Hydrogen Conversion in Nanocages
Abstract
1. Hydrogen Conversion in the XX th Century
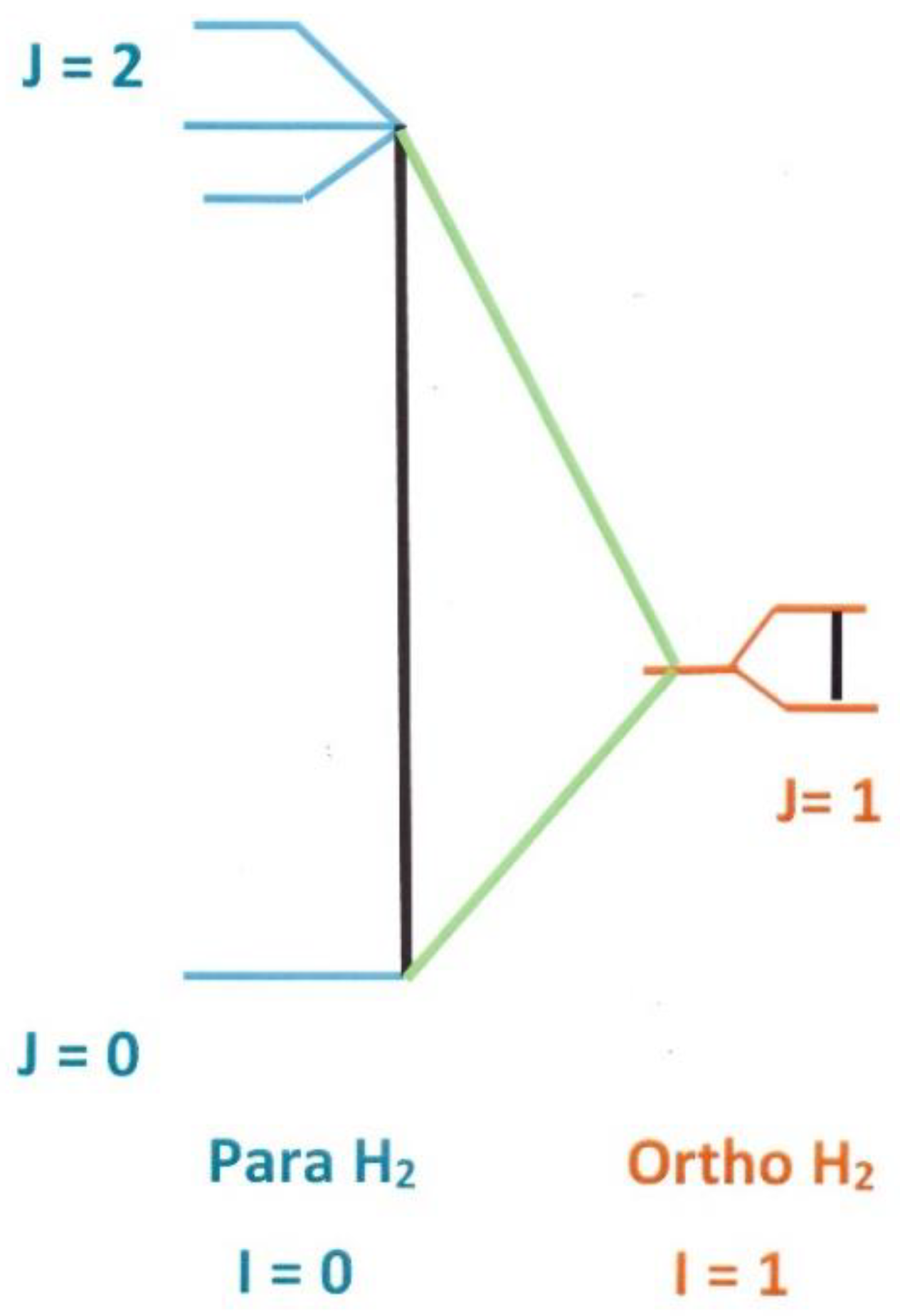
1.1. Molecular Symmetries in the Hydrogen Configuration Space
1.2. Thermal Properties of the Rotational System
1.2.1. Partitions, Populations and Energies
1.2.2. Rotational Entropies
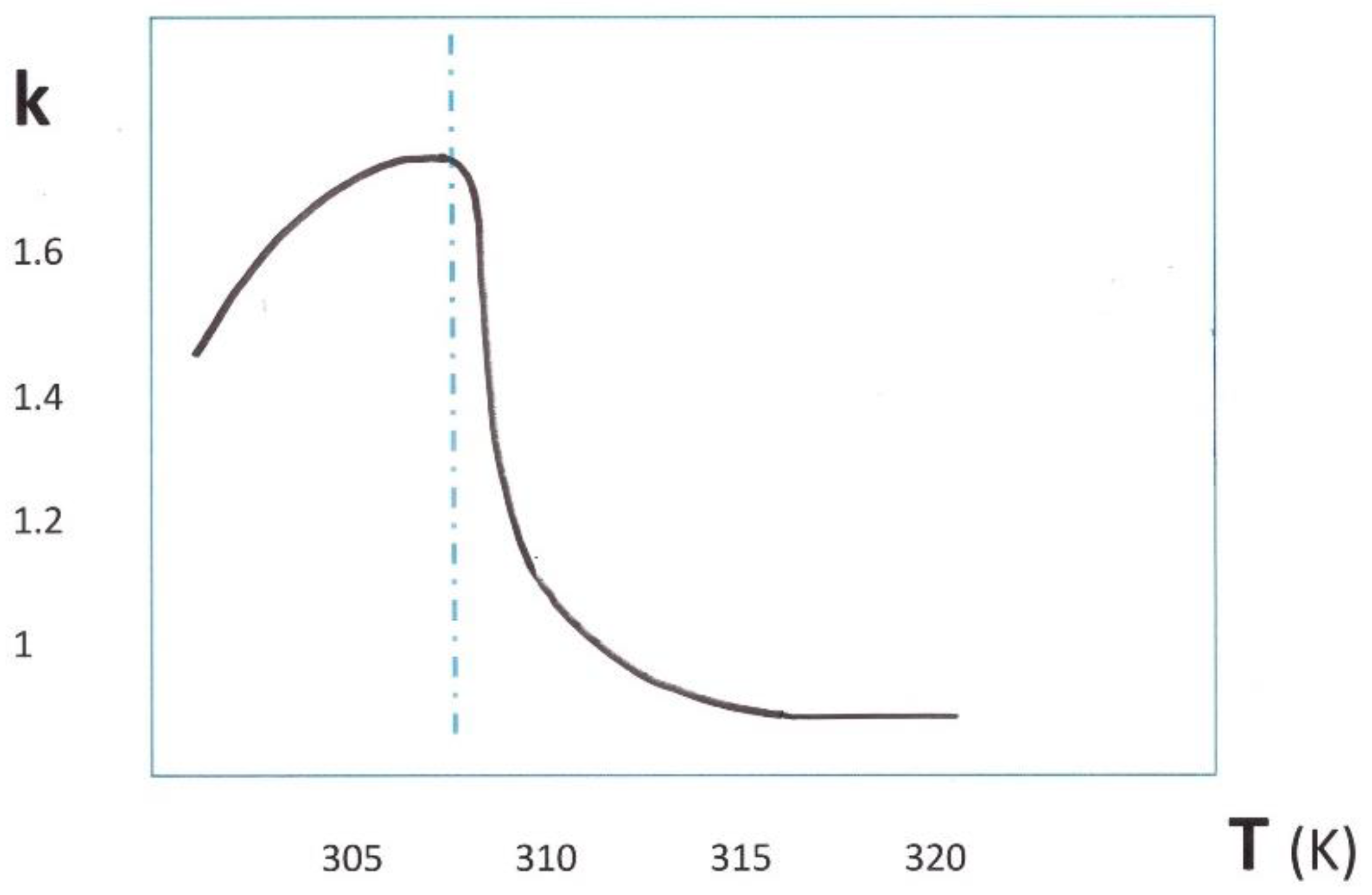
1.3. From Experimental Studies to Industrial Applications
1.4. First Theoretical Models
- (i)
- At low temperatures, T ≤ 100 K, only the two lowest ortho and para ground states are populated (at T = 100 K about 99% of the molecules are in the J = 0 and J = 1 states)
- (ii)
- When a hydrogen molecule is adsorbed, its rotational motion is seriously altered by the surface, and behaves approximately as a plane rotator parallel to the surface.
- (iii)
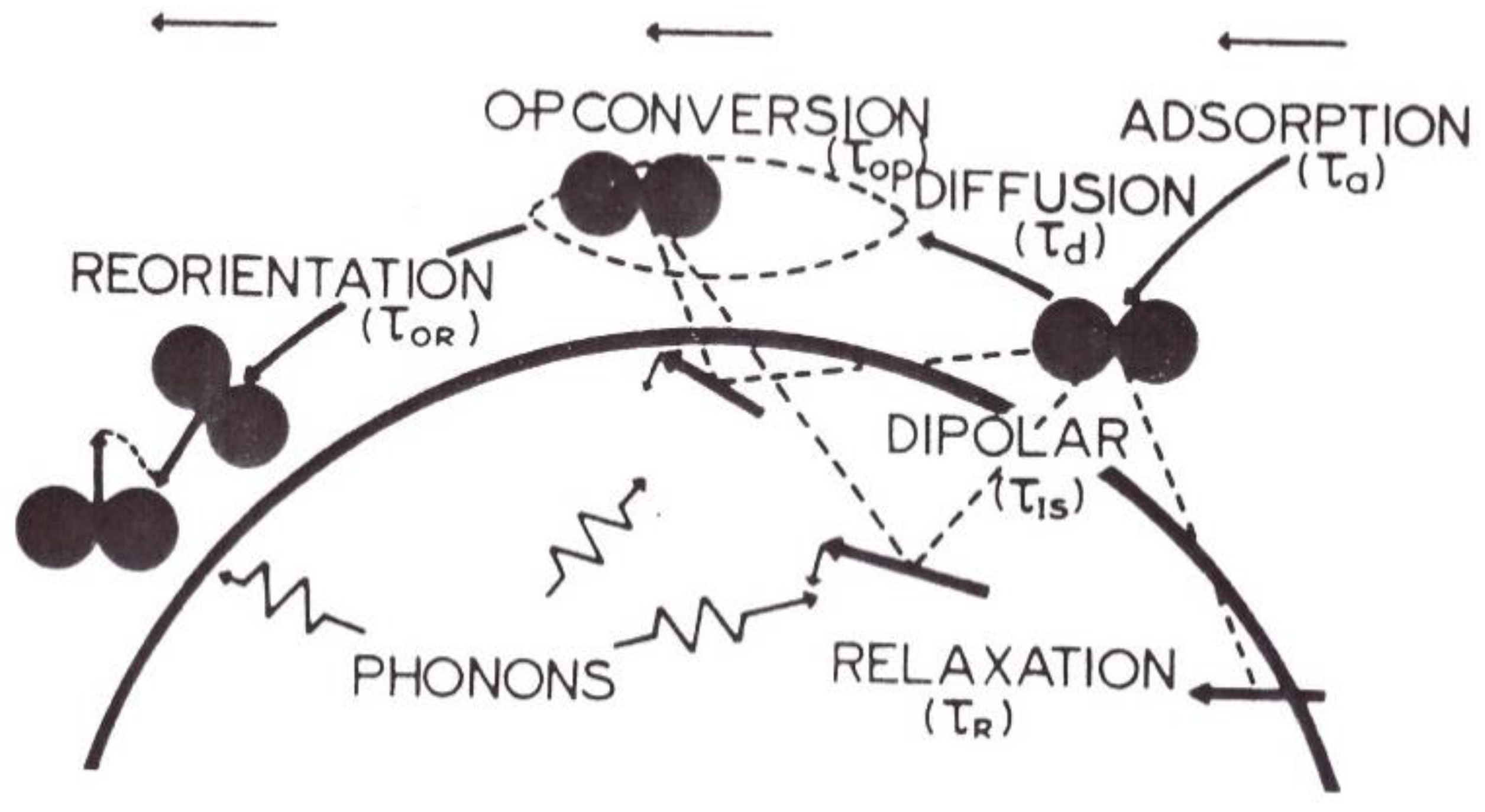
- The surface of the catalyst is planar on the scale of the molecular travels. A few cases of physical adsorption were investigated: The almost filled adsorbed monolayer behaves as a two-dimensional ideal gas, (described by a two-dimensional diffusion equation); or the adsorption is localized and each molecule jumps from one site to another in a random walk.
