Abstract
The aim of the study was to fabricate and characterize composite macroporous hydrogels based on a hyaluronic acid/chitosan (Hyal/Ch) polyelectrolyte complex (PEC) loaded with homogeneously distributed hydroxyapatite nanoparticles (nHAp), and to evaluate them in vitro using mouse fibroblasts (L929), osteoblast-like cells (HOS) and human mesenchymal stromal cells (hMSC). Hydrogel morphology as a function of the hydroxyapatite nanoparticle content was studied using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). The mean pore size in the Hyal/Ch hydrogel was 204 ± 25 μm. The entrapment of nHAp (1 and 5 wt. %) into the Hyal/Ch hydrogel led to a mean pore size decrease (94 ± 2 and 77 ± 9 μm, relatively). Swelling ratio and weight loss of the hydrogels in various aqueous media were found to increase with an enhancement of a medium ionic strength. Cell morphology and localization within the hydrogels was studied by CLSM. Cell viability depended upon the nHAp content and was evaluated by MTT-assay after 7 days of cultivation in the hydrogels. An increase of the hydroxyapatite nanoparticles loading in a range of 1–10 wt. % resulted in an enhancement of cell growth and proliferation for all hydrogels. Maximum cell viability was obtained in case of the Hyal/Ch/nHAp-10 sample (10 wt. % nHAp), while a minimal cell number was found for the Hyal/Ch/nHAp-1 hydrogel (1 wt. % nHAp). Thus, the proposed simple original technique and the design of PEC hydrogels could be promising for tissue engineering, in particular for bone tissue repair.
1. Introduction
Natural polysaccharides are of great interest for various biomedical applications due to their biodegradation, biocompatibility and bioactivity. For instance, chitosan and hyaluronic acid are widely employed in drug delivery systems [1] and for tissue engineering [2,3,4]. Hyaluronic acid is a highly abundant component of an extracellular matrix (ECM) consisting of D-glucuronic acid and N-acetyl-glucosamine linked by alternating β(1→4) and β(1→3) glycosidic bonds and carrying a high-density negative charge due to the carboxyl groups in its chain [5]. Chitosan is a cationic linear polysaccharide, containing glucosamine and residual N-acetyl-glucosamine units linked by β(1→4) glycosidic bonds [6]. However, use of these polymers in their native forms separately is limited because of possible undesirable degradation rates (rather long in case of Ch and rapid in case of Hyal), a lack of mechanical integrity as well as high water solubility (in case of Hyal). These drawbacks can be overcome by cross-linking. However, cross-linking could lead to a reduction of chitosan or Hyal swelling, as well as a decrease of the degradation ratio [7,8]. Moreover, a commonly used residual cross-linking agent, for instance, glutaraldehyde, can cause cytotoxicity [9].
A combination of these two natural polymers allows for composite hydrogels with enhanced characteristics, which are considered to be promising for tissue engineering [10]. Since Hyal and Ch are oppositely charged polyelectrolytes, they can form a water-insoluble polyelectrolyte complex. As is well known, PEC-based composite materials from various polymers have been widely used for fabrication of membranes and microcapsules for cell cultivation [11], various drug and gene delivery systems [12] as well as scaffolds for tissue engineering, for instance for dental pulp regeneration [13].
Nano-hydroxyapatite is a main mineral component of hard tissues, in particular bones. Due to its biocompatibility and osteoconductivity the nHAp-based composites proved to be promising biomaterials for bone tissue engineering [14]. Composite scaffolds containing either chitosan [15,16] or hyaluronic acid [17], which were loaded with hydroxyapatite have been reported previously. However, it should be noted that fabrication of PEC-based scaffolds loaded with hydroxyapatite is rather difficult challenge. Regarding chitosan/hyaluronic acid scaffolds, Chen at al. proposed an original approach to fabricate hydroxyapatite-loaded macroporous chitosan/hyaluronic acid scaffolds via in situ crystallization of hydroxyapatite precursors, in particular Ca(NO3)2 and K2HPO4 [18]. However, morphology and size of the obtained hydroxyapatite crystals formed via in situ crystallization were found to be strongly dependent on polymer type, concentration and pH values of polymer solutions [19,20,21].
Since morphology and size of hydroxyapatite particles are of great importance for successful bone tissue repair [22,23], hydrogels should be loaded with nanoparticles with desirable characteristics. For this purpose, commercially available nHAp could be introduced simultaneously with PEC formation as described earlier for chitosan-polyacrylic acid polyelectrolyte complexes [24]. In this case, PEC formation could impede the uniform nHAp distribution within the polymer network. An alternative approach has been also reported, where pre-formed hydroxyapatite nanoparticles were introduced into composite Hyal/silk fibroin hydrogels during the course of their fabrication [25].
We proposed a novel simple technique for preparation of Hyal/Ch hydrogels and an optimized design of these macroporous PEC-based hydrogels, providing homogeneous nHAp distribution within the polymer network. In the current study, we suggested first to disperse nHAp in a sodium hyaluronate solution just before preparation of Hyal/Ch hydrogels, in order to fix nHAp in a Hyal network. Then, to form the Hyal/Ch polyelectrolyte complex by adding another oppositely charged polyelectrolyte, namely Ch. Thus, the proposed approach allowed us to develop an original and very simple technique for fabrication of macroporous Hyal/Ch-based scaffolds loaded with hydroxyapatite nanoparticles.
This study was aimed at the preparation of macroporous hydrogels based on the polyelectrolyte Hyal/Ch complex loaded with homogeneously distributed hydroxyapatite nanoparticles and in vitro evaluation of the hydrogels using mouse fibroblasts, osteoblast-like cells and human mesenchymal stromal cells.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Sodium hyaluronate of bacterial origin (Mw 1 × 106 Da, pharmacy grade) was from Shiseido (Tokyo, Japan). Chitosan (Mw 5 × 104 Da; deacetylation degree (DD) 0.96) was prepared using solvent-free mechanochemical synthesis as reported by us previously [26]. Nanoparticles of hydroxyapatite (with a mean size of ≤200 nm) and Type I collagenase solution were from Sigma-Aldrich. Acetic acid (Chemmed, Moscow, Russia) of analytical grade was used without any further purification. Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM), Eagle’s minimal essential medium (α-MEM), phosphate buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.4), streptomycin, penicillin, a Trypsin/EDTA solution, Hoechst and 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenil-2H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) were purchased from PanEco (Moscow, Russia). Propidium iodide (PI) was from Immunotech/Beckman Coulter (Marseille, France), fetal bovine serum (FBS) was purchased from PAA Laboratories GmbH (Pasching, Austria) and Calcein AM was from eBioscience (San Diego, CA, USA).
