Abstract
The combination of antimicrobial agents with different mechanisms of action is an important step in the fight against drug-resistant microorganisms. In this study, the interaction of the lysozyme enzyme with ampicillin and colistin was investigated. These antibiotics are highly effective against Gram-positive (ampicillin) and Gram-negative (colistin) pathogenic microorganisms. Spectroscopic and kinetic methods and molecular docking were used in the research. The results of the spectroscopic analysis confirmed the intermolecular interaction of lysozyme with ampicillin or colistin. The formation of the lysozyme complex with ampicillin was accompanied by mixed quenching of the enzyme fluorescence and changes in its secondary structure (a slight decrease in the content of α-helices). The interaction of lysozyme with colistin was complemented by dynamic quenching of the enzyme fluorescence. The method of molecular docking established that the interactions of lysozyme with colistin were predominantly van der Waals, while hydrogen bonds predominated in the lysozyme complex with ampicillin. Despite the presence of interactions of ampicillin and colistin with amino acid residues from the active site of lysozyme, this did not affect its ability to cause destruction of bacterial cell walls. The results obtained can be used in the development of antibacterial drugs.
1. Introduction
The discovery of antibiotics has enabled the suppression and control of infectious disease spread. The research into the interaction between antimicrobial agents and proteins is an important task for biotechnology, pharmacology, and medicine. Scientists most frequently study how proteins bind with antibiotics, as well as how antibiotics affect their structure and biological function [1,2,3]. Preliminary in vitro and in silico studies can be essential for interpreting pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamics data on low-molecular-weight antimicrobials. As antibiotics are used in animal farming and other areas of agriculture, they can be located in water bodies, soil, milk, meat, and eggs. Hence, it is essential to assess the impact of antibiotics on human and animal health and the environment.
Lysozyme was first isolated and described by Alexander Fleming in 1922. This enzyme was discovered by the scientist in nasopharyngeal secretions. Later, lysozyme was found in various biological fluids of humans and animals, such as tears, saliva, and breast milk [4,5]. There are several types of lysozymes: c (chicken, with human lysozyme belonging to this type), g (goose), i (invertebrate), etc. [6]. For now, hen egg-white lysozyme is considered to be the most studied; its three-dimensional structure was identified in 1965 using X-ray analysis [7]. Hen egg-white lysozyme consists of 129 amino acid residues and has a molecular weight of 14.3 kDa [7,8]. The compactness and high stability of the enzyme molecule are due to disulfide bonds. The structure of lysozyme contains two domains: the hydrophobic α-domain and the hydrophilic β-domain [9,10,11]. The active site of lysozyme includes catalytic groups at position 35 (Glu35) and position 52 (Asp52) [12].
As hen egg-white lysozyme is available and has a low cost, the enzyme has been extensively used in various industrial fields. In chemistry, biology, and medicine, researchers often use lysozyme as a model protein. In the food industry, it is used in the production of cheese, wine, beer, and other food products [13]. In healthcare, lysozyme is used to treat infectious diseases in otolaryngology and ophthalmology, as well as to treat burn wounds. Apart from its antimicrobial qualities, lysozyme has antiviral and antitumor properties, though these have not yet been applied in practice [14,15,16]. A significant amount of research has focused on studying the interaction of lysozyme with various additives, for example, mucin [17], polymers [18,19], and surfactants [20,21]. But of greatest interest are lysozyme complexes with antibiotics of different classes, for example, fluoroquinolones, penicillins, cephalosporins, tetracyclines, amphenicols, macrolides, and sulfanilamides [22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36].
As hen egg-white lysozyme is widely used in biotechnology and has 60% homology with human lysozyme, the study of its interaction with different ligands is an important and relevant task. This enzyme is able to bind numerous ligands: the important physiological function of lysozyme is the ability to carry drugs. The study of the interaction of lysozyme with various medicinal substances is fundamental and useful for the molecular design of drugs and the development of new drugs. When developing medicines, it is important to consider that lysozyme can play a role not only as a therapeutic component but also as a carrier for drug delivery [22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36].
During the last two decades, numerous academic papers have been devoted to studying the interaction of lysozyme with cephalosporins [22,23,24,25,26] and tetracyclines [27,28,29]. Although penicillins are one of the most widely used antibiotics, there is no detailed study on the interaction of these antibiotics with lysozyme. Forty years ago, a study on the interaction of lysozyme with penicillin G, penicillin V, and methicillin was carried out using the equilibrium dialysis method [30]. An investigation of the interaction of hen egg-white lysozyme with cloxacillin and dicloxacillin was carried out using a combination of spectroscopic and computational methods [31]. Information on the interaction of lysozyme with peptide antibiotics is not currently available in the literature. The best-known peptide antibiotics are polymyxins (polymyxin B, polymyxin E). We selected ampicillin and polymyxin E (colitin) as representatives of the above groups of antibiotics. These two antibiotics are commonly used in healthcare and veterinary medicine and are highly effective against Gram-positive pathogenic microorganisms (ampicillin) and Gram-negative pathogenic microorganisms (colistin).
Ampicillin is a semi-synthetic antibiotic, derived from penicillin, that has a broad range of effects. This antibiotic inhibits the synthesis of the bacterial cell wall at later stages. Ampicillin inhibits transpeptidase, which is responsible for the formation of peptide bonds in the peptidoglycan. Ampicillin is sensitive to the action of penicillinase enzymes. Ampicillin is active against Gram-positive and Gram-negative aerobic bacteria that do not produce penicillinases (Staphylococcus spp., Streptococcus spp., Listeria monocytogenes, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, Escherichia coli, Shigella spp., Salmonella spp., and Bordetella pertussis). This antibiotic can be obtained both synthetically and by isolation from microorganisms (Kluyvera citrophila, Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides, and Micrococcus ureae) [37,38,39,40].
Polymyxins are polypeptide antibiotics, with the molecule consisting of a polycationic cyclic heptapeptide with a tripeptide side chain N-acylated by a fatty acid tail. Polymyxin E (colistin) and Polymyxin B are in most common use. Currently, all antibiotics of the polymyxin group are obtained as metabolites of Paenibacillus polymyxa bacteria. The mechanism of polymyxins’ influence on a bacterial cell (for Gram-negative microorganisms) consists of their interaction with lipopolysaccharides of the outer and inner membranes [41,42,43,44,45]. The range of action of polymyxins is rather narrow, but they exhibit in vitro activity against Gram-negative pathogens, including Acinetobacter baumannii and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. These antibiotics also have bactericidal activity against most representatives of the Enterobacteriaceae family [46,47].
Although enough papers have been published to date on the interaction of lysozyme with antibiotics, in the analysis of the literature published so far, we saw a number of problems. Researchers often use fluorescent spectroscopy to analyze the interaction of lysozyme with antibiotics, but they do not always adjust the fluorescence spectra of the enzyme. Although the combination of spectroscopic and computational methods gives a good understanding of the molecular basis of lysozyme interaction with antibiotics, very few studies have investigated the influence of antibiotics on the biological function of the lysozyme. In our work, we have studied the interaction of lysozyme with colistin and ampicillin. To conduct the study, we have used multispectroscopic techniques, molecular docking, and turbidimetry.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
We used the lyophilized powder of hen egg-white lysozyme from Sigma Aldrich (L6876; Burlington, MA, USA), ampicillin sodium salt (C16H18N3NaO4S, 371.4 g/mol) from MP Biomedicals (194526; Santa Ana, CA, USA), and colistin sulfate (C52H100N16O17S, 1253 g/mol) manufactured by Hebei Shengxue Dacheng Pharmaceutical (0e8555; Shijiazhuang City, China). Microccocus lysodeikticus ATCC No. 4698 from Sigma Aldrich (M3770) was used as a substrate for lysozyme. Distilled water and phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) tablets from Sigma Aldrich (P4417) were used to prepare the enzyme and antibiotic solutions.