- (iv)
- When the molecule receives enough energy from the solid (phonons) or from the gas (collision with another molecule), it leaves the surface.
- (v)
- Magnetic impurities are randomly dispersed on the surface and their isotropic relaxation is described by an exponential decrease.
2. The New Conversion Measures of the XXI th Century
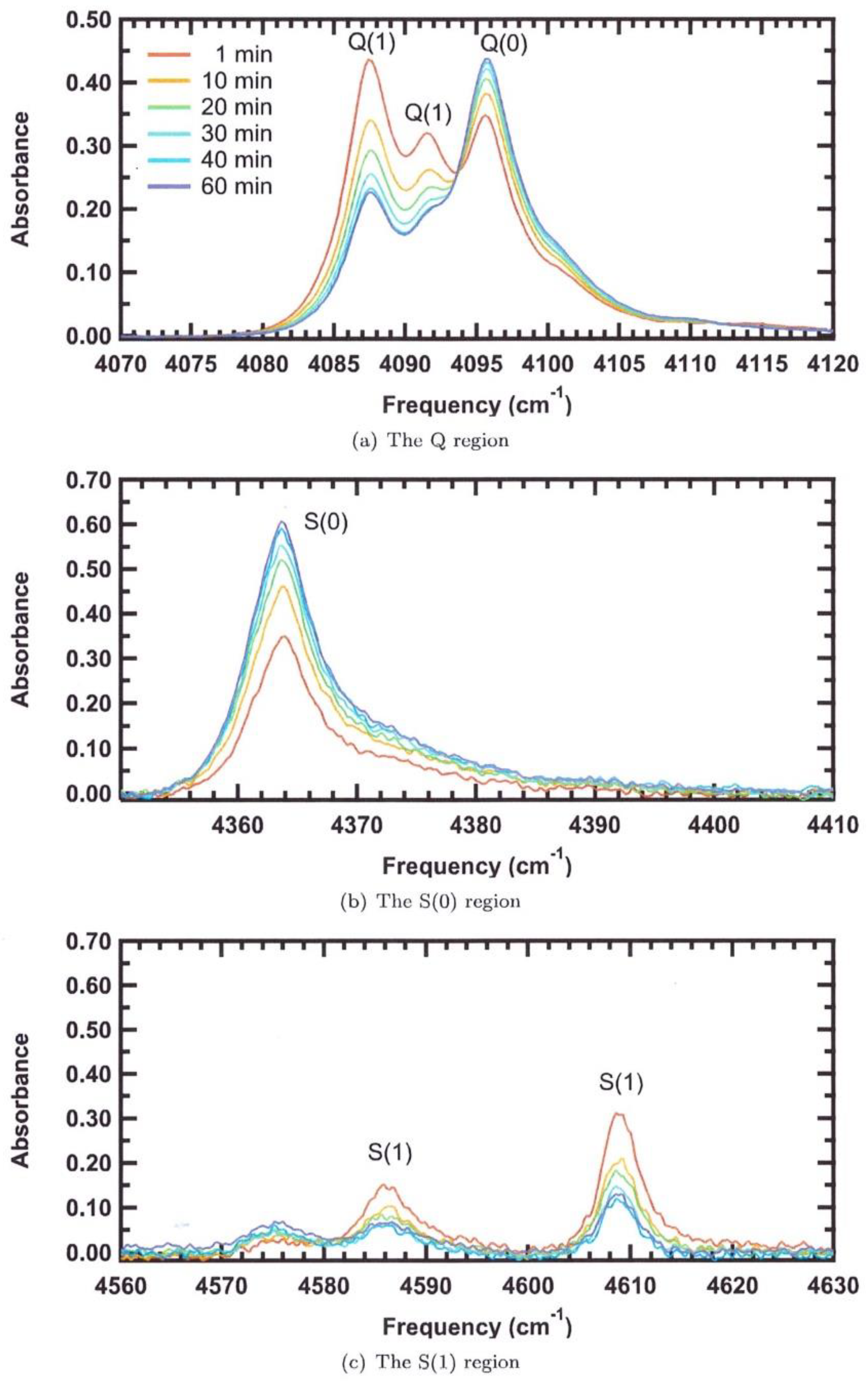
2.1. Infra-Red Spectroscopy
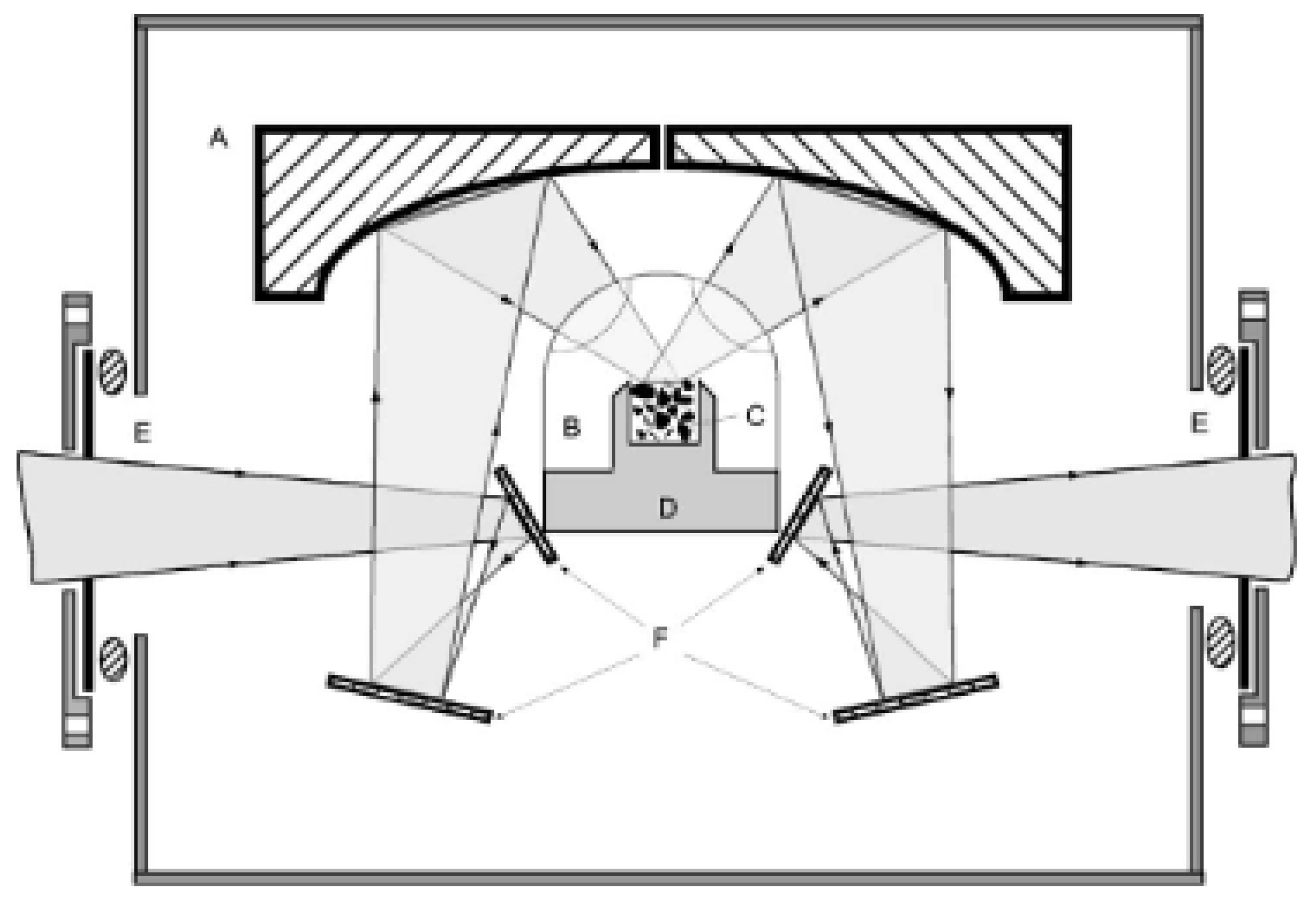
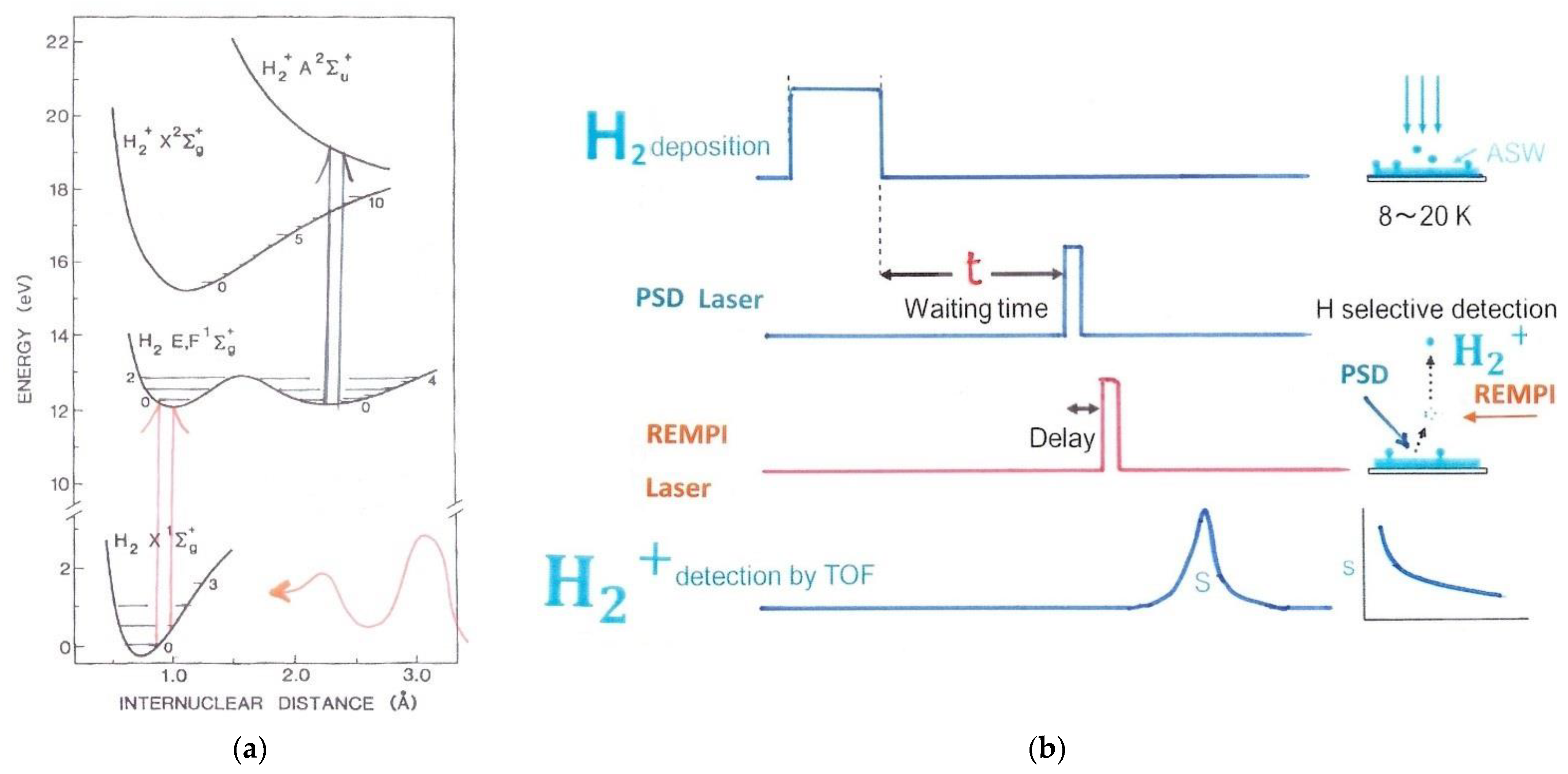
2.2. UV Photo-Ionization Methods
2.3. Radio Frequency Pulses
3. New Devices and New Materials
3.1. Amorphous Catalysts
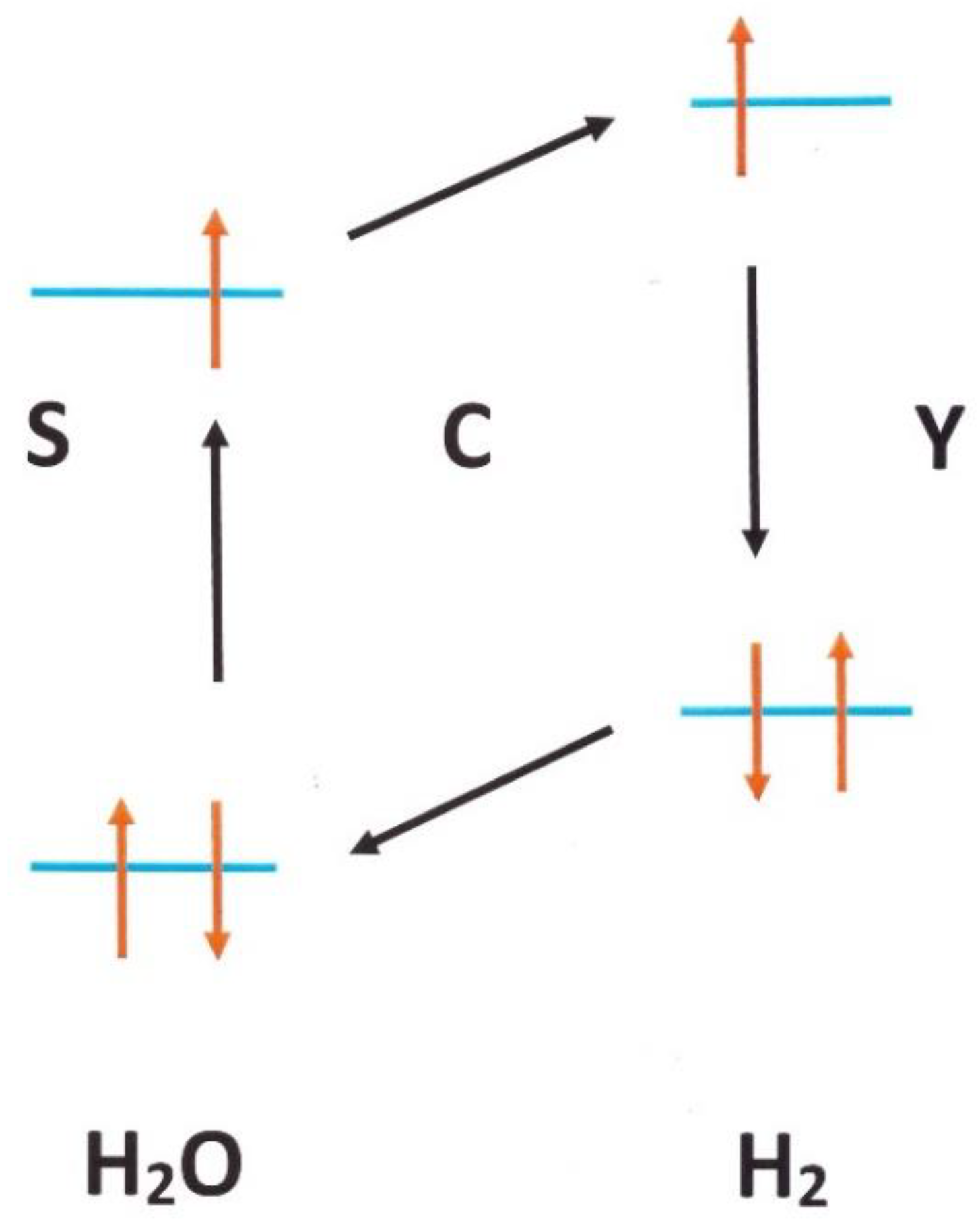
3.1.1. H2 Adsorbed on Solid Water
3.1.2. H2 Diluted into Semi-Conductors
3.2. Porous Catalysts
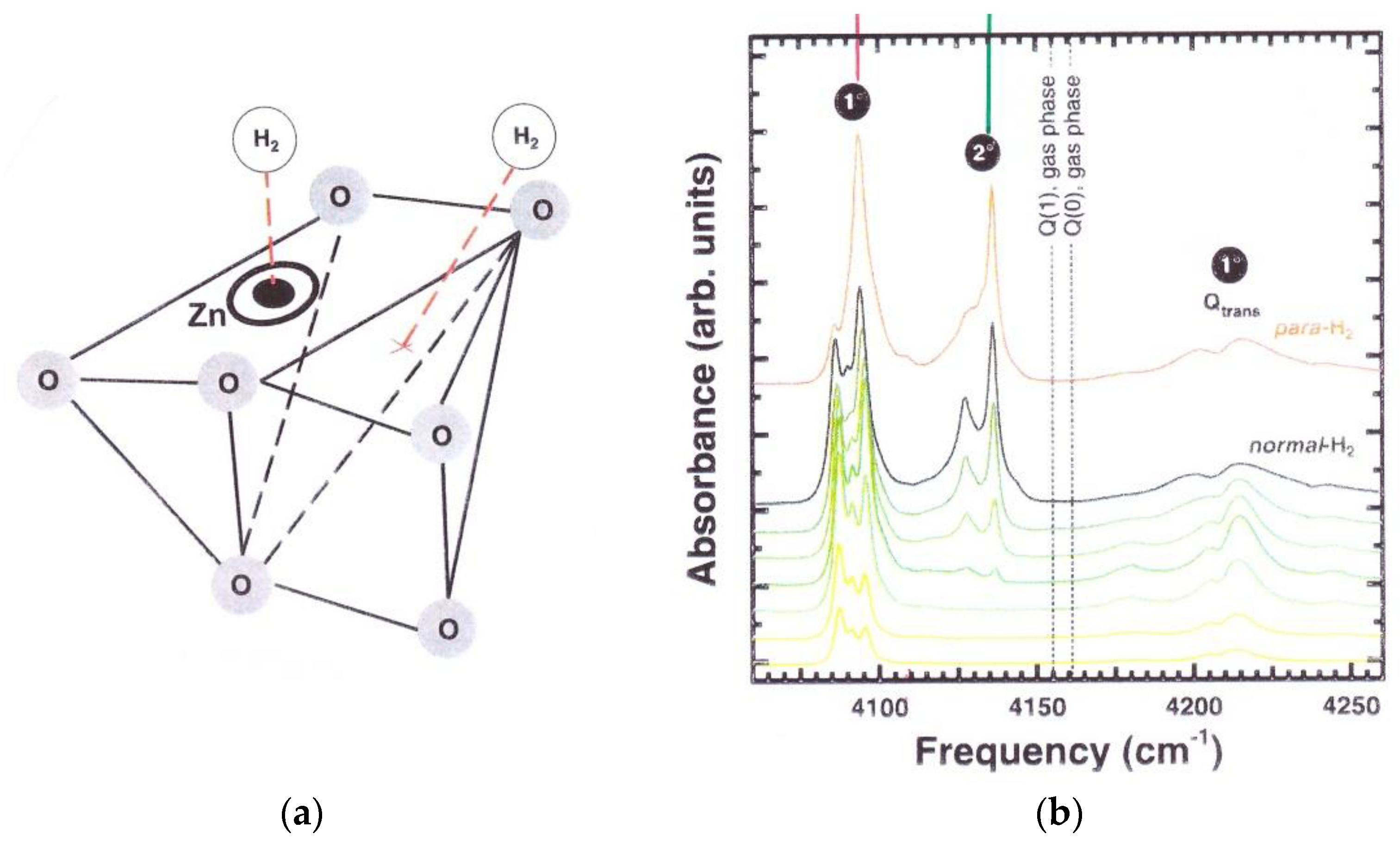
3.2.1. H2 Adsorbed in Metal-Organic Frameworks
3.2.2. H2 Diluted into Polymers
3.3. H2 in Solid Nano-Cages
3.4. H2 in Viscous Organic Solutions
4. Qualitative Analyses and Theoretical Advances
4.1. Electromagnetic Hyperfine Catalysis
4.1.1. Paramagnetic Conversion
4.1.1.1. Magnetic Catalysis on Solid Surfaces
