Thermo-Fluid Dynamics Modelling of Liquid Hydrogen Storage and Transfer Processes
Abstract
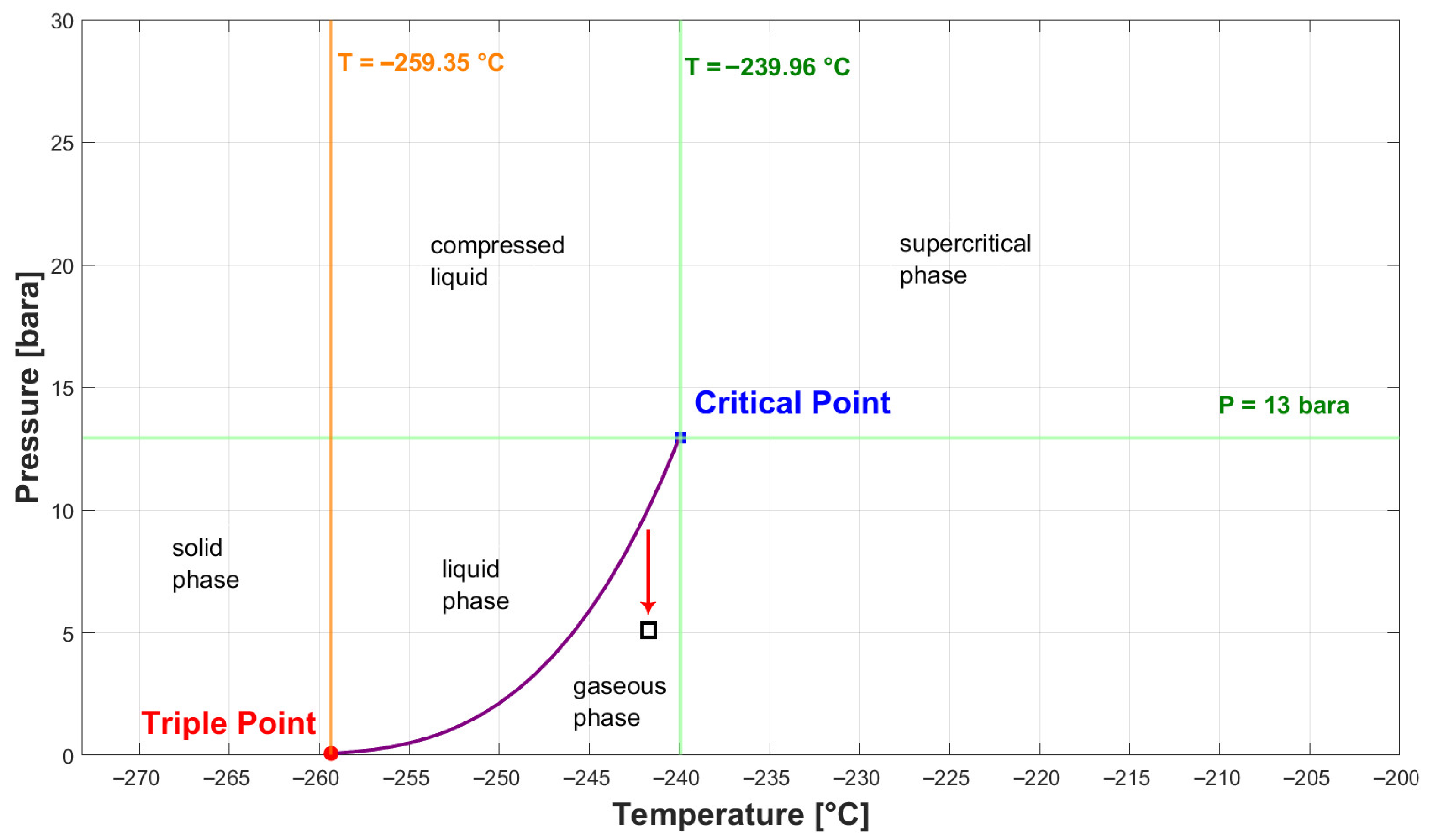
1. Introduction
- Thermodynamic behaviour within LH2 storage tanks;
- Multi-phase flow dynamics in storage and transfer systems.
- Map the current landscape of LH2 modelling techniques;
- Evaluate the extent of model validation against experimental data;
- Identify persistent knowledge gaps;
- Provide guidance for future research and model development.
2. State of the Art
- Thermodynamic behaviour of the storage tank:
- ○
- Heat transfer;
- ○
- Mass transfer including evaporation/condensation;
- ○
- Thermal stratification and pressurization;
- ○
- Venting and depressurization.
- Multi-phase flow:
- ○
- Sloshing;
