DNA Barcoding Reveals a Critical Spawning Ground in the Paranapanema River Basin, Southern Brazil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
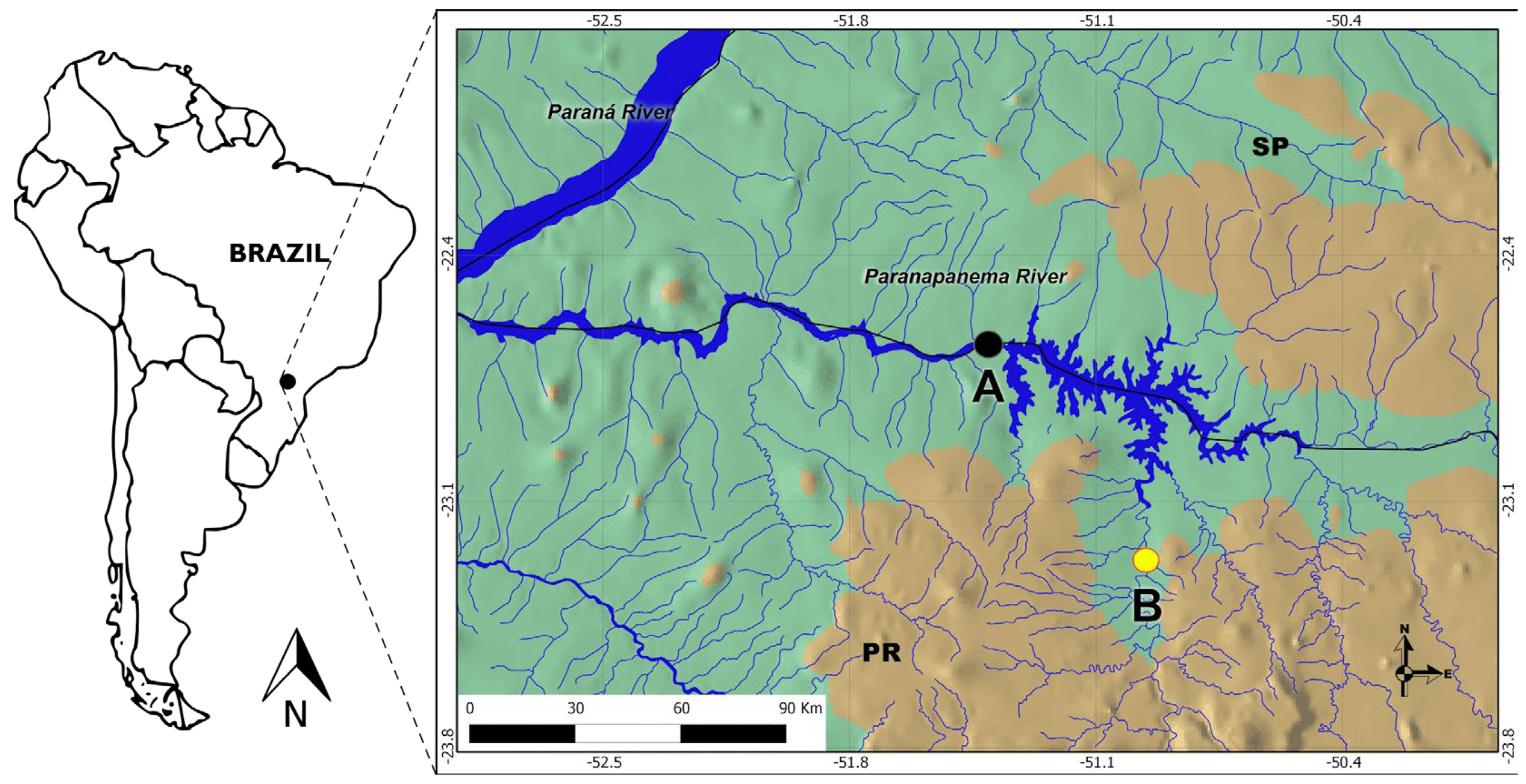
2.1. Area of Study
2.2. Ichthyoplankton Sampling and Screening
2.3. DNA Extraction
2.4. Amplification, Purification, and Sequencing of COI
2.5. Sequence Data Analysis
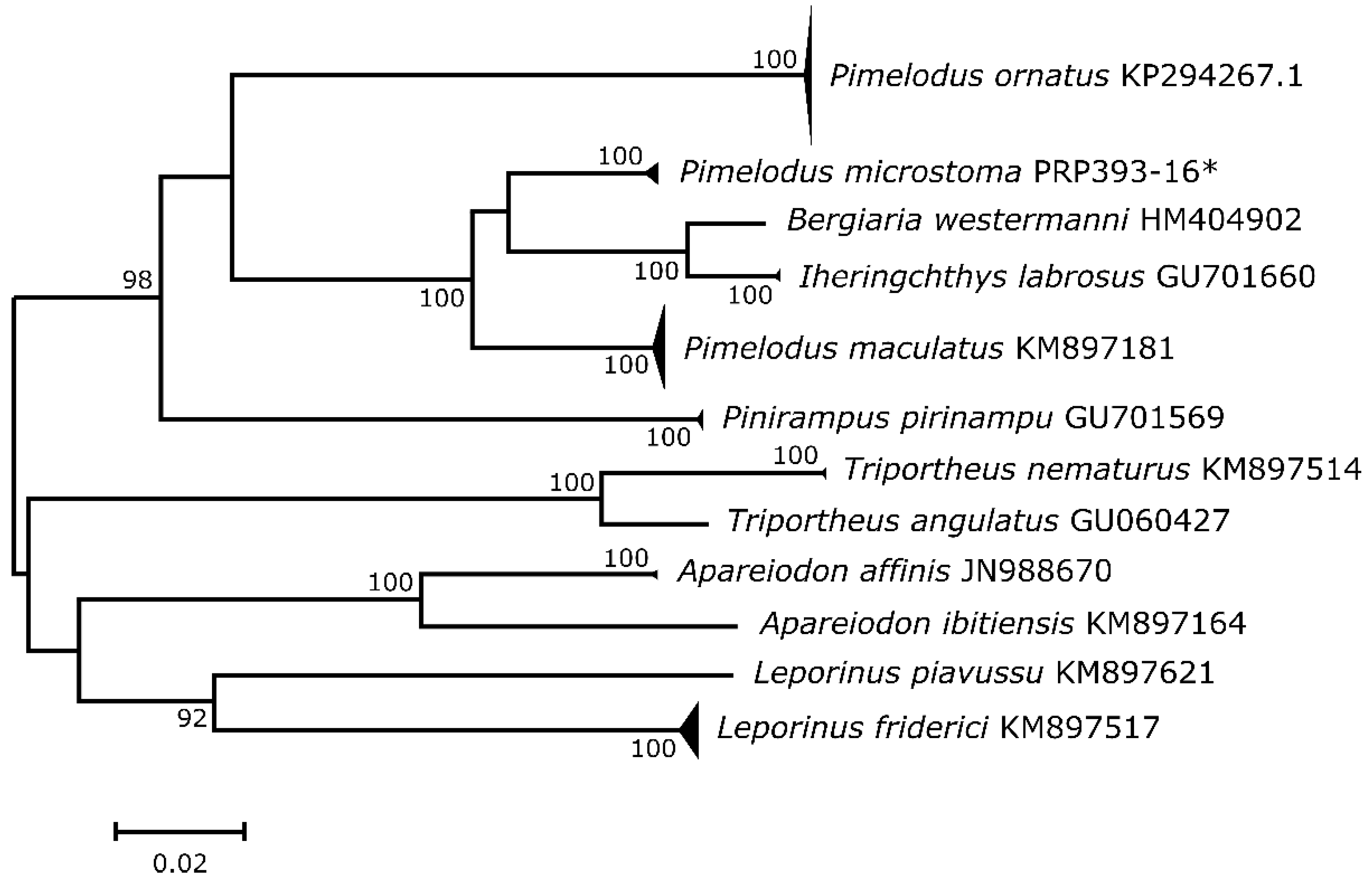
3. Results
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Lehner, B.; Liermann, C.R.; Revenga, C.; Vorosmarty, C.; Fekete, B.; Crouzet, P.; Döll, P.; Endejan, M.; Frenken, K.; Magome, J.; et al. High-resolution mapping of the world’s reservoirs and dams for sustainable river-flow management. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2011, 9, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarfl, C.; Lumsdon, A.E.; Berlekamp, J.; Tydecks, L.; Tockner, K. A global boom in hydropower dam construction. Aquat. Sci. 2015, 77, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Chen, J.; Xu, J.; Zeng, G.; Sang, L.; Liu, Q.; Yin, Z.; Dai, J.; Yin, D.; Liang, J.; et al. Effects of dam construction on biodiversity: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 221, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chucholl, F.; Chucholl, C. Differences in the functional responses of four invasive and one native crayfish species suggest invader-specific ecological impacts. Freshw. Biol. 2021, 66, 2051–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostinho, A.A.; Pelicice, F.M.; Gomes, L.C. Dams and the fish fauna of the Neotropical region: Impacts and management related to diversity and fisheries. Braz. J. Biol. 2008, 68, 1119–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbarossa, V.; Schmitt, R.J.; Huijbregts, M.A.; Zarfl, C.; King, H.; Schipper, A.M. Impacts of current and future large dams on the geographic range connectivity of freshwater fish worldwide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 3648–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Olden, J.D.; Wu, R.; Ouyang, S.; Wu, X. Dam construction impacts fish biodiversity in a subtropical river network, China. Diversity 2022, 14, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, K.; Zhu, G.; Wu, Z.