Abstract
The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of the superoxide dismutase mimic compound “tempol” on liver and renal damage in Long Evans male rats administered with carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). Methods: The antioxidant enzyme activity and oxidative stress parameters were investigated in the liver, kidney, and plasma tissues. Histological examination of the liver and kidney sections affirmed inflammatory cell infiltration, collagen deposition, and iron deposition. RT-PCR was also employed to evaluate the expression of oxidative stress and inflammatory genes. Results: The CCl4-administered rats exhibited increased plasma activities of ALT, AST, and ALP compared to the control rats. The tempol treatment in the CCl4-administered rats significantly lowered ALT, AST, and ALP enzyme activities compared to the CCl4 group. Oxidative stress parameters, such as the MDA, NO, and APOP levels in various tissues of the CCl4-administered rats, showed increased concentrations, whereas tempol significantly lowered the level of oxidative stress. Moreover, CCl4 administration decreased the antioxidant enzyme activities, which were further significantly restored by the tempol treatment. The control rats that underwent treatment with tempol did not present with any abnormality or toxicity. Furthermore, the tempol treatment in the CCl4-administered rats increased Nrf-2-HO-1-mediated gene expression and enhanced related antioxidant enzyme gene expressions. The tempol treatment in the CCl4-administered rats also decreased anti-inflammatory gene expressions in the liver. In histological sections of the liver, CCl4 increased inflammatory cell infiltration, collagen deposition, and iron deposition, which were reduced significantly due to the tempol treatment. Conclusion: The results of this investigation revealed that tempol could protect against liver and kidney damage in CCl4-administered rats by modulating antioxidant gene expressions and restoring antioxidant defense mechanisms.
1. Introduction
In today’s world, liver diseases are increasing day by day and have become a public health concern [1,2]. Recently, worldwide mortality and morbidity due to liver diseases have also significantly increased [3]. Recent evidence suggests that increased oxidative stress and alterations in relation to antioxidant enzyme activities, such as catalase and superoxide dismutase (SOD), might participate in the development of liver dysfunction [4]. In recent years, several investigations have suggested that oxidative stress is related to hepatocellular carcinoma, cirrhosis, fatty liver, fibrosis, and chronic hepatitis [5,6]. The excessive production of nitric oxide radicals, hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl, and superoxide-like free radicals in living beings may initiate damage to different types of biomolecules, such as membrane lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins [7]. The sources of oxygen-free radicles in the liver could be related to the metabolism of chemical agents and drug molecules due to cytochrome P450 action, inflammatory mononuclear cells, Kupffer cells, and hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) [8,9]. Free radicles and oxidative stress may also activate HSCs to secrete extracellular matrix proteins, mainly collagen, leading to the development of fibrosis in tissues [10]. Previous literature has shown that inflammation and oxidative stress work together, contributing to the development of fibrosis and hepatic dysfunction, followed by increasing the transaminase activities in the plasma [11]. A well-known compound, carbon tetrachloride (CCl4), is applicable to the development of hepatic injury in laboratory animals [12]. Liver damage and necrosis are caused by the production of chloromethyl and trichloromethyl free radicals as a metabolic product of CCl4. These free radicles start lipid peroxidation and, finally, the membrane disruption of hepatocytes, initiating hepatic necrosis [13]. An earlier report suggests that inflammatory cytokines are also released, enhancing intracellular Ca2+ concentrations and activating Kupffer cells in CCl4-administered animals [14].
Oxidative stress and free radical production can be reduced/prevented through antioxidant supplementation and treatment [11]. Antioxidant compounds may either directly scavenge the free radicles [15,16] or stimulate the antioxidant defense system by up-regulating the prominent signaling axis, such as the nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2-Heme oxygenase-1 (Nrf-2-HO-1) pathway, in the liver [17]. Nrf-2 is considered to be the main regulatory factor for redox homeostasis in cells and is the regulator for Phase II enzymes and antioxidant enzymes gene expression [18]. The phase II mediated enzymes are NADPH, NQO1, GST, GSH-Px, ferritin, and HO-1, whose gene expressions are regulated by Nrf-2 [19]. Antioxidant enzymes, such as SOD and catalase, gene expressions are also regulated by Nrf-2 activation [20]. Our previous investigation showed that liver SOD and catalase activities decreased significantly due to the oxidative stress mediated through CCl4 administration in rats [21]. It is assumed that antioxidants may restore liver SOD and catalase activities through the activation of Nrf-2 [16].
Considering this fact, tempol could be used as an antioxidant to prevent experimental liver damage. Tempol (4-hydroxy tempo) is a membrane-permeable radical scavenger [22]. Previous reports have suggested that tempol shows a wide range of biological activity by promoting the induction of the antioxidant enzyme SOD [22]. Tempol prevents lipid peroxidation and malondialdehyde production in the blood vessels of spontaneously hypertensive rats and increases intercellular antioxidant capabilities [23]. Tempol decreased the plasma levels of glucose and normalized the plasma levels of insulin in obese Zucker rats fed a high-fat diet [24]. Tempol treatment improved SOD activity, significantly reducing lipid peroxidation and peroxidase activity and reducing renal inflammatory, proliferative, and fibrotic changes in obese ZSF1 rats [25]. One week of tempol treatment prevented oxidative stress and the formation of apoptotic cells in the hearts of STZ-induced diabetic rats [26]. The previous report also showed that tempol prevents ethanol-induced liver damage [27] or reduced hepatic ischemia–reperfusion injury [28]. Tempol treatment is also effective in preventing hepatic ROS, steatosis, fibrosis, and hepatic mitochondrial damage in transgenic Ren2 rats [29]. Though tempol has exhibited promising biological activities in various diseases in animal models, its therapeutic effect in experimental liver damage is not fully explained. Thus, this investigation was undertaken to evaluate the efficacy of tempol treatment and the underlying mechanisms in experimental liver damage induced by CCl4 in rats.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
Tempol was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (3050 Spruce St. 63103 St. Louis, MO, USA). Carbon Tetrachloride was obtained from Merck (KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany). Sigma-Aldrich (Sigma-Aldrich 3050 Spruce St. 63103 St. Louis, MO, USA provided the thiobarbituric acid (TBA) and the 5,5-dithiobis-2-nitrobenzoic acid (DTNB) (Ellman’s reagent). J.T. Baker (Phillipsburg, NJ 8865, USA) supplied the reduced glutathione (GSH), acetic acid, and trichloroacetic acid (TCA) (USA). Alkaline phosphatase (ALP), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) were purchased from LabKits (Barcelona-Spain)), and sodium hydroxide was purchased from Merck (KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany). All of the chemicals and reagents used were of analytical grade.
