Influence of a Shaft Shoulder on the Torsional Load-Bearing Behaviour of Trochoidal Profile Contours as Positive Shaft–Hub Connections
Abstract
1. Introduction
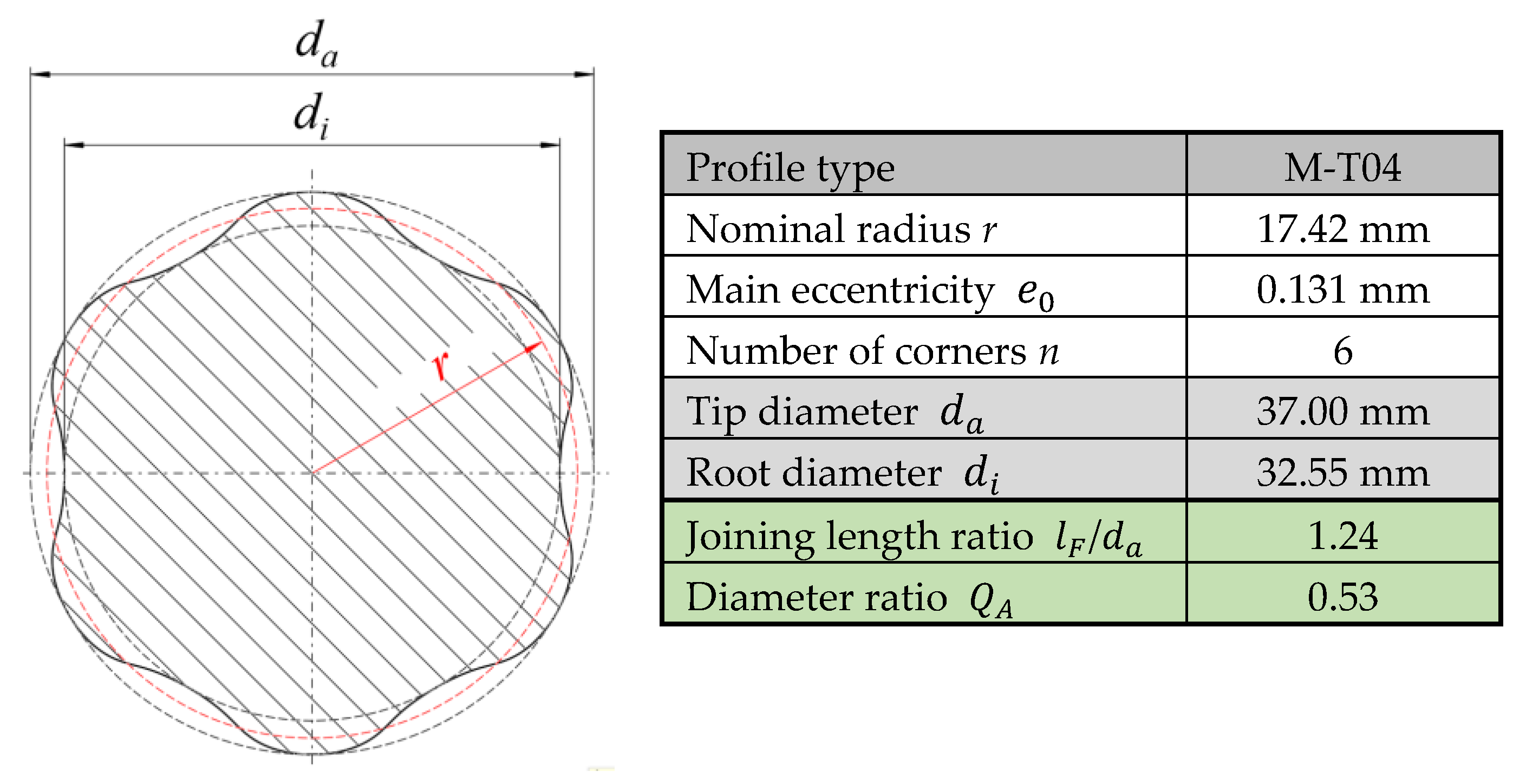
2. Profile Geometry