2.2. Preparation of the Macroporous Hydrogels
Hydroxyapatite nanoparticles (0, 1, 5, and 10 wt. %) were dispersed in a 1 wt. % water solution of sodium hyaluronate using an ultrasound bath (PBS-GALS, Russia) for a 15 min treatment at a frequency of 35 kHz. Macroporous hydrogels were prepared as follows: 10 mL of nHAp/Hyal dispersions were frozen at −5 °C and freeze-dried. To provide polyelectrolyte complex formation, the obtained macroporous hydrogels were immersed in 30 mL of a 1 wt. % chitosan solution in 2% acetic acid for 2 h. Then, the samples were thoroughly washed from a chitosan excess with milli-Q until a neutral pH value was reached, and finally lyophilized. The obtained samples containing various nHAp amounts in the Hyal solution (0, 1, 5, 10 wt. %) were marked as Hyal/Ch, Hyal/Ch/nHAp-1, Hyal/Ch/nHAp-5 and Hyal/Ch/nHAp-10 samples, respectively.
2.3. CHN Elemental Analysis
The CHN elemental composition of the hydrogel samples was studied using a FLASH-2000 Organic Elemental Analyzer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The mean and standard deviation values of atomic concentrations were calculated based on results of three experiments. The polymeric composition was calculated from changes in the C-to-N ratio in the samples.
2.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy
The morphology of the vertically and horizontally cross-sectioned hydrogel samples was examined using Zeiss EVO 40 scanning electron microscopy (Oberkochen, Germany) equipped with an X-Flash 1106 silicon drift detector. To ensure a charge drain, a sample surface was coated with a thin conducting Al film by sputtering. The microscope chamber was evacuated to a working vacuum of 6 × 10−4 Pa, and examinations were performed with a maximum accelerating voltage of 10–15 kV, a minimum probe current of 15–50 pA, and a minimal working distance of 5–15 mm.
2.5. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
The morphology of the hydrogels in a swollen state was examined using confocal laser scanning microscopy (Nikon TE-2000 inverted microscope, Tokyo, Japan) equipped with an EZ-C1 confocal laser. The hydrogel samples (5 × 5 × 1 mm) were incubated in milli-Q for at least for 24 h to reach a swelling equilibrium. The swollen hydrogel samples were stained with fluorescent Propidium iodide dye, which is known to provide rather good non-specific staining. The hydrogel samples were incubated in PI solution (1.25 μg/mL in milli-Q) for 10 min at room temperature, then washed with milli-Q and placed on a glass coverslip for microscopic observations. The Propidium iodide fluorescence was excited by an Argon-ion (488 nm) and Helium/Neon (543 nm) lasers and detected through a long pass emission filter (650 nm). The images were acquired with Nikon EZ-C1 software with identical settings for each sample. Image analysis software (ImageJ, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA) was used to determine a mean pore size of the hydrogel samples and for 3D reconstruction of the hydrogel structure.
To study the complicated morphology of the obtained macroporous hydrogels, a quantitative evaluation of micrographs was carried out by calculation of an effective pore diameter (d) using an Equation (1):
where L is a pore long axis length and S is a pore short axis length. The mean pore size was determined by randomly measuring at least 100 pores from each hydrogel sample.
d = (L × S)1/2
2.6. Study of Swelling Ratio and Weight Loss in Aqueous Medium
The swelling behavior and a weight loss of the prepared hydrogel samples were studied in various aqueous media, namely in milli-Q, physiological solution (0.9% NaCl), PBS (pH 7.4) and DMEM. For this purpose, the samples (5 × 5 × 2 mm) were sterilized using 70% ethanol, washed with milli-Q and immersed in 5 mL of the solutions mentioned above at 37 °C for 24 h. Before weighing, the surface water of the hydrogel samples was removed with a filter paper. The swelling ratio (Sw) of the hydrogels was calculated according to Equation (2):
where Md is the weight of the dried sample and Mw is the weight of the sample after immersion in various solutions.
The weight loss was measured by the immersion of hydrogel samples in 5 mL of the solutions mentioned above for 1 and 4 weeks at 37 °C. The solutions were refreshed once a week. After incubation, the samples were washed 3 times with milli-Q and freeze-dried. The weight loss (Wl) of the hydrogels was calculated according to Equation (3):
where Mi is the initial weight and Mt is the weight of the samples after incubation in the various solutions. The results of swelling and mass loss experiments were presented as the average ± SD.
2.7. In Vitro Study
2.7.1. Cell Cultivation
In the current study, the mouse fibroblast cell line L929, osteoblast-like cells, namely HOS cells and human mesenchymal stromal cells were used. The mouse fibroblast L929 and human osteosarcoma HOS cell lines were obtained from the Russian cell culture collection of vertebrates at the Institute of Cytology RAS, St. Petersburg. Human mesenchymal stromal cells were isolated from an adipose tissue as previously described [27], and the first 10 passages were used. Adipose tissue samples were obtained after an elective liposuction under a local anesthesia from four healthy patients. Briefly, 2–3 adipose tissue samples were chopped and washed twice by centrifugation with sterile PBS (pH 7.4) to remove any contaminating debris and red blood cells. Then the tissue material was incubated at gentle agitation (30 min, 37 °C) with a 0.075% Type I collagenase solution. Then collagenase was inactivated with an equal volume of α-MEM supplemented with 10% FBS, and the obtained mixture was precipitated using centrifugation (400× g, 10 min). Finally, the obtained cellular pellet was re-suspended in α-MEM with 10% FBS, 50 U/mL penicillin and 50 μg/mL streptomycin, and cultured in a CO2 incubator. After 24 h, non-adherent cells were discarded, and a fresh medium was added. The medium was replaced twice a week.
Fibroblast L929 and HOS cells were cultured in DMEM, while hMSC were cultured in α-MEM. Both media were supplemented with 10% FBS and contained 2 mM L-glutamine, 1 mM sodium pyruvate, 50 μM 2-mercaptoethanol, 100 µg/mL streptomycin and 100 U/mL penicillin in 25 and 75 cm2 flasks in a 5% CO2 humidified atmosphere at 37 °C (CO2 incubator Heraeus B5060 EK/CO2, Hanau, Germany). The cells were reseeded every 2–4 days.
2.7.2. The Hydrogel Sterilization
The hydrogel samples were sterilized by incubation in 70% ethanol for 1 h. After sterilization, the samples were washed 3 times with milli-Q.
