Abstract
Our four-year interdisciplinary behavioral weight loss program is fully covered by public health insurance for patients with a body mass index of ≥35 kg/m2. We evaluated the real-world outcomes of anthropometric, metabolic and psychologic parameters collected prior to the start (t0, n = 381, 71% women) and after each segment of the program (t1–4, n = 243, 126, 94, and 77). It is a prospective evaluation of clinical real-world data including all patients who started the first segment of behavioral treatment until they quit/finished the program. The mean dropout rates per treatment segment were 23%. Body weight after one year decreased from 127.3 kg to 122.2 (p < 0.001). Average hemoglobin A1c value decreased from 5.8% to 5.6% in all patients (p < 0.001) and from 6.6% to 6.2% in patients with type 2 diabetes (p < 0.001). Further metabolic and psychological parameters improved significantly as well. The average weight nadir was reached after two segments, co-occurring with the most beneficial changes in laboratory parameters. Afterwards, mean weight slightly increased accompanied by a discrete loss of benefits in laboratory parameters. Our real-world data with significant health improvements adds important value to discussions about the funding of obesity therapy and thus has the chance to improve therapy availability for obesity patients worldwide.
1. Introduction
Obesity, defined as a body mass index (BMI) of ≥30 kg/m2 is a major public health concern associated with increased risks for metabolic diseases (e.g., diabetes mellitus type 2, arterial hypertension), as well as psychological disorders (e.g., depression) and higher risks for incapacity for work and early retirement [1,2]. Without intervention, individuals with obesity typically experience progressive weight gain over time, regardless of baseline weight [3]. Even modest weight loss can lead to clinically meaningful improvements in comorbidities and cardiovascular risk factors [4]. Other important goals of obesity treatment are an increase in quality of life, prevention of disability and loss of productive years [5].
Therefore, national [6] and international [7] guidelines recommend interdisciplinary behavioral treatment as the foundation of obesity treatment. These programs combine nutritional counseling, exercise and behavioral therapy [6] focused on problem identification and problem solving. This includes self-monitoring, goal-setting and stress management. By individualizing component therapy, adherence can be increased [8]. Behavioral weight loss treatment can be the basis for further treatment steps, such as bariatric surgery, but also, if successful, a relevant therapeutic intervention with important clinical improvements for patients.
Despite its proven effectiveness, access to such programs remains limited—particularly for individuals with lower socioeconomic status—due to a lack of reimbursement by health insurance providers [9]. In Germany, behavioral weight loss therapy is generally not covered by statutory health insurance, creating a significant treatment gap.
Here, we report the clinical real-world data of the Leipzig Obesity Management Program, an interdisciplinary four-year, fully health insurance-funded behavioral weight loss program at the Leipzig University Hospital. Unlike many existing programs [10,11,12], our intervention deliberately excluded meal replacement products to ensure accessibility for individuals with medical, personal, or financial barriers to such approaches. This design also aligns with current reimbursement policies in the German healthcare system.
While randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are considered the gold standard for evaluating treatment efficacy, their findings often lack generalizability due to strict inclusion criteria and controlled settings. In contrast, real-world data can provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of interventions under routine clinical conditions [13]. The present study aimed to evaluate the long-term effects of the program on anthropometric, metabolic, and psychological outcomes using prospective real-world data. Data of the first segment of treatment was already published [14]. By analyzing the full course of the four-year program, we sought to contribute meaningful evidence to the ongoing discussion about the funding and implementation of behavioral obesity treatment in routine care.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
This observational study included all individuals who enrolled in the Leipzig Obesity Management Program between August 2014 and September 2016. Interested persons contacted the Obesity Outpatient Clinic of the Leipzig University Hospital by email or telephone and were informed in detail about the program modalities. A physician’s recommendation was not required for participation. Inclusion criteria for participation were a BMI ≥ 35 kg/m2, age ≥ 18 years and an insurance contract with the local health insurance company AOK PLUS. In Germany, behavioral weight loss therapy is not generally covered by health insurance. Our program was, to our knowledge, the first four-year program in Germany which secured full coverage through a contract between the hospital and the health insurance company.
Exclusion criteria were severe mental disorders, substance abuse and other conditions, which would impair the regular participation in the therapy program, or secondary causes of obesity like endocrine disorders.
Reported data are observational real-world data; all patients with data were part of the program and there was no untreated control group. The low entry barriers for enrolling in the program and the lack of treatment costs for patients guaranteed easy access to the program and we are therefore confident that our sample was representative of adult persons with a BMI ≥ 35 kg/m2 in our region.
2.2. Interventions and Assessments
At baseline assessment (t0), a blood draw was performed and routine medical and metabolic laboratory parameters were determined (Supplementary Information, Table S1). Medical history and anthropometric parameters were assessed by a physician in a standardized way. The anthropometric data collected included height, body weight and the resulting BMI. Height and body weight were measured using the Seca 764 measuring station (Seca GmbH, Hamburg, Germany), which consists of a digital scale (calibration level 3) including an electronic stadiometer. Participants were measured in light clothing and without shoes. To measure body composition, a Biacorpus RX4004M bioelectrical impedance analyzer, (Medical Healthcare GmbH, Karlsruhe, Germany), was used. The EUROHIS-QOL 8 item index [15] and the patient health questionnaire (PHQ-9) [16] were used to assess quality of life and depressive symptoms, respectively. If the psychological assessment by questionnaires suggested clinically relevant problems in comparison to population norms, an in-person session with a clinical psychologist was scheduled. Furthermore, a nutritional history was assessed by a dietitian.
Following baseline assessments, the interdisciplinary board meeting, consisting of a physician from the department of internal medicine, a dietitian, a psychologist, and a case manager, decided on each patient’s treatment plan. If the patient had a primary indication for bariatric surgery (based on the national German guidelines [17]) and the patient agreed, bariatric surgery was offered. From August 2014 until September 2016, 411 patients performed baseline assessments; by the end of May 2020 all patients had either completed the whole Leipzig Obesity Management Program or dropped out. Of the 411 baseline patients, 29 (7%) had a primary indication for bariatric surgery and were transferred to the department of surgery. One patient was included a second time into the program after dropping out after first inclusion during the first program segment. The second time, this patient was excluded from further evaluation. All other patients (n = 381, 93%) started the behavioral weight loss program (Figure 1) and were included into the courses of n = 11–18 patients.
