Abstract
Aloe Vera (Aloe barbadensis Miller), a historically revered medicinal plant, has garnered great scientific attention due to its polysaccharide-rich bioactive compounds with significant therapeutic potential. This review examines the role of Aloe Vera polysaccharides as therapeutic agents in biomedical applications, highlighting their benefits as well as the risks. Traditionally recognized for its anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects, which are very important in wound healing, the Aloe Vera relies on its polysaccharides, which confer immunomodulatory, antioxidant, and tissue-regenerative properties. These compounds have shown promise in various applications, including skin repair, tissue engineering scaffolds, and antiviral therapies, with their delivery being facilitated via gels, thin films, or oral formulations. This review explores also their mechanisms of action and applications in modern medicine, including in the development of topical gels, dietary supplements, and innovative delivery systems such as thin films and scaffolds. Despite the promising benefits, the review addresses the possible side effects too, including allergic reactions, gastrointestinal disorders, and drug interactions, emphasizing the importance of understanding these risks for their safe clinical use. Assessing both the advantages and challenges of Aloe Vera polysaccharide medical use, this review contributes to the ongoing dialog regarding the integration of natural products into therapeutic practices, ultimately supporting informed decisions regarding their clinical application.
1. Introduction
Aloe Vera, scientifically known as “Aloe barbadensis Miller”, has a rich history of medicinal use that spans thousands of years. This succulent plant is believed to have originated in the Arabian Peninsula, but it has been cultivated in various regions worldwide for its therapeutic properties. Historical texts indicate that Aloe Vera was utilized by ancient civilizations, including the Egyptians, Greeks, and Chinese, for its healing abilities. The ancient Egyptians referred to Aloe Vera as the “plant of immortality”, using it to treat wounds, skin ailments, and digestive issues [1]. The Ebers Papyrus, one of the oldest medical texts from around 1550 BC, documents the use of Aloe Vera in treating various ailments, including burns and skin diseases, highlighting its significance in early medicine [1].
In traditional Chinese medicine, Aloe Vera has been employed for its cooling properties and its ability to promote healing and detoxification [2]. The Greeks, notably Dioscorides, documented the use of Aloe Vera for treating a wide range of conditions, from insomnia to skin irritations, further emphasizing its versatility as a medicinal herb [2]. The plant’s gel and latex have been used for centuries, with the gel primarily applied topically for wound healing and the latex used for its laxative effects [3].
In modern times, Aloe Vera has gained popularity in the healthcare and cosmetic industries due to its bioactive compounds, particularly polysaccharides, which are known for their anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and wound-healing properties [4,5,6]. The polysaccharide acemannan, a major component of Aloe Vera, is recognized for its immunomodulatory and wound healing properties, making it a focal point in modern therapeutic research [7]. Research has increasingly focused on the pharmacological effects of Aloe Vera, leading to its incorporation into various therapeutic formulations, including topical gels, creams, and dietary supplements [4,8]. The historical context of Aloe Vera’s medicinal use underscores its enduring relevance in both traditional and contemporary medicine, paving the way for ongoing research into its bioactive compounds and their potential applications in biomedical fields.
The necessity of a comprehensive review of Aloe Vera polysaccharides’ bioactive compounds use as therapeutic agents arises from the increasing interest in natural products as alternatives to synthetic pharmaceuticals. With the rising prevalence of chronic diseases and the side effects associated with conventional medications, there is a growing demand for herbal remedies that offer therapeutic benefits with fewer adverse effects [9]. Aloe Vera, with its rich composition of bioactive compounds, presents a viable candidate for addressing various health issues, including skin disorders, inflammation, and even cancer [10]. However, despite its promising therapeutic potential, there is a need to critically assess the benefits and potential side effects associated with Aloe Vera’s use, particularly in clinical settings [9]. This review aims for synthesizing the existing literature on Aloe Vera polysaccharides, elucidating their therapeutic applications while addressing the associated risks and interactions with other medications. More specifically, this review offers three novel contributions that are not comprehensively addressed in the existing literature. Thus, while prior reviews have focused on Aloe Vera’s therapeutic benefits only, this work also critically evaluates its side effects (e.g., allergic reactions and drug interactions) and toxicity risks (e.g., liver damage from excessive aloin), providing a holistic view of its clinical safety. In addition, our review highlights innovative delivery methods, such as thin films, nanogels, and tissue-engineered scaffolds, for the controlled release of polysaccharides, which were underexplored in earlier reviews. Moreover, this review uniquely discusses Aloe Vera’s role in enhancing the efficacy of chemotherapy/radiotherapy while reducing the side effects (e.g., mucositis), which represents a niche area of cancer care.
2. Aloe Vera and Its Bioactive Compounds
2.1. Chemical Composition
Aloe Vera is renowned for its diverse chemical composition, which contributes to its extensive therapeutic properties. The plant primarily consists of two main components: the gel obtained from the inner leaf pulp and the latex extracted from the leaf’s outer layer (Figure 1). This complex composition includes a series of mono- and polysaccharides, essential and secondary amino acids, chromones, anthraquinones, vitamins, minerals and trace elements, enzymes, and sterols [1,11,12].
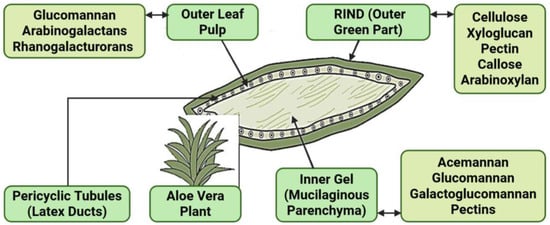
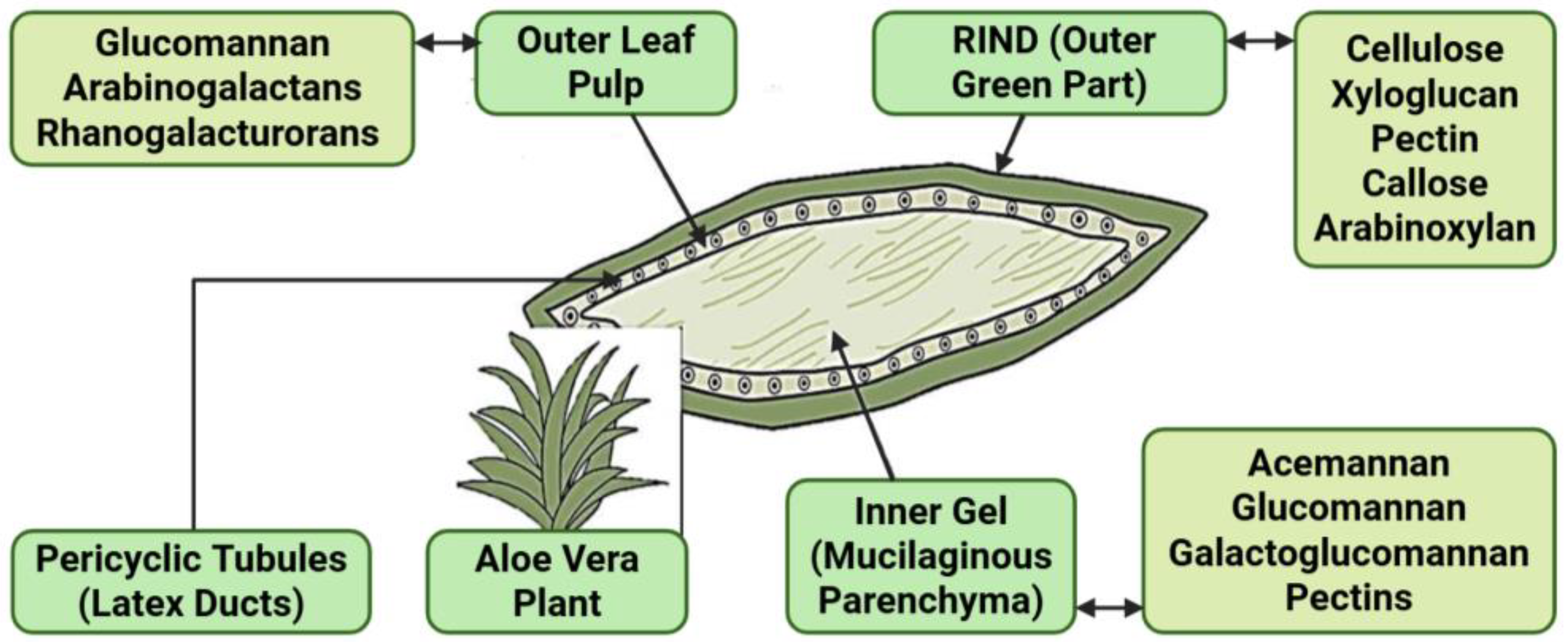
Figure 1.
Main polysaccharides in different regions of Aloe Vera leaf (adapted from [13]).
Among the bioactive constituents, polysaccharides are particularly significant, with acemannan being the most studied. Acemannan is a β-(1→4)-linked glucomannan, characterized by its polydispersity and the presence of O-acetyl groups, which contribute to its biological activity [14]. The other polysaccharides identified in Aloe Vera include glucomannan, rhamnogalaturonans, homogalacturorans, xyloglucans, arabinogalactans, galactoglucomannans, fructans, cellulose, and hemicellulose [15,16,17].
2.1.1. Aloe Vera Gel
The gel, which constitutes the majority of the leaf’s inner parenchyma, is composed of approximately 99% water, with the remaining 1% containing a rich array of bioactive compounds. The main components are polysaccharides (acemannan, glucomannan, galactoglucomannan, and pectins), glycoproteins and enzymes (amylase, peroxidase, and catalase), vitamins and minerals (A, C, E, zinc, and selenium), and amino acids and hormones (auxins and gibberellins) [1,16]. The most prevalent polysaccharide and the most-studied is acemannan, a β-(1→4)-linked glucomannan, characterized by its polydispersity and the presence of O-acetyl groups, which are critical for its biological activity [1].
The polysaccharides in Aloe Vera gel are primarily composed of mannose and glucose, with mannose-to-glucose (M/G) ratios varying depending on the extraction methods and growing conditions. For instance, some fractions exhibit ratios of approximately 5.9:1, while others show ratios of 2.5:1 or 4.1:1 [18]. These polysaccharides are known for their immunomodulatory, anti-inflammatory, and wound-healing properties, making them crucial for biomedical applications [4,5,12]. In addition to acemannan, other polysaccharides, such as mannans and pectins, also contribute to the gel’s health benefits [14]. The polysaccharides in Aloe Vera gel exhibit strong antioxidative properties, effectively scavenging free radicals and providing hepatoprotective and anti-inflammatory benefits [5,19].
Additionally, Aloe Vera is known to contain anthraquinones, which are phenolic compounds with potent antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties [20]. While the gel is primarily composed of non-irritating components, the latex contains anthraquinones such as aloin, which can cause irritation and allergic reactions in some individuals [20,21]. This distinction highlights the importance of processing methods in the production of Aloe Vera products, as most manufacturers focus on extracting the gel to minimize its adverse effects [20].
The gel is rich in vitamins A, B-complex, C, and E, which are potent antioxidants that protect cells from oxidative stress and promote skin health [4,5,12]. Furthermore, Aloe Vera contains a variety of minerals, including calcium, magnesium, and zinc, which are essential for numerous physiological functions [1,12]. The presence of enzymes such as amylase and lipase enhance the digestibility of Aloe Vera, contributing to its gastrointestinal benefits [1].
The overall chemical composition of Aloe Vera reinforces its potential as a therapeutic agent. The synergistic effects of its various bioactive compounds contribute to its efficacy in treating a wide range of health conditions, from skin disorders to gastrointestinal issues [4,5]. As research continues to explore the specific mechanisms of action of these compounds, Aloe Vera remains a prominent subject of interest in the field of natural medicine and therapeutic applications.
2.1.2. Aloe Vera Latex
The latex, found in the pericyclic tubules of the leaf’s outer layer, contains a distinct set of bioactive compounds, primarily anthraquinones. These phenolic compounds, such as aloin, aloe-emodin, and barbaloin, are responsible for the latex’s laxative effects but can also cause irritation and allergic reactions in some individuals [20,21]. Due to these potential adverse effects, most commercial Aloe Vera products focus on extracting the gel while minimizing the latex content [20].
2.1.3. Extraction and Isolation of Polysaccharides
Isolating polysaccharides from Aloe Vera involves several methodologies, which affect the yield and structural integrity of the polysaccharides. Studies have shown that the extraction methods can significantly alter the physical and chemical properties of Aloe Vera polysaccharides. For instance, variations in extraction techniques can lead to differences in the molecular sizes and types of polysaccharides obtained [18,22].
The choice of techniques utilized for their extraction and purification depends to a large extent on the type of polysaccharide and the structural changes that may occur during the process. The structural variability is influenced by factors such as cultivars, plant maturity, environmental conditions, and seasonal changes, which can alter the polysaccharide composition significantly [23,24]. Alterations in the acemannan structure could even be induced during storage, due to light, temperature, and oxygen exposure, or during pretreatment, as the acetyl groups are sensitive to pH and dehydration temperatures above 60 °C [25].
