Hierarchy of Electrorheological Responses in Aqueous Smectite Clay Dispersions in Relation to DLVO Potential Barriers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Particle Size and Zeta Potential Measurements
2.3. Transmittance Measurements and Macroscopic Observations
2.4. Rheological Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
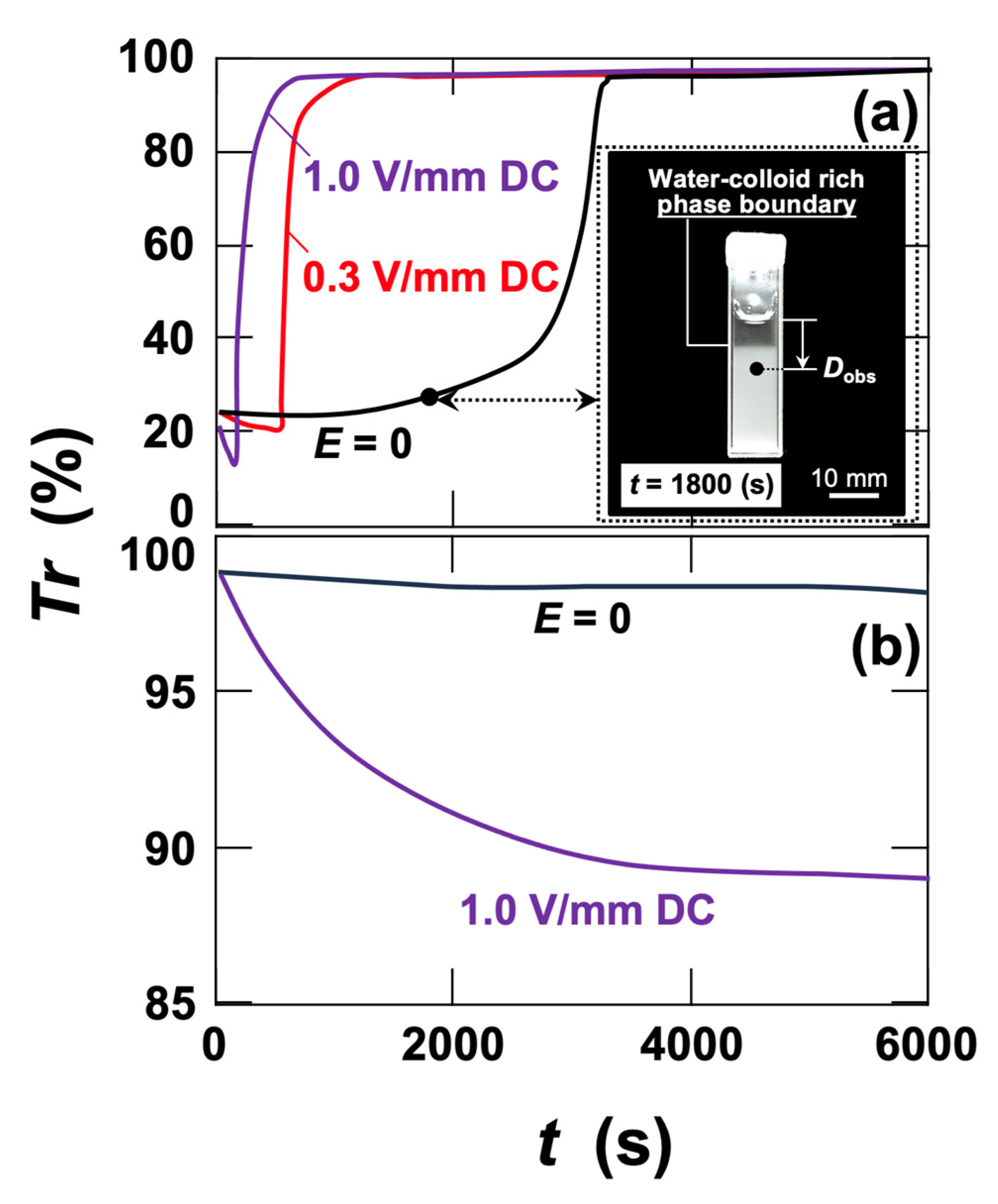
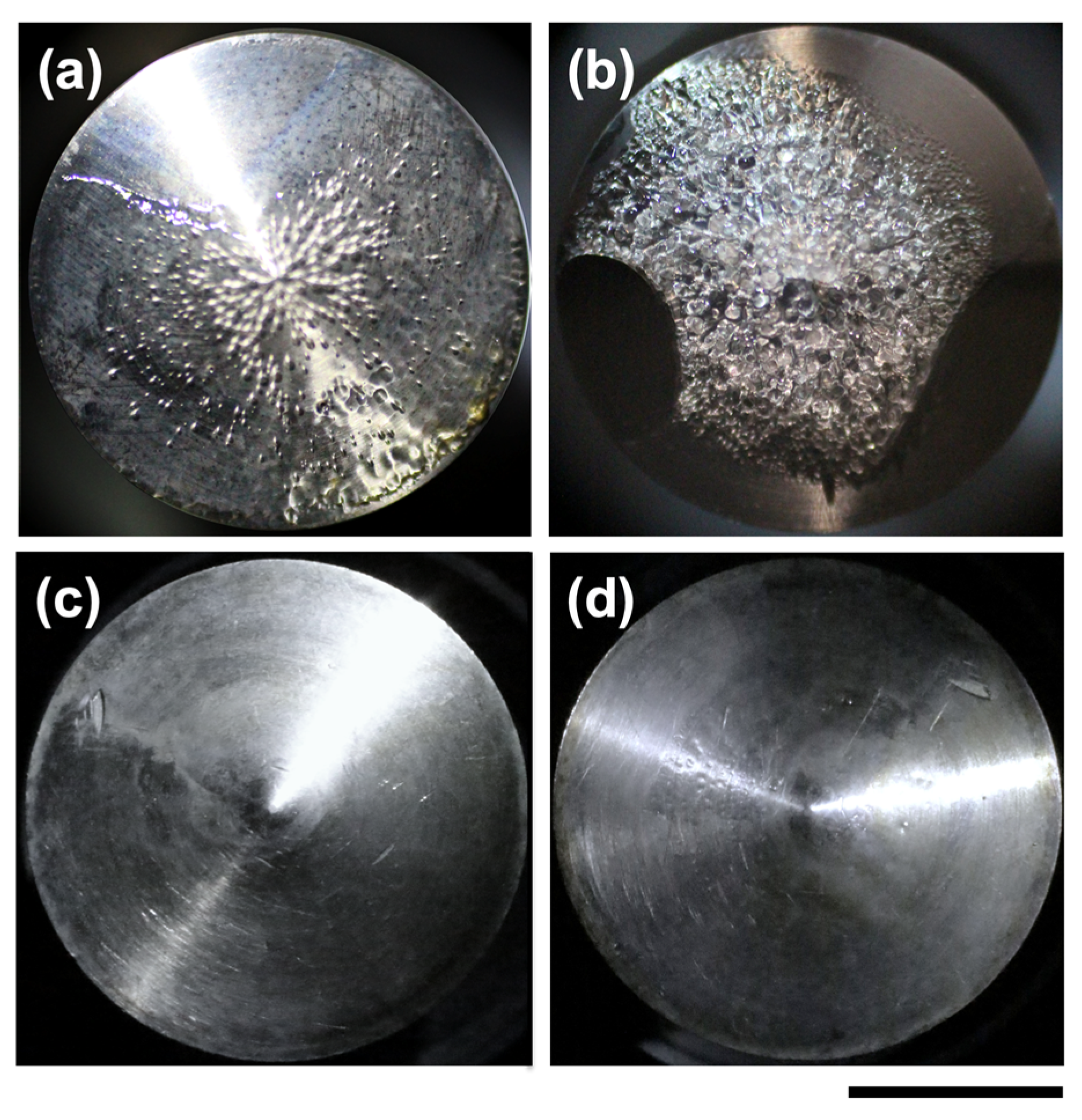
3.1. Transmittance Measurements and Macroscopic Observations
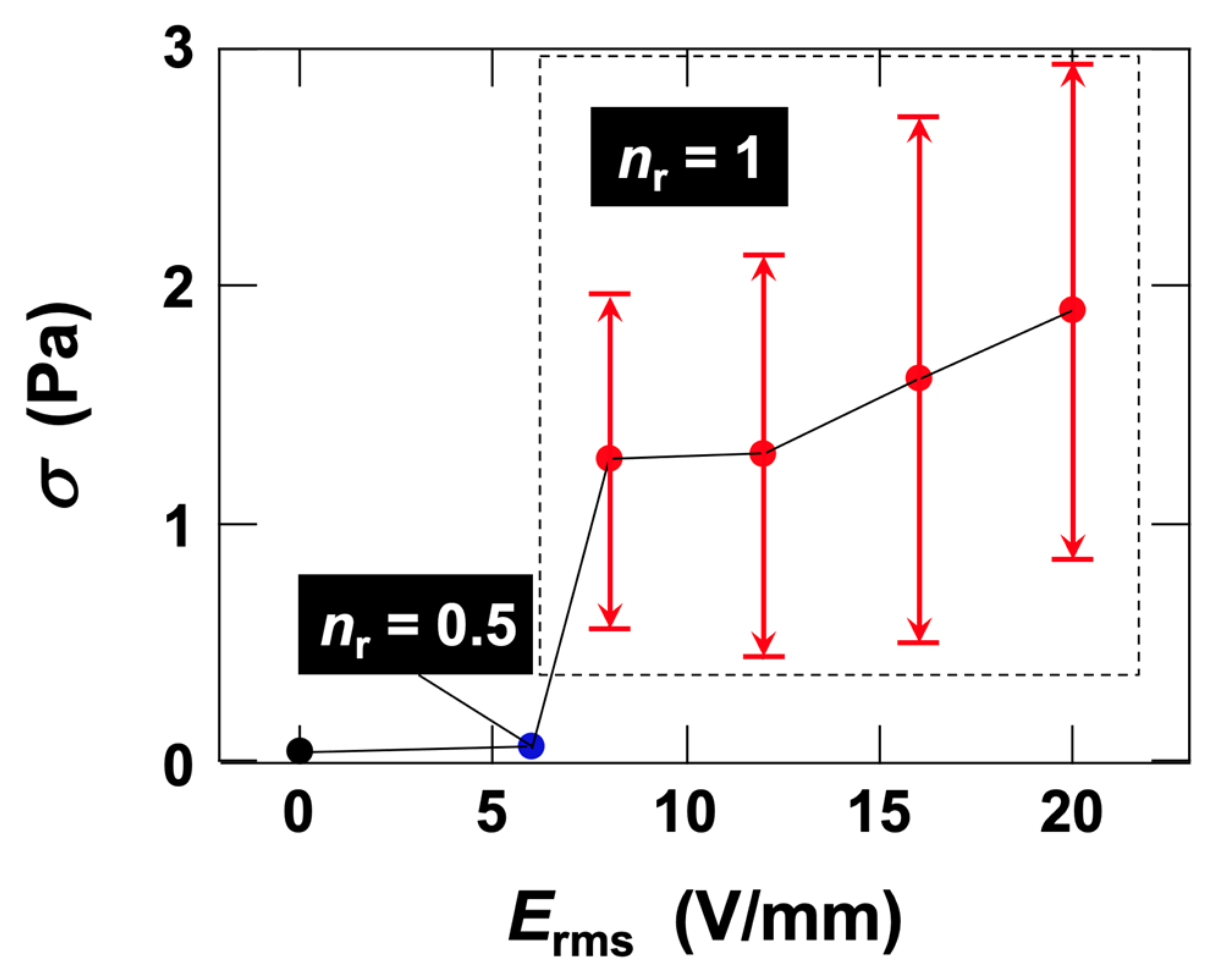
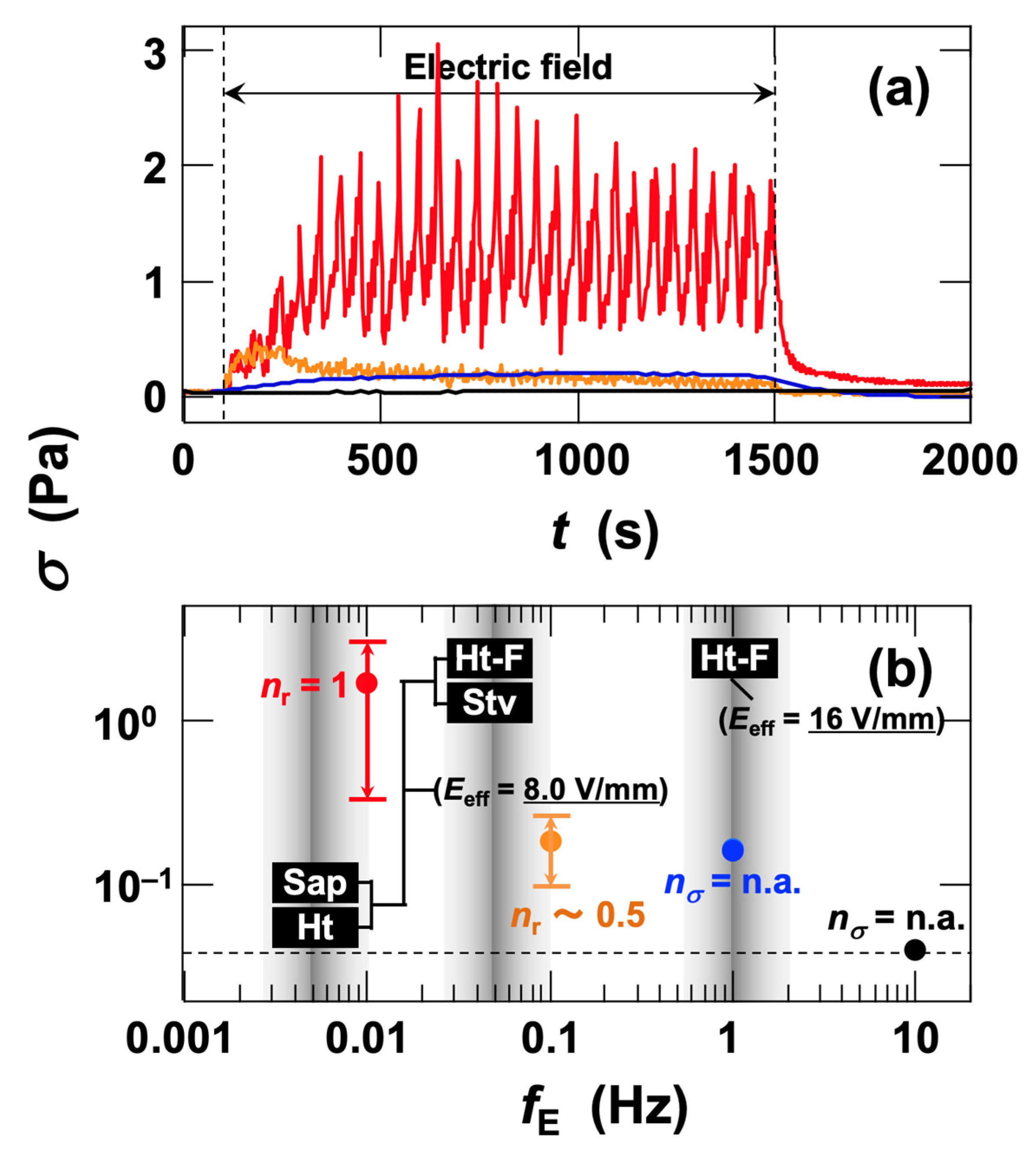
3.2. Rheological Measurements
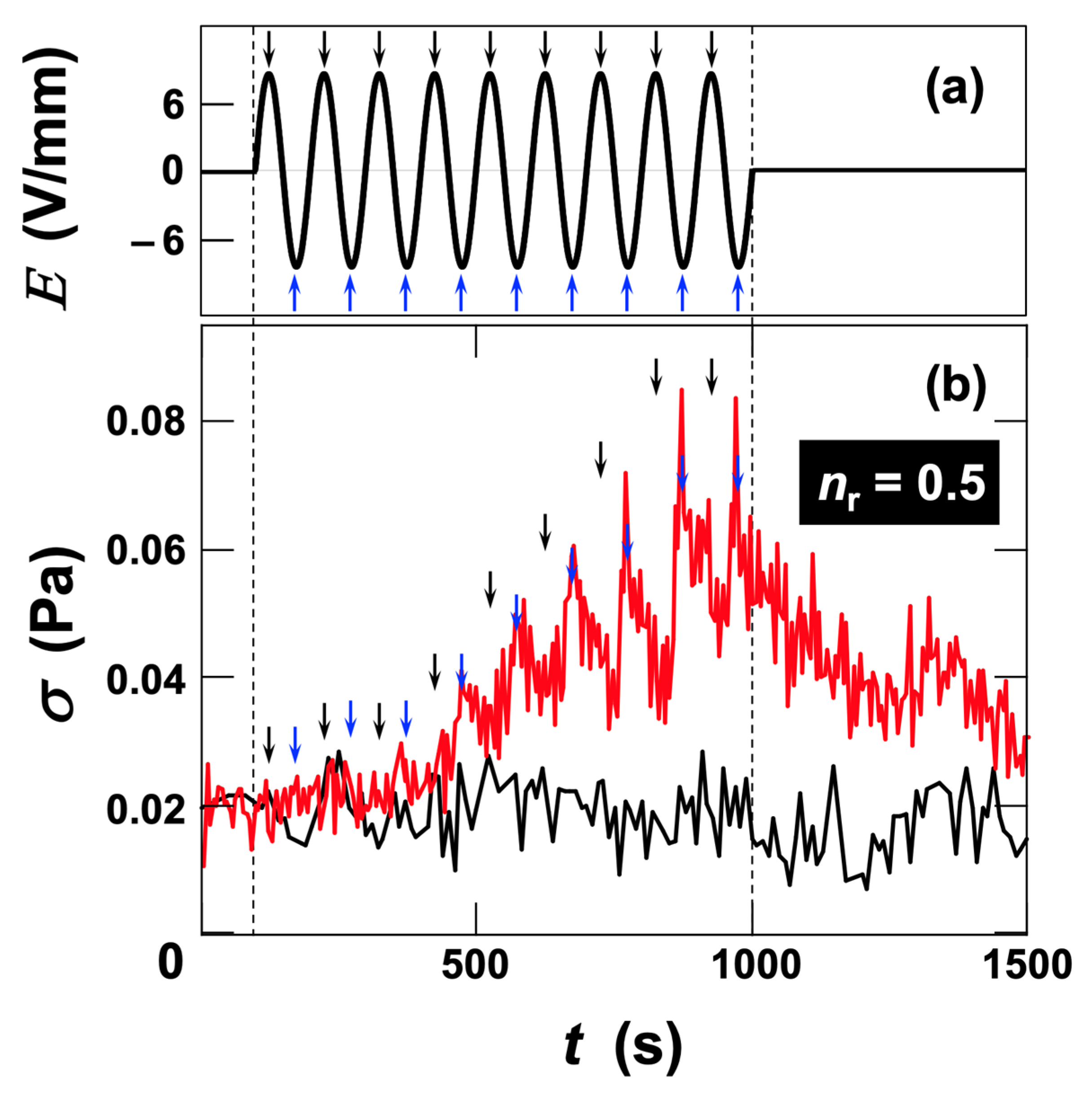
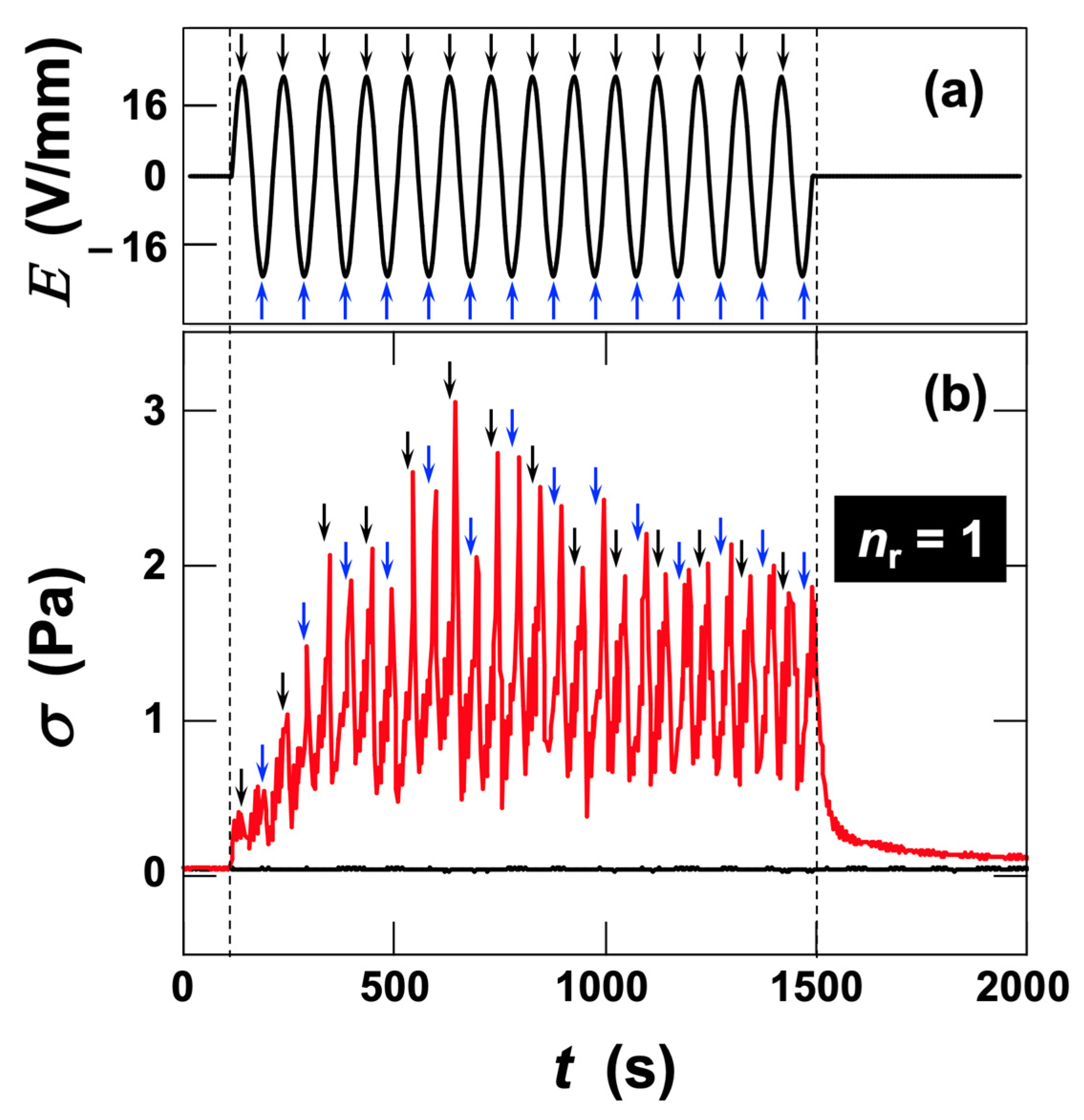
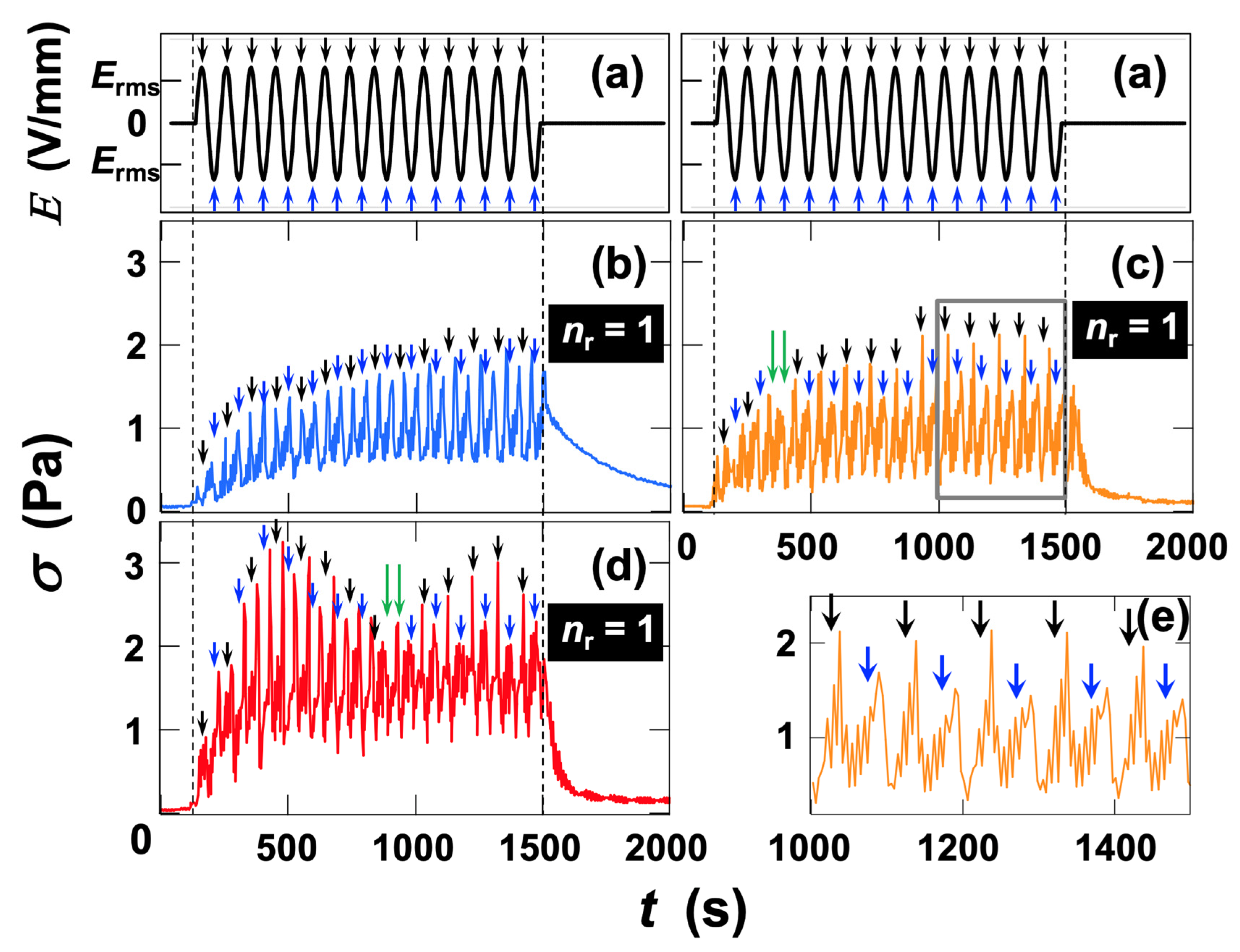
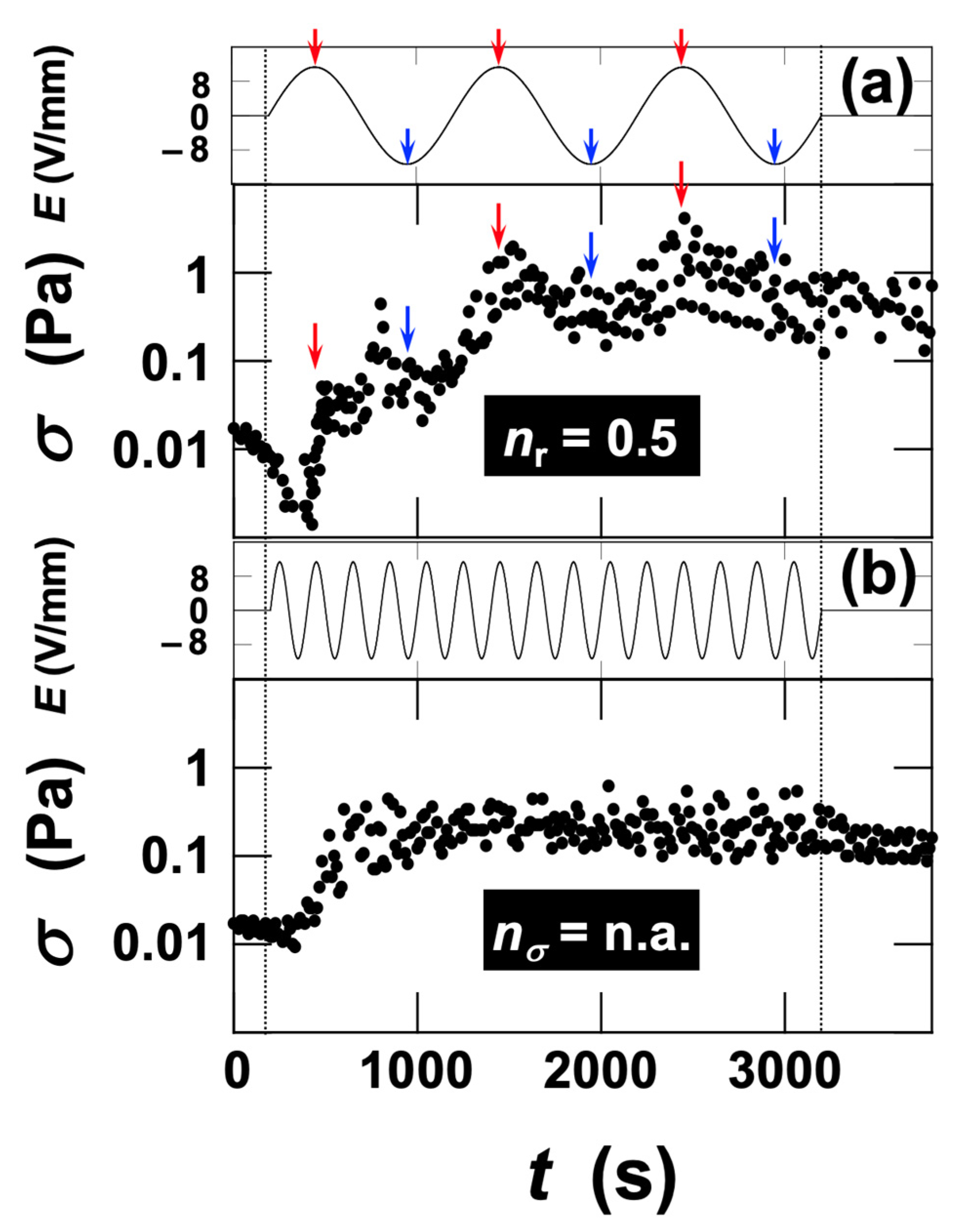
3.2.1. Stress Response of Ht-F Dispersions to AC Electric Fields
3.2.2. Stress Response of Sap Dispersions to AC Electric Fields
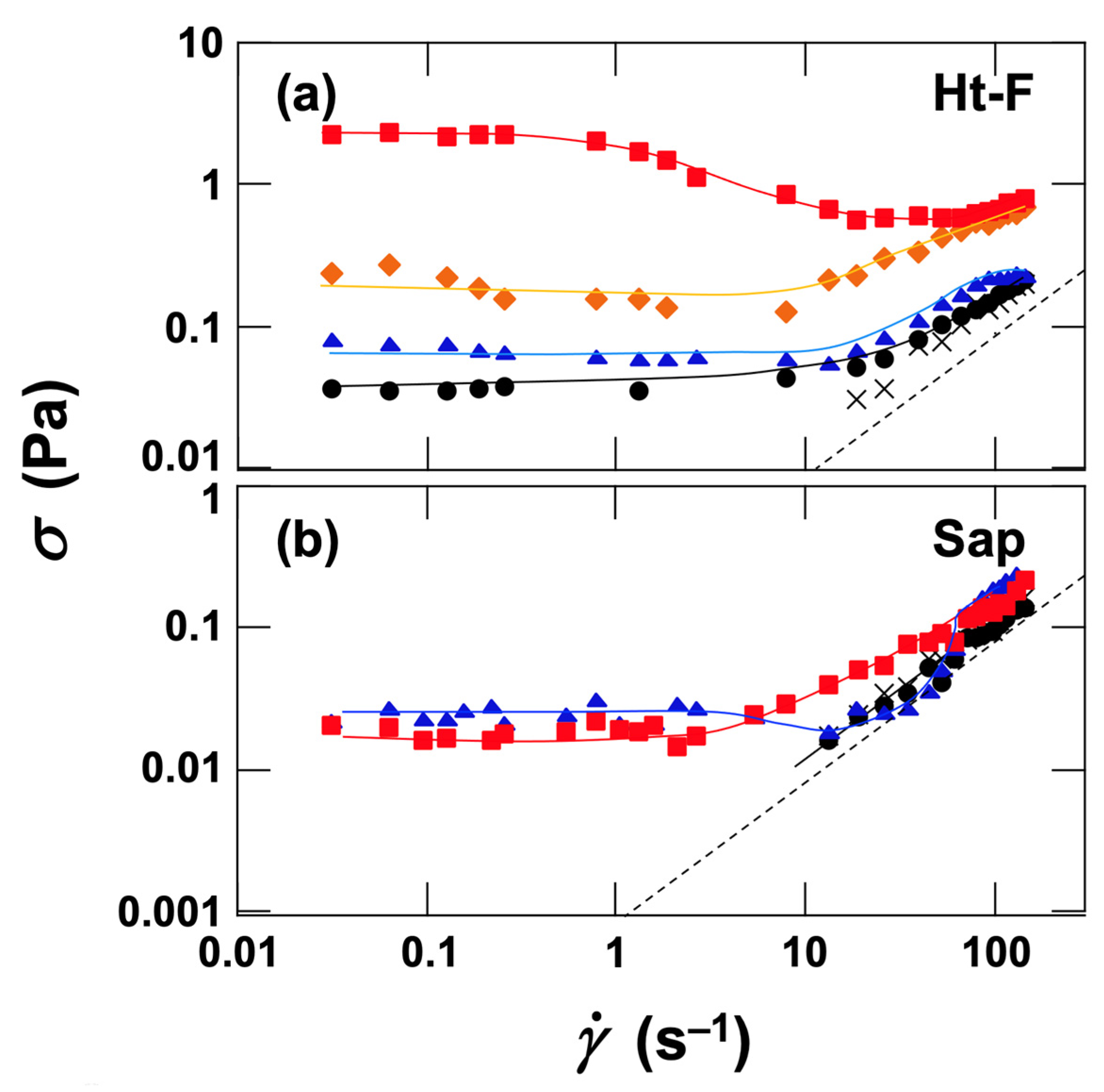
3.2.3. Flow Curves
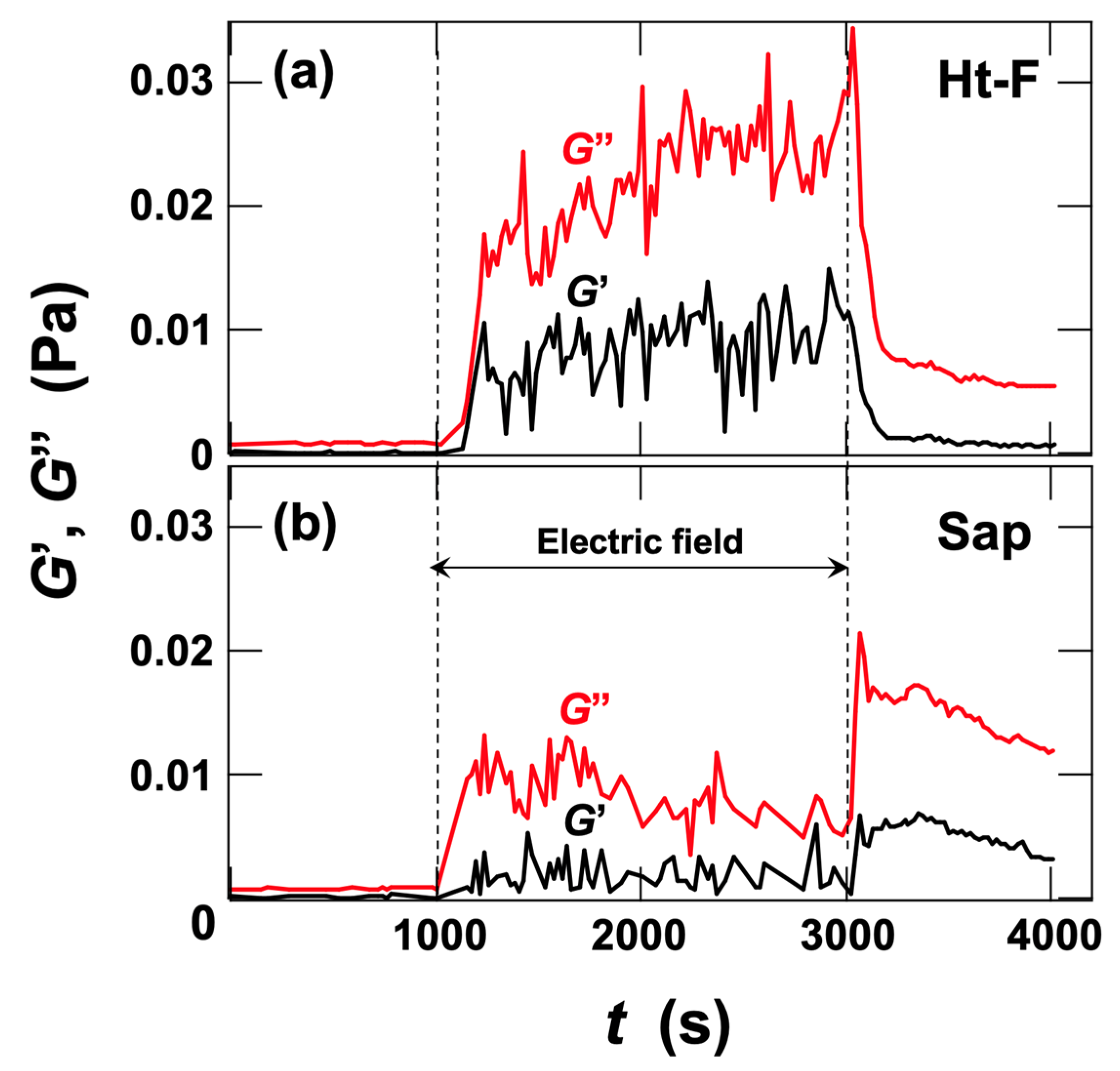
3.2.4. Rheological Measurements Under Dynamic Deformation
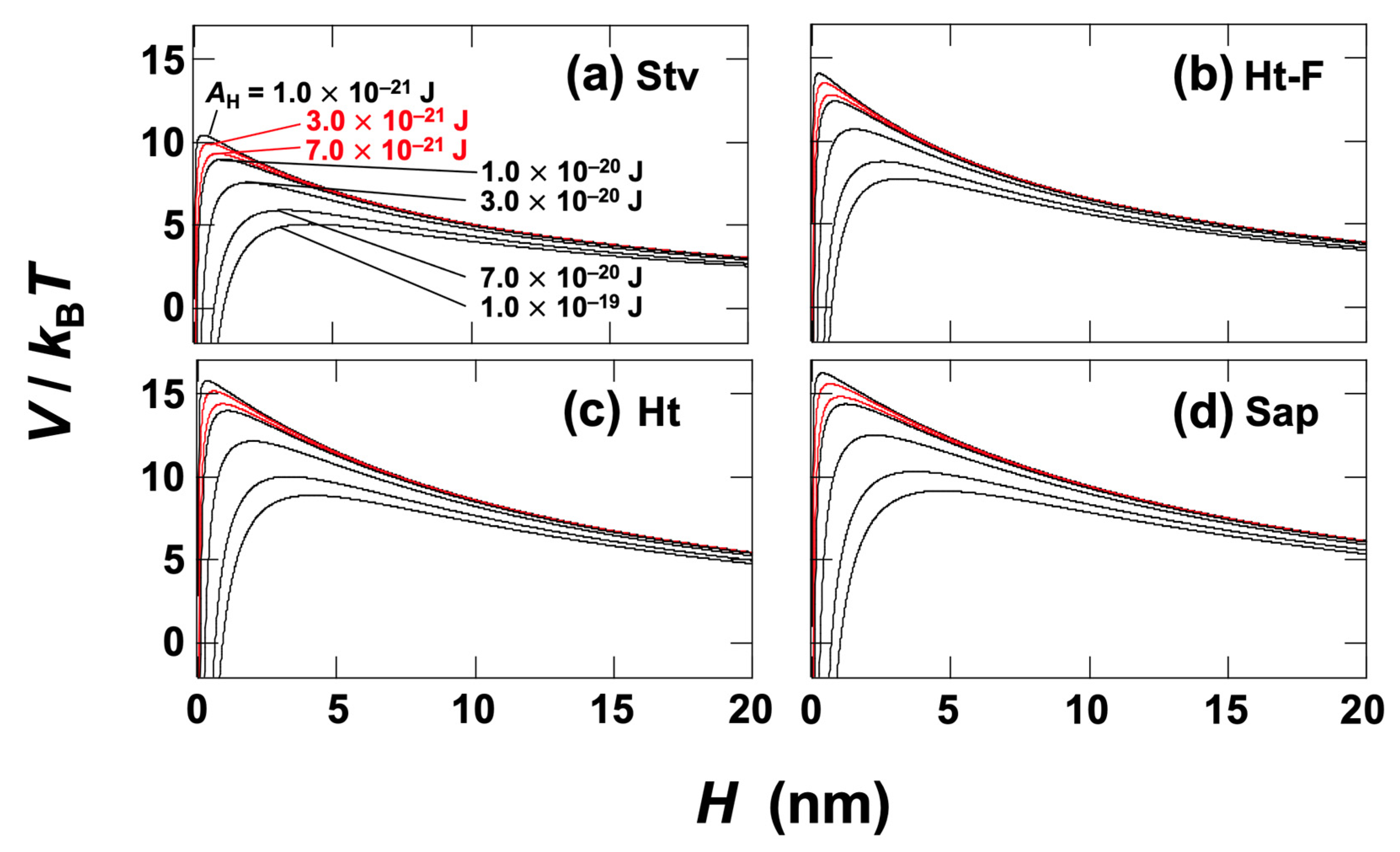
3.3. DLVO Potential Calculation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Winslow, W.M. Induced fibration of suspensions. J. Appl. Phys. 1949, 20, 1137–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, H.; Kelly, J.P. Electro-rheology. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1988, 21, 1661–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halsey, T.C. Electrorheological fluids. Science 1992, 258, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munteanu, L.; Munteanu, A.; Sedlacik, M. Electrorheological fluids: A living review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2025, 151, 