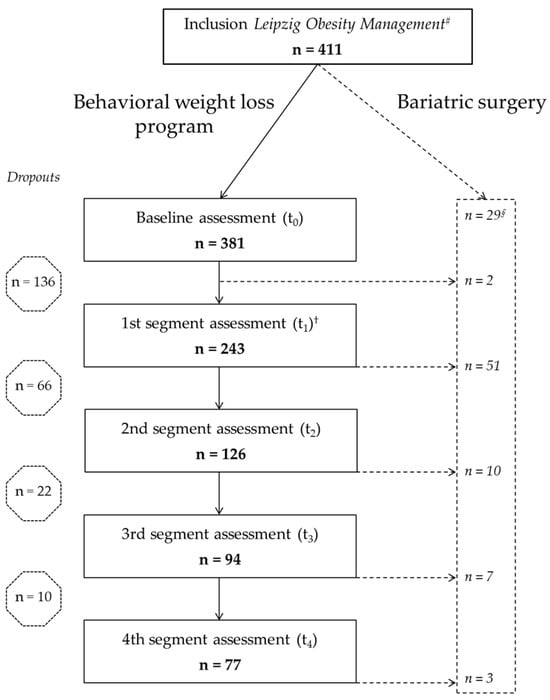
Figure 1.
Participant flow through the Leipzig Obesity Management Program. Number of participants at each stage of the four-year program # First and † second obesity board, § primary indication for bariatric surgery. One participant was enrolled twice; the second enrollment was excluded from analysis. T1–4, 1st to 4th segment assessment.
There were three options for similar behavioral treatment programs during the first segment. Patients were grouped regarding their physical ability for participation in the exercise sessions and the time of day when they could best participate (Supplementary Information, Table S2).
Participants absolved one of the three program options, which lasted approximately one year. Each course consisted of dietary counseling, behavioral therapy and sports courses and lasted approximately twelve months. The whole program consisted of four successive one-year courses (“segments”), with the first segment having the highest intensity (i.e., most therapy hours), and the following segments having less scheduled classes. During the first segment of the program, there were up to six individual diet therapy sessions, 6–12 nutritional group therapy sessions, 10–12 behavioral group therapy sessions and 40–48 group exercise sessions. The appointments took place in the obesity clinic of the University Hospital Leipzig, Germany, while some of the exercise courses were conducted by associated regional partners (health sports clubs) [18,19,20].
Exercise sessions consisted of 45–60 min of aerobic (e.g., Nordic walking, swimming) and anaerobic (e.g., weightlifting) exercises of light to medium intensity, adapted to the physical abilities of participants. Dietary counselling group sessions were 90 min, and individual sessions 30 min long. Treatment focused on increasing the intake of complex carbohydrates, a reduction in the intake of short-chained carbohydrates and saturated fatty acids, taking into account individual needs. Behavioral therapy group sessions lasted 90 min and focused on goal-setting developing sustainable implementation strategies and problem solving. The sessions of all components (behavioral, diet and exercise therapy) took place within the year in a coordinated sequence so that the topics complement each other (Supplementary Information, Table S2).
At the end of the first segment of the behavioral weight loss program, an assessment comparable to the baseline assessment took place (t1). Thereafter, the interdisciplinary board meeting reviewed each patient`s progression to determine the further progression of therapy. If the patient wished to obtain bariatric surgery, a physician from the department of bariatric surgery was consulted. After completing the first program segment, bariatric surgery could be performed at any time of the program following the aforementioned algorithm.
In the second to fourth segments, the frequency of the appointments decreased (Supplementary Information Table S2). After completion of each segment lasting approximately one year, a segment assessment (t2–t4) identical to the baseline assessment was performed. If necessary, patients could be assigned to additional appointments with the dietitian and/or psychologist throughout the whole time of treatment.
The aim was to achieve a participation rate of at least 80%. Patients with irregular attendance without giving reasons were excluded prematurely. Patients who did not reach the 80% target for health reasons were allowed to continue participating in the program. Patients who ended the program prematurely were defined as dropouts. All patients included in the analysis of the Leipzig Obesity Management Program terminated the program (after completing t4 or prematurely) until 31 May 2020. The first therapy segment was started by 381 patients (n = 272, 71.4% female). Mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) age was 43.3 ± 0.7 years, mean BMI 44.3 ± 0.4 kg/m2 and mean body weight 127.3 ± 1.3 kg (Table 1). At first presentation, 118 (31%) patients had type 2 diabetes mellitus and 233 (61%) arterial hypertension. On average, costs per patient ranged between EUR 2000 for the first segment of therapy and EUR 700 for each of the second to fourth segments and were fully covered by the health insurance company.
2.3. Assessments of Laboratory Parameters
Laboratory analyses were conducted at the Institute for Laboratory Medicine, Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics at the Leipzig University Hospital. The calculation of the homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) was used to determine insulin resistance. Therefore, fasting glucose (mmol/L) was multiplied by fasting insulin (pmol/L) and divided by 156.2625 [21].
Patients were classified as “patients with diabetes” if patients reported a prior established diagnosis of type 2 diabetes, use of diabetes medication, hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) ≥6.5% (48 mmol/mol) and/or a fasting plasma glucose ≥ 7 mmol/L. Patients with changes in diabetes medication during the program were excluded from the respective analysis (n = 24). For assessment of HOMA-IR, additionally all patients with insulin treatment were excluded (n = 21). Concordantly, for the assessment of parameters of lipid metabolism, patients with changes in lipid lowering medication during the program were excluded from respective analyses (n = 15).
2.4. Statistical Analysis of Medical Data
All patients who began the first segment (n = 381) were included in the evaluation. Data from participants who dropped out or underwent bariatric surgery were included up to the point of behavioral weight loss program termination. Controlling for patient’s age at baseline and correcting for multiple testing due to the different time set points according to Bonferroni [22], linear mixed-model analyses were used to evaluate changes of parameters of interest of repeated measurements from t0 to t4 for all assessed parameters. Missing data were taken into account. Parameters with large gender differences were depicted also separated for gender (Table 1, Tables S6 and S7).
To model BMI changes over time, all available measurements were used in a sequence of linear mixed models that treated time as a continuous variable and patient as a random term. The first model in the sequence only contained time linearly, the second added its square, the third its cube, and the fourth added time to the fourth power. The optimal model was selected by minimizing the Bayesian information criterion. Gender did not show a significant difference in the linear model, which is why it was not included [23].
Data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). For analysis, Excel 2016 (Microsoft Corporation version 16.0; Redmond, WA, USA), SPSS (IBM® version 25.0; Chicago, IL, USA), STATA (version 16.0) and R (The R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Version 3.5.1, Vienna, Austria) were used. All analyses used a two-tailed α < 0.05 as level of significance.
2.5. Assessment and Statistical Analysis of Healthcare Costs
Average treatment and program costs were evaluated for the program group over a period of time starting three years before program and ending with the fourth year of treatment. Treatment costs included inpatient, outpatient and drug costs. There were also patients who did not incur any further healthcare costs in addition to the costs of the therapy program. These patients were also included in the evaluation. Because of dropouts and different durations of participation in the program, we standardized the cost outcomes to cost per capita and 30 days. We analyzed the changes of cost per time period and tested for significance with the Mann–Whitney U test correcting for multiple testing according to Bonferroni–Holm to maintain a global significance level of 5% [24].
3. Results
Of 411 eligible patients who fulfilled the inclusion and exclusion criteria and wanted to participate, 381 participants started the Leipzig Obesity Management Program. During the whole time of treatment, 73 (19%) participants underwent bariatric surgery and 234 (61%) quit the program prematurely. Self-reported reasons for dropping out were personal and familial (28%) or health reasons (16%) (Supplementary Information, Table S3).