- ○
- LH2 transfer;
- ○
- Flash boiling and pressure recovery.
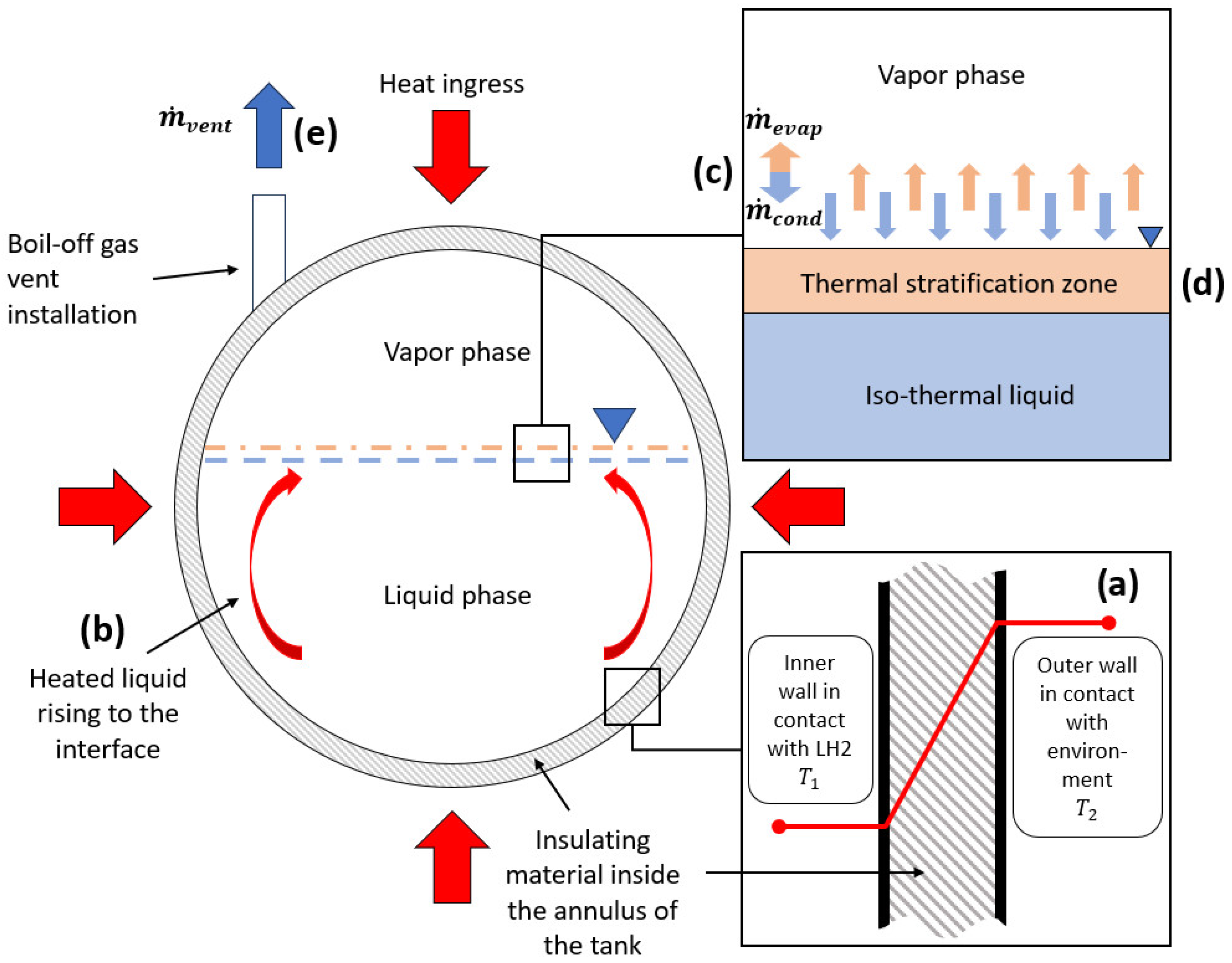
2.1. Heat Transfer
2.2. Mass Transfer Including Evaporation and Condensation
2.3. Thermal Stratification and Tank Pressurization
2.4. Venting and Tank Depressurization
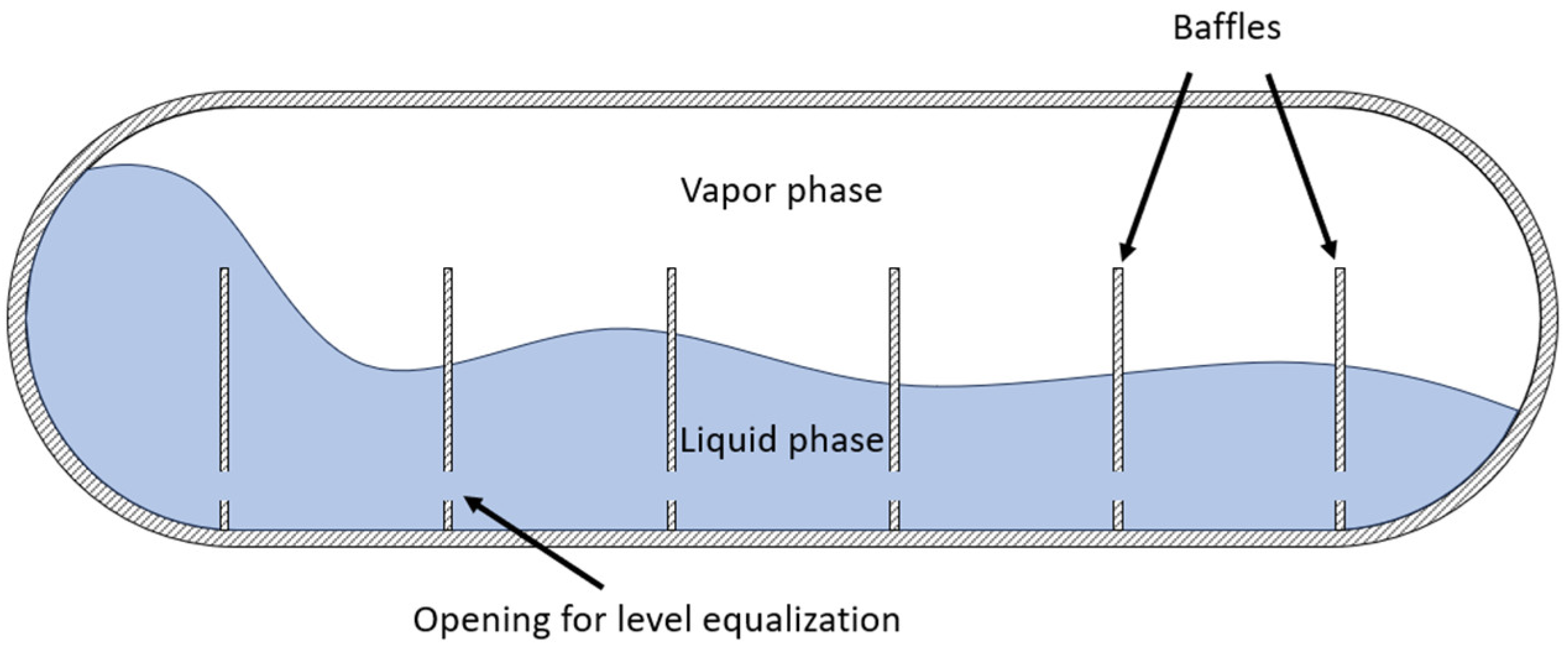
2.5. Sloshing
- Heat transfer—Sloshing dissipates kinetic energy into the tank system, transferring heat and accelerating fuel evaporation.
- Increased surface area—The motion increases the liquid–vapour interface, enhancing evaporation.
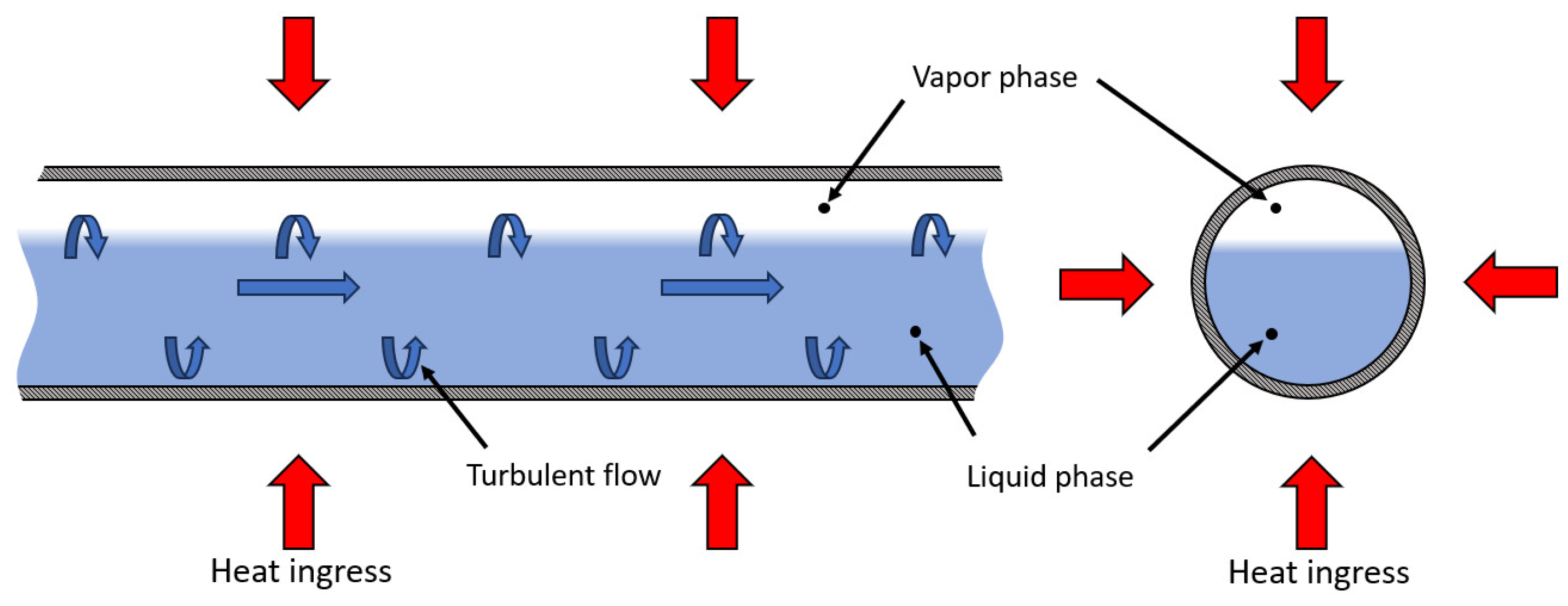
2.6. LH2 Transfer Operations
2.7. Flash Boiling and Pressure Recovery
3. Methodology
- What thermodynamic phenomena are covered by the existing literature for LH2?