4.1.1.2. Magnetic Catalysis in Solvent Solutions
4.1.2. Metallic Physical Conversion
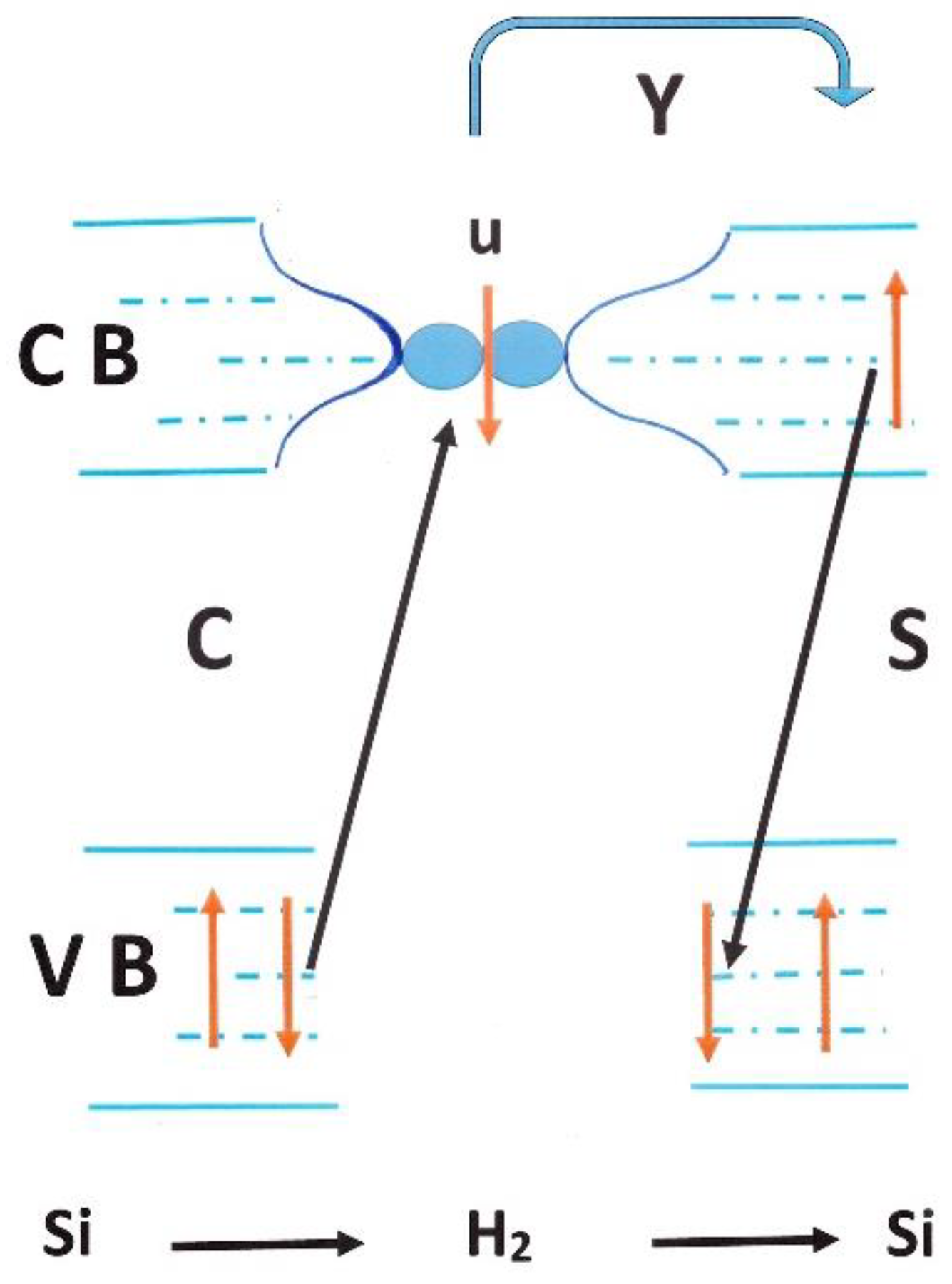
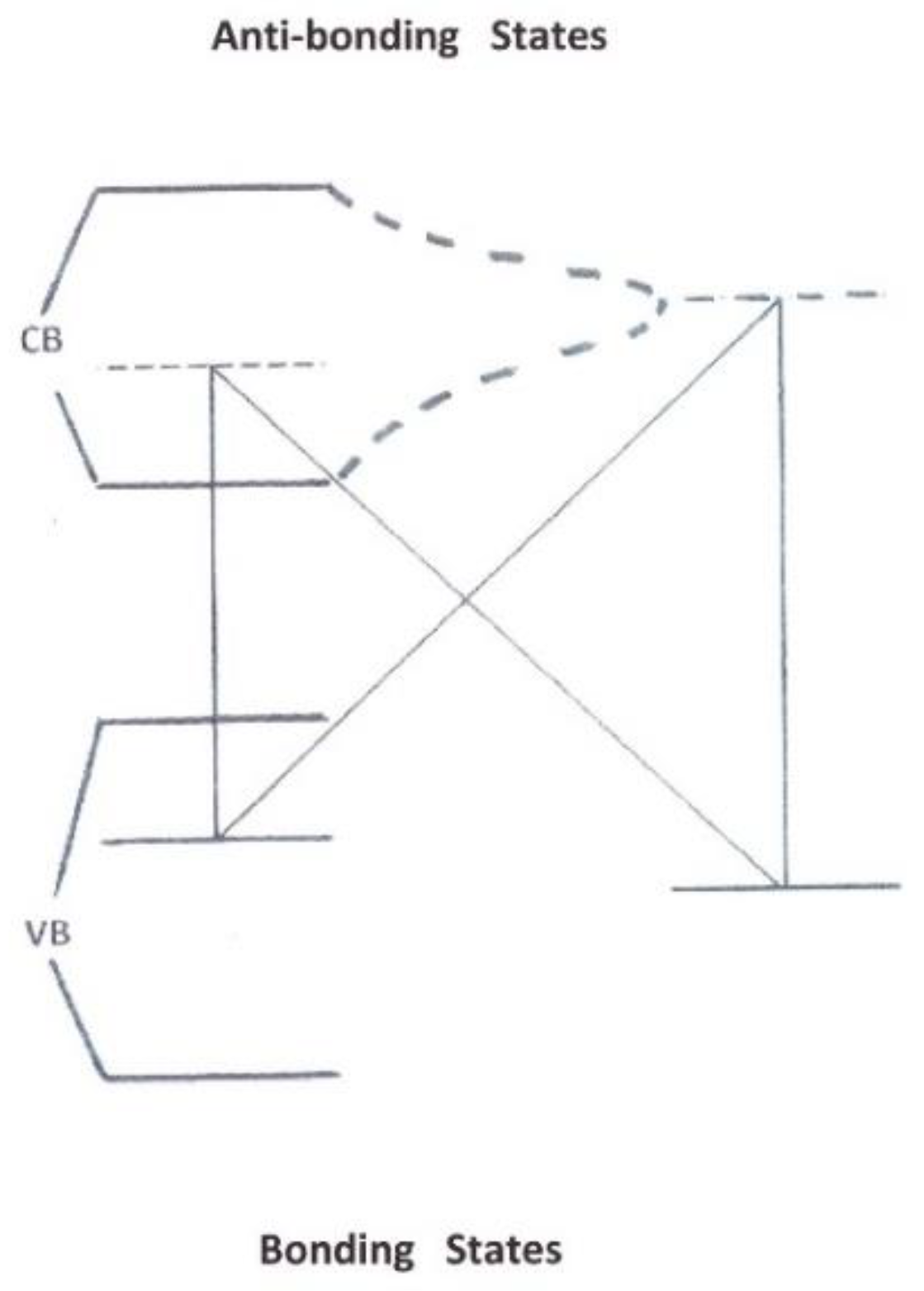
4.1.3. Conversion in Dielectric Insulators
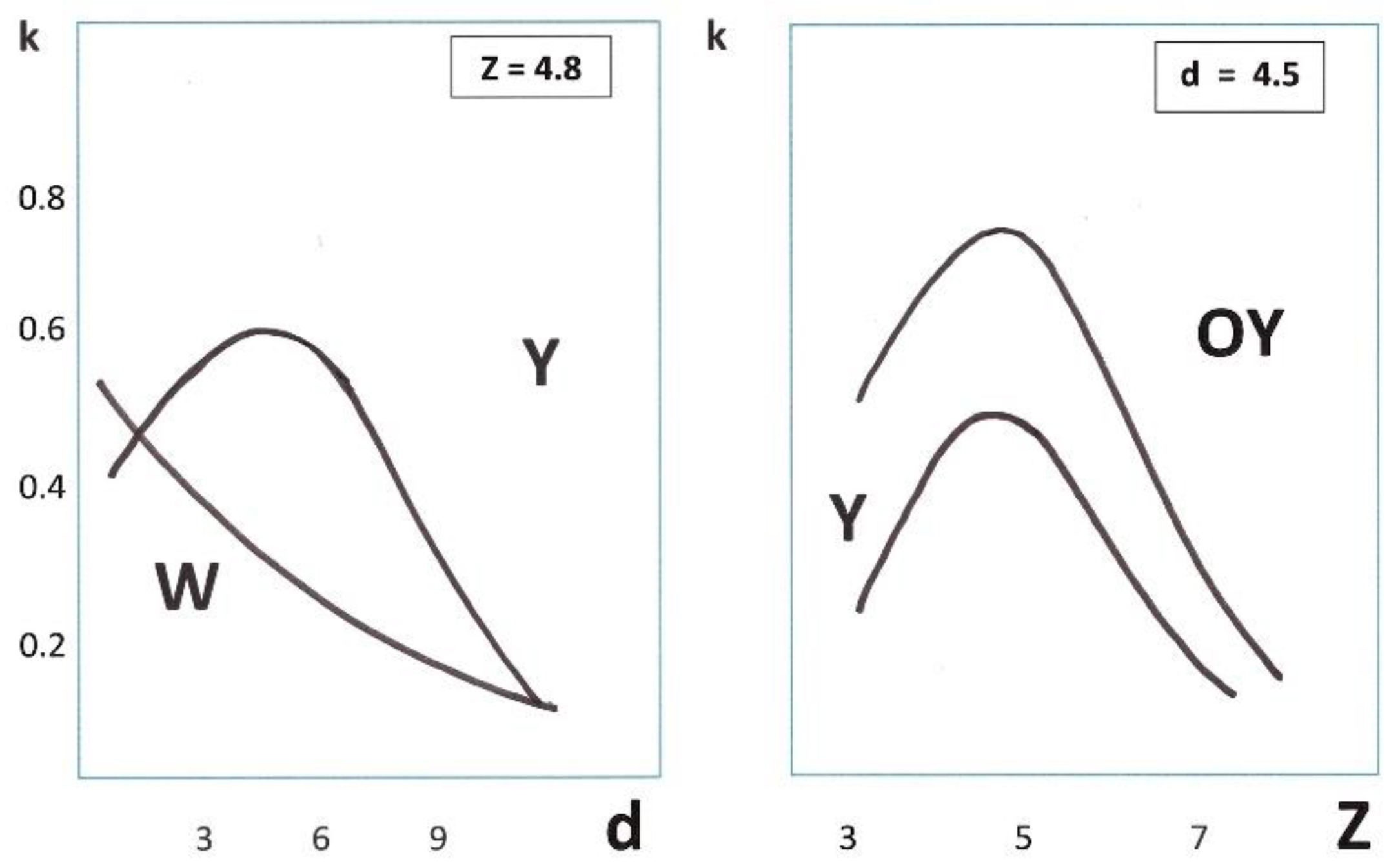
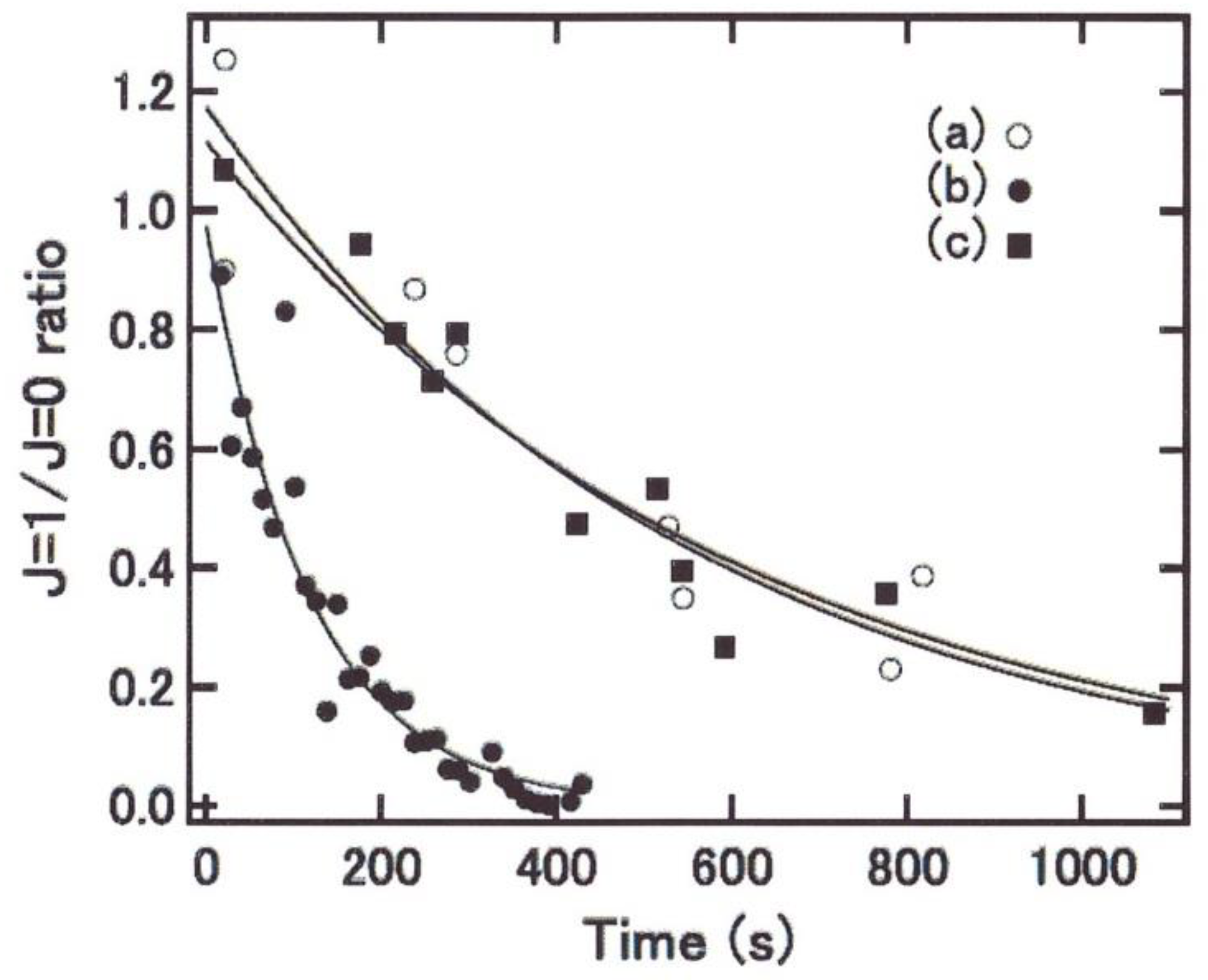
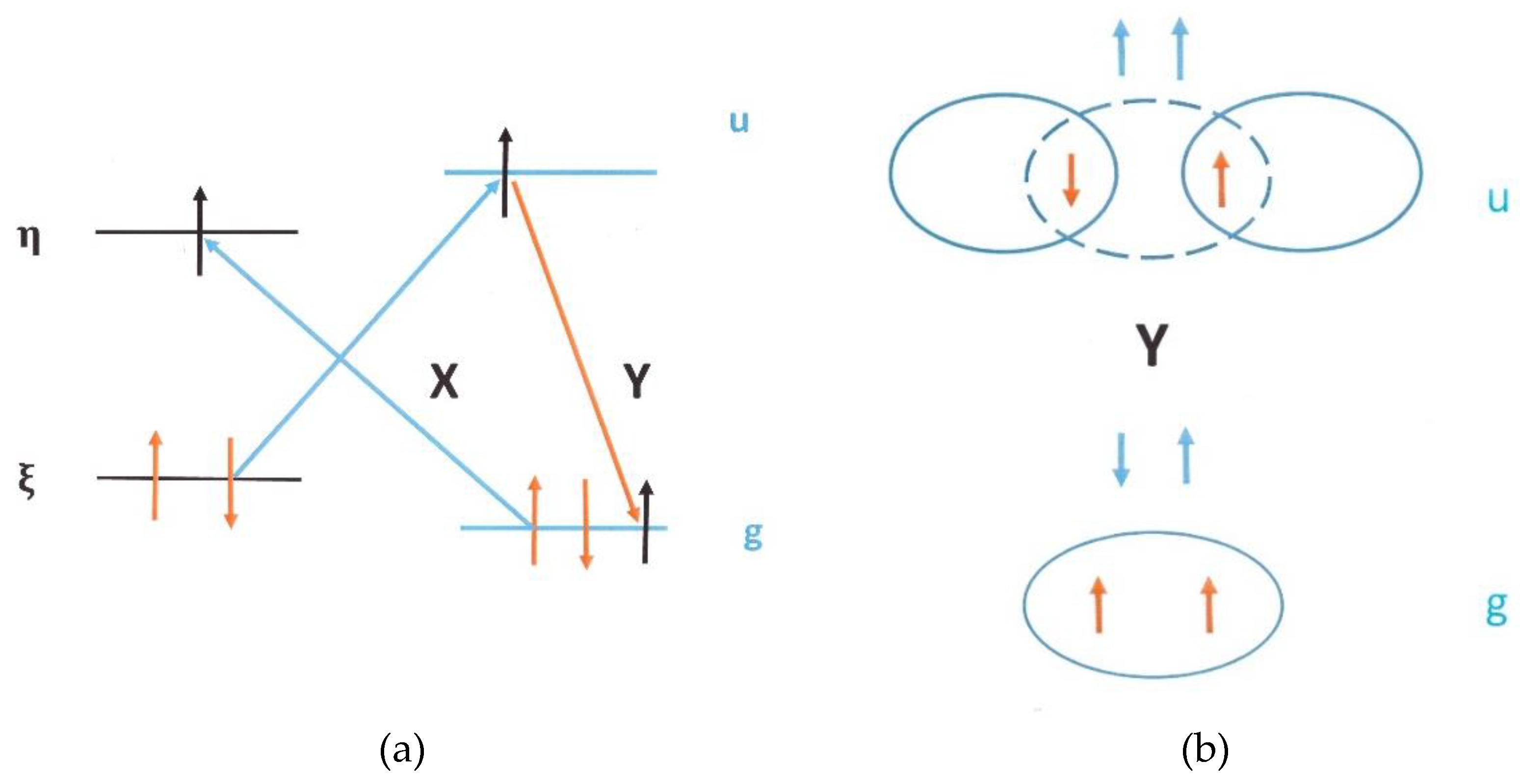
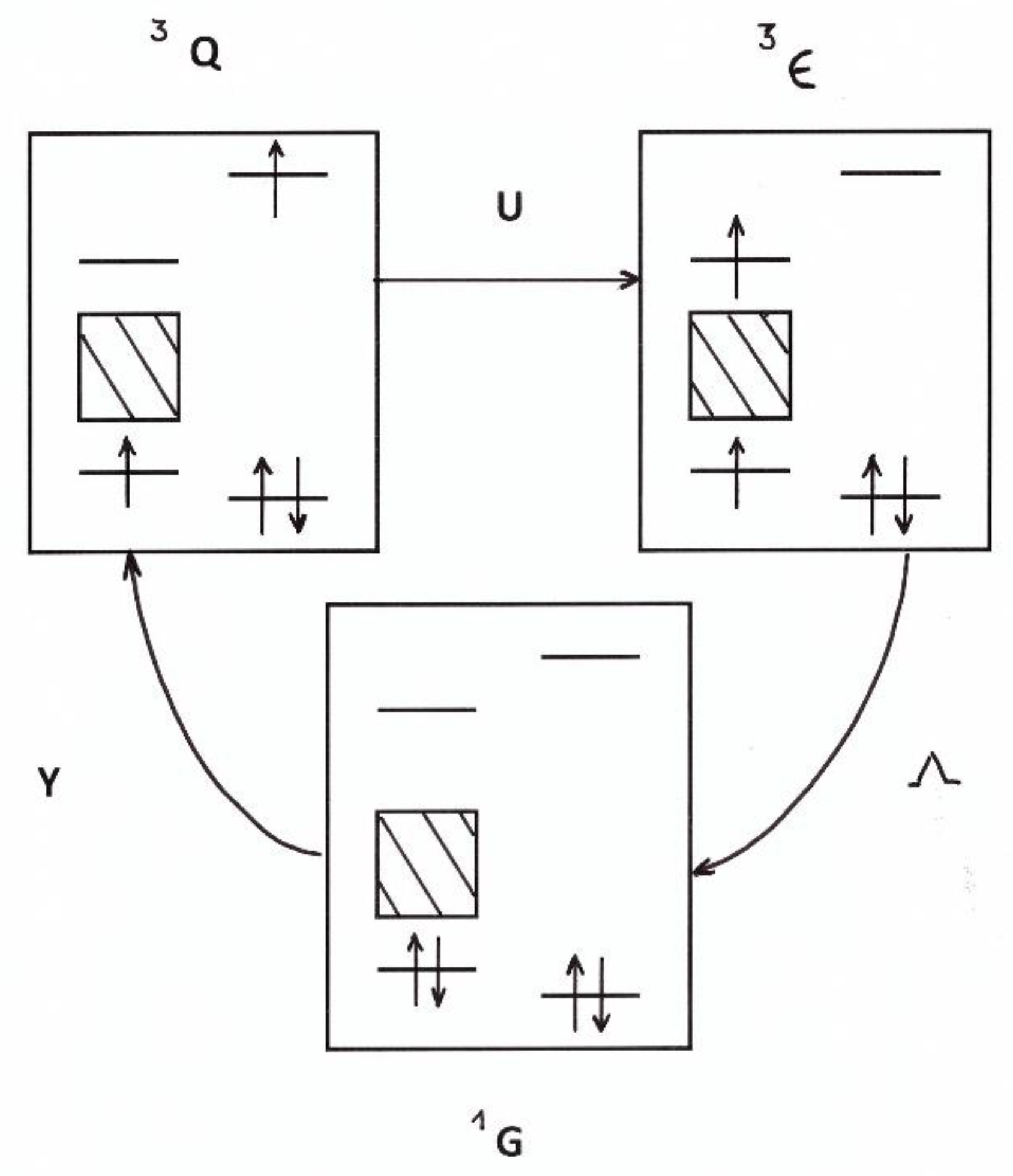
4.1.4. Conversion in Nano-Cages
4.2. Collective Phenomena in Catalyzed Conversion
4.2.1. Ferromagnetic Catalysis by Magnon Emission
4.2.2. Excitonic Dissipations in Dielectric Conversion
4.2.3. Thermal Accommodations in Nano-Cages
5. Industrial Prospects and Concluding Comments
5.1. Memory and Imagery
5.1.1. Purity and Imagery
5.1.2. Memory and Dating
5.2. Hydrogen Liquefaction and Storage
5.2.1. Hydrogen Liquefaction
5.2.2. Hydrogen Storage
5.3. Concluding Comments
5.3.1. Identification
Concepts
Measurements Methods
Materials for Hydrogen Conversion Studies
5.3.2. Questions
5.3.3. Anticipation
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Farkas, A. Orthohydrogen, Parahydrogen and Heavy Hydrogen; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1935. [Google Scholar]
