Abstract
Cellulose is a natural, unbranched, and fibrous homopolymer that is a major component in several agroindustrial residues. The aim of this study was to extract cellulose from oat hulls and then to modify it using a green route to obtain esterified cellulose through reaction with organic acids employing the reactive extrusion process, which is a process that presents some advantages, including low effluent generation, short reaction times, and it is scalable for large scale use. Citric (CA) and succinic (SA) acids were employed as esterifying agents in different concentrations (0, 5, 12.5, and 20%). Modified cellulose samples were characterized by their degree of substitution (DS), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), X-ray diffraction (DRX), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), wettability, oil and water absorption capacities, and thermal stability. DS of modified samples ranged from 2.28 to 3.00, and FTIR results showed that the esterification occurred in all samples for both acids by observation of important bands at 1720 and 1737 cm−1 for samples modified with CA and SA, respectively. All modified samples presented increased hydrophobicity. The modification did not have an influence on the morphological structure or crystallinity pattern of all samples. This study proved to be possible to modify cellulose using a simple and ecofriendly process based on reactive extrusion with organic acids.
1. Introduction
Cellulose is one of the most abundant natural, renewable, and biodegradable polymers; it is an unbranched and fibrous homopolymer that can be obtained from plants or synthesized by bacteria. The cellulose chain consists of β-D-glucose units repetedly joined by β (1-4) glycosidic bonds, with three hydroxyl groups per monosaccharide unit [1,2,3], which makes cellulose an excellent platform for chemical modifications [4]. So, cellulose can be modified to be used in the cosmetic, pharmaceutic, and food industries and in agricultural systems, among others [5,6,7].
Agroindustrial residues can be considered interesting sources for cellulose extraction, and in the last few years, an increased interest in the obtainment of cellulose from these materials using different approaches was seen, which can be considered a promising alternative for the production of sustainable products at affordable prices to reduce the dependency on petroleum-based products [8]. The use of agroindustrial residues to obtain new products is inserted into the concept of biorefineries, meeting the vision of a sustainable economy using biological resources, maximizing benefits and profits through strategies to add value to the plant biomass chain [9,10].
Oat hull is a by-product from oat grain milling and represents 25 to 30% of oat grain weight, with approximately 28–35% of cellulose, 18–28% of hemicellulose, and 18–22% of lignin [4,11,12], being considered an interesting raw material for cellulose obtainment.
Modifications in the cellulose structure are largely studied to enhance its properties. Among all the possible modification types, esterification is one of the most reported approaches [13,14]. The esterified cellulose transfers from a hydrophilic to hydrophobic nature due to the introduction of hydrophobic aliphatic branches [15].
In the last few years, a great interest in green routes to obtain new materials from renewable sources, including modified cellulose, was seen. According to Liyanage et al. [16], the use of green technologies for the production of versatile materials can reduce carbon footprint. Organic acids such as citric or succinic acids gained attention as esterifying and crosslinking agents for carbohydrate polymers in many aspects, they are safe, inexpensive, UV resistant, and biocompatible multifunctional monomers that are listed in the generally regarded as safe (GRAS) category by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) [3,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20].
Citric acid and other polycarboxylic acids are described as efficient esterification and crosslinking agents for polysaccharides, such as cellulose. The reaction of cellulose with polycarboxylic acids occurs due to the attachment of the carboxylic group from acid via esterification with a cellulosic hydroxyl group, and a further reaction via esterification with another cellulosic hydroxyl group can produce a crosslink between cellulose chains [3,4,14,19,21]. Although the catalytic mechanism of cellulose esterification with organic acids is not completely elucidated, esterification catalyzed by α-hydroxy acids is proposed to proceed via a nucleophilic attack of the acylant by the hydroxyl groups of the α-hydroxy acid, followed by a second nucleophilic attack of the intermediate formed by the hydroxyl groups of cellulose [1,22].
According to Gil-Giraldo et al. [4], the reactive extrusion process is an efficient method for modifying cellulose, and it is considered an ecofriendly technological solution since the extruder is used as a reactor where chemical reactions such as esterification and crosslinking can be performed. Reactive extrusion combines the thermomechanical energy to promote the reaction between cellulose and organic acids in a single process without using other reagents. Additionally, reactive extrusion is a continuous process that has commercial viability, and it is easy to adapt to large industrial scales, offering short reaction times (2–3 min) [23,24].
The use of reactive extrusion to obtain esterified cellulose through reaction with organic acids is not fully exploited in the literature. The aim of this study was to extract cellulose from oat hulls and then to modify it using a green route to obtain esterified cellulose through a reaction with organic acids (citric and succinic acids) employing the reactive extrusion process.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The oat hull was acquired from a local oat processing industry (SL Alimentos, Mauá da Serra, PR, Brazil). The citric acid (CA) and succinic acid (SA) of analytical grades were purchased from Synthlab (Synthlab, Diadema, Brazil), like all other reagents and solvents.
