The Combined Effect of the Mediterranean Diet and Physical Activity on the Components of Metabolic Syndrome in Adults: A Systematic Review of Randomised Controlled Trials
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Physical Activity
1.2. Mediterranean Diet
1.3. Metabolic Syndrome
1.4. Impact of Physical Activity and the Mediterranean Diet on Metabolic Syndrome
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Information Sources and Search Strategies
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction Process
2.4. Methodological Quality Assessment
3. Presentation of Results
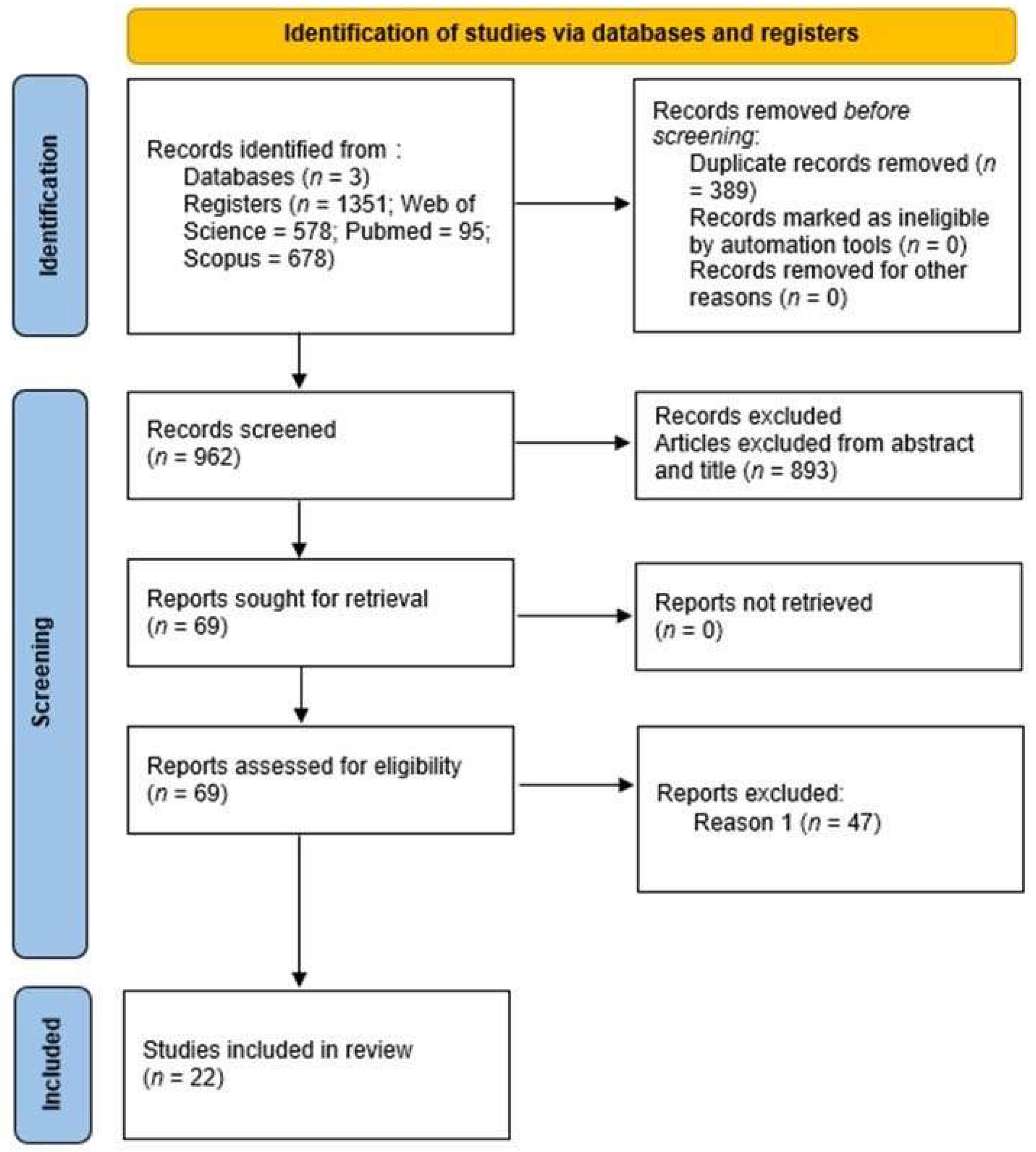
3.1. Selection of Studies
3.2. Studies Characteristics
3.2.1. Origin
3.2.2. Participants
3.2.3. Interventions
Mediterranean Diet
Physical Activity
Behavioural Support
3.3. Duration, Frequency, and Timing of Interventions
Variables Assessed
4. Results
4.1. Body Weight
4.2. Body Mass Index
4.3. Waist Circumference
4.4. Body Composition
4.5. Blood Pressure
4.6. Blood Glucose and Insulin
4.7. Lipid Profile (Total Cholesterol, Hdl, Ldl and Triglycerides)
5. Discussion
5.1. Behavioural Support
5.2. Waist Circumference
5.3. Body Mass Index
5.4. Blood Pressure
5.5. HDL and LDL
5.6. Blood Glucose
5.7. Triglycerides
5.8. Strengths
5.9. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PA | Physical Activity |
| ALT | Alanine Aminotransferase |
| AST | Aspartate Aminotransferase |
| MD | Mediterranean Diet |
| HDL | High-Density lipoprotein |
| HIIT | High-intensity Interval Training |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| LDL | Low-Density lipoprotein |
| METS | Metabolic Syndrome |
| TG | Triglycerides |
References
- World Health Organization. Guidelines on Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour: At a Glance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bull, F.C.; Al-Ansari, S.S.; Biddle, S.; Borodulin, K.; Buman, M.P.; Cardon, G.; Carty, C.; Chaput, J.-P.; Chastin, S.; Chou, R.; et al. World Health Organization 2020 Guidelines on Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Martínez, P.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Athyros, V.G.; Bullo, M.; Couture, P.; Covas, M.I.; de Koning, L.; Delgado-Lista, J.; Díaz-López, A.; Drevon, C.A.; et al. Lifestyle Recommendations for the Prevention and Management of Metabolic Syndrome: An International Panel Recommendation. Nutr. Rev. 2017, 75, 307–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chomiuk, T.; Niezgoda, N.; Mamcarz, A.; Śliż, D. Physical Activity in Metabolic Syndrome. Front. Physiol. 