Anti-Metastatic Activity of Tagitinin C from Tithonia diversifolia in a Xenograft Mouse Model of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Tagitinin C Preparation
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
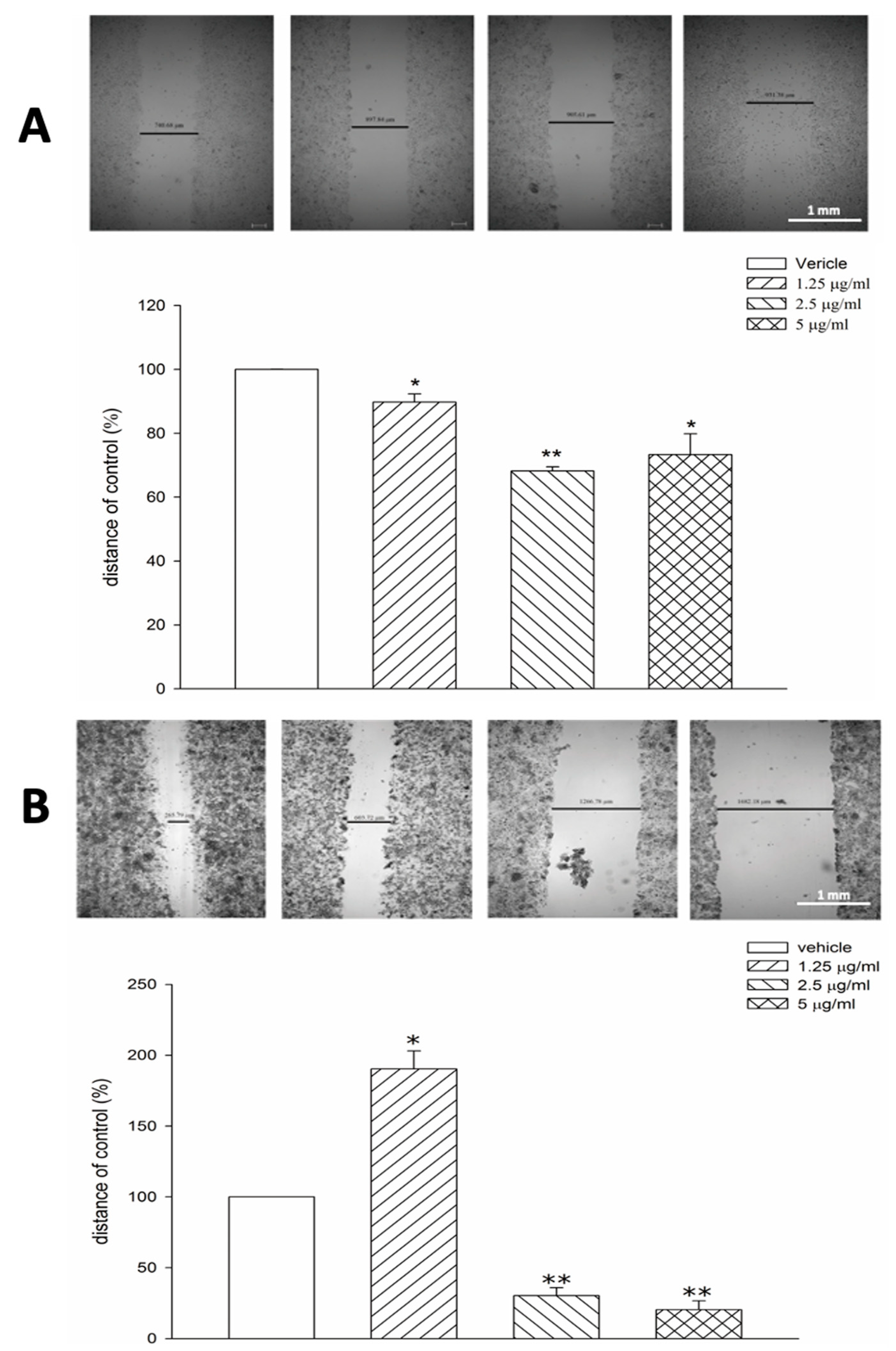
2.4. Cell Migration Assay
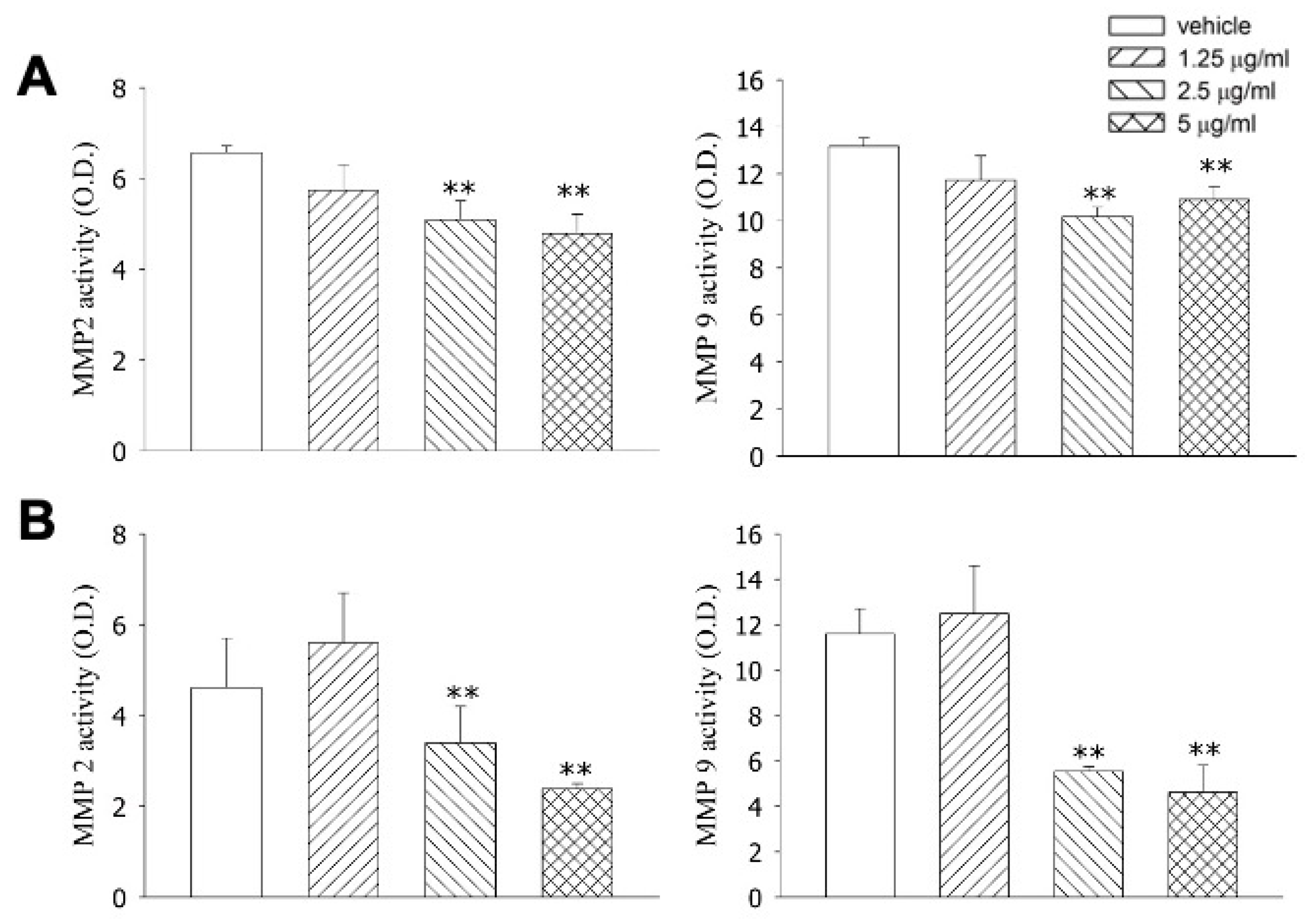
2.5. MMP2 and MMP9 Activity Assay
2.6. Tumorigenicity in Nude Mice
2.7. In Vivo MR Analysis
2.8. Serologic Tests
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jemal, A.; Murray, T.; Ward, E.; Samuels, A.; Tiwari, R.C.; Ghafoor, A.; Feuer, E.J.; Thun, M.J. Cancer Statistics, 2005. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2005, 55, 10–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, A.-J.; Chen, L.-H.; Lu, T.-H. Ten leading causes of death in Taiwan: A comparison of two grouping lists. J. Formos Med. Assoc. 2015, 114, 679–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberg, R.A.; Weinberg, R.A. The Biology of Cancer; WW Norton & Company: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.C.; Lin, M.L.; Lin, J.M. The antiinflammatory and liver protective effect of Tithonia diversifolia (Hemsl.) gray and Dicliptera chinensis Juss. Extracts in rats. Phytother. Res. 1993, 7, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, M.; Yokosuka, A.; Kobayashi, R.; Jitsuno, M.; Kando, H.; Nosaka, K.; Ishii, H.; Yamori, T.; Mimaki, Y. Sesquiterpenoids and flavonoids from the aerial parts of Tithonia diversifolia and their cytotoxic activity. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 55, 1240–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, M.-H.; Lin, W.-C.; Wen, H.-C.; Pu, H.-F. Tithonia diversifolia and its main active component tagitinin C induce survivin inhibition and G2/M arrest in human malignant glioblastoma cells. Fitoterapia 2011, 82, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.-Y.; Liao, M.-H.; Tsai, Y.-N.; Chiu, K.-H.; Wen, H.-C. Identification and anti-human glioblastoma activity of tagitinin C from Tithonia diversifolia methanolic extract. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 2347–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, M.H.; Tsai, Y.N.; Yang, C.Y.; Juang, C.L.; Lee, M.Y.; Chang, L.H.; Wen, H.C. Anti-human hepatoma Hep-G2 proliferative, apoptotic, and antimutagenic activity of tagitinin C from Tithonia diversifolia leaves. J. Nat. Med. 2013, 67, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egeblad, M.; Werb, Z. New functions for the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page-McCaw, A.; Ewald, A.J.; Werb, Z. Matrix metalloproteinases and the regulation of tissue remodelling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissell, M.; Kenny, P.; Radisky, D. Microenvironmental regulators of tissue structure and function also regulate tumor induction and progression: The role of extracellular matrix and its degrading enzymes. In Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 343–356. [Google Scholar]
- Bizzi, A.; Movsas, B.; Tedeschi, G.; Phillips, C.L.; Okunieff, P.; Alger, J.R.; Di Chiro, G. Response of non-Hodgkin lymphoma to radiation therapy: Early and long-term assessment with H-1 MR spectroscopic imaging. Radiology 1995, 194, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, A.; Maisey, N.; Collins, D.; Cunningham, D.; Huddart, R.; Leach, M. Early in vivo detection of metabolic response: A pilot study of 1H MR spectroscopy in extracranial lymphoma and germ cell tumours. Br. J. Radiol. 2002, 75, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radermacher, K.A.; Magat, J.; Bouzin, C.; Laurent, S.; Dresselaers, T.; Himmelreich, U.; Boutry, S.; Mahieu, I.; Vander Elst, L.; Feron, O. Multimodal assessment of early tumor response to chemotherapy: Comparison between diffusion-weighted MRI, 1H-MR spectroscopy of choline and USPIO particles targeted at cell death. NMR Biomed. 2012, 25, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, P.; Shukla, S.; Gupta, S. Plant flavonoid apigenin inactivates Akt to trigger apoptosis in human prostate cancer: An in vitro and in vivo study. Carcinogenesis 2008, 29, 2210–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.R.; Huang, H.L.; Chiou, W.F.; Huang, R.L. Induction of Apoptosis by Tithonia diversifolia in Human Hepatoma Cells. Pharmacogn Mag 2017, 13, 702–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragg, G.M.; Grothaus, P.G.; Newman, D.J. Impact of natural products on developing new anti-cancer agents. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 3012–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandela, W. Pengaruh Senyawa Isolat Aktif daun Kembang Bulan (T. diversifolia) Terhadap Ekspresi Protein p53 Pada Sel Hela Dengan Metode Immunohistokimia [Skripsi]; Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Gadjah Mada: Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Mh, H.R. Aktivitas Isolat Aktif Daun Kembang Bulan [Tithonia diversifolia (Hemsley) a. Gray] Pada Siklus sel dan Angiogenesis sel Widr Secara In Vitro; Universitas Gadjah Mada: Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rüngeler, P.; Lyß, G.; Castro, V.; Mora, G.; Pahl, H.L.; Merfort, I. Study of three sesquiterpene lactones from Tithonia diversifolia on their anti-inflammatory activity using the transcription factor NF-κB and enzymes of the arachidonic acid pathway as targets. Planta Med. 1998, 64, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.; Delgado, G. Constituents from Tithonia diversifolia: Stereochemical revision of 2α-hydroxytirotundin. J. Mex. Chem. Soc. 2006, 50, 180–183. [Google Scholar]
- Hassannia, B.; Vandenabeele, P.; Berghe, T.V. Targeting ferroptosis to iron out cancer. Cancer Cell 2019, 35, 830–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Fei, J.; Hao, X.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Tagitinin C induces ferroptosis through PERK-Nrf2-HO-1 signaling pathway in colorectal cancer cells. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 2703–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottlieb, Y.; Truman, M.; Cohen, L.A.; Leichtmann-Bardoogo, Y.; Meyron-Holtz, E.G. Endoplasmic reticulum anchored heme-oxygenase 1 faces the cytosol. Haematologica 2012, 97, 1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, S.-K.; Chen, S.-E.; Chang, L.-C. A dual role of heme oxygenase-1 in cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 20, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malfa, G.A.; Tomasello, B.; Acquaviva, R.; Genovese, C.; La Mantia, A.; Cammarata, F.P.; Ragusa, M.; Renis, M.; Di Giacomo, C. Betula etnensis Raf.