2.2. Experimental Animals
From the animal house of North South University, twenty-four male Long Evans rats (body weight 220 to 240 g) were collected. All of the rats were kept in individual animal cages under a 12 h light and day cycle at a room temperature of 24 ± 2 °C. Free access to water and a standard pelleted diet was ensured for every rat. The Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) approved the experimental protocol; the approval number is 2019/OR-NSU/IACUC-No.0914.
2.3. Treatment and Study Design
The rats were separated into four groups containing six rats in each group. There were four groups: control, CCl4, control + tempol, and CCl4 + tempol. Standard pelleted food and water were supplied to the control rats. The CCl4 group received solely CCl4 at a dosage of 1 mL/kg twice a week for two weeks, which was combined with olive oil at a 1:3 ratio. The control + tempol group received 5 mg/kg tempol every day for two weeks, while the CCl4 + tempol group received both 1 mL/kg CCl4 twice a week for two weeks and 5 mg/kg tempol every day for two weeks. Food intake, water intake, and body weight were all tracked on a regular basis. After 14 days, all of the rats were sacrificed using ketamine hydrochloride, which was given intraperitoneally at a dosage of 90 mg/kg. The blood, liver, and kidney tissues were promptly taken. The organs were weighed and separated for two reasons. One half was preserved at −18 °C for biochemical analysis, while the other part was stored in neutral buffer formalin (pH 7.4) for staining and histological analysis. For biochemical studies, the liver and kidney tissue were homogenized by using sonication, centrifuged with phosphate-buffered solution, and the supernatants were collected for biochemical assays. To obtain the plasma, the collected blood samples were centrifuged at 4000 rpm for 15 min at 4 °C and kept in 1.5 mL microcentrifuge tubes at −18 °C for subsequent biochemical testing.
2.4. Biochemical Assays
2.4.1. Liver Toxicity Assessment
To assess hepatic function, plasma alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activities were examined. Each of these tests was performed using the commercial kit in Clindiag semi-automatic analyzer following the manufacturer’s protocol (Labkit, Spain).
2.4.2. Malondialdehyde (MDA) Estimation
To assess lipid peroxidation, MDA was measured both in the plasma and tissues. A previously described assay method was followed to assay the lipid peroxidation as thiobarbituric reactive substances (TBRAS) [30]. The units of the MDA levels were expressed as nmol/mL in the plasma and nmol/g in the tissues.
2.4.3. Nitric Oxide (NO) Estimation
The NO levels in the plasma and tissues were measured following a Griess–Illosvoy-reaction-based assay method, which was described previously [30,31].
2.4.4. Advanced Protein Oxidation Product (APOP) Determination
The APOP concentrations in the plasma and tissues were measured [30,32]. In a phosphate-buffered solution, the plasma and tissue homogenates were taken at a ratio of 1:5 and mixed with 0.1 mL potassium iodide (KI). After two minutes, absolute acetic acid was added to stop the reaction, and finally, the absorbance was taken at 340 nm.
2.4.5. Estimation of Catalase Activity
In terms of oxidative stress, H2O2 may be generated, which is detoxified by the enzyme catalase. Catalase enzyme activity was determined, followed by a previously described method [30,33].
2.4.6. Estimation of SOD Enzyme Activity
The antioxidant enzyme SOD activity was assayed using a previously published protocol based on adrenalin auto-oxidation [20,30]. The inhibition of the auto-oxidation of adrenaline was considered, and absorbance was taken At 480 nm. A control reaction was also performed without the tissue or plasma sample together with the other reaction reagents.
2.4.7. Myeloperoxidase (MPO) Activity Estimation
The dianisidine-H2O2-based reaction method was used to assess the MPO activity [33,34]. The absorbance was taken at 460 nm. MPO units were expressed as U/min/mg protein.
2.5. RT-PCR Analysis for Liver Sample for Oxidative Stress and Inflammation Related Genes Expression
Following sacrifice and under RNAse-free conditions, the renal tissues taken from the representative animals were obtained. Using the Thermo-Fisher Scientific kit, mRNA extraction and purification were carried out (Waltham, MA, USA). One gram of mRNA from each material was used to make cDNA using Thermo-Fisher Scientific’s (Waltham, MA, USA) cDNA Synthesis Kit after the RNA content was determined by using NanoDrop 2000. qRT-PCR in the CT method utilizing SYBRTM Green PCR Master Mix (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and predesigned primers in the Primer3 web portal was used to determine the relative amount of the mRNA of proteins associated with inflammation and oxidative stress (Table 1).

Table 1.
The forward and reverse sequence of the primer applied in this experiment.
A 40-cycle repetition of denaturation at 95 °C, specific annealing at 60 °C, and synthesis at 72 °C was used in the quantitative PCR, which was carried out in a CFX96 C1000 Touch Real-Time PCR Detection System (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) in accordance with a program previously developed and validated by Khan et al., 2016. Following the manufacturer’s instructions, the data were examined using CFX ManagerTM Software. The normalization of the target proteins’ gene expression was conducted by comparing it to the transcript level of β-actin.
2.6. Procedure of Histopathology
Part of the liver tissues and one whole kidney were fixed for several days in neutral buffered formalin (NBF, 10% v/v). These fixed tissues were treated with graded xylene and embedded in paraffin wax. The paraffin block tissues were sliced into 5-micron-thick pieces and placed on glass slides. All of the sections were de-paraffinized with xylene and dehydrated and rehydrated successively with graded alcohol. Finally, the slices were stained with hematoxylin and eosin to detect fundamental tissue architecture and inflammatory cell infiltration. Sirius red staining was also performed on tissue sections, which suggests collagen deposition, whereas the staining protocol for Prussian blue indicates free iron deposition. All of the images were taken at 40× magnification using a light microscope [21,33].