101421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, B.D.; Winter, H.H. Field-induced gelation, yield stress, and fragility of an electro-rheological suspension. Rheol. Acta 2002, 41, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, M.; Klingenberg, D.J. Electrorheology: Mechanisms and models. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 1996, 17, 57–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-B.; Hong, S.-R. Dynamic modeling and vibration control of electrorheological mounts. J. Vib. Acoust. 2004, 126, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, Q.-A.; Jorgensen, S.J.; Ho, J.; Sentis, L. Characterization and testing of an electrorheological fluid valve for control of ERF actuators. Actuators 2015, 4, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitczuk, J.; Weinberg, B.; Canavan, P.K.; Mavroidis, C. Active knee rehabilitation orthotic device with variable damping characteristics implemented via an electrorheological fluid. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2010, 15, 952–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abend, S.; Lagaly, G. Sol–gel transitions of sodium montmorillonite dispersions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2000, 16, 201–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Tanabe, H.; Shinoki, S. Zeta potential as a key indicator of network structure and rheological behavior in smectite clay dispersions. Fluids 2025, 10, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombácz, E.; Ábrahám, I.; Gilde, M.; Szánto, F. The pH-dependent colloidal stability of aqueous montmorillonite suspensions. Colloid Surf. A 1990, 49, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, R.K. Ionic forces in thick