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y. Thermal stratification dynamics in a large and deep subtropical reservoir revealed by high-frequency buoy data. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 614–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posch, T.; Köster, O.; Salcher, M.M.; Pernthaler, J. Harmful filamentous cyanobacteria favoured by reduced water turnover with lake warming. Nat. Clim. Change 2012, 2, 809–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, J.H.; Britto, S.G.C.; Vianna, N.C.; Garavello, J.C. Biological and ecological aspects of Pinirampus pirinampu (Spix, 1829), Siluriformes, Pimelodidae, Capivara Reservior, Paranapanema River, Southern Brazil. Acta Limnol. Brasiliensia 2004, 16, 293–304. [Google Scholar]
- Frantine-Silva, W.; Savada, C.S.; de Almeida, F.S.; Orsi, M.L. Polygynandry and high genetic diversity supported by kinship and population genetics from neotropical catfish ichthyoplankton. Ecol. Freshw. Fish 2023, 32, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, D.G.; Carlsson, J.; Galindo, B.A.; Frantine-Silva, W.; Apolinário-Silva, C.; Meschini, J.S.; Zanatta, A.S.; Almeida, F.S.; Sofia, S.H. The role of free-flowing tributary rivers in the maintenance of genetic diversity of a migratory fish species living in a river fragmented by dams. Hydrobiologia 2022, 849, 1221–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostinho, A.A.; Gomes, L.C.; Latini, J.D. Fisheries management in Brazilian reservoirs: Lessons from/for South America. Interciencia 2004, 29, 334–338. [Google Scholar]
- Pegg, G.G.; Sinclair, B.; Briskey, L.; Aspden, W.J. MtDNA barcode identification of fish larvae in the southern Great Barrier Reef–Australia. Scientia Marina 2006, 70 (Suppl. 