A Novel Purification Process of Sardine Lipases Using Protein Ultrafiltration and Dye Ligand Affinity Chromatography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Crude Extract of Viscera (CEV)
2.3. Lipase Activity Assay
2.4. Preparation of Semi-Purified Lipases (SPLSV)
2.5. Preparation of Purified Lipases from Sardine Viscera (PLSV)
2.6. Purity and Molecular Weight Determination
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Crude Extract Activity
3.2. Semi-Purified Lipases (SPLSV)
3.3. Purified Lipases from Sardine Viscera (PLSV)
3.4. Purity and Molecular Weight of PLSV
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Melani, N.B.; Tambourgi, E.B.; Silveira, E. Lipases: From Production to Applications. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2019, 49, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Kanwar, S.S. Organic Solvent Tolerant Lipases and Applications. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 625258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Fernandez, J.; Benaiges, M.; Valero, F. Rhizopus Oryzae Lipase, a Promising Industrial Enzyme: Biochemical Characteristics, Production and Biocatalytic Applications. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, P.; Enespa Singh, R.; Arora, P.K. Microbial Lipases and their Industrial Applications: A Comprehensive Review. Microb. Cell Factories 2020, 19, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira-Dias, S.; Sandoval, G.; Plou, F.; Valero, F. The Potential Use of Lipases in the Production of Fatty Acid Derivatives for the Food and Nutraceutical Industries. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 16, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karia, M.; Kaspal, M.; Alhattab, M.; Puri, M. Marine-Derived Lipases for Enhancing Enrichment of Very-Long-Chain Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids with Reference to Omega-3 Fatty Acids. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navvabi, A.; Razzaghi, M.; Fernandes, P.; Karami, L.; Homaei, A. Novel Lipases Discovery Specifically from Marine Organisms for Industrial Production and Practical Applications. Proc. Biochem. 