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Extraction of the Cellulose from Oat Hulls
The extraction of the cellulose was performed following the process described by Marim et al. [25]. Oat hulls (10 g) were treated with 250 mL of peracetic acid (50% acetic acid, 38% hydrogen peroxide, and 12% distilled water). The suspensions were maintained on a mechanical stirrer with a controlled temperature of 60 °C for 24 h. After this procedure, the samples were filtered, washed with distilled water to reach pH 5–6, and dried at 35 °C for 24 h in an air circulation oven.
Cellulose and hemicellulose contents were determined by the Van Soest method [26]. Lignin contents were determined by the TAPPIT222 om-88 method [27].
2.2.2. Modification of Cellulose by Reactive Extrusion
The citric acid (CA) and succinic acid (SA) were used in different concentrations (0, 5.0, 12.5, and 20.0% g acid/100 g cellulose) as esterifying agents. CA or SA in different concentrations were dissolved in distilled water and mixed with the cellulose (100 g), resulting in a final moisture content of 32% (g water/100 g cellulose). Each mixture was slowly added to sealed plastic bags and equilibrated for 1 h before extrusion. A control sample was extruded without any reagent other than water, resulting in the same final moisture content of 32%. The reactive extrusion parameters were based on a previous study by Gil-Giraldo et al. [4]. All samples were extruded in a single screw extruder (AX Plastics, Diadema, SP, Brazil) with a screw diameter of 1.6 cm and a screw length/diameter ratio (L/D) of 40, with four heating zones and a matrix of 0.8 cm in diameter. The temperature in all zones was 100 °C, and the screw speed was 60 rpm. The modified cellulose was collected, placed in an oven, dried to constant weight at 45 °C, and grounded and sieved through an 80-mesh sieve. The samples were washed three times with absolute ethanol to remove the unreacted CA or SA, and finally, the washed samples were air-dried at 45 °C before being characterized. Cellulose samples prepared by reaction with CA were labeled CA5%, CA12.5%, and CA20% throughout the study, while samples prepared with SA were labeled SA5%, SA12.5%, and SA20% throughout the study.
2.2.3. Determination of the Degree of Substitution (DS)
The DS of the modified cellulose was determined using the method of Karnitiz et al. [28]. The carboxylic acid concentration (CCOOH) per gram of the modified cellulose was determined by retro titration using hydrochloride acid and sodium hydroxide. The DS was calculated according to the equation as follows: DS = [(CNaOH·VNaOH) − (4·CHCl·VHCl)]/Mm, where: CNaOH is the sodium hydroxide solution concentration (mmol/L), CHCl is the hydrochloric acid solution concentration (mmol/L), VNaOH is the sodium hydroxide volume (L), VHCL is the hydrochloric acid volume spent on the titration of sodium hydroxide unreacted (L), and Mm is the cellulose mass used (g).
2.2.4. Fourier Transform-Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
The pulverized and dried samples were mixed with potassium bromide and compressed into tablets. The FTIR analyses were carried out with a Shimadzu FTIR—8300 (Kyoto, Japan), which has a spectral resolution of 4 cm−1 and a spectral range of 4000–500 cm−1.
2.2.5. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
The crystallinity of each sample was investigated using XRD. The samples were finely powdered using an analytical mill (IKA basic 23), and the analysis was performed using a PANalytical X’Pert PRO MPD diffractometer (Almelo, The Netherlands) with copper Kα radiation (λ = 1.5418 Ǻ) under the operational conditions of 40 kV and 30 mA. All the assays were performed with a ramp rate of 1°/min. The relative crystallinity index (CI) was calculated as follows: CI (%) = [(I002 − Iam) /(I002)].100, where I002 is the intensity at 2θ = 22° and Iam is the amorphous intensity at 2θ = 18°.
2.2.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
SEM analyses were performed on the FEI Quanta 200 equipment (Hillsboro, OR, USA). Samples were incubated in an air circulation oven (Marconi MA 035, Piracicaba, SP, Brazil) at 60 °C for 3 h and then kept in desiccators containing anhydrous calcium chloride for 7 d. The dried samples were assembled for viewing on bronze stumps using double-sided tape. Afterward, the samples were covered with a thin layer of gold (40–50 nm), and an accelerated voltage of 20 kV was used for all samples.
2.2.7. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
DSC analyses were performed on a Shimadzu DSC 60 (Kyoto, Japan) calorimeter. Approximately 3.0 mg of each sample were placed in platinum containers and heated from 30 to 450 °C at a heating rate of 5 °C/min in a helium atmosphere.
2.2.8. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
TGA of the samples was performed using the Shimadzu TGA-50 (Kyoto, Japan) equipment. The scans were performed from room temperature up to 600 °C with a heating rate of 20 °C/min under a nitrogen flow of 20 mL/min.