2.7.3. Cytotoxicity of the Hydrogel Samples
The cytotoxicity of the hydrogel samples was studied in an extract test using L929 and HOS cell lines. For this purpose, sterile hydrogel samples were incubated with the culture medium (25 mg per 1 mL of the medium) at 37 °C for 24 h. Then supernatants (extracts) were collected and diluted with the culture medium. In this study, three extract samples were used, namely, dilution 1:10, dilution 1:2 and non-diluted extract. The cells were seeded in a 96-well plate (2 × 104 cells/well) and transferred to the CO2 incubator. Then, in 24 h the medium in each well was replaced with 100 μL of the extracts. Cell viability was assessed using MTT-assay after 24 h of cell cultivation in the extracts. For this purpose, the extracts were replaced with 100 µL of MTT solution (0.5 mg/mL in DMEM) and incubated at 37 °C for 3 h. Then, formazan crystals formed in the living cells were dissolved by adding 100 µL DMSO, and an optical density was measured at 540/690 nm using a Titertek Multiskan MCC/340 plate reader (Flow Laboratories, McLean, VA, USA). The relative cell viability (V) was calculated according to Equation (4):
where ODt is the optical density in test wells and ODc is the optical density in control wells. The cells cultivated in a fresh medium (without the extracts) were used as a control.
2.7.4. Study of Cell Morphology
The hydrogel samples (5 × 5 × 2 mm) were placed in a 96-well plate, sterilized as described in Section 2.7.2 and incubated with the culture medium for 24 h. The L929 cells were seeded on the hydrogel samples by dropping 200 μL of cell suspension (105 cells/mL), and cultured for 1 week. After 7 days of cultivation, the cells were stained with the Calcein AM fluorescent vital cell marker and the fluorescent DNA dye (Hoechst). The mixture of Calcein AM and the Hoechst dye in the medium (1 µg/mL) was added to the hydrogel samples, and the samples were incubated at 37 °C for 30 min. Then, the solution was replaced with a fresh medium, and the samples were observed using confocal laser microscope Nikon TE-2000 (Tokyo, Japan).
2.7.5. Cell Growth on the Hydrogel Samples
The L929, HOS cells and hMSC were used in the study. The hydrogel samples (5 × 5 × 2 mm) were placed in a 96-well plate, sterilized as described in Section 2.7.2 and incubated with the culture medium for 24 h. The cells were seeded on the hydrogel samples by dropping 200 μL of cell suspension (105 cells/mL), and cultured for 1 week. The medium was refreshed every 2–3 days. Cell viability was evaluated by MTT-test. For this purpose, the culture medium was replaced with 100 µL of the MTT solution (0.5 mg/mL in DMEM), and the plate was incubated at 37 °C for 3 h. Formazan crystals were dissolved in 200 µL of DMSO. Then, 100 µL aliquots were taken to measure an absorbance (540/690 nm) using the Titertek Multiskan MCC/340 plate reader (Flow Laboratories, McLean, VA, USA).
To estimate an effect of the hydrogels on results on the MTT-test, which is usually performed for the monolayer culture, a control experiment was carried out. For this purpose, control hydrogel samples were pre-incubated with the culture medium for 1 week, and then the cells at previously determined cell densities were seeded on them. Finally, the MTT-assay in the presence of the hydrogel samples was carried out after cell attachment (approx. in 3 h). For each sample, a calibration curve was plotted: optical density for the cells cultivated in the presence of the hydrogel sample (abscissa X) versus an optical density for the cells without the hydrogel sample (ordinate Y). Based on the obtained curve, the optical densities were determined for all hydrogel samples. The relative cell viability was calculated according to the Equation (4) (see Section 2.7.3).
2.7.6. Statistics
The data were analyzed using GraphPad Prism 5.0 software (Graph-Pad Software, San Diego, CA, USA). All values were expressed as mean ± standard error of at least three parallel replicates and compared using two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Dunnett’s Multiple Comparison Test as a post hoc test. Values of p < 0.05 were considered significant.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Hydrogel Characterization
To provide homogenous distribution and fixation of the hydroxyapatite nanoparticles in the polymer network, the following scheme for the hydrogel fabrication was proposed (see Figure 1). First, nHAp were dispersed in the Hyal solution by ultrasound treatment using conditions that provided stable uniform nHAp dispersions in the Hyal solution [28]. Then this nHAp/Hyal dispersion was freeze-dried and incubated in chitosan solution to form a polyelectrolyte Hyal/Ch complex. Thus, use of this technique allowed us to evenly spread nHAp and fix them within the macroporous composite polymer matrix.

Figure 1.
A scheme for fabrication of composite hyaluronic acid/chitosan hydrogels loaded with hydroxyapatite nanoparticles (Hyal/Ch/nHAp). Photographs of the macroporous hydrogel samples prepared from the Hyal solution with hydroxyapatite nanoparticles (10 wt. %) before (a) and after (b) immersion in the chitosan solution. Scale bar is 10 mm.
Images of the samples are shown in Figure 1. Cross-linking the Hyal macromolecules by electrostatic interactions with polyvalent ions and via hydrogen bond formation, could be a reason for the rather specific matrix architectonics. The strongest structure of the hydroxyapatite/hyaluronic acid network has been obtained using 10 wt. % of hydroxyapatite, as has been reported earlier by Ishikawa et al. [29]. The macroporous structures of the freeze-dried Hyal/nHAp matrices allowed uniform swelling in the chitosan solution and homogeneous chitosan coating of the Hyal macroporous hydrogels via polyelectrolyte complex formation, which was revealed in a color change from white to slightly yellow (Figure 1a,b).
The polyelectrolyte hyaluronic acid/chitosan complex could be formed through electrostatic interactions of chitosan amino groups with carboxylic groups of the hyaluronic acid, i.e., NH3+-OOC. To confirm uniformity and to calculate the polymer complex composition, an elemental analysis of the hydrogel samples was carried out. As seen in Table 1, the polymeric composition was similar for all samples with minor variations.

Table 1.
Elemental analysis data and the calculated composition of polymer matrix.
3.1.1. Structure
An open interconnected macroporous structure is needed to provide large specific surface for cell attachment and growth, as well as for nutrients, oxygen supply and effective mass and gas exchange [30,31]. The morphology of the dried hydrogel samples was evaluated using SEM (Figure 2a,b). The secondary and partially undeveloped pores within the primary wall structure can be seen. This was caused by an additional freeze-dry cycle after the complexation with chitosan. The hydroxyapatite nanoparticles obviously located within pore walls could not be clearly seen in the SEM images. Nevertheless, the Ca and P atoms related to hydroxyapatite were revealed by energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) of a wall spot in the Hyal/Ch/nHAp-10 sample in contrast to the Hyal/Ch sample (Figure 2c,d).