2018, 70, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noriega-Rodríguez, J.A.; Baeza-Jimenez, R.; García, H.S. Digestive Enzymes from Marine Sources. In Marine Proteins and Peptides: Biological Activities and Applications; Kim, S.-K., Ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; Chapter 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khiari, Z. Enzymes from Fishery and Aquaculture Waste: Research Trends in the Era of Artificial Intelligence and Circular Bio-Economy. Mar. Drugs 2024, 22, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, C.; Xia, G.; Shen, X. Novel Lipase from Golden Pompano (Trachinotus ovatus) Viscera: Purification, Characterization, and Application in the Concentrating of n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids. J. Ocean Univ. China 2023, 22, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.K.; Nasser, J.M.; Shaker, K.A. Extraction, Purification and Characterization of Lipase from the Digestive Duct of Common Carp Cyprinus Carpio L. Iraqi J. Agric. Sci. 2022, 53, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar]
- Zied, Z.; Ali, M.B.; Fendri, A.; Louati, H.; Mejdoub, H.; Gargouri, Y. Purification and biochemical properties of Hexaplex trunculus digestive lipase. Proc. Biochem. 2012, 47, 2434–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtovic, I.; Marshall, S.N.; Zhao, X.; Simpson, B.K. Purification and Properties of Digestive Lipases from Chinook Salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) and New Zealand Hoki (Macruronus novaezelandiae). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 36, 1041–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, D.E.; Kula, C.; Demirci, H. Biochemical characterization of lipase from Cryptococcus albidus (D24) and its application in sugar fatty acid ester synthesis. Arch. Microbiol. 2025, 207, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basso, A.; Serban, S. Industrial Applications of Immobilized Enzymes—A Review. Mol. Catal. 