- What are the proposed modelling approaches to simulate these phenomena?
- Are the proposed approaches validated?
- Why are certain models not validated/is there an identifiable knowledge gap or need for data?
- Liquid hydrogen or LH2;
- Model or Modelling;
- Simulation;
- Pressurization;
- Storage;
- Tank;
- Thermodynamic;
- Fluid dynamics.
- Publications in languages other than English and German were excluded;
- Models referring to substances other than LH2 were excluded;
- Excluded subject areas included the following terms:
- a.
- Medicine;
- b.
- Chemistry;
- c.
- Computer science;
- d.
- Social science;
- e.
- Pharmacology;
- f.
- Environmental science;
- g.
- Biology.
- Excluded keywords included the following terms:
- a.
- Combustion;
- b.
- Diffusion;
- c.
- Oxygen;
- d.
- Helium;
- e.
- Rocket engine;
- f.
- Ballistics;
- g.
- Viscosity;
- h.
- Cavitation;
- i.
- Catalyst.
4. Modelling of LH2 Thermal Dynamic Behaviour
- General analytical models;
- Lumped-parameter models (0D/1D models);
- Empirical and semi-empirical models;
- Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) models (2D/3D);
- Machine learning (ML) and artificial neural network (ANN) models;
- Numerical multidisciplinary simulation models.
4.1. Models Focusing on Thermodynamic Behaviour in Storage Tanks
4.1.1. Models Focusing on Heat Transfer
4.1.2. Models Focusing on Mass Transfer Including Evaporation and Condensation
4.1.3. Models Focusing on Thermal Stratification
4.1.4. Models Focusing on Tank Pressurization
4.1.5. Models Focusing on Venting and Tank Depressurization
4.2. Models Focusing on Multi-Phase Flow in Storage Tanks and Pipelines
4.2.1. Models Focusing on Sloshing
4.2.2. Models Focusing on Multi-Phase Flow During LH2 Transfer Operations
4.2.3. Models Focusing on Flash Boiling and Pressure Recovery
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- Development of reduced-order and hybrid models for real-time applications;
- Experimental campaigns under microgravity and maritime conditions;
- Integration of AI and sensor technologies for dynamic system monitoring;
- Systematic meta-analyses to assess model accuracy and generalizability.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hydrogen Storage. Available online: https://www.energy.gov/eere/fuelcells/hydrogen-storage (accessed on 2 May 2025).
- Møller, K.T.; Jensen, T.R.; Akiba, E.; Li, H. Hydrogen—A Sustainable Energy Carrier. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2017, 27, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIST Chemistry WebBook Hydrogen. Available online: https://webbook.nist.gov/cgi/cbook.cgi?Name=hydrogen&Units=SI (accessed on 10 December 2023).
- Vudumu, S.K. Experimental and Computational Investigations of Hydrogen Safety, Dispersion and Combustion for Transportation Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, Missouri University of Science and Technology, Rolla, MI, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Claussner Lucas, M.; Ustolin, F.; Scarponi, G.E. Design and Operation of Liquid Hydrogen Storage Tanks. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2024, 111, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Sun, P.; Li, P.; Zuo, Z.; Huang, Y. Transient Thermal Behavior of Multi-Layer Insulation Coupled with Vapor Cooled Shield Used for Liquid Hydrogen Storage Tank. Energy 2021, 231, 120859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, J.R.; Belcher, T.; Furby, J.; Giddens, P.; Hamill, B.; Nguyen, S.; Pedersen, K.; Smith, J.; Tashakkor, S.; Valenzuela, J.G.; et al. Long Duration Storage of Liquid Hydrogen via Two-Stage Active Cooling Hardware Characterization and Test Planning. In Proceedings of the AIAA SCITECH 2024 Forum, Orlando, FL, USA, 8–12 January 2024; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Orlando, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wooldridge, M.; Luebbers, R. Heat Transfer; McGraw Hill: Columbus, OH, USA, 2020; Available online: https://www.accessscience.com/content/article/a311100 (accessed on 30 November 2025).
- Matsuno, K.; Nemoto, A. Quantum as a Heat Engine—The Physics of Intensities Unique to the Origins of Life. Phys. Life Rev. 2005, 2, 227–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, R.F.; Nellis, G.F. Cryogenic Heat Transfer; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Webley, P.A.; Hughes, T.J. Thermodynamic Modelling of Low Fill Levels in Cryogenic Storage Tanks for Application to Liquid Hydrogen Maritime Transport. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 256, 124054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Zhang, X. Numerical Methods. In Modeling and Analysis of Modern Fluid Problems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 361–455. ISBN 978-0-12-811753-8. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.H. A Pressure Iteration Scheme for Two-Phase Flow Modeling. Tech. Rep. LA-UR 79-975 1980, 1, 407–431. [Google Scholar]