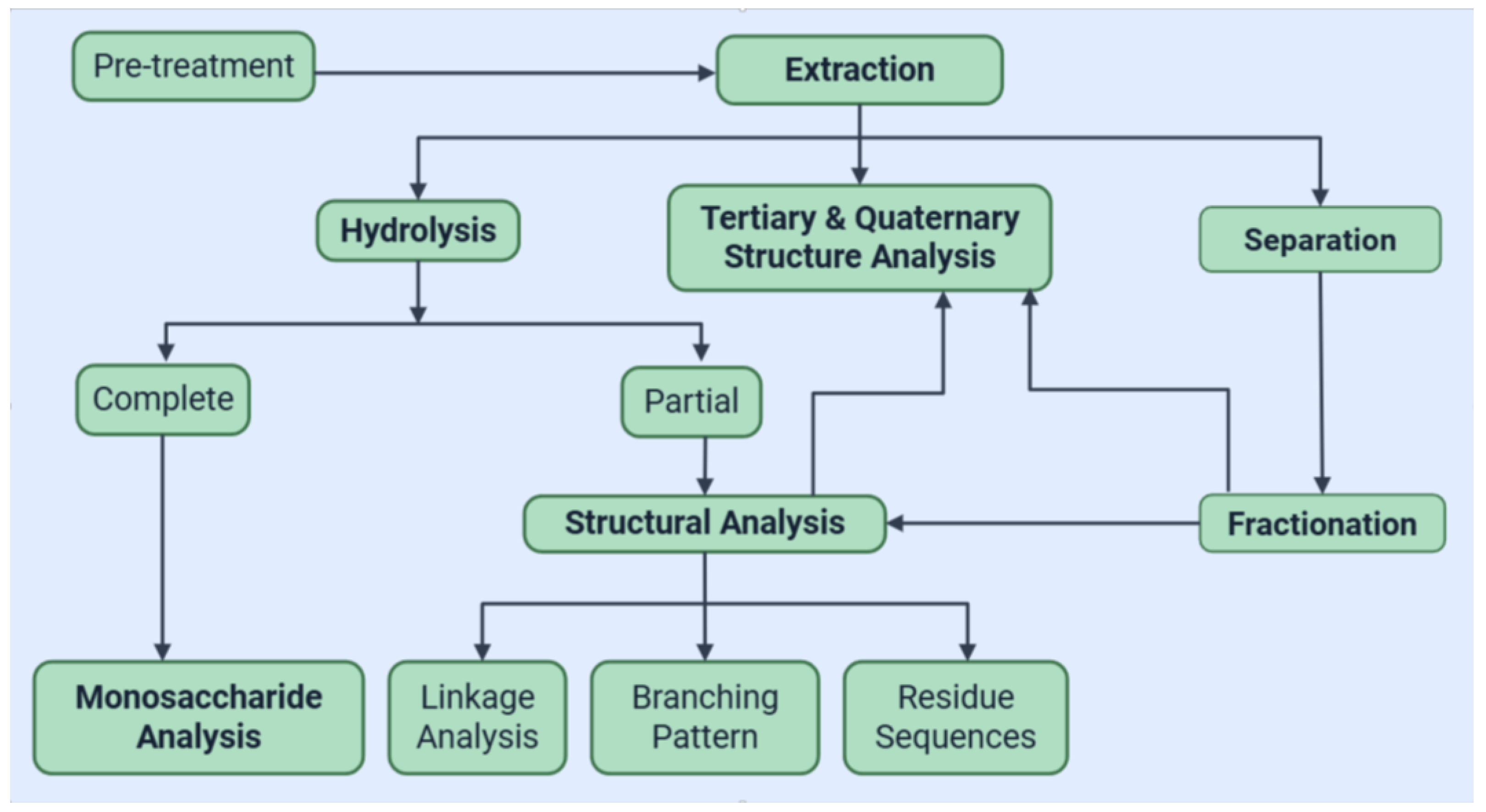
The workflow presented in Figure 2 evolves differently after selecting the polysaccharide (s) of interest and one of the appropriate extraction methods: hydrothermal, enzyme-assisted, ultrasound-assisted or microwave-assisted extraction, pressurized-liquid or supercritical fluid extraction, or ethanol precipitation. Conventional separation methods include ethanol fractionation, Sevag method, dialysis, membrane ultrafiltration, ion-exchange chromatography, and size-exclusion chromatography [26,27]. The optimal chain of processing and characterization techniques should help in achieving higher purity and a higher concentration of polysaccharides. If intended for industrial application, then they should also comply with pharmaceutical regulations, as well as the requirements regarding environmental sustainability and economic efficiency.
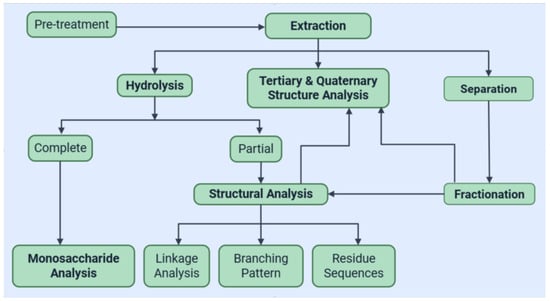
Figure 2.
Workflow outlining a chain of extraction, purification, and characterization steps for polysaccharides isolation from Aloe Vera (adapted from [26]).
2.2. Properties of Aloe Vera Polysaccharides Bioactive Compounds and Their Mechanisms of Action
Aloe Vera polysaccharides, particularly acemannan, are recognized for their diverse mechanisms of action, which contribute to their therapeutic efficacy in various biomedical applications. These bioactive compounds exhibit a wide range of biological activities, including immunomodulation, anti-inflammatory effects, antimicrobial properties, wound healing promotion, antioxidant activity, gastrointestinal health benefits, antidiabetic effects, and anticancer properties [17,28]. Table 1 summarizes the key mechanisms of action of Aloe Vera polysaccharides, particularly focusing on their therapeutic effects.

Table 1.
Main mechanisms of action of Aloe Vera polysaccharides (AVPs).
Later, we delve deeper into the specific pathways and molecular interactions through which these polysaccharides exert their therapeutic effects. However, an exact and singular classification per biological property, mechanism of action, or targeted effect cannot be presented. This task is made difficult by a series of factors: the complex composition of Aloe Vera, the synergies between different components, the pluri-faceted behavior of some polysaccharides and anthraquinones, and the multilayer pathology of some health conditions. Therefore, an approach based on potential therapeutic applications centered around a main biological property with other concurrent effects is more suitable for an extensive review.
One of the primary mechanisms through which Aloe Vera polysaccharides exert their effects is through the modulation of the immune system. Acemannan has been shown to activate macrophages, dendritic cells, and lymphocytes, enhancing their proliferation and activity, and thereby promoting a robust immune response [42,43]. This immunomodulatory effect is mediated through the toll-like receptor (TLR) pathway, specifically TLR4, which recognizes polysaccharides and triggers the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α).
Additionally, acemannan stimulates the production of nitric oxide (NO) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) in macrophages, which are critical for pathogen clearance [44]. Polysaccharides also enhance antigen presentation by dendritic cells, promoting a more robust adaptive immune response. This immunomodulatory activity is further supported by the upregulation of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecules and co-stimulatory molecules like CD80 and CD86 [45]. This immunomodulatory effect is particularly beneficial in conditions where the immune system is compromised or requires support, such as in chronic infections or during post-surgical recovery [28,46,47]. Additionally, Aloe Vera polysaccharides can stimulate the production of cytokines, which are signaling molecules that facilitate communication between immune cells, further enhancing the body’s defense mechanisms [10].
The anti-inflammatory properties of Aloe Vera polysaccharides are primarily mediated through the inhibition of key inflammatory pathways. Acemannan and other polysaccharides suppress the activation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), a transcription factor that regulates the expression of pro-inflammatory genes. By inhibiting NF-κB [48,49], Aloe Vera polysaccharides reduce the production of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and lipoxygenase (LOX), enzymes responsible for the synthesis of inflammatory mediators such as prostaglandins and leukotrienes [50,51]. This anti-inflammatory action is particularly valuable in wound healing, where excessive inflammation can impede the healing process [52,53]. Furthermore, Aloe Vera polysaccharides downregulate the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α, while upregulating anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-10 [49,51,52]. This dual action helps to mitigate inflammation in conditions such as arthritis, dermatitis, and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) [48,54,55]. The polysaccharides also inhibit the migration of neutrophils and monocytes to inflamed tissues, reducing tissue damage and promoting the resolution of inflammation [50,55].
Aloe Vera polysaccharides also exhibit significant antimicrobial activity, which is attributed to their ability to disrupt the cell membranes of bacteria, viruses, and fungi [20,56]. The primary mechanism of this involves the disruption of microbial cell membranes, leading to leakage of cellular contents and eventual cell death. For example, acemannan interacts with the lipopolysaccharides (LPS) in the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria, destabilizing the membrane and increasing permeability [44,57].
In addition to direct antimicrobial effects, Aloe Vera polysaccharides enhance the host’s immune response to infections. They stimulate the production of defensins and other antimicrobial peptides through epithelial cells, providing a first line of defense against pathogens [42,43].
The polysaccharides also exhibit antiviral activity by inhibiting viral replication and entry into host cells. For instance, acemannan has been shown to block the binding of herpes simplex virus (HSV) to host cell receptors [58,59]. Studies have shown that Aloe Vera extracts can effectively inhibit the growth of a wide range of pathogens, including Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, and various fungal species [32,55,60]. This antimicrobial property not only aids in preventing infections in wounds but also supports overall health by reducing the microbial load in the gastrointestinal tract [28]. The presence of phenolic compounds, such as p-coumaric acid and ascorbic acid, further enhances the antimicrobial efficacy of Aloe Vera [32].
Aloe Vera polysaccharides are highly effective in promoting wound healing through multiple mechanisms. They stimulate the proliferation and migration of fibroblasts, which are essential for collagen synthesis and remodeling the extracellular matrix (ECM). Acemannan enhances the expression of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), a key regulator of fibroblast activity and collagen production [61,62].
The polysaccharides also promote angiogenesis by upregulating the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), which are critical for the formation of new blood vessels. This ensures an adequate supply of oxygen and nutrients is provided to the wound site, facilitating tissue repair. Additionally, Aloe Vera polysaccharides maintain a moist wound environment, which is conducive to faster healing and reduces the risk of scarring [53,61].
Furthermore, Aloe Vera polysaccharides exhibit potent antioxidant activity by scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS) and free radicals, which are byproducts of cellular metabolism and inflammation. The polysaccharides enhance the activity of endogenous antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), which neutralize oxidative stress and protect cells from damage [17,63].
The antioxidant effects of Aloe Vera polysaccharides are further amplified through the presence of phenolic compounds and flavonoids, which synergistically reduce oxidative damage. This property is particularly beneficial in preventing lipid peroxidation, DNA damage, and protein oxidation, processes associated with chronic diseases and aging [17,63].
Aloe Vera polysaccharides support gastrointestinal health, acting as prebiotics and promoting the growth of beneficial gut microbiota such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium species [64]. These polysaccharides are fermented by gut bacteria, producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate, acetate, and propionate, which support intestinal health and reduce inflammation [65].
The polysaccharides also enhance the integrity of the intestinal epithelial barrier by upregulating the expression of tight junction proteins such as occludin and zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) [51,54]. This prevents the translocation of pathogens and toxins across the gut lining, reducing the risk of leaky gut syndrome and associated inflammatory conditions [45,48].
In diabetic conditions, Aloe Vera polysaccharides help regulate blood glucose levels by improving the sensitivity of insulin and enhancing glucose uptake in peripheral tissues [66,67,68]. Acemannan has been shown to activate AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), a key regulator of the glucose metabolism [69,70]. This leads to the increased translocation of glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4) to the cell membrane, facilitating glucose uptake in muscle and adipose tissues [71,72].
Additionally, Aloe Vera polysaccharides inhibit alpha-glucosidase and alpha-amylase, enzymes involved in carbohydrate digestion, thereby reducing postprandial blood glucose levels [73,74]. These mechanisms make Aloe Vera polysaccharides a promising adjunct in the management of type 2 diabetes.
Certain polysaccharides in Aloe Vera, including acemannan, have demonstrated antitumoral effects by inducing apoptosis (programmed cell death) in cancer cells. This is achieved through the activation of caspase-3 and caspase-9, key enzymes in the apoptotic pathway [45,48]. Aloe Vera polysaccharides also inhibit angiogenesis and metastasis by downregulating matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and VEGF [75].
Moreover, these polysaccharides enhance the immune system’s ability to recognize and destroy cancer cells through stimulating natural killer (NK) cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) [43,55]. The antioxidant properties of Aloe Vera polysaccharides further contribute to their anticancer effects through reducing oxidative stress, which is a key driver of carcinogenesis [76,77].
Continued research into the molecular mechanisms of Aloe Vera polysaccharides will further elucidate their therapeutic potential and expand their applications in healthcare.
3. Potential Aloe Vera Therapeutic Applications
The mechanisms of action of Aloe Vera polysaccharides are diverse, involving complex molecular interactions and signaling pathways. From their immunomodulation and anti-inflammatory effects to their antimicrobial activity, wound healing promotion, and anticancer properties, these bioactive compounds demonstrate remarkable therapeutic potential. Their ability to modulate key cellular processes highlights their value as natural agents in modern medicine, with applications ranging from wound care and gastrointestinal health to diabetes management and cancer therapy [1,60].
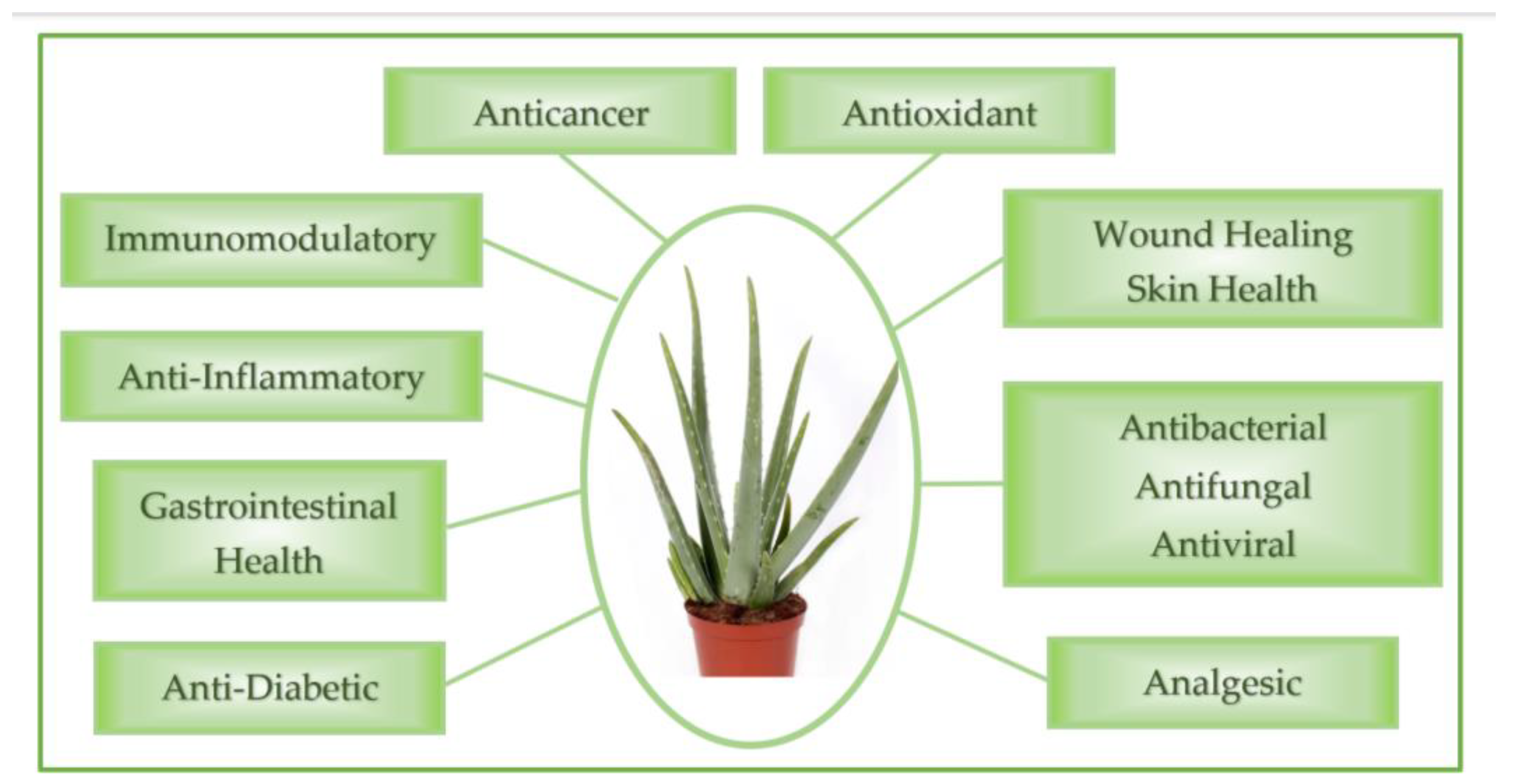
In exploring the diverse therapeutic applications of Aloe Vera, Figure 3 provides a schematic representation of the biological properties of Aloe Vera, which underpin its potential benefits in various medical fields.
