Bead-Free Electrospun Nanofibrous Scaffold Made of PVOH/Keratin/Chitosan Using a Box–Behnken Experimental Design and In Vitro Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Polymer Solutions
2.3. Characterization of the Polymer Solution
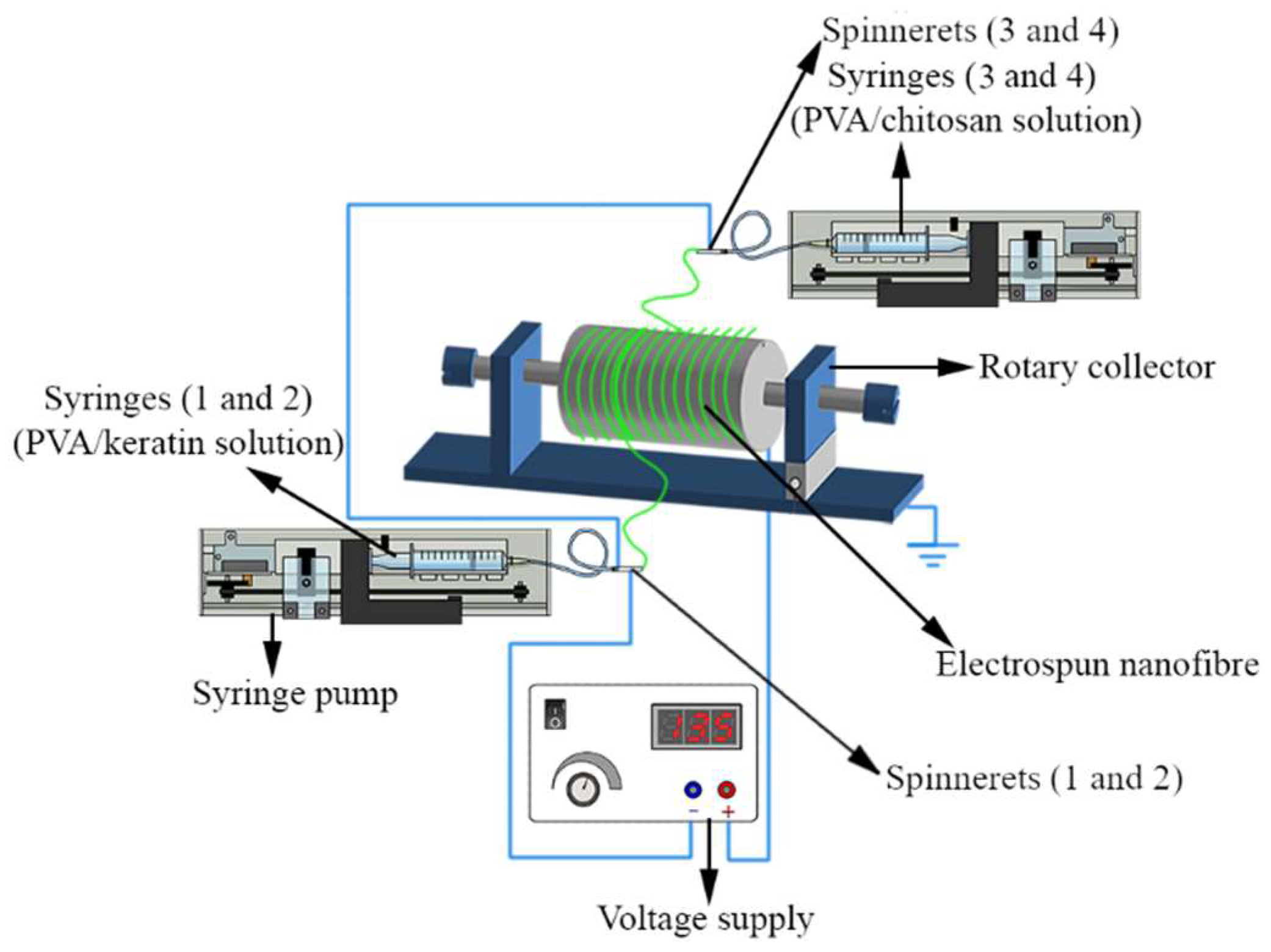
2.4. Production of PVOH/KP/CH ENS
2.5. Experimental Design
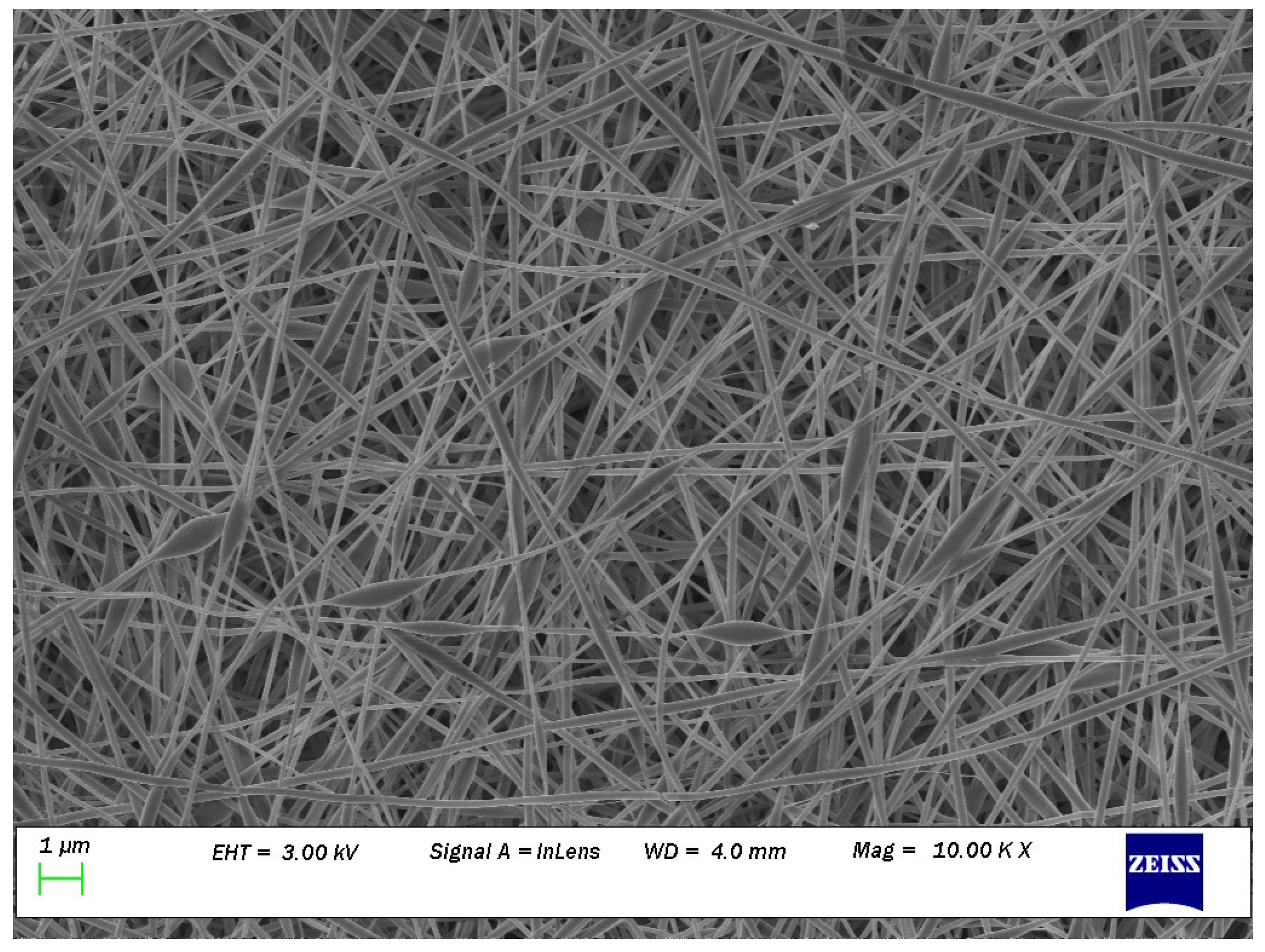
2.6. Determination of Mean Fibre Diameter and Mean Diameter of Fibre Defect
2.7. Optimisation
2.8. In Vitro Studies
3. Results and Discussions
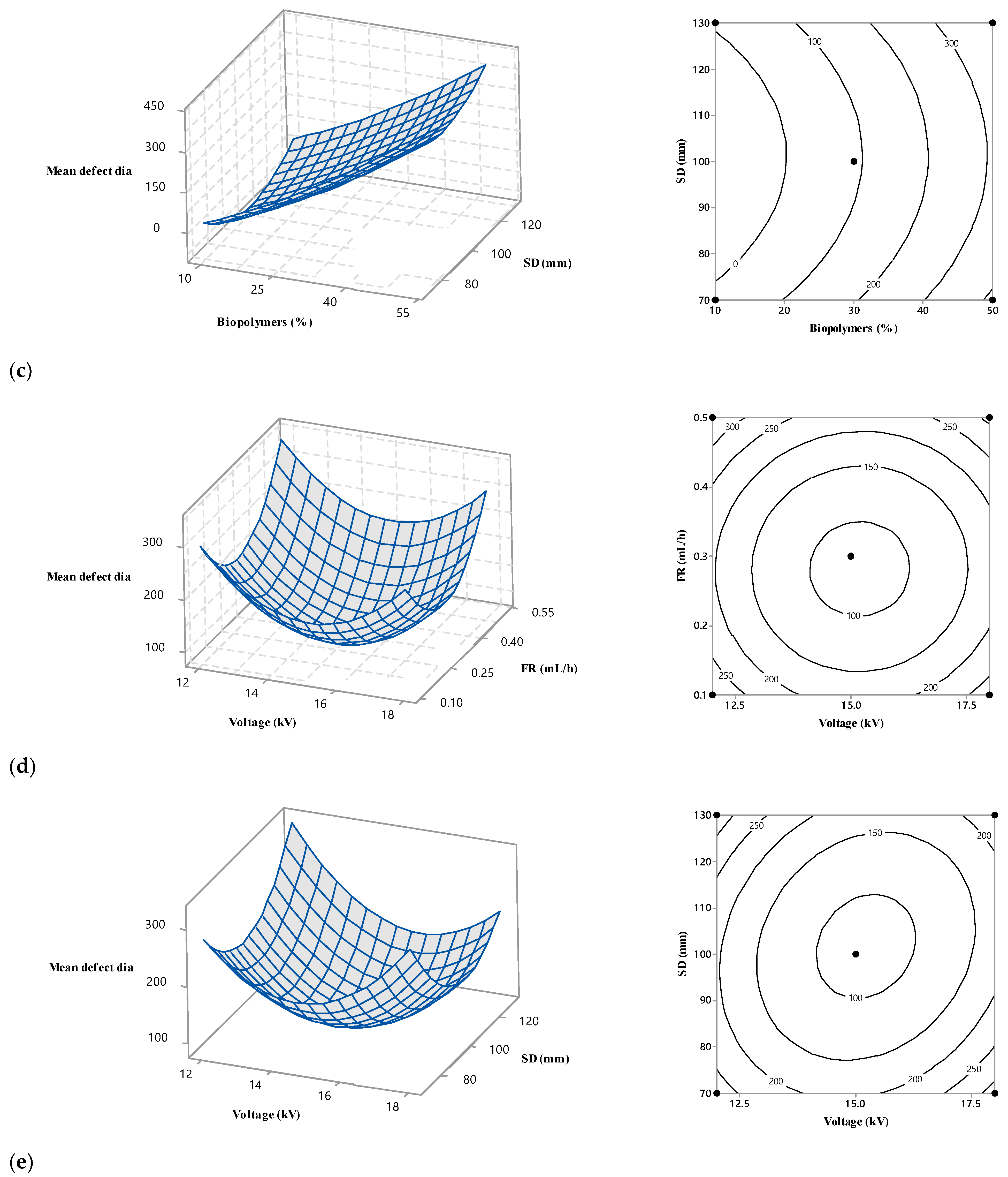
3.1. Development of RSM Models
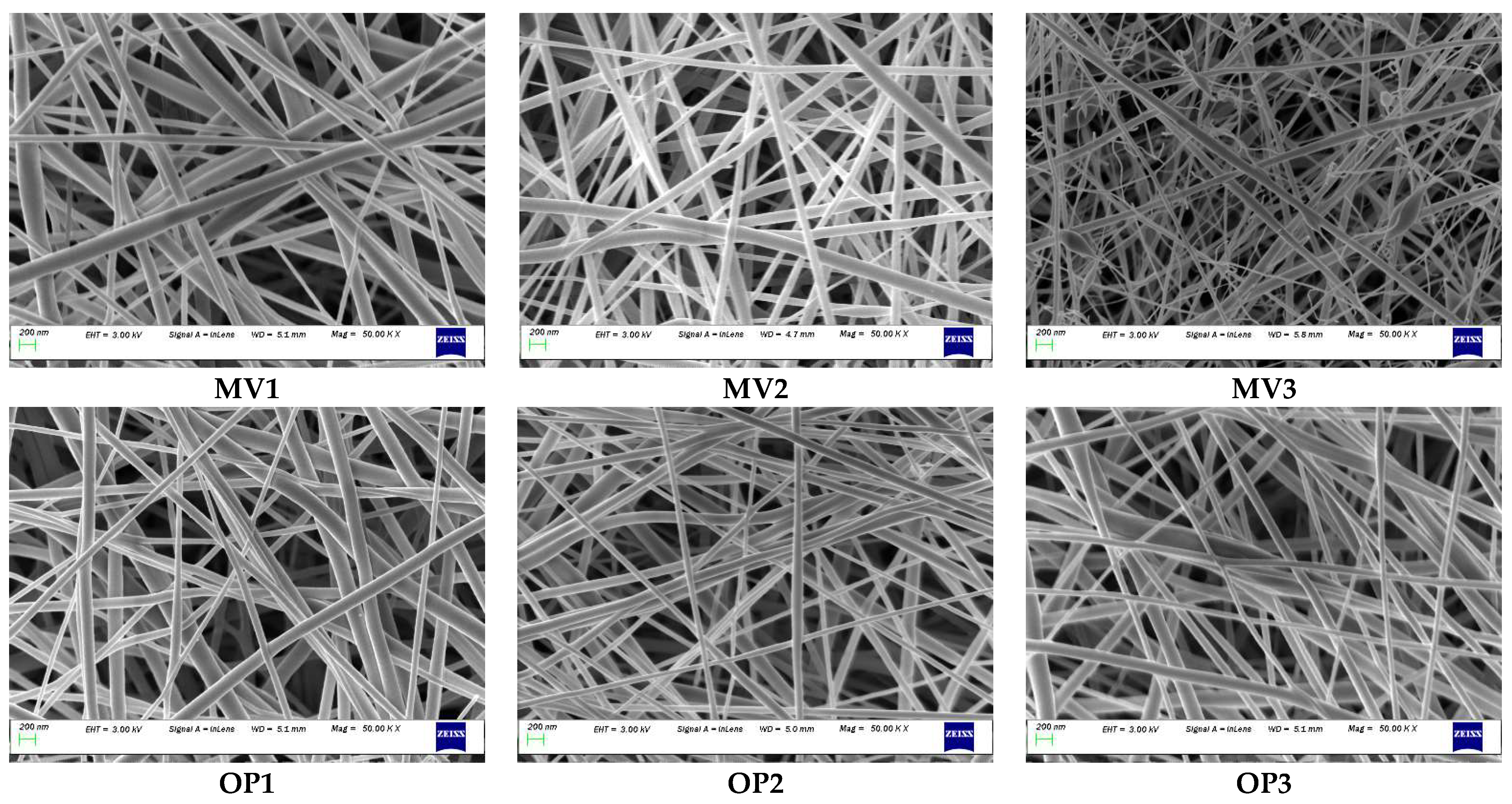
3.2. Determination of Optimal Conditions