2.2.9. Wettability
Samples were mixed into two different systems with two immiscible solvents with different density values: water (d: 1.000 g/cm−3) and dichloromethane (d: 1.335 g/cm−3) and water (d: 1.000 g/cm−3) and chloroform (d: 1.490 g/cm−3), allowing us to observe the affinity of each sample for each solvent [29].
2.2.10. Water Absorption Capacity (WAC) and Oil Absorption Capacity (OAC)
WAC and OAC were determined following the methodology described by Gil-Giraldo et al. [4]. Approximately 0.5 g of each sample (M0) and 15 mL of water (or soybean oil) (M1) were added to a centrifuge tube. Then, the samples were kept in a water bath for 30 min and centrifuged for 30 min at 9000 rpm (Hettich Centrifuge, Universal model 320R, Darmstadt, Germany). The non-adsorbed water (or soybean oil) (M2) was removed, and the water (or soybean oil) absorbed by the samples was estimated as the difference between M1 and M2. WAC was calculated as WAC (g/g) = (M1 − M2)/M0, and OAC was calculated as OAC (g/g) = (M1 − M2)/M0.
2.2.11. Statistical Analysis
Analyses of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey’s mean comparison test (p ≤ 0.05) were performed with the R program.
3. Results
Oat hull bleaching was performed with peracetic acid to obtain cellulose. Raw oat hull presented 26% cellulose, 30% hemicellulose, and 21% lignin, and these results are in agreement with other authors [4,11,30]. After bleaching with peracetic acid, the obtained sample presented a composition of 78% cellulose, 8% hemicellulose, and 3% lignin, and this sample was labeled as cellulose. The sample was employed in this study to obtain the modified samples by reactive extrusion with organic acids.
3.1. Degree of Substitution (DS)
Esterification implies the substitution of hydroxyl groups of cellulose by less polar ester groups, and the DS is indicative of the substitution level. DS can be defined as the average number of substituted hydroxyl groups per glucose unit, and it has a maximum value of 3 [1,22,31]. DS results of cellulose samples modified by reactive extrusion are shown in Table 1. It is possible to observe that the DS values increased with the increase of CA and SA concentration and that DS values were not affected by the type of acid employed. Ratanakamnuan et al. [31] reported similar DS values to those obtained in this study, their values ranged from 2.41 and 2.69 for cotton cellulose esterified with several fatty acids (C4 to C12) under microwave heating, and they stressed that shorter reaction times are required to obtain samples with higher DS when the microwave power increases.

Table 1.
Degree of substitution of all samples.
Hoang et al. [7] and Ji et al. [15] reported that in the esterification of cellulose with citric acid, the increased concentration of the acid enhances the interaction between carboxylic groups of citric acid and hydroxyl groups of cellulose.
Xin et al. [20] presented DS results ranging from 0.337 to 1.191 in cellulose succinates under a catalyze-free condition. Qin et al. [18] reported that cellulose succinates obtained by reaction with SA performed in a high-energy stirring ball mill presented higher degrees of substitution when subjected to higher SA concentrations.
3.2. Fourier-Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
The FTIR spectra of the cellulose, control sample and modified cellulose with CA and SA are shown in Figure 1. It is possible to see that all samples that were subjected to reactive extrusion with CA and SA presented a pronounced band located between 1720 and 1737 cm−1, which can be associated with the C=O stretching of carbonyl in the ester bonds, being an indication that esterification using CA and SA occurred. These results are similar to those presented by other authors [4,6,7,14,15,17,18,20,22], who also used CA or SA as esterifying agents for cellulose; these authors reported that bands between 1720 to 1750 cm−1 can be used to show the success of cellulose esterification.
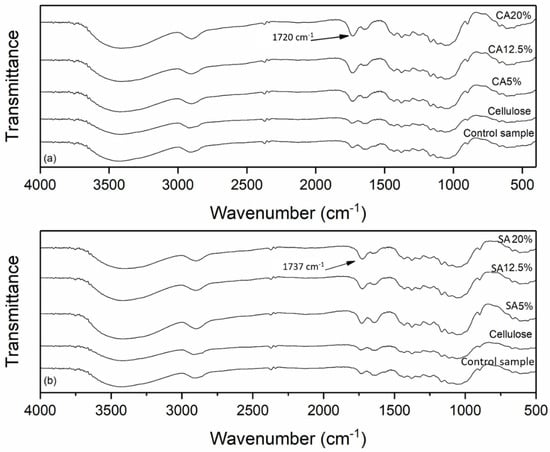
Figure 1.
FTIR spectra of cellulose, control sample, and modified cellulose with citric acid (a) and FTIR spectra of cellulose, control sample, and modified cellulose with succinic acid (b).