films of liquid between charged surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1946, 42, B219–B225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durán, J.D.; Ramos-Tejada, M.M.; Arroyo, F.J.; González-Caballero, F. Rheological and electrokinetic properties of sodium montmorillonite suspensions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 229, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Sugiyama, T.; Takahashi, S.; Tsuchida, A. Viscosity change in aqueous hectorite suspension activated by DC electric field. Rheol. Acta 2013, 52, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Ueno, M.; Takahashi, S.; Tsuchida, A.; Kurosaka, K. Electrically induced reversible viscosity change in hectorite aqueous dispersion under an AC electric field. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 99, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Nakashima, A.; Takahashi, S.; Tsuchida, A.; Kurosaka, K. Changes of viscosity in stevensite aqueous dispersions with application of an electric field of the order of a few V/mm. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 114, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H. Influence of alternating electric field on electrorheological effect of aqueous dispersions of stevensite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2024, 254, 107393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michels-Brito, P.H.; Malfatti-Gasperini, A.; Mayr, L.; Puentes-Martinez, X.; Tenorio, R.P.; Wagner, D.R.; Knudsen, K.D.; Araki, K.; Oliveira, R.G.; Breu, J.; et al. Unmodified clay nanosheets at the air–water interface. Langmuir 2021, 37, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worasith, N.; Goodman, B.A. Clay