Innovative Integration of Triboelectric Nanogenerators into Signature Stamps for Energy Harvesting, Self-Powered Electronic Devices, and Smart Applications
Abstract
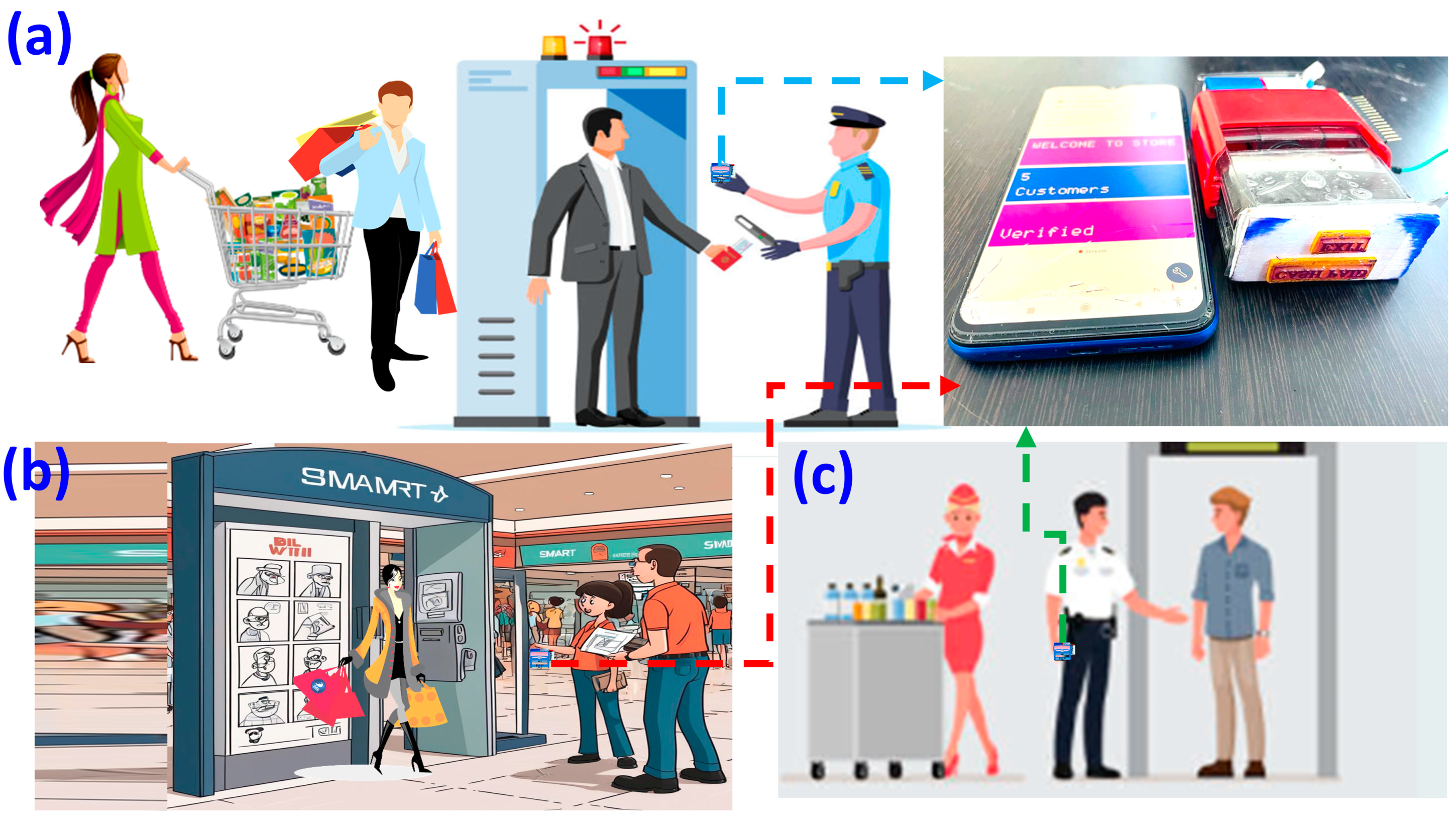
1. Introduction
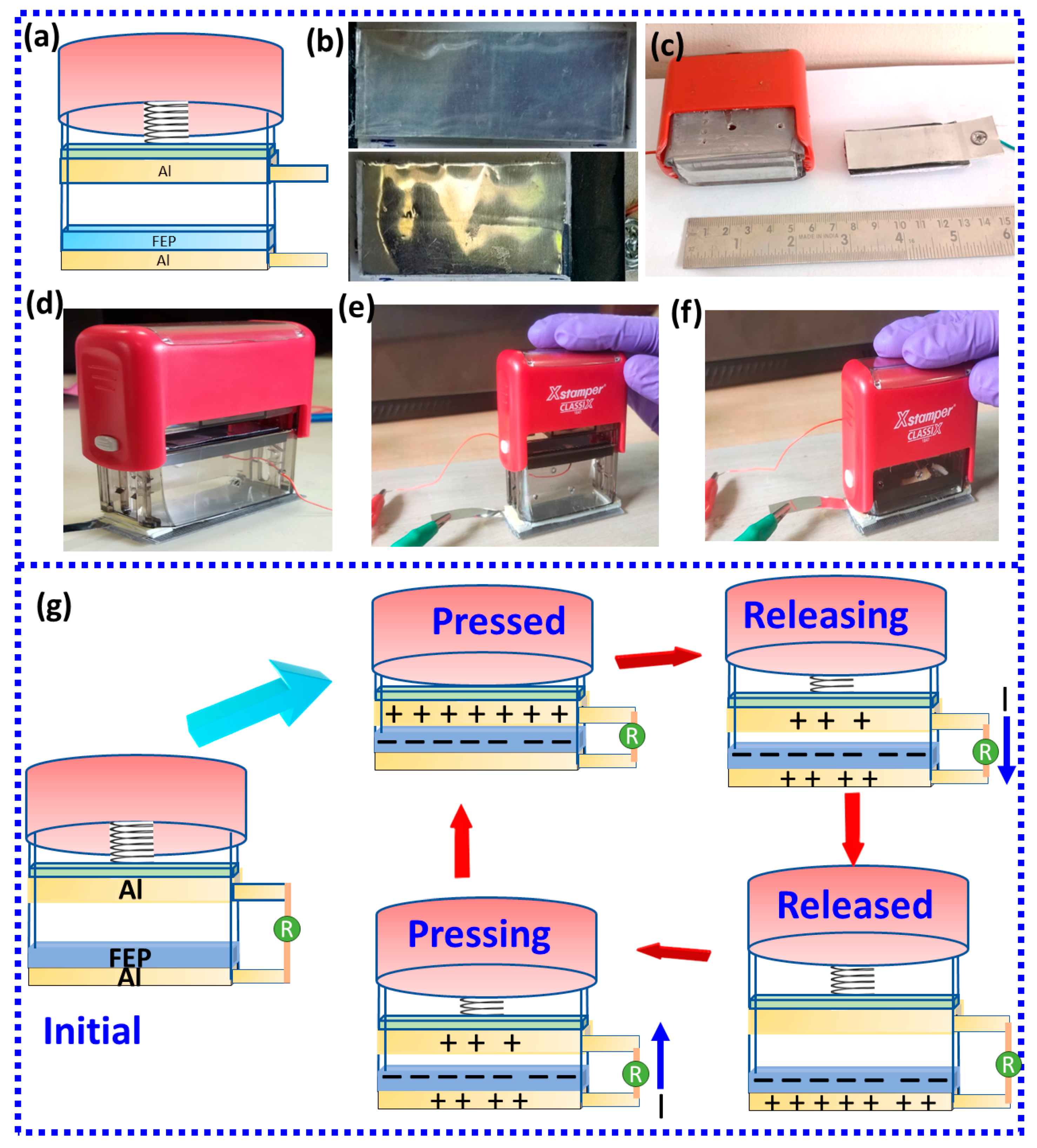
2. Experimental Details
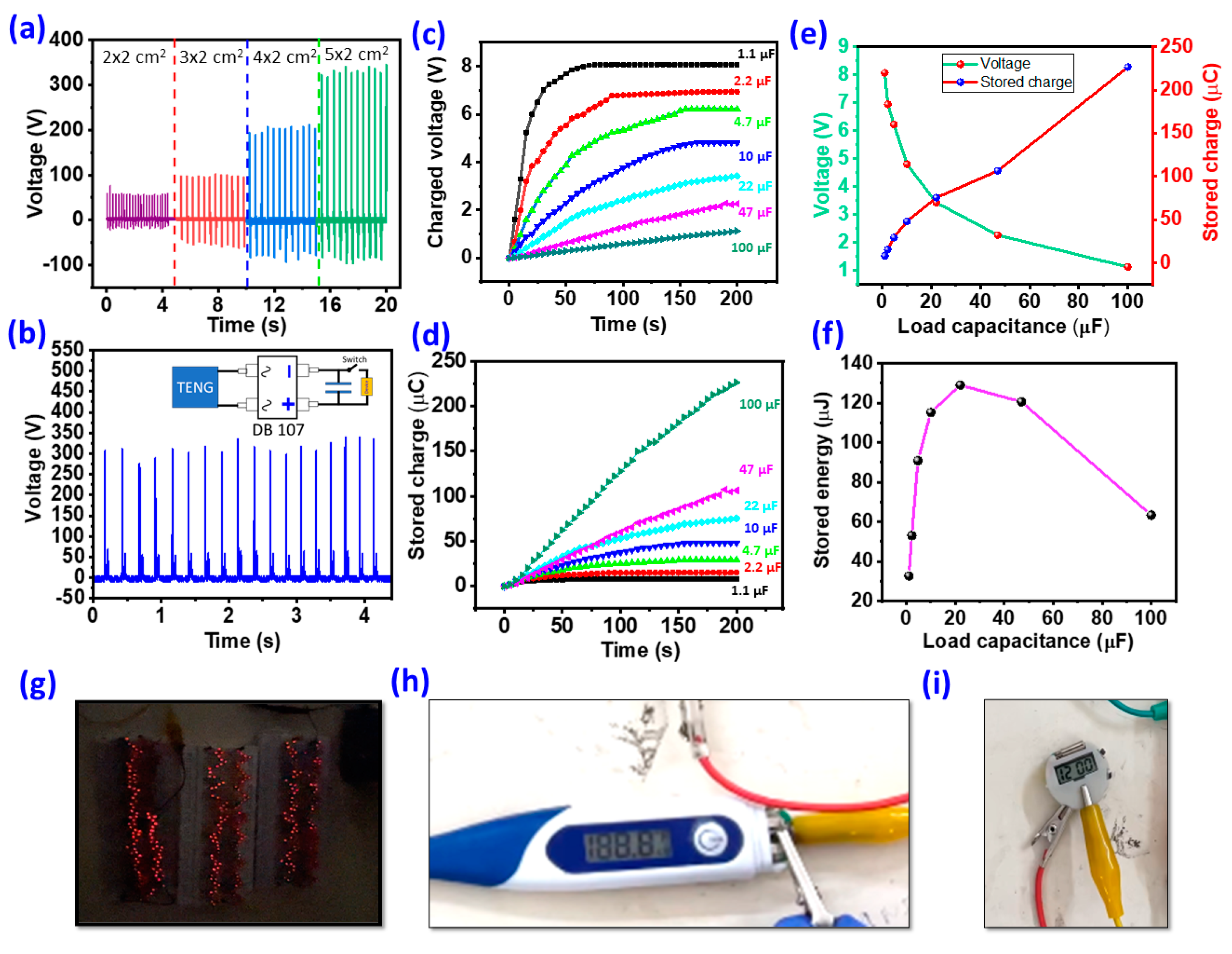
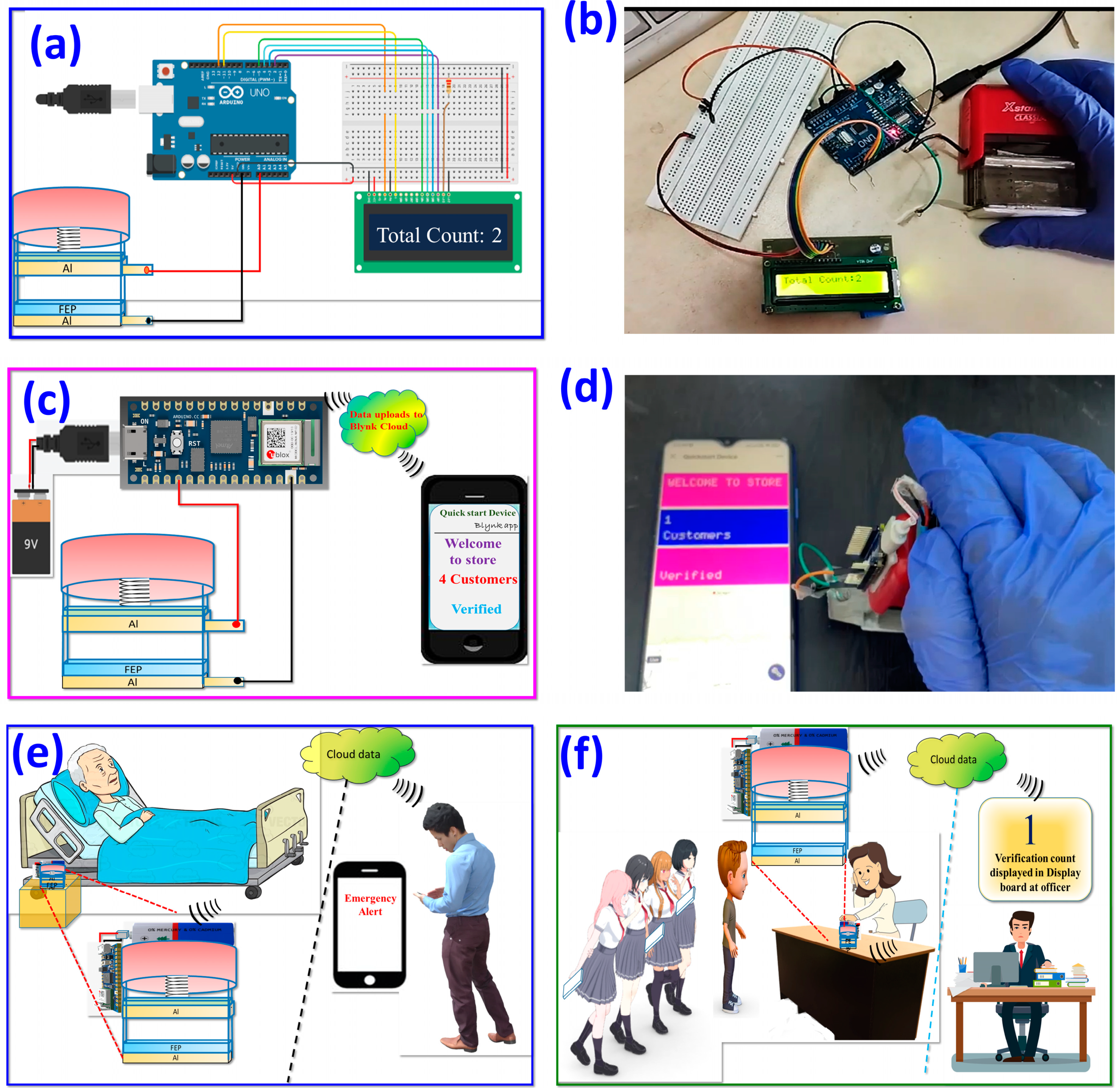
3. Results
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, J.; Wang, Z.L. Recent progress of triboelectric nanogenerators: From fundamental theory to practical applications. EcoMat 2020, 2, e12059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Liu, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerators: Fundamental physics and potential applications. Friction 2020, 8, 481–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.-R.; Tian, Z.-Q.; Wang, Z.L. Flexible triboelectric generator. Nano Energy 2012, 1, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.R.; Tang, W.; Wang, Z.L. Flexible Nanogenerators for Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Electronics. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4283–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Cheng, T.; Wang, Z.L. Self-powered sensors and systems based on nanogenerators. Sensors 2020, 20, 2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lone, S.A.; Lim, K.C.; Kaswan, K.; Chatterjee, S.; Fan, K.-P.; Choi, D.; Lee, S.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, J.; Lin, Z.-H. Recent advancements for improving the performance of triboelectric nanogenerator devices. Nano Energy 2022, 99, 107318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Bai, Y.; Shao, J.; Meng, H.; Li, Z. Strategies to Improve the Output Performance of Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Small Methods 2024, e2301682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.; Hassan, I.; Pourrahimi, A.M.; Helal, A.S.; El-Kady, M.F.; Khassaf, H.; Kaner, R.B. Toward High-Performance Triboelectric Nanogenerators by Engineering Interfaces at the Nanoscale: Looking into the Future Research Roadmap. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 2000520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.; Sahay, K.; Verma, A.; Maurya, D.K.; Yadav, B.C. Applications of multifunctional triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG) devices: Materials and prospects. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2023, 7, 3796–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Xiong, Y.; Sun, J.; Xie, X.; Sun, Q.; Wang, Z.L. Multidiscipline Applications of Triboelectric Nanogenerators for the Intelligent Era of Internet of Things. Nano-Micro Lett. 2023, 15, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Liu, G.; Zeng, J.; Dai, Y.; Zhou, W.; Xiao, C.; Dang, T.; Yu, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, C. Recent Progress of Switching Power Management for Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Sensors 2022, 22, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begum, S.R.; Begum, S.R.; Chandrasekhar, A.; Chandrasekhar, A. Opportunities and Challenges in Power Management Systems for Triboelectric Nanogenerators. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2023, 5, 1347–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Tong, T.; Bu, T.; Cao, Y.; Xu, S.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, C. Overview of Power Management for Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2020, 2, 1900129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macário, D.; Domingos, I.; Carvalho, N.; Pinho, P.; Alves, H. Harvesting circuits for triboelectric nanogenerators for wearable applications. iScience 2022, 25, 103977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Olin, H. Material choices for triboelectric nanogenerators: A critical review. EcoMat 2020, 2, e12062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaboina, R.K.; Rajaboina, R.K.; Khanapuram, U.K.; Khanapuram, U.K.; Vivekananthan, V.; Vivekananthan, V.; Khandelwal, G.; Khandelwal, G.; Potu, S.; Potu, S.; et al. Crystalline Porous Material-Based Nanogenerators: Recent Progress, Applications, Challenges, and Opportunities. Small 