2.2. Preparation of Lysozyme Complexes with Antibiotics
Lysozyme solutions (0.5 g/L) were mixed in a volume ratio of 1:1 with ampicillin or colistin solutions in the required concentrations and maintained at 277 K (4 °C) for 24 h. A series of solutions containing lysozyme (0.25 g/L) and an antibiotic were obtained in molar ratios of antibiotic/enzyme from 0.5:1 to 144:1. PBS was used as a solvent.
2.3. The Turbidimetric Identification of Lysozyme Activity
The bacteriolytic activity of lysozyme in the presence of antibiotics was measured at a wavelength of 450 nm in a 0.5 mL quartz cell at 298 K using a Beckman Coulter DU 720 UV–Vis spectrophotometer (Beckman Coulter, Brea, CA, USA).
A suspension of Microccocus lysodeikticus cells with different OD450nm values (from 0.2 to 1.5) was prepared in PBS. A lysozyme solution (a control solution) or a solution containing lysozyme and an antibiotic was added to 0.5 mL of the suspension with a specified OD450nm value. The enzyme concentration in the reaction medium was 5 μg/mL. After adding the enzyme to the substrate, the decrease in the turbidity of the cell suspension was monitored over time until the cell lysis ended (5–7 min). The enzyme activity was determined as the slope of the linear portion of the cell suspension turbidity versus time plot.
The Michaelis–Menten equation [48] was used to estimate the kinetic parameters:
which was analyzed by converting to the double-reciprocal plot 1/ν—1/[S] (the Lineweaver–Burk plot, where ν is the rate of the enzymatic reaction, [S]0 is the substrate concentration), from which Km (the Michaelis constant) and Vmax (the maximum rate of the enzymatic reaction) were determined.
2.4. Fluorescence Measurements
The fluorescence spectra of the enzyme solutions and their complexes with antibiotics (minus the background) were recorded using a Varian Cary Eclipse spectrofluorometer (Varian Optical Spectroscopy Instruments, Mulgrave, VIC, Australia) at temperatures of 298 K or 313 K in a quartz cell containing 1 mL of the test sample. The spectra were recorded in the emission wavelength range from 290 to 450 nm with an excitation wavelength of 280 nm. To record the spectra, samples with an enzyme concentration of 0.25 g/L were used; an antibiotic solution of the corresponding concentration was used as a background.
At the excitation and emission wavelengths of the protein, an inner filter effect may be observed that is caused by two reasons. Firstly, small antibiotic molecules and enzyme molecules competitively adsorb excited light, which results in a decrease in the actual fluorescence intensity of the enzyme. Secondly, absorption of radiation emitted by protein molecules by antibiotic molecules is possible, leading to a decrease in the fluorescence spectrum intensity and distortion of the spectral region. In order to eliminate the effects of the inner filter, the fluorescence intensity values can be corrected using the following equation [49]:
where RFUcorr and RFUobs are the corrected and observed lysozyme fluorescence intensities, respectively, and Aex and Aem are the absorption of the antibiotic at excitation and emission wavelengths, respectively.
2.5. UV–Vis Spectroscopy
UV–vis absorption spectra (minus the background) in the ultraviolet range of wavelengths 240–400 nm were recorded in a 0.5 mL quartz cell at 298 K using a Beckman Coulter DU 720 UV–Vis spectrophotometer (Beckman Coulter, Brea, CA, USA). The spectra were recorded using samples with an enzyme concentration of 0.25 g/L; an antibiotic solution of the appropriate concentration was used as the background.
2.6. CD Spectroscopy
The CD spectra for lysozyme were recorded using a Jasco J-815 spectrometer (Jasco Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) at 298 K, a scan rate of 2 nm/s, and an optical path length of 1 mm. The CD spectra were decoded using the CDNN program (version 2.1), which is based on the theory of neural networks [50]. The spectra were recorded using samples with an enzyme concentration of 0.25 g/L; an antibiotic solution of the appropriate concentration was used as the background.
2.7. Molecular Docking Approaches
The lysozyme structure chosen from the protein data bank (https://www.rcsb.org/) to conduct molecular docking had the 6LYZ identifier obtained using X-ray analysis (2 Å resolution). The molecules of sodium ampicillin (ChemSpider ID 389889, Figure S1) and colistin sulfate (ChemSpider ID 29739295, Figure S2) in the SDF format were obtained from the ChemSpider database. Ligands and protein were prepared for molecular docking using MGLTools (version 1.5.7). Water molecules were removed from the lysozyme molecule, and polar hydrogens and Kollman charges were added, while the missing atoms in amino acid residues were restored. The grid box size with dimensions of X = 126, Y = 126, and Z = 126 (0.375 Å) with grid center coordinates x = −0.462, y = 20.573, and z = 19.265, was selected as the docking box (blind docking). Counterions were removed from the antibiotic molecules, and Gasteiger charges were added. In the ampicillin molecule, the number of rotatable bonds was taken to be 4, and in the colistin molecule, 28. The docking procedure was performed using Autodock 4.2. The docking results were analyzed using Discovery Studio (version 4.5) and MGLTools (version 1.5.7).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Study of the Interaction of Lysozyme with Antibiotics Using UV–Vis Spectroscopy
UV–vis spectroscopy is a popular method in the research of the interaction of smaller molecules (antibiotics) with macromolecules (proteins). The presence of an interaction between a protein and a ligand can be determined by a change in the intensity and/or position of the absorption maximum of the protein molecule. Usually, a change in the spectral characteristics of proteins when interacting with ligands is caused by a change in the microenvironment of Tryptophan (Trp), Tyrosine (Tyr), and Phenylalanine (Phe) residues.
The UV absorption spectrum of the lysozyme molecule (without additives) is characterized by the presence of an absorption maximum at a wavelength of 280 nm (Figure 1A,B). This maximum is due to the π-π* transitions in the residues of aromatic amino acids, such as Trp, Tyr, and Phe, in the lysozyme molecule. It is known that the absorption maximum of lysozyme is mainly due to Trp residues [51].
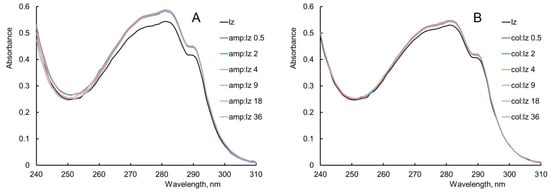
Figure 1.
The effect of (A) ampicillin (amp) and (B) colistin (col) on the UV absorption spectrum of lysozyme (lz). Experimental conditions: 298 K, enzyme concentration 0.25 g/L, PBS.
In order to identify the effect of the antibiotic on the UV–vis spectrum of the enzyme, the antibiotic spectrum was subtracted from the spectrum of the enzyme mixture with the antibiotic. Registration of the UV–vis spectra was carried out at the antibiotic/enzyme molar ratios from 0.5 to 144. When comparing the UV–vis spectra of the mixtures of the antibiotics with the enzyme with UV–vis spectra of the antibiotics in appropriate concentrations, a large contribution of the absorption of the antibiotics was found at their molar excesses greater than or equal to 72 (Figures S3 and S4). For this reason, the analysis of the UV–vis spectra of the enzyme was carried out with a molar excess of ampicillin/colistin from 0.5 to 36.
