgan, T.R. Alcoholic hepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 2758–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendenhall, C.; Roselle, G.A.; Gartside, P.; Moritz, T.; The Veterans Administration Cooperative Study Groups 119 and 275. Relationship of protein calorie malnutrition to alcoholic liver disease: A reexamination of data from two Veterans Administration Cooperative Studies. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1995, 19, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.C.; Tandon, P. Improving nutritional status in patients with cirrhosis. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. ACG 2018, 113, 1574–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, C.; Porayko, M.K.; Francisco-Ziller, N.; DiCecco, S. Nutrition and Chronic Liver Disease. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2002, 35, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galati, J.S.; Holdeman, K.P.; Dalrymple, G.V.; Harrison, K.A.; Quigley, E.M. Delayed gastric emptying of both the liquid and solid components of a meal in chronic liver disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1994, 89, 708–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaitzakis, E. Gastrointestinal dysfunction in liver cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 14686–14695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaitzakis, E.; Simren, M.; Olsson, R.; Henfridsson, P.; Hugosson, I.; Bengtsson, M.; Björnsson, E. Gastrointestinal symp- toms in patients with liver cirrhosis: Associations with nutritional status and health-related quality of life. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 41, 1464–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearns, P.J.; Young, H.; Garcia, G.; Blaschke, T.; O’Hanlon, G.; Rinki, M.; Sucher, K.; Gregory, P. Accelerated improvement of alcoholic liver disease with enteral nutrition. Gastroenterology 1992, 102, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.; Horowitz, J.; Henderson, J.M.; Heymsfield, S. Enteral hyperalimen- tation in undernourished patients with cirrhosis and ascites. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1982, 35, 56–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, M.C.; Friedman, L.S.; McClain, C.J. Medical Management of Severe Alcoholic Hepatitis: Expert Review from the Clinical Practice Updates Committee of the AGA Institute. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 15, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClave, S.A.; Martindale, R.G.; Vanek, V.W.; McCarthy, M.; Roberts, P.; Taylor, B.; American College of Critical Care Medicine. Guidelines for the provision and assessment of nutrition support therapy in the adult critically ill patient: Society of Critical Care Medicine (SCCM) and American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (ASPEN). J. Parenter. Enter. Nutri. 2009, 33, 277–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, P.; Thursz, M. Intensive Enteral Nutrition in Alcoholic Hepatitis: More Food for Thought. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 803–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Delgado, J.; Miquel, M. Role of rifaximin in the treatment of hepatic encephalopathy. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 39, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venu, M.; Martin, E.; Saeian, K.; Gawrieh, S. High prevalence of vitamin A deficiency and vitamin D deficiency in patients evaluated for liver transplantation. Liver Transplant. 2013, 19, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Association for The Study of The Liver. EASL clinical practical guidelines: Management of alcoholic liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 399–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manne, V.; Saab, S. Impact of Nutrition and Obesity on Chronic Liver Disease. Clin. Liver Dis. 2014, 18, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, M.K.; Zhou, Z.; Cave, M.; Barve, A.; McClain, C.J. Zinc and liver disease. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2012, 27, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, L.; Song, Z.; Saari, J.T.; McClain, C.J.; Kang, Y.J. Zinc Supplementation Prevents Alcoholic Liver Injury in Mice through Attenuation of Oxidative Stress. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 166, 1681–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merli, M.; Berzigotti, A.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Dasarathy, S.; Montagnese, S.; Genton, L.; Parés, A. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on nutrition in chronic liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 172–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, C.; Hipskind, P.; Tsien, C.; Malin, S.; Kasumov, T.; Shah, S.N.; Kirwan, J.P.; Dasarathy, S. Sarcopenia and a physiologically low respiratory quotient in patients with cirrhosis: A prospective controlled study. J. Appl. Physiol. 2013, 114, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, C.; Hipskind, P.; Cole, D.; Lopez, R.; Dasarathy, S. Handheld calorimeter is a valid instrument to quantify resting energy expenditure in hospitalized cirrhotic patients: A prospective study. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2012, 27, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasarathy, S.; Merli, M. Sarcopenia from mechanism to diagnosis and treatment in liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 1232–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasarathy, J.; McCullough, A.J.; Dasarathy, S. Sarcopenia in Alcoholic Liver Disease: Clinical and Molecular Advances. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 41, 1419–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, A.V.; Mingrone, G.; Benedetti, G.; Capristo, E.; Tataranni, P.A.; Gasbarrini, G. Daily energy and substrate metabolism in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 1998, 27, 346–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmi, F.W.; Panella, C.; Buda, A.; Budillon, G.; Caregaro, L.; Clerici, C.; Federico, A.; Gasbarrini, G.; Guglielmi, A.; Loguercio, C.; et al. Nutritional state and energy balance in cirrhotic patients with or without hypermetabolism. Multicentre prospective study by the ‘Nutritional Problems in Gastroenterology’ Section of the Italian Society of Gastroenterology (SIGE). Dig. Liver Dis. 2005, 37, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggio, O.; Angeloni, S.; Ciuffa, L.; Nicolini, G.; Attili, A.; Albanese, C.; Merli, M. Malnutrition is not related to alterations in energy balance in patients with stable liver cirrhosis. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 22, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondrup, J.; Nielsen, K.; Juul, A. Effect of long-term refeeding on protein metabolism in patients with cirrhosis of the liver. Br. J. Nutr. 1997, 77, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolz, C.; Raurich, J.M.; Ibanez, J.; Obrador, A.; Marse, P.; Gaya, J. Ascites increases the resting energy expenditure in liver cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 1991, 100, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madden, A.M.; Morgan, M.Y. Resting energy expenditure should be measured in patients with cirrhosis, not predicted. Hepatology 1999, 30, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knudsen, A.W.; Krag, A.; Nordgaard-Lassen, I.; Frandsen, E.; Tofteng, F.; Mortensen, C.; Becker, U. Effect of paracentesis on metabolic activity in patients with advanced cirrhosis and ascites. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 51, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.J.; Böker, K.H.W.; Selberg, O. Are patients with liver cirrhosis hypermetabolic? Clin. Nutr. 1994, 13, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Plank, L.D.; McCall, J.L.; Gillanders, L.K.; McIlroy, K.; Gane, E.J. Body composition, muscle function, and energy expenditure in patients with liver cirrhosis: A comprehensive study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 1257–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasa, M.; Iwata, K.; Hara, N.; Hattori, A.; Ishidome, M.; Sekoguchi-Fujikawa, N.; Mifuji-Moroka, R.; Sugimoto, R.; Fujita, N.; Kobayashi, Y.; et al. Nutrition therapy using a multidisciplinary team improves survival rates in patients with liver cirrhosis. Nutrition 2013, 29, 1418–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsien, C.D.; McCullough, A.J.; Dasarathy, S. Late evening snack: Exploiting a period of anabolic opportunity in cirrhosis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 27, 430–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaisman, N.; Katzman, H.; Carmiel-Haggai, M.; Lusthaus, M.; Niv, E. Breakfast improves cognitive function in cirrhotic patients with cognitive impairment. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 92, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, K.; Kondrup, J.; Martinsen, L.; Stilling, B.; Wikman, B. Nutritional assessment and adequacy of dietary intake in hospitalized patients with alcoholic liver cirrhosis. Br. J. Nutr. 1993, 69, 665–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swart, G.R.; van den Berg, J.W.; van Vuure, J.K.; Rietveld, T.; Wattimena, D.L.; Frenkel, M. Minimum protein requirements in liver cirrhosis deter- mined by nitrogen balance measurements at three levels of protein intake. Clin. Nutr. 1989, 8, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenton, J.; Knight, E.; Humpherson, P. Milk-and-cheese diet in portal-systemic encephalopathy. Lancet 1966, 287, 164–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberger, N.J.; Carley, J.; Schenker, S.; Bettinger, I.; Stamnes, C.; Beyer, P. Effect of vegetable and animal protein diets in chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Am. J. Dig. Dis. 1977, 22, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheorghe, L.; Iacob, R.; Vădan, R.; Iacob, S.; Gheorghe, C. Improvement of hepatic encephalopathy using a modified high-calorie high-protein diet. Rom. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 14, 231–238. [Google Scholar]
- Córdoba, J.; López-Hellín, J.; Planas, M.; Sabín, P.; Sanpedro, F.; Castro, F.; Esteban, R.; Guardia, J. Normal protein diet for episodic hepatic encephalopathy: Results of a randomized study. J. Hepatol. 2004, 41, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaya, Y.; Harada, N.; Kakui, S.; Okada, K.; Takahashi, A.; Inoi, J.; Ito, S. Severe catabolic state after prolonged fasting in cirrhotic patients: Effect of oral branched-chain amino-acid-enriched nutrient mixture. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 37, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Muto, Y.; Moriwaki, H.; Yamato, M. Effect of long-term oral supplementation with branched-chain amino acid granules on the prognosis of liver cirrhosis. Gastroenterol. JPN 1989, 24, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fialla, A.D.; Israelsen, M.; Hamberg, O.; Krag, A.; Gluud, L.L. Nutritional therapy in cirrhosis or alcoholic hepatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 2072–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koretz, R.L.; Avenell, A.; Lipman, T.O. Nutritional support for liver disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 23, CD008344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singal, A.K.; Charlton, M.R. Nutrition in alcoholic liver disease. Clin. Liver Dis. 2012, 16, 805–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, P.; Adams, S.; Boullata, J.; Gervasio, J.; Holcombe, B.; Kraft, M.D.; American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition. ASPEN parenteral nutrition safety consensus recommendations. J. Parenteral Enteral Nutr. 2014, 38, 296–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharshi, S.; Sharma, B.C.; Sachdeva, S.; Srivastava, S.; Sharma, P. Efficacy of Nutritional Therapy for Patients With Cirrhosis and Minimal Hepatic Encephalopathy in a Randomized Trial. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 14, 454–460.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calmet, F.; Martin, P.; Pearlman, M. Nutrition in Patients With Cirrhosis. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 15, 248–254. [Google Scholar]
- Bunchorntavakul, C.; Reddy, K.R. malnutrition/sarcopenia and frailty in patients with cirrhosis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 51, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roongpisuthipong, C.; Sobhonslidsuk, A.; Nantiruj, K.; Songchitsomboon, S. Nutritional assessment in various stages of liver cirrhosis. Nutrition 2001, 17, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fried, L.P.; Tangen, C.M.; Walston, J.; Newman, A.B.; Hirsch, C.; Gottdiener, J.; Seeman, T. Cardiovascular Health Study Collaborative Research Group. Frailty in older adults: Evidence for a phenotype. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2001, 56, M146–M156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.; Lee, S.S.; Raman, M. Prevalence and Mechanisms of Malnutrition in Patients With Advanced Liver Disease, and Nutrition Management Strategies. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puneeta, T.; Maitreyi, R.; Marina, M.; Manuela, M. A practical approach to nutritional screening and assessment in cirrhosis. Hepatology 2017, 65, 1044–1057. [Google Scholar]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on nutrition in chronic liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 172–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, H.J.; Yen, C.H.; Wu, I.W.; Liu, M.H.; Cheng, H.Y.; Lin, Y.T.; Wang, C.H. The association between low protein diet and body composition, muscle function, inflammation, and amino acid-based metabolic profile in chronic kidney disease stage 3–5 patients. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2021, 46, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, M.J.; Böttcher, J.; Selberg, O.; Weselmann, S.; Böker, K.H.; Schwarze, M.; Mühlen, A.V.Z.; Manns, M.P. Hypermetabolism in clinically stable patients with liver cirrhosis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 69, 1194–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, S.; Kwarta, E.; Azzam, R.; Sentongo, T. Nutrition assessment and support in children with end-stage liver disease. Nutr. Clin. Prac. 2013, 28, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, A.; Williams, R. Nutrition in End-Stage Liver Disease: Principles and Practice. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 1729–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsome, P.N.; Beldon, I.; Moussa, Y.; Delahooke, T.E.; Poulopoulos, G.; Hayes, P.C.; Plevris, J.N. Low serum retinol levels are associated with hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic liver disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2000, 14, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahelić, D.; Kujundzić, M.; Romić, Z.; Brkić, K.; Petrovecki, M. Serum concentration of zinc, copper, manganese and magnesium in patients with liver cirrhosis. Coll. Antropol. 2006, 30, 523–528. [Google Scholar]
- Vidot, H.; Carey, S.; Allman-Farinelli, M.; Shackel, N. Systematic review: The treatment of muscle cramps in patients with cirrhosis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 40, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskol, M.; Ozbakir, O.; Coşkun, R.; Baskol, G.; Saraymen, R.; Yucesoy, M. The Role of Serum Zinc And Other Factors on the Prevalence of Muscle Cramps in Non-alcoholic Cirrhotic Patients. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2004, 38, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plauth, M.; Cabre, E.; Campillo, B.; Kondrup, J.; Marchesini, G.; Schütz, T.; Wendon, J. ESPEN Guidelines on Parenteral Nutrition. Hepatol. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 28, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, O.E.; Trapp, V.E.; Reichard, G.A.; Mozzoli, M.A.; Moctezuma, J.; Paul, P.; Boden, G. Nature and quantity of fuels consumed in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis. J. Clin. Investig. 1983, 72, 1821–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amodio, P.; Bemeur, C.; Butterworth, R.; Cordoba, J.; Kato, A.; Montagnese, S.; Uribe, M.; Vilstrup, H.; Morgan, M.Y. The nutritional management of hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis: International society for hepatic encephalopathy and nitrogen metabolism consensus. Hepatology 2013, 58, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plank, L.D.; Gane, E.J.; Peng, S.; Muthu, C.; Mathur, S.; Gillanders, L.; McIlroy, K.; Donaghy, A.J.; McCall, J.L. Nocturnal nutritional supplementation improves total body protein status of patients with liver cirrhosis: A randomized 12-month trial. Hepatology 2008, 48, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merli, M. Nutrition in cirrhosis: Dos and Don’ts. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 1563–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakaya, Y.; Okita, K.; Suzuki, K.; Moriwaki, H.; Kato, A.; Miwa, Y.; Shiraishi, K.; Okuda, H.; Onji, M.; Kanazawa, H.; et al. BCAA-enriched snack improves nutritional state of cirrhosis. Nutrition 2007, 23, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muto, Y.; Sato, S.; Watanabe, A.; Moriwaki, H.; Suzuki, K.; Kato, A.; Kato, M.; Nakamura, T.; Higuchi, K.; Nishiguchi, S.; et al. Effects of Oral Branched-Chain Amino Acid Granules on Event-Free Survival in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2005, 3, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toshikuni, N.; Arisawa, T.; Tsutsumi, M. Nutrition and exercise in the manage- ment of liver cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 7286–7297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, F.; Momoki, C.; Yuikawa, M.; Simotani, Y.; Kawamura, E.; Hagihara, A.; Fujii, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Iwai, S.; Morikawa, H.; et al. Nutritional status in relation to lifestyle in patients with compensated viral cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 5759–5770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campillo, B.; Fouet, P.; Bonnet, J.C.; Atlan, G. Submaximal oxygen consumption in liver cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 1990, 10, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berzigotti, A.; Garcia-Tsao, G.; Bosch, J.; Grace, N.D.; Burroughs, A.K.; Morillas, R.; Escorsell, A.; Garcia-Pagan, J.C.; Patch, D.; Matloff, D.S.; et al. Obesity is an independent risk factor for clinical decompensation in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 2011, 54, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everhart, J.E.; Lok, A.S.; Kim, H.; Morgan, T.R.; Lindsay, K.L.; Chung, R.T.; Bonkovsky, H.L.; Ghany, M.G. Weight-Related Effects on Disease Progression in the Hepatitis C Antiviral Long-Term Treatment Against Cirrhosis Trial. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macías-Rodríguez, R.U.; Ilarraza-Lomelí, H.; Ruiz-Margáin, A.; Ponce-De-León-Rosales, S.; Vargas-Vorácková, F.; García-Flores, O.; Torre, A.; Duarte-Rojo, A. Changes in Hepatic Venous Pressure Gradient Induced by Physical Exercise in Cirrhosis: Results of a Pilot Randomized Open Clinical Trial. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2016, 7, e180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenith, L.; Meena, N.; Ramadi, A.; Yavari, M.; Harvey, A.; Carbonneau, M.; Ma, M.; Gonzalez-Abraldes, J.; Paterson, D.I.; Haykowsky, M.J.; et al. Eight Weeks of Exercise Training Increases Aerobic Capacity and Muscle Mass and Reduces Fatigue in Patients With Cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 1920–1926.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidot, H.; Bowen, D.G.; Carey, S.; McCaughan, G.W.; Allman-Farinelli, M.; Shackel, N.A. Aggressive nutrition intervention reduces ascites and frequency of paracentesis in malnourished patients with cirrhosis and ascites. JGH Open 2017, 1, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campillo, B. Nutritional aspects of liver and biliary disease. In Textbook of Hepatology: From Basic Science to Clinical Practice, 3rd ed.; Rodes, J., Benhamou, J.P., Blei, A.T., Reichen, J., Rezzetto, M., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2007; pp. 1922–1930. [Google Scholar]
- Møller, S.; Bendtsen, F.; Christensen, E.; Henriksen, J.H. Prognostic variables in patients with cirrhosis and oesophageal varices without prior bleeding. J. Hepatol. 1994, 21, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautz, H.U.; Selberg, O.; Körber, J.; Burger, M.; Muller, M.J. Proteincalorie malnutrition in liver cirrhosis. Clin. Investig. 1992, 70, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, M.; Gow, P.J.; Grossmann, M.; Angus, P.W. Review article: Sarcopenia in cirrhosis—Aetiology, implications and potential therapeutic interventions. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 43, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montano-Loza, A.J. Clinical relevance of sarcopenia in patients with cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 8061–8071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.M. The methodology of nutritional screening and assessment tools. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2002, 15, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bémeur, C.; Butterworth, R.F. Reprint of: Nutrition in the Management of Cirrhosis and its Neurological Complications. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2015, 5, S131–S140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasse, J.; Strong, S.; Gorman, M.A.; Liepa, G. Subjective global assessment: Alternative nutrition-assessment technique for liver-transplant candidates. Nutrition 1993, 9, 339–343. [Google Scholar]
- Bin, C.M.; Flores, C.; Alvares-da-Silva, M.R.; Francesconi, C.F.M. Comparison between handgrip strength, subjective global assessment, anthropometry, and biochemical markers in assessing nutritional status of patients with Crohn’s disease in clinical remission. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2010, 55, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, C.P.; Buchanan, E.; Holden, C.E.; Preece, M.A.; Green, A.; Booth, I.W.; Tarlow, M.J. Intensive enteral feeding in advanced cirrhosis: Reversal of malnutrition without precipitation of hepatic encephalopathy. Arch. Dis. Child. 1992, 67, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, M.L.S.; Razlan, H.; Goh, K.L.; Taib, S.H.M.; Huzaini, A.H.M.; Rampal, S.; Mahadeva, S. Short-term nasogastric versus oral feeding in hospitalised patients with advanced cirrhosis. e-SPEN Eur. e-J. Clin. Nutr. Metab. 2011, 6, e242–e247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadeva, S.; Goh, K.-L. Letter: Enteral nutrition in advanced cirrhosis—A case of missing the boat? Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 36, 205–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arroyo, V.; Gines, P.; Gerbes, A.L.; Dudley, F.J.; Gentilini, P.; Laffi, G.; Schölmerich, J. Definition and diagnostic criteria of refractory ascites and hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhosis. Hepatology 1996, 23, 164–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teiusanu, A.; Andrei, M.; Arbanas, T.; Nicolaie, T.; Diculescu, M. Nutritional status in cirrhotic patients. Maedica 2012, 7, 284. [Google Scholar]
- Bémeur, C.; Desjardins, P.; Butterworth, R.F. Role of Nutrition in the Management of Hepatic Encephalopathy in End-Stage Liver Failure. J. Nutr. Metab. 2010, 2010, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campillo, B.; Richardet, J.-P.; Scherman, E.; Bories, P.N. Evaluation of nutritional practice in hospitalized cirrhotic patients: Results of a prospective study. Nutrition 2003, 19, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Changani, K.K.; Jalan, R.; Cox, I.J.; Ala-Korpela, M.; Bhakoo, K.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D.; Bell, J.D. Evidence for altered hepatic gluconeogenesis in patients with cirrhosis using in vivo 31-phosphorus magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Gut 2001, 49, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plauth, M.; Cabré, E.; Riggio, O.; Assis-Camilo, M.; Pirlich, M.; Kondrup, J.; Ferenci, P.; Holm, E.; Dahl, S.V.; Müller, M.; et al. ESPEN Guidelines on Enteral Nutrition: Liver disease. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 25, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherlock, S. Hepatic encephalopathy. In Diseases of the Liver and Biliary System, 8th ed.; Blackwell Scientific: Oxford, UK, 1989; pp. 109–110. [Google Scholar]
- Donaghy, A. Issues of malnutrition and bone disease in patients with cirrhosis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2002, 17, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyman, J.K.; Rn, C.J.W.; Brock, K.E.; Mccaughan, G.; Donaghy, A.J. Dietary protein intakes in patients with hepatic encephalopathy and cirrhosis: Current practice in NSW and ACT. Med. J. Aust. 2006, 185, 542–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, K.D.; Dasarathy, S. Protein restriction in hepatic encephalopathy: Necessary evil or illogical dogma? J. Hepatol. 2004, 41, 147–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plauth, M.; Merli, M.; Kondrup, J.; Weimann, A.; Ferenci, P.; Müller, M. ESPEN guidelines for nutrition in liver disease and transplantation. Clin. Nutr. 1997, 16, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plauth, M.; Merli, M.; Kondrup, J. Management of hepatic encephalopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 337, 1921–1922. [Google Scholar]