(Betulaceae) extract induced HO-1 expression and ferroptosis cell death in human colon cancer cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, M.-Y.; Park, E.; Lee, S.-J.; Chung, S.W. Heme oxygenase-1 accelerates erastin-induced ferroptotic cell death. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 24393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.-C.; Chiang, S.-K.; Chen, S.-E.; Yu, Y.-L.; Chou, R.-H.; Chang, W.-C. Heme oxygenase-1 mediates BAY 11–7085 induced ferroptosis. Cancer Lett. 2018, 416, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Wang, H.; Han, D.; Xie, E.; Yang, X.; Wei, J.; Gu, S.; Gao, F.; Zhu, N.; Yin, X. Ferroptosis as a target for protection against cardiomyopathy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 2672–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassannia, B.; Wiernicki, B.; Ingold, I.; Qu, F.; Van Herck, S.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Bayır, H.; Abhari, B.A.; Angeli, J.P.F.; Choi, S.M. Nano-targeted induction of dual ferroptotic mechanisms eradicates high-risk neuroblastoma. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 3341–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeeshan, H.M.A.; Lee, G.H.; Kim, H.-R.; Chae, H.-J. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and associated ROS. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.S.; Kaufman, R.J. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and oxidative stress in cell fate decision and human disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 396–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Kaufman, R.J. The impact of the endoplasmic reticulum protein-folding environment on cancer development. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 581–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaisiya, M.; Zabetta, C.D.C.; Bellarosa, C.; Tiribelli, C. Bilirubin mediated oxidative stress involves antioxidant response activation via Nrf2 pathway. Cell. Signal. 2014, 26, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, R.; Reed, J.C. ER stress-induced cell death mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res. 2013, 1833, 3460–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Häcker, G. ER-stress and apoptosis: Molecular mechanisms and potential relevance in infection. Microbes Infect. 