2023, 20, e2306209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulandaivel, A.; Potu, S.; Babu, A.; Madathil, N.; Velpula, M.; Rajaboina, R.K.; Khanapuram, U.K. Advances in ferrofluid-based triboelectric nanogenerators: Design, performance, and prospects for energy harvesting applications. Nano Energy 2024, 120, 109110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Tcho, I.-W.; Choi, Y.-K. Triboelectric nanogenerator based on rolling motion of beads for harvesting wind energy as active wind speed sensor. Nano Energy 2018, 52, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Ha, J.; Lee, B.-S.; Park, Y.; Choong, C.; Kim, J.-B.; Wang, Z.L.; Kim, H.-Y.; et al. Flutter-driven triboelectrification for harvesting wind energy. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazar, A.M.; Egbe, K.-J.I.; Abdollahi, A.; Hariri-Ardebili, M.A. Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Energy Harvesting in Ocean: A Review on Application and Hybridization. Energies 2021, 14, 5600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xu, L.; Liu, G.; Yang, H.; Bu, T.; Fu, X.; Xu, S.; Fang, C.; Zhang, C. Network Topology Optimization of Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Effectively Harvesting Ocean Wave Energy. iScience 2020, 23, 101848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, C.; Nunes, D.; Clemente, D.; Mathias, N.; Correia, J.M.; Rosa-Santos, P.; Taveira-Pinto, F.; Morais, T.; Pereira, A.; Ventura, J. Emerging triboelectric nanogenerators for ocean wave energy harvesting: State of the art and future perspectives. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 2657–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, K.; Yi, H.; Yang, Y.; Chang, H.; Wu, J.; Tang, L.; Yang, Z.; Wang, N.; Hu, L.; Fu, Y.; et al. Origami-inspired electret-based triboelectric generator for biomechanical and ocean wave energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2020, 67, 104197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Fu, X.; Li, C.; Liu, G.; Gao, Y.; Qi, Y.; Bu, T.