- Xavier, M.; Edwin Raj, R.; Narayanan, V. Thermal Stratification in LH2 Tank of Cryogenic Propulsion Stage Tested in ISRO Facility. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 171, 012063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, J.; Agrawal, G.; Agarwal, D.K.; Pisharady, J.C.; Sunil Kumar, S. Effect of Insulation Thickness on Pressure Evolution and Thermal Stratification in a Cryogenic Tank. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 111, 1629–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour Bonab, S.; Yazdani-Asrami, M. Investigation on the Heat Transfer Estimation of Subcooled Liquid Hydrogen for Transportation Applications Using Intelligent Technique. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 84, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydelott, J.C.; Spuckler, C.M. Venting of Liquid Hydrogen Tankage; National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Feng, Y.; Lei, G.; Li, Y. Fluid Sloshing Dynamic Performance in a Liquid Hydrogen Tank. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 13885–13894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inman, A.E.; Muehlbauer, J.G. Shuttle Performance Augmentation with the Titan Liquid Boost Module; National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Kartuzova, O.V.; Kassemi, M.; Hauser, D. Validation of a Two-Phase CFD Model for Predicting Propellant Tank Pressurization and Pressure Collapse in The Ground-Based K-Site Hydrogen Slosh Experiment. NASA Glenn Res. Cent. 2024, 15, 0547. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.R.; Gkantonas, S.; Mastorakos, E. Modelling of Boil-Off and Sloshing Relevant to Future Liquid Hydrogen Carriers. Energies 2022, 15, 2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tani, K.; Himeno, T.; Sakuma, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Kobayashi, H.; Toge, T.; Unno, S.; Kamiya, S.; Muragishi, O.; Kanbe, K. Pressure Recovery During Pressure Reduction Experiment with Large-Scale Liquid Hydrogen Tank. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 29583–29596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Watson, M. Guidance on Conducting a Systematic Literature Review. J. Plan. Educ. Res. 2019, 39, 93–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, C.; Byrne, J. The Benefits of Publishing Systematic Quantitative Literature Reviews for PhD Candidates and Other Early-Career Researchers. High. Educ. Res. Dev. 2014, 33, 534–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntley, S.C.; Gauntner, J.W.; Anderson, B.H. Wall and Bottom Heating of Liquid Hydrogen in a Propellant Tank; National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Yan, T.; Wang, J.; Ye, S.; Li, Y.; Zhuan, R.; Wang, B. CFD Investigation on Thermodynamic Characteristics in Liquid Hydrogen Tank During Successive Varied-Gravity Conditions. Cryogenics 2019, 103, 102973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.J.; Hastings, L. Large-Scale Liquid Hydrogen Testing of a Variable Density Multilayer Insulation with a Foam Substrate; National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, R.; Huang, Y.; Wu, J. Thermodynamic Analysis of Partially Filled Hydrogen Tanks in a Wide Scale Range. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2021, 193, 117007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustolin, F.; Iannaccone, T.; Cozzani, V.; Jafarzadeh, S.; Paltrinieri, N. Time to Failure Estimation of Cryogenic Liquefied Tanks Exposed to a Fire. In Proceedings of the 31st European Safety and Reliability Conference (ESREL 2021), Angers, France, 19–23 September 2021; Research Publishing Services: Singapore, 2021; pp. 935–942. [Google Scholar]
- Ustolin, F.; Scarponi, G.E.; Iannaccone, T.; Cozzani, V.; Paltrinieri, N. Cryogenic Hydrogen Storage Tanks Exposed to Fires: A CFD Study. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2022, 90, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pehr, K. Experimental Examinations on the Worst-Case Behaviour of LH2/LNG Tanks for Passenger Cars. In Proceedings of the 11th World Hydrogen Energy Conference, Stuttgart, Germany, 23–28 June 1996; 1996; pp. 2168–2187. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Li, M.; Qu, Z.; Tian, D.; Zhang, J. A Quasi-2D Thermodynamic Model for Performance Analysis and Optimization of Liquid Hydrogen Storage System with Multilayer Insulation and Vapor-Cooled Shield. J. Energy Storage 2023, 73, 109128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parello, R.; Defoort, S.; Benard, E.; Gourinat, Y. Design and Integration of a Liquid Hydrogen Tank on an Aircraft. In Proceedings of the AIAA SCITECH 2024 Forum, Orlando, FL, USA, 8–12 January 2024; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Orlando, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, N.; Li, S.; Yan, Y.; Hillmansen, S. Optimal Thermal Management on the Storage Vessle for Cryogenic Hydrogen-Powered Hybrid Train. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference (VPPC), Washington DC, USA, 7–10 October 2024; IEEE: Washington, DC, USA, 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, H.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, S.; Hou, Y. Thermodynamic Analysis of Vapor-Cooled Shield with Para-to-Ortho Hydrogen Conversion in Composite Multilayer Insulation Structure for Liquid Hydrogen Tank. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 50, 1448–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Wen, J.; Xin, B.; Zhou, A.; Wang, S. Transient-State Modeling and Thermodynamic Analysis of Self-Pressurization Liquid Hydrogen Tank Considering Effect of Vacuum Multi-Layer Insulation Coupled with Vapor-Cooled Shield. Energy 2024, 286, 129450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, W.A. Experimental and Analytical Investigation of Interfacial Heat and Mass Transfer in a Pressurized Tank Containing Liquid Hydrogen; National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.; Hasan, M.; Nyland, T. Mixing and Transient Interface Condensation of a Liquid Hydrogen Tank. In Proceedings of the 29th Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit, Monterey, CA, USA, 28–30 June 1993; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Monterey, CA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Schweickart, R.B. Thermodynamic Analysis of a Demonstration Concept for the Long-Duration Storage and Transfer of Cryogenic Propellants. Cryogenics 2014, 64, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, M. Pressurization of a Flightweight, Liquid Hydrogen Tank: Evaporation & Condensation at the Liquid/Vapor Interface. In Proceedings of the 53rd AIAA/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference, Atlanta, GA, USA, 10–12 July 2017; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, B.; Li, R.; Shen, X.; Wu, Y.; Quanwen, P.; Yuanxin, H.; Weiming, Z.; Zhihua, G. Theoretical Investigation on Heat Leakage Distribution between Vapor and Liquid in Liquid Hydrogen Tanks. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 17187–17201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Cao, J. CFD Simulation of Heat Transfer and Phase Change Characteristics of the Cryogenic Liquid Hydrogen Tank Under Microgravity Conditions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 7026–7037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Mérida, W. Thermal Performance of Cylindrical and Spherical Liquid Hydrogen Tanks. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 53, 667–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Lee, S.; Kim, S. A Thermodynamic Model for Cryogenic Liquid Hydrogen Fuel Tanks. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, B.; Sun, J.; Pan, Q.; Luo, G.; Tao, X.; He, Y.; Pfotenhauer, J.; Jin, T.; Gan, Z. Experimental and Computational Fluid Dynamic Investigation on Thermal Behaviors of Liquid Hydrogen During the No-Vented Storage Process: A Literature Review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 57, 822–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnett, R.W.; Voth, R.O. A Computer Program for the Calculation of Thermal Stratification and Self-Pressurization in a Liquid Hydrogen Tank; National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Grayson, G.D. Coupled Thermodynamic-Fluid-Dynamic Solution for a Liquid-Hydrogen Tank. J. Spacecr. Rockets 1995, 32, 918–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daigle, M.J.; Smelyanskiy, V.N.; Boschee, J.; Foygel, M. Temperature Stratification in a Cryogenic Fuel Tank. J. Thermophys. Heat Transf. 2013, 27, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhou, G. Study on Thermal Stratification in Liquid Hydrogen Tank Under Different Gravity Levels. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 9369–9378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydelott, J.C. Self Pressurization of Liquid Hydrogen Tankage. Master’s Thesis, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Gursu, S.; Sherif, S.A.; Veziroglu, T.N.; Sheffield, J.W. Analysis and Optimization of Thermal Stratification and Self-Pressurization Effects in Liquid Hydrogen Storage Systems—Part 1: Model Development. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 1993, 115, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gursu, S.; Sherif, S.A.; Veziroglu, T.N.; Sheffield, J.W. Analysis and Optimization of Thermal Stratification and Self-Pressurization Effects in Liquid Hydrogen Storage Systems—Part 2: Model Results and Conclusions. J. Energy Resour. Technol. 1993, 115, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsi, S.; Kassemi, M. Numerical and Experimental Comparisons of the Self-Pressurization Behavior of an LH2 Tank in Normal Gravity. Cryogenics 2008, 48, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartuzova, O.V.; Kassemi, M.; Moder, J.P.; Agui, J.H. Self-Pressurization and Spray Cooling Simulations of the Multipurpose Hydrogen Test Bed (MHTB) Ground-Based Experiment. In Proceedings of the 50th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference, Cleveland, OH, USA, 28–30 July 2014; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Cleveland, OH, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kassemi, M.; Kartuzova, O. Effect of Interfacial Turbulence and Accommodation Coefficient on CFD Predictions of Pressurization and Pressure Control in Cryogenic Storage Tank. Cryogenics 2016, 74, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, M.; Moder, J.P. Self-Pressurization of a Flightweight, Liquid Hydrogen Tank: Simulation and Comparison with Experiments. In Proceedings of the 52nd AIAA/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 25–27 July 2016; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Majumdar, A.; Valenzuela, J.; LeClair, A.; Moder, J. Numerical Modeling of Self-Pressurization and Pressure Control by a Thermodynamic Vent System in a Cryogenic Tank. Cryogenics 2016, 74, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, P.; Jeong, B.; Wang, H. Design and Optimization of a Type-C Tank for Liquid Hydrogen Marine Transport. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 34885–34896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahluwalia, R.K.; Peng, J.-K.; Roh, H.-S.; Papadias, D.; Wang, X.; Aceves, S.M. Liquid Hydrogen Storage System for Heavy Duty Trucks: Capacity, Dormancy, Refueling, and Discharge. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 34120–34131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matveev, K.I.; Leachman, J.W. The Effect of Liquid Hydrogen Tank Size on Self-Pressurization and Constant-Pressure Venting. Hydrogen 2023, 4, 444–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, S.; Lee, S.; Moon, S. CFD Thermo-Hydraulic Evaluation of a Liquid Hydrogen Storage Tank with Different Insulation Thickness in a Small-Scale Hydrogen Liquefier. Fluids 2023, 8, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.R.; Wang, B.; Pan, Q.W.; Wu, Y.Z.