2019, 479, 110607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.C.; Virgen-Ortíz, J.J.; Dos Santos, J.C.S.; Berenguer-Murcia, A.; Alcantara, A.R.; Barbosa, O.; Ortiz, C.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Immobilization of Lipases on Hydrophobic Supports: Immobilization Mechanism, Advantages, Problems, and Solutions. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 746–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjørnelund, H.D.; Brask, J.; Woodley, J.M.; Günther, H.; Peters, J. Active Site Studies to Explain Kinetics of Lipases in Organic Solvents Using Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Phys. Chem. B 2025, 129, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, S.; Ross, P.D. Dye-Ligand Affinity Chromatography: The Interaction of Cibacron Blue F3GA® with Proteins and Enzyme. Crit. Rev. Biochem. 1984, 16, 169–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrou, N.E. Dye-ligand affinity adsorbents for enzyme purification. Mol. Biotechnol. 2002, 20, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chronopoulou, E.G.; Premetis, G.; Varotsou, C.; Georgakis, N.; Ioannou, E.; Labrou, N.E. Synthesis and Evaluation of Dye-Ligand Affinity Adsorbents for Protein Purification. In Protein Downstream Processing; Methods in Molecular, Biology; Labrou, N.E., Ed.; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2021; Volume 2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang-Schenkelberg, J.; Fieg, G.; Waluga, T. Molecular Insight into Affinity Interaction between Cibacron Blue and Proteins. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 9691–9697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łacki, K.M.; Riske, F.J. Affinity Chromatography: An Enabling Technology for Large-Scale Bioprocessing. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 15, 1800397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Punekar, N.S. High-Throughput Screening of Dye-Ligands for Chromatography. In Protein Downstream Processing; Methods in Molecular Biology, 2178; Labrou, N.E., Ed.; Humana: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noriega-Rodríguez, J.A.; Gamez-Meza, N.; Alanis-Villa, A.; Medina-Juarez, L.A. Tejeda-Mansir, A.; Amgulo-Guerrero, O.; García, H.S. Extraction and Fractionation of Lipolytic Enzyme from Viscera of Monterey Sardine (Sardinops sagax caerulea). Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2009, 44, 1223–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa-Leyva, C.; Carrillo-Pérez, E.; Baeza-Jiménez, R.; Noriega Rodríguez, J.A. Effect of Temperature on the Kinetics of Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Sardine Oil by Different Lipases. Int. J. Biol. Nat. Sci. 2024, 4, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolasco-Soria, H.; Alvarez-González, C.A.; Tovar-Ramírez, D.; González-Bacerio, J.; del Monte-Martínez, A.; Vega-Villasante, F. Optimization of Classical Lipase Activity Assays for Fish Digestive Tract Samples. Fishes 2024, 9, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qinwei, S.; Jackowski, G. One-Dimensional Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis. In Gel Electrophoresis of Proteins: A Practical Approach; Hames, B.D., Ed.; Oxford Academic: Oxford, UK, 2023; pp. 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kielkopf, C.L.; Bauer, W.; Urbatsch, I.L. Bradford Assay for Determining Protein Concentration. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2020, 4, 102269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aryee, A.N.; Simpson, B.K.; Villalonga, R. Lipase Fraction from Viscera of Grey Mullet (Mugil cephalus) Isolation, Partial Purification and some Biochemical Characteristics. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2007, 40, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjellesvik, D.R.; Lombardo, D.; Walther, B.T. Pancreatic bile salt dependent lipase from cod (Gadus morhua): Purification and properties. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1992, 1124, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, N.; Tanaka, S.; Ota, Y. Purification and characterization of bile salt-activated lipase from the hepatopancreas of red sea bream, Pragus major. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 1998, 18, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halldorsson, A.; Kristinsson, B.; Haraldsson, G.G. Lipase selectivity toward fatty acids commonly found in fish oil. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Tech. 2004, 106, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
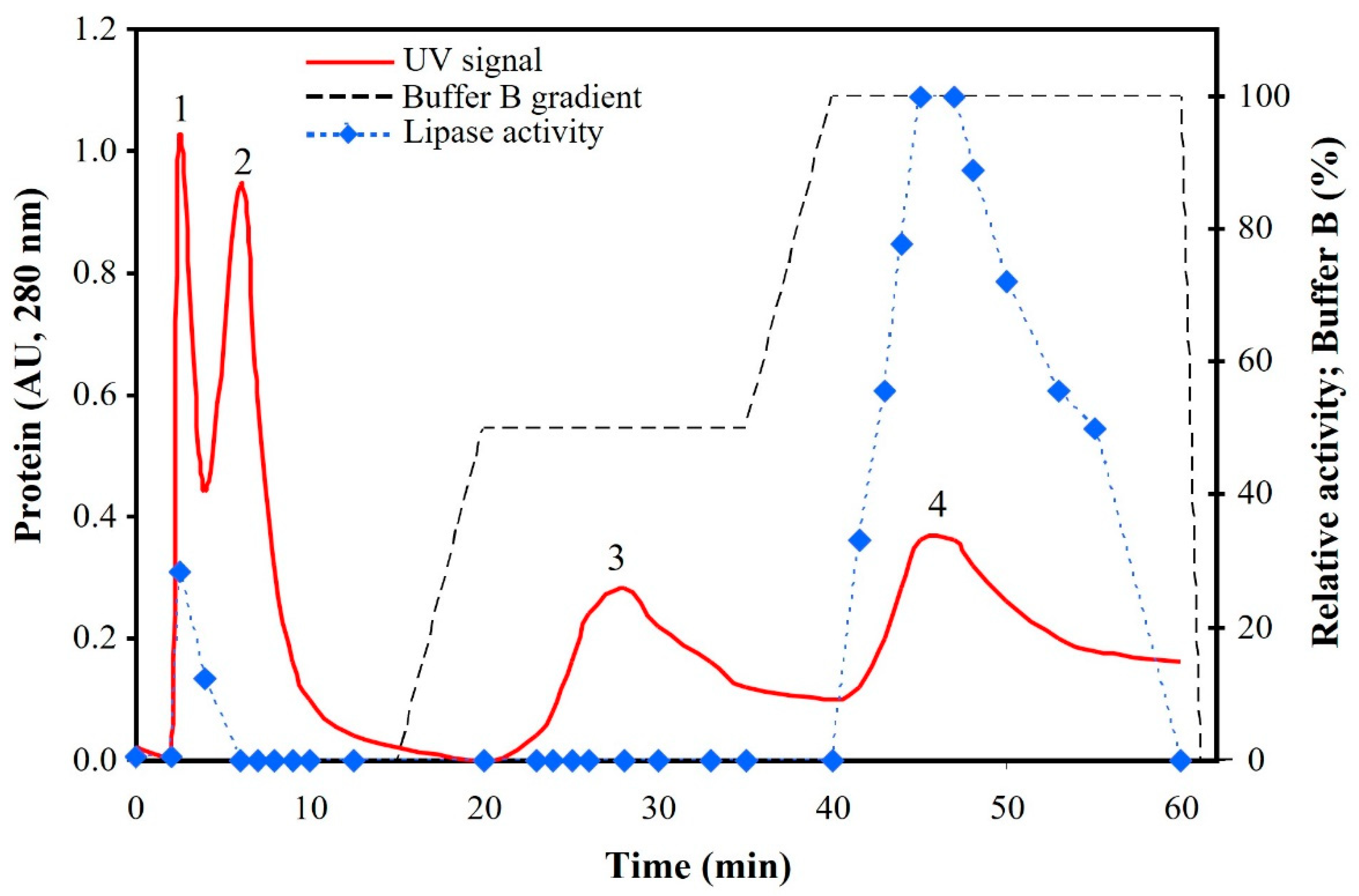
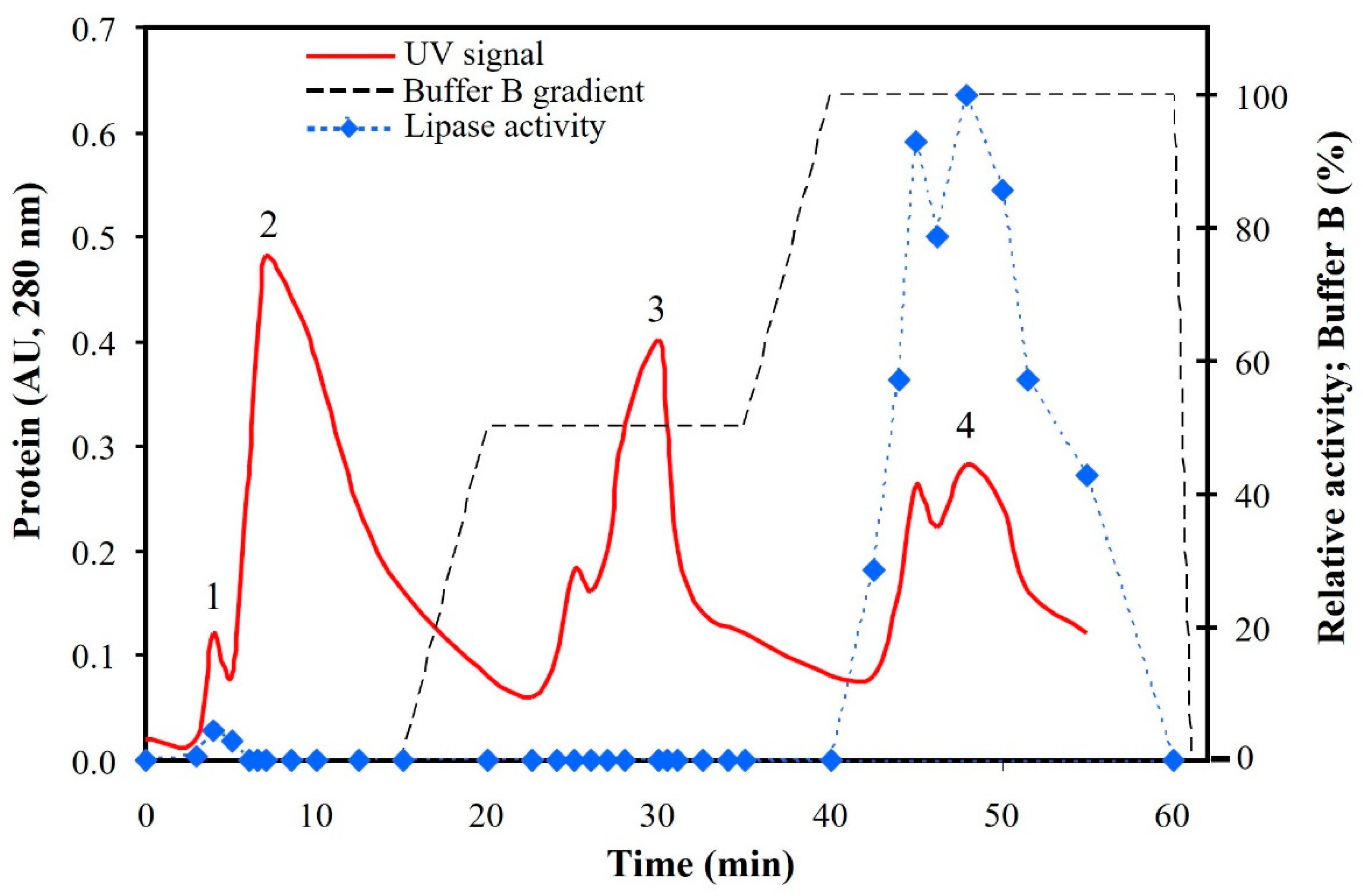
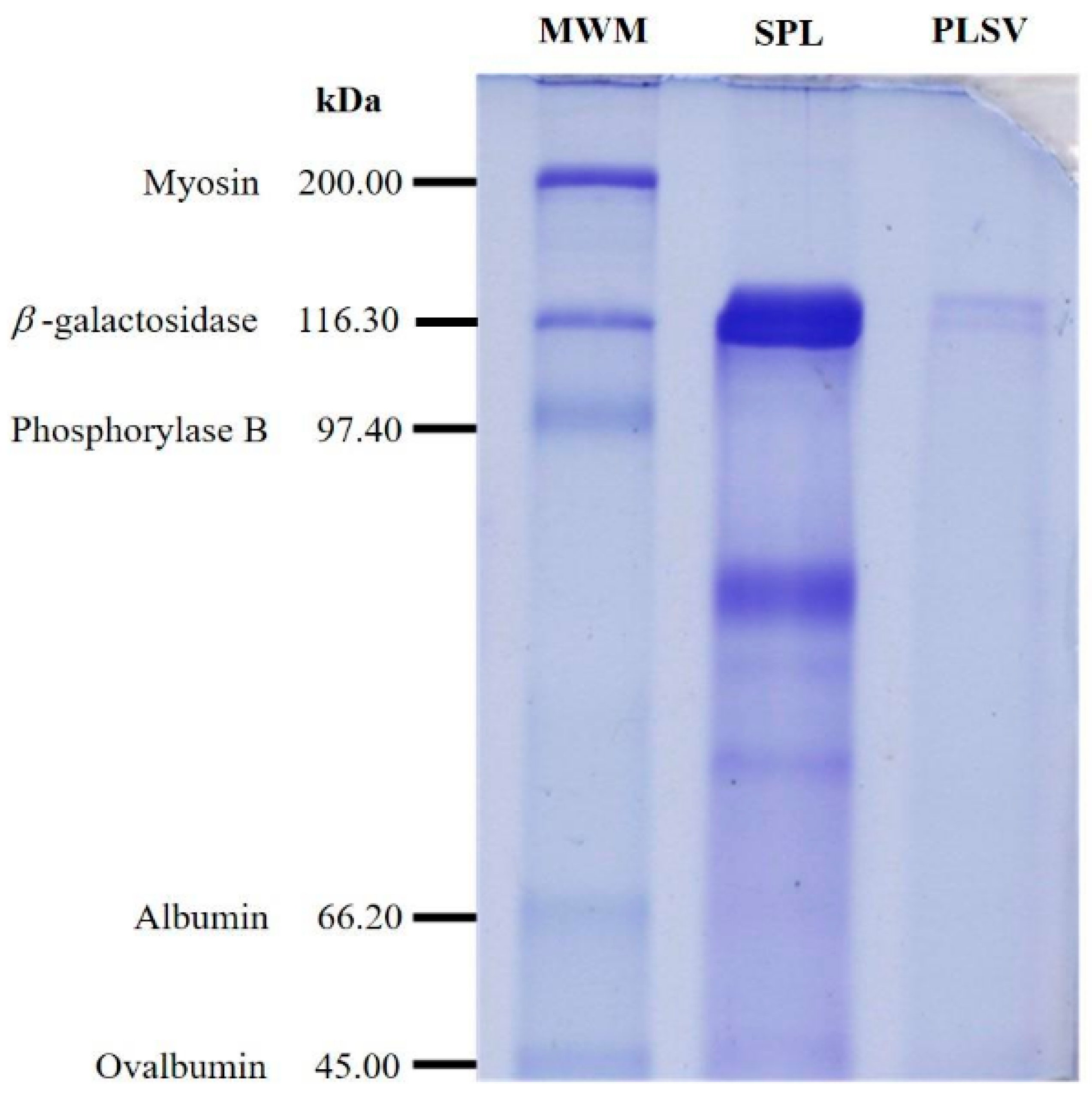
| Weight (mg) | Protein (mg mL−1) | Activity (U mL−1) | Specific Activity (U mg−1) | Purification (Fold) | Recovery Yield (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CEV | 28.9 | 18.0 | 59.94 | 3.33 | 1.0 | 100 |
| PF30-50 | 3.28 | 0.64 | 16.80 | 32.95 | 7.9 | 89.5 |
| SPLSV (UF30) | 0.16 | 0.17 | 26.62 | 156.58 | 47.0 | 26.7 |
| PLSV | 0.05 | 0.02 | 5.32 | 266.40 | 80.0 | 13.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Noriega-Rodríguez, J.A.; Tejeda-Mansir, A.; García, H.S. A Novel Purification Process of Sardine Lipases Using Protein Ultrafiltration and Dye Ligand Affinity Chromatography. Biophysica 2025, 5, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/biophysica5030035
Noriega-Rodríguez JA, Tejeda-Mansir A, García HS. A Novel Purification Process of Sardine Lipases Using Protein Ultrafiltration and Dye Ligand Affinity Chromatography. Biophysica. 2025; 5(3):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/biophysica5030035
Chicago/Turabian StyleNoriega-Rodríguez, Juan Antonio, Armando Tejeda-Mansir, and Hugo Sergio García. 2025. "A Novel Purification Process of Sardine Lipases Using Protein Ultrafiltration and Dye Ligand Affinity Chromatography" Biophysica 5, no. 3: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/biophysica5030035
APA StyleNoriega-Rodríguez, J. A., Tejeda-Mansir, A., & García, H. S. (2025). A Novel Purification Process of Sardine Lipases Using Protein Ultrafiltration and Dye Ligand Affinity Chromatography. Biophysica, 5(3), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/biophysica5030035


_Kim.png)



