Cross-European Patterns of Obesity: Where Does Croatia Stand?—Descriptive Analysis of Waves 2015–2022 of the Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe (SHARE) Including Adults Aged Over 50
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Trends in Obesity Prevalence in Europe and Croatia
1.2. Association of Obesity with Health Risks
1.3. Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease (CVD)
1.4. Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
2.2. Nutritional Status Assesment
2.3. Basic Characteristics of the Population
2.4. Statistical Analyses
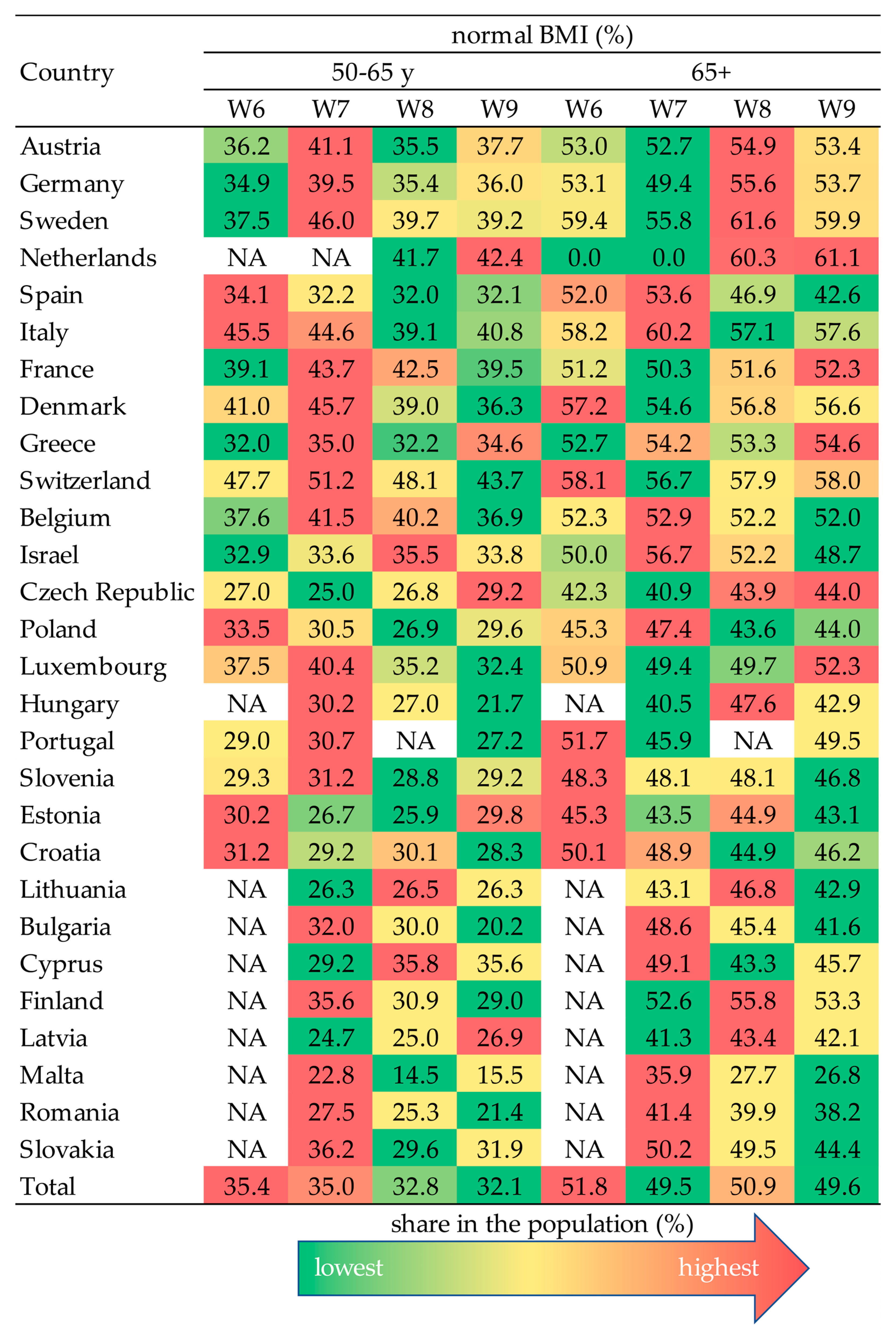
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BF | Body fat |
| BM | Body mass |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| SHARE | Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe |
| STROBE | STrengthening the Reporting of OBservational studies in Epidemiology |
Appendix A
| EU, BMI * (kg/m2) | HR, BMI * (kg/m2) | p-Value | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <18.5 | 18.5–24.9 | 25–29.9 | ≥30 | <18.5 | 18.5–24.9 | 25–29.9 | ≥30 | ||
| Cannot afford to eat it more often | 11.6 | 9.8 | 12.1 | 15.3 | 35.3 | 37.5 | 15.7 | 21.4 | <0.0001 |
| You follow a vegetarian diet | 19.3 | 15.3 | 11.6 | 8.8 | 25.0 | 10.0 | 5.0 | 0.0777 | |
| For other reasons | 68.7 | 74.5 | 75.9 | 75.7 | 64.7 | 37.5 | 74.3 | 73.6 | <0.0001 |
| EU, BMI # (kg/m2) | HR, BMI # (kg/m2) | p-Value | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <18.5 | 18.5–20.9 | 21–27.4 | 27.5–30.9 | 31–39.9 | ≥40 | <18.5 | 18.5–20.9 | 21–27.4 | 27.5–30.9 | 31–39.9 | ≥40 | ||
| Cannot afford to eat it more often | 14.6 | 8.3 | 10.6 | 12.9 | 16.1 | 20.2 | 36.0 | 12.5 | 18.7 | 20.5 | 22.8 | 20.0 | 0.0004 |
| You follow a vegetarian diet | 11.8 | 17.7 | 14.2 | 9.4 | 8.4 | 8.3 | 8.0 | 21.9 | 6.6 | 5.1 | 5.1 | 20.0 | 0.0002 |
| For other reasons | 72.3 | 73.6 | 74.8 | 77.5 | 75.3 | 71.4 | 56.0 | 65.6 | 74.7 | 74.4 | 72.2 | 60.0 | 0.1486 |
References
- Lin, X.; Li, H. Obesity: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Therapeutics. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 706978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- World Obesity Federation. World Obesity Atlas 2022. 2022. Available online: https://data.worldobesity.org/publications/World-Obesity-Atlas-2022-updated.pdf (accessed on 14 August 2025).
- European Health Information Portal (2022) The European Health Survey—Croatia, EHIS 3. Available online: https://www.healthinformationportal.eu/health-information-sources/european-health-survey-croatia. (accessed on 14 August 2025).
- Ministry of Health of the Republic of Croatia. Action Plan for Obesity Prevention 2024–2027; Ministry of Health of the Republic of Croatia: Zagreb, Croatia, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Donini, L.M.; Savina, C.; Gennaro, E.; De Felice, M.R.; Rosano, A.; Pandolfo, M.M.; Del Balzo, V.; Cannella, C.; Ritz, P.; Chumlea, W.C. A systematic review of the literature concerning the relationship between obesity and mortality in the elderly. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2012, 16, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sun, J.; Zhou, W.; Gu, T.; Zhu, D.; Bi, Y. A retrospective study on association between obesity and cardiovascular risk diseases with aging in Chinese adults. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, P.W.; Kannel, W.B. Obesity, diabetes, and risk of cardiovascular disease in the elderly. Am. J. Geriatr. Cardiol. 2002, 11, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castell, M.V.; van der Pas, S.; Otero, A.; Siviero, P.; Dennison, E.; Denkinger, M.; Pedersen, N.; Sanchez-Martinez, M.; Queipo, R.; van Schoor, N.; et al. Osteoarthritis and frailty in elderly individuals across six European countries: Results from the European Project on OSteoArthritis (EPOSA). BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2015, 16, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ghavami, T.; Kazeminia, M.; Ahmadi, N.; Rajati, F. Global Prevalence of Obstructive Sleep Apnea in the Elderly and Related Factors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Study. J. PeriAnesthesia Nurs. 2023, 38, 865–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, N.M.; Kaltsakas, G. Respiratory complications of obesity: From early changes to respiratory failure. Breathe 2023, 19, 220263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kralj, V.; Šekerija, M. Epidemiology of cardiovascular diseases in Croatia. Cardiol. Croat. 2022, 17, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell-Wiley, T.M.; Poirier, P.; Burke, L.E.; Després, J.-P.; Gordon-Larsen, P.; Lavie, C.J.; Lear, S.A.; Ndumele, C.E.; Neeland, I.J.; Sanders, P.; et al. Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease: A Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2021, 143, e984–e1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Welsh, A.; Hammad, M.; Piña, I.L.; Kulinski, J. Obesity and cardiovascular health. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2024, 31, 1026–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ndumele, C.E.; Matsushita, K.; Lazo, M.; Bello, N.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Gerstenblith, G.; Nambi, V.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Solomon, S.D.; Selvin, E.; et al. Obesity and Subtypes of Incident Cardiovascular Disease. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2016, 5, e003921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Alpert, M.A.; Lavie, C.J.; Agrawal, H.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, S.A. Cardiac Effects of Obesity: Pathophysiologic, Clinical, and Prognostic Consequences—A Review. J. Cardiopulm. Rehab. Prev. 2016, 36, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadde, K.M.; Martin, C.K.; Berthoud, H.-R.; Heymsfield, S.B. Obesity: Pathophysiology and Management. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kenchaiah, S.; Vasan, R.S. Heart Failure in Women—Insights from the Framingham Heart Study. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2015, 29, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shariq, O.A.; McKenzie, T.J. Obesity-related hypertension: A review of pathophysiology, management, and the role of metabolic surgery. Gland. Surg. 2020, 9, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hall, J.E.; do Carmo, J.M.; da Silva, A.A.; Wang, Z.; Hall, M.E. Obesity-induced hypertension: Interaction of neurohumoral and renal mechanisms. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 991–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wickramasinghe, M.; Weaver, J.U. Practical Guide to Obesity; Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2018; pp. 99–108. [Google Scholar]