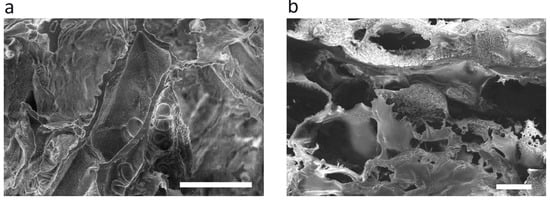
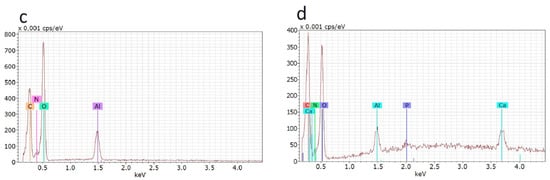
Figure 2.
SEM images of the dried Hyal/Ch (a) and Hyal/Ch/nHAp-10 (b) samples; and EDX spectra of Hyal/Ch (c) and Hyal/Ch/nHAp-10 (d) samples. Scale bar is 100 µm.
The structure of the swollen hydrogel samples was evaluated by CLSM. As can be seen in Figure 3, the prepared hydrogels in a swollen state possessed a clear interconnected porous network with the mean pore size in a range of 77–204 µm. Moreover, an introduction of nHAp did affect the hydrogel structure, and the mean pore size was found to be dependent on the nHAp content. Thus, the mean pore size of the Hyal/Ch hydrogel was 204 ± 25 μm. An introduction of 1 and 5 wt. % of nHAp led to the mean pore size decrease from 204 ± 25 μm, to 94 ± 2 and 77 ± 9 μm in case of the Hyal/Ch/nHAp-1 and Hyal/Ch/nHAp-5 samples, respectively. This could be explained by electrostatic interactions of hyaluronic acid macromolecules with polyvalent hydroxyapatite ions (e.g., Ca2+) which resulted in a two-fold reduction of the mean pore size providing more unimodal pore size distribution. However, loading the hydrogel with 10 wt. % of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles led to an increase of the pore mean size up to 99 ± 10 µm. This phenomenon could be attributed to the nanoparticles aggregation and, as a result, the nanoparticles’ effect on the hydrogel structure was diminished.
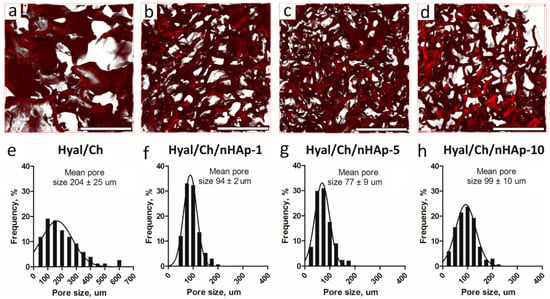
Figure 3.
CLSM images (a–d) and the pore size distributions (e–h) in the swollen macroporous hyaluronic acid/chitosan hydrogel samples. Hyal/Ch sample was without hydroxyapatite nanoparticles (a,e); Hyal/Ch/nHAp-1 (b,f), Hyal/Ch/nHAp-5 (c,g) and Hyal/Ch/nHAp-10 (d,h) samples were loaded with 1, 5 and 10 wt. % of nanoparticles, respectively. Scale bar is 500 µm.
The mean pore sizes of the obtained hydrogels were large enough to provide animal cell adhesion, migration and proliferation [32]. However, for osteoblasts preferable pore sizes is within the range of 100–350 μm [31]. Nonetheless, Teixeira et al. reported that in case of porous titanium surfaces, a decrease of pore sizes from 312 μm to near 62 μm resulted in the increase of osteoblast phenotype and bone markers expression, and led to the decreased proliferation rate of osteogenic cells derived from human alveolar bone [33]. In our study, an entrapment of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles maintained a macroporous hydrogel structure suitable to support 3D cell growth and proliferation within the macropores. However, in case our hydrogels are used for mesenchymal stem cells differentiation, these issues should be taken into consideration.
3.1.2. Study of Swelling Ratio and Weight Loss
To estimate the stability of the hydrogel samples at physiological conditions, swelling ratio and weight loss in various aqueous media were studied. As seen from Figure 4, both parameters were highly affected by medium properties. Thus, the ionic strength of the solution where the samples were incubated played a key role in the sample behavior. The presence of ions in the 0.9% NaCl solution, PBS (pH 7.4) and the culture medium led to a weakening of ion bonds within the polyelectrolyte Hyal/chitosan complexes. Similar trends were observed for all hydrogel samples. An increase of the nHAp content in the hydrogels resulted in swelling enhancement, which was markedly expressed the in case of the culture medium use (Figure 4a). All the hydrogel samples were stable in milli-Q and did not resorb after 4 weeks of incubation (Figure 4c). In the physiological solution (pH 7.2), all the hydrogel samples were relatively stable for at least 4 weeks of incubation (weight loss was less than 45 wt. %). Incubation in DMEM and PBS (pH 7.4) resulted in a significant degradation of the samples (Figure 4b). After 7 days of incubation in PBS (pH 7.4) and DMEM the weight loss values were 40% and 70%, respectively. After 4 weeks incubation in PBS (pH 7.4) and DMEM, the weight loss reached a plateau of about 80%. An increase in the nHAp amount within the hydrogels led to degradation decrease. Nevertheless, further increase in the nHAp content (up to 10 wt. %) resulted in the swelling decrease again, while the weight loss again increased. However, it should be noted that differences in swelling and weight loss for the samples with different nHAp contents were not significant. The results on weight loss analysis in PBS (pH 7.4) was in a good agreement with those reported earlier [13]. Coimbra et al. reported that weight loss of Hyal/Ch PEC hydrogel reached a plateau at about 35% after 3 days of incubation. However, differences in the behavior of the hydrogel at further incubation was observed, which could be explained by the difference in the experiment design, since in the work of Coimbra et al. the medium was not replaced, while in our study the medium was refreshed once a week.
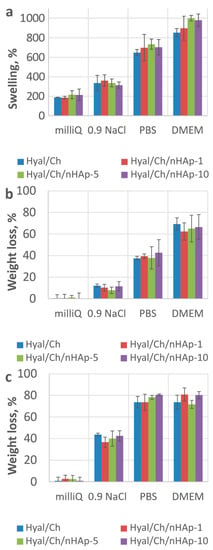
Figure 4.
Swelling ratio after 24 h (a) and weight loss after 1 week (b) and 4 weeks (c) incubation of the hydrogel samples in various aqueous media. Hyal/Ch sample was without hydroxyapatite nanoparticles; Hyal/Ch/nHAp-1, Hyal/Ch/nHAp-5 and Hyal/Ch/nHAp-10 samples were loaded with 1, 5 and 10 wt. % of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles, respectively.