2.7. Statistical Analysis
For the calculation of the data, mean ± SEM was used for every assay parameter. In this study, all of the data were analyzed by using Graph Pad Prism 9. For the comparison of various groups, One-Way ANOVA followed by a Tukey test was performed. For statistical significance, all of the differences were considered at p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Tempol Administration Modulated the Body Weight, Liver Wet Weight, and Kidneys Wet Weight in CCl4-Administered Rats
The findings of the study demonstrated a decrease in the body weight of CCl4-treated rats compared to the control group (Figure 1A). An increase in the body weight of the rats was observed in the control +tempol and CCl4 + tempol groups compared to the control and CCl4 treated groups, respectively (Figure 1A).
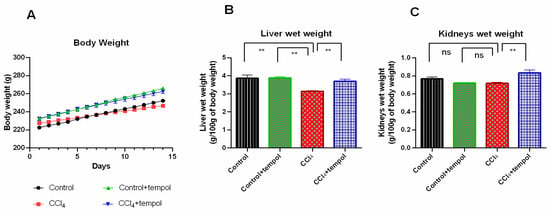
Figure 1.
Effect of tempol on body weight, liver wet weight, and kidneys wet weight in CCl4 induced rats. For body weight, 14 days of body weight are shown here, which was recorded every day. Every value was represented as mean ± SEM. Every value was represented as mean ± SEM. N = 6. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test were performed for statistical analysis. For statistical significance, p < 0.05 is considered significant in all cases. Here, ns means p > 0.05, ** means p < 0.001.
The impact of tempol on the liver wet weight of CCl4-intoxicated rats was investigated, and the result (Figure 1B) exhibited that the liver wet weight was significantly (p < 0.001) reduced in the CCl4-treated rats’ compared to the control group (Figure 1B). Importantly, rats pretreated with both tempol and CCl4 were found to have a significantly increased liver wet weight (p < 0.01) compared to rats treated with CCl4 (Figure 1B). Both the control and tempol-treated groups of rats showed an increase in liver wet weight that was statistically significant (p < 0.001).
Similarly, the impact of tempol on the wet weight of the kidneys in rats was investigated. The results revealed that the CCl4 + tempol group had significantly (p < 0.01) increased kidney wet weight compared to the CCl4 group (Figure 1C). However, there was no discernible difference in kidney wet weight between the control + tempol and CCl4 groups, nor between CCl4 and the control groups (Figure 1C).
3.2. Tempol Administration Lowered the ALT, AST, and ALP Enzymes Activities in Plasma of CCl4-Administered Rats
The severity of the liver damage caused by CCl4 was demonstrated by the observation of a significant (p < 0.0001) increase in the plasma levels of ALT, AST, and ALP in CCl4-treated rats compared to the control rats (Figure 2A–C). Investigation into the effect of tempol on these biochemical parameters demonstrated a significant (p < 0.01) decrease in the plasma levels of ALT, AST, and ALP in the CCl4 + tempol group compared to the CCl4-intoxicated group (Figure 2A–C). Additionally, the plasma levels of ALT, AST, and ALP were significantly (p < 0.0001) lower in the control + tempol group than in the CCl4-treated group (Figure 2A–C).
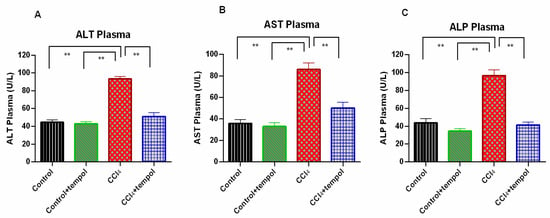
Figure 2.
Effect of tempol on ALT, AST and ALP activities in plasma of CCl4-administered rats. Every value was represented as mean ± SEM. N = 6. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test were performed for statistical analysis. For statistical significance, p < 0.05 is considered significant in all cases. Here, ** means p < 0.001.
3.3. Tempol Treatment Prevented the Oxidative Stress and Lowered the MDA, NO and AOPP Level in CCl4-Administered Rats
The MDA levels in the plasma, liver, and kidneys were found to be considerably higher in the CCl4 group compared to the control group, as shown in Figure 3A–C. It is important to mention that the treatment of rats with tempol demonstrated a marked reduction in MDA level (Figure 3A–C). In comparison to the CCl4 group, the control + tempol group displayed lower levels of MDA (Figure 3A–C).
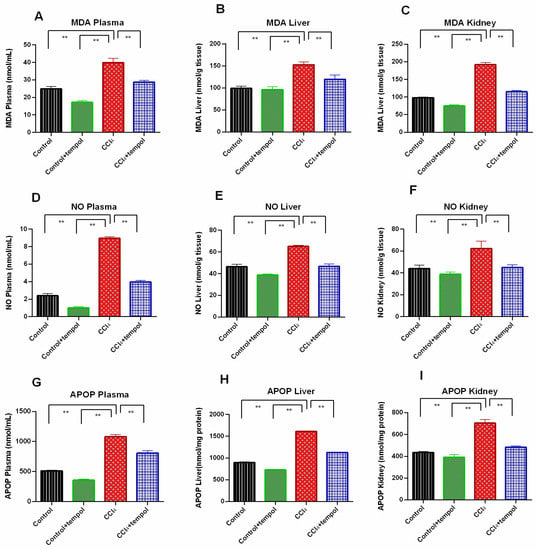
Figure 3.
Effect of tempol on oxidative stress parameters in CCl4-administered rats. In this figure (A). MDA plasma (B). NO Plasma (C). APOP Plasma (D). MDA Liver (E). NO Liver (F). APOP Liver (G). MDA Kidney (H). NO Kidney (I). APOP Kidney. Every value was represented as mean ± SEM. N = 6. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test were performed for statistical analysis. For statistical significance, p < 0.05 is considered significant in all cases. Here, ** means p < 0.001.
In comparison to the control group, the plasma, liver, and kidney homogenates of the CCl4 group had significantly higher levels of the oxidative stress marker, NO (p < 0.001). (Figure 3D–F). As compared to the CCl4 group, a significant decrease in plasma, liver, and kidney NO levels was evidenced in the CCl4 + tempol group, where the rats were treated with tempol (p < 0.01) (Figure 3D–F). In the control + tempol group, as opposed to the CCl4 group, a significant decrease in liver and kidney NO levels was also seen (Figure 3E,F).