When comparing the UV absorption spectrum of lysozyme with the UV absorption spectrum of lysozyme in mixtures with antibiotics, it can be noted that the addition of ampicillin and colistin leads to a slight hyperchromic effect in the absorption maximum of the enzyme, while the position of this maximum remains unchanged (Figure 1A,B). This means that interactions between lysozyme and these antimicrobial agents are possible. This suggests a possible change in the conformation of the enzyme molecule or a possible exposure of Trp, Tyr, and Phe residues. It can be concluded that the hyperchromic effect presumably results from an interaction between lysozyme and antibiotics, ampicillin and colistin.
Changes in the UV absorption spectrum of lysozyme during its interaction with antibiotics of different classes (sulfanilamides, fluoroquinolones, cephalosporins, tetracyclines, macrolides) were previously discovered by researchers. When interacting with lysozyme cephalosporins or sulfanilamides, a blue shift of the enzyme absorption maximum and a hyperchromic effect were found [23,24,32]. When forming a ternary complex of lysozyme with lacosamide and levofloxacin or a double complex of lysozyme with levofloxacin, a red shift of the enzyme absorption maximum and a hyperchromic effect were found [33,34]. When interacting with lysozyme, ceftazidime, cefoperazone, tetracyclines, and azithromycin, a hypochromic effect was observed [22,26,28,29,35].
3.2. The Study of the Interaction of Lysozyme with Antibiotics by Fluorescence Measurements
Fluorescence measurements are common in the study of the interaction of proteins with different ligands. As a rule, a fluorescence measurement is used to detect changes in the tertiary structure of proteins. The fluorescence spectrum of lysozyme at a temperature of 298 K (λex 280 nm) has a maximum fluorescence emission (λmax) at a wavelength of 345 ± 2 nm (Figure 2A and Figure 3A). This maximum is due to the presence of six Trp residues, three Tyr residues, and three Phe residues in the enzyme molecule. In the lysozyme enzyme molecule, of the six Trp residues (Trp28, Trp62, Trp63, Trp108, Trp111, and Trp123), only two (Trp62 and Trp108) are located on the surface of the lysozyme molecule and provide 80% of the analytical fluorescent signal. The side chains of the amino acid residues Trp62 and Trp108 are directed towards the solvent, making the fluorescence spectra of lysozyme sensitive to changes in the parameters of the medium [52,53].
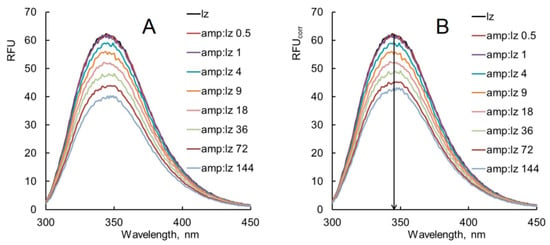
Figure 2.
(A) Observed fluorescence emission spectra of lysozyme (lz) in the presence of ampicillin (amp). (B) Corrected fluorescence emission spectra of lysozyme (lz) in the presence of ampicillin (amp). Experimental conditions: 298 K, enzyme concentration 0.25 g/L, PBS, λex 280 nm.
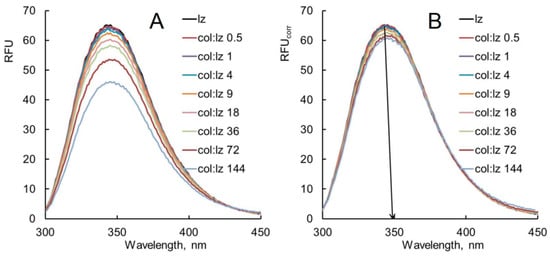
Figure 3.
(A) Observed fluorescence emission spectra of lysozyme (lz) in the presence of colistin (col). (B) Corrected fluorescence emission spectra of lysozyme (lz) in the presence of colistin (col). Experimental conditions: 298 K, enzyme concentration 0.25 g/L, PBS, and λex 280 nm.
The observed fluorescence emission spectra of lysozyme without and with various concentrations of antibiotics at 298 K are shown in Figure 2A and Figure 3A. The corrected fluorescence spectra (Equation (2)) of lysozyme without and with various concentrations of antibiotics are shown in Figure 2B and Figure 3B. Figure 2A,B and Figure 3A,B show a significant change in the fluorescence decrement of the corrected spectra compared with the observed spectra. The large decrement in the fluorescence of the observed spectra is ascribed to the inner filter effect by which the antibiotic molecules absorb the radiation emitted by protein molecules and obscure the apparent quenching [22]. The corrected fluorescence spectra were used for further analysis.
The interaction of lysozyme with varying molar excesses of ampicillin (Figure 2B) causes a shift in the position of the enzyme fluorescence maximum (λmax) by 1–3 nm toward shorter wavelengths (a hypsochromic, or blue shift). When lysozyme interacts with colistin, a shift in the position of the fluorescence emission maximum by 1–2 nm toward longer wavelengths (a bathochromic, or red shift) is observed (Figure 3B). This means that a change in the polarity of the microenvironment of Trp residues occurs due to the interaction of lysozyme with these antibiotics. The blue shift of maximum lysozyme fluorescence in the presence of ampicillin indicates a decrease in the polarity and the formation of the hydrophobic microenvironment of Trp residues in the enzyme molecule. This suggests the possibility of hydrophobic interactions between the aromatic amino acid rings of Trp residues and the aromatic ring of the ampicillin molecule. The red shift of maximum lysozyme fluorescence in the presence of colistin is associated with an increase in the polarity of Trp residues. The addition of colistin is likely to cause a transition of the enzyme molecule to a more extended state, and buried Trp residues become exposed to the aqueous medium.
Shifts in the fluorescence maximum of lysozyme have often been observed by researchers during the interaction of the enzyme with antibiotics. A blue shift of the enzyme fluorescence maximum was detected during the interaction of lysozyme with tetracyclines (oxytetracycline, tetracycline, doxycycline, metacycline, and tigecycline), during the formation of double complexes of lysozyme with 2-sulfanilamido-4-methylpyrimidine/3-sulfanilamido-5-methylisoxazole, and during the formation of a ternary complex of lysozyme with azithromycin and sodium dodecyl sulfate [27,29,32,35]. A red shift of the enzyme fluorescence maximum was detected during the interaction of lysozyme with cephalosporins and with levofloxacin [23,24,34].
When interacting with ampicillin or colistin, the fluorescence intensity of lysozyme decreases with increasing antibiotic concentration (quenching) at a temperature of 298 K (Figure 2B and Figure 3B). The fluorescence quenching of biomacromolecules can be static, dynamic, or mixed. During static fluorescence quenching, a non-fluorescent complex is formed between the protein and the ligand. During dynamic quenching, the interaction between the protein and the ligand occurs due to collisions. Mixed fluorescence quenching is a combination of static and dynamic quenching. Both static, dynamic, and mixed fluorescence quenching are described by the standard Stern–Volmer equation [49]:
where RFU0 and RFU are the intensities of the maximum fluorescence emission of lysozyme without and with the addition of an antibiotic, KSV is the Stern–Volmer constant, [Q] is the concentration of the quencher (antibiotic), τ0 is the average lifetime of the fluorophore without a quencher (5.9 ns [54]), and Kq is the quenching rate constant of the biological macromolecule.