- Merli, M.; Riggio, O. Dietary and nutritional indications in hepatic encephalopathy. Metab. Brain Dis. 2008, 24, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshavarzian, A.; Meek, J.; Sutton, C.; Emery, V.M.; Hughes, E.A.; Hodgson, H.J. Dietary protein supplementation from vegetable sources in the management of chronic portal systemic encephalopathy. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1984, 79, 945–949. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi, G.P.; Marchesini, G.; Fabbri, A.; Rondelli, A.; Bugianesi, E.; Zoli, M.; Pisi, E. Vegetable versus animal protein diet in cirrhotic patients with chronic encephalopathy. A randomized cross-over comparison. J. Intern. Med. 1993, 233, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louvet, A.; Artru, F.; Canva-Delcambre, V.; Dharancy, S.; Mathurin, P. Maladie alcoolique du foie. La Lett. De L’hépato-Gastroentérologue 2013, 16, 118–122. [Google Scholar]
- Sherlock, S. Diseases of the Liver and Biliary System, 9th ed.; Blackwell Scientific: Oxford, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Henkel, A.S.; Buchman, A.L. Nutritional support in patients with chronic liver disease. Nat. Clin. Pr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2006, 3, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCluskey, S.A.; Karkouti, K.; Wijeysundera, D.N.; Kakizawa, K.; Ghannam, M.; Hamdy, A.; Grant, D.; Levy, G. Derivation of a risk index for the prediction of massive blood transfusion in liver transplantation. Liver Transplant. 2006, 12, 1584–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusai, G.; Dhaliwal, P.; Rolando, N.; Sabin, C.A.; Patch, D.; Davidson, B.R.; Burroughs, A.K.; Rolles, K. Incidence and risk factors for the development of prolonged and severe intrahepatic cholestasis after liver transplantation. Liver Transplant. 2006, 12, 1626–1633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teperman, L.W.; Peyregne, V.P. Considerations on the Impact of Hepatic Encephalopathy Treatments in the Pretransplant Setting. Transplantation 2010, 89, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, B.; Wood, R.; Gordon, R.; Iwatsuki, S.; Gillquist, W.; Starzl, T. Influence of Selected Patient Variables and Operative Blood Loss on Six-Month Survival Following Liver Transplantation. Semin. Liver Dis. 1985, 5, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selberg, O.; Bottcher, J.; Tusch, G.; Pichlmayr, R.; Henkel, E.; Muller, M.J. Identification of high- and low-risk patients before liver transplantation: A prospective cohort study of nutritional and metabolic parameters in 150 patients. Hepatology 1997, 25, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, C.; Iriyama, K.; Mayer, A.; Buckels, J.A.; Harrison, J.D.; Suzuki, H.; McMaster, P. Energy storage and cytokine response in patients undergoing liver transplantation. Cytokine 1999, 11, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasse, J.M.; Blue, L.S.; Liepa, G.U.; Goldstein, R.M.; Jennings, L.W.; Mor, E.; Husberg, B.S.; Levy, M.F.; Gonwa, T.A.; Klintmalm, G.B. Early Enteral Nutrition Support in Patients Undergoing Liver Transplantation. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 1995, 19, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reilly, J.; Mehta, R.; Teperman, L.; Cemaj, S.; Tzakis, A.; Yanaga, K.; Ritter, P.; Rezak, A.; Makowka, L. Nutritional Support after Liver Transplantation: A Randomized Prospective Study. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 1990, 14, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, K.N. The Role of Some Foods and Diet Habits in Cholecystitis and Gallstones in Mosul in Iraq. J. Cardiovasc Disease Res. 2020, 11, 189–193. [Google Scholar]
- Stinton, L.M.; Shaffer, E.A. Epidemiology of Gallbladder Disease: Cholelithiasis and Cancer. Gut Liver 2012, 6, 172–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.; Cheung, R.C.; Keeffe, E.B. Management of gallstones and their complications. Am. Fam. Physician 2000, 61, 1673–1680. [Google Scholar]
- Pixley, F.; Wilson, D.; McPherson, K.; Mann, J. Effect of vegetarianism on development of gall stones in women. BMJ 1985, 291, 11–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-J.; Leitzmann, M.F.; Willett, W.C.; Giovannucci, E.L. Fruit and Vegetable Consumption and Risk of Cholecystectomy in Women. Am. J. Med. 2006, 119, 760–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, J.A.; Hudes, E.S. Serum ascorbic acid and gallbladder disease prevalence among US adults: The Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III). Arch. Intern. Med. 2000, 160, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-J.; Leitzmann, M.F.; Willett, W.C.; Giovannucci, E.L. Dietary Protein and the Risk of Cholecystectomy in a Cohort of US Women: The Nurses’ Health Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2004, 160, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclure, K.M.; Hayes, K.C.; Colditz, G.A.; Stampfer, M.J.; Willett, W.C. Dietary predictors of symptom-associated gallstones in middle-aged women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1990, 52, 916–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.J.; Leitzmann, M.F.; Willett, W.C.; Giovannucci, E.L. The effect of long-term intake of cis unsaturated fats on the risk for gallstone disease in men: A prospective cohort study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2004, 141, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-J.; Leitzmann, M.F.; Willett, W.C.; Giovannucci, E.L. Long-term Intake of trans-Fatty Acids and Risk of Gallstone Disease in Men. Arch. Intern. Med. 2005, 165, 1011–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halldestam, I.; Kullman, E.; Borch, K. Incidence of and potential risk factors for gallstone disease in a general population sample. Br. J. Surg. 2009, 96, 1315–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlinger, S. Gallstones in obesity and weight loss. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2000, 12, 1347–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, J.R.; Emmett, P.M.; Heaton, K.W. Diet and gall stones: Effects of refined and unrefined carbohydrate diets on bile cholesterol saturation and bile acid metabolism. Gut 1983, 24, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-J.; Leitzmann, M.F.; Willett, W.C.; Giovannucci, E.L. Dietary carbohydrates and glycaemic load and the incidence of symptomatic gall stone disease in men. Gut 2005, 54, 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.-J.; Leitzmann, M.F.; Willett, W.C.; Giovannucci, E.L. Long-Term Intake of Dietary Fiber and Decreased Risk of Cholecystectomy in Women. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 99, 1364–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attili, A.F.; Scafato, E.; Marchioli, R.; Marfisi, R.M.; Festi, D.; The MICOL Group. Diet and gallstones in italy: The cross-sectional MICOL results. Hepatology 1998, 27, 1492–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everhart, J.E. Contributions of Obesity and Weight Loss to Gallstone Disease. Ann. Intern. Med. 1993, 119, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syngal, S.; Coakley, E.H.; Willett, W.C.; Byers, T.; Williamson, D.F.; Colditz, G. Long-Term Weight Patterns and Risk for Cholecystectomy in Women. Ann. Intern. Med. 1999, 130, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.-J.; Leitzmann, M.F.; Willett, W.C.; Giovannucci, E.L. Weight Cycling and Risk of Gallstone Disease in Men. Arch. Intern. Med. 2006, 166, 2369–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebhard, R.L.; Prigge, W.F.; Ansel, H.J.; Schlasner, L.; Ketover, S.R.; Sande, D.; Peterson, F.J. The role of gallbladder emptying in gallstone formation during diet-induced rapid weight loss. Hepatology 1996, 24, 544–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R.G. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A study of 49 patients. Hum. Pathol. 1989, 20, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, J.; Viggiano, T.R.; McGill, D.B.; Oh, B.J. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: Mayo Clinic experiences with a hitherto unnamed disease. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1980, 55, 434–438. [Google Scholar]