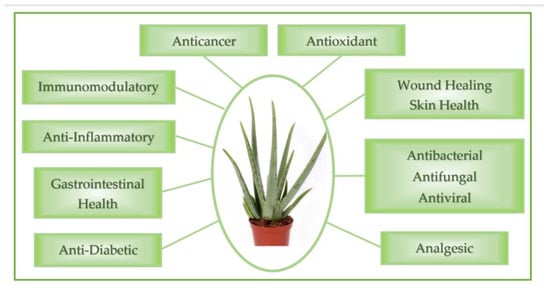
Figure 3.
Visual overview of Aloe Vera’s key biological properties, as described below.
3.1. Antiseptic
Aloe Vera has long been recognized for its antiseptic properties, making it a valuable component in wound care and infection prevention.
The plant contains various bioactive compounds, including saponins, which are known for their cleansing and antimicrobial effects. Saponins can effectively disrupt the membranes of microbial cells, thereby preventing the growth of bacteria and fungi that commonly infect wounds [78,79]. This property is particularly beneficial in clinical settings, where maintaining a sterile environment is crucial for patient recovery.
The differences between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria can be attributed to their distinct cell wall structures and the presence of various resistance mechanisms. Gram-positive bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan layer, which is more susceptible to certain antibiotics, while Gram-negative bacteria possess an outer membrane that acts as a barrier to many drugs. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting an appropriate antibiotic therapy and combating bacterial infections effectively. As antibiotic resistance continues to rise, ongoing research is essential to develop new strategies and agents that can target both Gram-positive and Gram-negative pathogens effectively.
In Table 2, we summarize the effects of Aloe Vera on various bacterial strains, including both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria:

Table 2.
Effects of Aloe Vera on Gram-positive (Gram+) and Gram-negative (Gram−) bacterial strains.
Key Notes:
Aloe Vera polysaccharides, particularly acemannan, disrupt bacterial cell membranes, interfere with biofilm formation, and inhibit quorum-sensing, making them effective against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Aloe Vera is particularly effective in preventing biofilm formation, which is a key factor in bacterial persistence and antibiotic resistance.
Aloe Vera exhibits antimicrobial activity against a wide range of pathogens, including drug-resistant strains. Targeted pathogens include Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli, which are often implicated in wound infections [80,81]. The gel’s effectiveness as an antiseptic is attributed not only to its saponin content but also to other compounds, such as flavonoids and polyphenols, which possess inherent antimicrobial properties [82]. These compounds work synergistically to enhance the overall antimicrobial efficacy of Aloe Vera, making it a potent natural antiseptic.
In addition to its antibacterial properties, Aloe Vera has shown antifungal activity, further broadening its application in wound care.
In Table 3, we summarize the antifungal properties of Aloe Vera, including the fungal strains studied, the mechanisms of action, and key findings.

Table 3.
Antifungal properties of Aloe Vera (AV).
Key Notes:
Aloe Vera exerts its antifungal effects through multiple mechanisms, including the disruption of fungal cell membranes, the inhibition of biofilm formation, interference with cell wall synthesis, and the induction of oxidative stress. Aloe Vera exhibits antifungal activity against a wide range of fungal strains, including Candida albicans, Aspergillus niger, and Trichophyton mentagrophytes. The combination of polysaccharides, phenolic compounds, and flavonoids in Aloe Vera enhances its antifungal efficacy, making it a potent natural antifungal agent.
Studies have indicated that Aloe Vera gel can inhibit the growth of various fungal strains, providing a dual-action approach to infection prevention [81,83]. This antifungal capability is particularly relevant when treating wounds that may be susceptible to fungal infections, such as those in immunocompromised patients.
The application of Aloe Vera as an antiseptic is not limited to topical use; it has also been explored in dental practices. Aloe Vera gel has been used as an oral rinse and in periodontal treatments, demonstrating effectiveness against oral pathogens [81]. This versatility adds to the plant’s potential as a natural antiseptic in various medical fields, including dentistry and general wound care.
Moreover, Aloe Vera’s ability to promote healing while providing antiseptic benefits makes it an ideal candidate for incorporation into thin film dressings and other wound care products. The use of Aloe Vera in such formulations can enhance the healing process by maintaining a moist environment, which is conducive to tissue regeneration, while simultaneously preventing microbial colonization [6,84]. This characteristic is particularly advantageous in the management of chronic wounds, where infection and delayed healing are common challenges.
The antiseptic properties of Aloe Vera due to its rich composition of bioactive compounds make it a valuable therapeutic agent in wound care. Its ability to inhibit bacterial and fungal growth, combined with its healing-promoting effects, positions Aloe Vera as a promising natural alternative to synthetic antiseptics in both clinical and home settings.
3.2. Anti-Inflammatory Action
Aloe Vera is widely recognized for its potent anti-inflammatory properties, which are primarily attributed to its rich composition of bioactive compounds, including polysaccharides, flavonoids, and phenolic acids. These compounds work synergistically to modulate inflammatory responses, making Aloe Vera an effective therapeutic agent in managing various inflammatory conditions [83,85].
One of the key mechanisms through which Aloe Vera exerts its anti-inflammatory effects is through inhibiting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Studies have shown that Aloe Vera can downregulate the expression of cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), which play critical roles in the inflammatory process [86,87]. By reducing the levels of these cytokines, Aloe Vera helps to mitigate the inflammatory response, thereby alleviating symptoms associated with conditions such as arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease [88].
Additionally, Aloe Vera contains enzymes like carboxypeptidase, which has been reported to inactivate bradykinin, a peptide that promotes vasodilation and increases vascular permeability during inflammation [83]. This action not only reduces swelling and pain but also limits the infiltration of leukocytes into inflamed tissues, further contributing to its anti-inflammatory effects [88]. Furthermore, Aloe Vera has been shown to inhibit the cyclooxygenase (COX) pathway, which is involved in the synthesis of prostaglandins that mediate inflammation [32,89]. By blocking this pathway, Aloe Vera can effectively reduce inflammation and associated pain.
The antioxidant properties of Aloe Vera also play a significant role in its anti-inflammatory action. By scavenging free radicals and reducing oxidative stress, Aloe Vera helps to prevent cellular damage that can exacerbate inflammation [10,87]. This antioxidant activity is particularly beneficial in chronic inflammatory conditions, where oxidative stress is often a contributing factor [10].
Aloe Vera’s ability to promote tissue regeneration and healing further enhances its anti-inflammatory effects. The polysaccharides in Aloe Vera stimulate fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis, which are essential for repairing damaged tissues [90,91]. This regenerative capability not only aids in recovery from inflammation but also helps to restore normal tissue function.
In clinical applications, Aloe Vera has been utilized in various formulations, including topical gels and creams, to treat inflammatory skin conditions such as psoriasis and eczema [37,92]. Its soothing properties make it an ideal candidate for managing inflammation and promoting healing in dermatological applications. Additionally, Aloe Vera has been incorporated into oral supplements aimed for reducing systemic inflammation, showcasing its versatility as an anti-inflammatory agent [93,94].
The anti-inflammatory action of Aloe Vera is multifaceted, involving the inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokines, modulation of the COX pathway, antioxidant activity, and the promotion of tissue-healing.
3.3. Skin Health
The polysaccharides present in Aloe Vera, especially acemannan, play a crucial role in enhancing skin health by facilitating various biological processes involved in tissue repair [13,95].
One of the primary mechanisms through which Aloe Vera promotes skin tissue healing is through stimulating fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis. Fibroblasts are essential cells in the dermis, producing collagen and extracellular matrix components, which are vital for maintaining the structure and elasticity of the skin [95,96]. Research has shown that the application of Aloe Vera gel can significantly increase fibroblast activity, leading to enhanced collagen deposition and improved wound healing outcomes [95,97]. This effect is particularly beneficial in the context of chronic wounds, where fibroblast activity is often impaired.
In addition to promoting fibroblast proliferation, Aloe Vera has been shown to enhance the overall healing process by improving blood supply to the affected area. Increased blood flow ensures that essential nutrients and oxygen are delivered to the skin tissue, facilitating faster recovery [61,98]. The presence of bioactive compounds in Aloe Vera, such as vitamins and minerals, further supports this process by providing the necessary building blocks for tissue repair [99,100].
Aloe Vera’s anti-inflammatory properties also contribute to its effectiveness in skin tissue applications. By reducing inflammation at the wound site, Aloe Vera helps to create a more favorable environment for healing [97,101]. This is particularly important in cases of burns or other injuries where inflammation can impede the healing process and lead to complications.
Moreover, Aloe Vera’s moisturizing properties play a significant role in skin health. The gel extracted from Aloe Vera leaves contains a high percentage of water, which helps to hydrate the skin and prevent excessive fluid loss [100,102]. This moisture retention is crucial for maintaining skin integrity and promoting healing, especially in dry or damaged tissues [89].
Clinical studies have demonstrated the efficacy of Aloe Vera in treating various skin conditions, including burns, abrasions, and chronic ulcers. For instance, Aloe Vera has been shown to accelerate the healing of second-degree burns and reduce the severity of erythema and pain associated with skin injuries [96,103]. Additionally, its application has been linked to improved outcomes in patients with diabetic ulcers, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic agent in managing complex skin conditions [13,95].
Through its stimulation of fibroblast activity, the improvements it provides in blood supply, its anti-inflammatory effects, and its moisturizing properties, Aloe Vera serves as a valuable therapeutic agent in wound healing and skin regeneration. Its application in various formulations, including gels and creams, reinforces its potential for broader use in dermatological and cosmetic products.
3.4. Tissue Engineering
One of the significant advantages of using Aloe Vera in tissue engineering is its ability to enhance the proliferation and differentiation of stem cells. Research has shown that Aloe Vera extracts can induce the expression of integrin genes in human adipose-derived stem cells (hASCs), which are essential for cell adhesion and tissue integration [104]. This property is particularly valuable in tissue engineering, where the successful integration of scaffolds with host tissues is critical for the functionality of engineered constructs.
Aloe Vera’s polysaccharides also contribute to the mechanical properties of tissue engineering scaffolds. When combined with other materials, such as collagen or chitosan, Aloe Vera can improve the hydrophilicity and mechanical stability of the resulting composites [36,105]. For instance, studies have demonstrated that Aloe Vera-coated polylactic acid (PLA) scaffolds exhibit an enhanced affinity for cell attachment and growth, making them suitable for various tissue engineering applications, including bone and skin regeneration [105].
Aloe Vera’s inherent antimicrobial properties make it an ideal candidate for preventing infections in tissue engineering applications. The presence of bioactive compounds in Aloe Vera helps to inhibit bacterial growth, thereby reducing the risk of infection in implanted scaffolds [106]. This is particularly important in clinical settings, where infections can significantly compromise the success of tissue engineering interventions.
In addition to its mechanical and antimicrobial properties, Aloe Vera promotes angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels, which is vital for supplying nutrients and oxygen to the engineered tissues [11,107]. The polysaccharides in Aloe Vera have been shown to stimulate the release of growth factors that facilitate angiogenesis, thereby enhancing the viability and functionality of tissue-engineered constructs.
Aloe Vera has also been incorporated into various types of scaffolds, including hydrogels and nanofibrous membranes, to create a conducive environment for cell growth and tissue regeneration [11,107]. For example, Aloe Vera-based hydrogels have been developed for wound healing applications, providing a moist environment that promotes faster healing while delivering bioactive compounds directly to the wound site [107].
3.5. Antiviral and Anti-Tumoral Action
Aloe Vera bioactive compounds, polysaccharides, flavonoids, and anthraquinones have been shown to exhibit significant biological activities that can inhibit viral replication and tumor growth, making Aloe Vera a promising candidate for therapeutic applications in virology and oncology [108,109].
Research has demonstrated that acemannan can interfere with viral replication through inhibiting the adsorption of viruses to host cells and disrupting their life cycle [110,111]. In vitro studies have shown that Aloe Vera extracts can significantly reduce the replication of various viruses, including herpes simplex virus (HSV) and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) [112]. Their mechanism of action involves the interaction of polysaccharides with viral particles, preventing them from binding to host cell receptors, thereby blocking infection [110].
Aloe Vera has also been investigated for its potential in treating viral infections such as the influenza virus and, more recently, SARS-CoV-2. A study utilizing molecular docking techniques indicated that compounds derived from Aloe Vera could serve as potential inhibitors of the main protease of SARS-CoV-2, suggesting a role for Aloe Vera in the development of antiviral therapies against COVID-19 [108,109]. This highlights the relevance of Aloe Vera in addressing emerging viral threats and its potential as a natural antiviral agent.
In addition to its antiviral effects, Aloe Vera has demonstrated anti-tumoral properties in various studies. The presence of bioactive compounds such as aloesin and emodin has been linked to the inhibition of cancer cell proliferation and the induction of apoptosis in several cancer types, including ovarian and colon cancers [113,114]. These compounds exert their effects by modulating key signaling pathways involved in cell growth and survival, such as the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway [114].
An interesting approach is to develop different means of extracting and purifying polysaccharides from Aloe Vera gel to achieve targeted responses for specific tumors. Thus, through using different solvents for the elution of Aloe Vera polysaccharides, distinct structures are obtained, with considerable variations in the contents of acemannan and O-acetyl groups. These variations are directly reflected in their biological activity. When colorectal cancer cells were exposed to phthalates, it was proven that the polysaccharides eluted from Aloe Vera showed distinct regulatory effects according to their correspondent fractions, depending on the eluent that was used: either water or ethanol [115].
Furthermore, Aloe Vera’s antioxidant properties contribute to its anticancer effects by reducing oxidative stress, which is a known contributor to cancer development. By scavenging free radicals and enhancing the body’s antioxidant defenses, Aloe Vera helps to protect cells from damage that can lead to tumorigenesis [100].
Clinical studies have also explored the use of Aloe Vera in conjunction with conventional cancer therapies. For instance, Aloe Vera has been shown to enhance the efficacy of chemotherapy while reducing the side effects associated with treatment, such as mucositis and skin irritation [116]. This synergistic effect points to Aloe Vera’s potential as an adjunctive treatment in cancer care, providing both therapeutic benefits and supportive care. Aloe Vera’s ability to inhibit viral replication and tumor growth, coupled with its antioxidant and immunomodulatory effects, positions it as a valuable therapeutic agent in the fields of virology and oncology. However, further research and clinical trials are warranted to fully elucidate its mechanisms of action and potential applications in these areas.