- Sniderman, A.D.; Thanassoulis, G.; Glavinovic, T.; Navar, A.M.; Pencina, M.; Catapano, A.; Ference, B.A. Apolipoprotein B Particles and Cardiovascular Disease: A Narrative Review. JAMA Cardiol. 2019, 4, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Rosell, M.; Appleby, P.; Spencer, E.; Key, T. Weight gain over 5 years in 21,966 meat-eating, fish-eating, vegetarian, and vegan men and women in EPIC-Oxford. Int. J. Obes. 2006, 30, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klop, B.; Elte, J.W.F.; Cabezas, M.C. Dyslipidemia in obesity: Mechanisms and potential targets. Nutrients 2013, 5, 1218–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Volpe, M.; Gallo, G. Obesity and cardiovascular disease: An executive document on pathophysiological and clinical links promoted by the Italian Society of Cardiovascular Prevention (SIPREC). Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1136340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, P.; Weiskirchen, R. The Role of Obesity in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus—An Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastaldelli, A.; Miyazaki, Y.; Pettiti, M.; Matsuda, M.; Mahankali, S.; Santini, E.; DeFronzo, R.A.; Ferrannini, E. Metabolic effects of visceral fat accumulation in type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 5098–5103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franz, M.J.; Boucher, J.L.; Rutten-Ramos, S.; VanWormer, J.J. Lifestyle weight-loss intervention outcomes in overweight and obese adults with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2015, 115, 1447–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Börsch-Supan, A.; Brandt, M.; Hunkler, C.; Kneip, T.; Korbmacher, J.; Malter, F.; Schaan, B.; Stuck, S.; Zuber, S. Data resource profle: The survey of health, ageing and retirement in Europe (SHARE). Int. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 42, 992–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, M.; Kneip, T.; De Luca, G.; Scherpenzeel, A. Survey participation in the Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe (SHARE), Wave 1–7. Based on Release 7.0.0. SHARE Work. Pap. Ser., 41–2019. Munich: MEA, Max Planck Institute for Social Law and Social Policy. 2019. Available online: https://share-eric.eu/fileadmin/user_upload/SHARE_Working_Paper/WP_Series_41_2019_Bergmann_et_al.pdf (accessed on 11 November 2024).
- CDC. Adult BMI Categories. 2024. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/bmi/adult-calculator/bmi-categories.html (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- Volkert, D.; Beck, A.M.; Cederholm, T.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.; Hooper, L.; Kiesswetter, E.; Maggio, M.; Raynaud-Simon, A.; Sieber, C.; Sobotka, L.; et al. ESPEN practical guideline: Clinical nutrition and hydration in geriatrics. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 958–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maltarić, M.; Kljusurić, J.G.; Kolak, M.; Smolić, Š.; Kolarić, B.; Bender, D.V. Dietary Habits and Obesity in Middle-Aged and Elderly Europeans—The Survey of Health, Ageing, and Retirement in Europe (SHARE). Nutrients 2025, 17, 2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- STROBE—Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology. Available online: https://www.strobe-statement.org/ (accessed on 4 September 2025).
