Benzo[a]pyrene (B[a]P) Degradation Enhanced by Soils Mixing Effects: Validation Study of Stirring Test and Discrete Element Method (DEM)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Soils
2.2. Experimental Equipment
2.3. Experimental Design
2.3.1. Stirring Test
2.3.2. The Oxidative Degradation Test of B[a]p
2.3.3. Sample Analysis
2.4. Calculation Method of Mixing Quality
2.5. DEM Simulation
2.5.1. Device Model Construction
2.5.2. Particle Model Construction
3. Results and Discussion
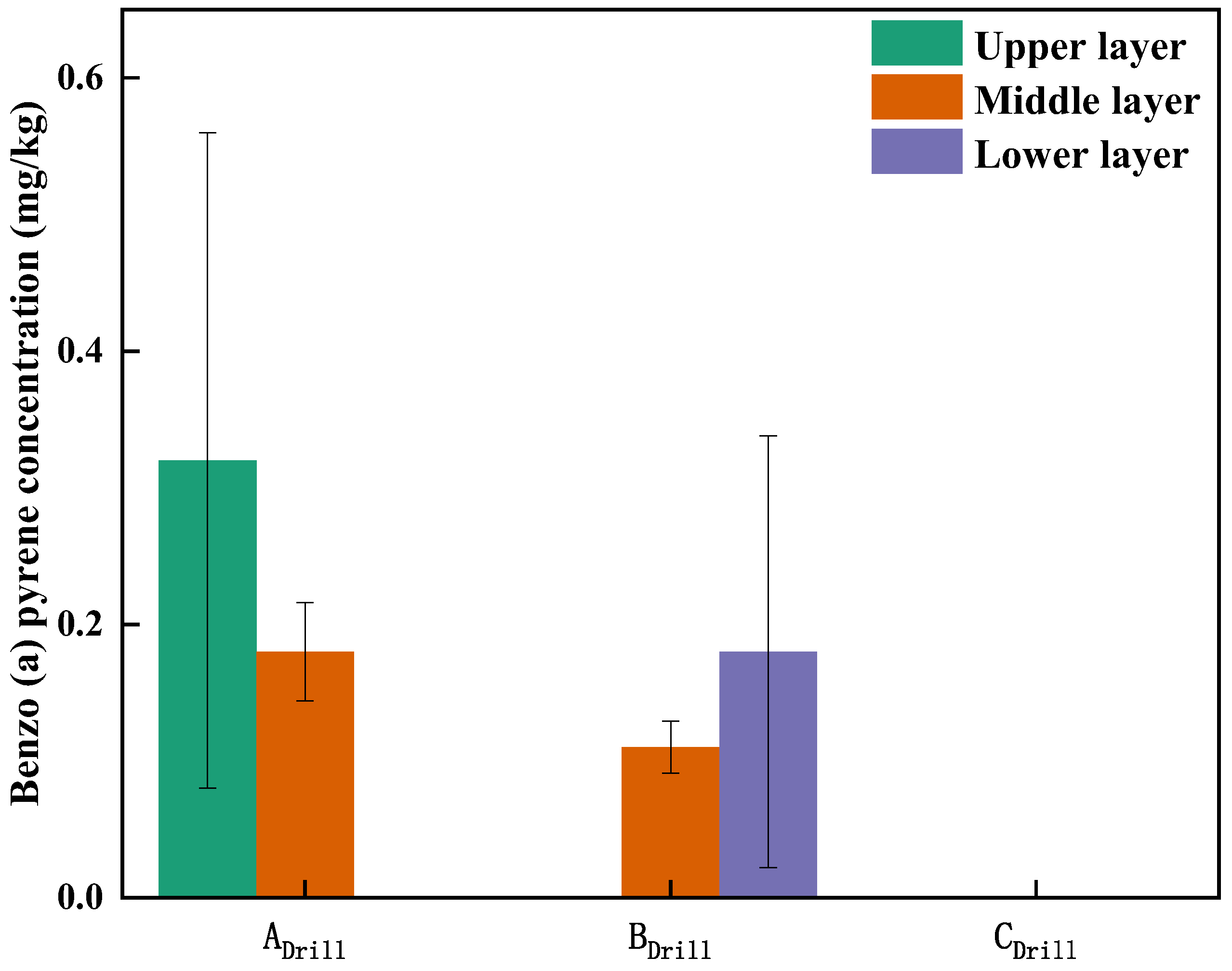
3.1. Stirring Test Results
3.2. DEM Simulation Results
3.2.1. Accuracy of DEM Simulation Results
3.2.2. Effect of Drilling/Raising Rates on Mixing Effects
3.2.3. Effect of Blade Angles on Mixing Effects
3.2.4. Effect of Multi-Stage Drill Bits on Mixing Effects
3.3. The Degradation Effects and Mechanism of B[a]p
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.L.; Han, Z.M.; Zhang, C.H.; Wang, M.Q.; Li, H.X.; Gao, D.W. Effects of soil colloids on adsorption and migration of benzo(a)pyrene on contaminated sites under runoff infiltration processes. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 353, 124150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, P.F.; Lin, Z.P.; Zhao, X.Q.; Waigi, M.G.; Vasilyeva, G.K.; Gao, Y.Z. Enhanced transformation capability towards benzo(a)pyrene by Fe (III)-modified manganese oxides. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 431, 128637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.R.; Wang, L.T.; Liang, H.; Chen, G.Y.; Wu, J.; Xia, W.J.; Gao, D.W. Removal of benzo[a]pyrene from the soil by adsorption coupled with degradation on saponin-modified bentonite immobilized crude enzymes. Environ. Res. 2024, 261, 119716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Huang, M.; Tong, X.; Chen, L.; Sun, P.; Yang, Y. Important role of cosolvent addition and soil permeability on electrokinetic-persulfate remediation of benzo(a)pyrene. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 33, 103480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.T.; Li, Y.; Du, X.R.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, H.X.; Liang, H.; Gao, D.W. Performance enhancement of white rot fungi extracellular enzymes via new hydrogel microenvironments for remediation of benzo[a]pyrene contaminated soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 454, 131505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vipotnik, Z.; Michelin, M.; Tavares, T. Biodegradation of chrysene and benzo[a]pyrene and removal of metals from naturally contaminated soil by isolated Trametes versicolor strain and laccase produced thereof. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 28, 102737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.S.; Lim, S.H.; Jung, S.R.; Lingamdinne, L.P.; Koduru, J.R.; Kwak, M.Y.; Yang, J.K.; Kang, S.H.; Chang, Y.Y. Experimentally and spectroscopically evidenced mechanistic study of butyl peroxyacid oxidative degradation of benzo[a]pyrene in soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 317, 115403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazarji, M.; Minkina, T.; Sushkova, S.; Mandzhieva, S.; Fedorenko, A.; Bauer, T.; Soldatov, A.; Barakhov, A.; Dudnikova, T. Biochar-assisted Fenton-like oxidation of benzo[a]pyrene-contaminated soil. Environ. Geochem. Health 2022, 44, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.C.; Peng, Y.P.; Chen, K.F.; Chen, T.Y.; Tang, C.T. The effect of different in situ chemical oxidation (ISCO) technologies on the survival of indigenous microbes and the remediation of petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soil. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 163, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.Y.; Li, S.H.; Yue, Y.; Tian, Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Qin, Z.R.; Ji, L.J.; Han, D.L.; Jiao, W.T. Enhancing remediation of PAH-contaminated soil through coupling electrical resistance heating using Na2S2O8. Environ. Res. 2021, 198, 110457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.Y.; Gao, Q.F.; Yang, S.Q.; Zheng, F.; Du, B.X.; Wen, S.L.; Wang, D.Y. Degradation of pyrene in contaminated water and soil by Fe2+-activated persulfate oxidation: Performance, kinetics, and background electrolytes (Cl−, HCO3− and humic acid) effects. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 146, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.J.; Tian, Y.; Yan, C.; Li, D.; Liu, T.T.; Liu, G.H.; Chen, D.H.; Feng, Y.J. Potassium peroxoborate: A sustained-released reactive oxygen carrier with enhanced PAHs contaminated soil remediation performance. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 470, 134259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazarji, M.; Minkina, T.; Sushkova, S.; Mandzhieva, S.; Bidhendi, G.N.; Barakhov, A.; Bhatnagar, A. Effect of nanomaterials on remediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons-contaminated soils: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 284, 112023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Singh, R.K. An overview on remediation technologies for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in contaminated lands: A critical approach. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2025, 27, 2753–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Xia, H.H. A review of the discrete element method/modelling in agricultural engineering. J. Agric. Eng. 2023, 54, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Sakai, M. Recent progress on the discrete element method simulations for powder transport systems: A review. Adv. Powder Technol. 2022, 33, 103664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alian, M.; Ein-Mozaffari, F.; Upreti, S.R. Analysis of the mixing of solid particles in a plowshare mixer via discrete element method (DEM). Powder Technol. 2015, 274, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.Y.; Li, T.C.; Wang, D.F.; Cai, Z.Q.; Gao, Z.M. Discrete element method study of effects of the impeller configuration and operating conditions on particle mixing in a cylindrical mixer. Particuology 2020, 49, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, X.L.; Li, S.B.; Wang, L.; Wang, D.C.; You, Y. Study on silage mixing device of King Grass stalk particles based on DEM simulation and bench test. Powder Technol. 2024, 437, 119581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.S.; Gao, C.Q.; Nie, Y.J.; Yang, B.; Ge, R.Y.; Xu, Z.H. Numerical simulation of Fertilizer Shunt-Plate with uniformity based on EDEM software. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 178, 105737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Wu, B.; Lai, X.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Cui, X.Y. Abiotic and biotic dissipation in natural attenuation of phenanthrene and benzo[a]pyrene: A systematic quantification study in contrasting soils. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 368, 125705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdeldayem, M.A.A.; Tekeste, M.Z. Multiresponse optimization of DEM Elasto-plastic model for soil-to-bulldozer blade interaction. Powder Technol. 2025, 460, 121056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.X.; Li, J.J.; Sun, Q.; He, F.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, W.H.; Sheng, D.C. Minimum mesh quality for reliable morphology characterization of 3D soil particles. Powder Technol. 2025, 460, 121062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.P.; Zhu, T.; Wang, Y.Z.; Ma, F.; Zhao, C.Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.P. Optimisation of parameters of a dual-axis soil remediation device based on response surface methodology and machine learning algorithm. Particuology 2025, 96, 26–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Song, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, Z.X.; Zhang, M.; Chen, X.; Tang, Z.W.; Liu, X. Thermally enhanced biodegradation of benzo[a]pyrene and benzene co-contaminated soil: Bioavailability and generation of ROS. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 455, 131494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.Q.; Luo, T.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.X.; Ma, Y.S.; Wang, B. Effects of combined remediation of pre-ozonation and bioaugmentation on degradation of benzo[a]pyrene and microbial community structure in soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 55557–55568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.Y.; Zhai, H.Y.; Huang, Y.H.; Yuan, T.F.; Li, J.; Li, M.; Wang, R.Y.; Yu, H.B.; Ji, M. Enhanced bioremediation of benzo [a]pyrene-polluted soil using high-efficiency soil microbial fuel cells with artificial solute transport. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 363 Pt 2, 132031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Y.W.; Li, X.T.; Feng, S.X.; Zhao, H.X. Key role of persistent free radicals in soil for persulfate activation: Impacts on benzo[a]pyrene degradation. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2025, 27, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.H.; Xue, J.Q.; Sun, M.Z.; Li, K.G.; Wang, J.Y.; Zhang, G.S.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Superefficient non-radical degradation of benzo[a]pyrene in soil by Fe-biochar composites activating persulfate. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 481, 148585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Grid Number | Mixing Quality (%) | |||||
| Test 1 | Test 2 | Test 3 | Simulation 1 | Simulation 1 | Simulation 1 | |
| 25 | 91.47 | 87.65 | 88.63 | 94.15 | 94.92 | 93.73 |
| 100 | 83.91 | 80.42 | 81.05 | 88.75 | 89.15 | 86.10 |
| 225 | 77.44 | 75.96 | 76.55 | 83.03 | 84.12 | 82.29 |
| 400 | 70.77 | 71.04 | 71.34 | 77.28 | 79.31 | 76.75 |
| 625 | 63.91 | 65.38 | 65.69 | 72.37 | 72.33 | 71.00 |
| 900 | 58.97 | 60.84 | 61.28 | 67.00 | 68.37 | 66.79 |
| 1225 | 53.63 | 56.14 | 56.11 | 62.29 | 62.80 | 60.68 |
| 1600 | 50.31 | 53.77 | 53.98 | 53.25 | 57.40 | 55.82 |
| 2025 | 47.11 | 50.16 | 50.43 | 49.54 | 51.25 | 50.60 |
| 2500 | 43.30 | 47.09 | 47.94 | 46.20 | 44.86 | 46.21 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, X.; Xu, R.; Wu, Z.; Fu, R. Benzo[a]pyrene (B[a]P) Degradation Enhanced by Soils Mixing Effects: Validation Study of Stirring Test and Discrete Element Method (DEM). Eng 2025, 6, 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6060132
Guo X, Xu R, Wu Z, Fu R. Benzo[a]pyrene (B[a]P) Degradation Enhanced by Soils Mixing Effects: Validation Study of Stirring Test and Discrete Element Method (DEM). Eng. 2025; 6(6):132. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6060132
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Xiaopin, Rong Xu, Zhigen Wu, and Rongbing Fu. 2025. "Benzo[a]pyrene (B[a]P) Degradation Enhanced by Soils Mixing Effects: Validation Study of Stirring Test and Discrete Element Method (DEM)" Eng 6, no. 6: 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6060132
APA StyleGuo, X., Xu, R., Wu, Z., & Fu, R. (2025). Benzo[a]pyrene (B[a]P) Degradation Enhanced by Soils Mixing Effects: Validation Study of Stirring Test and Discrete Element Method (DEM). Eng, 6(6), 132. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6060132