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Z.H.; Gan, Z.H. Modeling and Thermodynamic Analysis of Thermal Performance in Self-Pressurized Liquid Hydrogen Tanks. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 30530–30545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.A.; Wang, H.; Wang, B.; Xu, T.; Li, J.; He, Y.; Jin, T.; Gan, Z. Prediction of Pressure Evolution in Non-Venting Self-Pressurized Liquid Hydrogen Tanks Using Artificial Neural Network Approach. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 68, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, B.; Xu, T.; Shen, X.; He, Y.; Zhou, W.; Pfotenhauer, J.; Jin, T.; Gan, Z. Thermal Models for Self-Pressurization Prediction of Liquid Hydrogen Tanks: Formulation, Validation, Assessment, and Prospects. Fuel 2024, 365, 131247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blatt, M.H. Impirical Correlations for Pressure Rise in Closed Cryogenic Containers. JSR Spacecr. Rockets 1968, 5, 733–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Webley, P.A.; Hughes, T.J. Thermodynamic Modelling of Pressurised Storage and Transportation of Liquid Hydrogen for Maritime Export. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 62, 1273–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Lim, Y. Changes in Holding Time Depending Liquid Filling Ratio, Heat Transfer Parameters, and Shape of the Tank. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 82, 836–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandell, D.A.; Roudebush, W.H. Parametric Investigation of Liquid Hydrogen Tank Pressurization During Outflow; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Roudebush, W.H.; Mandell, D.A. Analytical Investigation of Some Important Parameters in the Pressurized Liquid Hydrogen Tank Outflow Problem; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Winters, W.S.; Houf, W.G. Simulation of Small-Scale Releases from Liquid Hydrogen Storage Systems. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 3913–3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitpas, G. Boil-Off Losses Along LH2 Pathway; Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory: Livermore, CA, USA, 2018; p. LLNL-TR-750685. [Google Scholar]
- Zuo, Z.; Jiang, W.; Qin, X.; Huang, Y. Numerical Investigation on Full Thermodynamic Venting Process of Liquid Hydrogen in an On-Orbit Storage Tank. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 27792–27805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Ghafri, S.Z.S.; Swanger, A.; Jusko, V.; Siahvashi, A.; Perez, F.; Johns, M.L.; May, E.F. Modelling of Liquid Hydrogen Boil-Off. Energies 2022, 15, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamacher, J.; Stary, A.; Stops, L.; Siebe, D.; Kapp, M.; Rehfeldt, S.; Klein, H. Modeling the Thermodynamic Behavior of Cryo-Compressed Hydrogen Tanks for Trucks. Cryogenics 2023, 135, 103743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Yang, P.; Liu, Y.; Ye, W.; Yan, C.; Wang, X. Control Strategy Optimization of Thermodynamic Venting System in Liquid Hydrogen Storage Tank Under Microgravity. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 2024, 37, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stops, L.; Siebe, D.; Stary, A.; Hamacher, J.; Sidarava, V.; Rehfeldt, S.; Klein, H. Generalized Thermodynamic Modeling of Hydrogen Storage Tanks for Truck Application. Cryogenics 2024, 139, 103826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, J.; Mukhopadhyay, A. Thermodynamic Model of Storage and Discharge of Liquid Hydrogen and Oxygen in Pressure Vessels Under Cryogenic Conditions. In Advances in Energy and Sustainability; De, S., Roy, P.C., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024; pp. 171–184. ISBN 978-981-97-7307-7. [Google Scholar]
- Okpeke, B.E.; Ait Aider, C.; Baetcke, L.; Ehlers, S. Assessment of Boil-Off Losses and Their Cost Implication during Liquid Hydrogen Tank Filling with and without Precooling. Energies 2024, 17, 4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, L.; Sleiti, A. Modeling and Analysis of Effect of Various Tank Geometries and Relief Pressure on Liquid Hydrogen (LH2) Boil-Off Losses. Energy Proc. 2024, 44, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yan, Y.; Wei, W.; Wang, Z.; Ni, Z. Numerical Simulation on the Thermal Dynamic Behavior of Liquid Hydrogen in a Storage Tank for Trailers. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 40, 102520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; Gao, B.; Fan, X. Numerical Study of the Effect of Sloshing on the Properties of Fluids in Tanks of Liquid Hydrogen Carriers. In Proceedings of the Ninth International Symposium on Energy Science and Chemical Engineering (ISESCE 2024), Nanjing, China, 22–24 March 2024; Ensafi, A., Abdullah, A.Z., Aruna, K.K., Eds.; SPIE: Nanjing, China, 2024; p. 30. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, H.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, S.; Hou, Y. Numerical Study on Thermodynamic Characteristics of Large-Scale Liquid Hydrogen Tank with Baffles Under Sloshing Conditions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 57, 562–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L.; Chen, S.; Yang, T.; Zhang, K.; Hou, Y. Study on Thermohydrodynamic Responses of Liquid Hydrogen in Baffled Tankers During Braking Process. Int. J. Heat Fluid Flow 2024, 110, 109612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Shi, S.; Yuan, H.; Yang, K. Study on Coupled Motion of Floating Hydrogen Storage Platform with Liquid Hydrogen Sloshing. China Ocean Eng. 2024, 38, 999–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xinjia, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xu, C. Thermodynamic Study on Condensation Heat Transfer and Sloshing of the Liquid Hydrogen Storage. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Green Energy, Environment, and Sustainable Development (GEESD 2024), Mianyang, China, 28–30 June 2024; Aghaei, M., Ren, H., Zhang, X., Eds.; SPIE: Mianyang, China, 2024; p. 93. [Google Scholar]