4. Delivery Methods
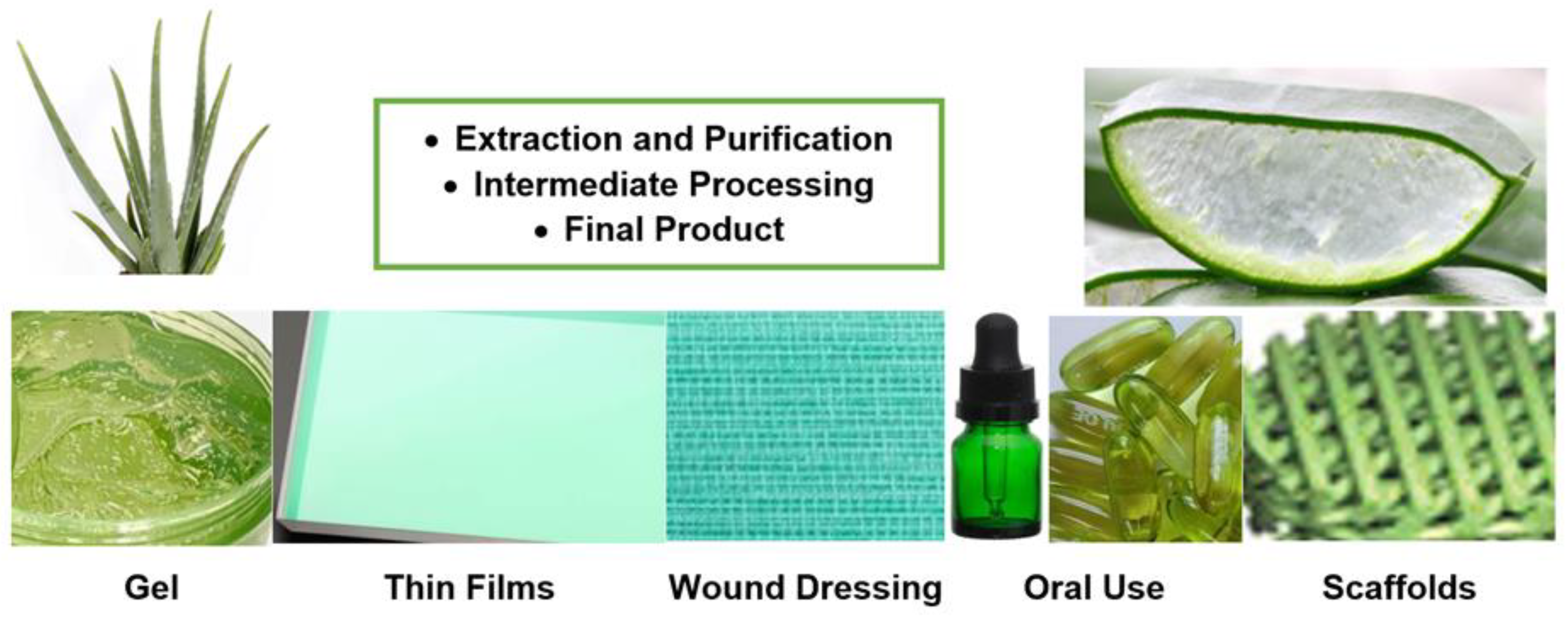
Delivery methods for Aloe Vera (Figure 4) have evolved significantly, offering a range of convenient options for harnessing the plant’s healing properties, from topical gels and juices to capsules and infused skincare products.
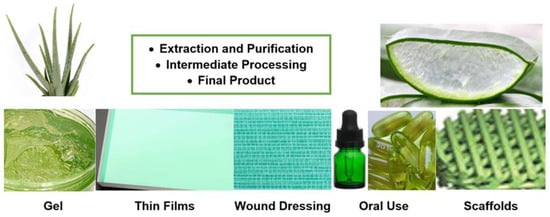
Figure 4.
Aloe Vera delivery methods for therapeutic applications [13].
Table 4 illustrates the diverse applications of Aloe Vera polysaccharides in biomedical contexts, highlighting their mechanisms of action, their delivery method, and the evidence supporting their efficacy in various clinical and experimental settings.

Table 4.
Aloe Vera delivery methods.
4.1. Gels
Aloe Vera gels are among the most common delivery methods for its bioactive compounds. The gel formulation allows for easy application on the skin, providing localized treatment for wounds, burns, and other skin conditions [100].
Acemannan has been shown to stimulate fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis, which are essential processes for tissue repair and regeneration [127,128]. This makes Aloe Vera gel particularly effective in treating skin injuries, burns, and chronic wounds, where rapid healing is crucial [4,128].
The hydrophilic nature of Aloe Vera gel enhances moisture retention and promotes healing, making it an effective vehicle for delivering therapeutic agents [10]. Aloe Vera gel acts as a humectant, drawing moisture into the skin and preventing dehydration, which is vital for maintaining skin integrity during the healing process [37,129,130]. This hydrating effect promotes faster healing and also improves the overall appearance and texture of the skin, making Aloe Vera gel a popular ingredient in cosmetic formulations [102,131].
In addition, Aloe Vera gel exhibits significant antimicrobial activity. The gel contains various bioactive compounds, including saponins and anthraquinones, which have been shown to inhibit the growth of bacteria and fungi [128,132]. This antimicrobial action is particularly beneficial in preventing infections in wounds and skin lesions, further enhancing the therapeutic potential of Aloe Vera gel [132,133].
Recent advancements in formulation technology have led to the development of Aloe Vera gel-based hydrogels and nanogels, which offer improved drug delivery and the sustained release of bioactive compounds [134,135]. These innovative formulations enhance the therapeutic potential of Aloe Vera gel, making it suitable for a wider range of biomedical applications, including tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [37,131]. The incorporation of Aloe Vera gel into edible coatings has been explored in food preservation, proving that it can help extend the shelf life of fruits and vegetables by reducing microbial contamination [92,136]. This application highlights the versatility of Aloe Vera gel beyond therapeutic uses, showcasing its potential in the food industry as a natural preservative.
Furthermore, the incorporation of Aloe Vera in gel formulations can enhance the stability and bioavailability of other active ingredients, improving overall efficacy [137].
4.2. Thin Films
Thin films made from Aloe Vera polysaccharides offer a novel approach to drug delivery and wound healing [13,138]. These films can be applied directly to the skin, providing a protective barrier while allowing for the controlled release of bioactive compounds [139].
When incorporated into thin film formulations, Aloe Vera polysaccharides, particularly acemannan, can create a supportive environment for cell growth and migration, facilitating the healing process in damaged tissues [37,140]. Aloe Vera thin films also exhibit excellent moisture-retention capabilities. The hydrophilic nature of Aloe Vera allows these films to draw moisture from the surrounding environment, preventing dehydration of the wound site and promoting faster recovery [10,141]. Similarly to the gel, Aloe Vera thin films possess antimicrobial activity, with the presence of bioactive compounds such as saponins and anthraquinones in Aloe Vera helping to inhibit the growth of bacteria and fungi [13,134].
Also, Aloe Vera-based thin films that can be tailored for specific applications. For instance, researchers have explored the incorporation of Aloe Vera into polymeric matrices to create composite films with enhanced mechanical properties and the controlled release of bioactive compounds [120,142]. These innovative formulations not only improve the stability and efficacy of the therapeutic agents but also expand the potential applications of Aloe Vera in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
Aloe Vera thin films have also been investigated for their use in food preservation. The antimicrobial properties of Aloe Vera can help extend the shelf life of perishable products by reducing microbial contamination [92,143].
The versatility of Aloe Vera thin films extends beyond their therapeutic applications, demonstrating their potential as valuable tools in wound healing, tissue engineering, and food preservation, ultimately contributing to improved patient outcomes.
4.3. Wound Dressings
Aloe Vera-infused dressings have attracted attention for their ability to promote healing and prevent infection in wounds. The incorporation of Aloe Vera into wound dressings enhances their antimicrobial properties, providing a natural alternative to conventional dressings [100].
Studies have shown that Aloe Vera dressings can significantly reduce healing time and improve patient comfort, making them a preferred choice in clinical settings [117].
Moreover, these dressings are proven to retain moisture, preventing desiccation of the wound bed and facilitating the migration of epithelial cells necessary for re-epithelialization [144,145]. This moisture-retentive property is particularly beneficial in the treatment of chronic wounds, where maintaining hydration is critical for effective healing [146]. Recent advancements in material science have led to the development of innovative Aloe Vera-based dressings, which not only enhance the mechanical properties and stability of the dressing but also improve the controlled release of bioactive compounds, further augmenting their therapeutic efficacy [125,147]. For example, studies have demonstrated that chitosan–alginate hydrogels containing Aloe Vera can provide a sustained release of active ingredients while maintaining favorable swelling and degradation profiles [148]. Clinical trials have shown that Aloe Vera gel dressings can significantly reduce healing time and improve patient comfort in individuals with diabetic foot ulcers and pressure sores [126,149]. Combining Aloe Vera’s natural healing properties with modern dressing technologies positions these products as promising options in the field of wound care.
4.4. Oral Administration
The oral delivery of Aloe Vera has been explored for its potential health benefits, particularly in managing gastrointestinal disorders and promoting overall wellness. Aloe Vera juice and supplements are commonly used to support digestive health thanks to their soothing properties [150]. Research has indicated that the oral consumption of Aloe Vera can help alleviate symptoms of conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome and acid reflux [151]. The bioactive compounds in Aloe Vera, including polysaccharides, contribute to its therapeutic effects when taken orally, making it a valuable addition to dietary regimens [152]. Aloe Vera contains a rich array of active ingredients with beneficial action for various gastrointestinal conditions [152,153,154,155]. The oral consumption of Aloe Vera has been found to promote the attachment and enhance the healing of wounded cells, potentially contributing to its therapeutic effects [154].
Furthermore, studies have suggested that Aloe Vera can have a positive impact on blood pressure and glucose levels, making it a potential complementary treatment for conditions such as diabetes and hypertension [32,156]. The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of Aloe Vera may also contribute to its beneficial effects on the gastrointestinal system [151,155]. However, it is important to note that the effects of Aloe Vera as a dietary supplement can be subtle, and long-term intervention may be necessary to observe significant improvements in symptoms [151]. Additionally, some studies have reported potential adverse effects, such as abdominal pain and muscle weakness, associated with Aloe Vera supplementation [157]. Therefore, it is crucial to consult with healthcare professionals before incorporating Aloe Vera into one’s dietary regimen, especially for individuals with pre-existing medical conditions.
4.5. Scaffolds
Scaffolds play a crucial role in the field of tissue engineering, particularly when considering the application of Aloe Vera polysaccharides as therapeutic agents. The unique properties of Aloe Vera have garnered significant attention for their potential in creating biocompatible scaffolds that can support cellular activities and promote tissue regeneration. Polysaccharides such as acemannan and glucomannan are known for their ability to enhance cell proliferation, migration, and differentiation, which are essential processes in wound healing and tissue repair [158,159].
The structural characteristics of Aloe Vera polysaccharides contribute to their effectiveness as scaffolding materials. For instance, the molecular structure of acemannan, which consists of a backbone of β-(1→4)-D-mannose residues with various side chains, allows for the formation of hydrogels that can retain moisture and provide a conducive environment for cell attachment and growth [38,159,160].
Furthermore, the rheological behavior of Aloe Vera-based hydrogels indicates that they can be tailored to meet specific mechanical and physical requirements, making them suitable for various biomedical applications [120]. In addition to their structural properties, Aloe Vera polysaccharides exhibit significant biological activities that enhance their utility in scaffolding. This is particularly relevant in the context of chronic wounds, where excessive inflammation can impede healing. By incorporating Aloe Vera polysaccharides into scaffolds, researchers can potentially create materials that not only support tissue regeneration but also modulate the inflammatory response, thereby improving healing outcomes [99,161,162]. To further enhance their appeal as scaffold materials, the presence of compounds such as anthraquinones and salicylic acid in Aloe Vera has been linked to its antibacterial effects, which can help prevent infections in wound-healing applications [106,134]. Scaffolds that incorporate Aloe Vera polysaccharides can thus provide a dual function: serving as a physical support structure while also delivering bioactive compounds that promote healing and prevent infection [159,163]. This multifunctionality is particularly advantageous in the development of advanced wound dressings and tissue engineering constructs. The integration of Aloe Vera polysaccharides into various scaffold designs has been explored in numerous studies. For instance, electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds that incorporate Aloe Vera extracts have shown promise in bone tissue engineering applications due to their enhanced mechanical properties and biocompatibility [164]. Additionally, the use of Aloe Vera-based hydrogels has been investigated for their potential in treating skin conditions such as psoriasis, highlighting the versatility of these materials in addressing a range of biomedical challenges [158,165]. Furthermore, the ability of Aloe Vera polysaccharides to form hydrogels that can encapsulate therapeutic agents opens new avenues for controlled drug delivery systems. These systems can provide a sustained release of bioactive compounds, thereby enhancing therapeutic efficacy while minimizing side effects [159,166]. The incorporation of Aloe Vera polysaccharides into drug delivery scaffolds can facilitate localized treatment, which is particularly beneficial in managing chronic conditions or localized injuries. In conclusion, the application of Aloe Vera polysaccharides in scaffold development represents a promising area of research within the field of biomedical engineering. Their unique structural and biological properties make them suitable candidates for creating advanced scaffolds that can support tissue regeneration, modulate inflammatory responses, and deliver therapeutic agents effectively. As research continues to explore the full potential of Aloe Vera polysaccharides, it is likely that we will see further innovations in scaffold design that leverage these natural compounds for improved clinical outcomes.
5. Benefits and Risks
5.1. Advantages
Aloe Vera polysaccharides, particularly acemannan, have garnered significant attention for their therapeutic properties and applications in various biomedical fields. One of the primary advantages of Aloe Vera polysaccharides is their potent anti-inflammatory effects, which are crucial for promoting wound healing and tissue regeneration. Research indicates that these polysaccharides can modulate inflammatory responses, thereby reducing swelling and pain associated with injuries [99,161]. This property makes Aloe Vera particularly beneficial in treating skin injuries, such as burns, cuts, and insect bites, where inflammation can hinder the healing process [99,161]. In addition to their anti-inflammatory capabilities, Aloe Vera polysaccharides exhibit strong antimicrobial properties. Studies have shown that these compounds possess antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal activities, which can help prevent infections in wounds and enhance overall healing outcomes [99,167]. The presence of bioactive compounds such as aloin and aloesin contributes to these antimicrobial effects, making Aloe Vera a valuable natural alternative to conventional antiseptics [99,161]. This dual action of promoting healing while preventing infection accentuates the therapeutic potential of Aloe Vera polysaccharides in clinical settings. Another significant advantage of Aloe Vera polysaccharides is their ability to enhance skin hydration and elasticity. The mucilage derived from Aloe Vera is rich in polysaccharides that can retain moisture, providing a protective barrier that helps maintain skin integrity [166,168]. This property is particularly beneficial in cosmetic applications, where Aloe Vera is used to formulate moisturizers and skin care products aimed for improving skin texture and reducing signs of aging [31,120]. Furthermore, the antioxidant properties of Aloe Vera polysaccharides help combat oxidative stress, which is a contributing factor to skin aging and various dermatological conditions [169,170]. Moreover, the immunomodulatory effects of Aloe Vera polysaccharides are noteworthy. These compounds can stimulate immune responses, enhancing the body’s ability to fight infections and diseases [99,171]. This immunostimulatory action is particularly relevant in the context of chronic diseases and conditions where the immune system may be compromised. Through supporting immune function, Aloe Vera polysaccharides can play a role in the prevention and management of various health issues, including metabolic syndrome and certain cancers [135,172]. The versatility of Aloe Vera polysaccharides extends to their applications in functional foods and dietary supplements. The incorporation of these polysaccharides into food products not only enhances the nutritional profile of the products but also provides health benefits, such as improved digestion and gut health [173,174]. The prebiotic effects of Aloe Vera polysaccharides can promote the growth of beneficial gut microbiota, contributing to overall digestive health [168,175]. This aspect of Aloe Vera polysaccharides highlights their potential as a functional ingredient in health-promoting foods. In conclusion, the advantages of Aloe Vera polysaccharides as therapeutic agents are multifaceted, encompassing anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, hydrating, immunomodulatory, and nutritional benefits. These properties make Aloe Vera polysaccharides a promising candidate for various biomedical applications, from wound healing to functional food development. As research continues to unveil the mechanisms underlying these benefits, the potential for Aloe Vera polysaccharides to enhance health and well-being remains significant.