mineral products for improving environmental quality. Appl. Clay Sci. 2023, 242, 106980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Gao, C.Y.; Nam, J.D.; Choi, H.J. Cellulose-based smart fluids under applied electric fields. Materials 2017, 10, 1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Q.; Ranjith, P.G.; Long, X.; Kang, Y.; Huang, M. A review of shale swelling by water adsorption. J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2015, 27, 1421–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Takahashi, S.; Tsuchida, A. Rapid sedimentation of poly(methyl methacrylate) spheres and montmorillonite particles in water upon application of a DC electric field of the order of a few V/mm. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 101, 623–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Tsuchida, A. Sedimentation behavior of poly(methyl methacrylate) spheres in water upon application of a DC vertical electric field of the order of a few V/mm. Powder Technol. 2017, 320, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H. Co-flocculation of mixed-sized colloidal particles in aqueous dispersions under a DC electric field. Materials 2025, 18, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H. Rapid ascent of hollow particles in water induced by an electric field. Powders 2023, 2, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Sakakibara, M. Electric field-induced settling and flotation of flocs in mixed aqueous suspensions of poly(methyl methacrylate) and aluminosilicate hollow particles. Materials 2025, 18, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H. Impact of DC electric field direction on sedimentation behavior of colloidal particles in water. Materials 