3. Numerical Investigations of Static Torsional Load
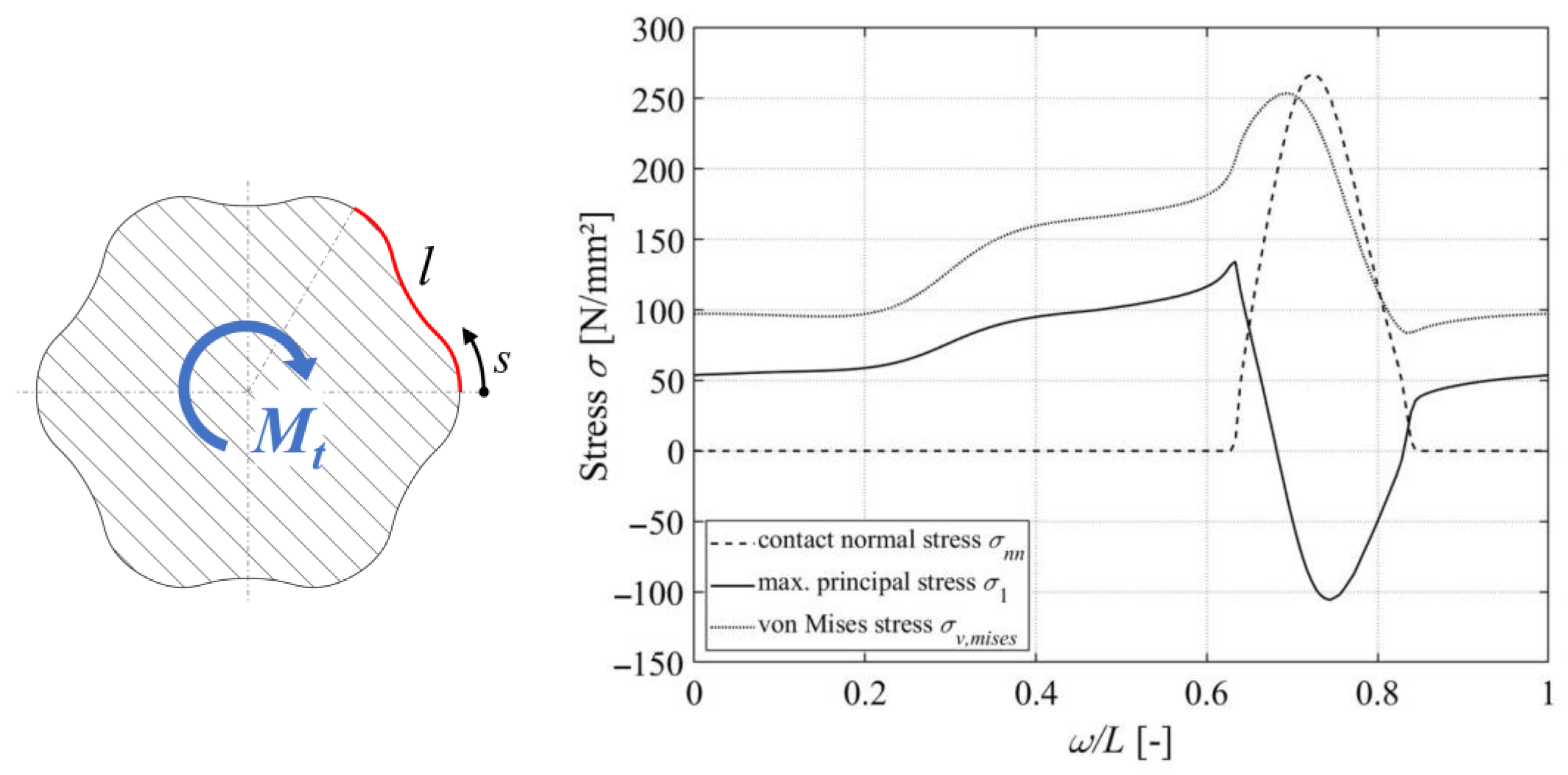
3.1. Finite Element (FE) Model Structure
- -
- Von Mises stress σv,mises;
- -
- Maximum principal stress σ1;
- -
- Contact normal stress σnn.