2024, 15, 1365761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finicelli, M.; Di Salle, A.; Galderisi, U.; Peluso, G. The Mediterranean Diet: An Update of the Clinical Trials. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonekamp, N.E.; Visseren, F.L.J.; Cramer, M.J.; Dorresteijn, J.A.N.; van der Meer, M.G.; Ruigrok, Y.M.; van Sloten, T.T.; Teraa, M.; Geleijnse, J.M.; Koopal, C. Long-Term Lifestyle Change and Risk of Mortality and Type 2 Diabetes in Patients with Cardiovascular Disease. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2024, 31, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-González, M.A.; Gea, A.; Ruiz-Canela, M. The Mediterranean Diet and Cardiovascular Health. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 779–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Alvarez, I.; Zazpe, I.; Pérez de Rojas, J.; Bes-Rastrollo, M.; Ruiz-Canela, M.; Fernandez-Montero, A.; Hidalgo-Santamaría, M.; Martínez-González, M.A. Mediterranean Diet, Physical Activity and Their Combined Effect on All-Cause Mortality: The Seguimiento Universidad de Navarra (SUN) Cohort. Prev. Med. 2018, 106, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP). Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) Final Report. Circulation 2002, 106, 3143–3421. [Google Scholar]
- Castro-Barquero, S.; Ruiz-León, A.M.; Sierra-Pérez, M.; Estruch, R.; Casas, R. Dietary Strategies for Metabolic Syndrome: A Comprehensive Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhondge, R.H.; Agrawal, S.; Patil, R.; Kadu, A.; Kothari, M. A Comprehensive Review of Metabolic Syndrome and Its Role in Cardiovascular Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Mechanisms, Risk Factors, and Management. Cureus 2024, 16, e67428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z. The Metabolic Syndrome. Lancet 2005, 365, 1415–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blüher, M. Obesity: Global Epidemiology and Pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahed, G.; Aoun, L.; Bou Zerdan, M.; Allam, S.; Bou Zerdan, M.; Bouferraa, Y.; Assi, H.I. Metabolic Syndrome: Updates on Pathophysiology and Management in 2021. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villamil-Parra, W.; Moscoso-Loaiza, L. Effects of Physical Exercise on Irisin and BDNF Concentrations, and Their Relationship with Cardiometabolic and Mental Health of Individuals with Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review. Exp. Gerontol. 