The level of another vital oxidative stress marker, AOPP, was also found to be increased significantly in the plasma, liver, and kidney homogenates of the CCl4 group as compared to the control group (p < 0.001) (Figure 3G–I). It is noteworthy to mention that the AOPP level in the plasma, liver, and kidney homogenates was significantly reduced in the rats that received both CCl4 and tempol compared to the CCl4 group (p < 0.001) (Figure 3G–I). The AOPP concentration in the plasma, liver, and kidney homogenates of the control + tempol group also decreased significantly compared to the CCl4 group (Figure 3G–I).
3.4. Tempol Administration in CCl4-Administered rats Restored the Antioxidant Enzymes, Catalase and SOD Activities
The catalase activity in the plasma, liver, and kidney was significantly lower in the CCl4 group than in the control group, as shown in Figure 4A–C (p > 0.05). The rats receiving tempol (CCl4 + tempol) therapy had considerably (p < 0.001) higher levels of declining catalase activity in their plasma, livers, and kidneys (Figure 4A–C). In addition, compared to the CCl4 group, the control + tempol group demonstrated considerably increased catalase activity (Figure 4A–C).
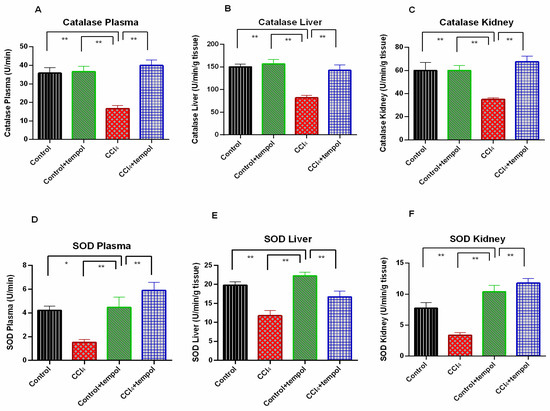
Figure 4.
Effect of tempol on antioxidant enzyme activity in CCl4-administered rats. In this figure (A) Catalase Plasma, (B) SOD Plasma, (C) Catalase Liver, (D) SOD Liver, (E) Catalase Kidney, (F) SOD Kidney. Every value was represented as mean ± SEM. N = 6. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test were performed for statistical analysis. For statistical significance, p < 0.05 is considered significant in all cases. Here, * means p < 0.05, ** means p < 0.001.
The SOD activity in the plasma, liver, and kidney was found to be significantly decreased in the CCl4 group (p < 0.05) compared to the control rats (Figure 4D–F). In the rats that received tempol, the diminished plasma, liver, and kidney SOD activity in the CCl4-intoxicated group was significantly (p < 0.01) restored (Figure 4D–F). SOD activity significantly increased in the control + tempol group when compared to the CCl4 group (p < 0.01). (Figure 4D–F).
3.5. Tempol Administration Modulated the Antioxidant Genes Expression in Liver of CCl4-Administered Rats
Figure 5 represents the gene expression for tissue antioxidant-related genes. This investigation revealed that CCl4 administration in rats decreased the Nrf-2 expression in the liver significantly (p < 0.01) compared to the control rats (Figure 5A). Tempol treatment restored Nrf-2 expression in the livers of CCl4-administered rats (Figure 5A). In line with this finding, HO-1 and HO-2 gene expressions were also decreased due to CCl4 administration (p < 0.01), which were also restored by tempol treatment in rats (Figure 5B,C). Tempol treatment also preserved the normal expression of antioxidant enzymes such as SOD, catalase, and GPx gene expression in the livers of CCl4-administered rats (Figure 5D–F).
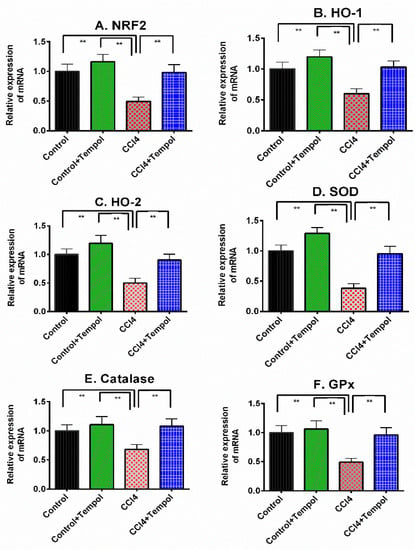
Figure 5.
Effect of tempol on antioxidant gene expression in the liver of CCl4-administered rats. Every value was represented as mean ± SEM. Every value was represented as mean ± SEM. N = 6. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test were performed for statistical analysis. For statistical significance, p < 0.05 is considered significant in all cases. Here, ** means p < 0.001.
3.6. Tempol Treatment Lowered the MPO Activity in Liver and Kidney of CCl4-Administered Rats
The MPO activity in the livers and kidneys of the CCl4-intoxicated group was found to be significantly (p < 0.01) higher compared to the control group (Figure 6A,B). Tempol administration caused a significant (p < 0.01) decline in MPO liver and kidney activity in the CCl4 group (tempol + CCl4 group) (Figure 6A,B). When compared to the CCl4 group, the control + tempol group likewise showed a substantial (p < 0.01) decrease in liver and kidney MPO activity (Figure 6A,B).
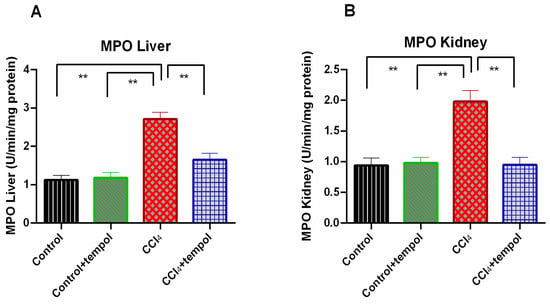
Figure 6.
Effect of tempol on MPO liver and MPO kidney in CCl4-administered rats. Every value was represented as mean ± SEM. Every value was represented as mean ± SEM. N = 6. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test were performed for statistical analysis. For statistical significance, p < 0.05 is considered significant in all cases. Here, ** means p < 0.001.