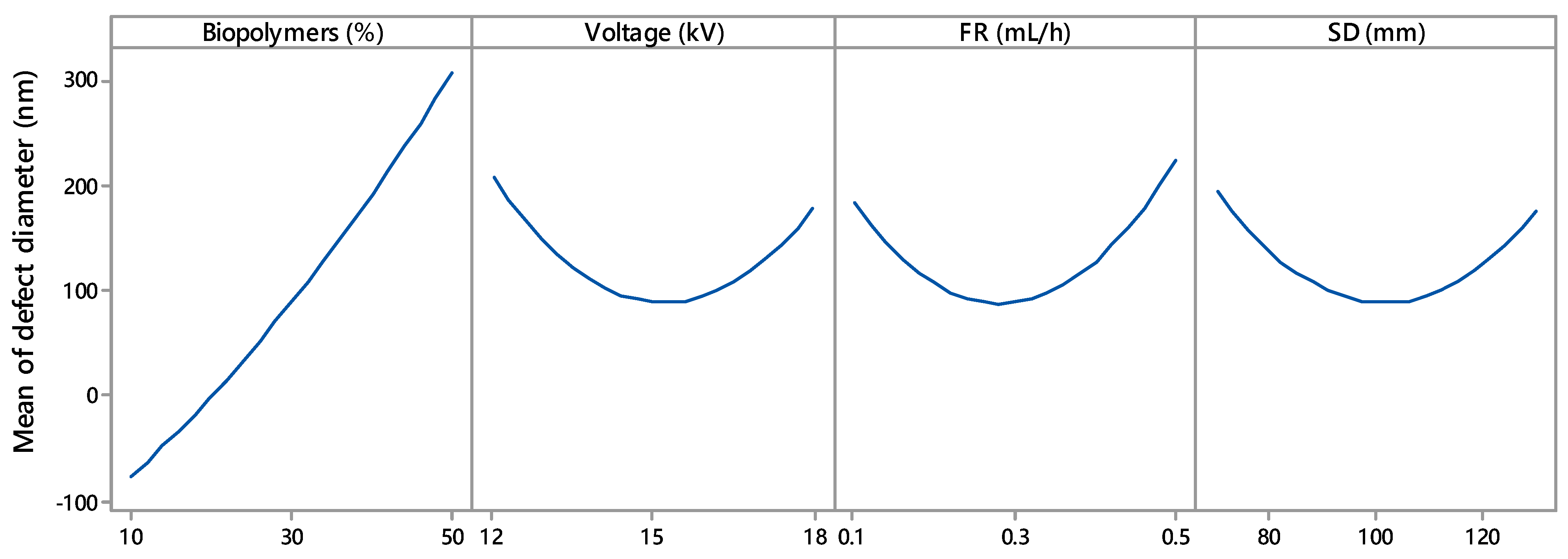
3.3. Influence of Processing Variables on Surface Topography
3.3.1. Effect of Biopolymer Contents
3.3.2. Effect of Voltage
3.3.3. Effect of Flow Rate
3.3.4. Effect of Spinning Distance
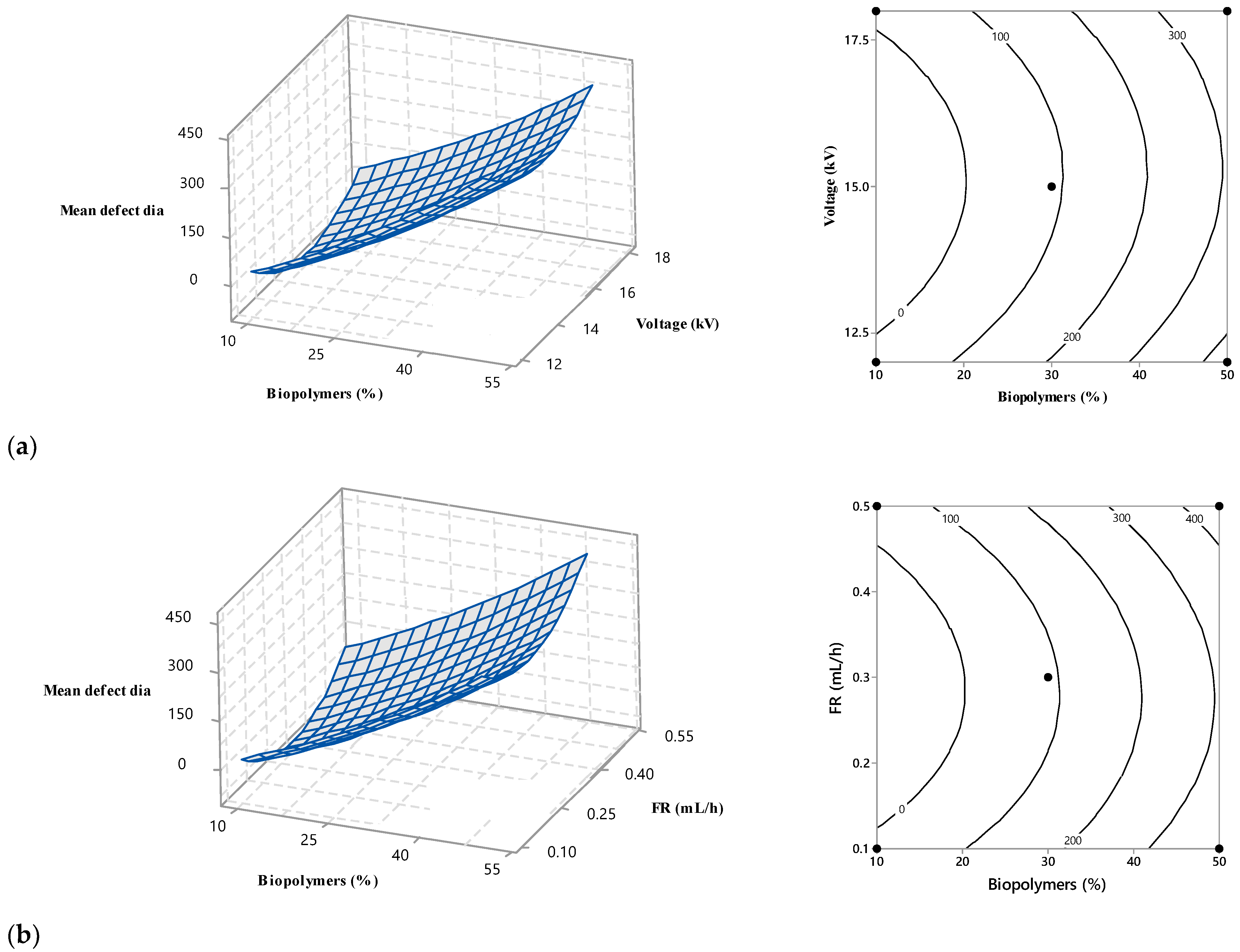
3.4. Interaction among the Operational Variables
3.5. Confirmation Test
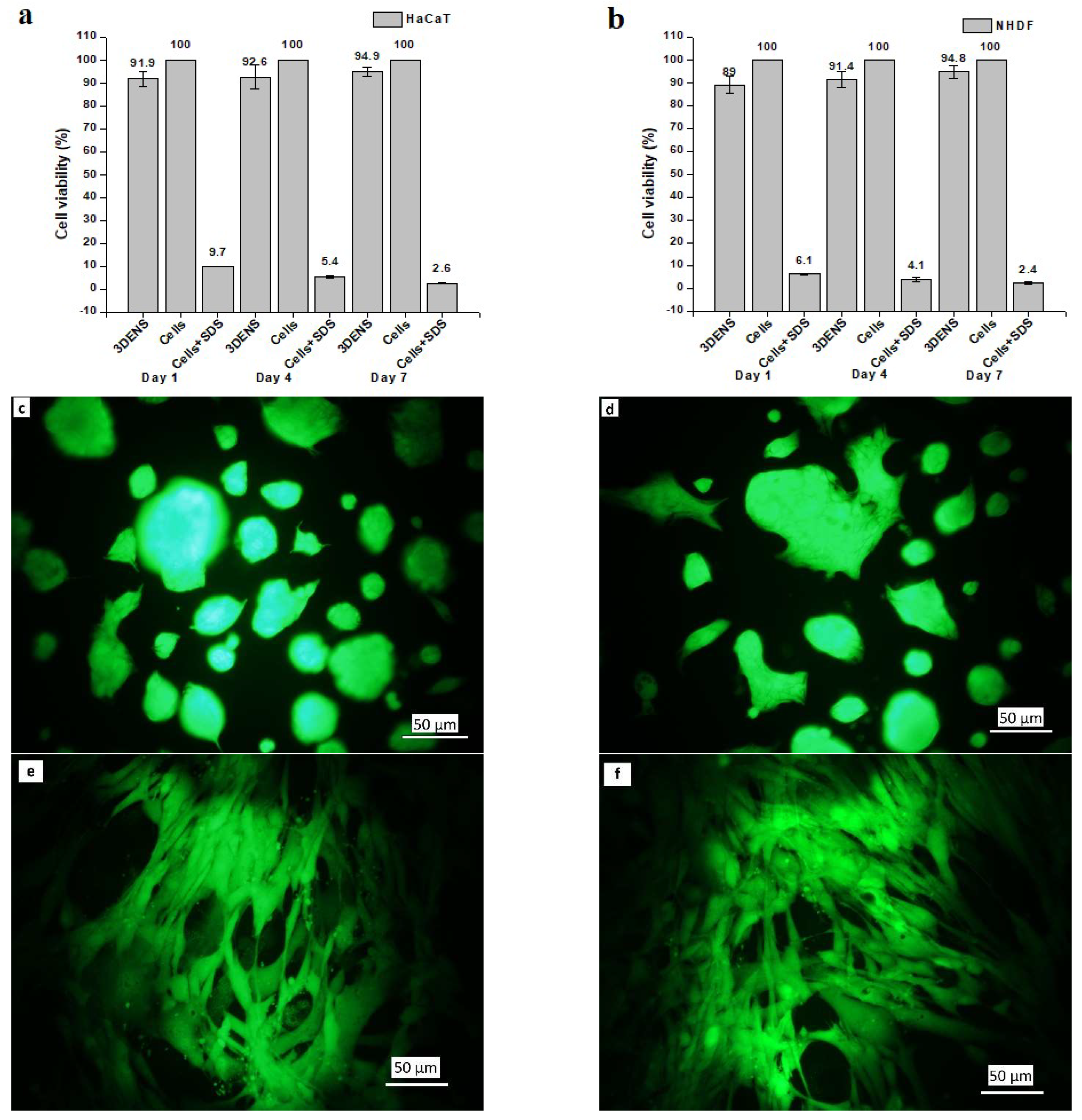
3.6. In Vitro Results
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, X.; Ding, B.; Li, B. Biomimetic electrospun nanofibrous structures for tissue engineering. Mater. Today 2013, 16, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Wu, T.; Dai, Y.; Xia, Y. Electrospinning