- Schmauch, G.E.; Singleton, A.H. Technical Aspects of Ortho-Parahydrogen Conversion. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1964, 56, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Züttel, A.; Borgschulte, A.; Schlapbach, L. Hydrogen as a Future Energy Carrier; WILEY-VCH Verlag, GmbH & Co.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Silvera, I.F. The solid molecular hydrogens in the condensed phase: Fundamentals and static properties. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1980, 52, 393–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilisca, E. Ortho-Para Conversion of Hydrogen on Surfaces. Prog. Surf. Sci. 1992, 41, 213–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukutani, K.; Sugimoto, T. Ortho-Para Conversion of Molecular Hydrogen in Physisorption States on Solid Surfaces. Prog. Surf. Sci. 2013, 88, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigner, E.P. Über die paramagnetische Umwandlung von Para-Orthowasserstoff. III. Part I Phys. Chem. Part II Solid State Phys. 1997, 23, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, M. Nuclear spin relaxation in hydrogen. Physics 1957, 23, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.E.; Dahler, J.S. Paramagnetic Catalysis of the Ortho-Parahydrogen Conversion. J. Chem. Phys. 1967, 46, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitzel, D.H. Standards. J. Res. Nat. Bur. 1958, A60, 2840. [Google Scholar]
- Buyanov, R.A. Hydrogen conversion on transition oxides. Kinetica i Kataliz 1980, 1, 306, 418, 617. [Google Scholar]
- Selwood, P. Extrinsic field conversion of parahydrogen over the rare earths. J. Catal. 1970, 19, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.F.; Selwood, P.W. Magnetic effects on the ortho-parahydrogen conversion over α-Cr2O3, CoO, and MnO. J. Catal. 1976, 43, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selwood, P. Magnetic field effects on the catalyzed nondissociative parahydrogen conversion rate. J. Catal. 1977, 50, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Survey Study of the Efficiency and Economics of Hydrogen Liquefaction; Linde-Union Carbide Report: Seadrift, TX, USA, 1975.