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhang, C. Raindrop energy-powered autonomous wireless hyetometer based on liquid–solid contact electrification. Microsystems Nanoeng. 2022, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Lin, Z.-H.; Cheng, G.; Wu, W.; Wen, X.; Lee, S.; Wang, Z.L. Silicon-based hybrid cell for harvesting solar energy and raindrop electrostatic energy. Nano Energy 2014, 9, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, G.M.; Wu, C.-M.; Motora, K.G.; Umapathi, R.; Jose, C.R.M. Acoustic-electric conversion and triboelectric properties of nature-driven CF-CNT based triboelectric nanogenerator for mechanical and sound energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2023, 108, 108211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, W.; Su, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectrification-based organic film nanogenerator for acoustic energy harvesting and self-powered active acoustic sensing. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 2649–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Que, R.; Shao, Q.; Li, Q.; Shao, M.; Cai, S.; Wang, S.; Lee, S. Flexible Nanogenerators Based on Graphene Oxide Films for Acoustic Energy Harvesting. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 5418–5422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navaneeth, M.; Potu, S.; Babu, A.; Lakshakoti, B.; Rajaboina, R.K.; Kumar, K.U.; Divi, H.; Kodali, P.; Balaji, K. Transforming Medical Plastic Waste into High-Performance Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Sustainable Energy, Health Monitoring, and Sensing Applications. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 12145–12154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Sun, X.; Diao, N.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B.; Qin, C.; Liang, E.; Mao, Y. Triboelectric Touch-Free Screen Sensor for Noncontact Gesture Recognizing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1907893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basith, S.A.; Chandrasekhar, A. COVID-19 clinical waste reuse: A triboelectric touch sensor for IoT-cloud supported smart hand sanitizer dispenser. Nano Energy 2023, 108, 108183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behera, S.A.; Kim, H.