- Gluck, D.F.; Kline, F. Gas Requirements in Pressurized Transfer of Liquid Hydrogen; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Campi, F.A.; Chi, J.W.H.; DeZubay, E.A.; Holmgren, J.D.; Vetere, A.M. Transient Two-Phase Heat Transfer and Flow Characteristics of Liquid Hydrogen; Westinghouse Electric Corporation Astronuclear Laboratory: Large, PA, USA, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Rame, E.; Hartwig, J.W.; McQuillen, J.B. Flow Visualization of Liquid Hydrogen Line Chill Down Tests. In Proceedings of the 52nd Aerospace Sciences Meeting, National Harbor, MD, USA, 13–17 January 2014; American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics: National Harbor, MD, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Darr, S.R.; Hartwig, J.W. Two-Phase Convection Heat Transfer Correlations for Liquid Hydrogen Pipe Chilldown. Cryogenics 2020, 105, 102999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Yun, S.; Kim, B.; Kim, J.; Kim, G.; Lee, H.; Choi, S. Numerical Investigation of the Initial Charging Process of the Liquid Hydrogen Tank for Vehicles. Energies 2022, 16, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangold, J.; Silberhorn, D.; Moebs, N.; Dzikus, N.; Hoelzen, J.; Zill, T.; Strohmayer, A. Refueling of LH2 Aircraft—Assessment of Turnaround Procedures and Aircraft Design Implication. Energies 2022, 15, 2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.S.; Chung, S.-M.; Park, J.-C. Multiphase-Thermal Flow Simulation in a Straight Vacuum-Insulated LH2 Pipe: Fuel Gas Supply System in a LH2-Fueled Ship. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.-M.; Ahn, H.-J.; Park, J.-C. Numerical Approach to Analyze Fluid Flow in a Type C Tank for Liquefied Hydrogen Carrier (Part 2: Thermal Flow). J. Energy Storage 2024, 76, 109599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Lei, G. Modeling and Analysis of the Flow Characteristics of Liquid Hydrogen in a Pipe Suffering from External Transient Impact. Energies 2022, 15, 4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeClair, A.; Baldwin, M.; Majumdar, A.; Hartwig, J.; Ganesan, V.; Mudawar, I. Modeling of Cryogenic Heated-Tube Flow Boiling Experiments of Hydrogen and Helium with the Generalized Fluid System Simulation Program. Cryogenics 2024, 143, 103926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesich, J.M.; Hauser, D.M.; Yamashita, K.G.; Baker, M.C.; Sakowski, B.A. Liquid Hydrogen Tank Chill and No-Vent Fill Prediction Using Computational Fluid Dynamics. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2024, 1301, 012065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, M.E.; Nyland, T.W. Liquid Transfer Cryogenic Test Facility-Initial Hydrogen and Nitrogen No-Vent Fill Data; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Molkov, V.; Ebne-Abbasi, H.; Makarov, D. Liquid Hydrogen Refuelling at HRS: Description of sLH2 Concept, Modelling Approach and Results of Numerical Simulations. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 93, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour Bonab, S.; Yazdani-Asrami, M. Artificial Intelligence-Based Model to Predict the Heat Transfer Coefficient in Flow Boiling of Liquid Hydrogen as Fuel and Cryogenic Coolant in Future Hydrogen-Powered Cryo-Electric Aviation. Fuel 2025, 381, 133323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangwanpongpan, T.; Makarov, D.; Cirrone, D.; Molkov, V. LES Model of Flash-Boiling and Pressure Recovery Phenomena During Release from Large-Scale Pressurised Liquid Hydrogen Storage Tank. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 50, 390–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

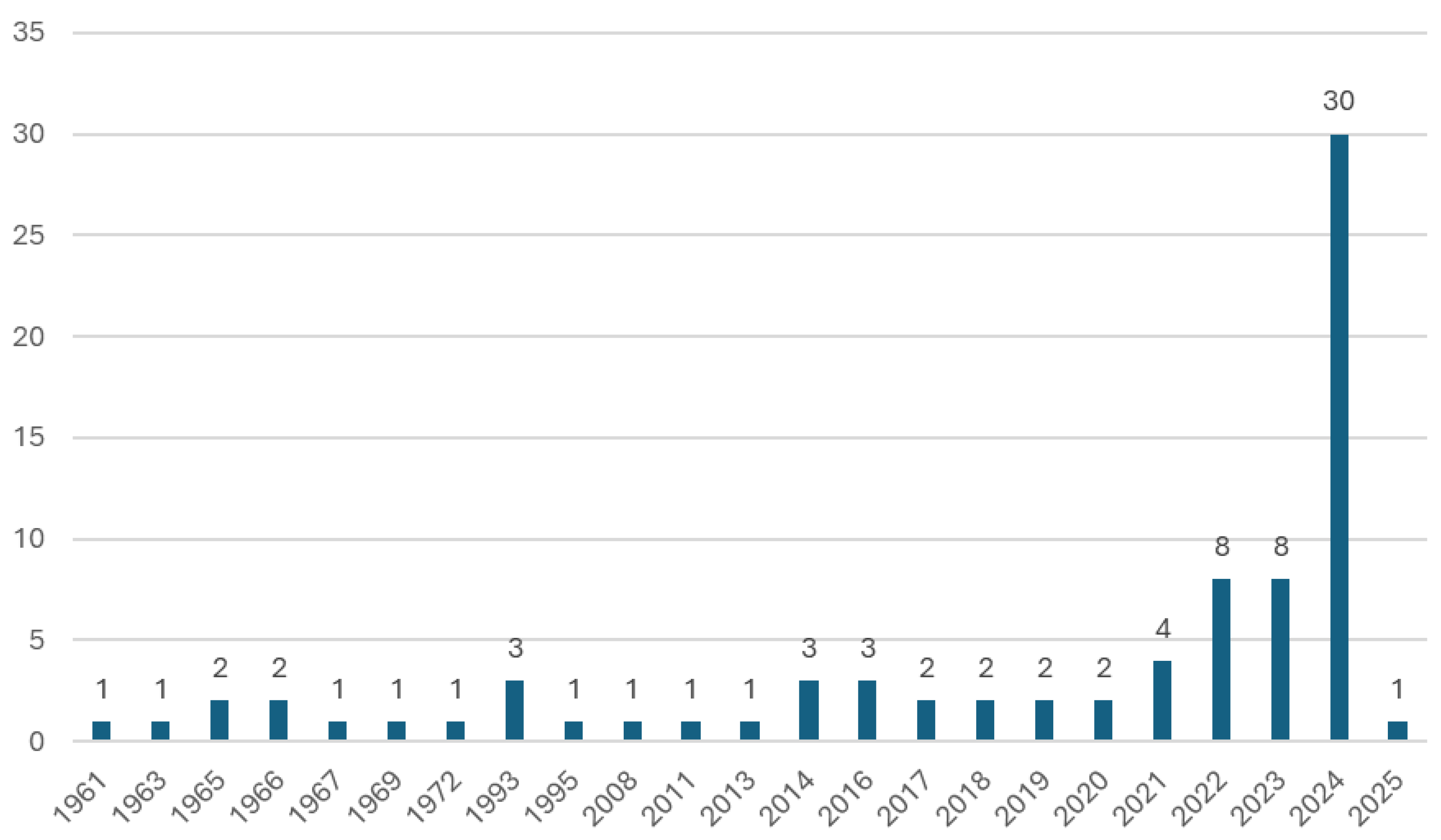
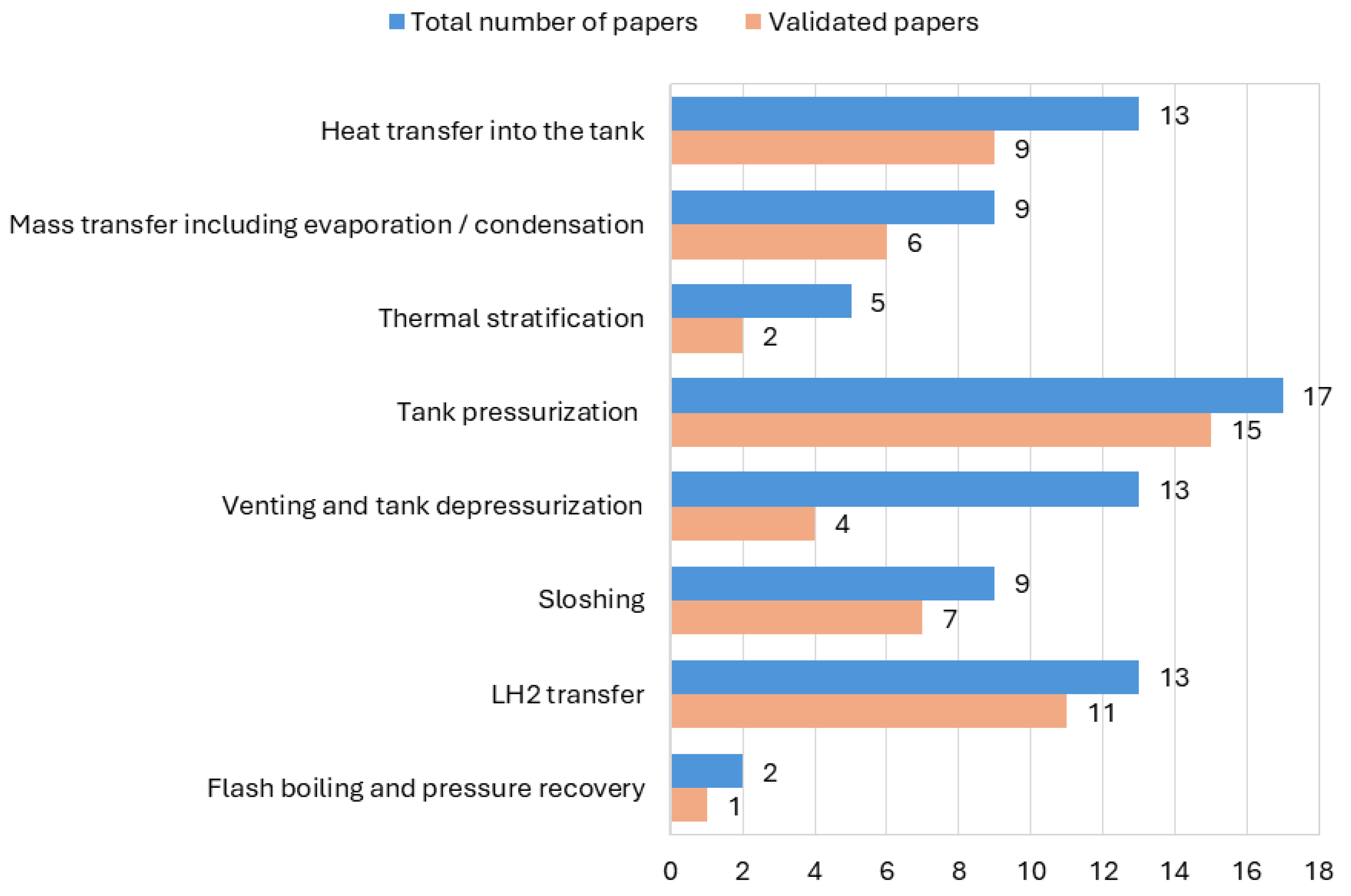
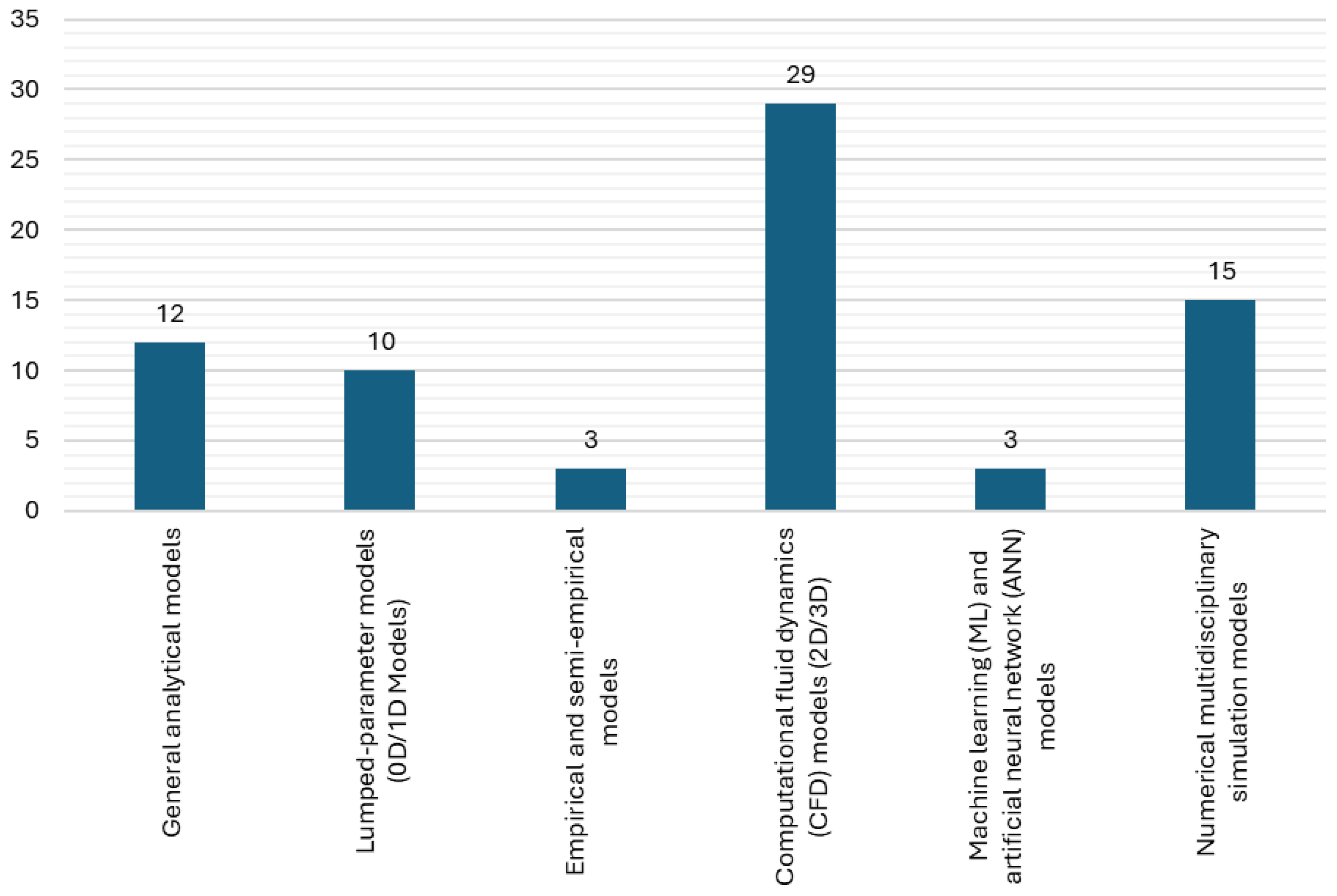
| Properties | CGH2 (700 bar) | LH2 | NG (250 bar) | LNG | Gasoline |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Storage temperature | Ambient | Ca. −253 °C | Ambient | Ca. −162 °C | Ambient |
| Gravimetric energy density (MJ/kg) | 120 | 53.6 | 44 | ||
| Volumetric energy density (MJ/L) | 5.6 | 8 | 9 | 22.2 | 32.0 |
| At atm. conditions | |||||
| Flammability limits in air (vol%) | 4–74 | 5–15 | 1–7 | ||
| Minimum ignition energy in air (mJ) | 0.02 | 0.30 | 0.30 | ||
| Stoichiometric flame speed (m/s) | 2.1 | 0.4 | 0.3 | ||
| Diffusion coefficient in air (cm2/s) | 0.61 | 0.16 | 0.05 | ||
| Authors | Year | Type of Model | Validated |
|---|---|---|---|
| S. C. Huntley et al. [25] | 1966 | Experimental and analytical | Yes |
| L. Wang et al. [26] | 2019 | FLUENT-CFD | No |
| W. Jiang et al. [6] | 2021 | Numerical model | Yes |
| R. Lv et al. [28] | 2021 | CFD, VoF method | Yes |
| F. Ustolin et al. [29] | 2021 | Analytical equations | Yes |
| F. Ustolin et al. [30] | 2022 | 2D CFD | Yes |
| Z. Sun et al. [32] | 2023 | Numerical, 2D | Yes |
| J. Wang et al. [11] | 2024 | Analytical equations | Yes |
| R. Parello et al. [33] | 2024 | Multi-phase thermodynamic | No |
| S. Alipour Bonab and M. Yazdani-Asrami [16] | 2024 | CFNN | Yes |
| Z. Xu et al. [34] | 2024 | Numerical model | No |
| H. Lv et al. [35] | 2024 | Numerical model | No |
| K. Li et al. [36] | 2024 | Numerical model | Yes |