Quenching of lysozyme fluorescence by colistin at a temperature of 298 K is well described by the standard Stern–Volmer equation (Figure 4A). The calculated values of KSV and Kq are (40 ± 10) M−1 and (6.4 ± 1.7) × 109 M−1s−1. It is known that if Kq exceeds the limiting diffusion constant of the biomacromolecule (2 × 1010 M−1s−1), then the quenching is static [24,55]. It can be assumed that dynamic fluorescence quenching is observed during the interaction of lysozyme with colistin at 298 K.
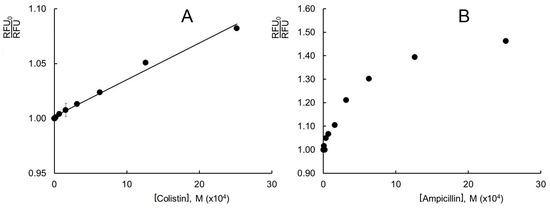
Figure 4.
Change in lysozyme fluorescence intensity under the influence of (A) colistin and (B) ampicillin in the plot of the standard Stern–Volmer equation. Experimental conditions: 298 K, enzyme concentration 0.25 g/L, PBS, λex 280 nm, and λem 345 nm.
Analysis of the temperature dependence of fluorescence quenching can be very informative. When lysozyme interacts with colistin at 313 K, the enzyme fluorescence is activated (Figure S5). It is possible that an increase in temperature affects the spatial structure of the colistin peptide. Possible changes in the structure of colistin under the influence of temperature lead to large differences in the fluorescence spectra at 298 K and 313 K.
Quenching of lysozyme fluorescence by ampicillin at 298 and 313 K is not well described by the linear Stern–Volmer equation (Figure 4B and Figure S6). The plot is linear at lower ampicillin concentrations and deviates towards the x-axis at higher ampicillin concentrations. The negative deviation from the linear Stern–Volmer plot indicates the presence of both static (formation of a ground–state complex) and dynamic (collision) quenching. As discussed in the literature [56], the presence of fluorophores with different accessibilities to a quencher is a common cause for the downward deviation from the linear Stern–Volmer equation.
Quenching of the enzyme fluorescence by ampicillin at 298 K and 313 K can be described by the modified Stern–Volmer equation (Lehrer equation) [57]:
where f is the fraction of the accessible fluorescent centers. To determine the fluorescence quenching parameters, is plotted against 1/[Q] (the reciprocal of the quencher concentration). The fraction of the accessible fluorescent centers is determined using the y-intercept; the Stern–Volmer constant is determined using the y-intercept/slope. The plots of versus 1/[Ampicillin] are linear at 298 K and 313 K (Figure 5 and Figure S7). Using these dependences, the Stern–Volmer constants (KSV), the biomolecular quenching rate constants Kq, and the fractions of the accessible fluorophores in the lysozyme molecule (f) are determined. The obtained results are shown in Table 1.
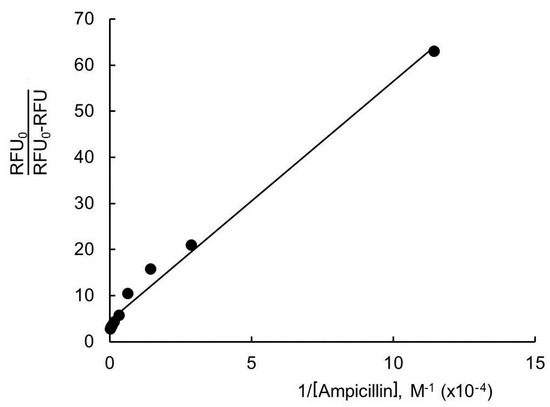
Figure 5.
Change in lysozyme fluorescence intensity under the influence of ampicillin in the plot of the modified Stern–Volmer equation. Experimental conditions: 298 K, enzyme concentration 0.25 g/L, PBS, λex 280 nm, and λem 345 nm.

Table 1.
Fluorescence quenching parameters for the interaction of lysozyme with ampicillin.
The value of f is nearly equal to 0.15–0.20 at the temperatures considered (Table 1). This means that ≤20% of the Trp residues are available for the quencher (ampicillin). This suggests a possible change in the conformation of the enzyme molecule. As stated above, the interaction of lysozyme with ampicillin causes an increase in the hydrophobicity of the microenvironment of Trp residues in the lysozyme molecule (Figure 2B). The Trp62/Trp108 residues [52] are likely to be buried (completely or partially) inside a protein globule or shielded from the solvent by parts of the enzyme molecule [56,58]. This leads to a decrease in the accessibility of the Trp residues for the quencher (ampicillin).
Table 1 shows that the Kq values decrease with increasing temperature and exceed the limiting diffusion constant of the macromolecule (2 × 1010 M−1s−1). This suggests a static quenching mechanism at 298 K and 313 K. The quencher (ampicillin) and the fluorophore (lysozyme) form a non-fluorescent complex. An increase in temperature weakens the binding of lysozyme with ampicillin (heating accelerates the decomposition of the lysozyme–ampicillin complex). The KSV values calculated from the linear fit of versus lower concentrations of [Ampicillin] are relatively small compare to the KSV values calculated from the Lehrer equation (Table 1). This observation suggests that quenching during the ground–state complex formation is very weak. The dynamic process plays a leading role in the quenching mechanism despite the existence of static quenching.
It has been previously shown that very few antibiotics cause dynamic or mixed types of lysozyme fluorescence quenching. In the case of a lysozyme interaction with ceftazidime or with cefoperazone, dynamic fluorescence quenching was observed with an increase in Kq, with an increase in temperature from 288 K to 328 K [22,23]. When lysozyme interacted with levofloxacin, Ksv increased with the temperature (from 298 to 310 K), and mixed quenching of the enzyme fluorescence was observed [34].
In conclusion, the mechanisms of lysozyme fluorescence quenching were investigated using the Stern–Volmer and Lehrer equations. Dynamic fluorescence quenching is observed upon interaction of lysozyme with colistin at a temperature of 298 K. When lysozyme interacted with ampicillin, a mixed quenching of the enzyme fluorescence was discovered at temperatures of 298 K and 313 K. This may mean that the enzyme molecule has specific binding sites with ampicillin. As discussed above, the specific binding may be due to hydrophobic interactions.
3.3. The Study of the Interaction of Lysozyme with Antibiotics by Circular Dichroism Spectroscopy
Circular dichroism (CD) is a simple, sensitive, and effective spectroscopic method for monitoring conformational changes in the protein structure upon binding to ligand molecules. To study the effect of antibiotics on the secondary structure of lysozyme, CD spectra were recorded for the enzyme in the absence and presence of antibiotics. The CD spectrum for lysozyme (in the far UV region) has two ellipticity minima at 208 nm and at 222 nm, which is typical for proteins with an α-helical structure (Figure 6). The minimum at 208 nm corresponds to the π-π* transitions of the α-helix, and the minimum at 222 nm is due to the n-π* transitions for α-helices [33,35].