- Bacon, B.R.; Farahvash, M.J.; Janney, C.G.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: An expanded clinical entity. Gastroenterology 1994, 107, 1103–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathya, P.; Martin, S.; Alvarez, F. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in children. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2002, 14, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, L.M.; Lisker-Melman, M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Ann. Hepatol. 2004, 3, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gashgari, A.M.N.; Alhusainy, K.M.; Alharbi, F.O.E.; Hani, M.A.Q.F.; Omer, A.M.; Alali, A.H.; Alsharif, M. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). Egypt. J. Hosp. Med. 2018, 70, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirmiran, P.; Amirhamidi, Z.; Ejtahed, H.-S.; Bahadoran, Z.; Azizi, F. Relationship between Diet and Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Review Article. Iran. J. Public Health 2017, 46, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar]
- Kalafati, I.P.; Borsa, D.; Dimitriou, M.; Revenas, K.; Kokkinos, A.; Dedoussis, G.V. Dietary patterns and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in a Greek case–control study. Nutrition 2019, 61, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelber-Sagi, S.; Ivancovsky-Wajcman, D.; Isakov, N.F.; Webb, M.; Orenstein, D.; Shibolet, O.; Kariv, R. High red and processed meat consumption is associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Li, Y.; Guo, X.; Zhong, L.; Tang, S. Food groups and the likelihood of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Nutr. 2020, 124, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luukkonen, P.K.; Sädevirta, S.; Zhou, Y.; Kayser, B.; Ali, A.; Ahonen, L.; Lallukka, S.; Pelloux, V.; Gaggini, M.; Jian, C.; et al. Saturated Fat Is More Metabolically Harmful for the Human Liver Than Unsaturated Fat or Simple Sugars. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 1732–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astrup, A.; Magkos, F.; Bier, D.M.; Brenna, J.T.; De Oliveira Otto, M.C.; Hill, J.O.; King, J.C.; Mente, A.; Ordovas, J.M.; Volek, J.S.; et al. Saturated Fats and Health: A Reassessment and Proposal for Food-Based Recommendations: JACC State-of-the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 844–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, T.-T.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, Y.-F.; Han, Y.-J.; Xiong, J.-J.; Wu, X.-X.; Chen, Y.-P.; Zheng, M.-H. Lifestyle interventions for patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A network meta-analysis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 30, 747–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, V.W.-S.; Wong, G.L.-H.; Chan, R.S.-M.; Shu, S.S.-T.; Cheung, B.H.-K.; Li, L.S.; Chim, A.M.-L.; Chan, C.K.-M.; Leung, J.K.-Y.; Chu, W.C.-W.; et al. Beneficial effects of lifestyle intervention in non-obese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshakbayev, K.; Bimbetov, B.; Manekenova, K.; Bedelbayeva, G.; Mustafin, K.; Dukenbayeva, B. Severe nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and type 2 diabetes: Liver histology after weight loss therapy in a randomized clinical trial. Curr. Med Res. Opin. 2018, 35, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promrat, K.; Kleiner, D.E.; Niemeier, H.M.; Jackvony, E.; Kearns, M.; Wands, J.R.; Fava, J.L.; Wing, R.R. Randomized controlled trial testing the effects of weight loss on nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2010, 51, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, L.M.; Dickson, R.C.; Anderson, J.C.; Suriawinata, A.A.; Putra, J.; Berk, B.S.; Toor, A. Total Body Weight Loss of ≥10 % Is Associated with Improved Hepatic Fibrosis in Patients with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2014, 60, 1024–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebbeling, C.B.; Feldman, H.A.; Klein, G.L.; Wong, J.M.W.; Bielak, L.; Steltz, S.K.; Luoto, P.K.; Wolfe, R.R.; Wong, W.W.; Ludwig, D.S. Effects of a low carbohydrate diet on energy expenditure during weight loss maintenance: Randomized trial. BMJ 2018, 363, k4583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra-Vargas, M.; Rodriguez-Echevarria, R.; Jimenez-Chillaron, J.C. Nutritional Approaches for the Management of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: An Evidence-Based Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.D.; Hainaut, P.; Gores, G.J.; Amadou, A.; Plymoth, A.; Roberts, L.R. A global view of hepatocellular carcinoma: Trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 589–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziouziou, I.; Shariat, S.F.; Ajdi, F.; Khabbal, Y. Association of Processed Meats and Alcohol Consumption with Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Worldwide Population-Based Study. Nutr. Cancer 2020, 73, 2665–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golabi, P.; Rhea, L.; Henry, L.; Younossi, Z.M. Hepatocellular carcinoma and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol. Int. 2019, 13, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulik, L.; El-Serag, H.B. Epidemiology and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 477–491.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, N.; Inoue, M.; Iwasaki, M.; Sasazuki, S.; Shimazu, T.; Yamaji, T.; Takachi, R.; Tanaka, Y.; Mizokami, M.; Tsugane, S. Consumption of n-3 Fatty Acids and Fish Reduces Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1468–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanders, A.J.; van den Borne, J.J.G.C.; De Graaf, C.; Hulshof, T.; Jonathan, M.C.; Kristensen, M.; Mars, M.; Schols, H.A.; Feskens, E.J.M. Effects of dietary fibre on subjective appetite, energy intake and body weight: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Obes. Rev. 2011, 12, 724–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babio, N.; Balanza, R.; Basulto, J.; Bulló, M.; Salas-Salvadó, J. Dietary fibre: Influence on body weight, glycemic control and plasma cholesterol profile. Nutr. Hosp. 2010, 25, 327–340. [Google Scholar]
- Duarte-Rojo, A.; Ruiz-Margáin, A.; Montaño-Loza, A.J.; Macías-Rodríguez, R.U.; Ferrando, A.; Kim, W.R. Exercise and physical activity for patients with end-stage liver disease: Improving functional status and sarcopenia while on the transplant waiting list. Liver Transplant. 2017, 24, 122–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montano-Loza, A.J.; Meza-Junco, J.; Prado, C.M.; Lieffers, J.R.; Baracos, V.E.; Bain, V.G.; Sawyer, M.B. Muscle wasting is associated with mortality in patients with cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Margáin, A.; Román-Calleja, B.M.; Moreno-Guillén, P.; González-Regueiro, J.A.; Kúsulas-Delint, D.; Campos-Murguía, A.; Flores-García, N.C.; Macías-Rodríguez, R.U. Nutritional therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2021, 13, 1440–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, O.; Akbarzadeh, S.; Ghazanfari Hashemi, M.; Gholami, M.; Amini, P.; Yekanipour, Z.; Poortahmasebi, V. Hepatitis A: Viral Structure, Classification, Life Cycle, Clinical Symptoms, Diagnosis Error, and Vaccination. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2023, 2023, 4263309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, N.P.; Weng, M.K.; Hofmeister, M.G.; Moore, K.L.; Doshani, M.; Kamili, S.; Harris, A.M. Prevention of hepatitis A virus infection in the United States: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices. MMWR Recomm. Rep. 2020, 69, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linder, K.A.; Malani, P.N. Hepatitis A. JAMA 2017, 318, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noël, L.; Tubiana, R.; Simon, A.; Valantin, M.-A.; Palich, R.; Blanc, C.; Katlama, C.; Marcelin, A.-G.; Calvez, V.; Todesco, E. Low immune response rate of HIV-infected patients to a single injection of hepatitis A vaccine. Infect. Dis. Now 2021, 51, 94–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, R.V.; Shinde, A.R.; Patil, A.D.; Pawar, S.; Mohite, S.; Patil, S. Co-infection of Hepatitis A and Hepatitis E Viruses among the Acute Viral Hepatitis Cases in Tertiary Care Hospital—A Four Years Retrospective Study. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 14, 2047–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndumbi, P.; Freidl, G.S.; Williams, C.J.; Mårdh, O.; Varela, C.; Avellón, A.; Severi, E. Members of the european hepatitis a outbreak investigation teamhepatitis a outbreak disproportionately affecting men who have sex with men (MSM) in the European Union and European Economic Area. Euro Surveill. 2018, 23, 1700641. [Google Scholar]