5.2. Side Effects
While Aloe Vera polysaccharides are widely recognized for their therapeutic benefits, it is essential to consider the potential side effects associated with their use. One of the primary concerns is the risk of allergic reactions. Some individuals may experience skin irritation or allergic dermatitis when using Aloe Vera topically, particularly in those with sensitive skin or allergies to plants in the Liliaceae family, to which Aloe Vera belongs [159,161]. Such reactions can manifest as redness, itching, or rashes, necessitating caution when applying Aloe Vera products on the skin. Ingesting Aloe Vera, particularly in the form of supplements or juices, can also lead to gastrointestinal disturbances. Reports indicate that consuming large quantities of Aloe Vera can cause abdominal cramps, diarrhea, and nausea [129,176]. The laxative effect of certain compounds in Aloe Vera, such as anthraquinones, can be particularly pronounced, leading to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances if consumed excessively [31,129]. Therefore, it is advisable for individuals to adhere to recommended dosages and consult healthcare professionals before starting any Aloe Vera supplementation, especially those with pre-existing gastrointestinal conditions. Another significant concern is the potential for toxicity associated with Aloe Vera extracts.
Some studies have indicated that high doses of Aloe Vera can exhibit cytotoxic effects, particularly in animal models [120,159]. For instance, research has shown that excessive Aloe Vera consumption can lead to liver damage and other organ toxicity [171,177]. This toxicity is often attributed to the presence of compounds like aloin, which, while beneficial in moderate amounts, can become harmful at elevated levels [171,177]. Consequently, it is crucial to monitor the concentration of active compounds in Aloe Vera products to mitigate the risk of adverse effects.
Moreover, the interaction of Aloe Vera with certain medications poses another risk. Aloe Vera may enhance or inhibit the effects of various drugs, particularly those metabolized by the liver. Lastly, there are concerns regarding the quality and purity of commercial Aloe Vera products. Contaminants and additives in poorly manufactured products can lead to adverse reactions [158,178]. Therefore, consumers should be vigilant in selecting high-quality, reputable brands that provide transparency regarding their product formulations.
While Aloe Vera polysaccharides offer numerous health benefits, potential side effects such as allergic reactions, gastrointestinal disturbances, toxicity, drug interactions, and concerns regarding product quality must be carefully considered. Individuals should approach the use of Aloe Vera with caution, particularly in high doses or when used in conjunction with other medications.
5.3. Combined Medical Association
The therapeutic applications of Aloe Vera polysaccharides, particularly acemannan, are enhanced when considered in conjunction with other medical treatments or dietary components (Table 5). Understanding the interactions between Aloe Vera and various medications or supplements is crucial for optimizing its benefits while minimizing potential risks.

Table 5.
Aloe Vera combination therapies.
One significant area of interaction involves the immunomodulatory effects of Aloe Vera polysaccharides. Research has shown that these compounds can enhance immune responses, which may influence the efficacy of immunosuppressive drugs used in conditions such as autoimmune diseases or organ transplantation [99,141]. For instance, the polysaccharides in Aloe Vera were reported to preserve the morphology of immunosuppressive cells, suggesting that their use could potentially interfere with the intended effects of immunosuppressive therapies [99]. Therefore, patients undergoing such treatments should consult healthcare providers before incorporating Aloe Vera into their regimen.
Moreover, Aloe Vera’s ability to modulate blood sugar levels presents both opportunities and challenges for individuals with diabetes. Studies indicate that Aloe Vera can lower blood glucose levels, which may enhance the effects of antidiabetic medications [9,31]. While this can be beneficial for managing diabetes, it also raises concerns about the risk of hypoglycemia if not monitored properly. Patients on antidiabetic medications should be cautious and seek medical advice when considering Aloe Vera supplementation to avoid adverse interactions [9].
In addition to its effects on blood sugar, Aloe Vera polysaccharides may interact with anticoagulant medications. Some studies suggest that Aloe Vera can enhance the effects of anticoagulants, potentially increasing the risk of bleeding [173,175]. This interaction calls attention to the need for careful monitoring of patients taking blood thinners who wish to use Aloe Vera products.
Furthermore, the combination of Aloe Vera with other herbal supplements can lead to synergistic effects or enhanced therapeutic outcomes. For example, Aloe Vera has been studied in conjunction with chamomile for its protective effects on the intestinal mucosa, demonstrating improved outcomes in models of colitis [184]. Such combinations may offer novel approaches to managing gastrointestinal disorders, but they also necessitate a thorough understanding of the pharmacological profiles of each component to avoid adverse effects.
The incorporation of Aloe Vera into functional foods and dietary supplements also raises questions about its interactions with other food components. For instance, Aloe Vera’s polysaccharides can act as prebiotics, promoting the growth of beneficial gut microbiota [166]. This interaction can enhance overall gut health, but it may also influence the absorption and efficacy of certain medications when taken concurrently.
Lastly, the quality and formulation of Aloe Vera products can significantly impact their interactions with other substances. Variability in the concentration of active compounds, such as anthraquinones, can lead to unpredictable effects when combined with other treatments [119,185]. Therefore, it is essential for consumers to choose high-quality Aloe Vera products and to be aware of their potential interactions with other medications or supplements.
5.4. Comparison of Aloe Vera Polysaccharides with Synthetic Counterparts
The therapeutic potential of Aloe Vera polysaccharides, particularly acemannan, has been increasingly recognized in biomedical applications. However, their efficacy and safety are often compared to their synthetic counterparts, which are widely used in pharmaceutical products and medical treatments. This subsection explores the advantages of Aloe Vera polysaccharides compared to synthetic compounds, focusing on the reduced side effects, as well as their biocompatibility and cost-effectiveness.
Aloe Vera polysaccharides exhibit a broad spectrum of biological activities, including immunomodulation, anti-inflammatory effects, antimicrobial properties, and wound healing promotion [49,51]. These properties are comparable to, or in some cases superior to, those of synthetic compounds. For example, synthetic anti-inflammatory drugs such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) often come with significant side effects, including gastrointestinal bleeding and renal toxicity [50]. In contrast, Aloe Vera polysaccharides, particularly acemannan, have been shown to inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α and IL-6 without causing severe adverse effects [52]. This makes them a safer alternative for long-term use in chronic inflammatory conditions such as arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease.
Similarly, synthetic antimicrobial agents, such as triclosan and chlorhexidine, are effective against a wide range of pathogens but can lead to resistance and toxicity with prolonged use [186]. Aloe Vera polysaccharides, on the other hand, have demonstrated significant antimicrobial activity against bacteria, viruses, and fungi without promoting resistance [55,57]. Their natural origin and complex structure make it difficult for pathogens to develop resistance, offering a sustainable alternative to synthetic antimicrobials.
One of the most significant advantages of Aloe Vera polysaccharides over synthetic counterparts is their biocompatibility. Synthetic polymers and drugs often trigger immune responses or cause tissue irritation, limiting their use in sensitive applications such as wound healing and tissue engineering [187]. Aloe Vera polysaccharides, however, are highly biocompatible and have been shown to promote cell proliferation and tissue regeneration without eliciting adverse immune reactions [45,54]. This makes them ideal for use in biomedical scaffolds, wound dressings, and drug delivery systems where biocompatibility is critical.
Moreover, synthetic compounds often require extensive purification and processing to remove toxic by-products, which can increase the risk of contamination and side effects. Aloe Vera polysaccharides, being naturally derived, are less likely to contain harmful impurities, reducing the risk of toxicity and allergic reactions [188,189]. This is particularly important in topical applications, where synthetic compounds can cause skin irritation or allergic dermatitis.
The production of synthetic compounds often involves complex chemical processes, which can be costly and environmentally damaging. In contrast, Aloe Vera polysaccharides can be extracted using relatively simple and sustainable methods, making them more cost-effective and environmentally friendly [60,64]. The widespread cultivation of Aloe Vera in various regions further reduces production costs, making it an economically viable option for large-scale biomedical applications. Additionally, the multifunctionality of Aloe Vera polysaccharides reduces the need for multiple synthetic drugs. For example, a single Aloe Vera-based formulation can provide anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and wound-healing effects, whereas synthetic treatments often require separate drugs for each therapeutic goal [1,43]. This not only lowers the overall cost of treatment but also simplifies patient care.
While synthetic compounds have played a crucial role in modern medicine, Aloe Vera polysaccharides offer several advantages, including reduced side effects, enhanced biocompatibility, and cost-effectiveness. Their natural origin, combined with their multifunctional properties, makes them a promising alternative to synthetic counterparts in various biomedical applications. However, further research is needed to fully understand their mechanisms of action and optimize their use in clinical settings.
6. Conclusions
In conclusion, Aloe Vera polysaccharides represent a promising class of bioactive compounds with significant therapeutic potential across various biomedical applications. This review highlights their efficacy in wound healing, anti-inflammatory responses, antimicrobial activity, and immunomodulation, supported by both their historical uses and contemporary scientific research. The polysaccharides’ ability to promote tissue regeneration, reduce inflammation, and combat infections positions them as a valuable natural alternative to synthetic drugs. However, their use must be carefully balanced against their potential side effects, such as allergic reactions, gastrointestinal disturbances, and interactions with other medications. Rigorous standardization, quality control, and long-term safety studies are essential to ensure their safe and effective integration into clinical practice.
While Aloe Vera polysaccharides offer numerous therapeutic benefits, their interactions with other medical treatments and dietary components require careful consideration. Patients should engage in open discussions with healthcare providers to ensure the safe and effective use of Aloe Vera in conjunction with other therapies, particularly in the context of immunosuppression, diabetes management, and anticoagulation therapy.
The growing interest in natural therapeutics, coupled with the limitations of synthetic drugs, underscores the importance of Aloe Vera polysaccharides in modern medicine. Their biocompatibility, cost-effectiveness, and multifunctionality make them particularly appealing for applications in wound care, tissue engineering, and drug delivery systems. As the demand for sustainable and patient-friendly treatments increases, Aloe Vera polysaccharides offer a promising avenue for addressing unmet medical needs.
7. Future Perspectives
The future of Aloe Vera polysaccharides in biomedical applications is bright, with several promising research directions and clinical opportunities on the horizon. Advances in nanotechnology, such as nanogels, electrospun scaffolds, and nanoparticle-based carriers, could enhance the bioavailability and targeted delivery of Aloe Vera polysaccharides [45,75]. These systems may improve therapeutic outcomes by ensuring controlled release and localized action, particularly in wound healing and cancer therapy.
Developing eco-friendly and scalable extraction techniques will be crucial to meet the global demand for Aloe Vera polysaccharides. Innovations in green chemistry and biotechnology could optimize yield and purity while minimizing environmental impact [60,64].
Tailoring Aloe Vera-based formulations to individual genetic profiles or specific pathologies could revolutionize their clinical application. Personalized therapies may enhance efficacy and reduce adverse effects, particularly in chronic conditions such as diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease, and cancer [1,43].
Exploring the synergistic effects of Aloe Vera polysaccharides when used alongside other natural compounds or synthetic drugs could unlock new therapeutic possibilities. For example, combining Aloe Vera with chemotherapy or radiotherapy may enhance treatment efficacy while mitigating side effects such as mucositis and skin irritation [55].
Further research is needed to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying the biological activities of Aloe Vera polysaccharides. Understanding their interactions with cellular pathways, immune responses, and microbial targets will provide a stronger foundation for their clinical use.
Comprehensive studies on the long-term safety, dosage, and potential toxicity of Aloe Vera polysaccharides are essential. Establishing standardized protocols for their extraction, formulation, and quality control will ensure consistency and reliability in their therapeutic applications [1,51].
The role of Aloe Vera polysaccharides in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine holds immense promise. Their ability to promote cell proliferation, angiogenesis, and tissue repair makes them ideal candidates for developing advanced biomaterials and scaffolds for skin, bone, and cartilage regeneration [45,54].