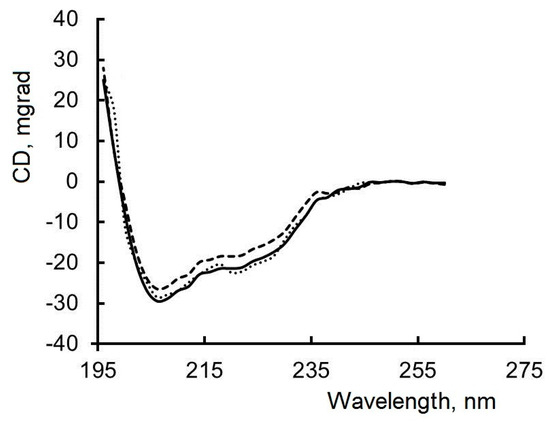
Figure 6.
CD spectra of lysozyme (black line); lysozyme in complex with colistin (black dots); lysozyme in complex with ampicillin (black dotted line). Experimental conditions: lysozyme concentration 0.25 g/L, PBS, and 298 K.
Quantitative analysis of the CD spectra obtained for lysozyme showed that the secondary structure of the enzyme molecule consists of 20% α-helices, 30% β-structures, and 50% disordered structures (Table 2). The secondary structure of the enzyme depends on many factors (production techniques, storage and transport conditions, accuracy of CD spectrometer settings, and spectrum processing software). The proportion of α-helices in the lysozyme molecule is approximately 25–45% as reported by different researchers [22,24,32,35]. However, the content of α-helices in the lysozyme molecule can be equal to 70.0% [28] or 17.8% [34]. Thus, our findings are consistent with the results of previous studies.

Table 2.
Effects of the antibiotics on the lysozyme secondary structure.
When antibiotics (ampicillin, colistin) are added, minor changes in the shape and intensity of the CD spectrum of lysozyme are observed (Figure 6). The proportion of α-helices decreases by 1% when lysozyme interacts with colistin, and by 2% when lysozyme interacts with ampicillin, while the content of disordered structures in the protein globule increases by the same amount. Changes in the content of α-helices in an α-helical protein are indicative of changes in its secondary structure [59,60]. In the secondary structure of proteins, the α-helix has high stability, and a small decrease in the percentage of α-helices means a partial unfolding of the protein.
The proportion of α-helices in the lysozyme molecule changed (usually decreased) when the enzyme interacted with antibiotics. For lysozyme that was bound with azithromycin, there was a decrease in the proportion of α-helices from 26% to 23% [35]. When lysozyme interacted with 2-sulfanilamido-4-methylpyrimidine or with 3-sulfanilamido-5-methylisoxazole, there was a decrease in the content of α-helices from 42% to 39% and from 42% to 40%, respectively [32]. Upon the addition of ceftazidime (lysozyme/antibiotic 1:1 mol/mol), the content of α-helices in the lysozyme molecule decreased from 36% to 34%, and with a further increase in the concentration of antibiotic (lysozyme/antibiotic 1:3 mol/mol), it fell to 30% [22]. Upon interaction of lysozyme with cephalosporins (cefoperazone, ceftizoxime, and ceftriaxone), changes occurred in the shape and intensity of the CD spectra for the enzyme. The proportion of α-helices decreased from 35% to 23—29%, and the proportions of disordered structures and β-sheets increased [24]. When lysozyme interacted with chloramphenicol, the content of α-helices in the enzyme molecule decreased from 39.4% to 32.5% (lysozyme/antibiotic 1:4 mol/mol) [36]. The proportion of α-helices in the lysozyme molecule decreased when the enzyme interacted with cefpirome or with tetracyclines [25,28,29].
Summing up the above, we can conclude that an antibiotic should be chosen so as to avoid the denaturation of the enzyme.
3.4. The Study of the Effect of Antibiotics on the Kinetic Parameters of Lysozyme
Previously, microbiological methods were used to assess the effect of antibiotics on the biological activity of lysozyme. There are a few studies in the literature aimed at investigating the effectiveness of combinations of lysozyme with ampicillin or colistin on bacterial cells. The choice of microorganisms is usually determined by the specificity of an antibiotic: colistin is effective against Gram-negative microorganisms, and ampicillin is highly effective against Gram-positive microorganisms.
Study [61] focused on the effect of a combined use of colistin and hen egg-white lysozyme against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The combined use of lysozyme and colistin resulted in a synergistic effect, which was expressed in a decrease in the survival rate of pathogen cells by approximately an order of magnitude compared to the action of the antibiotic or enzyme separately.
Two more studies examined the antibacterial effect of lysozyme with polymyxin B, an antibiotic of the polymyxin group. In 2019, Russian scientists studied combinations of hen egg-white lysozyme with various antibiotics, including polymyxin B [62]. The synergistic effect of lysozyme and polymyxin B was found on Gram-negative microorganisms, Escherichia coli (ML-35p) and Acinetobacter baumannii (a clinical isolate). The additive effect of lysozyme and polymyxin B was observed on Gram-positive bacteria, Micrococcus luteus (CIP A270) and MRSA (ATCC 33591). It was found that polymyxin B accelerated the lysis of Escherichia coli ATCC 9723e cells by lysozyme in the stationary phase and in the log phase (LB medium, 0.3 mg/mL MgSO4, 25 μg/mL lysozyme). It was suggested that polymyxin B disrupts the structure of the outer cell membrane due to electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions [63].
A combined use of ampicillin and lysozyme did not show any significant effect of the added ampicillin on the growth of an 8-h Listeria monocytogenes cell culture in the presence of hen egg-white lysozyme [64].
In our study, we decided to use a kinetic approach to assess the effect of antibiotics on the functioning of the active site of lysozyme. The addition of antibiotics does not significantly affect the values of the Michaelis constant and the maximum rate of the enzymatic reaction for lysozyme (Figure 7A,B). This means that, despite the presence of partial unfolding in the lysozyme molecule, there is no disruption of the structure of the active site of the enzyme when interacting with antibiotics.
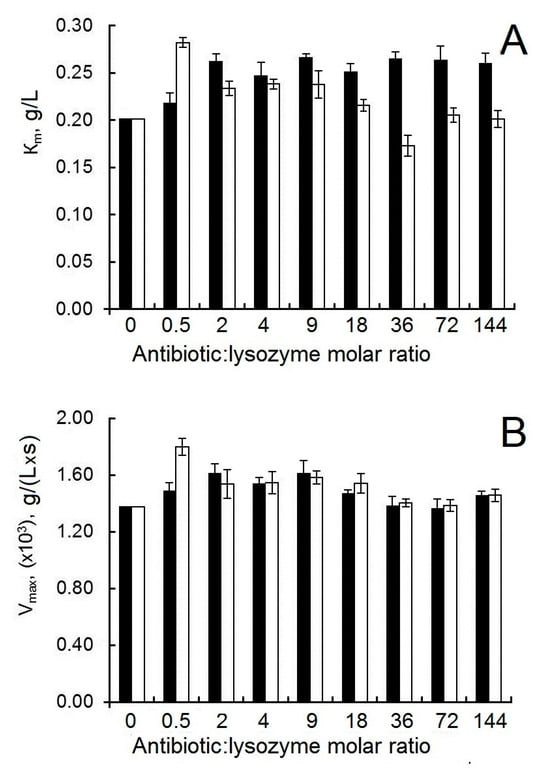
Figure 7.
(A) The effect of antibiotics on the Km of the interaction between lysozyme and Micrococcus luteus. (B) The effect of antibiotics on the Vmax of the interaction between lysozyme and Micrococcus luteus. Experimental conditions: 298 K, PBS, and enzyme concentration in the reaction medium 5 μg/mL. The black bars correspond to the combination of lysozyme and ampicillin; the white bars correspond to the combination of lysozyme and colistin.