For the cellulose and control sample, this band appeared with lower intensity (Figure 1). Considering that cellulose was extracted from oat hulls, and it remained with 8% of hemicellulose, this band in the cellulose and control samples (extruded without organic acids) possibly corresponds to the acetyl or uronic groups of the hemicelluloses [25]. Gil-Giraldo et al. [4] reported that this band could also be explained by the thermomechanical treatment applied to cellulose during extrusion, being attributed to the C=O group from the opened terminal glucopyranose rings.
As observed in Figure 1, all samples presented a broad band near 3500 cm−1 that can be assigned to O-H stretching groups. The band at 2900 cm−1 appeared due to C-H stretching [4,6]. All the bands between 1057 and 1162 cm−1 correspond to C-O and C-O-C stretching vibration in cellulose [4,11,25].
3.3. X-ray Diffraction (XRD)
The X-ray diffractograms and relative crystallinity indexes (IC) of the cellulose, control sample, and modified cellulose with CA and SA are shown in Figure 2. It is possible to see that all samples presented characteristic peaks of cellulose type I, at 2θ = 16, 22, and 34° [4,11,18,31]. New peaks at 2θ = 26 and 32° were observed only for the SA20% sample, and these peaks are reported by other authors as typical peaks of SA [32], which possibly remained in the sample after modification.
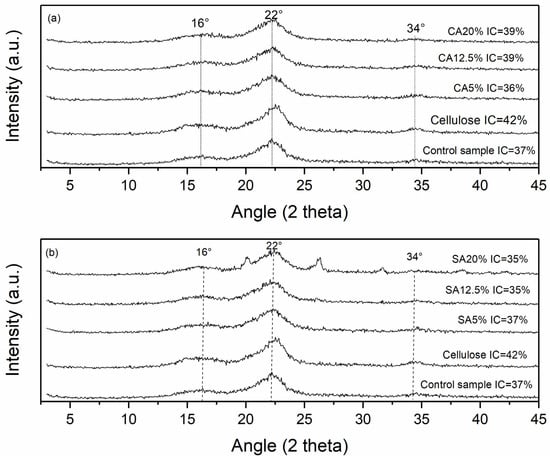
Figure 2.
X-ray diffractograms of cellulose, control sample, and modified cellulose with citric acid (a), and X-ray diffractograms of cellulose, control sample, and modified cellulose with succinic acid (b).
The extrusion process with CA and SA employed in this study did not affect the polymorph type of cellulose compared to the cellulose sample. Other authors that subjected cellulose extracted from oat hulls to modification by reactive extrusion also reported that this process did not affect the inherent crystalline structure of the extruded samples [4,11]. Ji et al. [15] reported that esterification of nanocellulose with CA has no influence on the position of peaks and no changes on the crystalline allomorph of the cellulose. Gil-Giraldo et al. [4] also reported that esterification with CA possibly occurred mainly at the cellulose surface, without affecting the inner crystalline structure. According to Qin et al. [18], chemical reagents are difficult to enter into the crystalline region of cellulose because of their stable structure.
The crystallinity index (CI) of cellulose was 42%, which is typical of a semicrystalline material, and a very close value (43%) was reported by Gil-Giraldo et al. [4] for cellulose from oat hull. The CI for all extruded samples (with and without reagent) slightly decreased, and the CI values ranged from 37 to 39% for samples modified with CA (Figure 2) and for 36 to 37% for samples modified with SA (Figure 2). During the reactive extrusion process, cellulose fibers were exposed to high temperatures and high shear forces; however, these processing conditions did not affect the crystallinity pattern of the modified samples. These results agreed with other authors that used reactive extrusion to esterify cellulose [4]. Qin et al. [18] reported a decrease in CI of cellulose esterified through a reaction with SA in a high-energy stirring ball mill. They attributed this decrease to the disruption of the intramolecular and intermolecular hydrogen bonds in cellulose, which effectively can destroy its crystalline structure.
3.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
Figure 3 show the SEM images of the oat hull, cellulose, and cellulose samples modified with citric acid 20% (CA20% sample) and succinic acid 20% (SA20% sample). It is possible to observe that raw oat hull presented a compact and uniform structure, with the fibers bundled with hemicellulose and lignin components, which are typical for lignocellulosic materials [4,6,25,33]. The extraction process with peracetic acid removed the external layer composed mainly of hemicellulose and lignin; as a result, the cellulose sample showed a different morphology, with long and individualized fibers [4,30,34].
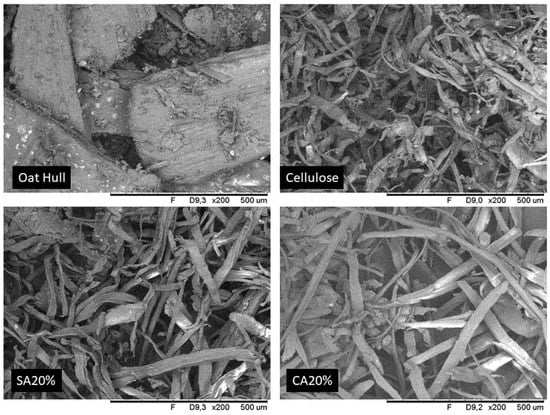
Figure 3.