2), 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakatani, K. Ovos e Larvas de Peixes de Água Doce: Desenvolvimento e Manual de Identificação; EDUEM: Panama City, Brazil, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Frantine-Silva, W.; Sofia, S.H.; Orsi, M.L.; Almeida, F.S. DNA barcoding of freshwater ichthyoplankton in the Neotropics as a tool for ecological monitoring. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2015, 15, 1226–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, P.D.; Cywinska, A.; Ball, S.L.; DeWaard, J.R. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2003, 270, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajibabaei, M.; Singer, G.A.; Hebert, P.D.; Hickey, D.A. DNA barcoding: How it complements taxonomy, molecular phylogenetics and population genetics. Trends Genet. 2007, 23, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, F.S.; Frantine-Silva, W.; Lima, S.C.; Garcia, D.A.; Orsi, M.L. DNA barcoding as a useful tool for identifying non-native species of freshwater ichthyoplankton in the neotropics. Hydrobiologia 2018, 817, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, R.A.; Sales, N.G.; Santos, G.M.; Santos, G.B.; Carvalho, D.C. DNA barcoding and morphological identification of neotropical ichthyoplankton from the Upper Paraná and São Francisco. J. Fish Biol. 2015, 87, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.D.; Zemlak, T.S.; Innes, B.H.; Last, P.R.; Hebert, P.D. DNA barcoding Australia’s fish species. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2005, 360, 1847–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togawa, R.C.; Brigido, M.M. PHPH: Web based tool for simple electropherogram quality analysis. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Bioinformatics and Computational Biology-IcoBiCoBi, Ribeirão Preto, Brazil, 14–16 May 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D. BOLD: The Barcode of Life Data System. Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ICMBio—Chico Mendes Institute for Biodiversity Conservation. Biodiversity Extinction Risk Assessment System—SALVE. Available online: https://salve.icmbio.gov.br/ (accessed on 16 July 2025).