It should be noted that swelling behavior could drastically affect mechanical properties of hydrogels. Earlier, it was shown that an incubation of polymers under physiological conditions (an aqueous environment and a body temperature), led to a mechanical strength decrease due to an increase in a free volume and chain mobility of the polymer [34]. A decreased ability to resist deformation was shown after incubation in PBS of Ch-L-glutamic acid/Hyal hydrogels, containing silver nanoparticles [35]. Tensile strength markedly decreased, while an elongation at a break point increased compared to appropriated values of dry samples. At the same time, an introduction of silver nanoparticles led to an enhancement of mechanical properties of the hydrogels in a dry state, while in a wet state all samples had similar mechanical properties.
In the current study, we did not evaluate mechanical properties of the obtained hydrogels. Nevertheless, we have found literature data, in order to analyze mechanical properties of the similar hydrogels. Some results on mechanical properties, namely compressive modulus values of various hydrogels based on either pure chitosan or its combination with Hyal, are summarized in Table 2. It should be noted that characteristics of Ch and Hyal used for the preparation of the hydrogels in the Table 2 differed from those of our samples.
As seen in Table 2, in case of Ch/Hyal PEC hydrogels a compressive modulus of the hydrogels in a wet state was much lower compared to that in a dry state. Moreover, due to an ability of hyaluronic acid to absorb a lot of water, Hyal introduction into Hyal/Ch PEC matrices reduced the compressive modulus of a porous matrix [10]. Erickson et al. reported that increasing chitosan content in the Ch/Hyal PEC hydrogels resulted in an enhancement of mechanical properties. A compressive modulus value was varied from 1.41 kPa for the sample prepared from a 2 % wt. Ch solution, to 27.7 kPa for the hydrogel sample from a 8 % wt. Ch solution.
Most of natural polymers are known to possess rather poor mechanical properties. Therefore, a quite low mechanical strength of Ch/Hyal composite matrices could be expected. However, a main goal of researches focusing on preparation and characterization of Ch/Hyal PEC hydrogels is to combine the bioactive properties of Hyal and Ch. Hyal is known to play an important role in a regulation of cell behavior, including cell proliferation, survival, motility, migration and differentiation [36], while Ch provides bioadhesive, antimicrobial and hemostatic properties. Moreover, both Hyal and Ch were proposed for dentistry application, where a mechanical characteristics of matrices were not crucial parameters [37,38].
To improve mechanical properties of hydrogels, several methods can be used, including cross-linking (see Table 2). Thus, mechanical properties of Ch/Hyal PEC hydrogels cross-linked with genipin (Gen) were a function of the genipin amount in the polymer mixture. The maximum value of the compressive modulus was 4.16 kPa and 2.19 kPa for the hydrogels cross-linked with 3 mg and 1 mg of Gen, relatively. Gen was added to a polymer mixture (25 mL of Ch and 25 mL of Hyal) [39]. Moreover, to obtain cross-linked PEC hydrogels, amino and aldehyde groups of polysaccharide derivatives could be used [40].
However, it is still difficult to increase the hydrogel compressive modulus up to a MPa scale, which is needed for hard tissue repair. For example, mean compressive modulus values of the tibial and talar surfaces of the ankle were 12.2 and 13.1 MPa, respectively [41]. Nevertheless, earlier it was shown that various injectable hydrogels being implanted in a bone or a cartilage can improve tissue regeneration, whereas they cannot support damaged tissues [42,43].

Table 2.
Mechanical properties of hydrogel matrices based on chitosan and chitosan/hyaluronic acid.
Table 2.
Mechanical properties of hydrogel matrices based on chitosan and chitosan/hyaluronic acid.
| Matrix Composition | Porosity, % | Compressive Modulus, kPa | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry | Wet | ||||
| PEC | Ch (4% wt.)/Hyal (1% wt.) * | 87 | 209.00 | 1.29 | [44] |
| Ch | porous | 291.03 | 2.84 | [10] | |
| Ch/Hyal-1% ** | 144.33 | 2.43 | |||
| Ch/Hyal-10% ** | 40.73 | 1.21 | |||
| Ch (2% wt.)/Hyal (1% wt.) * | 99 | 1.41 | [45] | ||
| Ch (8% wt.)/Hyal (1% wt.) * | 94 | 27.70 | |||
| Cross-linked | Ch (1% wt.)/Hyal (0.2% wt.)/Gen 1 mg *** | 85 | 32.70 | 2.19 | [39] |
| Ch (1% wt.)/Hyal (0.2% wt.)/Gen 3 mg *** | 72 | 58.26 | 4.16 | ||
| Ch/Hyal(30/70 v/v) | non-porous | 12.00 | [40] | ||
| Ch/Hyal(70/30 v/v) | 28.00 | ||||
* Concentration of the polymer solution used for the hydrogel preparation. ** Polymer quantity (% wt.) in the hydrogel. *** Genipin quantity in the polymer mixture used for the hydrogel preparation.
3.2. In Vitro Study
3.2.1. Cytotoxicity
Since the hydrogels tended to degrade in the culture medium with rather high ionic strength, it was of great importance to evaluate an effect of hydrogel extracts on cell viability. A relationship between cell viability and the nHAp content was demonstrated in extract tests using L929 and HOS cell lines. As seen from Figure 5, the entrapment of nHAp into the hydrogels resulted in a slight decrease in the cell viability compared to that observed from the Hyal/Ch sample. However, the increase of the hydroxyapatite nanoparticles content entrapped in the hydrogels up to 10 wt. % resulted in a slight increase in the cell viability, which could be explained by the difference in sample stabilities in the culture medium. The difference in the cell viability values was more evident in case of the non-diluted extracts than diluted ones (1:2 and 1:10 diluted extracts). A similar tendency was observed for both cell lines. However, in the case of the L929 fibroblasts, the effect was found to be more pronounced. The obtained cytotoxic effect could be attributed to an acidic environment resulted from a partial polyelectrolyte complex destruction.
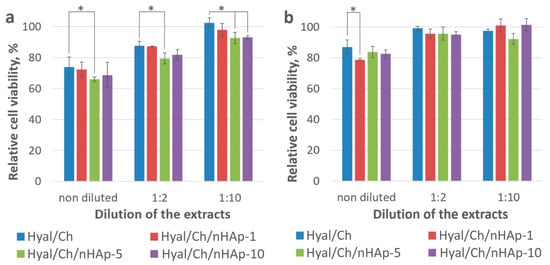
Figure 5.