3.5. Molecular Docking
An analysis of the structures of ampicillin and colistin suggests that a broad range of interactions is possible between lysozyme and these antibiotics. It is essential and urgent to investigate the interactions occurring between the antibiotic and the active site of the enzyme; this task can be implemented using molecular docking. Amino acid residues Trp62, Trp108 [65], Trp63, and Asp101 [66] participate in the formation of the binding region of the active site of lysozyme. The amino acid residues Asp52 and Glu35 are fundamentally important for the implementation of the catalytic function; the residues Ala107 and Trp63 can also be involved in chemical transformations of the substrate [65]. Molecular docking was carried out with Autodock 4.2 using a Lamarckian Genetic Algorithm [67,68].
Van der Waals forces, hydrogen bonds, Pi-Pi T-shaped interactions, and Pi-Alkyl interactions were revealed during the modeling of the interaction of lysozyme with ampicillin (Figure 8A,B). The negatively charged oxygen atom of the carboxyl group of ampicillin and the hydrogen atom of the amino group of the Arg112 side chain of the enzyme molecule form a hydrogen bond. The amino acid residues Val109, Asp52, and Gln57 of the lysozyme molecule form hydrogen bonds with the ampicillin molecule. The benzene ring of the ampicillin molecule interacts with the benzene ring of the side chain of Trp108 and the methyl groups of both Ala107 and I Ile98 of the lysozyme molecule. Van der Waals forces result from the interaction of the ampicillin molecule with Ala110, Trp63, Ile58, and Asn59 of the lysozyme molecule (Figure 8B). The interaction between ampicillin and Trp108 of the lysozyme molecule can explain the blue shift of lysozyme fluorescence maximum and the quenching of lysozyme fluorescence by the antibiotic. It is worth noting that Trp63 and Trp108 are part of the binding region of the active site of lysozyme, and Asp52 is part of the catalytic region of the active site of lysozyme. Based on the kinetic measurement data we obtained (Figure 7B), the interaction of ampicillin with the active site of lysozyme does not affect the ability of the enzyme to cleave the bacterial cell wall. The ampicillin molecule is located in a cleft on the surface of the lysozyme molecule (Figure 8A); the minimum calculated value of ΔG for the formation of such a complex is −7.8 kcal/mol (−32.5 kJ/mol).
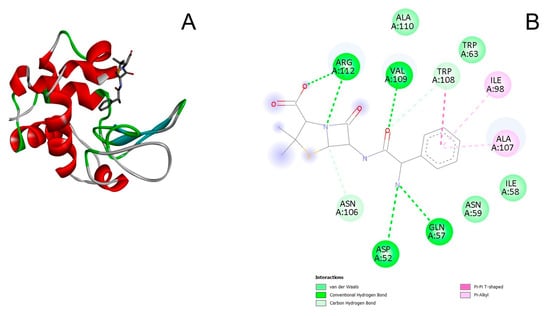
Figure 8.
(A) 3D docked structure of the optimized lysozyme–ampicillin complex. (B) 2D diagram of the interaction between lysozyme and ampicillin. The light green color corresponds to the van der Waals interactions; the green color corresponds to the conventional hydrogen bonding; the blue-green color corresponds to the carbon hydrogen bonding; the pink color corresponds to the Pi-Pi T-shaped interactions, the light pink color corresponds to the Pi-Alkyl interactions.
The interaction of lysozyme with colistin is ensured by van der Waals forces, hydrogen bonds, alkyl and Pi-alkyl interactions (Figure 9A,B). The amino acid residues Thr47, Trp63, Asp52, and Asn59 of the lysozyme molecule participate in the formation of hydrogen bonds with the colistin molecule; the residues Arg61, Asn103, Leu56, Glu35, Gln57, Val109, Ile58, Ala107, Asp48, and Asn46 of the lysozyme molecule take part in the formation of van der Waals interactions; and the residues Ile98, Trp108, Trp63, and Trp62 of the lysozyme molecule are important for both alkyl and Pi-alkyl interactions (Figure 9B). The interaction with colistin involves the Trp62 and Trp108 residues of the lysozyme molecule, which may be the reason for the small changes in the fluorescence spectra of lysozyme. The colistin molecule interacts with the Asp52 and Glu35 residues, which are important for catalysis, but the enzyme does not lose catalytic activity (apparently due to the weak interaction) (Figure 7B). Despite the large number of interactions, the colistin molecule has a small contact area with the surface of the enzyme molecule (Figure 9A). The above-described interactions between lysozyme and colistin molecules correspond to the minimum calculated value of ΔG, equal to −1.5 kcal/mol (−6.2 kJ/mol).
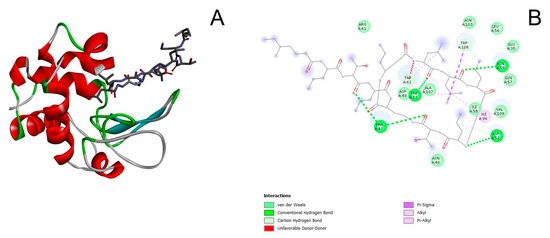
Figure 9.
(A) 3D docked structure of the optimized lysozyme–colistin complex. (B) 2D diagram of the interaction between lysozyme and colistin. The light green color corresponds to the van der Waals interactions; the green color corresponds to the conventional hydrogen bonding; the blue-green color corresponds to the carbon hydrogen bonding; the red color corresponds to the unfavorable donor-donor interactions; the pink color corresponds to the Pi-Sigma interactions, the light pink color corresponds to Alkyl and Pi-Alkyl interactions.
The free Gibbs energy of binding of the protein and the ligand is an important parameter in modeling the interaction of a protein and a ligand. ΔG is calculated based on the total energy of intermolecular forces, including van der Waals, electrostatic, hydrophobic, and other interactions. The above calculated values of the minimum ΔG values for protein–ligand interaction have negative values that are relevant for spontaneous interaction processes. The free Gibbs energy of binding of the enzyme and ampicillin obtained by docking calculations (−32.5 kJ/mol) is different from that obtained by fluorescent spectroscopy (Δ ~ −20 kJ/mol). The reason might be the discrepancies in methodologies, which are the exclusion of the solvent, pH, and ionic strength in docking calculations. To simplify the docking calculations, the enzyme molecule is considered as rigid, which is not true [67,68].
4. Conclusions
Combining antimicrobial agents with different mechanisms of action on bacterial cells is an important step in combating antibiotic resistance in pathogenic microorganisms. Spectroscopic methods (UV–vis spectroscopy, CD spectroscopy, and fluorescence measurements) showed the interaction between lysozyme and two antibiotics, colistin and ampicillin. The intermolecular interaction between lysozyme and ampicillin or colistin is found to be very weak at pH 7.4 and a temperature of 298 K. UV–vis and fluorescence spectroscopy data indicate that lysozyme forms a complex with ampicillin. The binding of lysozyme to ampicillin is accompanied by an increase in the hydrophobicity of the microenvironment of Trp residues in the lysozyme molecule. The intermolecular interaction between lysozyme and colistin is carried out by means of dynamic collisions. During an interaction with antibiotics, conformational changes occur in the lysozyme molecule that do not affect the functioning of the enzyme’s active site.
Using the molecular docking method, it was shown that the interactions between lysozyme and colistin are provided mainly by van der Waals forces, and the formation of a complex between lysozyme and ampicillin occurs mainly due to hydrogen bonding. The calculated negative values of ΔG indicate spontaneous interactions between lysozyme and antibiotics.