and Electrospun Nanofibers: Methods, Materials, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 5298–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, Y.-S.; Sharmin, A.A.; Islam, M.T.; Halim, A.F.M.F. Future direction of wound dressing research: Evidence From the bibliometric analysis. J. Ind. Text. 2022, 52, 15280837221130518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madni, A.; Kousar, R.; Naeem, N.; Wahid, F. Recent advancements in applications of chitosan-based biomaterials for skin tissue engineering. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2021, 6, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjit, E.; Hamlet, S.; George, R.; Sharma, A.; Love, R.M. Biofunctional approaches of wool-based keratin for tissue engineering. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2022, 7, 100398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjani, M.E.; Hmtshirazi, R.; Mohammadi, T. CDI crosslinked chitosan/poly (vinyl alcohol) electrospun nanofibers loaded with Achillea millefolium and Viola extract: A promising wound dressing. Carbohyd. Polym. 2024, 336, 122117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aadil, K.R.; Nathani, A.; Rajendran, A.; Sharma, C.S.; Lenka, N.; Gupta, P. Investigation of human hair keratin-based nanofibrous scaffold for skin tissue engineering application. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2024, 14, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.T.; Laing, R.M.; Wilson, C.A.; McConnell, M.; Ali, M.A. Fabrication and characterization of 3-dimensional electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol)/keratin/chitosan nanofibrous scaffold. Carbohyd. Polym. 2022, 275, 118682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Mai, S.; Norton, D.; Haycock, J.W.; Ryan, A.J.; MacNeil, S. Self-organization of skin cells in three-dimensional electrospun polystyrene scaffolds. Tissue Eng. 2005, 11, 1023–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carley, K.M.; Kamneva, N.Y.; Reminga, J. Response Surface Methodology; CMU-ISRI-04-136; School of Computer Science, Institute for Software Research, Center for Computational Analysis of Social and Organizational Systems, Carnegie Mellon University: Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 2004; pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Box, G.E.P.; Behnken, D.W. Some New Three Level Designs for the Study of Quantitative Variables. Technometrics 1960, 2, 455–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minitab. Minitab 17.0; Minitab, LLC.: State College, PA, USA, 2018; Available online: https://www.minitab.com (accessed on 26 February 2024).