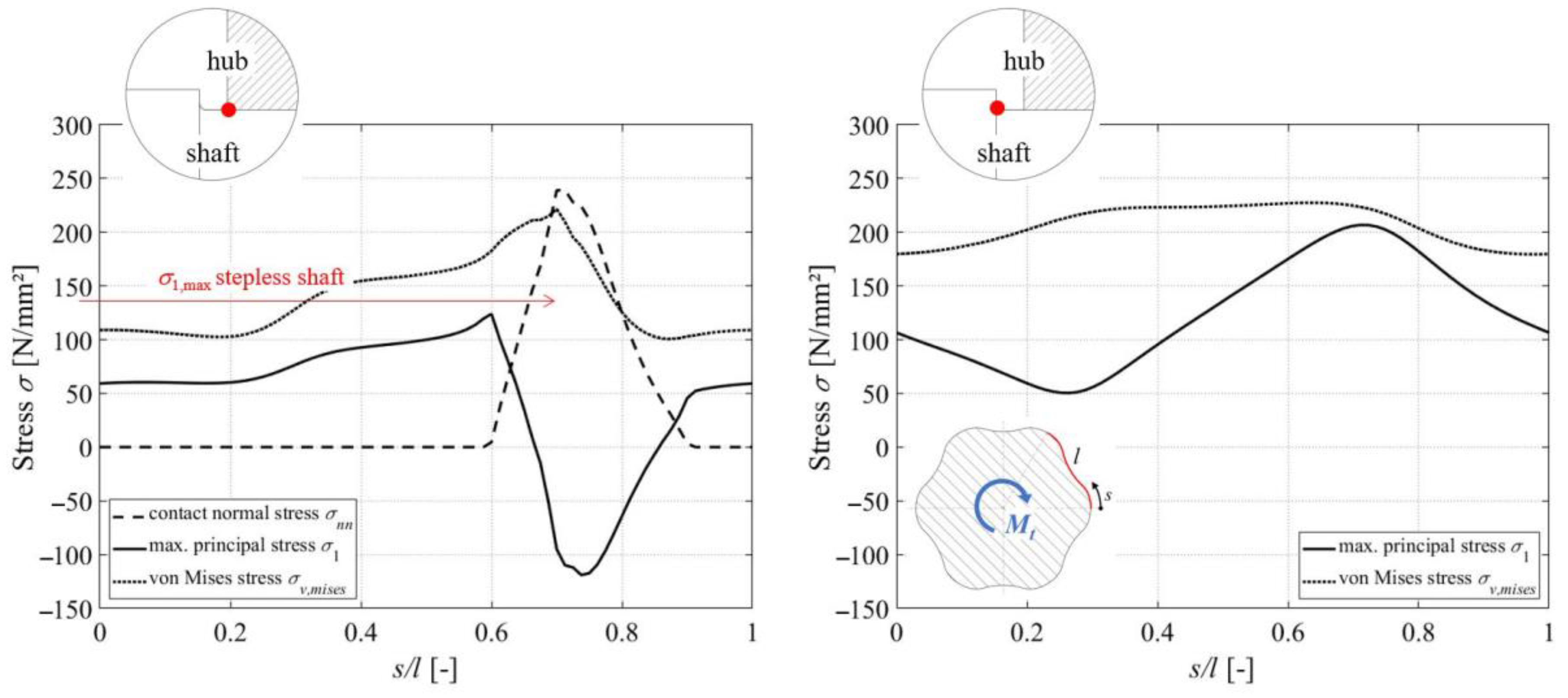
3.2. Load Condition in the Connection