2014, 16, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, L.-J.; Zhang, J.-H.; Gomez, H.; Murugan, R.; Hong, X.; Xu, D.; Jiang, F.; Peng, Z.-Y. Reactive oxygen species-induced lipid peroxidation in apoptosis, autophagy, and ferroptosis. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 5080843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-S.; Lee, D.-H.; Choudry, H.A.; Bartlett, D.L.; Lee, Y.J. Ferroptosis-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress: Cross-talk between ferroptosis and apoptosis. Mol. Cancer Res. 2018, 16, 1073–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindskog, M.; Kogner, P.; Ponthan, F.; Schweinhardt, P.; Sandstedt, B.; Heiden, T.; Helms, G.; Spenger, C. Noninvasive estimation of tumour viability in a xenograft model of human neuroblastoma with proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H MRS). Br. J. Cancer 2003, 88, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tedeschi, G.; Lundbom, N.; Raman, R.; Bonavita, S.; Duyn, J.H.; Alger, J.R.; Di Chiro, G. Increased choline signal coinciding with malignant degeneration of cerebral gliomas: A serial proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy imaging study. J. Neurosurg. 1997, 87, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
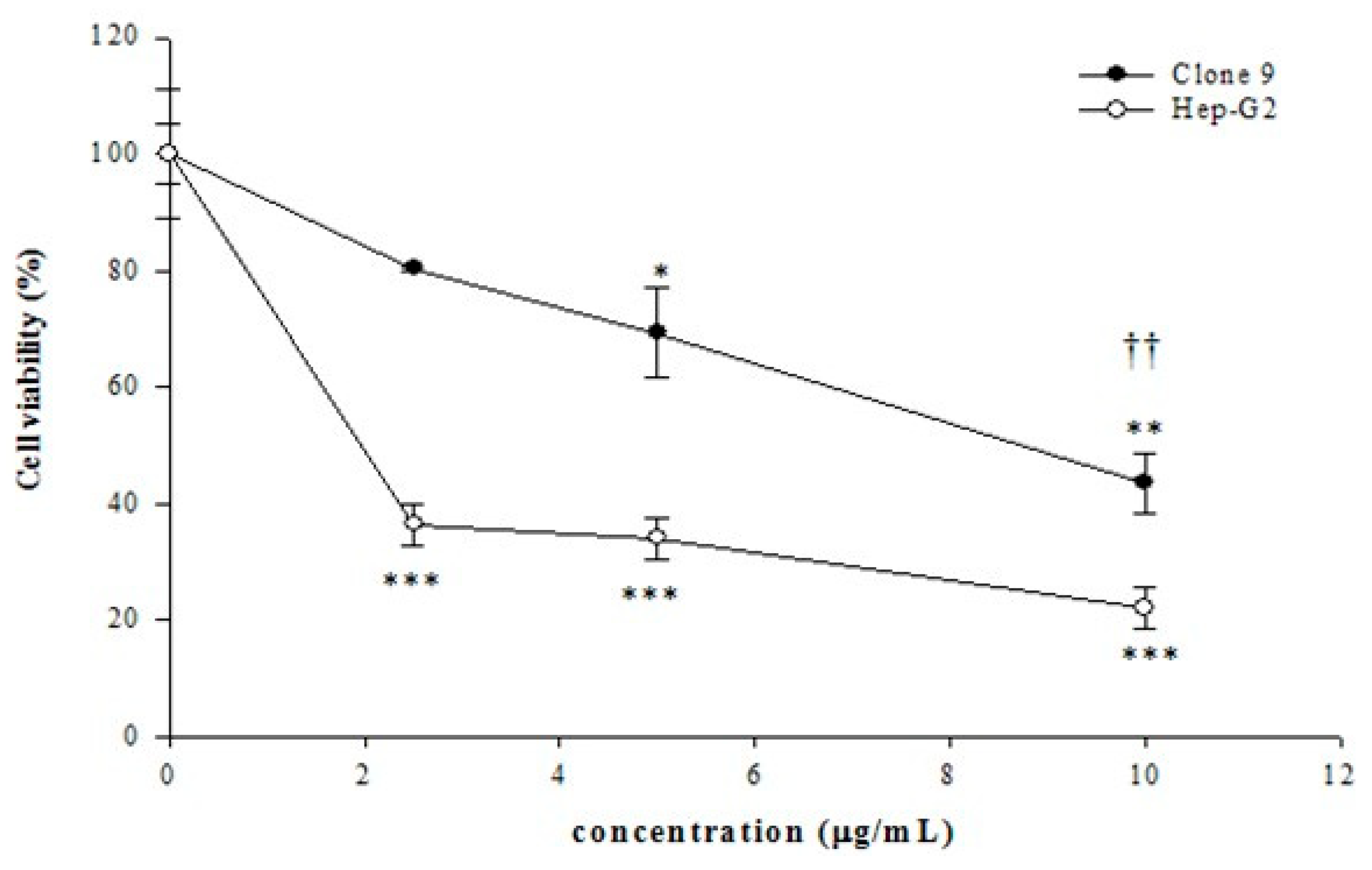



| Cells | IC50 (mg/mL) |
|---|---|
| Clone 9 | 8.6 ± 6.0 |
| Hep-G2 | 2.0 ± 0.1 |
| Huh 7 | 1.2 ± 0.1 |
| % of Total Cells | Sub G1 | G1 | G2/M | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 1.14 ± 0.19 | 57.64 ± 1.36 | 28.83 ± 0.63 | 10.56 ± 0.96 |
| 1.25 μg/mL | 46.48 ± 4.89 *** | 31.60 ± 2.21 *** | 5.34 ± 0.71 *** | 8.71 ± 0.75 ** |
| 2.5 μg/mL | 93.64 ± 1.10 *** | 4.94 ± 0.88 *** | 0.26 ± 0.08 *** | 1.03 ± 0.30 *** |
| 5 μg/mL | 89.88 ± 4.57 *** | 8.48 ± 3.97 *** | 0.20 ± 0.72 *** | 1.33 ± 0.64 *** |
| Cell | Day | Group | AFP (ng/mL) | GPT (U/L) | Cho/Cr at Inoculated Pixel | Cho/Cr at Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hep-G2 | 5 | Vehicle | <0.61 | 136.0 ± 46.6 | 0.93 ± 0.93 | 55.81 ± 16.02 |