- Conforto, R.; Rizzo, V.; Russo, R.; Mazza, E.; Maurotti, S.; Pujia, C.; Succurro, E.; Arturi, F.; Ferro, Y.; Sciacqua, A.; et al. Advances in body composition and gender differences in susceptibility to frailty syndrome: Role of osteosarcopenic obesity. Metabolism 2024, 161, 156052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wu, W.; Sun, F.; Lu, H.; Xu, X.; Su, Y.; Cheng, W.; Wang, H. Aging related obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus suppress neuromuscular communication and aggravate skeletal muscle dysfunction in rhesus monkeys. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianfredi, V.; Nucci, D.; Lattanzio, R.; Piccinelli, S.; Cicconi, G.; Santisteban Farfan, S.J.; Berti, A.; D’Amico, M.; Sabatelli, N.; Guzzardi, F.; et al. Food insecurity and body mass index among older people: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2025, 128, 105606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaleghi, A.A.; Salari, N.; Darvishi, N.; Bokaee, S.; Jafari, S.; Hemmati, M.; Mohammadi, M. Global prevalence of obesity in the older adults: A meta-analysis. Public Health Pract. 2025, 9, 100585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait-hadad, W.; Bédard, A.; Orsi, L.; Chanoine, S.; Dumas, O.; Laouali, N.; Le Moual, N.; Leynaert, B.; Siroux, V.; Boutron-Ruault, M.-C.; et al. Mediating role of the body mass index in the prospective association between a healthy diet and evolution of asthma symptoms in elderly women. J. Aging Res. Lifestyle 2025, 14, 100011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Jiang, S.; Li, H.; Xie, G.; Pavel, V.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Huang, C. Obesity induces osteoimmunology imbalance: Molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 177, 117139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshram, I.I.; Nagalla, B.; Kodavanti, M.R.; Avula, L.; Veera, B.G.N. Overweight/obesity, pre-diabetes, diabetes and its association with hypertension and other factors among rural adults (≥18 years) in India. Indian Heart J. 2024, 76, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilk, P.; Stranges, S.; Cuschieri, S. Does sex modify the effect of pre-pandemic body mass index on the risk of Long COVID? Evidence from the longitudinal analysis of the Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe. Int. J. Obes. 2005, 48, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodryzlova, Y.; Nasri, B.; Razafindratovo, R.M.R.; Kestens, Y.; Bélanger, E.; Moullec, G. Cognitive maintenance in older adults in social classes: A secondary analysis of the longitudinal SHARE data. Journal of epidemiology and community health. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2025, 79, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, S.C.; Bäck, M.; Rees, J.M.B.; Mason, A.M.; Burgess, S. Body mass index and body composition in relation to 14 cardiovascular conditions in UK Biobank: A Mendelian randomization study. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Data Collected in Year. | Number of Countries (Included Individuals) | Wave of Data Collection |
|---|---|---|
| 2015 | 18 (66,907) | Wave 6 (W6) |
| 2017 | 27 (76,106) | Wave 7 (W7) |
| 2019/20 | 27 (46,466) | Wave 8 (W8) |
| 2021/22 | 28 (69,447) | Wave 9 (W9) |
| Nutritional Status. | BMI (kg/m2) | |
|---|---|---|
| Under 65 Years # | Age 65+ * | |