The whole four years of the behavioral weight loss program were completed by 77 (20%) participants (Figure 1). The average time between t0 and t4 was four years and seven months.
Between t0 and the last available measurement before completion (t4) or drop out, respectively, including measurements between the segment assessments, 61% of patients lost weight, and mean weight loss was 2.9 ± 0.6 kg (2.3 ± 0.4%), p < 0.001 (Figure 2). Taking into account all available data at the two comparative time points irrespective of therapy adherence, mean body weight change during the first segment from t0 to t1 (n = 243) was −5 ± 0.6 kg (p < 0.001), from t0 to t2 (n = 126) −5.6 ± 1.1 kg, from t0 to t3 (n = 94) −4.9 ± 1.2 kg and from t0 to t4 (n = 77) −4.7 ± 1.4 kg.
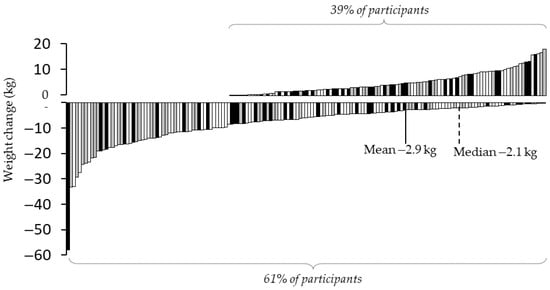
Figure 2.
Changes in body weight from baseline (t0) to last available measurement.
Weight changes of participants from baseline assessment t0 until the last available measurement. All data assessed in the program, including additional weight measurements between segment assessments, were included. Grey bars = program completers; black bars = participants who switched to bariatric surgery; white bars = participants who quit the program early (dropouts).
3.1. Mixed-Model Analysis (Starting at t0 with n = 381)
All patients who started the behavioral weight loss program (n = 381) were included in the mixed-model analysis regarding all measured parameters. For all assessed parameters, mean values from t0 to t4 and tests for significant time effects using mixed-model analysis are depicted in Table 1; results are listed for the whole sample, anthropometric data are also listed separately for women and men. Available patient measurements with data at different assessments for each parameter are shown in Supplementary Information, Table S4.

Table 1.
Anthropometric, metabolic and psychological parameters over the course of the Leipzig Obesity Management Program (n = 381).
Table 1.
Anthropometric, metabolic and psychological parameters over the course of the Leipzig Obesity Management Program (n = 381).
| t0 | t1 | t2 | t3 | t4 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients n | 381 | 243 | 126 | 94 | 77 | |
| Women n (%) | 272 (71.4%) | 173 (71.2%) | 89 (70.6%) | 67 (71.3%) | 55 (71.4%) | |
| Body weight (kg) | 127.3 ± 1.3 | 122.2 ± 1.3 *** | 123.2 ± 1.4 *** | 124.2 ± 1.4 ** | 124.2 ± 1.5 ** | <0.001 |
| Women | 120.4 ± 1.3 | 115.3 ± 1.3 *** | 116.8 ± 1.4 *** | 117.6 ± 1.5 * | 117.6 ± 1.5 | <0.001 |
| Men | 144.3 ± 2.6 | 139.4 ± 2.7 *** | 138.2 ± 2.9 ** | 140.3 ± 2.7 ** | 140.4 ± 2.9 | <0.01 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 44.3 ± 0.4 | 42.6 ± 0.4 *** | 42.9 ± 0.4 *** | 43.3 ± 0.4 ** | 43.4 ± 0.5 ** | <0.001 |
| Women | 44.2 ± 0.5 | 42.3 ± 0.4 *** | 42.9 ± 0.5 *** | 43.2 ± 0.5 * | 43.2 ± 0.5 | <0.001 |
| Men | 44.7 ± 0.7 | 43.2 ± 0.7 *** | 42.9 ± 0.8 ** | 43.5 ± 0.8 ** | 43.5 ± 0.8 | <0.01 |
| Waist ratio (cm) | 129.7 ± 1.0 | 125.4 ± 1.0 *** | 124.9 ± 1.0 *** | 125.0 ± 1.0 *** | 126.4 ± 1.2 ** | <0.001 |
| Women | 125.1 ± 1.1 | 120.4 ± 1.1 *** | 120.0 ± 1.0 *** | 119.6 ± 1.1 *** | 120.1 ± 1.2 *** | <0.001 |
| Men | 140.9 ± 1.7 | 137.6 ± 1.6 ** | 136.8 ± 1.6 *** | 138.3 ± 1.8 | 141.9 ± 2.4 | <0.001 |
| Hip ratio (cm) | 138.6 ± 0.9 | 134.4 ± 0.9 *** | 133.1 ± 0.9 *** | 133.6 ± 1.0 *** | 134.7 ± 1.2 ** | <0.001 |
| Women | 139.4 ± 1.1 | 135.0 ± 1.1 *** | 133.6 ± 1.1 *** | 133.8 ± 1.1 *** | 134.7 ± 1.3 *** | <0.001 |
| Men | 136.9 ± 1.8 | 132.8 ± 1.7 *** | 131.7 ± 1.7 *** | 133.4 ± 2.0 | 138.1 ± 3.0 | <0.001 |
| Fasting glucose (mmol/L) | 6.1 ± 0.1 | 5.9 ± 0.1 ** | 6.1 ± 0.1 | 6.3 ± 0.2 | 6.3 ± 0.1 | <0.001 |
| Patients with diabetes § | 7.7 ± 0.2 | 7.4 ± 0.2 * | 7.8 ± 0.3 | 8.0 ± 0.4 | 8.0 ± 0.4 | <0.05 |
| (t0: 28.0%) | ||||||
| No diagnosed diabetes | 5.5 ± 0.0 | 5.4 ± 0.0 | 5.5 ± 0.1 | 5.7 ± 0.1 | 5.6 ± 0.1 | <0.01 |
| HbA1c (%) | 5.8 ± 0.0 | 5.6 ± 0.0 *** | 5.6 ± 0.0 *** | 5.7 ± 0.1 ** | 5.7 ± 0.1 | <0.001 |
| Patients with diabetes § | 6.6 ± 0.1 | 6.2 ± 0.1 *** | 6.2 ± 0.1 ** | 6.4 ± 0.1 | 6.4 ± 0.1 | <0.001 |
| No diagnosed diabetes | 5.5 ± 0.0 | 5.3 ± 0.0 *** | 5.4 ± 0.0 *** | 5.4 ± 0.0 *** | 5.4 ± 0.0 | <0.001 |
| C-peptide (nmol/L) | 1.4 ± 0.0 | 1.3 ± 0.0 ** | 1.2 ± 0.0 *** | 1.1 ± 0.0 *** | 1.1 ± 0.1 ** | <0.001 |
| Patients with diabetes § | 1.6 ± 0.1 | 1.5 ± 0.1 | 1.3 ± 0.1 * | 1.2 ± 0.1 *** | 1.4 ± 0.2 | <0.01 |