| Tc | <0.61 | 29.3 ± 5.9 | 11.52 ± 4.80 a | 31.83 ± 8.12 a | ||
| 15 | Vehicle | 890.0 ± 191.7 | 28.4 ± 2.5 | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 72.40 ± 9.70 | |
| Tc | 961.8 ± 185.3 | 68.8 ± 38.1 | 6.53 ± 3.83 a | 29.32 ± 6.30 a | ||
| 25 | Vehicle | >12,100 | 362.4 ± 124.00 | 0.15 ± 0.15 | 34.49 ± 5.52 b | |
| Tc | >12,100 | 74.3 ± 27.00 c | 1.87 ± 0.87 a | 13.19 ± 2.52 c | ||
| Huh 7 | 5 | Vehicle | <0.61 | 125.05 ± 61.52 | 9.72 ± 6.63 | 42.75 ± 17.79 |
| Tc | <0.61 | 195.00 ± 79.80 | 11.10 ± 2.02 | 29.28 ± 7.66 | ||
| 15 | Vehicle | <0.61 | 49.66 ± 7.28 | 6.16 ± 2.41 | 47.34 ± 7.92 b | |
| Tc | <0.61 | 86.28 ± 25.10 b | 10.31 ± 3.67 | 22.62 ± 6.04 a | ||
| 25 | Vehicle | >12,100 | 32.3 ± 3.55 | 0.54 ± 0.38 | 67.85 ± 13.09 c | |
| Tc | >12,100 | 279 ± 208 | 3.90 ± 2.95 | 14.37 ± 4.46 a |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, C.-Y.; Liao, M.-H.; Yang, C.-Y.; Chang, C.-K.; Hsu, S.-M.; Juang, C.-L.; Wen, H.-C. Anti-Metastatic Activity of Tagitinin C from Tithonia diversifolia in a Xenograft Mouse Model of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Livers 2022, 2, 400-411. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers2040030
Lin C-Y, Liao M-H, Yang C-Y, Chang C-K, Hsu S-M, Juang C-L, Wen H-C. Anti-Metastatic Activity of Tagitinin C from Tithonia diversifolia in a Xenograft Mouse Model of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Livers. 2022; 2(4):400-411. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers2040030
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Chuan-Yi, May-Hua Liao, Chi-Yu Yang, Chao-Kai Chang, Shih-Mei Hsu, Chi-Long Juang, and Hsiao-Chuan Wen. 2022. "Anti-Metastatic Activity of Tagitinin C from Tithonia diversifolia in a Xenograft Mouse Model of Hepatocellular Carcinoma" Livers 2, no. 4: 400-411. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers2040030
APA StyleLin, C.-Y., Liao, M.-H., Yang, C.-Y., Chang, C.-K., Hsu, S.-M., Juang, C.-L., & Wen, H.-C. (2022). Anti-Metastatic Activity of Tagitinin C from Tithonia diversifolia in a Xenograft Mouse Model of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Livers, 2(4), 400-411. https://doi.org/10.3390/livers2040030