| Underweighted | <18.5 | <18.5 |
| 18.5–20.9 | ||
| Normal | 18.5–24.9 | 21–27.49 |
| Overweight | 25–29.9 | 27.5–30.9 |
| Obese | >30 | 31–39.9 |
| Morbid obesity | >40 | |
| Variables | All Countries | Croatia | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Female (N = 39,872) | Male (N = 29,575) | Total (N = 69,447) | p-Value | Female (N = 2647) | Male (N = 2040) | Total (N = 4687) | p-Value | |
| Age (%) | ||||||||
| 51–64 | 31 | 29.7 | 30.4 | 0.8907 | 39.1 | 36.4 | 37.9 | 0.7439 |
| 65–74 | 34.7 | 38.2 | 36.1 | 34.3 | 39.9 | 36.7 | ||
| 75–85 | 24.1 | 24.5 | 24.3 | 18.9 | 18.6 | 18.8 | ||
| >85 | 8.9 | 7.5 | 8.3 | 6,0 | 4.9 | 5.5 | ||
| BMI (%) | ||||||||
| Normal (under 65 y) | 35.1 | 28.5 | 32.3 | 0.1869 | 31.1 | 22.5 | 27.3 | 0.0646 |
| Normal (>65 y) | 47.8 | 51.1 | 49.2 | 47.3 | 44.9 | 46.2 | ||
| Marital status (%) | ||||||||
| Living with partner | 57.1 | 72.4 | 63.7 | 0.0006 | 62.4 | 78.6 | 69.5 | 0.0001 |
| Not living with a partner | 42.9 | 27.6 | 26.3 | 37.6 | 21.4 | 30.5 | ||
| Physical inactivity (%) | ||||||||
| Other * | 85.1 | 88 | 86.3 | 0.3542 | 89.8 | 91.9 | 90.7 | 0.4539 |
| Never vigorous nor moderate physical activity | 14.8 | 11.8 | 13.5 | 9.8 | 7.8 | 8.9 | ||
| Current job situation (%) | ||||||||
| Retired | 62 | 70.4 | 65.6 | 0.0658 | 57.8 | 73 | 64.4 | 0.0006 |
| Not retired | 38 | 29.6 | 34.4 | 42.2 | 27 | 35.6 | ||
| Ever diagnosed/currently having | ||||||||
| Heart attack | 10.7 | 15.5 | 12.7 | 0.6510 | 11.8 | 16.2 | 13.7 | 0.3260 |
| High blood pressure or hypertension | 47.2 | 47.3 | 47.2 | 52.9 | 50.1 | 51.7 | ||
| High blood cholesterol | 27.8 | 27.3 | 27.6 | 23.6 | 19.7 | 21.9 | ||
| Stroke | 3.5 | 5.1 | 4.2 | 3.8 | 6.3 | 4.9 | ||
| Diabetes or high blood sugar | 14 | 16.8 | 15.2 | 13.7 | 19.1 | 16 | ||
| Frequency of Food Consumption | EU, BMI * (kg/m2) | HR, BMI * (kg/m2) | p-Value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <18.5 | 18.5–24.9 | 25–29.9 | ≥30 | <18.5 | 18.5–24.9 | 25–29.9 | ≥30 | ||
| Dairy products | |||||||||
| Every day | 62.0 | 60.1 | 57.2 | 55.6 | 47.8 | 52.7 | 50.0 | 49.3 | 0.0694 |
| 3–6 times a week | 19.3 | 22.5 | 25.0 | 25.2 | 23.9 | 24.9 | 26.0 | 25.5 | 0.7583 |
| Twice a week | 8.6 | 8.9 | 9.7 | 10.0 | 15.2 | 10.3 | 13.0 | 12.5 | 0.2214 |
| Once a week | 3.5 | 3.7 | 3.8 | 4.4 | 2.2 | 5.2 | 5.0 | 6.1 | 0.5811 |
| Less than once a week | 6.2 | 4.6 | 4.3 | 4.7 | 10.9 | 6.8 | 6.0 | 6.5 | 0.2980 |
| Legumes or eggs | |||||||||
| Every day | 12.1 | 11.2 | 10.6 | 10.7 | 6.5 | 12.1 | 9.6 | 9.1 | 0.1595 |
| 3–6 times a week | 31.1 | 33.7 | 34.5 | 33.1 | 39.1 | 32.7 | 31.3 | 30.0 | 0.5115 |
| Twice a week | 31.1 | 29.2 | 29.5 | 29.8 | 32.6 | 32.4 | 35.9 | 37.3 | 0.3891 |
| Once a week | 15.6 | 18.1 | 18.2 | 18.6 | 10.9 | 17.0 | 18.5 | 19.3 | 0.5472 |
| Less than once a week | 9.4 | 7.6 | 7.1 | 7.7 | 10.9 | 5.6 | 4.7 | 4.2 | 0.1733 |
| Meat, fish, or chicken | |||||||||
| Every day | 29.7 | 29.0 | 31.8 | 34.4 | 26.1 | 46.3 | 54.1 | 55.9 | <0.0001 |
| 3–6 times a week | 42.9 | 48.7 | 50.3 | 48.7 | 56.5 | 42.7 | 38.6 | 36.2 | 0.0074 |
| Twice a week | 15.4 | 14.5 | 12.5 | 11.5 | 8.7 | 7.2 | 5.3 | 6.4 | <0.0001 |
| Once a week | 6.5 | 5.1 | 3.8 | 3.8 | 2.2 | 2.7 | 1.3 | 1.0 | <0.0001 |
| Less than once a week | 5.1 | 2.8 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 6.5 | 1.1 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.1003 |