| No diagnosed diabetes | 1.3 ± 0.0 | 1.2 ± 0.0 ** | 1.1 ± 0.0 *** | 1.0 ± 0.1 *** | 1.0 ± 0.0 *** | <0.001 |
| HOMA-IR | 6.0 ± 0.3 | 4.9 ± 0.2 *** | 5.1 ± 0.3 | 5.2 ± 0.3 | 5.0 ± 0.3 * | <0.01 |
| Patients with diabetes † | 8.1 ± 0.4 | 6.2 ± 0.8 * | 6.7 ± 1.1 | 6.8 ± 0.9 | - | <0.05 |
| (t0: 22.1%) | ||||||
| No diagnosed diabetes | 5.3 ± 0.2 | 4.5 ± 0.2 ** | 4.5 ± 0.3 * | 4.6 ± 0.4 | 4.3 ± 0.3 ** | <0.01 |
| Total cholesterol ‡ (mmol/L) | 5.1 ± 0.1 | 5.0 ± 0.1 ** | 4.9 ± 0.1 ** | 4.9 ± 0.1 * | 4.9 ± 0.1 ** | <0.01 |
| LDL cholesterol ‡ (mmol/L) | 3.3 ± 0.1 | 3.2 ± 0.1 * | 3.3 ± 0.1 | 3.2 ± 0.1 | 3.2 ± 0.1 * | <0.05 |
| HDL cholesterol ‡ (mmol/L) | 1.2 ± 0.0 | 1.3 ± 0.0 ** | 1.3 ± 0.0 ** | 1.3 ± 0.0 ** | 1.3 ± 0.0 *** | <0.001 |
| Triglycerides ‡ (mmol/L) | 1.8 ± 0.1 | 1.7 ± 0.1 | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 1.9 ± 0.1 | 1.8 ± 0.1 | <0.01 |
| C-reactive protein (mg/L) | 8.4 ± 0.3 | 7.6 ± 0.5 | 7.0 ± 0.6 | 8.7 ± 1.7 | 6.5 ± 0.5 ** | <0.01 |
| ASAT (µkat/L) | 0.5 ± 0.0 | 0.5 ± 0.1 *** | 0.5 ± 0.0 | 0.4 ± 0.0 *** | 0.4 ± 0.0 *** | <0.001 |
| ALAT (µkat/L) | 0.6 ± 0.0 | 0.5 ± 0.0 *** | 0.5 ± 0.0 | 0.5 ± 0.0 *** | 0.5 ± 0.0 *** | <0.001 |
| GGT (µkat/L) | 0.7 ± 0.0 | 0.6 ± 0.0 ** | 0.6 ± 0.0 | 0.6 ± 0.0 | 0.6 ± 0.0 * | <0.01 |
| Quality of life (EUROHIS-QOL) | 3.2 ± 0.0 | 3.4 ± 0.0 *** | 3.5 ± 0.1 *** | 3.6 ± 0.1 *** | 3.6 ± 0.1 *** | <0.001 |
| Depression (PHQ-9) | 7.9 ± 0.3 | 6.2 ± 0.3 *** | 5.9 ± 0.4 *** | 6.3 ± 0.3 *** | 6.3 ± 0.4 *** | <0.001 |
Average ± standard error of the mean. Derived from the mixed-model analysis, significance levels depicted through asterisks on the respective mean value refer to tests of differences between baseline (t0) and the respective time point, controlling for age and multiple testing according to Bonferroni [22]. Distinct p-values are shown for tests of significant time/treatment effects within the mixed-model analysis. ALAT, alanine aminotransferase; ASAT, aspartate aminotransferase; EUROHIS-QOL, EUROHIS-quality of life 8 item index [15]; GGT, gamma glutamyltransferase; HbA1c, hemoglobin A1c, HDL, high density lipoprotein; LDL, low density lipoprotein; PHQ-9, Patient Health Questionnaire [16]; t1–4, 1st to 4th segment assessment. § Patients with type 2 diabetes without changes in diabetes medication during the course of the program; n = 24 were thus excluded from this analysis: in 17 patients glucose lowering medication was intensified, in 7 patients reduced; † patients with type 2 diabetes without changes in diabetes medication during the course of the program and without insulin therapy; n = 45 were thus excluded from this analysis; ‡ patients without changes in lipid lowering medication, during the course of the program; n = 15 were thus excluded from this analysis: in 10 patients lipid lowering medication was intensified, in 5 patients reduced. *** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05.
Compared to t0, most health parameters showed statistically significant decreases at t4. Specifically, the BMI was reduced from 44.3 ± 0.4 kg/m2 at t0 to 43.4 ± 0.5 kg/m2 at t4 (p < 0.01), with a significant treatment effect over the whole time course (p < 0.001) (Table 1). HOMA-IR decreased from 6.0 ± 0.3 at t0 to 5.0 ± 0.3 at t4 (p < 0.05; whole time course p < 0.01). The HbA1c between t0 and t4 did not change statistically significantly for the whole cohort (p = 0.1), but the mixed-model analysis over the whole time course showed a statistically significant effect (p < 0.001). Analyses of subgroups of diabetic and non-diabetic patients revealed the same tendencies as the whole group (Table 1, Figure 3). For the whole sample, low density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol decreased from 3.3 ± 0.1 mmol/L at t0 to 3.2 ± 0.1 mmol/L at t4 (p < 0.05; whole time course p < 0.05). The quality of life score (EUROHIS-QOL) improved from 3.3 ± 0.0 points at t0 to 3.6 ± 0.1 points at t4 (p < 0.001; whole time course p < 0.001) One of the EUROHIS-QOL items, unrelated to health, “How satisfied are you with the conditions of your living place?”, did not change, unlike all other items (Supplementary Information, Tables S5 and S6). The depressive symptoms score (PHQ-9) decreased from 3.2 ± 0.0 points at t0 to 3.6 ± 0.1 points at t4 by (p < 0.001; whole time course p < 0.001). A total of 217 persons completed the PHQ-9-score for depressive symptoms at least twice; 43 (20%) people had a reduction of 5 points or less, and 17 (8%) had an increase of 5 points or more.