SEM images of oat hull, cellulose, and cellulose modified with CA 20% and SA 20%.
Both CA and SA samples presented long and individualized fibers, showing no difference from the cellulose sample, and these results were consistent with XRD results, which showed that reactive extrusion with the organic acids did not affect the crystallinity pattern of cellulose. Gil-Giraldo et al. [4] subjected cellulose to reactive extrusion with CA employing a higher acid concentration (40%) and also reported that the surface morphology of the cellulosic fibers did not change. He et al. [14] also reported that the morphology of nanocellulose was not significantly affected by esterification, suggesting that only the surface of the cellulose was modified during reaction with citric acid. Cui et al. [17] reported a slight increase in roughness on the cellulose fiber surface after esterification with CA.
3.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
Figure 4 present the DSC curves of the cellulose, control sample, and modified cellulose with CA and SA. All samples showed an endothermic peak near 50 °C, which can be associated with water loss [4,21]. It is possible to observe that all samples showed an exothermic peak near 350 °C, which can be attributed to cellulose depolymerization. This event was also reported by other authors [4,35], and it can be observed that the esterification of cellulose by reactive extrusion did not affect the thermal stability observed from DSC curves.
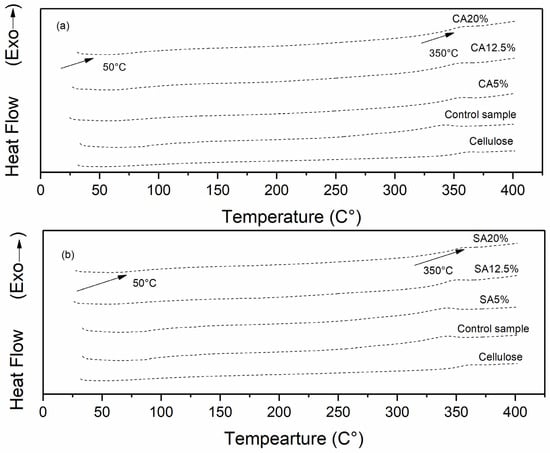
Figure 4.
DSC curves of cellulose, control sample, and cellulose modified with citric acid (a), and DSC curves of cellulose, control sample, and cellulose modified with succinic acid (b).
3.6. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
TGA and DTGA curves from the cellulose, control samples, and cellulose samples modified with CA and SA are shown in Figure 5 and Figure 6, respectively. All samples presented a small first degradation stage at 50–100 °C (Figure 5a and Figure 6a), which can be attributed to the loss of water from the samples [4,5,36].
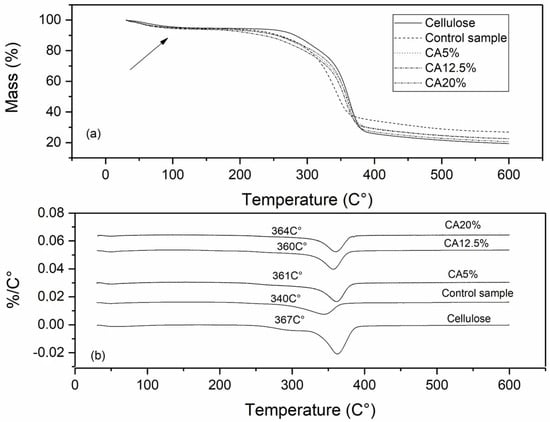
Figure 5.
TGA (a) and DTGA (b) curves of cellulose, control sample, and cellulose modified with citric acid.
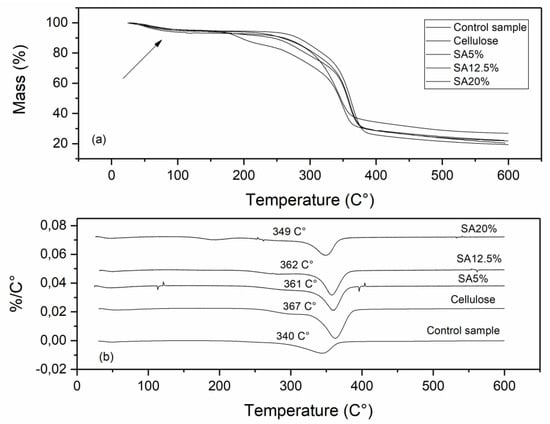
Figure 6.
TGA (a) and DTGA (b) curves of cellulose, control sample, and cellulose modified with succinic acid.
All samples started to decompose near 250 °C, and it can be observed that for unmodified cellulose, the temperature that corresponds to the maximum weight loss rate was 367 °C, and for all modified samples, this value decreased. Samples modified with CA had the maximum weight loss rate ranging from 360 to 364 °C, and for samples modified with SA these values ranged from 349 to 362 °C (Figure 5b and Figure 6b), which is an indication of a decrease in thermal stability of the modified samples. Ji et al. [15] also reported that the thermal stability of nanocellulose decreased after esterification with CA.