| Fruits and vegetables | |||||||||
| Every day | 72.9 | 76.3 | 73.5 | 71.7 | 65.2 | 79.3 | 79.4 | 79.8 | 0.5137 |
| 3–6 times a week | 19.0 | 17.6 | 20.3 | 21.2 | 21.7 | 13.9 | 15.0 | 14.0 | 0.0749 |
| Twice a week | 3.9 | 3.9 | 4.1 | 4.7 | 8.7 | 3.9 | 3.7 | 4.2 | 0.4414 |
| Once a week | 1.4 | 1.2 | 1.3 | 1.5 | 2.2 | 2.1 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 0.8868 |
| Less than once a week | 2.2 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 2.2 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 0.8560 |
| Frequency of Food Consumption | EU, BMI # (kg/m2) | HR, BMI # (kg/m2) | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <18.5 | 18.5–20.9 | 21–27.4 | 27.5–30.9 | 31–39.9 | ≥40 | <18.5 | 18.5–20.9 | 21–27.4 | 27.5–30.9 | 31–39.9 | ≥40 | p-Value | |
| Dairy products | |||||||||||||
| Every day | 54.6 | 61.2 | 59.0 | 56.1 | 55.3 | 58.0 | 30.9 | 56.0 | 51.2 | 50.2 | 48.0 | 59.0 | 0.0006 |
| 3–6 times a week | 25.4 | 20.0 | 23.7 | 25.5 | 25.3 | 24.1 | 27.3 | 23.6 | 25.9 | 24.8 | 26.8 | 14.8 | 0.2326 |
| Twice a week | 10.2 | 9.0 | 9.2 | 9.9 | 10.2 | 8.7 | 20.5 | 8.2 | 12.0 | 11.8 | 13.1 | 14.8 | 0.0965 |
| Once a week | 3.0 | 3.6 | 3.7 | 4.0 | 4.5 | 4.4 | 4.5 | 2.2 | 5.2 | 5.8 | 6.1 | 3.3 | 0.6839 |
| Less than once a week | 4.6 | 6.0 | 4.3 | 4.4 | 4.6 | 4.9 | 8.2 | 9.3 | 5.8 | 7.3 | 5.8 | 8.2 | 0.3206 |
| Legumes or eggs | |||||||||||||
| Every day | 11.1 | 11.9 | 10.9 | 10.5 | 10.5 | 13.0 | 6.8 | 13.7 | 10.7 | 9.8 | 8.7 | 11.5 | 0.6185 |
| 3–6 times a week | 36.3 | 31.1 | 34.2 | 34.5 | 33.1 | 33.4 | 27.7 | 32.4 | 32.6 | 30.1 | 30.5 | 19.7 | 0.0219 |
| Twice a week | 27.7 | 29.6 | 29.4 | 29.8 | 29.6 | 26.7 | 27.7 | 28.6 | 34.1 | 36.5 | 38.0 | 34.4 | 0.3589 |
| Once a week | 13.8 | 18.4 | 18.2 | 17.8 | 19.1 | 18.1 | 14.1 | 18.1 | 17.5 | 18.7 | 18.9 | 27.9 | 0.6249 |
| Less than once a week | 8.6 | 8.9 | 7.2 | 7.3 | 7.5 | 8.7 | 15.0 | 6.6 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 3.8 | 6.6 | 0.0734 |
| Meat, fish, or chicken | |||||||||||||
| Every day | 26.7 | 26.8 | 30.3 | 32.9 | 33.8 | 39.6 | 31.8 | 35.2 | 50.9 | 56.4 | 53.8 | 60.7 | <0.0001 |
| 3–6 times a week | 49.8 | 45.8 | 49.8 | 49.8 | 49.1 | 43.7 | 48.2 | 46.7 | 40.7 | 36.8 | 37.3 | 31.1 | 0.0087 |
| Twice a week | 13.8 | 15.6 | 13.4 | 12.3 | 11.7 | 10.3 | 7.3 | 8.2 | 6.0 | 5.2 | 7.1 | 6.6 | <0.0001 |
| Once a week | 4.6 | 7.4 | 4.3 | 3.6 | 3.8 | 4.0 | 1.8 | 5.5 | 1.8 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 0.0007 | |
| Less than once a week | 2.9 | 4.3 | 2.1 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 2.4 | 2.3 | 3.8 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.4 | 1.6 | 0.1995 |
| Fruits and vegetables | |||||||||||||
| Every day | 64.3 | 78.4 | 75.0 | 72.8 | 71.3 | 71.7 | 56.8 | 76.9 | 78.9 | 80.8 | 79.5 | 83.6 | 0.4757 |
| 3–6 times a week | 25.1 | 14.4 | 18.9 | 20.7 | 21.6 | 21.5 | 26.8 | 13.2 | 14.8 | 14.0 | 14.5 | 11.5 | 0.0049 |
| Twice a week | 5.9 | 4.2 | 3.9 | 4.4 | 4.7 | 3.8 | 5.5 | 6.0 | 3.8 | 3.3 | 4.3 | 3.3 | 0.9574 |
| Once a week | 1.4 | 1.6 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 2.2 | 1.8 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 1.6 | 0.9962 |
| Less than once a week | 1.1 | 1.2 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1.4 | 0.9 | 1.1 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.9502 | |