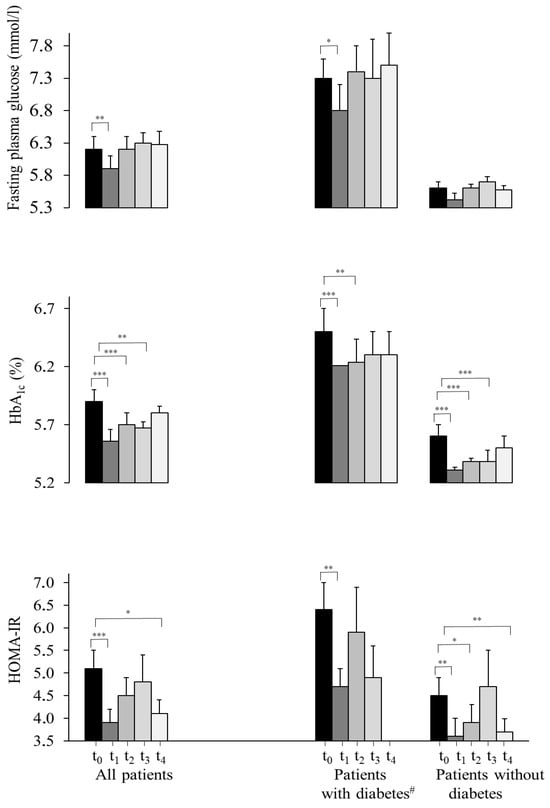
Figure 3.
Metabolic and psychological parameters over time. Progression of fasting glucose, HbA1c and HOMA-IR of all patients, persons with type 2 diabetes and without a diabetes diagnosis, quality of life and depressive symptoms from t0 to t4. Values are presented as average ± standard error of the mean. Derived from the mixed-model analysis, significance levels depicted through asterisks on the respective mean values refer to tests of differences between baseline (t0) and the respective time points, controlling for age and multiple testing according to Bonferroni [22]. # Patients were defined as patients with type 2 diabetes if patients reported a previously established diagnosis of type 2 diabetes, were taking diabetes medication, had an HbA1c ≥ 6.5% (48 mmol/mol) and/or a fasting plasma glucose ≥ 7 mmol/L. *** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05. HbA1c, hemoglobin A1c; HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance; t1–4, 1st to 4th segment assessment.
For the analysis of BMI changes, the model containing terms up to the cubic terms was optimal. All patients with at least two weight measurements were included, starting at t0 with n = 268. BMI reached its lowest value approximately two years after the beginning of the program. Subsequently, BMI increased moderately, but remained well below the baseline value (Figure 4).
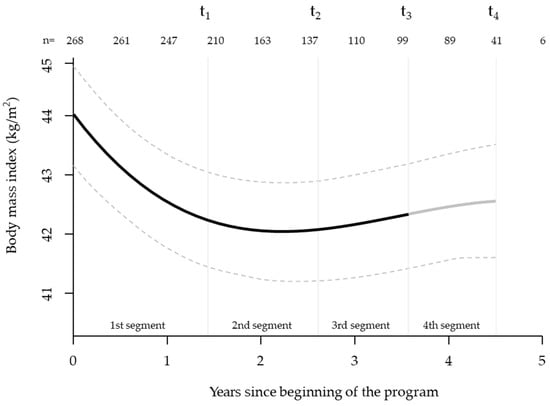
Figure 4.
Trajectory of body mass index during the four-year intervention. Mean body mass index (in kg/m2, black line) ± 95% confidence interval (grey lines) of all participants during the time of treatment. All available weight measurements, including those between segment assessments, were included. Markers for segment assessments t1–4 are mean time points for all participants who completed the respective examination. The x-axis shows the mean duration of each program segment. T1–4, 1st to 4th segment assessment.
3.2. Completer Analysis of Variance of All Measured Parameters (n = 77)
For the analysis of variance of all measured parameters, all patients who completed t4 were included (n = 77). Mean weight loss for this group was 4.6 ± 1.4 kg (−3.4 ± 1.1%, both t0 vs. t4 and whole time course p < 0.001, Supplementary Information, Table S7). At the last measurement (t4), 28 (36%) persons had a weight loss of 5% or more and 16 (21%) of 10% or more compared to the initial weight. Further, HbA1c decreased by 0.1 ± 0.1–points (p < 0.05; whole time course p < 0.001) and HOMA-IR by 0.9 ± 0.3 (p < 0.01; whole time course not statistically significant with p = 0.16, Table S7). For the whole sample, LDL cholesterol showed a trend for a decrease with −0.1 ± 0.1 mmol/L (p = 0.07; whole time course p = 0.18). The quality of life score (EUROHIS-QOL) improved by 0.2 ± 0.1 points (p < 0.01; whole time course p < 0.05) and the depressive symptoms score (PHQ-9) did not change statistically significantly (p = 0.45; whole time course p = 0.19).
3.3. Exploratory Analysis of Healthcare Cost Changes over Time (Starting Three Years Before Program)
When comparing the average costs for outpatient care before and during treatment, the trend increase did not reach a significant level (p = 0.12). Average costs for drugs also numerically changed up and down per year over time and increased continuously from the second year of the program. When comparing the average costs for drugs before and during treatment, the trend increase did not reach a significant level (p = 0.24). When comparing the average costs for hospital care before and during treatment, the trend increase did not reach a significant level (p = 0.51). In summary, all healthcare costs were numerically higher before and after the program, but none of the observed changes were statistically significant (Figure 5).
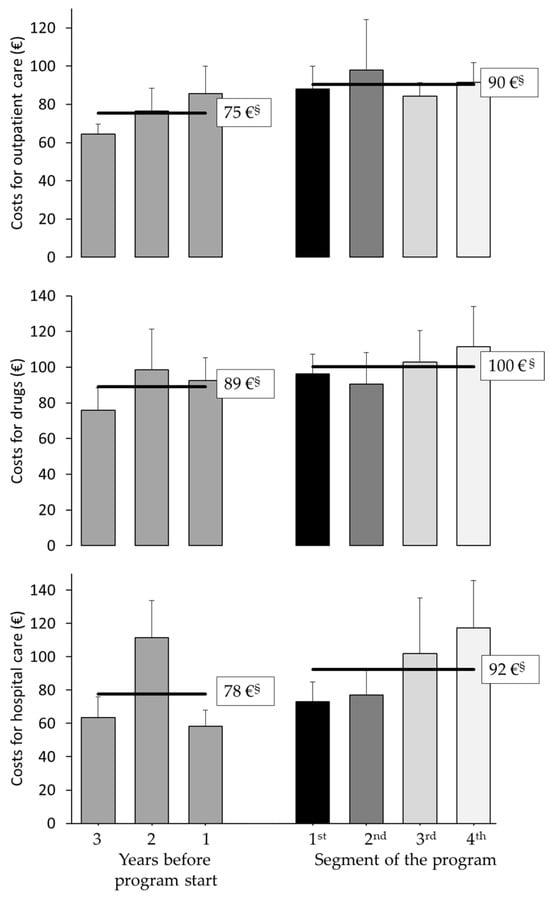
Figure 5.
Health care costs before and during program participation. Average per-patient costs for outpatient care, medication, and hospitalizations, excluding program costs. Costs were assessed for three years prior to program start and during the four-year intervention. No statistically significant differences were observed (t-test with independent, unpaired samples). § Mean costs of (left) three years before start of the program, and (right) four years of participation in the program.