In summary, while Aloe Vera polysaccharides offer immense therapeutic potential, their successful integration into mainstream medicine will require interdisciplinary collaboration, innovative research, and rigorous clinical validation [55,60]. By addressing these challenges, Aloe Vera polysaccharides could become a cornerstone of natural-based therapies, offering safer, more effective, and sustainable solutions for a wide range of health conditions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.E.M., A.I.V. and R.C.; writing—original draft preparation, A.I.V.; writing—review and editing, C.E.M. and R.C.; visualization, C.E.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors acknowledge the financial support of the Romanian Ministry of Education and Research, CNCS-UEFISCDI, projects no. PN-III-P4-ID-PCE-2020-2273 (11/2020, RENERI) and PNIII-P4-ID-PCE-2016-0884 (142/2017 BIOMATE) within PNCDI III, and Romanian Ministry of Research, Innovation and Digitalization under the Romanian National Nucleu Program LAPLAS VII—contract No. 30N/2023. AV acknowledges a grant of the Ministry of Research, Innovation and Digitalization, CNCS—UEFISCDI, project no. PN-IV-P2-2.1-TE-2023-0993 within PNCDI IV.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Boudreau, M.D.; Beland, F.A. An Evaluation of the Biological and Toxicological Properties of Aloe barbadensis (Miller), Aloe vera. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part C 2006, 24, 103–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golmohammadi, F. Medical Plant of Aloe vera in Desert Regions of Iran: Greenhouses, Economic Importance, Development, Extension, Processing and Marketing. Black Sea J. Agric. 2022, 5, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundarkar, P.; Govindwar, R.; Nyamati, S.B.; Alladwar, N.; Thombre, V.; Soni, A.; Raj, A. Use of Aloe vera in Dentistry. J. Indian Acad. Oral. Med. Radiol. 2011, 23, S389–S391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radha, M.H.; Laxmipriya, N.P. Evaluation of Biological Properties and Clinical Effectiveness of Aloe vera: A Systematic Review. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2015, 5, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taukoorah, U.; Mahomoodally, M.F. Crude Aloe vera Gel Shows Antioxidant Propensities and Inhibits Pancreatic Lipase and Glucose Movement In Vitro. Adv. Pharmacol. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 2016, 3720850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkhil, M.Z.; Prakash, K.G.; Haseeb, A.; Ahmed, K.; Udupa, P.; Muguregowda, H.T. Evaluation of Altered Ground Matrix and Matrix Metalloproeinase (MMP’S) in Wound Healing with Aloe vera Extract. Asian J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2020, 6, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbaeyi-Nwaoha, I.E.; Ojochegbe, A.F.; Nnamani, C.J. Effects of Utazi Leaf (Gongronema latifolium) and Aloe vera (Aloe barbadensis) on the Quality Attribute of Formulated Herbal Yoghurt. Braz. J. Sci. 2023, 2, 62–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangwar, C.; Singh, P.; Kewat, R.N.; Vikram, N. Biochemical Composition and Enzymatic Activity of Aloe vera (Aloe barbadensis L.). Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2017, 6, 3572–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakib, Z.; Shahraki, N.; Razavi, B.M.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Aloe vera as an Herbal Medicine in the Treatment of Metabolic Syndrome: A Review. Phytother. Res. 2019, 33, 2649–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirmala, G.N.; Sharma, A.; Ragunathan, V. Antagonistic Effect of Dichloromethane on Oreochromis Mossambicus and Immune Stimulation Activity of Aloe vera. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 913065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, O.M.; Buerki, S.; Symonds, M.R.E.; Forest, F.; Van Wyk, A.E.; Smith, G.F.; Klopper, R.R.; Bjorå, C.S.; Neale, S.; Demissew, S.; et al. Evolutionary History and Leaf Succulence as Explanations for Medicinal Use in Aloes and the Global Popularity of Aloe vera. BMC Evol. Biol. 2015, 15, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoruk, N.G.; Istanbullu Paksoy, Ö. GC/MS Evaluation of the Composition of the Aloe vera Gel and Extract. Food Chem. X 2024, 23, 101536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, S.; Carter, P.; Bhattarai, N.; Puoci, F. Aloe vera for Tissue Engineering Applications. J. Funct. Biomater. 2017, 8, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudreau, M.D.; Mellick, P.W.; Olson, G.R.; Felton, R.P.; Thorn, B.T.; Beland, F.A. Clear Evidence of Carcinogenic Activity by a Whole-Leaf Extract of Aloe barbadensis Miller (Aloe vera) in F344/N Rats. Toxicol. Sci. 2013, 131, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minjares-Fuentes, R.; Femenia, A.; Comas-Serra, F.; Rodríguez-González, V.M. Compositional and Structural Features of the Main Bioactive Polysaccharides Present in the Aloe vera Plant. J. AOAC Int. 2018, 101, 1711–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamman, J.H. Composition and Applications of Aloe vera Leaf Gel. Molecules 2008, 13, 1599–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Añibarro-Ortega, M.; Pinela, J.; Barros, L.; Ćirić, A.; Silva, S.P.; Coelho, E.; Mocan, A.; Calhelha, R.C.; Soković, M.; Coimbra, M.A.; et al. Compositional Features and Bioactive Properties of Aloe vera Leaf (Fillet, Mucilage, and Rind) and Flower. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souleymane, T.; Ibourahema, C.; Edith, A.A.; Gbogouri, G.A.; Kouakou, B.; Paquot, M. Effect of Extraction Methods on Chemical and Physical Properties of Aloe vera (Aloe barbadensis Miller) Polysaccharides Fraction: Liguid Gel and Powders. Asian J. Agric. Food Sci. 2018, 6, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yimam, M.; Jiao, P.; Moore, B.; Hong, M.; Cleveland, S.; Chu, M.; Jia, Q.; Lee, Y.C.; Kim, H.J.; Nam, J.B.; et al. Hepatoprotective Activity of Herbal Composition SAL, a Standardize Blend Comprised of Schisandra chinensis, Artemisia capillaris, and Aloe barbadensis. J. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 2016, 3530971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.; Teixeira, M.; Silva, E.; Selores, M. Allergic Contact Dermatitis to Aloe vera. Contact Dermat. 2007, 57, 278–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reider, N.; Issa, A.; Hawranek, T.; Schuster, C.; Aberer, W.; Kofler, H.; Fritsch, P.; Hausen, B.M. Absence of Contact Sensitization to Aloe vera (L.) Burm. f. Contact Dermat. 2005, 53, 332–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, X.L.; Chen, B.Y.; Feng, Y.M. Water-Soluble Polysaccharides Isolated from Skin Juice, Gel Juice and Flower of Aloe vera Miller. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2011, 42, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahl, L.I.; Al-Husseini, N.; Al-Helle, S.; Staerk, D.; Grace, O.M.; Willats, W.G.T.; Mravec, J.; Jørgensen, B.; Rønsted, N. Detection of Seasonal Variation in Aloe Polysaccharides Using Carbohydrate Detecting Microarrays. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 440013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badar, Z. Enhanced Production of Aloe Mannan Using Plant Biotechnology. Int. J. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2017, 3, 298–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Femenia, A.; Sánchez, E.S.; Simal, S.; Rosselló, C. Compositional Features of Polysaccharides from Aloe vera (Aloe barbadensis Miller) Plant Tissues. Carbohydr. Polym. 1999, 39, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesco, K.C.; Williams, S.K.R.; Laurens, L.M.L. Marine Algae Polysaccharides: An Overview of Characterization Techniques for Structural and Molecular Elucidation. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.W.; Lin, L.G.; Ye, W.C. Techniques for Extraction and Isolation of Natural Products: A Comprehensive Review. Chin. Med. 2018, 13, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hefny, A.; Awad, M.; Youssef, M. Aloe vera Aqueous Extract and Yogurt Enhance Peripheral Immune Cells, and Brain Astrocytes Response in Rats. SVU-Int. J. Vet. Sci. 2023, 6, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutapea, A.M.; Susanto, C. Hypoglycemic Potential of Aloe vera in Diabetes Mellitus Induced by Diabetogenic Substances and High Fat Diet: A Systematic Meta-Analysis Review. Int. J. Appl. Dent. Sci. 2021, 7, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Im, S.A.; Kim, J.; Lee, S.; Kwon, J.; Lee, H.; Kong, H.; Song, Y.; Shin, E.; Do, S.G.; et al. Modified Aloe Polysaccharide Restores Chronic Stress-Induced Immunosuppression in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Cui, Y.; Pi, F.; Cheng, Y.; Guo, Y.; Qian, H. Extraction, Purification, Structural Characteristics, Biological Activities and Pharmacological Applications of Acemannan, a Polysaccharide from Aloe vera: A Review. Molecules 2019, 24, 1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athiban, P.; Borthakur, B.; Ganesan, S.; Swathika, B. Evaluation of Antimicrobial Efficacy of Aloe vera and Its Effectiveness in Decontaminating Gutta Percha Cones. J. Conserv. Dent. 2012, 15, 246–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Españo, E.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.K. Utilization of Aloe Compounds in Combatting Viral Diseases. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Liu, H.; Ren, M.; Li, T.; Jiang, W.-K.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Z.; Yang, M. Aloe Polysaccharide Promotes Osteogenesis Potential of Adipose-Derived Stromal Cells via BMP-2/Smads and Prevents Ovariectomized-Induced Osteoporosis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 11913–11924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, W.; Guo, W.; Zou, C.H.; Fu, T.T.; Li, X.Y.; Zhu, M.; Qi, J.H.; Song, J.; Dong, C.H.; Li, Z.; et al. Acemannan Accelerates Cell Proliferation and Skin Wound Healing through AKT/MTOR Signaling Pathway. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2015, 79, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, S.S.; Popa, E.G.; Gomes, M.E.; Cerqueira, M.; Marques, A.P.; Caridade, S.G.; Teixeira, P.; Sousa, C.; Mano, J.F.; Reis, R.L. An Investigation of the Potential Application of Chitosan/Aloe-Based Membranes for Regenerative Medicine. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 6790–6797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- T, A.T.; Hermawati, E. Antioxidant Activity Test Combination Inclusion of Curcumin-β-Cyclodextrin Complex and Aloe vera. Pharm. J. Farm. Indones. 2022, 19, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullón, B.; Gullón, P.; Tavaria, F.; Alonso, J.L.; Pintado, M. In Vitro Assessment of the Prebiotic Potential of Aloe vera Mucilage and Its Impact on the Human Microbiota. Food Funct. 2015, 6, 525–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quezada, M.P.; Salinas, C.; Gotteland, M.; Cardemil, L. Acemannan and Fructans from Aloe vera (Aloe barbadensis Miller) Plants as Novel Prebiotics. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 10029–10039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retiu, A.; Budescu, T.; Menae, I. Aloe vera Extract For Stomach Acid Use Safe And Effective Treatment. Int. J. Pap. Adv. Sci. Rev. 2021, 2, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra-García, G.D.; Castro-Ríos, R.; González-Horta, A.; Lara-Arias, J.; Chávez-Montes, A. Acemannan, an Extracted Polysaccharide from Aloe vera: A Literature Review. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2014, 9, 1217–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, S.A.; Lee, Y.R.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, M.K.; Park, Y.I.; Lee, S.; Kim, K.; Lee, C.K. In Vivo Evidence of the Immunomodulatory Activity of Orally Administered Aloe vera Gel. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2010, 33, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugh, N.; Ross, S.A.; ElSohly, M.A.; Pasco, D.S. Characterization of Aloeride, a New High-Molecular-Weight Polysaccharide from Aloe vera with Potent Immunostimulatory Activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 1030–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Tizard, I.R. Activation of a Mouse Macrophage Cell Line by Acemannan: The Major Carbohydrate Fraction from Aloe vera Gel. Immunopharmacology 1996, 35, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Leung, M.Y.K.; Koon, J.C.M.; Zhu, L.F.; Hui, Y.Z.; Yu, B.; Fung, K.P. Macrophage Activation by Polysaccharide Biological Response Modifier Isolated from Aloe vera L. Var. Chinensis (Haw.) Berg. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2006, 6, 1634–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.K.; Lee, M.K.; Yun, Y.P.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, K.; Han, S.S.; Lee, C.K. Acemannan Purified from Aloe vera Induces Phenotypic and Functional Maturation of Immature Dendritic Cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2001, 1, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaca, K.; Sharma, J.M.; Nordgren, R. Nitric Oxide Production by Chicken Macrophages Activated by Acemannan, a Complex Carbohydrate Extracted from Aloe vera. Int. J. Immunopharmacol. 1995, 17, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.Y.; Kwon, H.J.; Sung, M.K. Evaluation of Aloin and Aloe-Emodin as Anti-Inflammatory Agents in Aloe by Using Murine Macrophages. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2009, 73, 828–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habeeb, F.; Stables, G.; Bradbury, F.; Nong, S.; Cameron, P.; Plevin, R.; Ferro, V.A. The Inner Gel Component of Aloe vera Suppresses Bacterial-Induced pro-Inflammatory Cytokines from Human Immune Cells. Methods 2007, 42, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, B.; Avila, G.; Segura, D.; Escalante, B. Antiinflammatory Activity of Extracts from Aloe vera Gel. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1996, 55, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, L.; Makins, R.J.; Rampton, D.S. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Aloe vera Gel in Human Colorectal Mucosa in Vitro. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 19, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duansak, D.; Somboonwong, J.; Patumraj, S. Effects of Aloe vera on Leukocyte Adhesion and TNF-α and IL-6 Levels in Burn Wounded Rats. Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc. 2003, 29, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.W.; Kotta, S.; Ansari, S.H.; Sharma, R.K.; Kumar, A.; Ali, J. Formulation Development, Optimization and Evaluation of Aloe vera Gel for Wound Healing. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2013, 9, S6–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eamlamnam, K.; Patumraj, S.; Visedopas, N.; Thong-Ngam, D. Effects of Aloe vera and Sucralfate on Gastric Microcirculatory Changes, Cytokine Levels and Gastric Ulcer Healing in Rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 2034–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talmadge, J.; Chavez, J.; Jacobs, L.; Munger, C.; Chinnah, T.; Chow, J.T.; Williamson, D.; Yates, K. Fractionation of Aloe vera L. Inner Gel, Purification and Molecular Profiling of Activity. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2004, 4, 1757–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahboub, F.; Nourizadeh, A.; Izadpanah, A. The Comparison of Color Stability of Aloe vera Gel and Chlorhexidine Solution on Acrylic Teeth. Int. J. Dent. 2022, 2022, 6196803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferro, V.A.; Bradbury, F.; Cameron, P.; Shakir, E.; Rahman, S.R.; Stimson, W.H. In Vitro Susceptibilities of Shigella Flexneri and Streptococcus Pyogenes to Inner Gel of Aloe barbadensis Miller. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 1137–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sydiskis, R.J.; Owen, D.G.; Lohr, J.L.; Rosler, K.H.A.; Blomster, R.N. Inactivation of Enveloped Viruses by Anthraquinones Extracted from Plants. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1991, 35, 2463–2466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlon, J.B.; Kemp, M.C.; Carpenter, R.H.; McAnalley, B.H.; McDaniel, H.R.; Shannon, W.M. Inhibition of AIDS Virus Replication by Acemannan in Vitro. Mol. Biother. 1991, 3, 127–135. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, T.; Dweck, A.C. Aloe vera Leaf Gel: A Review Update. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1999, 68, 3–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarameshloo, M.; Norouzian, M.; Zarein-Dolab, S.; Dadpay, M.; Mohsenifar, J.; Gazor, R. Aloe vera Gel and Thyroid Hormone Cream May Improve Wound Healing in Wistar Rats. Anat. Cell Biol. 2012, 45, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suksomboon, N.; Poolsup, N.; Punthanitisarn, S. Effect of Aloe vera on Glycaemic Control in Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2016, 41, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, A.; De Tangil, M.S.; Vega-Orellana, O.; Ramírez, A.S.; Rico, M. Phenolic Constituents, Antioxidant and Preliminary Antimycoplasmic Activities of Leaf Skin and Flowers of Aloe vera (L.) Burm. f. (Syn. A. barbadensis Mill.) from the Canary Islands (Spain). Molecules 2013, 18, 4942–4954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minjares-Fuentes, R.; Rodríguez-González, V.M.; González-Laredo, R.F.; Eim, V.; González-Centeno, M.R.; Femenia, A. Effect of Different Drying Procedures on the Bioactive Polysaccharide Acemannan from Aloe vera (Aloe barbadensis Miller). Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 168, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gullón, B.; Gullón, P.; Tavaria, F.K.; Yáñez, R. Assessment of the Prebiotic Effect of Quinoa and Amaranth in the Human Intestinal Ecosystem. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 3782–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beppu, H.; Koike, T.; Shimpo, K.; Chihara, T.; Hoshino, M.; Ida, C.; Kuzuya, H. Radical-Scavenging Effects of Aloe Arborescens Miller on Prevention of Pancreatic Islet B-Cell Destruction in Rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2003, 89, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekaran, S.; Sivagnanam, K.; Ravi, K.; Subramanian, S. Hypoglycemic Effect of Aloe vera Gel on Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes in Experimental Rats. J. Med. Food 2004, 7, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yongchaiyudha, S.; Rungpitarangsi, V.; Bunyapraphatsara, N.; Chokechaijaroenporn, O. Antidiabetic Activity of Aloe vera L. Juice. I. Clinical Trial in New Cases of Diabetes Mellitus. Phytomedicine 1996, 3, 241–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misawa, E.; Tanaka, M.; Nabeshima, K.; Nomaguchi, K.; Yamada, M.; Toida, T.; Iwatsuki, K. Administration of Dried Aloe vera Gel Powder Reduced Body Fat Mass in Diet-Induced Obesity (DIO) Rats. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2012, 58, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Kim, H.; Kwon, J.; Lee, S.; Kong, H.; Im, S.A.; Lee, Y.H.; Lee, Y.R.; Oh, S.T.; Jo, T.H.; et al. Hypoglycemic and Hypolipidemic Effects of Processed Aloe vera Gel in a Mouse Model of Non-Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus. Phytomedicine 2009, 16, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okyar, A.; Can, A.; Akev, N.; Baktir, G.; Sütlüpinar, N. Effect of Aloe vera Leaves on Blood Glucose Level in Type I and Type II Diabetic Rat Models. Phytother. Res. 2001, 15, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekaran, S.; Ravi, K.; Sivagnanam, K.; Subramanian, S. Beneficial Effects of Aloe vera Leaf Gel Extract on Lipid Profile Status in Rats with Streptozotocin Diabetes. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2006, 33, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, M.; Misawa, E.; Ito, Y.; Habara, N.; Nomaguchi, K.; Yamada, M.; Toida, T.; Hayasawa, H.; Takase, M.; Inagaki, M.; et al. Identification of Five Phytosterols from Aloe vera Gel as Anti-Diabetic Compounds. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 29, 1418–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noor, A.; Gunasekaran, S.; Vijayalakshmi, M.A. Improvement of Insulin Secretion and Pancreatic β-Cell Function in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats Treated with Aloe vera Extract. Pharmacogn. Res. 2017, 9, S99–S104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harlev, E.; Nevo, E.; Lansky, E.P.; Ofir, R.; Bishayee, A. Anticancer Potential of Aloes: Antioxidant, Antiproliferative, and Immunostimulatory Attributes. Planta Med. 2012, 78, 843–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Xu, J.; Hu, Q. Evaluation of Antioxidant Potential of Aloe vera (Aloe barbadensis Miller) Extracts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 7788–7791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekaran, S.; Sivagnanam, K.; Subramanian, S. Modulatory Effects of Aloe vera Leaf Gel Extract on Oxidative Stress in Rats Treated with Streptozotocin. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 57, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidiq, F. Review of the Healing Potential of Burn Wounds with Aloe vera Extract Cream: The Influence of Formula and Virgin Coconut Oil Application: Review of the Healing Potential of Burn Wounds with Aloe vera Extract Cream: The Influence of Formula and Virgin Coconut Oil Application. Int. J. Health Med. Sports 2023, 1, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, P.K.; Giri, D.D.; Singh, R.; Pandey, P.; Gupta, S.; Shrivastava, A.K.; Kumar, A.; Pandey, K.D.; Sahu, P.K.; Giri, D.D.; et al. Therapeutic and Medicinal Uses of Aloe vera: A Review. Pharmacol. Amp Pharm. 2013, 4, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, A.; Ballal, S.; Velmurugan, N. Comparative Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Activity of Natural Extracts of Morinda Citrifolia, Papain and Aloe vera (All in Gel Formulation), 2% Chlorhexidine Gel and Calcium Hydroxide, against Enterococcus Faecalis: An in Vitro Study. J. Conserv. Dent. 2012, 15, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonea, A.; Badea, M.; Oana, L.; Sava, S.; Vodnar, D. Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity of Endodontic Intracanal Medications. Med. Pharm. Rep. 2017, 90, 344–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeumpa, A.; Alam, N.; Jailani, M.; Hajar, S. The Use of Aloe vera Gel on Scar Collagen. J. Rekonstr. Dan. Estet. 2019, 4, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, G.; Kudva, P.; Dodwad, V. Aloe vera: Nature’s Soothing Healer to Periodontal Disease. J. Indian. Soc. Periodontol. 2011, 15, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenawy, E.R.S.; Kamoun, E.A.; Ghaly, Z.S.; Shokr, A.b.M.; El-Meligy, M.A.; Mahmoud, Y.A.G. Novel Physically Cross-Linked Curcumin-Loaded PVA/Aloe vera Hydrogel Membranes for Acceleration of Topical Wound Healing: In Vitro and In Vivo Experiments. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2023, 48, 497–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudalkar, M.; Nayak, A.; Bhat, K.; Nayak, R. Effect of Azadirachta Indica (Neem) and Aloe vera as Compared to Subantimicrobial Dose Doxycycline on Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMP)-2 and MMP-9: An in-Vitro Study. AYU (Int. Q. J. Res. Ayurveda) 2014, 35, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Wang, L.; Hu, C. Treatment-Related Changes after Short-Term Exposure of SD Rats to Aloe vera Whole-Leaf Freeze-Dried Powder. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2017, 98, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.K.; Phung, H.H.; Choi, W.J.; Ahn, H.C. Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Study on the Multi-Target Mechanisms of Aloe vera for Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis Treatment. Plants 2022, 11, 3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soesilawati, P.; Rachmat, E.A.; Arundina, I.; Naomi, N. The Possibility of Polymorphonuclear Leukocyte Activation in Dental Socket Healing by Freeze-Dried Aloe vera Induction. Dent. J. 2021, 54, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrugia, C.J.E.; Burke, E.S.; Haley, M.E.; Bedi, K.T.; Gandhi, M.A. The Use of Aloe vera in Cancer Radiation: An Updated Comprehensive Review. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2019, 35, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepa, J.; Rajkumar, P.; Preetha, P. Development of Yogurt with Bioactive Molecules. Asian J. Dairy Food Res. 2016, 35, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaikeaw, N.; Wongphoom, J.; Werawatganon, D.; Chayanupatkul, M.; Siriviriyakul, P. Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Oxidant Effects of Aloe vera in Rats with Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. World J. Hepatol. 2020, 12, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzulla, S.; Sesti, S.; Schella, A.; Perrotta, I.; Anile, A.; Drogo, S.; Mazzulla, S.; Sesti, S.; Schella, A.; Perrotta, I.; et al. Protective Effect of Aloe vera (Aloe barbadensis Miller) on Erythrocytes Anion Transporter and Oxidative Change. Food Nutr. Sci. 2012, 3, 1697–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logaranjan, K.; Devasena, T.; Pandian, K.; Logaranjan, K.; Devasena, T.; Pandian, K. Quantitative Detection of Aloin and Related Compounds Present in Herbal Products and Aloe vera Plant Extract Using HPLC Method. Am. J. Anal. Chem. 2013, 4, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneshwari, E.K.; Roshni, N.; Karandeep, S.; Bill, T. The Effect of Anti-Inflammatory Agents (Glucosamine Sulphate and Aloe vera ) on Mouse Mesenchymal Stem Cells. J. Appl. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2020, 7, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Hady, A.-N.A.A.; Mohi-Eldin, M.M.; Allaam, A.A.A. Clinical and Pathological Assessment of Aloe vera and Propolis for Wound Healing in Normal and Diabetic Albino Rats. Zagazig Vet. J. 2017, 45, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramz, K.; Abbasi, N.; Hafeziahmadi, M.; Azizi, M.; Hedayatpour, A.; Abbaszadeh, H.; Moayeri, A. Effect of Different Concentrations of Aloe vera Leave’s Extract on the Healing Process of Rat’s Second Degree Burn. J. Basic Res. Med. Sci. 2016, 3, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avijgan, M.; Alinaghian, M.; Esfahani, M.H.; Avijgan, M.; Alinaghian, M.; Esfahani, M.H. Aloe vera Gel as a Traditional and Complementary Method for Chronic Skin Burn: A Case Report. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2017, 7, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Prakoso, Y.A.; Kurniasih. The Effects of Aloe vera Cream on the Expression of CD4+ and CD8+ Lymphocytes in Skin Wound Healing. J. Trop. Med. 2018, 2018, 6218303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AL-Dhamary, N.; Al-Adhal, A.; Kadi, H.; AL-Kamarany, M.A. Investigation Effect of Aloe vera in Fresh Gel Form on Rabbit’s Model Wound. J. Complement. Altern. Med. Res. 2024, 25, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Tiwari, S.; Prakash, K.; Yadav, R.; Kailash, S. Pharmaceutical Assessment of Aloe vera Skin Gel: A Herbal Formulation and Its Potential Benefits. World J. Biol. Pharm. Health Sci. 2023, 15, 043–050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beneke, C.; Viljoen, A.; Hamman, J. In Vitro Drug Absorption Enhancement Effects of Aloe vera and Aloe Ferox. Sci. Pharm. 2012, 80, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putri Bunga Anggreno Setiawan, B.; Teti Vani, A.; Yulhasfi Febrianto, B.; Tri Septiana, V.; Bunga Anggreno Setiawan, P. The Effectiveness of Using Aloe vera Facial Soap and Aloe Gel on the Degree of Acne Vulgaris in Students of SMA Negeri 2 Bayang. J. EduHealth 2020, 11, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avijgan, M.; Avijgan, M.; Hakamifard, A.; Razavi, N. An Innovation for Retarded Healing Process of a Chronic Ulcer by Aloe vera Gel Treatment. J. Nat. Remedies 2016, 16, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigaroodi, F.; Shafaei, H.; Karimipour, M.; Dolatkhah, M.A.; Delazar, A. Aloe vera /Collagen Mixture Induces Integrin A1β1 and PECAM-1 Genes Expression in Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 9, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donate, R.; Alemán-Domínguez, M.E.; Monzón, M.; Yu, J.; Rodríguez-Esparragón, F.; Liu, C. Evaluation of Aloe vera Coated Polylactic Acid Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabala, L.F.G.; Cuartas, C.E.E.; López, M.E.L.O. Release Behavior and Antibacterial Activity of Chitosan/Alginate Blends with Aloe vera and Silver Nanoparticles. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piaia, L.; Pittella, C.Q.P.; De Souza, S.S.; Berti, F.V.; Porto, L.M. Incorporation of Aloe vera Extract in Bacterial Nanocellulose Membranes. Polímeros 2022, 32, e2022002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mpiana, P.T.; Ngbolua, K.; Te, N.; Tshibangu, D.S.T.; Kilembe, J.T.; Gbolo, B.Z.; Mwanangombo, D.T.; Inkoto, C.L.; Lengbiye, E.M.; Mbadiko, C.M.; et al. Identification of Potential Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease from Aloe vera Compounds: A Molecular Docking Study. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2020, 754, 137751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaji, D.; Das, A. Recognition of Aloe vera Compounds as Potential Inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 NSP-16: Molecular Docking Approach for Drug Development. ChemRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, P.; Kumar, A. Development of a Microbial Coating for Cellulosic Surface Using Aloe vera and Silane. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2020, 1, 100015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poorkazemi, D.; Shafaroudi, A.M.; Nasiri, P.; Aarabi, M.; Sabet, J.M. Evaluation of Aloe vera as a Natural Pharmaceutic in Mouthwashes: A Narrative Review. Jundishapur J. Nat. Pharm. Prod. 2022, 17, 122155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, N.; Sharma, M.; Faridi, F.N.; Grover, R. Antifungal Activity of Aloe vera Extracts Against Phytopathogenic Fungus Aspergillus Spp. Int. J. Health Sci. Res. 2022, 12, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesari, M.; Shafaei, H.; Khamnei, S.; Kalasour, N.K. The Role of Aloe vera in Inhibiting the P53 Protein Expression and Enhancing the HT29 Colon Cancer Cells Proliferation. Zahedan J. Res. Med. Sci. 2023, 25, 118505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.Q.; Lv, R.W.; Qu, X.D.; Chen, X.J.; Lu, H.S.; Wang, Y. Aloesin Suppresses Cell Growth and Metastasis in Ovarian Cancer SKOV3 Cells through the Inhibition of the MAPK Signaling Pathway. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2017, 2017, 8158254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, P.C.; Lin, C.H.; Chokkalingam, U.; Prakash, E.; Kao, C.N.; Chang, C.F.; Lin, W.L. The Aloe vera Acemannan Polysaccharides Inhibit Phthalate-Induced Cell Viability, Metastasis, and Stemness in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 288, 117351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafoor, B.; Ali, M.N.; Ansari, U.; Bhatti, M.F.; Mir, M.; Akhtar, H.; Darakhshan, F. New Biofunctional Loading of Natural Antimicrobial Agent in Biodegradable Polymeric Films for Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Biomater. 2016, 2016, 6964938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menna, C.; Calista, N.; Aurino, L.; Dwijayanti, A. Aloe vera vs. Silver sulfadiazine for treating second-degree burn wounds: Evidence-based case report. Int. J. Appl. Pharm. 2019, 11, 146–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamman, J.; Fox, L.; Plessis, J.; Gerber, M.; Zyl, S.; Boneschans, B. In Vivo Skin Hydration and Anti-Erythema Effects of Aloe vera, Aloe Ferox and Aloe Marlothii Gel Materials after Single and Multiple Applications. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2014, 10, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hekmatpou, D.; Mehrabi, F.; Rahzani, K.; Aminiyan, A. The Effect of Aloe vera Gel on Prevention of Pressure Ulcers in Patients Hospitalized in the Orthopedic Wards: A Randomized Triple-Blind Clinical Trial. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 18, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Torres, L.; Guillen, I.H.G.; Núñez-Ramírez, D.M.; García-Guzmán, P.; Calderas, F.; González Laredo, R.F.; Gonzalez Lozano, M.A.; Ramirez Torres, L.A.; Manero, O. Rheological Behavior and Modeling of an Ultrafiltration Process for Aloe vera. J. Food Process Eng. 2023, 46, e14416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuradha, A.; Patil, B.; Asha, V.R. Evaluation of Efficacy of Aloe vera in the Treatment of Oral Submucous Fibrosis—A Clinical Study. J. Oral. Pathol. Med. 2017, 46, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudarshan, R.; Annigeri, R.G.; Vijayabala, S.S. Aloe vera in the Treatment for Oral Submucous Fibrosis—A Preliminary Study. J. Oral. Pathol. Med. 2012, 41, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, A.; Israilevich, R.; Moy, R. Management of Acute Radiation Dermatitis: A Review of the Literature and Proposal for Treatment Algorithm. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 81, 558–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liao, J.; Zheng, L.; Zhou, Y.; Jin, Q.; Wu, Y. Aloe vera for Prevention of Radiation-Induced Dermatitis: A Systematic Review and Cumulative Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 976698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek Hosseini, A.; Rostam Khani, M.; Abdi, S.; Abdi, S.; Sharifi, N. Comparison of Aloe vera Gel Dressing with Conventional Dressing on Pressure Ulcer Pain Reduction: A Clinical Trial. BMC Res. Notes 2024, 17, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, H.; Pu, L.; Xu, L.; Shi, X.; Ji, J.; Chen, K. Effects of Aloe Polysaccharide, a Polysaccharide Extracted from Aloe vera, on TNF-a-Induced HaCaT Cell Proliferation and the Underlying Mechanism in Psoriasis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 3537–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavyashree, D.; Shilpa, C.J.; Nagabhushana, H.; Daruka Prasad, B.; Sreelatha, G.L.; Sharma, S.C.; Ashoka, S.; Anandakumari, R.; Premkumar, H.B. ZnO Superstructures as an Antifungal for Effective Control of Malassezia Furfur, Dermatologically Prevalent Yeast: Prepared by Aloe vera Assisted Combustion Method. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 1066–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Malhotra, S. Pharmacological Attribute of Aloe vera: Revalidation through Experimental and Clinical Studies. AYU (Int. Q. J. Res. Ayurveda) 2012, 33, 193–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Said, F.; Rahmawati, I.; Ningsih, N.S. Clinical Study and Toxicity Tests of Disclosing Agent Aloe vera Gel. Asian J. Pharm. Res. Dev. 2023, 11, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelu, M.; Popa, M.; Ozon, E.A.; Pandele Cusu, J.; Anastasescu, M.; Surdu, V.A.; Calderon Moreno, J.; Musuc, A.M. High-Content Aloe vera Based Hydrogels: Physicochemical and Pharmaceutical Properties. Polymers 2023, 15, 1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlawat, K.S.; Khatkar, B.S. Processing, Food Applications and Safety of Aloe vera Products: A Review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 48, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janurianti, N.M.D.; Utama, I.M.S.; Gunam, I.B.W. Antibacterial Activity of Aloe vera Gel-Based Edible Coating with the Addition of Gum Arabic and Ascorbic Acid. AJARCDE | Asian J. Appl. Res. Community Dev. Empower. 2021, 5, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharmin, M.R.; Islam, M.N.; Alim, M.A. Shelf-Life Enhancement of Papaya with Aloe vera Gel Coating at Ambient Temperature. J. Bangladesh Agric. Univ. 2015, 13, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorsi, F.I.; Kausar, T.; Murtaza, M.A. Evaluation of Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activity of Aloe vera (Aloe barbadensis Miller) Gel Powder Using Different Solvents. Pesqui. Agropecu. Bras. 2019, 8, 1265–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinzon, M.I.; Garcia, O.R.; Villa, C.C. The Influence of Aloe vera Gel Incorporation on the Physicochemical and Mechanical Properties of Banana Starch-Chitosan Edible Films. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 4042–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandegara, V.; Varshney, A. Effect of Centrifuge Speed on Gel Extraction from Aloe vera Leaves. J. Food Process Technol. 2014, 5, 1000295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handayani, R.; Qamariah, N.; Bestary, Y. Formulasi Sediaan Gel Hand Sanitizer Dengan Kombinasi Ekstrak Lidah Buaya (Aloe vera L.) Dan Ekstrak Daun Mengkudu (Morinda citrifolia L.). J. Surya Med. 2022, 8, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cellini, L.; Di Bartolomeo, S.; Di Campli, E.; Genovese, S.; Locatelli, M.; Di Giulio, M. In Vitro Activity of Aloe vera Inner Gel against Helicobacter Pylori Strains. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 59, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Nizam, N.H.; Mohammad Rawi, N.F.; Mhd Ramle, S.F.; Abd Aziz, A.; Abdullah, C.K.; Rashedi, A.; Mohamad Kassim, M.H. Physical, Thermal, Mechanical, Antimicrobial and Physicochemical Properties of Starch Based Film Containing Aloe vera: A Review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 1572–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misir, J.; Brishti, F.H.; Hoque, M.M. Aloe vera Gel as a Novel Edible Coating for Fresh Fruits: A Review. Am. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 2, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, B.; Albayrak, S.; Antolak, H.; Kręgiel, D.; Pawlikowska, E.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Uprety, Y.; Fokou, P.V.T.; Yousef, Z.; Zakaria, Z.A.; et al. Aloe Genus Plants: From Farm to Food Applications and Phytopharmacotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goudarzi, M.; Fazeli, M.; Azad, M.; Seyedjavadi, S.S.; Mousavi, R. Aloe vera Gel: Effective Therapeutic Agent against Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas Aeruginosa Isolates Recovered from Burn Wound Infections. Chemother. Res. Pract. 2015, 2015, 639806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Budiman, A.; Khoerunnisa, R.; Tazyinul Qoriah, A. Wound-Healing Test of Piper Betle Leaf Extract and Aloe vera in Gel Preparation. Int. J. Appl. Pharm. 2018, 10, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kania, A.; Kałużyński, G.; Pełka, M.; Fijałkowska, J.; Ciulkiewicz, Ł. An Overview of Aloe vera Impact on the Healing Process of Diabetic Foot Ulcer. J. Educ. Health Sport. 2024, 54, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriyama, M.; Moriyama, H.; Uda, J.; Kubo, H.; Nakajima, Y.; Goto, A.; Akaki, J.; Yoshida, I.; Matsuoka, N.; Hayakawa, T. Beneficial Effects of the Genus Aloe on Wound Healing, Cell Proliferation, and Differentiation of Epidermal Keratinocytes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, R.; Mendes, A.; Bártolo, P. Evaluating the Properties of an Alginate Wound Dressing for Skin Repair. Adv. Mat. Res. 2013, 683, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseri-Nosar, M.; Farzamfar, S.; Salehi, M.; Vaez, A.; Tajerian, R.; Azami, M. Erythropoietin/Aloe vera-Releasing Wet-Electrospun Polyvinyl Alcohol/Chitosan Sponge-like Wound Dressing: In Vitro and in Vivo Studies. J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 2017, 33, 269–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, C.M.P.; Pacheco, M.S.; de Moraes, M.A.; Lopes, P.S.; Severino, P.; Souto, E.B.; da Silva, C.F. Effect of Chitosan and Aloe vera Extract Concentrations on the Physicochemical Properties of Chitosan Biofilms. Polymers 2021, 13, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jajah, A.; Yusof, M. Fluid Intake Capacity of Aloe vera and Sea Cucumber Thin Film. Mater. Sci. Forum 2021, 1030, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuvas-Limon, R.B.; Ferreira-Santos, P.; Cruz, M.; Teixeira, J.A.; Belmares, R.; Nobre, C. Effect of Gastrointestinal Digestion on the Bioaccessibility of Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity of Fermented Aloe vera Juices. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangil-Monroy, M.; Serra-Majem, L.; Monroy, J.M.M.; Andrellucchi, A.O.; Sánchez-Villegas, A.; Doreste, J.; Knipschild, P. Effects of Intake of Milk Enriched with Aloe vera on Patients with Gastrointestinal Reflux Disease. Food Nutr. Sci. 2014, 5, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubayyina, F.; Hidayati, N.; Program, Z.M.; Kebidanan, S.; Kesehatan, F.; Nahdlatul, U.; Mataram, W. The effectiveness of red betel leaf and Aloe vera in the treatment of perineal wounds: Literature review. Int. J. Nurs. Midwifery Sci. 2023, 7, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghani, F.; Arabnezhad, M.R.; Mohammadi, S.; Ghaffarian-Bahraman, A. Aloe vera and Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes Mellitus. Rev. Bras. Farmacogn. 2022, 32, 174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadoyu, S.; Rungruang, C.; Wattanavijitkul, T.; Sawangjit, R.; Thakkinstian, A.; Chaiyakunapruk, N. Aloe vera and Health Outcomes: An Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 555–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewi, P.S.; Hani, U.; Anwar, M. The Effectiveness of Aloe vera Gel in Reducing the Pain of Perineal Wound. Medisains 2020, 18, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, M.; Kochhar, A.; Sangha, J. Hypoglycemic and Hypolipidemic Effect of Aloe vera L. in Non-Insulin Dependent Diabetics. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumi, S.J.; Mehrabani, D.; Hassanshahi, N.; Hashemi, S.S.; Zare, M. The Healing Effect of Aloe vera Gel on Acetic Acid-Induced Ulcerative Colitis in Rat. Middle East J. Dig. Dis. 2020, 12, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jales, S.T.L.; Barbosa, R.D.M.; de Albuquerque, A.C.; Duarte, L.H.V.; da Silva, G.R.; Meirelles, L.M.A.; da Silva, T.M.S.; Alves, A.F.; Viseras, C.; Raffin, F.N.; et al. Development and Characterization of Aloe vera Mucilaginous-Based Hydrogels for Psoriasis Treatment. J. Compos. Sci. 2022, 6, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelu, M.; Musuc, A.M.; Popa, M.; Calderon Moreno, J. Aloe vera-Based Hydrogels for Wound Healing: Properties and Therapeutic Effects. Gels 2023, 9, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouksey, A.; Dilliwal, H.; Agrawal, R.; Khashu, H. Efficacy of Aloe vera Gel Delivered Locally as an Adjunct to Scaling and Root Planing in the Treatment of Chronic Periodontitis: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Oral Care Res. 2017, 5, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, M.; González-Burgos, E.; Iglesias, I.; Gómez-Serranillos, M.P. Pharmacological Update Properties of Aloe vera and Its Major Active Constituents. Molecules 2020, 25, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woźniak, A.; Paduch, R. Aloe vera Extract Activity on Human Corneal Cells. Pharm. Biol. 2012, 50, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulliero, A.; Profumo, A.; Izzotti, A.; Saccà, S.C. Release of Aloe vera Extracts from Therapeutic Lenses. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 9055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugavel, S.; Reddy, V.J.; Ramakrishna, S.; Lakshmi, B.S.; Dev, V.G. Precipitation of Hydroxyapatite on Electrospun Polycaprolactone/Aloe vera /Silk Fibroin Nanofibrous Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. J. Biomater. Appl. 2013, 29, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, E.; Joseph, S.; Joy, M. Aloe vera and its biological activities. World J. Curr. Med. Pharm. Res. 2021, 3, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, T.; Yilmaz-Ersan, L.; Keser, R.A. The Effect of Plant Mucilaginous Gel Polysaccharides on Oxidative Tolerance and Fermentation of Dietetic Yoghurts. Mljekarstvo J. Dairy Prod. Process. Improv. 2024, 74, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maan, A.A.; Nazir, A.; Khan, M.K.I.; Ahmad, T.; Zia, R.; Murid, M.; Abrar, M. The Therapeutic Properties and Applications of Aloe vera: A Review. J. Herb. Med. 2018, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornero-Martínez, A.; Cruz-Ortiz, R.; Jaramillo-Flores, M.E.; Osorio-Díaz, P.; Ávila-Reyes, S.V.; Alvarado-Jasso, G.M.; Mora-Escobedo, R. In Vitro Fermentation of Polysaccharides from Aloe vera and the Evaluation of Antioxidant Activity and Production of Short Chain Fatty Acids. Molecules 2019, 24, 3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalado, Y.A.; Tijjani, A. Qualitative and Quantitative Phytochemical Analysis of Aloe barbadensis Miller Leaf Extracts. UMYU Sci. 2023, 2, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isager Ahl, L.; Pedersen, H.L.; Jørgensen, B.; Willats, W.G.T.; Grace, O.M.; Barnes, C.J.; Rønsted, N. Exploring the Polysaccharide Composition of Plant Cell Walls in Succulent Aloes. Plants People Planet. 2023, 5, 335–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charan Kumar, N.; Arora, P. Development of ready to serve beverage (rts) from a blend of orange, Aloe vera and mint. Biotech. Environ. Sc 2023, 25, 713–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni’Maturrohmah, D.; Chandra, E.C.; Wulandari, R.; Nisa, K.; Sefrienda, A.R.; Indrianingsih, A.W.; Suryani, A.E.; Darsih, C.; Mujiyanto; Haryanti, S.; et al. Creamer Encapsulated Aloe vera: Physical and Chemical Screening for A Beverage Prospect. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2024, 1364, 012061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaksar Manshad, A.; Kabipour, A.; Mohammadian, E.; Yan, L.; Ali, J.A.; Iglauer, S.; Keshavarz, A.; Norouzpour, M.; Azdarpour, A.; Sajadi, S.M.; et al. Application of a Novel Green Nano Polymer for Chemical EOR Purposes in Sandstone Reservoirs: Synergetic Effects of Different Fluid/Fluid and Rock/Fluid Interacting Mechanisms. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 43930–43954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comas-Serra, F.; Martínez-García, J.J.; Pérez-Alba, A.; Sáenz-Esqueda, M.d.l.Á.; Candelas-Cadillo, M.G.; Femenia, A.; Minjares-Fuentes, R. A New Functional Food Ingredient Obtained from Aloe Ferox by Spray Drying. Foods 2023, 12, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, R.U.; Naz, S.; De Marzo, D.; Dimuccio, M.M.; Bozzo, G.; Tufarelli, V.; Losacco, C.; Ragni, M. Aloe vera: A Sustainable Green Alternative to Exclude Antibiotics in Modern Poultry Production. Antibiotics 2022, 12, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hęś, M.; Dziedzic, K.; Górecka, D.; Jędrusek-Golińska, A.; Gujska, E. Aloe vera (L.) Webb.: Natural Sources of Antioxidants—A Review. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2019, 74, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Sethi, S.; Sharma, R.R.; Singh, S.; Varghese, E. Improving the Shelf Life of Fresh-Cut ‘Royal Delicious’ Apple with Edible Coatings and Anti-Browning Agents. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 3767–3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriati, L.; Utama, I.; Harjosuwono, B.; Gunam, I. Chromatic Characteristics Edible Coating of Aloe Gel. SCITEPRESS–Sci. Technol. Publ. 2020, 1, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamil Shalash, W. Antitumor and Antioxidant Activity of Aloe vera Leaf Gel Extract. Ecol. Environ. Conserv. Pap. 2022, 28, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, T.; Khurram Shahzad, M.; Hanif, N.; Anwar, M.; Ambreen, A.; Waheed, M.U. Effectiveness of Aloe vera Mouthwash in Comparison with Triamcinolone Acetonide 0.1% in Patients with Oral Lichen Planus at A Tertiary Care Hospital. Pak. J. Med. Health Sci. 2021, 15, 3138–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pol, J.S. Evaluation of Therapeutic Effect of Aloe vera Juice and Gel in the Management of Symptomatic Oral Lichen Planus. Int. J. Med. Dent. Sci. 2016, 5, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, I.M.V.; Fernandes, G.V.d.O.; Cavalcante, L.C.; Leite, Y.K.P.d.C.; Bezerra, D.d.O.; Carvalho, M.A.M.d.; Carvalho, C.M.R.S. The Influence of Aloe vera with Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Dental Pulp on Bone Regeneration: Characterization and Treatment of Non-Critical Defects of the Tibia in Rats. J. Appl. Oral. Sci. 2019, 27, e20180103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasin, R.; Cintra Gomes-Marcondes, M.C. Oral Administration of Aloe vera and Honey Reduces Walker Tumour Growth by Decreasing Cell Proliferation and Increasing Apoptosis in Tumour Tissue. Phytother. Res. 2011, 25, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisio, C.; Lucarini, E.; Micheli, L.; Toti, A.; Mannelli, L.D.C.; Antonini, G.; Panizzi, E.; Maidecchi, A.; Giovagnoni, E.; Lucci, J.; et al. Researching New Therapeutic Approaches for Abdominal Visceral Pain Treatment: Preclinical Effects of an Assembled System of Molecules of Vegetal Origin. Nutrients 2019, 12, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamdouh, E.; Youssef, M. The Adverse Impact of Aloe vera Gel Extract and Aloe vera -Fortified Yogurt on Hepatic and Renal Functions. SVU-Int. J. Vet. Sci. 2022, 5, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N.A.; El-Zairy, E.M.R.; Eid, B.M. Eco-Friendly Modification and Antibacterial Functionalization of Viscose Fabric. J. Text. Inst. 2017, 108, 1406–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakides, T.R.; Kim, H.J.; Zheng, C.; Harkins, L.; Tao, W.; Deschenes, E. Foreign Body Response to Synthetic Polymer Biomaterials and the Role of Adaptive Immunity. Biomed. Mater. 2022, 17, 022007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.M.; Parus, A.; Barnes, C.W.; Hiro, M.E.; Robson, M.C.; Payne, W.G. Aloe vera—Mechanisms of Action, Uses, and Potential Uses in Plastic Surgery and Wound Healing. Surg. Sci. 2020, 11, 312–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelu, M.; Musuc, A.M. Polymer Gels: Classification and Recent Developments in Biomedical Applications. Gels 2023, 9, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).