| Ever Diagnosed/Currently Having | EU, BMI * (kg/m2) | HR, BMI * (kg/m2) | p-Value | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <18.5 | 18.5–24.9 | 25–29.9 | ≥30 | <18.5 | 18.5–24.9 | 25–29.9 | ≥30 | ||
| Heart attack | |||||||||
| Not selected | 87.8 | 89.3 | 87.1 | 84.6 | 93.5 | 88.9 | 85.6 | 84.3 | 0.9454 |
| Selected | 11.9 | 10.6 | 12.8 | 15.4 | 6.5 | 11.0 | 14.4 | 15.7 | 0.1941 |
| High blood pressure or hypertension | |||||||||
| Not selected | 70.4 | 64.9 | 51.6 | 37.4 | 63.0 | 59.5 | 48.9 | 36.2 | 0.6687 |
| Selected | 29.4 | 35.0 | 48.3 | 62.6 | 37.0 | 40.5 | 51.1 | 63.8 | 0.4793 |
| High blood cholesterol | |||||||||
| Not selected | 82.6 | 77.3 | 70.7 | 67.4 | 91.3 | 80.9 | 78.0 | 73.7 | 0.5319 |
| Selected | 17.2 | 22.7 | 29.2 | 32.5 | 8.7 | 19.1 | 21.9 | 26.3 | 0.0050 |
| Stroke | |||||||||
| Not selected | 94.0 | 96.1 | 96.0 | 95.3 | 87.0 | 95.2 | 95.1 | 95.6 | 0.8997 |
| Selected | 5.8 | 3.8 | 3.9 | 4.7 | 13.0 | 4.8 | 4.9 | 4.4 | 0.2195 |
| Diabetes or high blood sugar | |||||||||
| Not selected | 92.9 | 90.9 | 85.3 | 75.5 | 97.8 | 90.3 | 85.6 | 74.3 | 0.9660 |
| Selected | 6.8 | 9.0 | 14.7 | 24.5 | 2.2 | 9.6 | 14.4 | 25.7 | 0.0175 |
| Ever Diagnosed/Currently Having | EU, BMI * (kg/m2) | HR, BMI * (kg/m2) | p-Value | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| <18.5 | 18.5–20.9 | 21–27.4 | 27.5–30.9 | 31–39.9 | ≥40 | <18.5 | 18.5–20.9 | 21–27.4 | 27.5–30.9 | 31–39.9 | ≥40 | ||
| Heart attack | |||||||||||||
| Not selected | 84.0 | 89.3 | 88.6 | 86.5 | 84.3 | 81.3 | 79.1 | 86.3 | 87.5 | 86.4 | 82.7 | 82.0 | 0.9933 |
| Selected | 14.0 | 10.5 | 11.4 | 13.5 | 15.6 | 18.7 | 12.3 | 13.7 | 12.4 | 13.6 | 17.3 | 18.0 | 0.9368 |
| High blood pressure or hypertension | |||||||||||||
| Not selected | 52.5 | 71.8 | 59.6 | 46.5 | 36.8 | 26.6 | 38.2 | 61.0 | 54.8 | 45.6 | 35.2 | 31.1 | 0.1326 |
| Selected | 45.5 | 28.0 | 40.3 | 53.5 | 63.2 | 73.4 | 53.2 | 39.0 | 45.1 | 54.4 | 64.8 | 68.9 | 0.4071 |
| High blood cholesterol | |||||||||||||
| Not selected | 74.5 | 80.5 | 74.3 | 69.7 | 67.0 | 64.6 | 78.6 | 84.6 | 79.8 | 76.2 | 73.1 | 73.8 | 0.7006 |
| Selected | 23.5 | 19.3 | 25.6 | 30.2 | 33.0 | 35.4 | 12.7 | 15.4 | 20.1 | 23.8 | 26.9 | 26.2 | 0.0030 |
| Stroke | |||||||||||||
| Not selected | 91.8 | 95.7 | 96.1 | 96.0 | 95.2 | 93.6 | 83.6 | 94.0 | 95.3 | 95.0 | 95.9 | 90.2 | 0.9648 |
| Selected | 6.3 | 4.1 | 3.8 | 3.9 | 4.7 | 6.4 | 7.7 | 6.0 | 4.6 | 5.0 | 4.1 | 9.8 | 0.7752 |
| Diabetes or high blood sugar | |||||||||||||
| Not selected | 82.8 | 93.2 | 88.8 | 82.7 | 75.3 | 59.7 | 77.7 | 90.7 | 88.7 | 82.5 | 74.4 | 55.7 | 0.9827 |
| Selected | 15.2 | 6.6 | 11.1 | 17.3 | 24.6 | 40.3 | 13.6 | 9.3 | 11.2 | 17.5 | 25.6 | 44.3 | 0.9253 |
| Variable | EU, Overweighed and Obese | HR, Overweighed and Obese | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AOR (95% CI) | p-Value | AOR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Dairy products | ||||
| Every day | 1.16 (0.99–1.35) | 0.064 | 1.55 (1.07–2.25) | 0.020 |
| 3–6 times a week | 1.22 (1.04–1.44) | 0.015 | 1.42 (0.96–2.09) | 0.078 |
| Twice a week | 1.35 (1.13–1.62) | 0.001 | 1.59 (1.03–2.43) | 0.035 |
| Once a week | 1.25 (1–1.56) | 0.047 | 1.48 (0.88–2.49) | 0.139 |
| Less than once a week | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| Legumes or eggs | ||||
| Every day | 0.88 (0.74–1.04) | 0.129 | 0.91 (0.56–1.49) | 0.719 |