3.7. Wettability
Figure 7 and Figure 8 show the wettability results in the two tested systems, water/dichloromethane and water/chloroform, respectively. The wettability property is directly influenced by the polar and non-polar groups present on the molecule's surface [4,37,38].
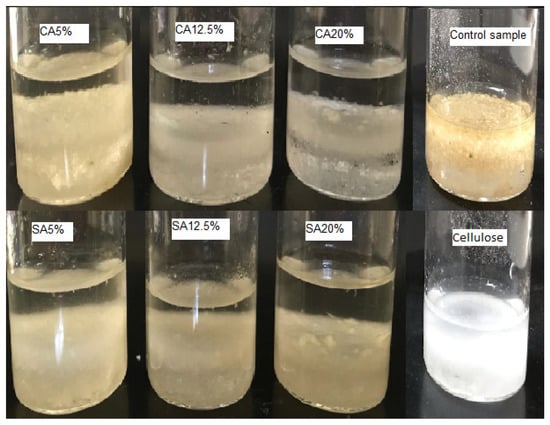

Figure 7.
Dispersion of cellulose, control sample, and modified cellulose with CA and SA in a water/dichloromethane system.
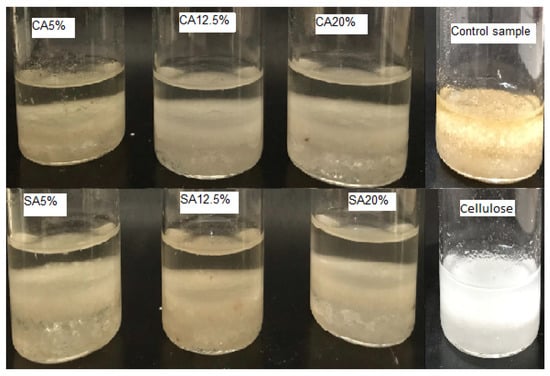
Figure 8.
Dispersion of cellulose, control sample, and modified cellulose with CA and SA in a water/chloroform system.
As can be seen in Figure 7 and Figure 8, the cellulose and control samples showed an affinity for water (polar solvent), while all the modified samples showed an affinity for dichloromethane and chloroform, which are non-polar solvents, indicating that the hydrophobic character of cellulose changed by chemical modification through reaction with CA and SA. According to Hubbe et al. [37], the substitution of polar hydroxyl groups in the cellulose surface for less polar groups can affect the wettability results. He et al. [14] reported increases in cellulose hydrophobicity upon esterification with CA. Gil-Giraldo et al. [4] also observed an increased affinity by non-polar solvents when cellulose was esterified by reactive extrusion with CA. According to Adewuyi and Pereira [39], the poor hydrophobicity of cellulose limits its application, and this limitation can be overcome by the surface modification of cellulose by replacing its hydroxyl groups, which can be an effective strategy to improve its hydrophobicity.
3.8. Water Absorption Capacity (WAC) and Oil Absorption Capacity (OAC)
WAC and OAC results are shown in Table 2. For the modified cellulose, WAC values ranged from 6.46 to 7.49 (g/g). When compared to cellulose (9.27 g/g) and the control sample (8.55 g/g), all the modified samples present significantly lower WAC values (Table 2). It is important to observe that the type of acid or the acid’s concentration did not significantly affect the WAC values of the modified samples.

Table 2.
Water absorption capacity and oil absorption capacity of samples.
From the OAC results (Table 2), it is possible to see that the cellulose sample presented the lowest OAC value (1.80 g/g), while the modified samples CA 12.5%, CA 20%, and SA 20% showed the highest values. It can also be observed that the increase of acid concentrations resulted in samples with higher OAC. This increase in hydrophobic capacity of the modified samples can be attributed to the decrease of free hydroxyl groups on the cellulose surface by reaction with CA and SA. Adewuyi and Pereira [39], in their study with modified cellulose through reaction with suberic acid, also reported the increase in hydrophobicity of modified samples, which was observed by the decrease in WAC and increase in OAC values. Gil-Giraldo et al. [4], in their study with modified cellulose with CA, also described lower WAC and higher OAC values for cellulose modified with CA.
4. Conclusions
All the results showed that it was possible to obtain cellulose samples with increased hydrophobicity after employing a reactive extrusion process to perform the esterification of cellulose with two organic acids, citric and succinic acid. FTIR confirmed the modification by the appearance of new bands at 1720 and 1737 cm−1 for samples modified with CA and SA, respectively. Regardless of the type of acid used, all modified samples showed higher affinity for non-polar solvents and increased oil absorption capacity.