-G.; Jang, I.R.; Hajra, S.; Panda, S.; Vittayakorn, N.; Kim, H.J.; Achary, P.G.R. Triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered traffic monitoring. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2024, 303, 117277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowacki, B.; Mistewicz, K.; Hajra, S.; Kim, H.J. 3D printed triboelectric nanogenerator for underwater ultrasonic sensing. Ultrasonics 2023, 133, 107045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Gu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yang, F.; Zhao, L.; Zheng, M.; Cheng, G.; Du, Z. The self-powered CO2 gas sensor based on gas discharge induced by triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2018, 53, 898–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, D.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W. Self-powered ammonia nanosensor based on the integration of the gas sensor and triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2018, 49, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, H.; Fan, Y.; Lyu, Y.; Liu, Z. A triboelectric nanogenerator based on white sugar for self-powered humidity sensor. Solid-State Electron. 2020, 174, 107920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Xie, G.; Wang, S.; Tai, H.; Zhang, Q.; Du, H.; Zhang, H.; Du, X.; Jiang, Y. Novel high-performance self-powered humidity detection enabled by triboelectric effect. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 251, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerators as new energy technology for self-powered systems and as active mechanical and chemical sensors. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 9533–9557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandelwal, G.; Deswal, S.; Dahiya, R. Triboelectric Nanogenerators as Power Sources for Chemical Sensors and Biosensors. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 44573–44590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanty, B.; Ghosh, S.K.; Maity, K.; Roy, K.; Sarkar, S.; Mandal, D. All-fiber pyro- and piezo-electric nanogenerator for IoT based self-powered health-care monitoring. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 4370–4379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouheir, M.; Zniber, M.; Qudsia, S.; Huynh, T.-P. Real-time humidity sensing by integration of copper sulfide nanocomposite with low-cost and wireless Arduino platform. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 319, 112541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Xia, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Han, S.; Li, Q.; Wang, X. Laser-induced graphene based triboelectric nanogenerator for accurate wireless control and tactile pattern recognition. Nano Energy 2023, 108, 108229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, A.; Bochu, L.; Potu, S.; Kaja, R.; Madathil, N.; Velpula, M.; Kulandaivel, A.; Khanapuram, U.K.; Rajaboina, R.K.; Divi, H.; et al. Facile Direct Growth of ZIF-67 Metal–Organic Framework for Triboelectric Nanogenerators and Their Application in the Internet of Vehicles. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 16806–16817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wu, W.; Song, G. Enhanced stretchable graphene-based triboelectric nanogenerator via control of surface nanostructure. Nano Energy 2019, 58, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seol, M.-L.; Woo, J.-H.; Jeon, S.-B.; Kim, D.; Park, S.-J.; Hur, J.; Choi, Y.-K. Vertically stacked thin triboelectric nanogenerator for wind energy harvesting. Nano Energy 2015, 14, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supraja, P.; Kumar, R.; Mishra, S.; Haranath, D.; Sankar, P.R.; Prakash, K. A simple and low-cost approach for the synthesis and fabrication of ZnO nanosheet-based nanogenerator for energy harvesting and sensing. Eng. Res. Express 2021, 3, 035022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Cheng, X.; Chen, H.; Huang, J.; Chen, X.; Han, M.; Su, Z.; Meng, B.; Song, Z.; Zhang, H. Integrated self-charging power unit with flexible supercapacitor and triboelectric nanogenerator. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. 2016, 4, 14298–14306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Feng, S.; He, D.; Xu, Y.; Yang, M.; Bai, J. An electret film-based triboelectric nanogenerator with largely improved performance via a tape-peeling charging method. Nano Energy 2018, 48, 256–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, R.R.; Sahoo, R.; Mishra, S.; Das, B.; Balasubramaniam, S.; Ramadoss, A. Fabrication and feasibility study of polymer-based triboelectric nanogenerator towards blue energy harvesting. Green Energy Resour. 2023, 1, 100006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bochu, L.; Potu, S.; Navaneeth, M.; Khanapuram, U.K.; Rajaboina, R.K.; Kodali, P. Innovative Integration of Triboelectric Nanogenerators into Signature Stamps for Energy Harvesting, Self-Powered Electronic Devices, and Smart Applications. Eng 2024, 5, 958-966. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5020052
Bochu L, Potu S, Navaneeth M, Khanapuram UK, Rajaboina RK, Kodali P. Innovative Integration of Triboelectric Nanogenerators into Signature Stamps for Energy Harvesting, Self-Powered Electronic Devices, and Smart Applications. Eng. 2024; 5(2):958-966. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5020052
Chicago/Turabian StyleBochu, Lakshakoti, Supraja Potu, Madathil Navaneeth, Uday Kumar Khanapuram, Rakesh Kumar Rajaboina, and Prakash Kodali. 2024. "Innovative Integration of Triboelectric Nanogenerators into Signature Stamps for Energy Harvesting, Self-Powered Electronic Devices, and Smart Applications" Eng 5, no. 2: 958-966. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5020052
APA StyleBochu, L., Potu, S., Navaneeth, M., Khanapuram, U. K., Rajaboina, R. K., & Kodali, P. (2024). Innovative Integration of Triboelectric Nanogenerators into Signature Stamps for Energy Harvesting, Self-Powered Electronic Devices, and Smart Applications. Eng, 5(2), 958-966. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5020052