The data obtained are important in fundamental and applied research of biological molecules with antimicrobial action. In our opinion, it will be most appropriate to obtain covalent complexes of lysozyme with colistin/ampicillin.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/biophysica5040055/s1, Figure S1: 2D structure of ampicillin sodium salt; Figure S2: 2D structure of colistin sulfate; Figure S3: Uv-vis absorption spectra of the mixtures of lysozyme (lz) with ampicillin (amp) (top), uv-vis absorption spectra of ampicillin (amp) (bottom); Figure S4: Uv-vis absorption spectra of the mixtures of lysozyme (lz) with colistin (col) (top), uv-vis absorption spectra of colistin (col) (bottom); Figure S5: Fluorescence emission spectra of lysozyme (lz) in the absence and presence of colistin (col); Figure S6: Fluorescence quenching of lysozyme in the presence of ampicillin; Figure S7: Modified Stern-Volmer plot for the quenching of lysozyme in the presence of ampicillin.
Funding
This research was funded by the state registration task (project 123032300028-0).
Data Availability Statement
Data are already contained in the present article.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline (137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 10 mM Na2HPO4, 1.8 mM KH2PO4) |
| UV | ultraviolet |
| CD | circular dichroism |
| lz | hen egg white lysozyme |
| amp | ampicillin |
| col | colistin |
References
- Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Shao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Guo, G.; Wang, X. Analytical methods for obtaining binding parameters of drug–protein interactions: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1219, 340012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vuignier, K.; Schappler, J.; Veuthey, J.-L.; Carrupt, P.-A.; Martel, S. Drug–protein binding: A critical review of analytical tools. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hage, D.; Jackson, A.; Sobansky, M.; Schiel, J.E.; Yoo, M.J.; Joseph, K.S. Characterization of drug-protein interactions in blood using high-performance affinity chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2009, 32, 835–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, A. On a remarkable bacteriolytic element found in tissues and secretions. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 1922, 93, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, W.T.; Wells, J.E. Lysozyme as an alternative to growth promoting antibiotics in swine production. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 6, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Tan, L.; Hu, N.; Dong, Z.; Hu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, P.; Pan, M.; Lu, C. C-lysozyme contributes to antiviral immunity in Bombyx mori against nucleopolyhedrovirus infection. J. Insect Physiol. 2018, 108, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, C.C.; Koenig, D.F.; Mairv, G.A.; North, A.C.; Phillips, D.C.; Sarma, V.R. Structure of hen egg–white lysozyme: A three–dimensional Fourier synthesis at 2 Å resolution. Nature 1965, 206, 757–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, D.C. The hen egg white lysozyme molecule. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1967, 57, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamatari, Y.O.; Yamada, H.; Akasaka, K.; Jones, J.A.; Dobson, C.M.; Smith, L.J. Response of native and denatured hen lysozyme to high pressure studied by 15N/1H NMR spectroscopy. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 1782–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.J.; van den Berg, B.; Pitkeathly, M.; Smith, L.J.; Bolin, K.A.; Keiderling, T.A.; Redfield, C.; Dobson, C.M.; Radford, S.E. Native-like secondary structure in a peptide from the a-domain of hen lysozyme. Fold Des. 1996, 1, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Williams, M.A.; Thornton, J.M.; Goodfellow, J.M. Modelling protein unfolding: Hen egg-white lysozyme. Prot. Eng. 1997, 10, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, J.; van Smaalen, S. The active site of hen egg-white lysozyme: Flexibility and chemical bonding. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2014, 70, 1136–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, F.E.; Proctor, V.A.; Goetsch, S.J. Egg-white lysozyme as a food preservative—An overview. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 1991, 47, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragland, S.A.; Criss, A.K. From bacterial killing to immune modulation: Recent insights into the functions of lysozyme. PLoS Path. 2017, 13, e1006512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Małaczewska, J.; Kaczorek-Łukowska, E.; Wójcik, R.; Siwicki, A.K. Antiviral effects of nisin, lysozyme, lactoferrin and their mixtures against bovine viral diarrhoea virus. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Ku, S.-K.; Na, D.H.; Bae, J.-S. Anti-inflammatory effects of lysozyme against HMGB1 in human endothelial cells and in mice. Inflammation 2015, 38, 1911–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filatova, L.Y.; Emelianov, G.P.; Balabushevich, N.G.; Klyachko, N.L. Supramolecular assemblies of mucin and lysozyme: Formation and physicochemical characterization. Proc. Biochem. 2022, 113, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filatova, L.Y.; Balabushevich, N.G.; Klyachko, N.L. A physicochemical, structural, microbiological and kinetic study of hen egg white lysozyme in complexes with alginate and chitosan. Biocatal. Biotransform. 2022, 40, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceron, A.A.; Nascife, L.; Norte, S.; Costa, S.A.; Oliveira do Nascimento, J.H.; Morisso, F.D.P.; Baruque-Ramos, J.; Oliveira, R.C.; Costa, S.M. Synthesis of chitosan-lysozyme microspheres, physicochemical characterization, enzymatic and antimicrobial activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 185, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, J.M.; Malik, A.; Ahmed, M.Z. Bimolecular interaction of zwitterionic surfactant with hen egg white lysozyme (HEWL): A biophysical study. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 101674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.-B.; Chen, J.; Liang, Y. Oxidative refolding of reduced, denatured lysozyme in AOT reverse micelles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 322, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.S.; Waseem, M.; Subbarao, N.; Al-Lohedan, H.A. Dynamic interaction between lysozyme and ceftazidime: Experimental and molecular simulation approaches. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 328, 115412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tan, X.; Chen, D.; Yue, Q.; Song, Z. Study on the binding behavior of lysozyme with cephalosporin analogues by fluorescence spectroscopy. J. Fluoresc. 2009, 19, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lu, H.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Hao, C. Molecular insights into the interaction between lysozyme and cephalosporins: From multi-spectral experiments to computational simulations. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 392, 123517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Liu, B.; Li, G.; Zhang, Q. Investigation on the interaction of cefpirome sulfate with lysozyme by fluorescence quenching spectroscopy and synchronous fluorescence spectroscopy. Luminescence 2016, 31, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.S.; Waseem, M.; Subbarao, N.; Alahamed, A.N.; Al-Lohedan, H.A. Probing the interaction of cephalosporin antibiotic “cefoperazone” with lysozyme using spectroscopic and in silico methods: Effect of paracetamol on binding. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 252, 126568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Ting Wang, T. Study of the interactions between tetracycline analogues and lysozyme. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2004, 12, 2043–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Z.; Liu, R. New insights into the characterization of the binding of tetracycline analogues with lysozyme: A biophysical study. Chemosphere 2012, 86, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Sun, Y.; Liang, Y.; Hu, Q. Formation Mechanism and Antibacterial Activity of Natural Antimicrobial Lysozyme with Antibiotics Doxycycline and Tigecycline. J. Mol. Biol. 2025, 437, 169304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, M.; Sheshadri, B.S.; Venkatappa, M.P. Interaction of lysozyme with antibiotics–binding of penicillins to lysozyme. J. Biosci. 1983, 5, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rial, R.; González-Durruthy, M.; Liu, Z.; Ruso, J.M. Conformational binding mechanism of lysozyme induced by interactions with penicillin antibiotic drugs. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 358, 119081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Sun, L.; Wan, J.; Xu, X.; Wei, X.; Hua, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Yang, X. New insights into the binding mechanism of lysozyme by 2-sulfanilamido-4-methylpyrimidine and 3-sulfanilamido-5-methylisoxazole: Density function theory, multispectral techniques and molecular docking. J. Lumin. 