Old Enzyme, New Role: The β-Glucosidase BglC of Streptomyces scabiei Interferes with the Plant Defense Mechanism by Hydrolyzing Scopolin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Heterologous Production of His6-Tagged Proteins and Purification
2.2. TLC for Hydrolysis of Carbohydrates
2.3. Determination of Kinetic Parameters for His6-BglC
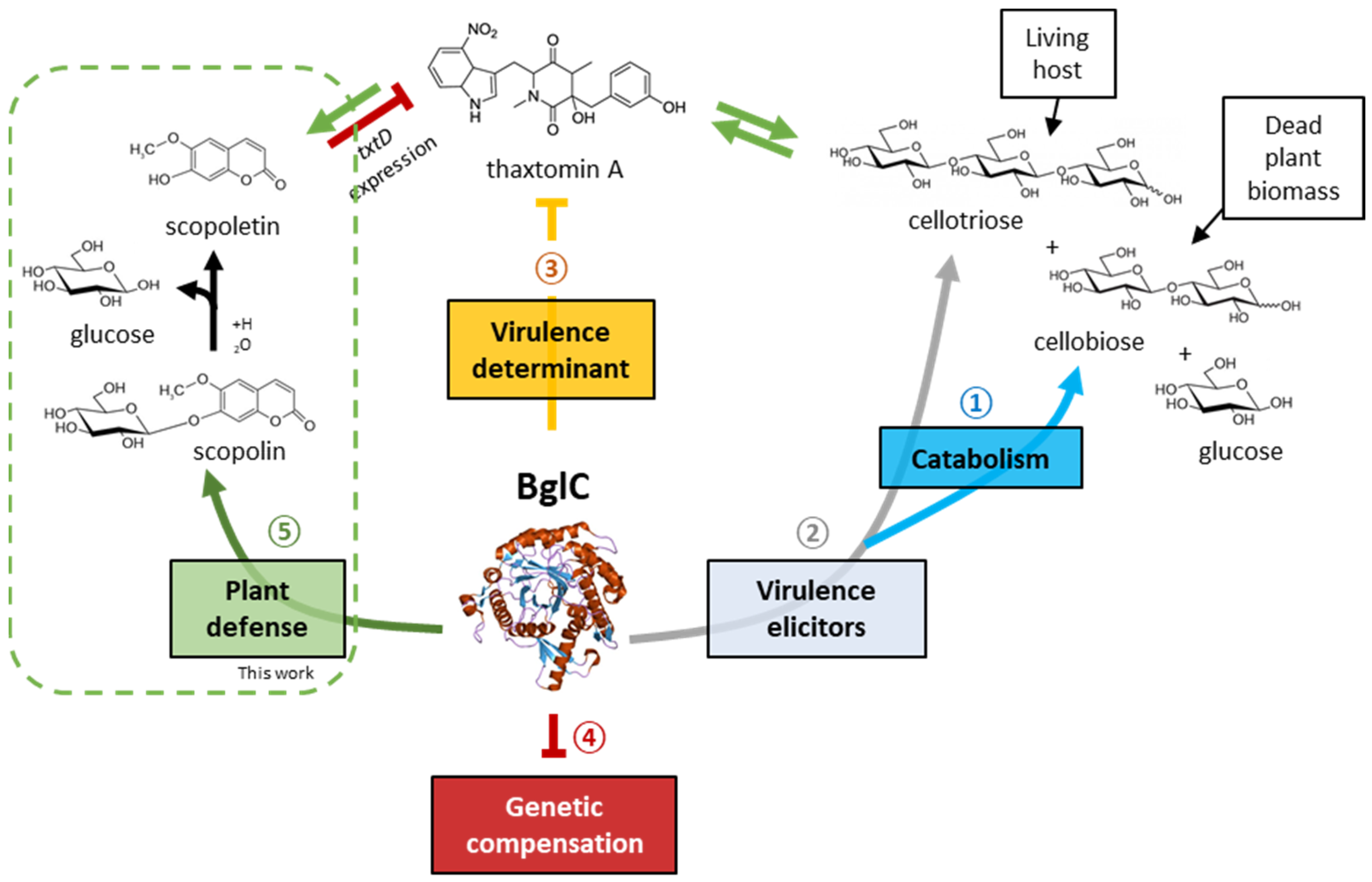
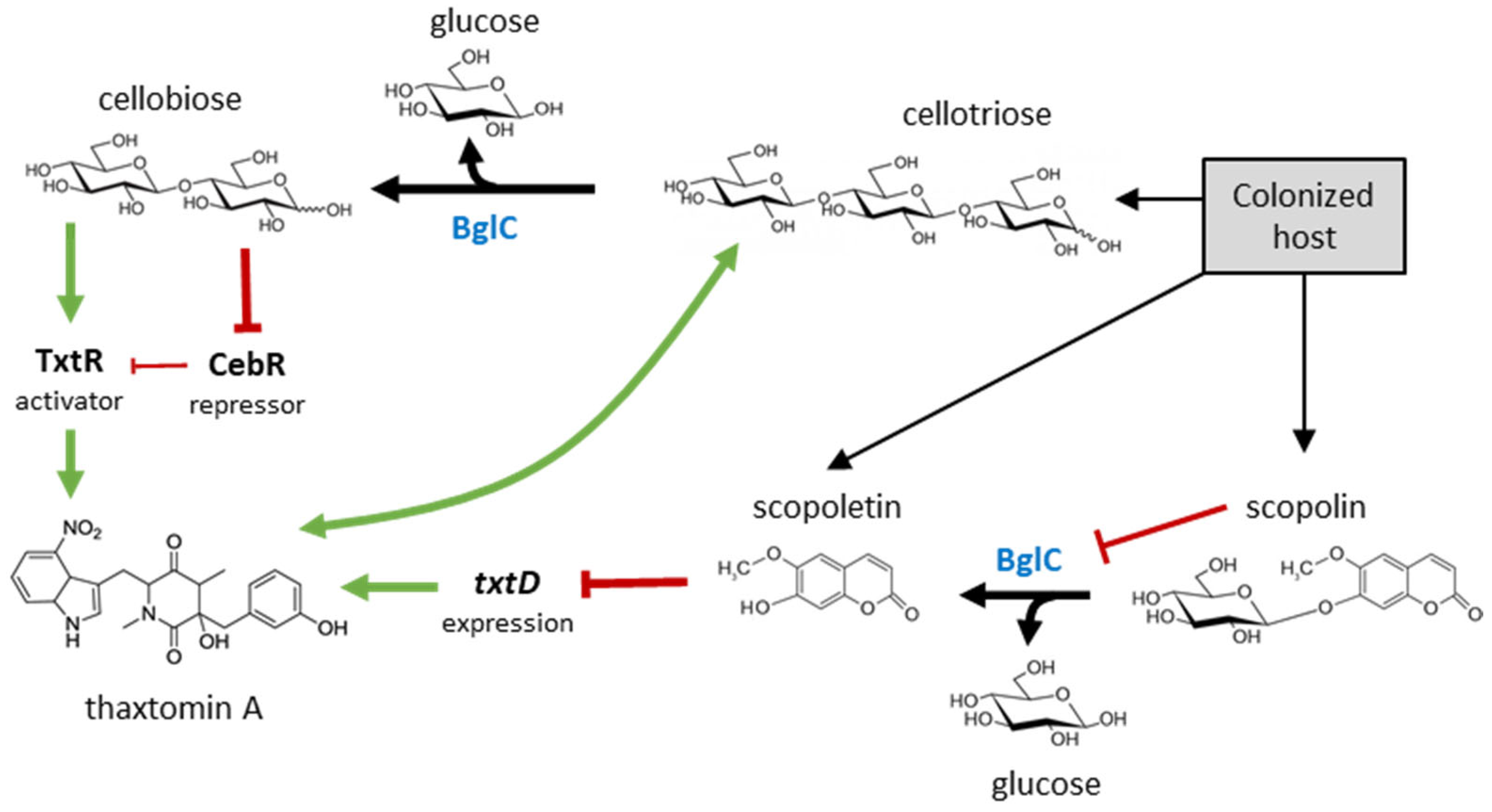
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Loria, R.; Bignell, D.R.D.; Moll, S.; Huguet-Tapia, J.C.; Joshi, M.V.; Johnson, E.G.; Seipke, R.F.; Gibson, D.M. Thaxtomin biosynthesis: The path to plant pathogenicity in the genus Streptomyces. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2008, 94, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Nothias, L.-F.; Dorrestein, P.C.; Tahlan, K.; Bignell, D.R.D. Genomic and metabolomic analysis of the potato common scab pathogen Streptomyces Scabiei. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 11474–11487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Díaz-Cruz, G.; Cheng, Z.; Bignell, D.R.D. Virulence mechanisms of plant-pathogenic Streptomyces species: An updated review. Microbiology 2019, 165, 1025–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bignell, D.R.D.; Huguet-Tapia, J.C.; Joshi, M.V.; Pettis, G.S.; Loria, R. What does it take to be a plant pathogen: Genomic insights from Streptomyces species. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2010, 98, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deflandre, B.; Stulanovic, N.; Planckaert, S.; Anderssen, S.; Bonometti, B.; Karim, L.; Coppieters, W.; Devreese, B.; Rigali, S. The virulome of Streptomyces Scabiei in response to cello-oligosaccharide elicitors. bioarXiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planckaert, S.; Deflandre, B.; de Vries, A.-M.; Ameye, M.; Martins, J.C.; Audenaert, K.; Rigali, S.; Devreese, B. Identification of novel rotihibin analogues in Streptomyces scabies, including discovery of its biosynthetic gene cluster. Microbiol Spectr. 2021, 9, e0057121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planckaert, S.; Jourdan, S.; Francis, I.M.; Deflandre, B.; Rigali, S.; Devreese, B. Proteomic response to thaxtomin phytotoxin elicitor cellobiose and to deletion of cellulose utilization regulator CebR in Streptomyces scabies. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 3837–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jourdan, S.; Francis, I.M.; Kim, M.J.; Salazar, J.J.C.; Planckaert, S.; Frère, J.