- Van Damme, P. Hepatitis a vaccines. In Pediatric Vaccines and Vaccinations; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 99–108. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, P.S.; Hong, S.-H.; Lee, J.; Park, S.-H.; Yoon, S.K.; Chung, W.J.; Shin, E.-C. CXCL10 is produced in hepatitis A virus-infected cells in an IRF3-dependent but IFN-independent manner. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arum, C.; Fraser, H.; Artenie, A.A.; Bivegete, S.; Trickey, A.; Alary, M.; Strathdee, S.A. Homelessness, unstable housing, and risk of HIV and hepatitis C virus acquisition among people who inject drugs: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Public Health 2021, 6, e309–e323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Win, N.N.; Kanda, T.; Ogawa, M.; Nakamoto, S.; Haga, Y.; Sasaki, R.; Nakamura, M.; Wu, S.; Matsumoto, N.; Matsuoka, S.; et al. Superinfection of hepatitis A virus in hepatocytes infected with hepatitis B virus. Int. J. Med Sci. 2019, 16, 1366–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, H.; Ushijima, Y.; Bikangui, R.; Ondo, G.N.; Zadeh, V.R.; Pemba, C.M.; Mpingabo, P.I.; Igasaki, Y.; De Vries, S.G.; Grobusch, M.P.; et al. First evidence for continuous circulation of hepatitis A virus subgenotype IIA in Central Africa. J. Viral Hepat. 2020, 27, 1234–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peak, C.M.; Stous, S.S.; Healy, J.M.; Hofmeister, M.G.; Lin, Y.; Ramachandran, S.; McDonald, E.C. Homelessness and hepatitis A—San diego county, 2016–2018. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 71, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaswamy, M.; Bruden, D.; Nolen, L.D.; Mosites, E.; Snowball, M.; Nelson, N.P.; Bruce, M.; McMahon, B.J. Hepatitis A vaccine immunogenicity 25 years after vaccination in Alaska. J. Med. Virol. 2020, 93, 3991–3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gedam, S.R.; Dhabarde, A.; Patil, P.S.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, K.; Babar, V. Psychiatric Comorbidity, Severity of Dependence and Liver Enzymes Dysfunction among Alcohol Dependent Individuals: A Cross-sectional Study from Central Rural India. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2019, 13, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, C.R.D.A.; Amado, L.A.; Tourinho, R.S.; Lima, L.R.P.; Melgaço, J.G.; De Almeida, A.J.; Bastos, L.S.; Lewis-Ximenez, L.L.; de Paula, V. Accuracy of rapid test for diagnosis of hepatitis A with different infection rate settings and with predictive modeling. Futur. Microbiol. 2019, 14, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahyuddin, D.; Amin, M.; Yamani, L.N.; Utsumi, T.; Sustini, F.; Lusida, M.I. Analysis of genetic and serology of hepatitis A virus infection during and after outbreak in two junior high schools in Surabaya, Indonesia. J. Med Virol. 2019, 91, 1048–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepard, C.W.; Simard, E.P.; Finelli, L.; Fiore, A.E.; Bell, B.P. Hepatitis B virus infection: Epidemiology and vaccination. Epidemiol. Rev. 2006, 28, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization WHO. Hepatitis B. 2020. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-b (accessed on 8 July 2021).
- Allain, J.P.; Candotti, D.; Soldan, K.; Sarkodie, F.; Phelps, B.; Giachetti, C.; Opare-Sem, O. The risk of hepatitis B virus infection by transfusion in Kumasi, Ghana. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2003, 101, 2419–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seal, K.H.; Edlin, B.R.; Ochoa, K.C.; Tulsky, J.P.; Moss, A.R.; Hahn, J.A. Risk of hepatitis B infection among young injection drug users in San Francisco: Opportunities for intervention. West. J. Med. 2000, 172, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.H.; Wong, G.; Gane, E.; Kao, J.-H.; Dusheiko, G. Hepatitis B Virus: Advances in Prevention, Diagnosis, and Therapy. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2020, 33, e00046-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koithan, M.; Devika, J. New Approaches to Nutritional Therapy. J. Nurse Pr. 2010, 6, 805–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose-Abrego, A.; Rivera-Iñiguez, I.; Torres-Reyes, L.A.; Roman, S. Anti-hepatitis B virus activity of food nutrients and potential mechanisms of action. Ann. Hepatol. 2022, 100766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finck, B.N.; Kelly, D.P. PGC-1 coactivators: Inducible regulators of energy metabolism in health and disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, C.-F.; Yu, C.-H.; Chang, H.-Y.; Hsieh, W.-C.; Wu, T.-H.; Lin, J.-H.; Wu, H.-C.; Jeng, L.-B.; Su, I.-J. Chemopreventive Effect of Phytosomal Curcumin on Hepatitis B Virus-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma in A Transgenic Mouse Model. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lim, J.; Kim, J.R.; Cho, S. Inhibitory effects of resveratrol on hepatitis B virus X protein-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Veter-Sci. 2017, 18, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praharaj, D.L.; Anand, A.C. Nutrition in Viral Hepatitis. Curr. Hepatol. Rep. 2023, 22, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Guo, C. Epidemiology and Prevention of Hepatitis A in Travelers. J. Travel Med. 2013, 20, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leblanc, D.; Poitras, E.; Gagné, M.-J.; Ward, P.; Houde, A. Hepatitis E virus load in swine organs and tissues at slaughterhouse determined by real-time RT-PCR. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 139, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yugo, D.M.; Meng, X.-J. Hepatitis E Virus: Foodborne, Waterborne and Zoonotic Transmission. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2013, 10, 4507–4533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasutake, K.; Kohjima, M.; Nakashima, M.; Kotoh, K.; Nakamuta, M.; Enjoji, M. Nutrition Therapy for Liver Diseases Based on the Status of Nutritional Intake. Gastroenterol. Res. Pr. 2012, 2012, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.P.; De Jesus, R.P.; Boulhosa, R.S.; Mendes, C.M.C.; Gnoatto, M.C.; Lemaire, D.C.; Toralles, M.B.P.; Cavalcante, L.N.; Lyra, A.C.; Lyra, L.G. Effect of soy protein supplementation in patients with chronic hepatitis C: A randomized clinical trial. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 2203–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggio, R.; Viscomi, C.; Andreozzi, P.; D’Ettorre, G.; Viscogliosi, G.; Barbaro, B.; Balsano, C. Normocaloric low cholesterol diet modulates Th17/Treg balance in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villar, L.M.; Del Campo, J.A.; Ranchal, I.; Lampe, E.; Romero-Gomez, M. Association between vitamin D and hepatitis C virus infection: A meta-analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 5917–5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Refaat, B.; El-Shemi, A.G.; Ashshi, A.; Azhar, E. Vitamin D and chronic hepatitis C: Effects on success rate and prevention of side effects associated with pegylated interferon-α and ribavirin. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 10284–10303. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mechie, N.-C.; Goralzcyk, A.D.; Reinhardt, L.; Mihm, S.; Amanzada, A. Association of serum vitamin B12 levels with stage of liver fibrosis and treatment outcome in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection: A retrospective study. BMC Res. Notes 2015, 8, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardin, R.; Piciocchi, M.; Martines, D.; Scribano, L.; Petracco, M.; Farinati, F. Effects of coffee consumption in chronic hepatitis C: A randomized controlled trial. Dig. Liver Dis. 2013, 45, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, D.M.; Harrison, S.A. Is It Time to Write a Prescription for Coffee? Coffee and Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 670–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, S.C.; Singer, P.; Koller, M.; Barazzoni, R.; Cederholm, T.; van Gossum, A. Standard operating procedures for ESPEN guidelines and consensus papers. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schütte, K.; Tippelt, B.; Schulz, C.; Röhl, F.-W.; Feneberg, A.; Seidensticker, R.; Arend, J.; Malfertheiner, P. Malnutrition is a prognostic factor in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Clin. Nutr. 2014, 34, 1122–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvares-da-Silva, M.R.; da Silveira, R.T. Comparison between handgrip strength, subjective global assessment, and prognostic nutritional index in assessing malnutrition and predicting clinical outcome in cirrhotic outpatients. Nutrition 2005, 21, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belarmino, G.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Torrinhas, R.S.; Sala, P.; Andraus, W.; D’Albuquerque, L.A.C.; Pereira, R.M.R.; Caparbo, V.F.; Ravacci, G.R.; Damiani, L.; et al. Phase angle obtained by bioelectrical impedance analysis independently predicts mortality in patients with cirrhosis. World J. Hepatol. 2017, 9, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.W.; Feng, S.; Covinsky, K.E.; Hayssen, H.; Zhou, L.Q.; Yeh, B.M.; Lai, J.C. A comparison of muscle function, mass, and quality in liver transplant can- didates: Results from the functional assessment in liver transplantation study. Transplantation 2016, 100, 1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.C. Defining the threshold for too sick for transplant. Curr. Opin. Organ Transplant. 2016, 21, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, M.; Poltavskiy, E.; Dodge, J.L.; Lai, J.C. Frailty is independently associated with increased hospitalisation days in patients on the liver transplant waitlist. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsien, C.; Shah, S.N.; McCullough, A.J.; Dasarathy, S. Reversal of sarcopenia predicts survival after a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic stent. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 25, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanai, T.; Shiraki, M.; Nishimura, K.; Imai, K.; Suetsugu, A.; Takai, K.; Shimizu, M.; Naiki, T.; Moriwaki, H. Free fatty acid as a marker of energy malnutrition in liver cirrhosis. Hepatol. Res. 2013, 44, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasarathy, S. Posttransplant sarcopenia: An underrecognized early conse- quence of liver transplantation. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2013, 58, 3103–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiMartini, A.; Cruz, R.J., Jr.; Dew, M.A.; Myaskovsky, L.; Goodpaster, B.; Fox, K. Muscle mass predicts outcomes following liver transplantation. Liver Transplant. 2013, 19, 1172–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englesbe, M.J.; Patel, S.P.; He, K.; Lynch, R.J.; Schaubel, D.E.; Harbaugh, C. Sarcopenia and mortality after liver transplantation. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2010, 211, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montano-Loza, A.J.; Angulo, P.; Meza-Junco, J.; Prado, C.M.M.; Sawyer, M.B.; Beaumont, C.; Esfandiari, N.; Ma, M.; Baracos, V.E. Sarcopenic obesity and myosteatosis are associated with higher mortality in patients with cirrhosis. J. Cachex-Sarcopenia Muscle 2015, 7, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, T.S.; Wigmore, S.J.; Hopton, P.; Richardson, R.; Lee, A. Energy expenditure in acetaminophen-induced fulminant hepatic failure. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 28, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathur, S.; Peng, S.; Gane, E.J.; McCall, J.L.; Plank, L.D. Hypermetabolism predicts reduced transplant-free survival independent of MELD and Child-Pugh scores in liver cirrhosis. Nutrition 2007, 23, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hipskind, P.; Glass, C.; Charlton, D.; Nowak, D.; Dasarathy, S. Do handheld calorimeters have a role in assessment of nutrition needs in hospitalized patients? A systematic review of literature. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2011, 26, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, K.; Kondrup, J.; Martinsen, L.; Døssing, H.; Larsson, B.; Stilling, B.; Jensen, M.G. Long-term oral refeeding of patients with cirrhosis of the liver. Br. J. Nutr. 1995, 74, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamond, I.R.; de Silva, N.T.; Tomlinson, G.A.; Pencharz, P.B.; Feldman, B.M.; Moore, A.M. The role of parenteral lipids in the development of advanced intestinal failure-associated liver disease in infants: A multiple- variable analysis. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2011, 35, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanko, R.T.; Nathan, G.; Mendelow, H.; Adibi, S.A. Development of hepatic cholestasis and fibrosis in patients with massive loss of intestine supported by prolonged parenteral nutrition. Gastroenterology 1987, 92, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, D.A. Intestinal failure-associated liver disease: What do we know today? Gastroenterology 2006, 130, S70–S77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pironi, L.; Arends, J.; Bozzetti, F.; Cuerda, C.; Gillanders, L.; Jeppesen, P.B.; Joly, F.; Kelly, D.; Lal, S.; Staun, M.; et al. ESPEN guidelines on chronic intestinal failure in adults. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 247–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calkins, K.L.; Dunn, J.C.; Shew, S.B.; Reyen, L.; Farmer, D.G.; Devaskar, S.U. Pediatric intestinal failure-associated liver disease is reversed with 6 months of intravenous fish oil. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2014, 38, 682–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, H.D.; de Meijer, V.E.; Zurakowski, D.; Meisel, J.A.; Gura, K.M.; Puder, M. Parenteral Fish Oil as Monotherapy Improves Lipid Profiles in Children With Parenteral Nutrition–Associated Liver Disease. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2010, 34, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandivada, P.; Chang, M.I.M.; Potemkin, A.K.B.; Carlson, S.J.M.; Cowan, E.; O’Loughlin, A.A.M.; Mitchell, P.D.M.; Gura, K.M.P.D.; Puder, M. The Natural History of Cirrhosis from Parenteral Nutrition-Associated Liver Disease after Resolution of Cholestasis with Parenteral Fish Oil Therapy. Ann. Surg. 2015, 261, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angsten, G.; Finkel, Y.; Lucas, S.; Kassa, A.M.; Paulsson, M.; Lilja, H.E. Improved outcome in neonatal short bowel syndrome using parenteral fish oil in combination with omega-6/9 lipid emulsions. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2012, 36, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomsits, E.; Pataki, M.; Tolgyesi, A.; Fekete, G.; Rischak, K.; Szollar, L. Safety and efficacy of a lipid emulsion containing a mixture of soybean oil, medium- chain triglycerides, olive oil, and fish oil: A randomised, double-blind clin- ical trial in premature infants requiring parenteral nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2010, 51, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowyer, B.A.; Fleming, C.R.; Ludwig, J.; Petz, J.; McGill, D.B. Does long-term home parenteral nutrition in adult patients cause chronic liver disease? J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 1985, 9, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavicchi, M.; Beau, P.; Crenn, P.; Degott, C.; Messing, B. Prevalence of Liver Disease and Contributing Factors in Patients Receiving Home Parenteral Nutrition for Permanent Intestinal Failure. Ann. Intern. Med. 2000, 132, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, D.L.; Gill, B.M. Reversal of Parenteral Nutrition–Associated Liver Disease With a Fish Oil–Based Lipid Emulsion (Omegaven) in an Adult Dependent on Home Parenteral Nutrition. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2012, 37, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venecourt-Jackson, E.; Hill, S.J.; Walmsley, R.S. Successful treatment of parenteral nutrition–associated liver disease in an adult by use of a fish oil–based lipid source. Nutrition 2013, 29, 356–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, B.; Li, J. Effect of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids to reverse biopsy-proven parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease in adults. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 31, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pironi, L.; Colecchia, A.; Guidetti, M.; Belluzzi, A.; D’Errico, A. Fish oil-based emulsion for the treatment of parenteral nutrition associated liver disease in an adult patient. e-SPEN Eur. e-J. Clin. Nutr. Metab. 2010, 5, e243–e246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemmesen, J.O.; Kondrup, J.; Ott, P. Splanchnic and leg exchange of amino acids and ammonia in acute liver failure. Gastroenterology 2000, 118, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilstrup, H.; Iversen, J.; Tygstrup, N. Glucoregulation in acute liver failure. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1986, 16, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemmesen, J.O.; Høy, C.-E.; Kondrup, J.; Ott, P. Splanchnic metabolism of fuel substrates in acute liver failure. J. Hepatol. 2000, 33, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClave, S.A.; Taylor, B.E.; Martindale, R.G.; Warren, M.M.; Johnson, D.R.; Braunschweig, C.; McCarthy, M.S.; Davanos, E.; Rice, T.W.; Cresci, G.A.; et al. Guidelines for the provision and assessment of nutrition support therapy in the adult critically ill patient: Society of critical care medicine (SCCM) and American society for parenteral and enteral nutrition (A.S.P.E.N.). J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2016, 40, 159–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabinowich, L.; Wendon, J.; Bernal, W.; Shibolet, O. Clinical management of acute liver failure: Results of an international multi-center survey. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 7595–7603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendenhall, C.L.; Tosch, T.; Weesner, R.E.; Garcia-Pont, P.; Goldberg, S.J.; Kiernan, T.; Seeff, L.B.; Sorell, M.; Tamburro, C.; Zetterman, R.; et al. VA cooperative study on alcoholic hepatitis II: Prognostic significance of protein-calorie malnutrition. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1986, 43, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, C.; Deltenre, P.; Senterre, C.; Louvet, A.; Gustot, T.; Bastens, B.; Hittelet, A.; Piquet, M.-A.; Laleman, W.; Orlent, H.; et al. Intensive Enteral Nutrition Is Ineffective for Patients With Severe Alcoholic Hepatitis Treated With Corticosteroids. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 903–910.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koretz, R.L. The evidence for the use of nutritional support in liver disease. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 30, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Shah, V.H. New prospects for medical management of acute alcoholic hepatitis. Clin. Liver Dis. 2019, 13, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonkovsky, H.L.; Singh, R.H.; Jafri, I.H.; Fiellin, D.A.; Smith, G.S.; Simon, D. A randomized, controlled trial of treatment of alcoholic hepatitis with parenteral nutrition and oxandrolone. II. Short-term effects on nitrogen metabolism, metabolic balance, and nutrition. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1991, 86, 1209–1218. [Google Scholar]
- Cabre, E.; Rodriguez-Iglesias, P.; Caballeria, J.; Quer, J.C.; Sanchez-Lombrana, J.L.; Pares, A. Short- and long-term outcome of severe alcohol-induced hepatitis treated with steroids or enteral nutrition: A multicenter randomized trial. Hepatology 2000, 32, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antar, R.; Wong, P.; Ghali, P. A Meta-Analysis of Nutritional Supplementation for Management of Hospitalized Alcoholic Hepatitis. Can. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 26, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foody, W.; Heuman, D.D.; Mihas, A.A.; Schubert, M.L. Nutritional therapy for alcoholic hepatitis: New life for an old idea. Gastroenterology 2001, 120, 1053–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Hepatic Dysfunction | Required Dietary Modifications | N. Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Patients with (ALF: acute liver failure, ASH: alcoholic steatohepatitis) and cirrhosis | REE is usually increased (REE, resting energy expenditure) | [222] |
| patients with NAFLD (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease) | Normal REE | [222] |
| Malnutrition and sarcopenia | Malnutrition can impair the whole spectrum of hepatic metabolic-functions, and malnutrition alone can cause severe fatty liver but is not known to cause chronic liver disease | [223] |
| Patients with chronic liver diseases and have a sedentary life style | Should receive a total energy supply of 1.3*REE | [224] |
| Acute Liver Failure (ALF) | A severe disorder of carbohydrate, protein, and lipid metabolism should be expected in ALF due to subtotal loss of hepatocellular function and ensuing multi-organ failure. This disorder is characterised by impaired hepatic glucose production and lactate clearance as well as protein catabolism linked to hyper-aminoacidemia and hyper-ammonemia | [72] |
| Acute Liver Failure (ALF) | In ALF patients, obesity is associated with an increased risk of death or need for transplantation and increased mortality ofter transplantation | [225] |
| In patients with mild hepatic encephalopathy | ONS “oral nutritional supplements” should be used when feeding goals cannot be attained by oral nutrition alone | [226] |
| In patients with severe hyper-acute disease with hepatic encephalopathy and highly elevated arterial ammonia who are at risk of cerebral edema | Nutritional protein support can be deferred for 24–48 h until hyper-ammonemia is controlled. When protein administration is commenced, arterial ammonia should be monitored to ensure no pathological elevation occurs. | [227] |
| Acute Liver Failure (ALF) who cannot be fed orally | Should receive EN via nasogastric Inaso-jejunal tube | [228] |
| EN: enteral nutrition in Acute Liver Failure (ALF) | ALF patients without malnutrition should be provided with nutritional support (preferentially EN) when they are considered unlikely to resume normal oral nutrition within the next 5 to 7 days | [72] |
| EN: enteral nutrition in Acute Liver Failure (ALF) | Standard enteral formulas can be given, as there are no data regarding the value of a disease specific composition | [229] |
| PN: parenteral nutrition in Acute Liver Failure (ALF) | In malnourished ALF patients, EN and/or PN should be initiated promptly, PN should be used as second-line treatment in patients who cannot be fed adequately by oral and/or EN | [228] |
| Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (ASH) | Individualized nutrition counselling should be used in order to improve food intake | [230] |
| Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (ASH) | ONS should be used when patients with severe ASH cannot meet their caloric requirements through normal food in order to improve survival: | [231] |
| EN: enteral nutrition in Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (ASH) |
| |
| PN: parenteral nutrition in Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (ASH) |
| |
| Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) |
| |
| Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) |
| |
| Liver Cirrhosis (LC) |
| |
| Liver Transplantation (LTx) and Surgery |
| |
| Liver Transplantation (LTx): Preoperative phase |
|
|
| Liver Transplantation (LTx): postoperative phase |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Elsebaie, E.M.; Abdel-Fattah, A.N.; Bakr, N.A.; Attalah, K.M.; Aweas, A.-H.A. Principles of Nutritional Management in Patients with Liver Dysfunction—A Narrative Review. Livers 2023, 3, 190-218. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers3020013
Elsebaie EM, Abdel-Fattah AN, Bakr NA, Attalah KM, Aweas A-HA. Principles of Nutritional Management in Patients with Liver Dysfunction—A Narrative Review. Livers. 2023; 3(2):190-218. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers3020013
Chicago/Turabian StyleElsebaie, Essam Mohamed, Alyaa Nasr Abdel-Fattah, Nagwa Awad Bakr, Kadry Mohamed Attalah, and Abdel-Hady Ahmed Aweas. 2023. "Principles of Nutritional Management in Patients with Liver Dysfunction—A Narrative Review" Livers 3, no. 2: 190-218. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers3020013
APA StyleElsebaie, E. M., Abdel-Fattah, A. N., Bakr, N. A., Attalah, K. M., & Aweas, A.-H. A. (2023). Principles of Nutritional Management in Patients with Liver Dysfunction—A Narrative Review. Livers, 3(2), 190-218. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers3020013