4. Discussion
Weight loss through behavioral weight loss programs leads to a clinically relevant improvement of obesity associated comorbidities [10]. However, therapy adherence and coverage of the costs of such programs by healthcare providers is essential for success. Often, the duration of programs fully financed by health insurance is too short or coverage is not available at all, or patients quit programs prematurely, yielding only partial effects. The reasons for limited motivation to participate include unrealistic weight loss expectations and a non-individualized therapy [25,26]. This may lead to an initial weight loss followed by more or less rapid weight regain, resulting in little benefit for patients [27]. Further reasons for unsatisfactory therapy effects may be a single focus on nutritional therapy or physical activity [6], but not a combination of both interventions, accompanied by cognitive behavioral training as recommended by international guidelines [6,7].
Some behavioral weight loss programs include a phase of formula diet at the beginning of the treatment [10,11,12]. In our Leipzig Obesity Management Program, we did not include a formula phase in order to also be able to offer the program to people who are not able to conduct a meal replacement diet due to personal preference, medical reasons or the high costs of such therapeutic options. In addition, the German healthcare system does not fund the use of meal replacement products.
During the first intensive segment of the multimodal treatment program, patients who absolved the first segment lost 5 kg of their initial bodyweight. The second to fourth segments aimed to maintain the weight loss achieved in the first segment. This goal was achieved considering all patients from the beginning up to the last measured weight. There was no statistically significant weight regain after t1, and mean bodyweight at the end of the program was significantly lower than at the beginning of the program. To achieve substantial metabolic benefit, guidelines recommend weight loss of ≥10% of the initial weight for this patient group [6]. This goal was only achieved by 21% of completers. However, weight loss as the only marker for success of lifestyle interventions in obesity is less and less considered. Instead, the focus is shifting to accompanying positive medical changes, such as metabolic and psychological improvements [7]. In the present study, the metabolic and psychological improvements were also significant, despite the fact that weight loss achieved in the majority of participants can be classified as low.
Up to date, few long-term behavioral weight loss intervention studies without meal replacement and with an intervention lasting longer than 1 year are available. In the US “Practice-based Opportunities for Weight Reduction” (POWER) study, participants were randomized into two different intervention groups and one control group. One of the intervention groups had remote support via telephone or internet, and the other intervention group had in-person weight loss support. The intervention groups had 6 months of intensive therapy with 1.5 years of follow-up program, which had more frequent diet counselling visits or general contact to clarify questions and increase motivation (in-person group: 30 group sessions, 10 individual sessions, 21 phone contacts; remote support group 33 phone contacts) than our program during the same time period. At the end of observation, a weight loss of 5.2%, or 5.1 kg, was achieved in the in-person treatment group, 5.0%, or 4.6 kg, in the remote support group, and 1.1%, or 0.8 kg, in the control group [28]. The more intense follow-up program may explain higher weight loss outcomes than in our study. Furthermore, the mean baseline BMI of the intervention groups were 36.0 kg/m2 in the remote support group and 36.8 kg/m2 in the in-person treatment group, which also differed clearly from the population of our study with an average BMI of 44.3 kg/m2.
As stated in the obesity guidelines of the American Diabetes Association of 2022, a weight reduction of 3 to 5% can improve relevant health parameters such as glycemic control and other cardiovascular risk factors [29]. In our cohort, all assessed parameters of glucose metabolism improved significantly in both groups, including participants with and without diagnosis of type 2 diabetes at baseline. As expected, in patients without diabetes, insulin resistance was common, with mean HOMA-IR at baseline at 5.3 ± 0.2. According to data from the American Diabetes Prevention Program, the risk of diabetes in this group is extremely high [30].
In both groups, persons with and without diabetes, a reduction of the LDL cholesterol concentrations leads to a risk reduction for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease [31,32]. The current analysis showed a significant decrease of LDL cholesterol during the time of treatment. Even a diet-induced change of 0.1 mmol/L, as achieved by the participants of our program, has a positive effect on the risk for cardiovascular disease [33].
The C-reactive protein (CRP) is associated with inflammatory processes in the human body. In our study, concentrations decreased with bodyweight reduction. It is known that lifestyle changes, especially exercise, have positive effects on CRP [34]. Another influencing factor appears to be nutritional behavior. Many components of a healthy and balanced diet seem to have a positive effect on inflammatory body processes [35]. All of these factors could have contributed the CRP decrease seen in our cohort.
In our study, scores for quality of life and depressive symptoms improved significantly. However, because the study lacked a placebo control group, nonspecific treatment expectation affecting mood cannot fully be ruled out (Hawthorne effect) [36]. Nevertheless, the EUROHIS-QOL item on life situation did not change, which could indicate that effects on PHQ-9 and EUROHIS-QOL were driven by the beneficial medical effects of the behavioral weight loss program. In contrast, in the other non-health related EUROHIS-QOL item regarding financial situation, we saw a significant improvement, probably because of an improved capability of our patients to being employed. However, this is speculative because socioeconomic data were not assessed at measurements t1-t4. For PHQ-9, a change of five or more points is considered clinically relevant [37]. In our cohort, 20% of the patients who completed the questionnaire at least twice had an improvement of five or more points from baseline to the last available measurement, whereas only 8% of the participants a deterioration of this magnitude.
Dropout rates during the four segments of our program were between 36% (first treatment segment) and 11% (fourth segment), and the mean dropout rate per treatment segment was 23%. Additionally, 19% of patients starting the program were transferred to surgical obesity treatment during the program and did not complete all four segments of the behavioral weight loss treatment (Figure 1). Neri et al. (2024) investigated reasons for dropouts in adults with overweight and obesity absolving a cognitive behavioral treatment [38]. They reported a dropout-rate between 5 and 62% in the studies included in their review. The focus was primarily on the reasons for dropping out. We only recorded these in categorized form. However, health and familial reasons appear to be a common reason. Looking at the dropout-rates of the studies in relation to the duration of the intervention, the duration seems to have an impact on the dropout rate [38]. To our knowledge, no other evaluation of a behavioral treatment program under real-world conditions with an intervention period of four years has yet been published. Thus, a comparison of the dropout rate is severely limited. However, the high dropout rate and the associated lack of follow-up data of dropped out participants have to be considered when interpreting our data.
Although the evaluation of the cost efficacy of reported behavioral weight loss programs is difficult due to inconsistent methodologies of analyses, behavioral weight loss interventions seem to be cost-effective [39], with a non-linear relationship between healthcare costs and BMI change [40]. Without intervention, in persons with obesity, further weight gain occurs with increasing age regardless of the initial weight [3]. Consequently, considering the previous literature [41], we hope that the program costs will be compensated on the long run by reduced healthcare costs for obesity associated comorbidities. However, this verification requires a longer observation period.