-M.; Matagne, A.; Kerff, F.; Devreese, B.; Loria, R.; et al. The CebE/MsiK transporter is a doorway to the cello-oligosaccharide-mediated induction of Streptomyces scabies pathogenicity. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.G.; Joshi, M.V.; Gibson, D.M.; Loria, R. Cello-oligosaccharides released from host plants induce pathogenicity in scab-causing Streptomyces species. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2007, 71, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourdan, S.; Francis, I.M.; Deflandre, B.; Loria, R.; Rigali, S. Tracking the subtle mutations driving host sensing by the plant pathogen Streptomyces scabies. mSphere 2017, 2, e00367-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Francis, I.M.; Jourdan, S.; Fanara, S.; Loria, R.; Rigali, S. The cellobiose sensor CebR is the gatekeeper of Streptomyces scabies pathogenicity. mBio 2015, 6, e02018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Joshi, M.V.; Bignell, D.R.D.; Johnson, E.G.; Sparks, J.P.; Gibson, D.M.; Loria, R. The AraC/XylS regulator TxtR modulates thaxtomin biosynthesis and virulence in Streptomyces scabies. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 66, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourdan, S.; Francis, I.M.; Deflandre, B.; Tenconi, E.; Riley, J.; Planckaert, S.; Tocquin, P.; Martinet, L.; Devreese, B.; Loria, R.; et al. Contribution of the β-glucosidase BglC to the onset of the pathogenic lifestyle of Streptomyces scabies. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018, 19, 1480–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deflandre, B.; Thiébaut, N.; Planckaert, S.; Jourdan, S.; Anderssen, S.; Hanikenne, M.; Devreese, B.; Francis, I.; Rigali, S. Deletion of BglC triggers a genetic compensation response by awakening the expression of alternative beta-glucosidase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2020, 1863, 194615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerat, S.; Babana, A.H.; El Oirdi, M.; El Hadrami, A.; Daayf, F.; Beaudoin, N.; Bouarab, K.; Beaulieu, C. Streptomyces scabiei and its toxin thaxtomin a induce scopoletin biosynthesis in tobacco and arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Rep. 2009, 28, 1895–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wakarchuk, W. Characterization of five β-glycoside hydrolases from cellulomonas fimi ATCC 484. J. Bacteriol. 