3.7. Tempol Treatment Decreased the Inflammation Related Genes Expression in Liver of CCl4-Administered Rats
The inflammatory cytokines expression in liver is presented in Figure 7. The related mRNA expression for IL-1, IL-6 and TNF-α were significantly increased (p < 0.01) in liver of CCl4-administered rats (Figure 7A–C). Administration of tempol in CCl4 group (tempol + CCl4 group) resulted in a significant (p < 0.01) decrease in IL-1, IL-6 and TNF-α expression (Figure 7A–C).
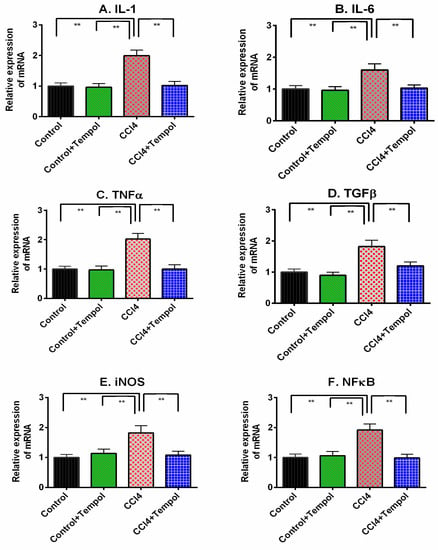
Figure 7.
Effect of tempol on inflammation related gene expression in liver of CCl4-administered rats. Every value was represented as mean ± SEM. N = 6. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey test were performed for statistical analysis. For statistical significance, p ≤ 0.05 is considered as significance in all cases. Here, ** means p ≤ 0.001.
CCl4 administration in rats also showed increased TGF-β expression in the liver compared to the control rats (Figure 7D). Tempol treatment normalized the TGF-β expression in the livers of CCl4-administered rats (Figure 7D). CCl4 administration in rats also showed increased iNOS and NF-кB expression in the liver compared to the control rats (Figure 7E,F). Tempol treatment normalized the iNOS and NF-кB expression in the livers of CCl4-administered rats (Figure 7E,F).
3.8. Tempol Treatment Improved the Histological Abnormalities in Liver and Kidneys of CCl4-Administered Rats
The findings related to liver and kidney histology in the tempol-treated rats are illustrated in Figure 8 and Figure 9. The results demonstrated that the livers taken from the rats of the control group did not show any hepatic inflammation as well as collagen deposition (Figure 8A,E). In contrast, the CCl4-treated group exhibited hepatic inflammation and massive collagen deposition (Figure 8C,F). The control + tempol exhibited a normal architecture and orientation in terms of the lobule and hepatocytes (Figure 8B). Pretreatment of rats with tempol was found to recover hepatic necrosis and inflammation and reduce collagen deposition (Figure 8D,H). Huge iron deposition was also observed in the CCl4-treated rats (Figure 8K); however, no iron deposition was observed in the control group (Figure 8I). Tempol treatment in the CCl4-intoxicated rats resulted in much less iron deposition, indicating that tempol may reduce iron deposition (Figure 8L).
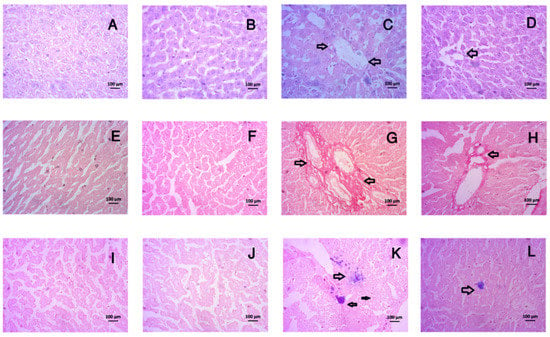
Figure 8.
Effect of tempol on liver histology in CCl4-administered rats. In this figure (A–D) is hematoxylin and eosin staining; (E–H) is Sirius red staining and (I–L) is Prussian blue staining. Here, (A,E,I)—Control; (B,F,J)—Control + tempol; (C,G,K)—CCl4 and (D,H,L)—CCl4 + tempol. All pictures were taken at 40× magnification.
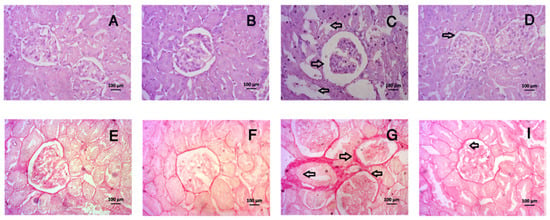
Figure 9.
Effect of tempol on kidney histology in CCl4-administered rats. In this figure (A–D) is hematoxylin and eosin staining and (E–H) is Sirius red staining. Here, (A,E)—Control; (B,F)—Control + tempol; (C,G)—CCl4 and (D,H)—CCl4 + tempol. All pictures were taken at 40× magnification.
CCl4 administration has a profound effect on kidney morphology in rats. This investigation revealed that CCl4 administration in rats led to necrosis in the glomerular structure, the breakdown of tubular linings, inflammation and fibrosis (Figure 9C,G), which were normalized by tempol treatment in CCl4-administered rats (Figure 9D,H). The control rats showed normal kidney structures, intact glomerulus, and no fibrosis (Figure 9A,E), which was also observed in the control rats treated with tempol (Figure 9B,F).
4. Discussion
CCl4 is an industrial poison that may cause liver damage by triggering the production of reactive oxygen species during metabolism. In this investigation, CCl4 was used to generate hepatic damage in rats. CCl4 administration showed increased transaminase activities in the plasma, such as in ALT, AST, and ALP. This investigation also revealed that CCl4 administration increased oxidative stress by elevating MDA, NO, and APOP concentrations in the plasma and tissues. In this study, tempol, as an antioxidant, prevented oxidative stress and restored antioxidant enzyme activity such as catalase and SOD in CCl4-administered rats. Finally, histological staining also revealed collagen and iron deposition in liver sections, which were normalized by using tempol treatment.