Viability of the L929 (a) and HOS (b) cells after incubation with the non-diluted extract and diluted extracts (1:2 and 1:10) for 24 h. Hyal/Ch sample was without hydroxyapatite nanoparticles; Hyal/Ch/nHAp-1, Hyal/Ch/nHAp-5 and Hyal/Ch/nHAp-10 samples were loaded with 1, 5 and 10 wt. % of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles, respectively. Results are presented as a percentage of viable cells compared to that of the cell monolayer culture (100%). Three parallel replicates were carried out for each sample. (*) Indicates statistical significance compared to the Hyal/Ch sample (p < 0.05).
3.2.2. Cell Growth on the Hydrogel Samples
To qualitatively evaluate cell viability and morphology within the hydrogels, L929 fibroblasts were seeded in the hydrogels, and after cultivation for 1 week, they were stained with the Calcein AM vital dye and observed by CLSM. The hydrogel structure was visualized by non-specific adsorption of fluorescent DNA dye Hoechst (in blue). As seen in Figure 6, alive cells (in green) were found in all hydrogel samples. The cells formed aggregates, which were mainly attached to hydrogel walls.
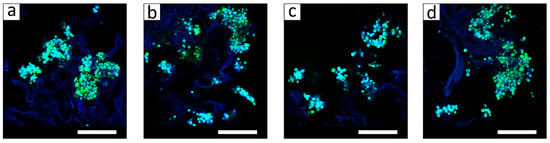
Figure 6.
CLSM images of the hyaluronic acid/chitosan hydrogel samples with the L929 cells after cultivation for 1 week. The Hyal/Ch sample was without hydroxyapatite nanoparticles (a); the Hyal/Ch/nHAp-1 (b), Hyal/Ch/nHAp-5 (c) and Hyal/Ch/nHAp-10 (d) samples were loaded with 1, 5 and 10 wt. % of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles, respectively. Scale bar is 200 μm.
It is well known, that mechanical properties of the matrices for tissue engineering are of great importance, in particular, matrix stiffness is involved in the regulation of cell behavior. Recently an influence of matrix stiffness on the cell morphology and behavior was shown [45]. Thus, Ch/Hyal PEC hydrogels with a compressive modulus of 1.41 kPa provided formation of the multicellular spheroids from human glioblastoma U-87 MG cells. A similar behavior of human glioblastoma U-118 MG cells was also reported by Florczyk et al. [44]. The U-118MG cells formed multicellular spheroids in the Ch/Hyal hydrogels with a compressive modulus of 1.29 kPa in a wet state.
Cell growth in the PEC hydrogel samples as a function of the nHAp content was quantitatively evaluated after cultivation of cells for 1 week. Here, HOS osteoblast-like cells were used, because they are widely employed as an experimental model of osteoblasts for orthopedic applications. The cells are immortal and proliferate more rapidly than primary cells, which make them easy to work with. Moreover, their adhesion ability is similar to that of human osteoblasts [46]. Human mesenchymal stromal cells have been selected due to their ability to response to various molecular keys/signals, and, as a result, a great potential for tissue engineering [47].
The results of the MTT-assay were presented as a percentage of viable cells compared to that of the control (Figure 7). It is worth noting that cell behavior was similar for all cell types. Initial cell density was 2.0 × 104 cells per well, while after cultivation for 7 days, we obtained in control wells 2.1 × 105, 2.5 × 105 and 9.6 × 104 per well for L929, HOS cell lines and hMSC, respectively. Obviously, the cells grew and proliferated in all hydrogel samples. Cell proliferation was found to be dependent upon the nHAp content in the hydrogels. Maximum cell viability in case of hMSC was obtained in case of the Hyal/Ch/nHAp-10 sample (155 ± 18%), while a minimal cell number was found for the Hyal/Ch/nHAp-1 hydrogel (118 ± 26%). Previously, it was shown that nHAp-loaded chitosan hydrogels provided enhanced cell adhesion, well spreading morphology and higher proliferation of pre-osteoblast (MC 3T3-E1) compared to the results for pure chitosan scaffold [48]. An enhanced cell growth of HOS on PEC chitosan-poly(acrylic acid) hydrogels loaded with nHAp has been also reported previously [49]. In our study, a positive effect of the nHAp entrapment in Hyal/Ch hydrogels on the cell growth for mouse fibroblasts L929, human osteosarcoma cells HOS and hMSC was observed. However, this effect was not markedly pronounced.
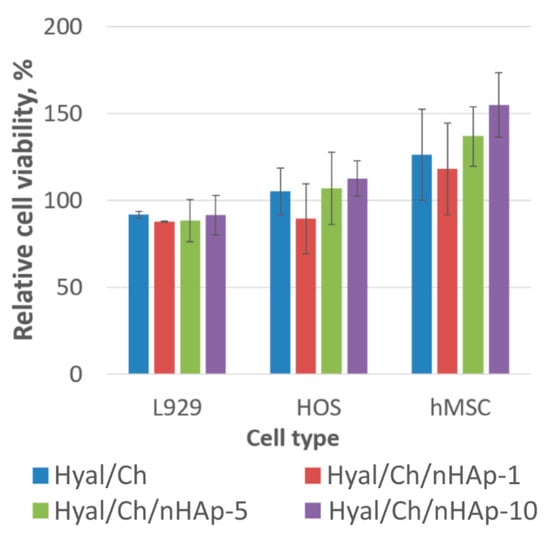
Figure 7.
Viability of mouse fibroblasts L929, human osteosarcoma cells (HOS) and human mesenchymal stromal cells (hMSC) after cultivation within the hyaluronic acid/chitosan hydrogels for 1 week. The Hyal/Ch sample was without hydroxyapatite nanoparticles; the Hyal/Ch/nHAp-1, Hyal/Ch/nHAp-5 and Hyal/Ch/nHAp-10 samples were loaded with 1, 5 and 10 wt. % of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles, respectively. Results of MTT-test. The monolayer culture (without the hydrogel sample) was taken as a control (100%). Three parallel replicates were carried out for each sample.