- Ilisca, E. Theoretical calculation of a new effect in ortho-para H2 conversion on magnetic surfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1970, 24, 797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilisca, E. Experimental evidence for a new effect in ortho-para H2 conversion on magnetic surfaces. Phys. Lett. 1970, 33A, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilisca, E. A Simple Example of Ferromagnetic Catalysis. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 1971, 25, 183. [Google Scholar]
- Ilisca, E.; Legrand, A.P. Theoretical rates and correlation functions in o-p hydrogen conversion on paramagnetic surfaces. Phys. Rev. 1972, B5, 4994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilisca, E.; Gallais, E. Orientation effect of the surface magnetization of ferromagnetic catalysts on the ortho-para H2 conversion. Phys. Rev. 1972, B6, 2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzinger, K.G.; Scalapino, D.J. Para- to Ortho-Hydrogen Conversion on Magnetic Surfaces. Phys. Rev. B 1973, 8, 266–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, P.W.; Clugston, M.J. Ortho-Para Hydrogen conversion in Paramagnetic Solutions. Mol. Phys. 1974, 27, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilisca, E. Introduction to a theory of paramagnetic catalysis: The magnetic field effect. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1978, 40, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilisca, E.; Debauche, M.; Motchane, J.L. Quantum formulation of a magneto-catalytic reaction. Phys. Rev. B 1980, 22, 687–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilisca, E. Ortho-para H2 conversion on paramagnetic catalysis. Butsuri Phys. Soc. Jap. 1982, 37, 856. [Google Scholar]
- Ilisca, E.; Debauche, M. Surface spin polarization by rotational libration. Surf. Sci. 1984, 144, L449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilisca, E.; Paris, S. Magnetic Field Acceleration of the o-p H2 conversion on Transition Oxides. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999, 82, 1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, J.; Liebsch, A. Dynamics of molecular collisions with surfaces. Phys. Scr. 1983, T4, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.S.; Temkin, A. Rotational Excitation of Diatomic Molecules by Electron Impact. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1969, 23, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balooch, M.; Cardillo, M.J.; Miller, D.R.; Stickney, R.E. The angular dependence of flux, mean energy and speed ratio for D2 molecules desorbing from a Ni(111) surface. Surf. Sci. 1974, 46, 358–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, M.; Okano, T.; Tuzi, Y. Ortho-para conversion of n-H2 physisorbed on Ag(111) near two-dimensional condensation conditions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1988, 33–34, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avouris, P.; Schmeisser, D.; Demuth, J.E. Observation of Rotational Excitations of hydrogen adsorbed on Ag surfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1982, 48, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, S.; Harris, J. Observation of Rotational Transitions for H2, D2 and HD Adsorbed on Cu(100). Phys. Rev. Lett. 1982, 48, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, R.E.; Willis, R.F. Rotational States of Physisorbed Hydrogen on Graphite. Surf. Sci. 1987, 179, L1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilisca, E. Ortho-para H2 conversion on a cold Ag(111) metal surface. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1991, 66, 667–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilisca, E. Ortho-para hydrogen conversion on noble metals. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 1991, 5, 1191–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilisca, E. Molecule-surface complexes and catalytic reaction. Surf. Sci. 1991, 242, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilisca, E. H2 conversion on noble metals. J. Phys. I 1991, 1, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilisca, E. Orbital process in o-p H2 conversion on noble metals. J. Phys. Cond. Matter 1992, 4, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilisca, E. Towards an hyperfine measure of noble metals Image “Surface states”. Opt. Commun. 1992, 89, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukutani, K.; Yoshida, K.; Wilde, M.; Diño, W.A.; Matsumoto, M.; Okano, T. Photostimulated Desorption and Ortho-Para Conversion ofH2on Ag Surfaces. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003, 90, 096103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niki, K.; Kawauchi, T.; Matsumoto, M.; Fukutani, K.; Okano, T. Mechanism of Ortho-Para H2 Conversion on Ag surfaces. Phys. Rev. 2008, B77, 201404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hixson, H.G.; Wojcik, M.J.; Devlin, M.S.; Devlin, J.P.; Buch, V. Experimental and Stimulated Vibrational Spectra of H2 adsorbed in Amorphous Ice. J. Chem. Phys. 1992, 97, 753–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrov, E.V.; Weber, J. Ortho and Para Interstitial H2 in Silicon. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 215501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiller, M.; Lavrov, E.V.; Weber, J. Ortho-Para Conversion of Interstitial in Si. Phys.Rev. Lett. 2007, 98, 055504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FitzGerald, S.A.; Allen, K.; Landerman, P.; Hopkins, J.; Matters, J.; Myers, R.; Rowsell, J.L.C. Quantum dynamics of adsorbed in the microporous framework MOF-5 analyzed using diffuse reflectance infrared spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. 2008, B77, 224301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Stavola, M.; Fowler, W.B.; Lockwood, M. Ortho-para transition of interstitial H2 and D2 in Si. Phys. Rev. 2009, B80, 125207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FitzGerald, S.A.; Hopkins, J.; Burkholder, B.; Friedman, M.; Rowsell, J.L.C. Quantum dynamics of adsorbed normal- and para-H2, HD, and D2 in the microporous framework MOF-74 analyzed using infrared spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 81, 104305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Kabbour, H.; Brown, C.M.; Neumann, D.A.; Ahn, C.C. Increasing the Density of Adsorbed Hydrogen with Coordinatively Unsaturated Metal Centers in Metal−Organic Frameworks. Langmuir 2008, 24, 4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, T.; Fukutani, K. Electric-field-induced nuclear-spin flips mediated by enhanced spin–orbit coupling. Nat. Phys. 2011, 7, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, S.A.; Churchill, H.O.H.; Korngut, P.M.; Simmons, C.B.; Strangas, Y.E. Cryogenic apparatus for diffuse reflection infrared spectroscopy with high-pressure capabilities. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2006, 77, 93110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.M.; Rinnen, K.D.; Zare, R.N. Rotational and vibrational effects in the E1Σg+−X1Σg+ two-photon transitions of H2, HD and D2. J. Chem. Phys. 1991, 95, 205. [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara, M.; Niki, K.; Okano, T.; Fukutani, K. Ortho-Para H2 Conversion on Cr2O3 (0001)/Cr (110) surfaces. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2010, 200, 22038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.; Kweon, S.-C.; Nah, I.W.; Karng, S.W.; Choi, J.-G.; Oh, I.-H. Spin conversion of hydrogen using supported iron catalysts at cryogenic temperature. Cryogenics 2015, 69, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Karng, S.W.; Oh, I.-H.; Nah, I.W. Ortho-para hydrogen conversion characteristics of amorphous and mesoporous Cr2O3 powders at a temperature of 77 K. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 14147–14153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagels, B.; Calas, N.; Roozemond, D.A.; Hermans, L.J.F.; Chapovsky, P.L. Level-Crossing Resonances in Nuclear Spin Conversion of Molecules. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 77, 4732–4735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapovsky, P.L.; Hermans, L.J.F. Nuclear Spin Conversion in Polyatomic Molecules. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 1999, 50, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapovsky, P.L.; Ilisca, E. Theory of nuclear-spin conversion in ethylene. Phys. Rev. A 2001, 63, 62504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estreicher, S.K.; Stavola, M.; Weber, J. Hydrogen in Si and Ge. In Silicon, Germanium, and their Alloys: Growth, Defects, Impurities, and Nanocrystals; Kissinger, G., Pizzini, S., Eds.; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Estreicher, S. The H2 Molecule in Semiconductors: An Angel in GaAs, a Devil in Si. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2002, 102, 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlos, W.E.; Taylor, P.C. Molecular hydrogen in a-Si: H. Phys. Rev. B 1982, 25, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitch, A.W.R.; Alex, V.; Weber, J. Raman Spectroscopy of Hydrogen Molecules in Crystalline Silicon. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1998, 81, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, E.R.; Ashwin, M.J.; Tucker, J.; Newman, R.C. Isolated interstitial hydrogen molecules in hydrogenated crystalline silicon. Phys. Rev. 1998, B57, R15048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.E.; Stavola, M.; Fowler, W.B.; Walters, P. Key to Understanding Interstitial H2 in Si. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 88, 105507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinnen, K.D.; Buntine, M.; Kliner, D.J. Quantitative determination of H2, HD, and D2 internal-state distributions by (2+1) resonance-enhanced multiphoton ionization. J. Chem. Phys. 1991, 95, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehrouri, M.; Fillion, J.-H.; Chaabouni, H.; Mokrane, H.; Congiu, E.; Dulieu, F.; Matar, E.; Michaut, X.; Lemaire, J.L. Nuclear Spin Conversion of Molecular Hydrogen on Amorphous Solid Water in the Presence of O2 traces. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsevier, C.J. NMR at elevated gas pressures and its application to homogeneous catalysis. J. Mol. Catal. 1994, 92, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, D.C.; Kating, P.M.; Krusic, P.J.; Smart, B.E. Gas-Phase NMR Technique. Top. Catal. 1998, 5, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bargon, J.; Giernoth, R.; Greiner, L.; Kuhn, L.; Laue, S. In Situ NMR Methods in Catalysis; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; Volume 276. [Google Scholar]
- Hunger, M.; Wang, W. Characterization of solid catalysts in the functioning state by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Adv. Catal. 2006, 50, 149–225. [Google Scholar]