- Lima, M.C.C.D.; Lima, S.C.; Savada, C.S.; Suzuki, K.M.; Orsi, M.L.; Almeida, F.S.D. Use of DNA barcode in the identification of fish eggs in tributaries of the Paranapanema River basin. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2020, 43, e20190352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alho, C.J. Hydropower dams and reservoirs and their impacts on Brazil’s biodiversity and natural habitats: A review. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 2020, 6, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarduli, L.R.; Garcia, D.A.Z.; Vidotto-Magnoni, A.P.; Casimiro, A.C.R.; Vianna, N.C.; de Almeida, F.S.; Jerep, F.C.; Orsi, M.L. Fish fauna from the Paranapanema River basin, Brazil. Biota Neotrop. 2019, 20, e20180707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes-Rojas, A.; Delgado-Morales, N.A.J.; Escucha, R.S.; Siabatto, L.C.; Link, A. Recovering connectivity through restoration corridors in a fragmented landscape in the magdalena river’s valley in Colombia. Biodivers. Conserv. 2024, 33, 3171–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Yuan, S.; Tang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wolter, C.; Nikora, V. Ecological connectivity of river-lake ecosystem: Evidence from fish population dynamics in a connecting channel. Water Resour. Res. 2024, 60, e2024WR037495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.D. DNA barcode divergence among species and genera of birds and fishes. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2009, 9, 1077–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.H.; Hanner, R.; Foresti, F.; Oliveira, C. Can DNA barcoding accurately discriminate megadiverse Neotropical freshwater fish fauna? BMC Genet. 2013, 14, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- April, J.; Mayden, R.L.; Hanner, R.H.; Bernatchez, L. Genetic calibration of species diversity among North America’s freshwater fishes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 10602–10607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, A.J.; Cruz, C.; Griffith, E.; Ross, H.; Ibáñez, R.; Lips, K.R.; Driskell, A.C.; Bermingham, E.; Crump, P. DNA barcoding applied to ex situ tropical amphibian conservation programme reveals cryptic diversity in captive populations. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2013, 13, 1005–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasier, M.J.; Wiklund, H.; Neal, L.; Jeffreys, R.; Linse, K.; Ruhl, H.; Glover, A.G. DNA barcoding uncovers cryptic diversity in 50% of deep-sea Antarctic polychaetes. Royal Soc. Open Sci. 2016, 3, 160432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibatta, O.A.; Gealh, A.M.; Bennemann, S.T. Ichthyofauna from the middle and upper stretches of rio Tibagi basin, Paraná, Brazil. Biota Neotrop. 2007, 7, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| ORDER/Family/Species | Migratory Status | N | BOLD Ø (%)–σ | D.I. (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SILURIFORMES | ||||
| Pimelodidae | ||||
| Pimelodus ornatus | Migratory | 34 | 100–0 | 0.06 |
| Pimelodus microstoma | Non–migratory | 3 | 99.82–0.18 | 0.21 |
| Pimelodus maculatus | Migratory | 20 | 100–0 | 0.14 |
| Pinirampus pirinampu | Migratory | 4 | 99.95–0.09 | 0 |
| Iheringichthys labrosus | Non–migratory | 2 | 100–0 | 0.11 |
| CHARACIFORMES | ||||
| Anostomidae | ||||
| Leporinus friderici | Migratory | 13 | 99.94–0.08 | 0.19 |
| Triportheinae | ||||
| Triportheus nematurus | Non–migratory | 2 | 100–0 | 0.11 |
| Parodontidae | ||||
| Apareiodon affinis | Non–migratory | 1 | 99.82–0 | 0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Depintor, T.S.; Frantine-Silva, W.; Orsi, M.L.; Almeida, F.S. DNA Barcoding Reveals a Critical Spawning Ground in the Paranapanema River Basin, Southern Brazil. Ecologies 2025, 6, 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecologies6030059
Depintor TS, Frantine-Silva W, Orsi ML, Almeida FS. DNA Barcoding Reveals a Critical Spawning Ground in the Paranapanema River Basin, Southern Brazil. Ecologies. 2025; 6(3):59. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecologies6030059
Chicago/Turabian StyleDepintor, Thiago S., Wilson Frantine-Silva, Mario L. Orsi, and Fernanda S. Almeida. 2025. "DNA Barcoding Reveals a Critical Spawning Ground in the Paranapanema River Basin, Southern Brazil" Ecologies 6, no. 3: 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecologies6030059
APA StyleDepintor, T. S., Frantine-Silva, W., Orsi, M. L., & Almeida, F. S. (2025). DNA Barcoding Reveals a Critical Spawning Ground in the Paranapanema River Basin, Southern Brazil. Ecologies, 6(3), 59. https://doi.org/10.3390/ecologies6030059