When compared to the conventional processes employed to obtain esterified cellulose, reactive extrusion can be considered an ecofriendly and efficient alternative for cellulose modification, with some advantages such as low effluent generation, short reaction times, lower investment costs, the simplicity of operation due to its continuous nature, and additionally, it is scalable for large scale use.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.F.P. and S.M.; methodology, J.F.P., S.M. and B.M.M.; software, J.F.P.; formal analysis J.F.P. and S.M.; investigation, J.F.P., S.M. and B.M.M.; writing—original draft preparation, J.F.P. and S.M.; writing—review and editing, J.F.P. and S.M.; supervision, S.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by CAPES-DS (Brazil) with a grant for the postgraduate students.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the State University of Londrina facilities at the Multiuser Laboratories Center (CMLP-UEL FINEP), where X-ray, FT-IR, and microscopy analyses were performed.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Nguyen, D.T.; Pham, Q.T. A theoretical and experimental study on esterification of citric acid with the primary alcohols and the hydroxyl groups of cellulose chain (n = 1–2) in parched condition. J. Chem. 2020, 8825456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raucci, M.; Alvarez-Perez, M.; Demitri, C.; Giugliano, D.; De Benedictis, V.; Sannino, A.; Ambrosio, L. Effect of citric acid crosslinking cellulose-based hydrogels on osteogenic differentiation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2015, 103A, 2045–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zainal, S.H.; Mohd, N.H.; Suhaili, N.; Anuar, F.H.; Lazim, A.M.; Othaman, R. Preparation of cellulose-based hydrogel: A review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 10, 935–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Giraldo, A.G.; Montovan, J.; Marim, B.M.; Kishima, J.O.F.; Mali, S. Surface modification of cellulose from oat hull with citric acid using ultrasonication and reactive extrusion assisted processes. Polysaccharides 2021, 2, 218–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capanema, N.S.V.; Mansur, A.A.P.; De Jesus, A.C.; Carvalho, S.M.; De Oliveira, L.C.; Mansur, H.S. Superabsorbent crosslinked carboxymethyl cellulose-PEG hydrogels for potential wound dressing applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 106, 1218–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.F.; Sun, R.C.; Zhang, A.P.; Ren, J.L.; Geng, Z.C. Structural and thermal characterization of sugarcane bagasse cellulose succinates prepared in ionic liquid. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 3040–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javanmard, Z.; Kouchaksaraei, M.T.; Hosseini, S.M.; Pandey, A.K. Assessment of anticipated performance index of some deciduous plant species under dust air pollution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 38987–38994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Prakash, P.; Rout, P.K.; Bhaladhare, S. Synthesis and characterization of superabsorbent cellulose-based hydrogel for agriculture application. Starch 2021, 73, 1900284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuin, V.G.; Ramin, L.Z. Green and sustainable separation of natural products from agro-industrial waste: Challenges, potentialities, and perspectives on emerging approaches. In Chemistry and Chemical Technologies in Waste Valorization. Topics in Current Chemistry Collections; Lin, C., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Bhowmick, G.; Sarmah, A.K.; Sen, R. Lignocellulosic biorefinery as a model for sustainable development of biofuels and value-added products. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 1144–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debiagi, F.; Faria-Tischer, P.C.S.; Mali, S. Nanofibrillated cellulose obtained from soybean hull using simple and eco-friendly processes based on reactive extrusion. Cellulose 2020, 27, 1975–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debiagi, F.; Faria-Tischer, P.C.S.; Mali, S. A Green approach based on reactive extrusion to produce nanofibrillated cellulose from oat hull. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2021, 12, 1051–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Cuadro, P.; Belt, T.; Kontturi, K.S.; Reza, M.; Kontturi, E.; Vuorinen, T.; Hughes, M. Cross-linking of cellulose and poly(ethylene glycol) with citric acid. React. Funct. Polym. 2015, 90, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Luzi, F.; Yang, W.; Xiao, Z.; Torre, L.; Xie, Y.; Puglia, D. Citric acid as green modifier for tuned hydrophilicity of surface modified cellulose and lignin nanoparticles. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 9966–9978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Xiang, Z.; Qi, H.; Han, T.; Pranovich, A.; Song, T. Strategy towards one-step preparation of carboxylic cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibrils with high yield, carboxylation and highly stable dispersibility using innocuous citric acid. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 1956–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liyanage, S.; Acharya, S.; Parajuli, P.; Shamshina, J.L.; Abidi, N. Production and surface modification of cellulose bioproducts. Polymers 2021, 13, 3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Ozaki, A.; Asoh, T.-A.; Uyama, H. Cellulose modified by citric acid reinforced poly(lactic acid) resin as fillers. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2020, 175, 109118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Zhou, J.; Huang, A.; Guan, J.