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 10993-5:2009; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 5: Tests for In Vitro Cytotoxicity. 3rd ed. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- Fischer, E.R.; Hansen, B.T.; Nair, V.; Hoyt, F.H.; Dorward, D.W. Scanning Electron Microscopy. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2012, 25, 2B.2.1–2B.2.47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, P.; Coats, B. Biological Sample Preparation for SEM Imaging of Porcine Retina. Microsc. Today 2012, 20, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayleigh, L. On the equilibrium of liquid conducting masses charged with electricity. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1882, 14, 184–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeleny, J. The electrical discharge from liquid points, and a hydrostatic method of measuring the electric intensity at their surfaces. Phys. Rev. 1914, 3, 69–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deitzel, J.M.; Kleinmeyer, J.; Harris, D.; Beck Tan, N.C. The effect of processing variables on the morphology of electrospun nanofibers and textiles. Polymer 2001, 42, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Fang, D.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B.; Chen, W. Optimization and Characterization of Dextran Membranes Prepared by Electrospinning. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y. Preparation and Properties of Electrospun Soy Protein Isolate/Polyethylene Oxide Nanofiber Membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 4331–4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Zhang, B.; Dou, Y.; Yin, G.; Cui, Y.; Chen, X. Fabrication and characterization of electrospun feather keratin/poly(vinyl alcohol) composite nanofibers. Rsc. Adv. 2017, 7, 9854–9861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, X.; Kim, K.; Fang, D.; Ran, S.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Structure and process relationship of electrospun bioabsorbable nanofiber membranes. Polymer 2002, 43, 4403–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargham, S.; Bazgir, S.; Tavakoli, A.; Rashidi, A.S.; Damerchely, R. The Effect of Flow Rate on Morphology and Deposition Area of Electrospun Nylon 6 Nanofiber. J. Eng. Fabr. Fibers (JEFF) 2012, 7, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, C.; Sheng, J. Morphology of ultrafine polysulfone fibers prepared by electrospinning. Polym. Int. 2004, 53, 1704–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.; Zhu, M.; Yang, W.; Yu, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y. Experimental study on relationship between jet instability and formation of beaded fibers during electrospinning. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2005, 45, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Kwon, O.-H.; Jang, J. Electrospinning of chitosan dissolved in concentrated acetic acid solution. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 5427–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathy, M.; Kashyout, A.B.; El Nady, J.; Ebrahim, S.; Soliman, M.B. Electrospun polymethylacrylate nanofibers membranes for quasi-solid-state dye sensitized solar cells. Alex. Eng. J. 2016, 55, 1737–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, L.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, J.; Fang, T. Predicting poly(vinyl pyrrolidone)s’ solubility parameter and systematic investigation of the parameters of electrospinning with response surface methodology. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 40304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neo, Y.P.; Ray, S.; Easteal, A.J.; Nikolaidis, M.G.; Quek, S.Y. Influence of solution and processing parameters towards the fabrication of electrospun zein fibers with sub-micron diameter. J. Food Eng. 2012, 109, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Independent Variables | Lower Limit | Upper Limit |
|---|---|---|
| Biopolymer (%) | 10 | 50 |
| Voltage (kV) | 12 | 18 |
| Flow rate (mL/h) | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| Spinning distance (mm) | 70 | 130 |