| 3–6 times a week | 1.01 (0.87–1.16) | 0.912 | 1.45 (0.93–2.26) | 0.102 |
| Twice a week | 1.03 (0.89–1.19) | 0.711 | 1.57 (1–2.44) | 0.048 |
| Once a week | 1.08 (0.93–1.26) | 0.331 | 1.83 (1.15–2.94) | 0.011 |
| Less than once a week | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| Meat, fish, or chicken | ||||
| Every day | 2.26 (1.79–2.86) | <0.001 | 1.35 (0.52–3.5) | 0.537 |
| 3–6 times a week | 1.94 (1.54–2.45) | <0.001 | 0.97 (0.38–2.52) | 0.955 |
| Twice a week | 1.62 (1.27–2.07) | <0.001 | 0.83 (0.31–2.26) | 0.720 |
| Once a week | 1.34 (1.01–1.77) | 0.041 | 0.55 (0.17–1.71) | 0.300 |
| Less than once a week | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| Fruits and vegetables | ||||
| Every day | 1.1 (0.74–1.63) | 0.651 | 1.03 (0.41–2.61) | 0.954 |
| 3–6 times a week | 1.22 (0.82–1.83) | 0.321 | 1.05 (0.41–2.72) | 0.917 |
| Twice a week | 1.2 (0.79–1.84) | 0.392 | 1.3 (0.46–3.72) | 0.618 |
| Once a week | 1.1 (0.68–1.78) | 0.691 | 0.62 (0.2–1.92) | 0.409 |
| Less than once a week | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| CVDs | ||||
| Heart attack | ||||
| Yes | 0.94 (0.84–1.06) | 0.340 | 0.94 (0.71–1.26) | 0.686 |
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| High blood pressure or hypertension | ||||
| Yes | 2.04 (1.89–2.21) | <0.001 | 1.84 (1.5–2.24) | <0.001 |
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| High blood cholesterol | ||||
| Yes | 1.13 (1.04–1.24) | 0.005 | 1.13 (0.88–1.44) | 0.347 |
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| Stroke | ||||
| Yes | 0.96 (0.8–1.16) | 0.670 | 0.7 (0.46–1.06) | 0.092 |
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
| Diabetes or high blood sugar | ||||
| Yes | 1.73 (1.54–1.95) | <0.001 | 1.71 (1.27–2.28) | <0.001 |
| No | 1.00 | 1.00 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maltarić, M.; Kolak, M.; Kolarić, B.; Vranešić Bender, D.; Gajdoš Kljusurić, J. Cross-European Patterns of Obesity: Where Does Croatia Stand?—Descriptive Analysis of Waves 2015–2022 of the Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe (SHARE) Including Adults Aged Over 50. Obesities 2025, 5, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5030066
Maltarić M, Kolak M, Kolarić B, Vranešić Bender D, Gajdoš Kljusurić J. Cross-European Patterns of Obesity: Where Does Croatia Stand?—Descriptive Analysis of Waves 2015–2022 of the Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe (SHARE) Including Adults Aged Over 50. Obesities. 2025; 5(3):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5030066
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaltarić, Manuela, Mirela Kolak, Branko Kolarić, Darija Vranešić Bender, and Jasenka Gajdoš Kljusurić. 2025. "Cross-European Patterns of Obesity: Where Does Croatia Stand?—Descriptive Analysis of Waves 2015–2022 of the Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe (SHARE) Including Adults Aged Over 50" Obesities 5, no. 3: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5030066
APA StyleMaltarić, M., Kolak, M., Kolarić, B., Vranešić Bender, D., & Gajdoš Kljusurić, J. (2025). Cross-European Patterns of Obesity: Where Does Croatia Stand?—Descriptive Analysis of Waves 2015–2022 of the Survey of Health, Ageing and Retirement in Europe (SHARE) Including Adults Aged Over 50. Obesities, 5(3), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/obesities5030066






