Evaluation of Adiponectin as a Metabolic Risk Indicator in the Panamanian Population
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Population and Sample
2.1.1. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
- Men and women between 18 and 60 years of age.
- Residents of the provinces of Panama or Panama Oeste.
- Willingness to participate voluntarily and sign informed consent.
- Availability for fasting blood collection and anthropometric evaluation.
- Pregnant women.
- Individuals with chronic inflammatory, autoimmune, or immunosuppressive diseases.
- Participants under corticosteroid or anti-inflammatory medication within the previous 15 days, to prevent pharmacological modulation of adiponectin levels.
- Individuals with a recent COVID-19 infection (within the previous 30 days), to avoid post-infectious inflammatory bias.
2.1.2. Selection of Cases and Controls
- Elevated triglycerides (≥150 mg/dL) or current treatment for hypertriglyceridemia
- Fasting glucose ≥ 100 mg/dL or use of hypoglycemic agents
- Systolic blood pressure ≥ 130 mmHg or diastolic ≥ 85 mmHg, or under antihypertensive treatment
- HDL < 40 mg/dL in men or <50 mg/dL in women
2.2. Biological Sample Collection
2.3. Adiponectin and Metabolic Biomarker Analysis
- Total Adiponectin Quantification:
- Lipid and Glycemic Profile:
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
3.1. Clinical and Biochemical Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Variation in Adiponectin Levels Concerning Sex
3.3. Relationship Between Adiponectin and Body Composition
3.4. Effect of Adiponectin on Triglyceride Levels
3.5. Adiponectin in Relation to Blood Pressure
3.6. Adiponectin and Glycemic Control
3.7. Effect of Adiponectin on Insulin Levels
3.8. Effect of Adiponectin on HDL Levels
3.9. Adiponectin and Metabolic Syndrome
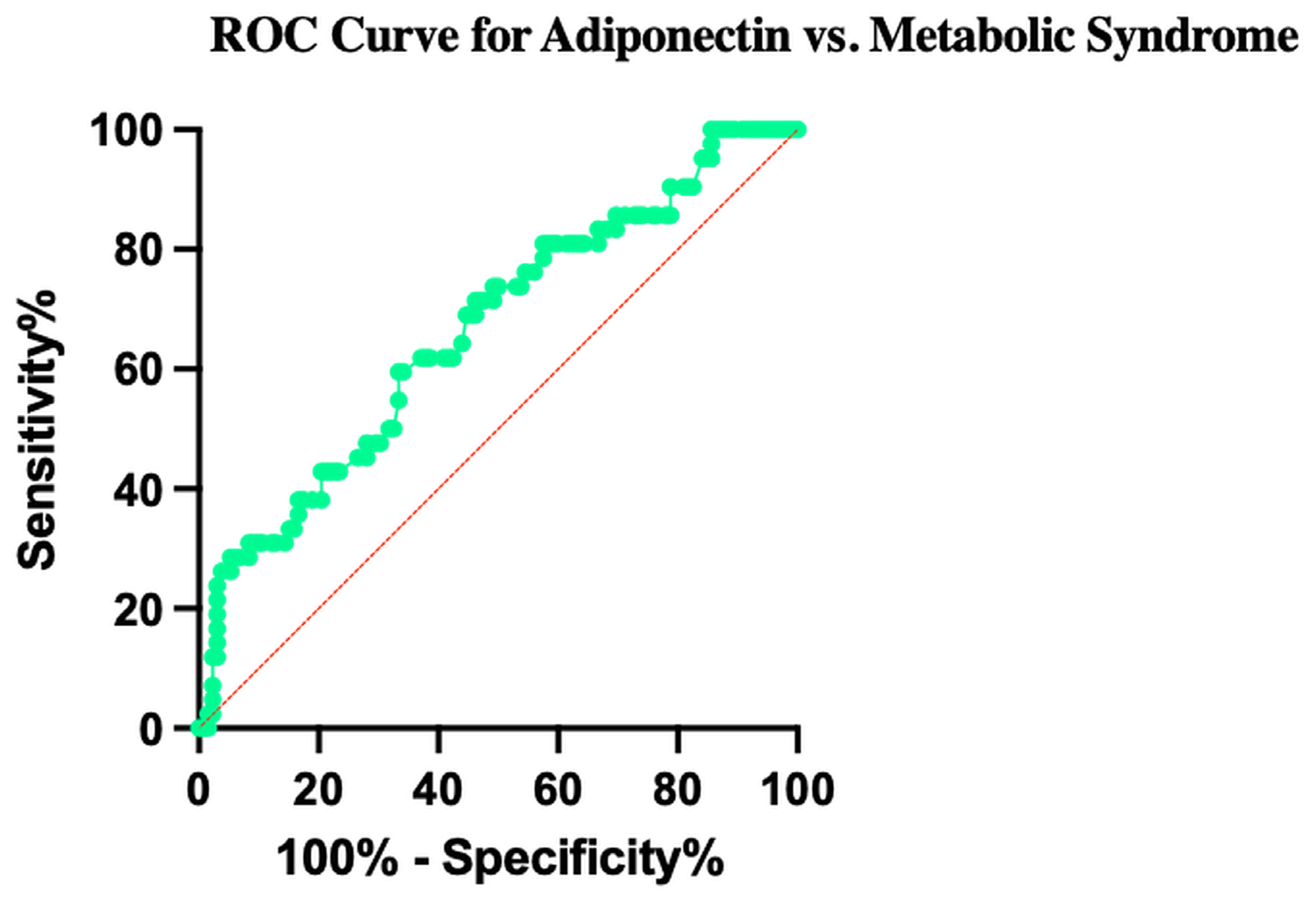
3.10. Diagnostic Accuracy of Adiponectin for Metabolic Syndrome
3.11. Independent Associations Between Serum Adiponectin and Metabolic Risk Factors
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALAD | Asociación Latinoamericana de Diabetes |
| AdipoQ | Adiponectin |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| BIA | Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CLIA | Chemiluminescence Immunoassay |
| HbA1c | Glycated Hemoglobin |
| HDL | High-Density Lipoprotein |
| HPLC | High-Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| MetS | Metabolic Syndrome |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor kappa B |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha |
| VLDL | Very-Low-Density Lipoprotein |
References
- Huang, P.L. A comprehensive definition for metabolic syndrome. DMM Dis. Models Mech. 2009, 2, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, B.K.; Sherpa, M.L.; Imran, M.; Mohammed, Y.; Jha, L.A.; Paudel, K.R.; Jha, S.K. Progress in Understanding Metabolic Syndrome and Knowledge of Its Complex Pathophysiology. Diabetology 2023, 4, 134–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, R.; Kumar, S.; Kant, R. An update on metabolic syndrome: Metabolic risk markers and adipokines in the development of metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2019, 13, 2409–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, H.; Roser, M. Obesity. Our World in Data. Oxford, United Kingdom: Global Change Data Lab. 2017. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/obesity (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Instituto Conmemorativo Gorgas de Estudios de la Salud. Sistema de información de la Encuesta Nacional de Salud de Panamá (ENSPA) 2019–2024. Panamá: Departamento de Investigación y Evaluación de Tecnología Sanitaria. 2024. Available online: https://www.gorgas.gob.pa/wp-content/uploads/external/SIGENSPA/Inicio.htm (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Berg, A.H.; Combs, T.P.; Du, X.; Brownlee, M.; Scherer, P.E. The adipocyte-secreted protein Acrp30 enhances hepatic insulin action. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Las Heras, N.; Valero-Muñoz, M.; Martín-Fernández, B.; Ballesteros, S.; López-Farré, A.; Ruiz-Roso, B.; Lahera, V. Molecular factors involved in the hypolipidemic- and insulin-sensitizing effects of a ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) extract in rats fed a high-fat diet. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 42, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cnop, M.; Havel, P.J.; Utzschneider, K.M.; Carr, D.B.; Sinha, M.K.; Boyko, E.J.; Retzlaff, B.M.; Knopp, R.H.; Brunzell, J.D.; Kahn, S.E. Relationship of adiponectin to body fat distribution, insulin sensitivity and plasma lipoproteins: Evidence for independent roles of age and sex. Diabetologia 2003, 46, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajvani, U.B.; Du, X.; Combs, T.P.; Berg, A.H.; Rajala, M.W.; Schulthess, T.; Engel, J.; Brownlee, M.; Scherer, P.E. Structure-Function Studies of the Adipocyte-secreted Hormone Acrp30/Adiponectin. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 9073–9085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waki, H.; Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Ito, Y.; Uchida, S.; Kita, S.; Hara, K.; Hada, Y.; Vasseur, F.; Froguel, P.; et al. Impaired Multimerization of Human Adiponectin Mutants Associated with Diabetes. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 40352–40363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Castro, C.; Fu, Y.; Chung, B.H.; Garvey, W.T. Adiponectin and the metabolic syndrome: Mechanisms mediating risk for metabolic and cardiovascular disease. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2007, 18, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, F.M.; Trujillo, M.E.; Hanif, W.; Barnett, A.H.; McTernan, P.G.; Scherer, P.E.; Kumar, S. Serum high molecular weight complex of adiponectin correlates better with glucose tolerance than total serum adiponectin in Indo-Asian males. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 1084–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadowaki, T.; Yamauchi, T.; Kubota, N.; Hara, K.; Ueki, K.; Tobe, K. Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in insulin resistance, diabetes, and the metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1784–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouchi, N.; Kihara, S.; Arita, Y.; Okamoto, Y.; Maeda, K.; Kuriyama, H.; Hotta, K.; Nishida, M.; Takahashi, M.; Muraguchi, M.; et al. Adiponectin, an adipocyte-derived plasma protein, inhibits endothelial NF-κB signaling through a cAMP-dependent pathway. Circulation 2000, 102, 1296–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, K.; Horikoshi, M.; Yamauchi, T.; Yago, H.; Miyazaki, O.; Ebinuma, H.; Imai, Y.; Nagai, R.; Kadowaki, T. Measurement of the high-molecular weight form of adiponectin in plasma is useful for the prediction of insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanai, H.; Yoshida, H. Beneficial effects of adiponectin on glucose and lipid metabolism and atherosclerotic progression: Mechanisms and perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Zou, C.; Van Der Westhuyzen, D.R.; Shao, J. Adiponectin reduces plasma triglyceride by increasing VLDL triglyceride catabolism. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1824–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.S.; Guo, S.X.; Ma, R.L.; Li, S.G.; Guo, H.; Zhang, J.Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, J.-M.; He, J.; Yan, Y.-Z.; et al. Association of Metabolic Syndrome with the Adiponectin to Homeostasis Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance Ratio. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 607364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liang, S.; Que, S.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, S.; Mardinoglu, A. Meta-analysis of adiponectin as a biomarker for the detection of metabolic syndrome. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, S.; Siddharth, S.; Sharma, D. Adiponectin, obesity, and cancer: Clash of the bigwigs in health and disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tylutka, A.; Morawin, B.; Walas, Ł.; Michałek, M.; Gwara, A.; Zembron-Lacny, A. Assessment of metabolic syndrome predictors in relation to inflammation and visceral fat tissue in older adults. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgary, S.; SamsamShariat, S.Z.; Ghorbani, A.; Keshvari, M.; Sahebkar, A.; Sarrafzadegan, N. Relationship between serum resistin concentrations with metabolic syndrome and its components in an Iranian population. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2015, 9, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Kokoeva, M.V.; Inouye, K.; Tzameli, I.; Yin, H.; Flier, J.S. TLR4 links innate immunity and fatty acid-induced insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 3015–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Quintero, A.E.; Cotero-de la Torre, I.I.; Bravo-Villagra, K.M.; Herrera-Salazar, A.; Picos-Cárdenas, V.J.; Morgan-Ortíz, F.; Trapero-Corona, I.M.; Muñoz-Valle, J.F. Estructura, señalización y regulación de la adiponectina en relación con la sensibilidad a la insulina y diabetes gestacional: Hallazgos clínicos y genéticos. Revmeduas 2022, 12, 345–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.S.; Lee, S.H.; Park, S.G.; Won, B.Y.; Chun, H.; Cho, D.Y.; Kim, M.-J.; Lee, J.E.; Haam, J.-H.; Han, K. Low levels of total and high-molecular-weight adiponectin may predict non-alcoholic fatty liver in Korean adults. Metabolism 2020, 103, 154026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Imachi, H.; Fukunaga, K.; Lyu, J.; Sato, S.; Saheki, T.; Ibata, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Japar, S.B.; Murao, K. HDL promotes adiponectin gene expression via the CAMKK/CAMKIV pathway. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2022, 68, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermsdorff, H.H.M.; Zulet, M.Á.; Bressan, J.; Martínez, J.A. Efecto de la dieta en la inflamación crónica y de bajo grado relacionada con la obesidad y el síndrome metabólico. Endocrinol. Nutr. 2008, 55, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gariballa, S.; Alkaabi, J.; Yasin, J.; Al Essa, A. Total adiponectin in overweight and obese subjects and its response to visceral fat loss. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2019, 19, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mester, P.; Räth, U.; Schmid, S.; Müller, M.; Buechler, C.; Pavel, V. Exploring the Relationship between Plasma Adiponectin, Gender, and Underlying Diseases in Severe Illness. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endukuru, C.K.; Gaur, G.S.; Yerrabelli, D.; Sahoo, J.; Vairappan, B. Cut-off values and clinical utility of surrogate markers for insulin resistance and beta-cell function to identify metabolic syndrome and its components among southern indian adults. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2020, 29, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Sun, Q.; Chen, W.; Gao, Y.; Ye, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, T.; Gao, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y. New advances of adiponectin in regulating obesity and related metabolic syndromes. J. Pharm. Anal. 2024, 14, 100913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Zuo, F.; Zhao, J.; Nian, X.; Shi, L.; Xu, Y.; Huang, J.; Kazumi, T.; Wu, B. Relationships of adiponectin to regional adiposity, insulin sensitivity, serum lipids, and inflammatory markers in sedentary and endurance-trained Japanese young women. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1097034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langkamp, M.; Pridzun, P.; Böttner, A.; Kiess, W.; Thiery, J.; Kratzsch, J. Reference intervals for adiponectin levels in human serum. In Proceedings of the DGKL Annual Meeting, Jena, Germany, 1–4 October 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Koh, S.B.; Yoon, J.; Kim, J.Y.; Yoo, B.S.; Lee, S.H.; Park, J.K.; Choe, K.-H. Relationships between serum adiponectin with metabolic syndrome and components of metabolic syndrome in non-diabetic Koreans: ARIRANG Study. Yonsei Med. J. 2011, 52, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Hu, C.; Yu, H.; Sun, L.; Chen, Z. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Plasma Adiponectin Deficiency: A Cross-Sectional Study in a Physical Examination Cohort from Southwest China. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2025, 18, 2945–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, N.; Auger, K.; Jialal, I. Biochemistry, Adiponectin; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilar-Salinas, C.A.; García, E.; Robles, L.; Riaño, D.; Ruiz-Gomez, D.G.; García-Ulloa, A.C.; Melgarejo, M.A.; Zamora, M.; Guillen-Pineda, L.E.; Mehta, R.; et al. High adiponectin concentrations are associated with the metabolically healthy obese phenotype. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 4075–4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparrenberger, K.; Cureau, F.V.; Teló, G.H.; Schaan, B.D. Adiponectin levels in Brazilian adolescents: Distribution and associated factors in ERICA survey. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 479, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoramipour, K.; Chamari, K.; Hekmatikar, A.A.; Ziyaiyan, A.; Taherkhani, S.; Elguindy, N.M.; Bragazzi, N.L. Adiponectin: Structure, physiological functions, role in diseases, and effects of nutrition. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.; Shao, J. Adiponectin and lipid metabolism in skeletal muscle. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2012, 2, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.S.; Lee, G.H.; Kim, D.; Lee, K.R.; Hur, M. Association of Serum Adiponectin Biomarker with Metabolic Syndrome Components in Koreans with Extremely High HDL Cholesterol Levels in General Health Checkup. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Yang, S.; Xiao, H.; Wang, M.; Ye, J.; Cao, L.; Sun, G. Role of Adiponectin in Cardiovascular Diseases Related to Glucose and Lipid Metabolism Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, N.; Gao, P.; Kondapally Seshasai, S.R.; Gobin, R.; Kaptoge, S.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Ingelsson, E.; Lawlor, D.A.; Selvin, E.; Stampfer, M.; et al. Diabetes mellitus, fasting blood glucose concentration, and risk of vascular disease: A collaborative meta-analysis of 102 prospective studies. Lancet 2010, 375, 2215–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; McClung, J.A.; Abraham, N.G. Adiponectin: A Mediator of Obesity, Insulin Resistance, Diabetes, and the Metabolic Syndrome. In Translational Research in Coronary Artery Disease: Pathophysiology to Treatment; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, J.J.M. Papel de la adiponectina en obesidad y diabetes tipo 2 Role of adiponectine on obesity and diabetes type 2. Med. Interna Méx. 2019, 35, 389–396. [Google Scholar]
- Cunha, W.R.; Gaspar, I.C.; de Souza, B.C.; Martins, B.D.L.; de Miranda, J.A.; Lanna, C.M.M.; Tanus-Santos, J.E.; Lacchini, R.; Belo, V.d.A. High molecular weight adiponectin as a biomarker of hypertension in children and adolescents with obesity. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2023, 182, 2925–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| No MetS (233 Control) | MetS (77 Cases) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Participants (n, %) | 233 (75%) | 77 (25%) | |
| Male | 100 | 34 | |
| Female | 133 | 43 | |
| Age (years) | 37.08 ± 11.53 | 46.86 ± 9.73 | <0.0001 |
| Adiponectin (µg/mL) | 9.53 ± 3.31 | 7.75 ± 2.58 | <0.0001 |
| Insulin (µU/mL) | 14.28 ± 7.16 | 22.24 ± 11.06 | <0.0001 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 89.57 ± 9.31 | 135.2 ± 75.84 | <0.0001 |
| HbA1c (%) | 5.55 ± 0.48 | 7.22 ± 2.29 | <0.0001 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 99.87 ± 58.66 | 194.14 ± 166.15 | 0.0294 |
| Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 193.68 ± 42.89 | 205.01 ± 42.43 | 0.0449 |
| Visceral Fat (%) | 7.57 ± 4.23 | 12.96 ± 6.06 | <0.0001 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 90.24 ± 14.29 | 108.22 ± 15.09 | 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garrido, O.S.; Adames, X.H.; Torres-Atencio, I.; De Ycaza, A.E.; Arce, M.F.P.; Espinosa, A.T.; Arteaga, G. Evaluation of Adiponectin as a Metabolic Risk Indicator in the Panamanian Population. Obesities 2025, 5, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5040081
Garrido OS, Adames XH, Torres-Atencio I, De Ycaza AE, Arce MFP, Espinosa AT, Arteaga G. Evaluation of Adiponectin as a Metabolic Risk Indicator in the Panamanian Population. Obesities. 2025; 5(4):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5040081
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarrido, Orlando Serrano, Xenia Hernandez Adames, Ivonne Torres-Atencio, Ana Espinosa De Ycaza, Maria Fabiana Piran Arce, Ana Tejada Espinosa, and Griselda Arteaga. 2025. "Evaluation of Adiponectin as a Metabolic Risk Indicator in the Panamanian Population" Obesities 5, no. 4: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5040081
APA StyleGarrido, O. S., Adames, X. H., Torres-Atencio, I., De Ycaza, A. E., Arce, M. F. P., Espinosa, A. T., & Arteaga, G. (2025). Evaluation of Adiponectin as a Metabolic Risk Indicator in the Panamanian Population. Obesities, 5(4), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5040081