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, Z.; Hu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, M.; Wu, J.; et al. A green technology for the synthesis of cellulose succinate for efficient adsorption of Cd(II) and Pb(II) ions. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 26817–26825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salihu, R.; Abd Razak, S.I.; Ahmad Zawawi, N.; Rafiq Abdul Kadir, M.; Izzah Ismail, N.; Jusoh, N.; Hasraf Mat Nayan, N. Citric acid: A green cross-linker of biomaterials for biomedical applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 146, 110271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, P.P.; Huang, Y.B.; Hse, C.Y.; Cheng, H.; Huang, C.; Pan, H. Modification of cellulose with succinic anhydride in TBAA/DMSO mixed solvent under catalyst-free conditions. Materials 2017, 10, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demitri, C.; Del Sole, R.; Scalera, F.; Sannino, A.; Vasapollo, G.; Maffezzoli, A.; Nicolais, L. Novel superabsorbent cellulose-based hydrogels crosslinked with citric acid. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 110, 2453–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, I.; Olivito, F.; Tursi, A.; Algieri, V.; Beneduci, A.; Chidichimo, G.; Maiuolo, L.; Sicilia, E.; De Nino, A. Totally green cellulose conversion into bio-oil and cellulose citrate using molten citric acid in an open system: Synthesis, characterization and computational investigation of reaction mechanisms. J. R. Soc. Chem. 2020, 10, 34738–34751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formela, K.; Zedler, L.; Hejna, A.; Tercjak, A. Reactive extrusion of bio-based polymer blends and composites—Current trends and future developments. Express Polym. Lett. 2018, 12, 24–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moad, G. Chemical modification of starch by reactive extrusion. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 218–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marim, B.M.; Montovan, J.; Giraldo, G.A.G.; Mali, S. Environment-friendly process based on a combination of ultrasound and peracetic acid treatment to obtain cellulose from orange bagasse. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 96, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Soest, P.J. Symposium on factors influencing the voluntary intake of herbage by ruminants: Voluntary intake in relation to chemical composition and digestibility. J. Anim. Sci. 1965, 24, 834–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tappi Test Method T222 om-88, Acid-Insoluble Lignin in Wood and Pulp, in Tappi Test Methods; Tappi Press: Atlanta, GA, USA, 1999.
- Karnitz Júnior, O.; Gurgel, L.V.A.; Perin de Melo, J.C.; Botaro, V.R.; Melo, T.M.S.; Gil, R.P.F.; Gil, L.F. Adsorption of heavy metal ion from aqueous solution single metal solution by chemically modified sugarcane bagasse. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 1291–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Namazi, H.; Dadkhah, A. Convenient method for preparation of hydrophobically modified starch nanocrystals with using fatty acids. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 79, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschoal, G.B.; Muller, C.M.O.; Carvalho, G.M.; Tischer, C.A.; Mali, S. Isolation and characterization of nanofibrillated cellulose from oat hulls. Quím. Nova 2015, 38, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratanakamnuan, U.; Atong, D.; Aht-Ong, D. Cellulose esters from waste cotton fabric via conventional and microwave heating. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setyawan, D.; Oktavia, I.P.; Fariska, R.; Sari, R. Physicochemical characterization and in vitro dissolution test of quercetin-succinic acid co-crystals prepared using solvent evaporation. Turk. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 14, 280–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, E.; Deepa, B.; Pothan, L.A.; Jacob, M.; Thomas, S.; Cvelbar, U.; Anandjiwala, R. Extraction of nanocellulose fibrils from lignocellulosic fibres: A novel approach. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 1468–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agu, O.S.; Tabil, L.G.; Dumonceaux, T. Microwave-assisted alkali pre-treatment, densification and enzymatic saccharification of canola straw and oat hull. Bioengineering 2017, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Orozco, R.S.; Hernández, P.B.; Morales, G.R.; Núñez, F.U.; Villafuerte, J.O.; Lugo, V.L.; Ramírez, N.F.; Díaz, C.E.B.; Vázquez, P.C. Characterization of lignocellulosic fruit waste as an alternative feedstock for bioethanol production. BioResources 2014, 9, 1873–1885. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, C.; Tao, F.; Cui, Y. Cellulose-based film modified by succinic anhydride for the controlled release of domperidone. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. 2018, 11, 1233–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubbe, M.A.; Gardner, D.J.; Shen, W. Contact angle and wettability of cellulosic surfaces: A review of proposed mechanisms and test strategies. Bioresources 2015, 10, 8657–8749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Da Conceição, I.D.; Da Silva, L.R.C.; Alves, T.S.; Silva, H.S.E.; Barbosa, R.; De Sousa, R.R.M. Investigation of the wettability using contact angle measurements of green polyethylene flat films and expanded vermiculite clay treated by plasma. Mater. Res. 2019, 22, 20180918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adewuyi, A.; Pereira, F.V. Surface modification of cellulose isolated from Sesamun indicum underutilized seed: A means of enhancing cellulose hydrophobicity. J. Sci.-Adv. Mater. Dev. 2017, 2, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).