2023, 255, 119559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, A.; Kashif, M. Interaction studies of levofloxacin with human lysozyme in a ternary complex using multispectroscopic and computational analysis: A circular dichroism method for the quantitation of levofloxacin. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 370, 121023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Guo, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. The study on interactions between levofloxacin and model proteins by using multi-spectroscopic and molecular docking methods. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2018, 36, 2032–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, S.; Ali, M.S.; Al-Lohedan, H.A.; Hoti, N.; Tabassum, S. Molecular interaction of lysozyme with therapeutic drug azithromycin: Effect of sodium dodecyl sulfate on binding profile. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 242, 124844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Zhao, G.; Huang, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, L. Fluorescence spectroscopic investigation of the interaction between chloramphenicol and lysozyme. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 4083–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashkiv, E. Ampicillin. In Analytical Profiles of Drug Substances; Florey, K., Ed.; Academic Press, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1973; Volume 2, pp. 1–61. [Google Scholar]
- Bereda, G. Clinical pharmacology of ampicillin. J. Pharm. Res. Rep. 2022, 3, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarannuma, N.; Khatoon, S.; Dzantiev, B.B. Perspective and application of molecular imprinting approach for antibiotic detection in food and environmental samples: A critical review. Food Control 2020, 118, 107381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tótoli, E.G.; Salgado, H.R.N. Development and validation of the quantitative analysis of ampicillin sodium in powder for injection by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR). Phys. Chem. 2012, 2, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialvaei, A.Z.; Samadi, K.H. Colistin, mechanisms and prevalence of resistance. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2015, 31, 707–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, S.; Brunel, J.-M.; Dubus, J.-C.; Reynaud-Gaubert, M.; Rolain, J.-M. Colistin: An update on the antibiotic of the 21st century. Expert Rev. Anti. Infect. Ther. 2012, 10, 917–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimble, M.J.; Mlynarcik, P.; Kolar, M.; Hancock, R.E.W. Polymyxin: Alternative mechanisms of action and resistance. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, a025288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finking, R.; Marahiel, M.A. Biosynthesis of nonribosomal peptides. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 58, 453–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabnis, A.; Lh Hagart, K.; Klöckner, A.; Becce, M.; Evans, L.E.; Furniss, R.C.D.; Ai Mavridou, D.; Murphy, R.; Stevens, M.M.; Davies, J.C.; et al. Colistin kills bacteria by targeting lipopolysaccharide in the cytoplasmic membrane. eLife 2021, 10, e65836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breazeale, S.D.; Ribeiro, A.A.; McClerren, A.L.; Raetz, C.R.H. A formyltransferase required for polymyxin resistance in Escherichia coli and the modification of lipid A with 4-Amino-4-deoxy-L-arabinose. Identification and function of UDP-4-deoxy-4-formamido-L-arabinose. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 14154–14167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, C.; Plésiat, P.; Jeannot, K. A two-component regulatory system interconnects resistance to polymyxins, aminoglycosides, fluoroquinolones and beta-lactams in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornish–Bowden, A. Fundamentals of Enzyme Kinetics; Portland Press: London, UK, 1995; pp. 1–75. [Google Scholar]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 1–381. [Google Scholar]
- Bohm, G.; Muhr, R.; Jaenicke, R. Quantitative analysis of protein far UV circular dichroism spectra by neural networks. Protein Eng. 1992, 5, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.M.; Malik, A.; Ahmed, A.; Rehman, M.T.; AlAjmi, M.F.; Khan, R.H.; Fatima, S.; Alamery, S.F.; Abdullah, E.M. Effect of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) on the conformation of a hen egg white lysozyme: A spectroscopic and molecular docking study. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 219, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imoto, T.; Forster, L.S.; Rupley, J.A.; Tanaka, F. Fluorescence of lysozyme: Emissions from tryptophan residues 62 and 108 and energy migration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1971, 69, 1151–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, B.; Muttathukattil, A.N.; Reddy, G.; Singh, P.C. Contrasting effects of guanidinium chloride and urea on the activity and unfolding of lysozyme. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 14119–14126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftink, M.R. Fluorescence quenching reactions. In Biophysical and Biochemical Aspects of Fluorescence Spectroscopy; Dewey, T.G., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1991; pp. 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.; Wu, X.; Pan, J.; Hu, X.; Gong, D.; Zhang, G. New insights into the inhibition mechanism of betulinic acid on α-glucosidase. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 7065–7075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szkudlarek, A.; Wilk, M.; Maciazek-Jurczyk, M. In Vitro Investigations of Acetohexamide Binding to Glycated Serum Albumin in the Presence of Fatty Acid. Molecules 2020, 25, 2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geethanjali, H.S.; Nagaraja, D.; Melavanki, R.M.; Kusanur, R.A. Fluorescence quenching of boronic acid derivatives by aniline in alcohols—A Negative deviation from Stern–Volmer equation. J. Lumin. 2015, 67, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matyus, L.; Szollosi, J.; Jenei, A. Steady-state fluorescence quenching applications for studying protein structure and dynamics. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2006, 83, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Chowdhury, J. Binding interaction of juglone with lysozyme: Spectroscopic studies aided by in silico calculations. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2019, 193, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, D.; Kumar, N.; Singh, A.; Tomar, V.; Dass, S.K.; Chandra, R. Deciphering the binding mechanism of noscapine with lysozyme: Biophysical and chemoinformatic approaches. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 16233–16241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrens, G.; Pérez-Gallego, M.; Moya, B.; Munar-Bestard, M.; Zamorano, L.; Cabot, G.; Blázquez, J.; Ayala, J.A.; Oliver, A.; Juan, C. Targeting the permeability barrier and peptidoglycan recycling pathways to disarm Pseudomonas aeruginosa against the innate immune system. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zharkova, M.S.; Orlov, D.S.; Golubeva, O.Y.u.; Chakchir, O.B.; Eliseev, I.E.; Grinchuk, T.M.; Shamova, O.V. Application of antimicrobial peptides of the innate immune system in combination with conventional antibiotics—A novel way to combat antibiotic resistance? Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, C.R.; Ward, O.P. The use of EDTA or polymyxin with lysozyme for the recovery of intracellular products from Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Tech. 1992, 6, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asensi, V.; Fierer, J. Synergistic effect of human lysozyme plus ampicillin or β-lysin on the killing of Listeria monocytogenes. J. Infect. Dis. 1991, 163, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gálvez-Iriqui, A.C.; Plascencia-Jatomea, M.; Bautista-Baños, S. Lysozymes: Characteristics, mechanism of action and technological applications on the control of pathogenic microorganisms. Mex. J. Phytopathol. 2020, 38, 360–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Mitra, R.K. Nonpolar hydrophobic amino acids tune the enzymatic activity of lysozyme. Biophys. Chem. 2022, 288, 106842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, G.M.; Huey, R.; Lindstrom, W.; Sanner, M.F.; Belew, R.K.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. Autodock4 and AutoDockTools4: Automated docking with selective receptor flexibility. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 30, 2785–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosconati, S.; Forli, S.; Perryman, A.L.; Harris, R.; Goodsell, D.S.; Olson, A.J. Virtual screening with AutoDock: Theory and practice. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2010, 5, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).