Oxidative stress in the liver is the main determinant factor for lipid peroxidation and the membrane disruption of hepatocytes. This leakier membrane thus facilitates the release of transaminases in the plasma and is considered a marker of hepatic dysfunction [11,21,35]. The CCl4-administered rats showed the significant elevation of AST, ALT, and ALP activities in the plasma, which was decreased by tempol treatment. Tempol is considered an antioxidant that may prevent or scavenge ROS and decreases lipid peroxidation to stabilize membrane integrity. The previous report also suggests that tempol treatment declines ALT and AST levels in the plasma of mice experiencing acute CCl4-induced hepatotoxicity [36]. Another report also showed that tempol also decreases ALP levels and cures hepatotoxicity in mice induced by acetaminophen [37].
Oxidative stress markers, such as MDA, NO, and APOP, increase because of excess free radical production [21]. Under oxidative stress, tissue antioxidant levels are lowered, and membrane phospholipids are hampered because of the increased amount of reactive oxygen species [38]. In this study, CCl4 administration increased MDA levels, which is a stress marker and is responsible for liver and kidney damage. The MDA level was declined by tempol treatment. Tempol is able to penetrate the lipid layer easily and scavenge the free radicles directly as an antioxidant [39]. The previous report showed that tempol decreased MDA levels and protected against apoptosis and oxidative stress in hypoxia in H9c2 Cells [40]. This investigation also found that CCl4 increases NO levels in the liver and kidney, which were decreased by the tempol treatment. NO may play dual roles in the tissues. NO regulates the signaling cascade required for tissue function; however, in the presence of superoxide, NO may convert into peroxynitrite, which is more damaging than superoxide itself. Thus, removing excess NO would be beneficial. Under oxidative stress and inflammation, the inducible form of nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) produces huge NO in the liver and produces nitrosative stress. The previous report also showed that tempol prevented the impairment of neurons and mitochondrial dysfunction [41]. Tempol also prevented nitrosative stress by lowering mitochondrial protein 3-nitrotyrosine in spinal cord injury [42].
As an oxidative stress marker, AOPP was also measured in this study [43]. A strong correlation was suggested between increased AOPP levels and hepatic dysfunction in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) [44] and acute liver failure patients [45]. CCl4 administration in rats increased AOPP concentration in the liver and kidneys, which were lowered by the tempol treatment. Our previous reports also suggest that antioxidants or antioxidant-rich supplementation may prevent AOPP formation in tissues [11,46]. The elevated lipid peroxidation and oxidative stress are the consequences of distorted antioxidant enzyme activity to counteract the free radicles and ROS. Superoxide anions and ROS are also scavenged by antioxidant activities such as SOD and catalase.
SOD is a first-line defense against the superoxide-mediated oxidation of biomolecules, such as lipids, functional proteins, and DNAs. SOD activity and gene expression levels declined in the liver and other tissues due to oxidative stress [46,47,48]. Antioxidant supplementation may increase SOD and catalase activities [11,49]. In this study, the tempol treatment also increased the SOD and catalase activities and restored the reduced glutathione levels in the livers and kidneys of CCl4-administered rats. These findings are in line with the previous report suggesting that tempol protected mitochondrial function and increased the SOD enzyme activity [41]. In a previous study, it was also confirmed that in a hypoxia situation, the declined catalase activity was restored by tempol treatment successfully [40]. These results are supported by the elevated gene expressions of these enzymes in the liver. This investigation also revealed that Nrf-2 expression and its associated gene HO-1 expression were also restored by the tempol treatment in the CCl4-administered rats. The Nrf-2-HO-1 axis is crucial in response to oxidative stress and modulates the antioxidant defense in tissues by raising the SOD, catalase, and Gpx protein function [50,51]. Moreover, Nrf-2 is also activated in response to inflammation in the liver [17].
Oxidative stress-mediated tissue damage may lead to the activation of inflammatory pathways in the liver. The histological staining of the liver section showed the inflamed hepatic architecture and fibrosis together with the free iron deposition in CCl4-administered rats. The free iron deposited in liver tissues may participate in Fenton reaction and could be considered one of the sources of oxidative stress. The ROS thus participate in the activation of Kuffer cells and hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) and trigger inflammation. The mononuclear cell infiltration in the liver may be a source of ROS as well, evidenced by the increased MPO activity. In this study, CCl4 administration increases MPO activity in the liver and kidney. The MPO activity in both tissues was decreased by the tempol treatment. This finding is also similar to the study, which mentioned that MPO activity was ameliorated by using 4-methoxy tempo in inflammatory bowel disease [52]. The ROS-mediated activation of Kuffer cells and HSCs may increase the release of extracellular matrix proteins and lead to the development of fibrosis. In fact, cytokines such as TNF-alpha and IL-6 may trigger the activation of fibrogenic pathways by activating TGF-β signaling in HSCs [9]. This investigation showed that TNF-α and IL-6 together with TGF-β expressions are all increased in the liver due to CCl4 administration. The cytokine production is also regulated by the NF-кB activation, which was also increased in the liver of CCl4-administered rats. Tempol treatment ameliorated the increased gene expression of cytokines and TGF-β, thus, could be responsible for preventing inflammation-mediated tissue fibrosis.
5. Conclusions
This study’s findings revealed that tempol treatment might ameliorate lipid peroxidation by restoring the function of antioxidant enzymes in the livers of CCl4-administered rats. The increased genetic expression of the Nrf-2 mediate pathway may be responsible for the restoration of antioxidant enzymes in the liver. Thus, it can be concluded that CCl4-mediated oxidative stress may be ameliorated by using tempol treatment.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization—M.A.A., N.S. and F.K.; methodology—M.A.A.; animal study/investigation—I.J., I.J.A., M.D.I., A.U.H.S. and S.S.; biochemical analysis—I.J., I.J.A., M.D.I., N.A. and F.I.C.; histopathological analysis—I.J., I.A., S.S. and A.U.H.S.; data Curation—M.A.A., I.A., N.S., R.A. and F.K.; writing—original draft preparation—M.A.A., N.S. and F.K.; writing—review and editing—M.A.A., R.A. and F.K.; supervision—M.A.A., N.S. and F.K.; project administration—M.A.A. and F.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) approved the experimental protocol; the approval number is 2019/OR-NSU/IACUC-No.0914.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data are presented in this manuscript. If required, the data can be provided upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
With the help of the Department of Pharmacy, North South University, Bangladesh, this research was conducted. The logistics support provided by the Department of Pharmacy, North South University, Bangladesh, is gratefully acknowledged by the authors.