Some limitations of our study have to be discussed. First, our study was not a randomized clinical trial with an untreated group, but an uncontrolled observation of real-world data. Therefore, we cannot exclude unspecific treatment effects (e.g., Hawthorne effect), and no conclusions about causality can be drawn. However, our aim was to evaluate a behavioral weight loss program which was fully covered by a health insurance company and open to all patients insured with that company under real-world conditions. We wanted to investigate if our program, which clearly differs in patient selection and available resources from controlled study conditions, which are usually far away from real-world situations, can achieve meaningful benefits for participants. Second, healthcare costs could only be collected for fully completed therapy years, and thus lacks statistical significance and is constrained by the short evaluation period and dropout-related data gaps. Nonetheless, in our opinion it provides a preliminary view of cost trends and justifies longer-term follow-up. Third, our evaluation only covers the effects on body weight and health parameters during the treatment period. To evaluate continuing change, a follow up assessment in the years after the end of the program should be conducted. A study on this issue is already ongoing. And fourth, socioeconomic variables were not collected. The absence of longitudinal data on socioeconomic variables constrains the ability to comprehensively assess the broader determinants influencing health trajectories. Socioeconomic data should be included in further analysis.
5. Conclusions
The current evaluation shows that the four-year Leipzig Obesity Management Program, which is fully funded by a health insurance company, is a promising treatment approach for people with obesity class 2 and 3. A comparison with other studies showed that the intensity of follow-up care is decisive for long-term success of therapy. Health effects were maintained until the end of the program, although there was a slight vanishing trend in achieved medical benefits after the first intensive segment of therapy. With regard to healthcare costs, there was no significant change during the period of evaluation. Here, more accurate studies with longer observation periods are necessary for a better assessment. However, the most outstanding feature of this evaluation is the real-world data. In contrast to randomized, controlled studies under research conditions, our real-world data allow an unbiased view of the achievable clinical effectiveness of the Leipzig Obesity Management Program and is thus an important contribution to the development of treatment strategies for obesity.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/obesities5030058/s1, Table S1: Laboratory parameters collected within the program (t0–t4); Table S2: Summary of the three courses of the Leipzig Obesity Management Program of the first treatment segment (each patient was included into one of the courses) and the classes of the second to fourth segment of the program; Table S3: Individual items of the EUROHIS-QOL-questionnaire; Table S4: Individual items of the PHQ9-questionnaire; Table S5: Self-reported reasons for dropping out (n = 237); Table S6: Available patient measurements with data at different assessments for each parameter (differences occurred due to missing data); Table S7: Development of anthropometric, metabolic and psychological parameters during therapy progress of the t4-completers (n = 77).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.V.F., M.S., M.F., A.H. and H.S.; methodology, S.V.F., M.F. and H.S.; validation, S.V.F., M.F. and H.S.; formal analysis, S.V.F., H.-C.P. and S.V.; investigation, S.V.F. and H.S.; resources, M.S., M.F. and M.B.; data curation, S.V.F., H.F., N.S. and H.S.; writing—original draft preparation, S.V.F., H.-C.P., S.V. and H.S.; writing—review and editing, S.V.F., H.-C.P., S.V., F.F., H.F., N.S., M.S., M.F., M.B., A.H. and H.S.; visualization, S.V.F. and H.S.; supervision, A.H. and H.S.; project administration, S.V.F., F.F. and N.S.; funding acquisition, M.S., M.F. and M.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Supported by the Open Access Publishing Fund of Leipzig University.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of the University of Leipzig [file number 157-12-12122011 and 06/23/2012].
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data that were generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available in pseudonymized form on request from the corresponding author in compliance with legal requirements and the informed consent.
Acknowledgments
We thank all participants of the Leipzig Obesity Management Program for agreeing to analyze their data. We thank to David Petroff for the statistical advice.
Conflicts of Interest
M.B. received honoraria as a consultant and speaker from Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Daiichi-Sankyo, Lilly, Novo Nordisk, Novartis, Pfizer and Sanofi. A.H. reported receiving grants from the Federal Ministry of Education and Research, German Research Foundation, and Roland Ernst Foundation for Healthcare outside the submitted work; royalties for books on the treatment of eating disorders and obesity with Hogrefe and Kohlhammer; honoraria for workshops and lectures on eating disorders and obesity and their treatment; honoraria as an editor of the International Journal of Eating Disorders and the journal Psychotherapeut; honoraria as a reviewer from Mercator Research Center Ruhr, Oxford University Press, and the German Society for Nutrition; and honoraria as a consultant for WeightWatchers, Zweites Deutsches Fernsehen, and Takeda. Susan Vogl and Franziska Frölich was employed by the company AOK PLUS—Health Insurance Company for Saxony and Thuringia. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Avila, C.; Holloway, A.C.; Hahn, M.K.; Morrison, K.M.; Restivo, M.; Anglin, R.; Taylor, V.H. An Overview of Links Between Obesity and Mental Health. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2015, 4, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Oganisation. Obesity. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/obesity#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 25 October 2024).
- Teuner, C.M.; Menn, P.; Heier, M.; Holle, R.; John, J.; Wolfenstetter, S.B. Impact of BMI and BMI change on future drug expenditures in adults: Results from the MONICA/KORA cohort study. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2013, 13, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, J. Updated review on the benefits of weight loss. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 2002, 26 (Suppl. S4), S25–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yumuk, V.; Tsigos, C.; Fried, M.; Schindler, K.; Busetto, L.; Micic, D.; Toplak, H. European Guidelines for Obesity Management in Adults. Obes. Facts 2015, 8, 402–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsche Adipositas-Gesellschaft (DAG) e. v. S3-Leitlinie Adipositas—Prävention und Therapie. Available online: https://register.awmf.org/de/leitlinien/detail/050-001 (accessed on 16 July 2025).