2014, 196, 4103–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kanehisa, M. A Database for post-genome analysis. Trends Genet. 1997, 13, 375–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, D.D. The accumulation of scopolin in potato tissue in response to infection. Physiol. Plant Pathol. 1973, 3, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolte, P.; Secor, G.A.; Gudmestad, N.C.; Henningson, P.J. Detection and identification of fluorescent compounds in potato tuber tissue with corky patch syndrome. Am. Potato J. 1993, 70, 649–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.O.; Shimizu, B.; Sakata, K.; Gantulga, D.; Zhou, Z.; Bevan, D.R.; Esen, A. Scopolin-hydrolyzing β-glucosidases in roots of arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2010, 51, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourdan, S.; Rigali, S. Use of a Sugar Tolerant Beta-Glucosidase. U.S. Patent US20190330607A1, 31 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Titgemeyer, F.; Bertram, R.; Schlicht, M.; van Wezel, G.P.; Rigali, S. Zuckertransport und C-regulation in antibiotika-produzierenden streptomyceten. BIOspektrum 2005, 3, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Deflandre, B. New Insights into the Enzymatic Properties and Metabolic Profile of the Phytopathogen Streptomyces scabiei. Ph.D. Thesis, Liège University, Liège, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Deflandre, B.; Rigali, S. Old Enzyme, New Role: The β-Glucosidase BglC of Streptomyces scabiei Interferes with the Plant Defense Mechanism by Hydrolyzing Scopolin. Biophysica 2022, 2, 1-7. https://doi.org/10.3390/biophysica2010001
Deflandre B, Rigali S. Old Enzyme, New Role: The β-Glucosidase BglC of Streptomyces scabiei Interferes with the Plant Defense Mechanism by Hydrolyzing Scopolin. Biophysica. 2022; 2(1):1-7. https://doi.org/10.3390/biophysica2010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleDeflandre, Benoit, and Sébastien Rigali. 2022. "Old Enzyme, New Role: The β-Glucosidase BglC of Streptomyces scabiei Interferes with the Plant Defense Mechanism by Hydrolyzing Scopolin" Biophysica 2, no. 1: 1-7. https://doi.org/10.3390/biophysica2010001
APA StyleDeflandre, B., & Rigali, S. (2022). Old Enzyme, New Role: The β-Glucosidase BglC of Streptomyces scabiei Interferes with the Plant Defense Mechanism by Hydrolyzing Scopolin. Biophysica, 2(1), 1-7. https://doi.org/10.3390/biophysica2010001