Conflicts of Interest
There are no conflict of interest related to the publication of this paper to be declared by the authors.
References
- Paik, J.M.; Golabi, P.; Younossi, Y.; Mishra, A.; Younossi, Z.M. Changes in the Global Burden of Chronic Liver Diseases From 2012 to 2017: The Growing Impact of NAFLD. Hepatology 2020, 72, 1605–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarin, S.K.; Kumar, M.; Eslam, M.; George, J.; Al Mahtab, M.; Akbar, S.M.F.; Jia, J.; Tian, Q.; Aggarwal, R.; Muljono, D.H.; et al. Liver diseases in the Asia-Pacific region: A Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology Commission. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 167–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asrani, S.K.; Devarbhavi, H.; Eaton, J.; Kamath, P.S. Burden of liver diseases in the world. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cichoż-Lach, H.; Michalak, A. Oxidative stress as a crucial factor in liver diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 8082–8091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, P.; Talukdar, A.D.; Nath, R.; Sarker, S.D.; Nahar, L.; Sahu, J.; Choudhury, M.D. Role of Natural Phenolics in Hepatoprotection: A Mechanistic Review and Analysis of Regulatory Network of Associated Genes. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, D.; Takaki, A.; Oyama, A.; Adachi, T.; Wada, N.; Onishi, H.; Okada, H. Oxidative stress management in chronic liver diseases and hepatocellular carcinoma. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, B.J.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.Y. The role of Salicornia herbacea in ovariectomy-induced oxidative stress. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 29, 1305–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muriel, P. Role of free radicals in liver diseases. Hepatol. Int. 2009, 3, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, P.; Chouhan, K.; Weiskirchen, S.; Weiskirchen, R. Cellular mechanisms of liver fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 671640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Tovar, E.; Muriel, P. Molecular mechanisms that link oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrosis in the liver. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Al Mamun, M.A.; Faruk, M.; Ul Islam, M.T.; Rahman, M.M.; Alam, M.N.; Rahman, A.; Reza, H.M.; Alam, M.A. Astaxanthin ameliorates hepatic damage and oxidative stress in carbon tetrachloride-administered rats. Pharmacogn. Res. 2017, 9, S84–S91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebayo, A.; Yakubu, O.F.; Balogun, T.M. Protective properties of Citrullus lanatus on carbon tetrachloride induced liver damage in rats. Eur. J. Med. Plants 2014, 4, 979–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Kader, M.S.; Abulhamd, A.T.; Hamad, A.M.; Alanazi, A.H.; Ali, R.; Alqasoumi, S.I. Evaluation of the hepatoprotective effect of combination between hinokiflavone and Glycyrrhizin against CCl4 induced toxicity in rats. Saudi Pharm. J. 2018, 26, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boll, M.; Weber, L.W.; Becker, E.; Stampfl, A. Mechanism of carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity. Hepatocellular damage by reactive carbon tetrachloride metabolites. Z. Naturforsch. C J. Biosci. 2001, 56, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, V.; Patil, A.; Phatak, A.; Chandra, N. Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: Impact on human health. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2010, 4, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurutas, E.B. The importance of antioxidants which play the role in cellular response against oxidative/nitrosative stress: Current state. Nutr. J. 2016, 15, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galicia-Moreno, M.; Lucano-Landeros, S.; Monroy-Ramirez, H.C.; Silva-Gomez, J.; Gutierrez-Cuevas, J.; Santos, A.; Armendariz-Borunda, J. Roles of Nrf2 in Liver Diseases: Molecular, Pharmacological, and Epigenetic Aspects. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Jiang, Y.F.; Ponnusamy, M.; Diallo, M. Role of Nrf2 in chronic liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 13079–13087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.M.; Luo, L.; Namani, A.; Wang, X.J.; Tang, X. Nrf2 signaling pathway: Pivotal roles in inflammation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaassen, C.D.; Reisman, S.A. Nrf2 the rescue: Effects of the antioxidative/electrophilic response on the liver. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2010, 244, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Rahman, M.M.; Kabir, F.; Nahar, K.; Mamun, F.; Lasker, S.; Subhan, N.; Hossain, M.H.; Nahar, L.; Sarker, S.D.; et al. Trichosanthes dioica Roxb. prevents hepatic inflammation and fibrosis in CCl4-induced ovariectomized rats. Clin. Nutr. Exp. 2020, 33, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, C.S. Effects of tempol and redox-cycling nitroxides in models of oxidative stress. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 126, 119–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, P.W.; Deutsch, C.; McClain, J.L.; Rogers, C.T.; Dorrance, A.M. Tempol, a superoxide dismutase mimetic, prevents cerebral vessel remodeling in hypertensive rats. Microvasc. Res. 2010, 80, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebenezer, P.J.; Mariappan, N.; Elks, C.M.; Haque, M.; Francis, J. Diet-induced renal changes in Zucker rats are ameliorated by the superoxide dismutase mimetic TEMPOL. Obesity 2009, 17, 1994–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafikova, O.; Salah, E.M.; Tofovic, S.P. Renal and metabolic effects of tempol in obese ZSF1 rats-distinct role for superoxide and hydrogen peroxide in diabetic renal injury. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2008, 57, 1434–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiordaliso, F.; De Angelis, N.; Bai, A.; Cuccovillo, I.; Salio, M.; Serra, D.M.; Bianchi, R.; Razzetti, R.; Latini, R.; Masson, S. Effect of beta-adrenergic and renin-angiotensin system blockade on myocyte apoptosis and oxidative stress in diabetic hypertensive rats. Life Sci. 2007, 81, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuhashi, T.; Karbowski, M.; Liu, X.; Usukura, J.; Wozniak, M.; Wakabayashi, T. Complete suppression of ethanol-induced formation of megamitochondria by 4-hydroxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-piperidine-1-oxyl (4-OH-TEMPO). Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1998, 24, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blonder, J.M.; McCalden, T.A.; Hsia, C.J.; Billings, R.E. Polynitroxyl albumin plus tempol attenuates liver injury and inflammation after hepatic ischemia and reperfusion. Life Sci. 2000, 67, 3231–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Clark, S.E.; Thyfault, J.P.; Uptergrove, G.M.; Li, W.; Whaley-Connell, A.T.; Ferrario, C.M.; Sowers, J.R.; Ibdah, J.A. Oxidative stress-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction contributes to angiotensin II-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in transgenic Ren2 rats. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2009, 174, 1329–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, F.; Rahman, M.M.; Zamila, M.; Subhan, N.; Hossain, H.; Raquibul Hasan, S.M.; Alam, M.A.; Haque, M.A. Polyphenolic compounds of litchi leaf augment kidney and heart functions in 2K1C rats. J. Funct. Foods. 2020, 64, 103662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracey, W.R.; Tse, J.; Carter, G. Lipopolysaccharide-induced changes in plasma nitrite and nitrate concentrations in rats and mice: Pharmacological evaluation of nitric oxide synthase inhibitors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1995, 272, 1011–1015. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Witko-Sarsat, V.; Friedlander, M.; Capeillere-Blandin, C.; Nguyen-Khoa, T.; Nguyen, A.T.; Zingraff, J.; Jungers, P.; Descamps-Latscha, B. Advanced oxidation protein products as a novel marker of oxidative stress in uremia. Kidney Int. 1996, 49, 1304–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.M.; Ferdous, K.U.; Roy, S.; Nitul, I.A.; Mamun, F.; Hossain, M.H.; Subhan, N.; Alam, M.A.; Haque, M.A. Polyphenolic compounds of amla prevent oxidative stress and fibrosis in the kidney and heart of 2K1C rats. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 3578–3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, P.P.; Priebat, D.A.; Christensen, R.D.; Rothstein, G. Measurement of cutaneous inflammation: Estimation of neutrophil content with an enzyme marker. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1982, 78, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; You, Y.; Yoon, H.G.; Lee, Y.H.; Kim, K.; Lee, J.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, J.C.; Jun, W. Hepatoprotective effects of fermented Curcuma longa L. on carbon tetrachloride-induced oxidative stress in rats. Food Chem. 2014, 151, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abouzied, M.M.; Eltahir, H.M.; Taye, A.; Abdelrahman, M.S. Experimental evidence for the therapeutic potential of tempol in the treatment of acute liver injury. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2016, 411, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonruamkaew, P.; Chonpathompikunlert, P.; Nagasaki, Y. Redox nanoparticle therapeutics for acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 4984597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde de la Rosa, L.; Goicoechea, L.; Torres, S.; Garcia-Ruiz, C.; Fernandez-Checa, J.C. Role of oxidative stress in liver disorders. Livers 2022, 2, 283–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuzzocrea, S.; McDonald, M.C.; Mazzon, E.; Dugo, L.; Lepore, V.; Fonti, M.T.; Ciccolo, A.; Terranova, M.L.; Caputi, A.P.; Thiemermann, C. Tempol, a membrane-permeable radical scavenger, reduces dinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced colitis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 406, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.; Li, Q.; He, L.; Sun, W.; Jia, Z.; Ma, H. Protective effect of tempol against hypoxia-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in H9c2 cells. Med. Sci. Monit. Basic Res. 2017, 23, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaiya, P.K.; Narayan, G.; Kumar, A.; Krishnamurthy, S. Tempol (4 hydroxy-tempo) inhibits anoxia-induced progression of mitochondrial dysfunction and associated neurobehavioral impairment in neonatal rats. J. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 375, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Singh, I.N.; Hall, E.D. Tempol protection of spinal cord mitochondria from peroxynitrite-induced oxidative damage. Free Radic. Res. 2009, 43, 604–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ouyang, X.; Jiang, Z.; Xie, Z.; Fan, L.; Zhu, D.; Li, L. Advanced oxidation protein products play critical roles in liver diseases. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 49, e13098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozenirler, S.; Erkan, G.; Konca Degertekin, C.; Ercin, U.; Cengiz, M.; Bilgihan, A.; Yilmaz, G.; Akyol, G. The relationship between advanced oxidation protein products (AOPP) and biochemical and histopathological findings in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Dig. Dis. 2014, 15, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Han, T.; Tian, J.; Zhu, Z.-Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Xiao, S.-X.; Li, Y.; Feng, Y.-Y. Monitoring oxidative stress in acute-on-chronic liver failure by advanced oxidation protein products. Hepatol. Res. 2012, 42, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miah, P.; Mohona, S.B.S.; Rahman, M.M.; Subhan, N.; Khan, F.; Hossain, H.; Sharker, S.M.; Alam, M.A. Supplementation of cumin seed powder prevents oxidative stress, hyperlipidemia and non-alcoholic fatty liver in high fat diet fed rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 141, 111908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmin, T.; Rahman, M.M.; Khan, F.; Kabir, F.; Nahar, K.; Lasker, S.; Islam, M.D.; Hossain, M.M.; Hasan, R.; Rana, S.; et al. Metformin treatment reverses high fat diet- induced non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases and dyslipidemia by stimulating multiple antioxidant and anti-inflammatory pathways. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2021, 28, 101168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, S.; Akter, N.; Nayan, S.I.; Chowdhury, F.I.; Saffoon, N.; Khan, F.; Ahmed, K.S.; Ahmed, M.I.; Hossain, M.M.; Alam, M.A. Flacourtia indica fruit extract modulated antioxidant gene expression, prevented oxidative stress and ameliorated kidney dysfunction in isoprenaline administered rats. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2021, 26, 101012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsawy, H.; Badr, G.M.; Sedky, A.; Abdallah, B.M.; Alzahrani, A.M.; Abdel-Moneim, A.M. Rutin ameliorates carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced hepatorenal toxicity and hypogonadism in male rats. PeerJ 2019, 7, e7011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bataille, A.M.; Manautou, J.E. Nrf2: A potential target for new therapeutics in liver disease. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 92, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q. Role of Nrf2 in oxidative stress and toxicity. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 401–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chami, B.; San Gabriel, P.T.; Kum-Jew, S.; Wang, X.; Dickerhof, N.; Dennis, J.M.; Witting, P.K. The nitroxide 4-methoxy-tempo inhibits the pathogenesis of dextran sodium sulfate-stimulated experimental colitis. Redox Biol. 2020, 28, 101333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).