| Experiments | Block | Coded Levels and (Actual Levels) | Responses, n = 100 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | Fibre Diameter | Defects Diameter | ||||
| Biopolymers (%) | Voltage (kV) | Flow Rate (mL/h) | SD (mm) | Experimental | Predicted | Experimental | Predicted | ||
| 1 | 3 | 1 (50) | 0 (15) | 1 (0.5) | 0 (100) | 94 | 95 | 453 | 452 |
| 2 | 3 | −1 (10) | 0 (15) | 1 (0.5) | 0 (100) | 202 | 203 | 41 | 48 |
| 3 | 3 | 0 (30) | 0 (15) | 0 (0.3) | 0 (100) | 183 | 180 | 77 | 88 |
| 4 | 3 | 1 (50) | 0 (15) | −1 (0.1) | 0 (100) | 87 | 82 | 402 | 394 |
| 5 | 3 | −1 (10) | 0 (15) | −1 (0.1) | 0 (100) | 196 | 190 | 25 | 25 |
| 6 | 3 | 1 (30) | −1 (12) | −1 (0.1) | 0 (100) | 146 | 153 | 306 | 297 |
| 7 | 3 | 1 (30) | 1 (18) | 1 (0.5) | 0 (100) | 138 | 142 | 302 | 310 |
| 8 | 3 | 1 (30) | 0 (15) | 0 (0.3) | 0 (100) | 178 | 180 | 89 | 88 |
| 9 | 3 | 1 (30) | −1 (12) | 1 (0.5) | 0 (100) | 151 | 155 | 355 | 346 |
| 10 | 3 | 1 (30) | 0 (15) | 0 (0.3) | 0 (100) | 172 | 180 | 86 | 88 |
| 11 | 3 | 1 (30) | 1 (18) | −1 (0.1) | 0 (100) | 112 | 119 | 269 | 277 |
| 12 | 3 | 1 (30) | 0 (15) | 0 (0.3) | 0 (100) | 188 | 180 | 90 | 88 |
| 13 | 3 | −1 (10) | 1 (18) | 0 (0.3) | 0 (100) | 200 | 198 | 22 | 20 |
| 14 | 3 | −1 (10) | −1 (12) | 0 (0.3) | 0 (100) | 230 | 225 | 30 | 31 |
| 15 | 3 | 1 (50) | 1 (18) | 0 (0.3) | 0 (100) | 96 | 94 | 389 | 390 |
| 16 | 3 | 1 (50) | −1 (12) | 0 (0.3) | 0 (100) | 119 | 114 | 431 | 435 |
| 17 | 3 | 1 (30) | 0 (15) | 0 (0.3) | 0 (100) | 178 | 180 | 97 | 88 |
| 18 | 2 | 1 (30) | −1 (12) | 0 (0.3) | 1 (130) | 165 | 163 | 321 | 328 |
| 19 | 2 | 1 (30) | 1 (18) | 0 (0.3) | 1 (130) | 152 | 147 | 238 | 231 |
| 20 | 2 | 1 (50) | 0 (15) | 0 (0.3) | 1 (130) | 95 | 101 | 390 | 394 |
| 21 | 2 | −1 (10) | 0 (15) | 0 (0.3) | 1 (130) | 203 | 209 | 10 | 10 |
| 22 | 2 | 1 (30) | 0 (15) | −1 (0.1) | 1 (130) | 129 | 128 | 284 | 286 |
| 23 | 2 | 1 (30) | 0 (15) | 1 (0.5) | 1 (130) | 156 | 151 | 301 | 295 |
| 24 | 1 | 1 (30) | 1 (18) | 0 (0.3) | −1 (70) | 153 | 150 | 327 | 319 |
| 25 | 1 | 1 (30) | −1 (12) | 0 (0.3) | −1 (70) | 181 | 181 | 270 | 276 |
| 26 | 1 | −1 (10) | 0 (15) | 0 (0.3) | −1 (70) | 215 | 220 | 31 | 25 |
| 27 | 1 | 1 (50) | 0 (15) | 0 (0.3) | −1 (70) | 107 | 112 | 415 | 414 |
| 28 | 1 | 1 (30) | 0 (15) | 1 (0.5) | −1 (70) | 158 | 152 | 344 | 344 |
| 29 | 1 | 1 (30) | 0 (15) | −1 (0.1) | −1 (70) | 150 | 148 | 264 | 272 |
| Code | Electrospinning Variables | Response | Error (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biopolymers (%) | Voltage (kV) | Flow Rate (mL/h) | Spinning Distance (mm) | Mean Fibre Diameter | |||
| Experimental | Predicted | ||||||
| MV1 | 20 | 16.00 | 0.3 | 110 | 192 | 196 | 2.04 |
| MV2 | 25 | 16.00 | 0.2 | 110 | 178 | 173 | 2.89 |
| MV3 | 35 | 13.00 | 0.2 | 110 | 149 | 155 | 3.87 |
| OP1 | 30 | 15.82 | 0.2 | 105 | 169 | 163 | 3.68 |
| OP2 | 30 | 15.82 | 0.2 | 105 | 158 | 163 | 3.07 |
| OP3 | 30 | 15.82 | 0.2 | 105 | 165 | 163 | 1.23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Islam, M.T.; Sharmin, A.A.; Laing, R.; McConnell, M.; Ali, M.A. Bead-Free Electrospun Nanofibrous Scaffold Made of PVOH/Keratin/Chitosan Using a Box–Behnken Experimental Design and In Vitro Studies. Polysaccharides 2024, 5, 112-128. https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides5020009
Islam MT, Sharmin AA, Laing R, McConnell M, Ali MA. Bead-Free Electrospun Nanofibrous Scaffold Made of PVOH/Keratin/Chitosan Using a Box–Behnken Experimental Design and In Vitro Studies. Polysaccharides. 2024; 5(2):112-128. https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides5020009
Chicago/Turabian StyleIslam, Mohammad Tajul, Afsana Al Sharmin, Raechel Laing, Michelle McConnell, and M. Azam Ali. 2024. "Bead-Free Electrospun Nanofibrous Scaffold Made of PVOH/Keratin/Chitosan Using a Box–Behnken Experimental Design and In Vitro Studies" Polysaccharides 5, no. 2: 112-128. https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides5020009
APA StyleIslam, M. T., Sharmin, A. A., Laing, R., McConnell, M., & Ali, M. A. (2024). Bead-Free Electrospun Nanofibrous Scaffold Made of PVOH/Keratin/Chitosan Using a Box–Behnken Experimental Design and In Vitro Studies. Polysaccharides, 5(2), 112-128. https://doi.org/10.3390/polysaccharides5020009