- Burueva, D.B.; Pokochueva, E.V.; Wang, X.; Filkins, M.; Svyatova, A.; Rigby, S.P.; Wang, C.; Pavlovskaya, G.E.; Kovtunov, K.V.; Meersmann, T.; et al. In Situ Monitoring of Heterogeneous Catalytic Hydrogenation via 129Xe NMR Spectroscopy and Proton MRI. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 1417–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovener, J.B.; Pravdivtsev, A.N.; Kidd, B.; Bowers, C.R.; Gloggler, S.; Kovtunov, K.V.; Plaumann, M.; Katz-Brull, R.; Buckenmaier, K.; Jerschow, A.; et al. Parahydrogen-Based Hyperpolarization for Biomedicine. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 11140–11162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenschmid, T.C.; Kirss, R.U.; Deutsch, P.P.; Hommeltoft, S.I.; Eisenberg, R.; Bargon, J.; Lawler, R.G.; Balch, A.L. H Polarization Transfer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987, 109, 8089–8091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, C.R.; Weitekamp, D.P. Transformation of symmetrization order to nuclear-spin magnetization by chemical reaction and nuclear magnetic resonance. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1986, 57, 2645–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, C.R.; Weitekamp, D.P. Parahydrogen and synthesis allow dramatically enhanced nuclear alignment. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1987, 109, 5541–5542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiryutin, A.S.; Sauer, G.; Yurkovskaya, A.V.; Limbach, H.H.; Ivanov, K.L.; Buntkowsky, G. Parahydrogen Allows Ultrasensitive Indirect NMR Detection of Catalytic Hydrogen Complexes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 9879–9888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, N.; Kimura, Y.; Kouchi, A.; Chigai, T.; Hama, T.; Pirronello, V. Direct Mesurements of Hydrogen atom diffusion and the Spin Temperature of Nascent H2 molecule on Amorphous Solid Water. Astrophys. J. 2010, 714, L233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwahata, K.; Hama, T.; Kouchi, A.; Watanabe, N. Signatures of Quantum-Tunneling Diffusion of Hydrogen Atoms on Water Ice at 10 K. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 115, 133201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueta, H.; Watanabe, N.; Hama, T.; Kouchi, A. Surface Temperature Dependence of Hydrogen Ortho-Para Conversion on Amorphous Solid Water. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2016, 116, 253201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, Y.; Tsuge, M.; Pirronello, V.; Kouchi, A.; Watanabe, N. Measurements of the Activation Energies for Atomic Hydrogen Diffusion on Pure Solid CO. Astrophys. J. 2018, 858, L23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuge, M.; Hama, T.; Kimura, Y.; Kouchi, A.; Watanabe, N. Interactions of Atomic and Molecular Hydrogen with a Diamond-like Carbon Surface: H2 Formation and Desorption. Astrophys. J. 2019, 878, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, N.; Tsuge, M. Experimental Approach to Physicochemical Hydrogen Processes on Cosmic Ice Dust. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2020, 89, 051015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukata, N.; Sasaki, S.; Murakami, K.; Ishioka, K.; Nakamura, K.G.; Kitajima, M.; Fujimura, S.; Kikuchi, J.; Haneda, H. Hydrogen Molecules and Hydrogen-related Defects in Crystalline Silicon. Phys. Rev. 1997, B56, 6642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, K.; Ishioka, K.; Kitajima, M.; Tateishi, S.; Nakanoya, K.; Mori, T.; Hishida, S. A New Type of Hydrogen Molecules in Silicon. Phys. B Condens. Matter 1999, 273–274, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estreicher, S.K.; Wells, K.; Fedders, P.A.; Ordejon, P.J. Dynamics of interstitial hydrogen molecules in crystalline silicon. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2001, 13, 6271–6283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, R.M. Hydrogen conversion in silicon. AIP Conf. Proc. 2010, 1290, 284. [Google Scholar]
- Hiller, M.; Lavrov, E.V.; Weber, J. Raman scattering study of H2 in Si. J. Phys. Rev. 2006, B74, 235214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiller, M.; Lavrov, E.V.; Weber, J. Hydrogen molecules in semiconductors. Physica 2007, B401, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiller, M.; Lavrov, E.V.; Weber, J. Raman scattering study of H2 trapped within {111}-oriented platelets in Si. Phys. Rev. 2009, B80, 045306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, S.; Lavrov, E.V.; Weber, J. Photoconductive detection of tetrahedrally coordinated hydrogen in ZnO. Phys. Rev. 2011, B83, 233203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socher, S.; Lavrov, E.V.; Weber, J. Hydrogen-induced defects in ion-implanted Si. Phys. Rev. 2012, B86, 125205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, S.; Lavrov, E.V.; Weber, J. Towards understanding the hydrogen molecule in ZnO. J. Phys. Rev. 2014, B90, 205212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FitzGerald, S.A.; Yildirim, T.; Santodonato, L.J.; Neumann, D.A.; Copley, J.R.D.; Rush, J.J.; Trouw, F. Quantum dynamics of interstitial H2 in solid C60. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 60, 6439–6451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Xu, M.; Fitzgerald, S.; Tchernyshyov, K.; Bačić, Z. H2 in solid C60: Coupled translation-rotation eigenstates in the octahedral interstitial site from quantum five-dimensional calculations. J. Chem. Phys. 2013, 138, 244707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkholder, S. Catalysis of Conversion between the Spin Isomers of H2 by MOF-74. Ph.D. Thesis, Oberlin College, Oberlin, OH, USA, 2009. (Unpublished). [Google Scholar]
- FitzGerald, S.A.; Burkholder, B.; Friedman, M.; Hopkins, J.B.; Pierce, C.J.; Schloss, J.M.; Thompson, B.; Rowsell, J.L.C. Metal-Specific Interactions of H2 Adsorbed within Isostructural Metal Organic Frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 20310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapelewski, M.T.; Geier, S.J.; Hudson, M.R.; Stück, D.; Mason, J.A.; Nelson, J.N.; Xiao, D.J.; Hulvey, Z.; Gilmour, E.; FitzGerald, S.A.; et al. M2 (m-dobdc) (M = Mg, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni) Metal–Organic Frameworks Exhibiting Increased Charge Density and Enhanced H2 Binding at the Open Metal Sites. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 12119–12129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natterer, F.D.; Patthey, F.; Brune, H. Distinction of Nuclear Spin States with the Scanning Tunneling Microscope. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 175303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natterer, F.D.; Patthey, F.; Brune, H. Resonant-Enhanced Spectroscopy of Molecular Rotations with a Scanning Tunneling Microscope. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 7099–7105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yu, A.; Toledo, F.; Han, Z.; Wang, H.; He, H.Y.; Wu, R.; Ho, W. Rotational and Vibrational Excitations of a Hydrogen Molecule Trapped within a Nanocavity of Tunable Dimension. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2013, 111, 146102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Yuan, D.; Yu, A.; Czap, G.; Wu, R.; Ho, W. Rotational Spectromicroscopy: Imaging the Orbital Interaction between Molecular Hydrogen and an Adsorbed Molecule. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 114, 206101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosone, T.; Hori, A.; Nishibori, E.; Kubota, Y.; Mishima, A.; Ohba, M.; Tanaka, H.; Kato, K.; Kim, J.; Real, J.A.; et al. Coordination nano-space as stage of hydrogen ortho-para conversion. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2015, 2, 150006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, M.; Nagel, U.; Hüvonen, D.; Rõõm, T.; Mamone, S.; Levitt, M.; Carravetta, M.; Murata, Y.; Komatsu, K.; Chen, J.Y.-C.; et al. Interaction potential and infrared absorption of endohedral H2 in C60. J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 134, 054507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FitzGerald, S.A.; Forth, S.; Rinkoski, M. Induced infrared absorption of molecular hydrogen in solid C60. Phys. Rev. B 2002, 65, 140302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carravetta, M.; Johannessen, O.G.; Levitt, M.; Heinmaa, I.; Stern, R.; Samoson, A.; Horsewill, A.; Murata, Y.; Komatsu, K. Cryogenic NMR spectroscopy of endohedral hydrogen-fullerene complexes. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 124, 104507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, Y.; Murata, M.; Komatsu, K. 100% Encapsulation of a Hydrogen Molecule into an Open-Cage Fullerene Derivative and Gas-Phase Generation of H2@C60. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 7152–7153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carravetta, M.; Murata, Y.; Murata, M.; Heinmaa, I.; Stern, R.; Tontcheva, A.; Samoson, A.; Rubin, Y.; Komatsu, K.; Levitt, M.H. Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy of Molecular Hydrogen Trapped Inside an Open-Cage Fullerene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 4092–4093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, K.; Murata, M.; Murata, Y. Encapsulation of Molecular Hydrogen in Fullerene C60 by Organic Synthesis. Science 2005, 307, 238–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, M.; Murata, Y.; Komatsu, K. Synthesis and Properties of Endohedral C60 Encapsulating Molecular Hydrogen. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 8024–8033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartori, E.; Ruzzi, M.; Turro, N.J.; Decatur, J.D.; Doetschman, D.C.; Lawler, R.G.; Buchachenko, A.L.; Murata, Y.; Komatsu, K. Nuclear Relaxation of H2 and H2@C60 in Organic Solvents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 14752–14753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carravetta, M.; Danquigny, A.; Mamone, S.; Cuda, F.; Johannessen, O.G.; Heinmaa, I.; Panesar, K.; Stern, R.; Grossel, M.C.; Horsewill, A.J.; et al. Solid-state NMR of endohedral hydrogen–fullerene complexes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2007, 9, 4879–4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horsewill, A.J.; Panesar, K.S.; Rols, S.; Johnson, M.R.; Murata, Y.; Komatsu, K.; Mamone, S.; Danquigny, A.; Cuda, F.; Maltsev, S.; et al. Quantum Translator-Rotator: Inelastic Neutron Scattering of Dihydrogen Molecules Trapped inside Anisotropic Fullerene Cages. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 013001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horsewill, J.; Rols, S.; Johnson, M.R.; Murata, Y.; Murata, M.; Komatsu, K.; Carravetta, M.; Mamone, S.; Levitt, M.H.; Chen, J.Y.-C.; et al. Inelastic Neutron Scattering of a quantum translator-roatator in a closed fullerene cage: Isotope effects and translation-rotation coupling in H2@C60. Phys. Rev. 2010, B82, 081410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horsewill, A.J.; Panesar, K.S.; Rols, S.; Ollivier, J.; Johnson, M.R.; Carravetta, M.; Mamone, S.; Levitt, M.H.; Murata, Y.; Komatsu, K.; et al. Inelastic neutron scattering investigations of the quantum molecular dynamics of a H2 molecule entrapped inside a fullerene cage. Phys. Rev. B 2012, 85, 205440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lei, X.; Lawler, R.G.; Murata, Y.; Komatsu, K.; Turro, N.J. Distance-Dependent para-H2→ortho-H2 Conversion in H2@C60 Derivatives Covalently Linked to a Nitroxide Radical. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2011, 2, 741–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.-C.; Li, Y.; Frunzi, M.; Lei, X.; Murata, Y.; Lawler, R.G.; Turro, N.J. Nuclear Spin Isomers of guest molecules in H2@C60 and other fullerenes. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2013, 371, 20110628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamone, S.; Johnson, M.R.; Ollivier, J.; Rols, S.; Levitt, M.H.; Horsewill, A.J. Symmetry-breaking in the H2@C60 endofullerene revealed by inelastic neutron scattering at low temperature. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 18, 1998–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilmarth, W.K.; Baes, C.F. The Catalytic Conversion of Parahydrogen by Paramagnetic Complex Ions in Aqueous Solution. J. Chem. Phys. 1952, 20, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salikhov, K.M.; Molin, Y.N.; Sagdeev, R.Z.; Buchachenko, A.L. Spin Polarization and Magnetic Effects in Radical Reactions; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Natterer, J.; Bargon, J. Progress in Nuclear Mag. Reson. Spectrosc. 1997, 31, 293–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uy, D.; Cordonnier, M.; Oka, T. Observation of Ortho-Para H3+ Selection Rules in Plasma Chemistry. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 78, 3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroulanda, C.; Starovoytova, L.; Canet, D. Longitudinal Nuclear Spin Relaxation ofOrtho- andPara-Hydrogen Dissolved in Organic Solvents. J. Phys. Chem. A 2007, 111, 10615–10624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canet, D.; Bouguet-Bonnet, S.; Aroulanda, C.; Reineri, F. About Long-Lived Nuclear Spin States Involved in Para-Hydrogenated Molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 1445–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terenzi, C.; Bouguet-Bonnet, S.; Canet, D. Direct 1H NMR evidence of spin-rotation coupling as a source of para ? ortho-H2 conversion in diamagnetic solvents. J. Chem. Phys. 2017, 146, 154203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M.; Espenson, J.H. Kinetics of the Interconversion of Parahydrogen and Orthohydrogen Catalyzed by Paramagnetic Complex Ions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 11447–11453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilisca, E. Nuclear Spin Relaxation, Conversion, and Polarization of Molecular Hydrogen in Paramagnetic Solvents. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 16631–16640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilisca, E. Hydrogen conversion on non-magnetic insulating surfaces. EPL Europhys. Lett. 2013, 104, 18001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilisca, E.; Ghiglieno, F. Electron exchanges in nuclear spin conversion of hydrogen physisorbed on diamagnetic insulators. Eur. Phys. J. B 2014, 87, 235–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilisca, E.; Ghiglieno, F. Nuclear conversion theory: Molecular hydrogen in non-magnetic insulators. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2016, 3, 160042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilisca, E.; Ghiglieno, F. Electronuclear paths in the nuclear conversion of molecular hydrogen in silicon. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2017, 667, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilisca, E. Electromagnetic nuclear spin conversion: Hydrogen on amorphous solid water. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2018, 713, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilisca, E.; Sugano, S. A new channel in ortho-para H2 conversion. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1986, 57, 2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilisca, E. Magneto-optic and magneto-catalytic effect. J. Magn. Soc. Jpn. 1987, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilisca, E.; Sugano, S. Optical studies in ortho-para conversion of a hydrogen molecule on a magnetic surface. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1988, 149, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilisca, E. Theory of ortho-parahydrogen conversion catalyzed by “d” electrons. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1990, 168, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makoshi, K.; Ilisca, E.M.R. Dipolar and contact processes in H2 o-p conversion on ionic surfaces. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 1993, 5, 7325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rami, M.; Makoshi, K.; Ilisca, E. Physical Conversion of H2 adsorbed on Cr2O3/Al2O3. Appl. Surf. Sci. 1993, 68, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilisca, E.; Paris, S. A charge transfer process in o-p H2 conversion induced by 3d impurities on a perovskite. Surf. Sci. 1996, 363, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilisca, E.; Bahloul, K. Orbital Paramagnetism and o-p H2 Conversion. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 1996, 29, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilisca, E.; Rami, M. Hyperfine measure of electron surface configurations. In Electronic Processes at Solid Surfaces; Ilisca, E., Makoshi, K., Eds.; World Scientific Publishing Co Pte Ltd.: Singapore city, Singapore, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Paris, S.; Ilisca, E. Electron-Nucleus Resonances and Magnetic Field Acceleration in H2 conversion. J. Phys. Chem. 1999, A103, 4964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundquist, B.I. Electron Transfer at Surfaces. In Electronic Processes at Solid Surfaces; Ilisca, E., Makoshi, K., Eds.; World Scientific Pub Co Pte Ltd.: Singapore, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Yucel, S. Theory of ortho-para conversion in hydrogen adsorbed on metal and paramagnetic surfaces at low temperatures. Phys. Rev. B 1989, 39, 3104–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakawa, K.; Fukutani, K. Nuclear Spin Conversion of H2, H2O, and CH4 Interacting with Diamagnetic Insulators. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2020, 89, 051016–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsivion, E.; Long, J.R.; Head-Gordon, M. Hydrogen Physisorption on Metal–Organic Framework Linkers and Metalated Linkers: A Computational Study of the Factors that Control Binding Strength. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 17827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janotti, A.; Van De Walle, C.G. Hydrogen multicentre bonds. Nat. Mater. 2006, 6, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, Y.; Sugano, S. Ortho-para conversion of hydrogen on magnetic surfaces. Surf. Sci. 1983, 127, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Huber, M.L. Analysis of Thermodynamical Processes involving Hydrogen Methods. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2008, 33, 4413–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leachman, J.W.; Jacobsen, R.T.; Penoncello, S.G.; Lemonn, E.W. Fundamental Equation of State for para hydrogen, normal hydrogen and orthohydrogen. J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data 2009, 38, 721–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakoda, N.; Shindo, K.; Shinzato, K.; Kohno, K.; Takata, Y.; Fuji, M. Review of the Thermodynamic Properties of Hydrogen Based on Existing Equations of State. Int. J. Thermophys. 2010, 31, 276–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colonna, G.; D’Angola, A.; Capitelli, M. Statistical thermodynamic description of H2 molecules in normal ortho/para mixture. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 9656–9668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovas, A.; Jørgensen, U.G. Improved partition functions and thermodynamic quantities for normal, equilibrium, and ortho and para molecular hydrogen. Astron. Astrophys. 2016, 595, A130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rury, T.B.M.; Sams, J.R. Ortho-para separation factors for hydrogen and deuterium. Mol. Phys. 1970, 19, 337–353. [Google Scholar]
- Hama, T.; Watanabe, N. Surface Processes on Interstellar Amorphous Solid Water: Adsorption, Diffusion, Tunneling Reactions, and Nuclear-Spin Conversion. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 8783–8839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakawa, K.; Fukutani, K. Infrared spectroscopy of water clusters co-adsorbed with hydrogen molecules on a sodium chloride film. Chem. Phys. 2016, 472, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golman, K.; Axelsson, O.; Johannesson, H.; Mansson, S.; Olofsson, C.; Petersson, J.S. Parahydrogen-induced polarization in imaging: Subsecond (13)C angiography. Magn. Reson. Med. 2001, 46, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartori, E.; Ruzzi, M.; Lawler, R.G.; Turro, N.J. Nitroxide Paramagnet-Induced Para−Ortho Conversion and Nuclear Spin Relaxation of H2 in Organic Solvents. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 12752–12756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turro, N.J.; Chen, J.Y.-C.; Sartori, E.; Ruzzi, M.; Marti, A.; Lawler, R.; Jockusch, S.; López-Gejo, J.; Komatsu, K.; Murata, Y. The Spin Chemistry and Magnetic Resonance of H2@C60. From the Pauli Principle to Trapping a Long Lived Nuclear Excited Spin State inside a Buckyball. Acc. Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, C.M.; Johnston, H.L. The surface catalysis of the ortho-to para-conversion in liquid hydrogen by paramagnetic oxides on alumina. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carravetta, M.; Johannessen, O.G.; Levitt, M.H. Beyond theT1Limit: Singlet Nuclear Spin States in Low Magnetic Fields. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 153003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carravetta, M.; Levitt, M.H. Theory of long-lived nuclear spin states in solution nuclear magnetic resonance. I. Singlet states in low magnetic field. J. Chem. Phys. 2005, 122, 214505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pileo, G. Singlet State Relaxation via intermolecular dipolar coupling. J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 134, 214505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhl, H.; Smith, J.H.; Kumar, P. Role of Spin Fluctuations in the Desorption of Hydrogen from Paramagnetic Metals. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1970, 25, 1442–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipman, M.S.; Cheung, H.; Roberts, O.P. Continuous conversion hydrogen liquefaction. CEP 1963, 59, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, C.R.; Paul, R.S. Purification of liquefaction grade hydrogen. Cryog. Eng. P. 1963, 59, 61. [Google Scholar]
- Newton, C.L. Hydrogen production, liquefaction and use. Cryog. Eng. News 1967, 2, 50. [Google Scholar]
- Barker, C.R.; Shaner, R.L. A study of the efficiency of hydrogen liquefaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 1978, 3, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, T. Cryogenic Engineering; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; ISBN 9780367578169. [Google Scholar]
- Singleton, A.H.; Lapin, A. Design of Para-Orthohydrogen Catalytic Reactors. Adv. Cryog. Eng. 1966, 11, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xiao, R.; Cheng, C.; Tian, G.; Chen, S.; Hou, Y. Thermodynamic analysis of the para-to-ortho hydrogen conversion in cryo-compressed hydrogen vessels for automotive applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 24928–24937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, L.-M.; Knudson, J.N.; Mocko, M.; Renneke, R.M. Practical in-situ determination of ortho-para hydrogen ratios via fiber-optic based Raman spectroscopy. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A Accel. Spectrometers Detect. Assoc. Equip. 2016, 810, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Kang, S.W.; Nah, I.W.; Oh, I.-H. Synthesis and characterization of Fe-modified zeolite for spin conversion of hydrogen at cryogenic temperature. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 15529–15533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitpas, G.; Aceves, S.M.; Matthews, M.J.; Smith, J.R. Para-H2 to ortho-H2 conversion in a full-scale automotive cryogenic pressurized hydrogen storage up to 345 bar. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 6533–6547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitpas, G.; Bénard, P.; Klebanoff, L.; Xiao, J.; Aceves, S. A comparative analysis of the cryo-compression and cryo-adsorption hydrogen storage methods. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 10564–10584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Blanco, J.; Petitpas, G.; Espinosa-Loza, F.; Elizalde-Blancas, F.; Martinez-Frias, J.; Aceves, S.M. The fill density of automotive cryo-compressed hydrogen vessels. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ilisca, E. Hydrogen Conversion in Nanocages. Hydrogen 2021, 2, 160-206. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrogen2020010
Ilisca E. Hydrogen Conversion in Nanocages. Hydrogen. 2021; 2(2):160-206. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrogen2020010
Chicago/Turabian StyleIlisca, Ernest. 2021. "Hydrogen Conversion in Nanocages" Hydrogen 2, no. 2: 160-206. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrogen2020010
APA StyleIlisca, E. (2021). Hydrogen Conversion in Nanocages. Hydrogen, 2(2), 160-206. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrogen2020010