4. Conclusions
Macroporous hyaluronic acid/chitosan hydrogels loaded with hydroxyapatite nanoparticles have been fabricated. To provide the unimodal nHAp distribution within the hydrogels, the hydroxyapatite nanoparticles were dispersed in the Hyal solutions by ultrasonication, and after lyophilization, the obtained polymer samples were treated with Ch solution to form polyelectrolyte Hyal/Ch complex. The hydrogels, which differed in nHAp content, were characterized in terms of their swelling behavior, weight loss as well as their structure and pore size distribution. The interconnected porous network was revealed by confocal microscopy. The introduction of nHAp resulted in a decrease in the mean pore size. Thus, a mean pore size in the Hyal/Ch hydrogel was 204 ± 25 μm. The introduction of nHAp (1 and 5 wt. %) into the Hyal/Ch hydrogel led to a mean pore size decrease (94 ± 2 and 77 ± 9 μm, relatively). The mean pore size in the Hyal/Ch/nHAp-10 sample was 99 ± 10 μm. Thus, although the entrapment of the hydroxyapatite nanoparticles led to a decrease of the mean pore sizes, the macroporous structure of all hydrogels was still suitable to support 3D cell growth and proliferation. Swelling ratio and weight loss of the hydrogels in various aqueous media were shown to increase with the increase of ionic strength. The potential of the nHAp-loaded hydrogels to support the growth and proliferation of osteoblast-like and human mesenchymal stromal cells was studied as a function of the nHAp content. The increase of the nHAp content in the hydrogels from 1 to 10 wt. % was found to result in an enhancement of cell growth and proliferation for all cell lines. The hybrid macroporous hyaluronic acid/chitosan hydrogels loaded with hydroxyapatite nanoparticles fabricated using an original simple technique are promising for tissue engineering, in particular bone regeneration.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.G.D. and T.S.D.; methodology, M.G.D. and T.S.D.; validation, M.G.D. and E.M.; formal analysis, M.G.D.; investigation, M.G.D., T.S.D., O.A.D. and A.I.G.; resources, E.R.A., A.N.Z., T.A.A. and E.M.; writing—original draft preparation, M.G.D. and T.S.D.; writing—review and editing, A.N.Z., T.A.A. and E.M.; visualization, M.G.D.; supervision, E.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was partly supported by the Russian Science Foundation grant 22-13-00261 (in vitro biocompatibility evaluation), partly by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education of the Russian Federation FFSM-2021-0006 (scaffold fabrication and characterization) and by project RF-2296.61321X0037 (equipment maintenance).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank A.M. Sapozhnikov and the Laboratory of cell interactions (Shemyakin-Ovchinnikov Institute of Bioorganic Chemistry, RAS) for providing some equipment.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Naskar, S.; Koutsu, K.; Sharma, S. Chitosan-based nanoparticles as drug delivery systems: A review on two decades of research. J. Drug Target. 2019, 27, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, S.; Choi, S.; Min, S.; Cho, S.-W. Hyaluronic Acid-Based Biomimetic Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering and Medical Applications. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2021, 26, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kean, T.; Thanou, M. Biodegradation, biodistribution and toxicity of chitosan. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kil’deeva, N.R.; Kasatkina, M.A.; Drozdova, M.G.; Demina, T.S.; Uspenskii, S.A.; Mikhailov, S.N.; Markvicheva, E.A. Biodegradablescaffolds based on chitosan: Preparation, properties, and use for the cultivation of animal cells. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2016, 52, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, A.; Ren, Y.; Li, J.; Sheng, Y.; Cao, C.; Zhang, K. Advances in Hyaluronic Acid for Biomedical Applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 910290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M.; Shahruzzaman, M.; Biswas, S.; Sakib, N.; Rashid, T.U. Chitosan Based Bioactive Materials in Tissue Engineering Applications—A Review. Bioact. Mater. 2020, 5, 164–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.S.H.; Ashton, M.; Dodou, K. Effect of Crosslinking Agent Concentration on the Properties of Unmedicated Hydrogels. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.-Y. Solvent Composition is Critical for Carbodiimide Cross-Linking of Hyaluronic Acid as an Ophthalmic Biomaterial. Materials 2012, 5, 1986–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.-Y. Biocompatibility of Genipin and Glutaraldehyde Cross-Linked Chitosan Materials in the Anterior Chamber of the Eye. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 10970–10985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, C.R.; Moreira-Teixeira, L.S.; Moroni, L.; Reis, R.L.; van Blitterswijk, C.A.; Karperien, M.; Mano, J.F. Chitosan Scaffolds Containing Hyaluronic Acid for Cartilage Tissue Engineering. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2011, 17, 717–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaytseva-Zotova, D.; Balysheva, V.; Tsoy, A.; Drozdova, M.; Akopova, T.; Vladimirov, L.; Chevalot, I.; Marc, A.; Goergen, J.-L.; Markvicheva, E. Biocompatible Smart Microcapsules Based on Chitosan-Poly(vinyl alcohol) Copolymers for Cultivation of Animal Cells. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2011, 13, B493–B503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borodina, T.; Markvicheva, E.; Kunizhev, S.; Möhwald, H.; Sukhorukov, G.B.; Kreft, O. Controlled Release of DNA from Self-Degrading Microcapsules. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2007, 28, 1894–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coimbra, P.; Alves, P.; Valente, T.A.M.; Santos, R.; Correia, I.J.; Ferreira, P. Sodium hyaluronate/chitosan polyelectrolyte complex scaffolds for dental pulp regeneration: Synthesis and characterization. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 49, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatesan, J.; Kim, S.-K. Nano-Hydroxyapatite Composite Biomaterials for Bone Tissue Engineering—A Review. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2014, 10, 3124–3140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepthi, S.; Venkatesan, J.; Kim, S.-K.; Bumgardner, J.D.; Jayakumar, R. An overview of chitin or chitosan/nano ceramic composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 1338–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, N.; Mokhtar, M.; Hassan, M.I.; Jin, R.M.; Roozbahani, F.; Khan, T.H. Chitosan-Based Nanocomposite Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering Applications. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2015, 30, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-L.; Lo, Y.-J.; Feng, S.-W.; Huang, Y.-C.; Tsai, H.-Y.; Lin, C.-T.; Fan, K.-H.; Huang, H.-M. Bone Healing Improvements Using Hyaluronic Acid and Hydroxyapatite/Beta-Tricalcium Phosphate in Combination: An Animal Study. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 8301624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, G.; Yang, S.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Q. Preparation and biocompatibility of nanohybrid scaffolds by in situ homogeneous formation of nano hydroxyapatite from biopolymer polyelectrolyte complex for bone repair applications. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2012, 93, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Zhang, H.; Yin, J.; Yang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Yao, F. Hydroxyapatite Crystal Formation in the Presence of Polysaccharide. Cryst. Growth Des. 2016, 16, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalmykova, T.P.; Kostina, Y.V.; Ilyin, S.O.; Bogdanova, Y.G.; Severin, A.V.; Ivanov, P.L.; Antonov, S.V. Effect of Synthesis Medium on the Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Biomineral Composites Based on Hydroxyapatite and Hyaluronic Acid. Polym. Sci. Ser. B 2020, 62, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Ma, L.; Chen, X.; Ran, Y.; Tong, Q.; Tang, L.; Li, X. Injectable hyaluronic acid/hydroxyapatite composite hydrogels as cell carriers for bone repair. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 216, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Zeng, H.; Hao, L.; Zhao, N.; Du, C.; Liao, H.; Wang, Y. Effects of hydroxyapatite microparticle morphology on bone mesenchymal stem cell behavior. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 4703–4710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pujari-Palmer, S.; Chen, S.; Rubino, S.; Weng, H.; Xia, W.; Engqvist, H.; Tang, L.; Ott, M.K. In vivo and in vitro evaluation of hydroxyapatite nanoparticle morphology on the acute inflammatory response. Biomaterials 2016, 90, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sailaja, G.S.; Velayudhan, S.; Sunny, M.C.; Sreenivasan, K.; Varma, H.K.; Ramesh, P. Hydroxyapatite filled chitosan-polyacrylic acid polyelectrolyte complexes. J. Mater. Sci. 2003, 38, 3653–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjama, M.; Mehnath, S.; Rajan, M.; Jeyaraj, M. Injectable cuttlefish HAP and macromolecular fibroin protein hydrogel for natural bone mimicking matrix for enhancement of osteoinduction progression. React. Funct. Polym. 2021, 160, 104841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akopova, T.A.; Zelenetskii, A.N.; Ozerin, A.N. Solid State Synthesis and Modification of Chitosan. In Focus on Chitosan Research; Ferguson, A.N., O’Neill, A.G., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2011; ISBN 9781613244548. [Google Scholar]
- Buravkova, L.B.; Rylova, Y.V.; Andreeva, E.R.; Kulikov, A.V.; Pogodina, M.V.; Zhivotovsky, B.; Gogvadze, V. Low ATP level is sufficient to maintain the uncommitted state of multipotent mesenchymal stem cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Gen. Subj. 2013, 1830, 4418–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svidchenko, E.; Solomatina, E.S.; Demina, T.S.; Uspenskii, S.A.; Surin, N.M.; Zelenetskii, A.N. Ultrasonic Dispersion and Stabilization of Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles within Sodium Hyaluronate Solutions and Materials Based on It. Nanobiotechnol. Rep. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa, Y.; Komotori, J.; Senna, M. Properties of Hydroxyapatite—Hyaluronic Acid Nano-Composite Sol and Its Interaction with Natural Bones and Collagen Fibers. Curr. Nanosci. 2012, 2, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Leong, K.-F.; Du, Z.; Chua, C.-K. The Design of Scaffolds for Use in Tissue Engineering. Part I. Traditional Factors. Tissue Eng. 2001, 7, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karageorgiou, V.; Kaplan, D. Porosity of 3D biomaterial scaffolds and osteogenesis. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 5474–5491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bružauskaitė, I.; Bironaitė, D.; Bagdonas, E.; Bernotienė, E. Scaffolds and cells for tissue regeneration: Different scaffold pore sizes—Different cell effects. Cytotechnology 2016, 68, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, L.N.; Crippa, G.E.; Lefebvre, L.-P.; De Oliveira, P.T.; Rosa, A.L.; Beloti, M.M. The influence of pore size on osteoblast phenotype expression in cultures grown on porous titanium. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 41, 1097–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boffito, M.; Bernardi, E.; Sartori, S.; Ciardelli, G.; Sassi, M.P. A mechanical characterization of polymer scaffolds and films at the macroscale and nanoscale. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2015, 103, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Lu, F.; Zou, Y.; Liu, J.; Rong, B.; Li, Z.; Dai, F.; Wu, D.; Lan, G. In situ reduction of silver nanoparticles by chitosan-l-glutamic acid/hyaluronic acid: Enhancing antimicrobial and wound-healing activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 173, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David-Raoudi, M.; Tranchepain, F.; Deschrevel, B.; Vincent, J.-C.; Bogdanowicz, P.; Boumediene, K.; Pujol, J.-P. Differential effects of hyaluronan and its fragments on fibroblasts: Relation to wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2008, 16, 274–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Khateeb, R.; Olszewska-Czyz, I. Biological molecules in dental applications: Hyaluronic acid as a companion biomaterial for diverse dental applications. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakhri, E.; Eslami, H.; Maroufi, P.; Pakdel, F.; Taghizadeh, S.; Ganbarov, K.; Yousefi, M.; Tanomand, A.; Yousefi, B.; Mahmoudi, S.; et al. Chitosan biomaterials application in dentistry. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 162, 956–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, S.D.; Abueva, C.; Kim, B.; Lee, B.T. Chitosan–hyaluronic acid polyelectrolyte complex scaffold crosslinked with genipin for immobilization and controlled release of BMP-2. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 115, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.; Chu, C.R.; Payne, K.A.; Marra, K.G. Injectable in situ forming biodegradable chitosan–hyaluronic acid based hydrogels for cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 2499–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, D.E.T.; Seedhom, B.B. The ‘Instantaneous’ Compressive Modulus of Human Articular Cartilage in Joints of the Lower Limb. Rheumatology 1999, 38, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeznach, O.; Kołbuk, D.; Sajkiewicz, P. Injectable hydrogels and nanocomposite hydrogels for cartilage regeneration. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2018, 106, 2762–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Kuang, R.; Liu, H.; Sun, D.; Mao, T.; Jiang, K.; Yang, X.; Watanabe, N.; Mayo, K.H.; et al. Injectable hydrogel-loaded nano-hydroxyapatite that improves bone regeneration and alveolar ridge promotion. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 116, 111158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florczyk, S.J.; Wang, K.; Jana, S.; Wood, D.L.; Sytsma, S.K.; Sham, J.G.; Kievit, F.M.; Zhang, M. Porous chitosan-hyaluronic acid scaffolds as a mimic of glioblastoma microenvironment ECM. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 10143–10150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, A.E.; Levengood, S.K.L.; Sun, J.; Chang, F.-C.; Zhang, M. Fabrication and Characterization of Chitosan-Hyaluronic Acid Scaffolds with Varying Stiffness for Glioblastoma Cell Culture. Adv. Health Mater. 2018, 7, e1800295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clover, J.; Gowen, M. Are MG-63 and HOS TE85 human osteosarcoma cell lines representative models of the osteoblastic phenotype? Bone 1994, 15, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, A.-M.; James, P.F.; Akbarzadeh, R.; Subramanian, A.; Flavin, C.; Oudadesse, H. Prospect of Stem Cells in Bone Tissue Engineering: A Review. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 6180487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thein-Han, W.W.; Misra, R.D.K. Biomimetic chitosan–nanohydroxyapatite composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 1182–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailaja, G.S.; Ramesh, P.; Kumary, T.V.; Varma, H.K. Human osteosarcoma cell adhesion behaviour on hydroxyapatite integrated chitosan–poly(acrylic acid) polyelectrolyte complex. Acta Biomater. 2006, 2, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).