2024, 198, 112640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saklayen, M.G. The Global Epidemic of the Metabolic Syndrome. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2018, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricò, D.; Moriconi, D.; Berta, R.; Baldi, S.; Quinones-Galvan, A.; Guiducci, L.; Taddei, S.; Mari, A.; Nannipieri, M. Effects of Low-Carbohydrate versus Mediterranean Diets on Weight Loss, Glucose Metabolism, Insulin Kinetics and β-Cell Function in Morbidly Obese Individuals. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, K.S.; Chang, Y.-H.; Yang, C.-T.; Chou, C.-K.; Ou, H.-T.; Kuo, S. Longitudinal Economic Burden of Incident Complications among Metabolic Syndrome Populations. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricardo, S.J.; Araujo, M.Y.C.; Santos, L.L.D.; Romanzini, M.; Fernandes, R.A.; Turi-Lynch, B.C.; Codogno, J.S. Burden of Metabolic Syndrome on Primary Healthcare Costs among Older Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study. Sao Paulo Med. J. 2024, 142, e2023215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guasch-Ferré, M.; Willett, W.C. The Mediterranean Diet and Health: A Comprehensive Overview. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 290, 549–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiris, C.L.; Gallagher, A.; Taylor, N.F.; McLean, S. Behavior Change Techniques Improve Adherence to Physical Activity Recommendations for Adults with Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review. Patient Prefer. Adherence 2023, 17, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greaves, C.J.; Sheppard, K.E.; Abraham, C.; Hardeman, W.; Roden, M.; Evans, P.H.; Schwarz, P.; IMAGE Study Group. Systematic Review of Reviews of Intervention Components Associated with Increased Effectiveness in Dietary and Physical Activity Interventions. BMC Public Health 2011, 11, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkman, N.D.; Sheridan, S.L.; Donahue, K.E.; Halpern, D.J.; Viera, A.; Crotty, K.; Holland, A.; Brasure, M.; Lohr, K.N.; Harden, E.; et al. Health Literacy Interventions and Outcomes: An Updated Systematic Review; Evidence Report/Technology Assessment Number 199; Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Rockville, MD, USA, 2011; pp. 1–941.