| Authors | Year | Type of Model | Validated |
|---|---|---|---|
| W. A. Olsen [37] | 1966 | Analytical equations | No |
| C. Lin et al. [38] | 1993 | Empirical model | No |
| R. B. Schweickart [39] | 2014 | SINDA/FLUINT | No |
| M. Stewart [40] | 2017 | 1D CFD | Yes |
| H. Wang et al. [41] | 2023 | Analytical, HDM | Yes |
| Y. Jiang [42] | 2023 | CFD, VoF method | Yes |
| Z. Wang and W. Mérida [43] | 2024 | Numerical, non-equilibrium | Yes |
| D. Choi [44] | 2024 | Numerical model | Yes |
| H. Wang et al. [45] | 2024 | 2D CFD, VoF method | Yes |
| Authors | Year | Type of Model | Validated |
|---|---|---|---|
| R. W. Arnett and R. O. Voth [46] | 1972 | Analytical equations | No |
| G. D. Grayson [47] | 1995 | CFD, Flow-3D | No |
| M. J. Daigle et al. [48] | 2013 | Dynamical, low-dimensional approach | No |
| J. Joseph et al. [15] | 2017 | Transient two-phase thermodynamic lumped model | Yes |
| Z. Liu et al. [49] | 2018 | CFD, VoF method | Yes |
| Authors | Year | Type of Model | Validated |
|---|---|---|---|
| J. C. Aydelott [50] | 1967 | Analytical equations | Yes |
| S. Gursu et al. [51] | 1993 | Homogeneous, SEM, TSM | Yes |
| S. Barsi and M. Kassemi [53] | 2008 | Lumped-vapour CFD | Yes |
| O. V. Kartuzova et al. [54] | 2014 | CFD, VoF method | Yes |
| M. Kassemi and O. Kartuzova [55] | 2016 | Sharp-interface CFD, VoF method | Yes |
| M. Stewart and J. P. Moder [56] | 2016 | CFD, ANSYS Fluent | Yes |
| A. Majumdar et al. [57] | 2016 | Multinode model in GFSSP | No |
| H. R. Wang et al. [62] | 2022 | TMZM | Yes |
| Y. Liu et al. [58] | 2023 | Analytical equations | Yes |
| R. K. Ahluwalia et al. [59] | 2023 | Numerical, Adams–Bashford–Molton method, Benedict–Webb–Rubin (BWR) equation | No |
| K. I. Metveev and J. W. Leachman [60] | 2023 | Lumped-element model | Yes |
| S. Jeong et al. [61] | 2023 | 3D CFD, VoF method | Yes |
| Anas. A. Rahman et al. [63] | 2024 | ANN | Yes |
| H. Wang et al. [64] | 2024 | TEM, SEM, TMZM, TSM, TMNM, CFD | Yes |
| J. Wang et al. [66] | 2024 | Analytical equations | Yes |
| T. Yu and Y. Lim [67] | 2024 | Lumped-element model | Yes |
| Authors | Year | Type of Model | Validated |
|---|---|---|---|
| D. A. Mandell and W. H. Roudebush [68] | 1965 | Dimensionless, Stanton numbers | Yes |
| W. H. Roudebush and D. A. Mandell [69] | 1965 | 1D equations | Yes |
| J. C. Aydelott and C. M. Spuckler [17] | 1969 | Analytical equations | No |
| W. S. Winters and W. G. Houf [70] | 2011 | Turbulent entrainment model, COLDPLUME code | No |
| G. Petitpas [71] | 2018 | 0D MATLAB code | No |
| Z. Zuo et al. [72] | 2020 | Numerical, VoF method | Yes |
| S. Z. S. Al Ghafri et al. [73] | 2022 | SHV, BoilFAST | Yes |
| J. Hamacher et al. [74] | 2023 | DAE | No |
| H. Chen et al. [75] | 2024 | Lumped-vapour model, Ansys FLUENT | No |
| L. Stops et al. [76] | 2024 | DAE | No |
| J. Dutta and A. Mukhopadhyay [77] | 2024 | Numerical, fourth-order Runge–Kutta method | No |
| B. E. Okpeke et al. [78] | 2024 | Analytical equations | No |
| L. Kumar and A. Sleiti [79] | 2024 | Numerical, BoilFast | No |
| Table Authors | Year | Type of Model | Validated |
|---|---|---|---|
| Z. Liu et al. [18] | 2019 | Numerical, VoF method | Yes |
| J. R. Smith et al. [21] | 2022 | Numerical | No |
| S. Li et al. [80] | 2022 | CFD-VoF | Yes |
| O. V. Kartuzova et al. [20] | 2024 | CFD | Yes |
| W. Kang et al. [81] | 2024 | 3D CFD | Yes |
| H. Lv et al. [82] | 2024 | CFD, Ansys FLUENT | Yes |
| J. Zhang et al. [84] | 2024 | Numerical, VoF method | No |
| H. Lv et al. [83] | 2024 | CFD | Yes |
| Z. Xinjia [85] | 2024 | Thermal stratified model | Yes |
| Table Authors | Year | Type of Model | Validated |
|---|---|---|---|
| D. F. Gluck and F. Kline [86] | 1961 | Analytical model, system- and experimentally determined parameters | Yes |
| F. A. Campi et al. [87] | 1963 | Numerical lumped-parameter model | Yes |
| E. Rame et al. [88] | 2014 | Analytical plug flow model | No |
| S. R. Darr and J. W. Hartwig [89] | 2020 | Numerical lumped-node model | Yes |
| Y. Liu et al. [94] | 2022 | 3D CFD | Yes |
| D. Kang et al. [90] | 2022 | CFD-VoF | Yes |
| J. Mangold et al. [91] | 2022 | Analytical equations | No |
| Y. S. Seo et al. [92] | 2024 | Numerical multi-phase thermal flow model | Yes |
| S.-M. Chung et al. [93] | 2024 | FVM model | Yes |
| A. LeClair et al. [95] | 2024 | Numerical model using a GFSSP and finite-volume flow network solver | Yes |
| J. M. Pesich et al. [96] | 2024 | CFD (STAR-CCM+, Fluent, and Flow3D) | Yes |
| V. Molkov et al. [98] | 2024 | CFD-based modified thermal stratified model | Yes |
| S. Alipour Bonab and M. Yazdani-Asrami [99] | 2025 | CFNN model | Yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Claussner, L.M.; Scarponi, G.E.; Ustolin, F. Thermo-Fluid Dynamics Modelling of Liquid Hydrogen Storage and Transfer Processes. Hydrogen 2025, 6, 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrogen6040122
Claussner LM, Scarponi GE, Ustolin F. Thermo-Fluid Dynamics Modelling of Liquid Hydrogen Storage and Transfer Processes. Hydrogen. 2025; 6(4):122. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrogen6040122
Chicago/Turabian StyleClaussner, Lucas M., Giordano Emrys Scarponi, and Federico Ustolin. 2025. "Thermo-Fluid Dynamics Modelling of Liquid Hydrogen Storage and Transfer Processes" Hydrogen 6, no. 4: 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrogen6040122
APA StyleClaussner, L. M., Scarponi, G. E., & Ustolin, F. (2025). Thermo-Fluid Dynamics Modelling of Liquid Hydrogen Storage and Transfer Processes. Hydrogen, 6(4), 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrogen6040122