2025, 18, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollah, M.Y.A.; Morkovsky, P.; Gomes, J.A.G.; Kesmez, M.; Parga, J.; Cocke, D.L. Fundamentals, present and future perspectives of electrocoagulation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 114, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, P.K.; Barton, G.W.; Mitchell, C.A. The future for electrocoagulation as a localised water treatment technology. Chemosphere 2005, 59, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emamjomeh, M.M.; Sivakumar, M. Review of pollutants removed by electrocoagulation and electrocoagulation/flotation processes. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 1663–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuokkanen, V.; Kuokkanen, T.; Rämö, J.; Lassi, U. Recent applications of electrocoagulation in treatment of water and wastewater—A review. Green Sustain. Chem. 2013, 3, 89–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Chaudhari, P.K.; Dubey, S.; Prajapati, A.K. Electrocoagulation treatment of electroplating wastewater: A review. J. Environ. Eng. 2020, 146, 03120009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H. Deionization-induced colorless transparency in physical gels formed by clay aqueous dispersions. Appl. Clay Sci. 2024, 249, 107261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroon, M.; Vos, W.L.; Wegdam, G.H. Structure and formation of a gel of colloidal discs. Phys. Rev. E 1998, 57, 1962–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonn, D.; Tanaka, H.; Wegdam, G.; Kellay, H.; Meunier, J. Aging of a colloidal “Wigner” glass. Europhys. Lett. 1998, 45, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourchid, A.; Levitz, P. Long-term gelation of laponite aqueous dispersions. Phys. Rev. E 1998, 57, R4887–R4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, H.Z. Liquid, glass, gel: The phases of colloidal laponite. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2007, 353, 3891–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Jdayil, B. Rheology of sodium and calcium bentonite–water dispersions: Effect of electrolytes and aging time. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2011, 98, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, P.-I.; Leong, Y.-K. Surface chemistry and rheology of laponite dispersions: Zeta potential, yield stress, ageing, fractal dimension and pyrophosphate. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 107, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, Y.K.; Clode, P.L. Time-dependent clay gels: Stepdown shear rate behavior, microstructure, ageing, and phase state ambiguity. Phys. Fluids 2023, 35, 123329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, H.S.; Mortland, M.M. Ion movement in Wyoming bentonite during electroosmosis. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1959, 23, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashihara, T.; Kinoshita, K.; Sato, S.; Kozaki, T. Electromigration of sodium ions and electro-osmotic flow in water-saturated, compacted Na-montmorillonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2004, 26, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loch, J.P.G.; Lima, A.T.; Kleingeld, P.J. Geochemical effects of electro-osmosis in clays. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2010, 40, 1249–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higashihara, T.; Kinoshita, K.; Akagi, Y.; Sato, S.; Kozaki, T. Transport number of sodium ions in water-saturated, compacted Na-montmorillonite. Phys. Chem. Earth 2008, 33, S142–S148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Noda, N.; Sato, S.; Kozaki, T.; Sato, H.; Hatanaka, K. Electrokinetic study of migration of anions, cations, and water in water-saturated compacted sodium montmorillonite. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2011, 48, 454–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachmadetin, J.; Mizuto, M.; Tanaka, S.; Kozaki, T.; Watanabe, N. Calcium carbonate precipitation in compacted bentonite using electromigration reaction method and its application to estimate the ion activity coefficient in the porewater. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 959–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadige, P.; Bandyopadhyay, R. Electric field induced gelation in aqueous nanoclay suspensions. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 6974–6982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, B.R.; Parslow, K. Particle size measurement: The equivalent spherical diameter. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1988, 419, 137–149. [Google Scholar]
- Derjaguin, B.; Landau, L.D. Theory of the stability of strongly charged lyophobic sols and of the adhesion of strongly charged particles in solutions of electrolytes. Acta Physicochim. URSS 1941, 14, 633–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verwey, E.J.W.; Overbeek, J.T.G. Theory of the Stability of Lyophobic Colloids; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, R.J. Foundations of Colloid Science, 2nd ed.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Bergström, L. Hamaker constants of inorganic materials. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1997, 70, 125–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tester, C.C.; Aloni, S.; Gilbert, B.; Banfield, J.F. Short- and long-range attractive forces that influence the structure of montmorillonite osmotic hydrates. Langmuir 2016, 32, 12039–12046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, C.; Kaufhold, S. Hamaker functions for kaolinite and montmorillonite. Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 2021, 43, 100442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Bourg, I.C. Interaction between hydrated smectite clay particles as a function of salinity (0–1 M) and counterion type (Na, K, Ca). J. Phys. Chem. C 2022, 126, 20990–20997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kimura, H.; Inoue, A. Hierarchy of Electrorheological Responses in Aqueous Smectite Clay Dispersions in Relation to DLVO Potential Barriers. Eng 2025, 6, 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6120351
Kimura H, Inoue A. Hierarchy of Electrorheological Responses in Aqueous Smectite Clay Dispersions in Relation to DLVO Potential Barriers. Eng. 2025; 6(12):351. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6120351
Chicago/Turabian StyleKimura, Hiroshi, and Akito Inoue. 2025. "Hierarchy of Electrorheological Responses in Aqueous Smectite Clay Dispersions in Relation to DLVO Potential Barriers" Eng 6, no. 12: 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6120351
APA StyleKimura, H., & Inoue, A. (2025). Hierarchy of Electrorheological Responses in Aqueous Smectite Clay Dispersions in Relation to DLVO Potential Barriers. Eng, 6(12), 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng6120351