- Malakou, E.; Linardakis, M.; Armstrong, M.E.G.; Zannidi, D.; Foster, C.; Johnson, L.; Papadaki, A. The Combined Effect of Promoting the Mediterranean Diet and Physical Activity on Metabolic Risk Factors in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Rodríguez, A.; Cuestas-Calero, B.J.; Martínez-Olcina, M.; Marcos-Pardo, P.J. Benefits of Adding an Aquatic Resistance Interval Training to a Nutritional Education on Body Composition, Body Image Perception and Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet in Older Women. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineda-Juárez, J.A.; Lozada-Mellado, M.; Hinojosa-Azaola, A.; García-Morales, J.M.; Ogata-Medel, M.; Llorente, L.; Alcocer-Varela, J.; Orea-Tejeda, A.; Martín-Nares, E.; Castillo-Martínez, L. Changes in Hand Grip Strength and Body Weight after a Dynamic Exercise Program and Mediterranean Diet in Women with Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Physiother. Theory Pract. 2022, 38, 504–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Gavilán, J.F.; Atzeni, A.; Babio, N.; Liang, L.; Belzer, C.; Vioque, J.; Corella, D.; Fitó, M.; Vidal, J.; Moreno-Indias, I.; et al. Effect of 1-Year Lifestyle Intervention with Energy-Reduced Mediterranean Diet and Physical Activity Promotion on the Gut Metabolome and Microbiota: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2024, 119, 1143–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montemayor, S.; Bouzas, C.; Mascaró, C.M.; Casares, M.; Llompart, I.; Abete, I.; Angullo-Martinez, E.; Zulet, M.Á.; Martínez, J.A.; Tur, J.A. Effect of Dietary and Lifestyle Interventions on the Amelioration of NAFLD in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome: The FLIPAN Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabiee, M.; Daryanoosh, F.; Salesi, M.; Tahmasebi, R.; Koushkie, M. The Effect of Eight Weeks of Mediterranean Diet and High-Intensity Interval Training on Body Composition in Obese and Overweight Premenopausal Women. Int. J. Nutr. Sci. 2023, 8, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tussing-Humphreys, L.; Lamar, M.; McLeod, A.; Schiffer, L.; Blumstein, L.; Dakers, R.; Karstens, A.; Hemphill, N.O.N.; Strahan, D.; Siegel, L.; et al. Effect of Mediterranean Diet and Mediterranean Diet plus Calorie Restriction on Cognition, Lifestyle, and Cardiometabolic Health: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Prev. Med. Rep. 2022, 29, 101955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavić, E.; Hadžiabdić, M.O.; Mucalo, I.; Martinis, I.; Romić, Ž.; Božikov, V.; Rahelić, D. Effect of the Mediterranean Diet in Combination with Exercise on Metabolic Syndrome Parameters: 1-Year Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2019, 89, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rumbo-Rodríguez, L.; Zaragoza-Martí, A.; Sánchez-SanSegundo, M.; Ferrer-Cascales, R.; Laguna-Pérez, A.; Hurtado-Sánchez, J.A. Effectiveness of a Two-Year Multicomponent Intervention for the Treatment of Overweight and Obesity in Older People. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, H.; Cárdenas-Fuentes, G.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Corella, D.; Vioque, J.; Romaguera, D.; Alfredo Martínez, J.; Tinahones, F.J.; Miranda, J.L.; Estruch, R.; et al. Effectiveness of the Physical Activity Intervention Program in the PREDIMED-Plus Study: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2018, 15, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monserrat-Mesquida, M.; Quetglas-Llabrés, M.; Bouzas, C.; García, S.; Mateos, D.; Gómez, C.; Gámez, J.M.; Poulsen, H.E.; Tur, J.A.; Sureda, A. Effects of 2-Year Nutritional and Lifestyle Intervention on Oxidative and Inflammatory Statuses in Individuals of 55 Years of Age and over at High Cardiovascular Risk. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panizza, C.E.; Lim, U.; Yonemori, K.M.; Cassel, K.D.; Wilkens, L.R.; Harvie, M.N.; Maskarinec, G.; Delp, E.J.; Lampe, J.W.; Shepherd, J.A.; et al. Effects of Intermittent Energy Restriction Combined with a Mediterranean Diet on Reducing Visceral Adiposity: A Randomized Active Comparator Pilot Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ficarra, S.; Di Raimondo, D.; Navarra, G.A.; Izadi, M.; Amato, A.; Macaluso, F.P.; Proia, P.; Musiari, G.; Buscemi, C.; Barile, A.M.; et al. Effects of Mediterranean Diet Combined with CrossFit Training on Trained Adults’ Performance and Body Composition. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, F.; Tarsitano, M.G.; Cosco, L.F.; Quinzi, F.; Folino, K.; Spadafora, M.; Afzal, M.; Segura-Garcia, C.; Maurotti, S.; Pujia, R.; et al. The Effects of Online Home-Based Pilates Combined with Diet on Body Composition in Women Affected by Obesity: A Preliminary Study. Nutrients 2024, 16, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monsalves-Álvarez, M.; Jiménez, T.; Bunout, D.; Barrera, G.; Hirsch, S.; Sepúlveda-Guzman, C.; Silva, C.; Rodriguez, J.M.; Troncoso, R.; de la Maza, M.P. High-Intensity Interval Training Prevents Muscle Mass Loss in Overweight Chilean Young Adults during a Hypocaloric-Mediterranean Diet: A Randomized Trial. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1181436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, A.R.; Pais, S.; Marreiros, A.; Correia, M. Impact of a Mediterranean-Inspired Diet on Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candás-Estébanez, B.; Fernández-Cidón, B.; Corbella, E.; Tebé, C.; Fanlo-Maresma, M.; Esteve-Luque, V.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Fitó, M.; Riera-Mestre, A.; Ros, E.; et al. The Impact of the Mediterranean Diet and Lifestyle Intervention on Lipoprotein Subclass Profiles among Metabolic Syndrome Patients: Findings of a Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prats-Arimon, M.; Puig-Llobet, M.; Barceló-Peiró, O.; Ribot-Domènech, I.; Vilalta-Sererols, C.; Fontecha-Valero, B.; Heras-Ojeda, M.; Agüera, Z.; Lluch-Canut, T.; Moreno-Poyato, A.; et al. An Interdisciplinary Intervention Based on Prescription of Physical Activity, Diet, and Positive Mental Health to Promote Healthy Lifestyle in Patients with Obesity: A Randomized Control Trial. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldevila-Domenech, N.; Forcano, L.; Vintró-Alcaraz, C.; Cuenca-Royo, A.; Pintó, X.; Jiménez-Murcia, S.; García-Gavilán, J.F.; Nishi, S.K.; Babio, N.; Gomis-González, M.; et al. Interplay between Cognition and Weight Reduction in Individuals Following a Mediterranean Diet: Three-Year Follow-up of the PREDIMED-Plus Trial. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 5221–5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanllorente, A.; Soria-Florido, M.T.; Castañer, O.; Lassale, C.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Subirana, I.; Ros, E.; Corella, D.; Estruch, R.; et al. A Lifestyle Intervention with an Energy-Restricted Mediterranean Diet and Physical Activity Enhances HDL Function: A Substudy of the PREDIMED-Plus Randomized Controlled Trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 114, 1666–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Vega, K.A.; Castañer, O.; Sanllorente, A.; Lassale, C.; Ros, E.; Pintó, X.; Estruch, R.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Corella, D.; Alonso-Gómez, Á.M.; et al. Mediterranean Diet, Energy Restriction, Physical Activity, and Atherogenicity of Very-Low Density Lipoproteins: Findings from Two Randomized Controlled Trials. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2023, 67, e2200338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernando-Redondo, J.; Toloba, A.; Benaiges, D.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Martínez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Corella, D.; Estruch, R.; Tinahones, F.J.; Ros, E.; Goday, A.; et al. Mid- and Long-Term Changes in Satiety-Related Hormones, Lipid and Glucose Metabolism, and Inflammation after a Mediterranean Diet Intervention with the Goal of Losing Weight: A Randomized, Clinical Trial. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 950900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassapidou, M.; Tziomalos, K.; Lazaridou, S.; Pagkalos, I.; Papadimitriou, K.; Kokkinopoulou, A.; Tzotzas, T. The Nutrition Health Alliance (NutriHeAl) Study: A Randomized, Controlled, Nutritional Intervention Based on Mediterranean Diet in Greek Municipalities. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2020, 39, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estruch, R.; Ros, E.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Covas, M.-I.; Corella, D.; Arós, F.; Gómez-Gracia, E.; Ruiz-Gutiérrez, V.; Fiol, M.; Lapetra, J.; et al. Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease with a Mediterranean Diet Supplemented with Extra-Virgin Olive Oil or Nuts. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinu, M.; Pagliai, G.; Casini, A.; Sofi, F. Mediterranean Diet and Multiple Health Outcomes: An Umbrella Review of Meta-Analyses of Observational Studies and Randomised Trials. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 72, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach-Faig, A.; Berry, E.M.; Lairon, D.; Reguant, J.; Trichopoulou, A.; Dernini, S.; Medina, F.X.; Battino, M.; Belahsen, R.; Miranda, G.; et al. Mediterranean Diet Pyramid Today. Science and Cultural Updates. Public Health Nutr. 2011, 14, 2274–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trost, S.G.; Owen, N.; Bauman, A.E.; Sallis, J.F.; Brown, W. Correlates of Adults’ Participation in Physical Activity: Review and Update. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2002, 34, 1996–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delahanty, L.M.; Peyrot, M.; Shrader, P.J.; Williamson, D.A.; Meigs, J.B.; Nathan, D.M. Pretreatment, Psychological, and Behavioral Predictors of Weight Outcomes Among Lifestyle Intervention Participants in the Diabetes Prevention Program (DPP). Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utrila, R.T.; Alexandrino, W.G.d.S.; Westphal-Nardo, G.; Christinelli, H.C.B.; de Souza, A.A.; Candido, I.C.; Junior, N.N.; Molena-Fernandes, C.A. Efetividade de um programa multiprofissional de tratamento da obesidade durante a pandemia de COVID-19: Aplicação do Monitoramento Remoto da Enfermagem. Rev. Cienc. Act. Física UCM 2023, 24, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arouca, A.B.; Meirhaeghe, A.; Dallongeville, J.; Moreno, L.A.; Lourenço, G.J.; Marcos, A.; Huybrechts, I.; Manios, Y.; Lambrinou, C.-P.; Gottrand, F.; et al. Interplay between the Mediterranean Diet and C-Reactive Protein Genetic Polymorphisms towards Inflammation in Adolescents. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 1919–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, K.; Kastorini, C.-M.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Giugliano, D. Mediterranean Diet and Weight Loss: Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2011, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deehan, E.C.; Zhang, Z.; Riva, A.; Armet, A.M.; Perez-Muñoz, M.E.; Nguyen, N.K.; Krysa, J.A.; Seethaler, B.; Zhao, Y.-Y.; Cole, J.; et al. Elucidating the Role of the Gut Microbiota in the Physiological Effects of Dietary Fiber. Microbiome 2022, 10, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojo, O.; Ojo, O.O.; Zand, N.; Wang, X. The Effect of Dietary Fibre on Gut Microbiota, Lipid Profile, and Inflammatory Markers in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, E.A.; Lenzi, A.; Migliaccio, S. The Obesity of Bone. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. 2015, 6, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippou, C.D.; Thomopoulos, C.G.; Kouremeti, M.M.; Sotiropoulou, L.I.; Nihoyannopoulos, P.I.; Tousoulis, D.M.; Tsioufis, C.P. Mediterranean Diet and Blood Pressure Reduction in Adults with and without Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 3191–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Gil, J.F.; García-Hermoso, A.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Rodríguez-Artalejo, F. Mediterranean Diet and Cardiometabolic Biomarkers in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2024, 7, e2421976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grao-Cruces, E.; Varela, L.M.; Martin, M.E.; Bermudez, B.; la Paz, S.M.D. High-Density Lipoproteins and Mediterranean Diet: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kechagia, I.; Tsiampalis, T.; Damigou, E.; Barkas, F.; Anastasiou, G.; Kravvariti, E.; Liberopoulos, E.; Sfikakis, P.P.; Chrysohoou, C.; Tsioufis, C.; et al. Long-Term Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet Reduces 20-Year Diabetes Incidence: The ATTICA Cohort Study (2002–2022). Metabolites 2024, 14, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mambrini, S.P.; Grillo, A.; Colosimo, S.; Zarpellon, F.; Pozzi, G.; Furlan, D.; Amodeo, G.; Bertoli, S. Diet and Physical Exercise as Key Players to Tackle MASLD through Improvement of Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Flexibility. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1426551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, A.V.; Marti, K.M.; Marti, K.E.; Weisman, N.; Cardona, M.; Biello, D.M.; Pasupuleti, V.; Benites-Zapata, V.A.; Roman, Y.M.; Piscoya, A. Effect of Mediterranean Diets on Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Disease in Overweight and Obese Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Am. Nutr. Assoc. 2025, 44, 387–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, C.R.; Bryan, J.; Hodgson, J.M.; Woodman, R.; Murphy, K.J. A Mediterranean Diet Reduces F2-Isoprostanes and Triglycerides among Older Australian Men and Women after 6 Months. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 1348–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Search Number | Research Content |
|---|---|
| 1 | “Mediterranean diet” or “mediterranean lifestyle” or “meddiet score” or meddiet or “mediterranean style diet” or “mediterranean diet score” or “mediterranean diet index” or “mediterranean dietary pattern” AND Exercis* or training or physical activit* or sport* AND “metabolic risks” or “metabolic risk” or “metabolic markers” or “metabolic syndrome” or “cardiovascular disease” or CVD or “cardiovascular risk factors” or “cardiovascular disease risk” or “cardiovascular disease risks” or “vascular markers” or adiposity or overweight or obesity or obese or “body weight” or “body composition” or BMI or “body mass” or “fat mass” or “waist circumference” or weight or “blood pressure” or cholesterol or triglycerides AND Intervention* or “controlled trial” or “controlled trials” or rct* or “randomized controlled trial” or “randomized controlled trial” |
| Studies | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Martínez-Rodríguez et al. [25] | − | + | + | + | + | − |
| Pineda-Juárez et al. [26] | + | + | − | + | + | − |
| García-Gavilán et al. [27] | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Montemayor et al. [28] | − | + | + | + | + | − |
| Rabiee et al. [29] | x | − | − | + | + | x |
| Tussing-Humphreys et al. [30] | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Pavić et al. [31] | − | + | − | + | + | − |
| Rumbo-Rodríguez et al. [32] | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Schröder et al. [33] | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Monserrat-Mesquida et al. [34] | + | + | + | + | + | + |
| Panizza et al. [35] | + | − | + | + | + | − |
| Ficarra et al. [36] | − | x | + | + | − | x |
| Greco et al. [37] | − | x | + | + | − | x |
| Monsalves-Álvarez et al. [38] | + | − | + | + | + | − |
| Barbosa et al. [39] | + | − | + | + | + | − |
| Candás-Estébanez et al. [40] | − | x | + | + | − | x |
| Prats-Arimon et al. [41] | − | x | − | − | − | x |
| Soldevila-Domenech et al. [42] | + | x | + | + | + | x |
| Sanllorente et al. [43] | + | x | + | + | + | x |
| Pérez-Veja et al. [44] | + | x | + | + | + | x |
| Hernando-Redondo et al. [45] | − | x | + | + | − | x |
| Hassapidou et al. [46] | + | − | x | − | x | x |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Teixeira, L.; Monteiro, D.; Matos, R.; Antunes, R.; Jacinto, M. The Combined Effect of the Mediterranean Diet and Physical Activity on the Components of Metabolic Syndrome in Adults: A Systematic Review of Randomised Controlled Trials. Obesities 2025, 5, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5040068
Teixeira L, Monteiro D, Matos R, Antunes R, Jacinto M. The Combined Effect of the Mediterranean Diet and Physical Activity on the Components of Metabolic Syndrome in Adults: A Systematic Review of Randomised Controlled Trials. Obesities. 2025; 5(4):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5040068
Chicago/Turabian StyleTeixeira, Luiza, Diogo Monteiro, Rui Matos, Raúl Antunes, and Miguel Jacinto. 2025. "The Combined Effect of the Mediterranean Diet and Physical Activity on the Components of Metabolic Syndrome in Adults: A Systematic Review of Randomised Controlled Trials" Obesities 5, no. 4: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5040068
APA StyleTeixeira, L., Monteiro, D., Matos, R., Antunes, R., & Jacinto, M. (2025). The Combined Effect of the Mediterranean Diet and Physical Activity on the Components of Metabolic Syndrome in Adults: A Systematic Review of Randomised Controlled Trials. Obesities, 5(4), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5040068