- Wharton, S.; Lau, D.C.W.; Vallis, M.; Sharma, A.M.; Biertho, L.; Campbell-Scherer, D.; Adamo, K.; Alberga, A.; Bell, R.; Normand Boulé, N.; et al. Obesity in adults: A clinical practice guideline. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2020, 192, E875–E891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swan, W.I.; Vivanti, A.; Hakel-Smith, N.A.; Hotson, B.; Orrevall, Y.; Trostler, N.; Howarter, K.B.; Papoutsakis, C. Nutrition Care Process and Model Update: Toward Realizing People-Centered Care and Outcomes Management. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2017, 117, 2003–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.J.; von dem Knesebeck, O. Income and obesity: What is the direction of the relationship? A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e019862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lean, M.E.; Leslie, W.S.; Barnes, A.C.; Brosnahan, N.; Thom, G.; McCombie, L.; Peters, C.; Zhyzhneuskaya, S.; Al-Mrabeh, A.; Hollingsworth, K.G.; et al. Primary care-led weight management for remission of type 2 diabetes (DiRECT): An open-label, cluster-randomised trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weimann, A.; Fischer, M.; Oberänder, N.; Prodehl, G.; Weber, N.; Andrä, M.; Krug, J.; Wallstabe, I.; Schiefke, I.; Bischoff, S.C. Willing to go the extra mile: Prospective evaluation of an intensified non-surgical treatment for patients with morbid obesity. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 1773–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wexler, D.J.; Chang, Y.; Levy, D.E.; Porneala, B.; McCarthy, J.; Rodriguez Romero, A.; Goldman, V.; Copeland, P.M.; Steppel-Reznik, J.; Delahanty, L.M. Results of a 2-year lifestyle intervention for type 2 diabetes: The Reach Ahead for Lifestyle and Health-Diabetes randomized controlled trial. Obesity 2022, 30, 1938–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, E.W.; Patorno, E.; Karter, A.J.; Mehta, R.; Huang, E.S.; White, M.; Patel, C.J.; McElvaine, A.T.; Cefalu, W.T.; Selby, J.; et al. Use of Real-World Data in Population Science to Improve the Prevention and Care of Diabetes-Related Outcomes. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, 1316–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenzel, S.V.; Bach, S.; Ahrens, S.; Hellbardt, M.; Hilbert, A.; Stumvoll, M.; Fasshauer, M.; Schlögl, H. Ausweg aus der Versorgungslücke: Voll Krankenkassen-finanzierte konservative Adipositas-Therapie. Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 2020, 145, e78–e86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brähler, E.; Mühlan, H.; Albani, C.; Schmidt, S. Teststatistische Prüfung und Normierung der deutschen Versionen des EUROHIS-QOL Lebensqualität-Index und des WHO-5 Wohlbefindens-Index. Diagnostica 2007, 53, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löwe, B.; Kroenke, K.; Herzog, W.; Gräfe, K. Measuring depression outcome with a brief self-report instrument: Sensitivity to change of the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9). J. Affect. Disord. 2004, 81, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, A. Aktuelle S3-Leitlinie „Therapie der Adipositas und metabolischer Erkrankungen“. Allg.-Und Visz. Up2date 2019, 13, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, D.; Hörmann, J.; Predel, H.G.; Berg, A. A 12-Month Lifestyle Intervention Program Improves Body Composition and Reduces the Prevalence of Prediabetes in Obese Patients. Obes. Facts 2018, 11, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, A.; Hellbardt, M.; Baldofski, S.; de Zwaan, M.; Hilbert, A. Evaluation des einjährigen multimodalen Therapieprogramms DOC WEIGHT® 1.0 zur Gewichtsreduktion bei Patienten mit Adipositas Grad II und III. Psychother. Psychosom. Med. Psychol. 2016, 66, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwalm, S.V.; Hilbert, A.; Stumvoll, M.; Striebel, R.; Sass, U.; Tiesler, U.; Kiess, W.; Alder, M.; Gausche, R.; Blüher, M.; et al. Das Leipziger Adipositasmanagement. Adipositas-Ursachen Folgeerkrankungen Ther. 2015, 09, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Matthews, D.R.; Hosker, J.P.; Rudenski, A.S.; Naylor, B.A.; Treacher, D.F.; Turner, R.C. Homeostasis model assessment: Insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985, 28, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtin, F.; Schulz, P. Multiple correlations and Bonferroni’s correction. Biol. Psychiatry 1998, 44, 775–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, G. Estimating the Dimension of a Model. Ann. Stat. 1978, 6, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, S. A Simple Sequentially Rejective Multiple Test Procedure. Scand. J. Stat. 1979, 6, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff, S.C.; Schweinlin, A. Obesity therapy. Clin Nutr ESPEN 2020, 38, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, G.A.; Heisel, W.E.; Afshin, A.; Jensen, M.D.; Dietz, W.H.; Long, M.; Kushner, R.F.; Daniels, S.R.; Wadden, T.A.; Tsai, A.G.; et al. The Science of Obesity Management: An Endocrine Society Scientific Statement. Endocr. Rev. 2018, 39, 79–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, D.H.; Yockey, S.R. Weight Loss and Improvement in Comorbidity: Differences at 5%, 10%, 15%, and Over. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2017, 6, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appel, L.J.; Clark, J.M.; Yeh, H.C.; Wang, N.Y.; Coughlin, J.W.; Daumit, G.; Miller, E.R., 3rd; Dalcin, A.; Jerome, G.J.; Geller, S.; et al. Comparative effectiveness of weight-loss interventions in clinical practice. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1959–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 8. Obesity and Weight Management for the Prevention and Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, S113–S124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnett, D.K.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Albert, M.A.; Buroker, A.B.; Goldberger, Z.D.; Hahn, E.J.; Himmelfarb, C.D.; Khera, A.; Lloyd-Jones, D.; McEvoy, J.W.; et al. 2019 ACC/AHA Guideline on the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2019, 140, e596–e646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grundy, S.M.; Stone, N.J.; Bailey, A.L.; Beam, C.; Birtcher, K.K.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Braun, L.T.; de Ferranti, S.; Faiella-Tommasino, J.; Forman, D.E.; et al. 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2019, 139, e1082–e1143. [Google Scholar]
- Authors/Task Force Members; ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines (CPG); ESC National Cardiac Societies. 2019 ESC/EAS guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: Lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. Atherosclerosis 2019, 290, 140–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Sadeghirad, B.; Ball, G.D.C.; da Costa, B.R.; Hitchcock, C.L.; Svendrovski, A.; Kiflen, R.; Quadri, K.; Kwon, H.Y.; Karamouzian, M.; et al. Comparison of dietary macronutrient patterns of 14 popular named dietary programmes for weight and cardiovascular risk factor reduction in adults: Systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomised trials. BMJ 2020, 369, m696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekhar, J.; Zaman, S. Associations Between C-Reactive Protein, Obesity, Sex, and PCI Outcomes: The Fat of the Matter. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2020, 13, 2893–2895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Lopez, O.; Martinez-Urbistondo, D.; Vargas-Nuñez, J.A.; Martinez, J.A. The Role of Nutrition on Meta-inflammation: Insights and Potential Targets in Communicable and Chronic Disease Management. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2022, 11, 305–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarney, R.; Warner, J.; Iliffe, S.; van Haselen, R.; Griffin, M.; Fisher, P. The Hawthorne Effect: A randomised, controlled trial. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2007, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroenke, K. Enhancing the clinical utility of depression screening. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2012, 184, 281–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, L.D.C.L.; Mariotti, F.; Guglielmetti, M.; Fiorini, S.; Tagliabue, A.; Ferraris, C. Dropout in cognitive behavioral treatment in adults living with overweight and obesity: A systematic review. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1250683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremmel, M.; Gerdtham, U.-G.; Nilsson, P.M.; Saha, S. Economic Burden of Obesity: A Systematic Literature Review. Int. J. Env. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.; Dixon, P.; Jones, H.E.; Davies, A.R.; Howe, L.D.; Davies, N.M. Long-term cost-effectiveness of interventions for obesity: A mendelian randomisation study. PLoS Med. 2021, 18, e1003725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Davies, A.; McCombie, L.; Briggs, A.; Messow, C.M.; Grieve, E.; Leslie, W.S.; Taylor, R.; Lean, M.E.J. Within-trial cost and 1-year cost-effectiveness of the DiRECT/Counterweight-Plus weight-management programme to achieve remission of type 2 diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).