with Stepless Profile Shaft
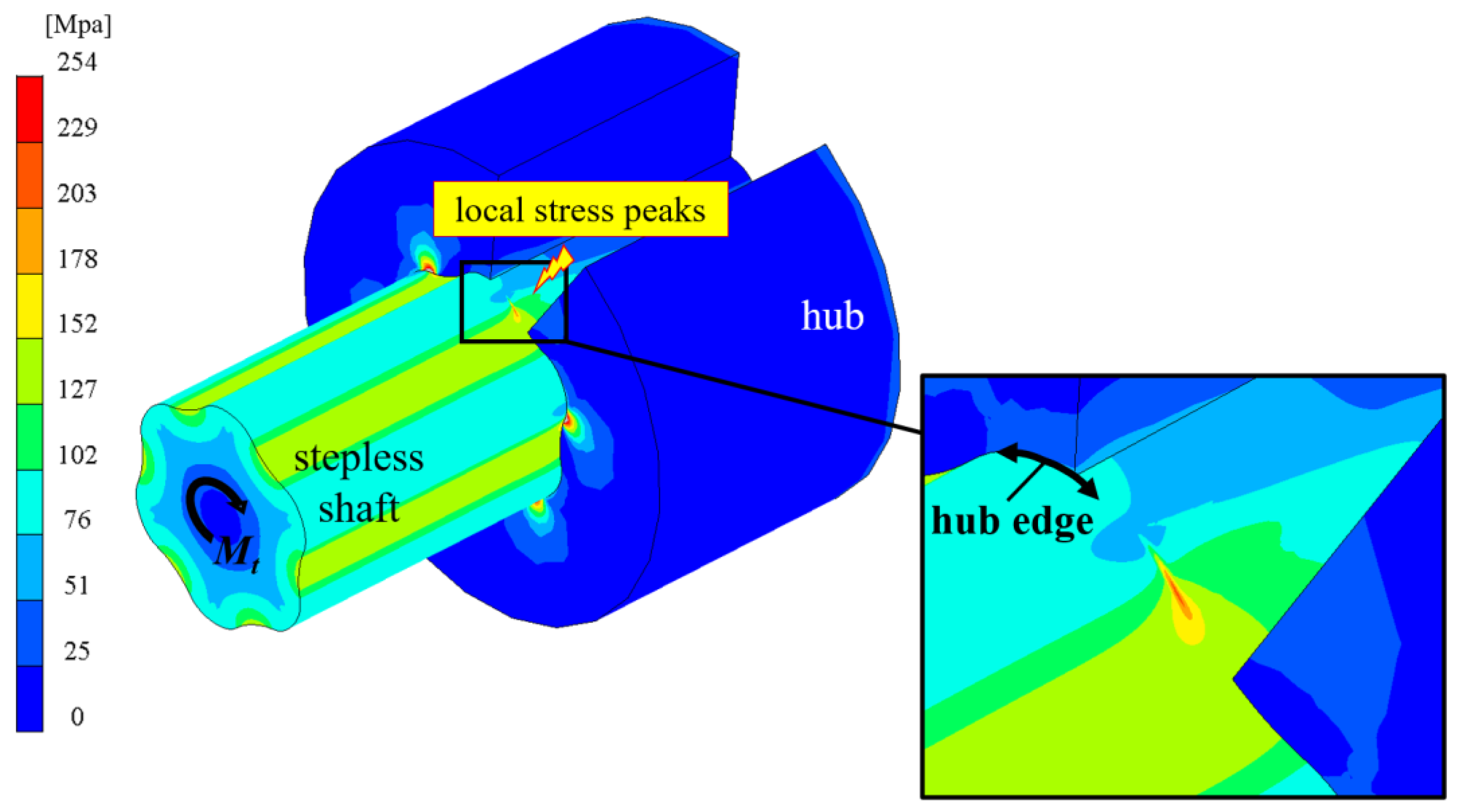
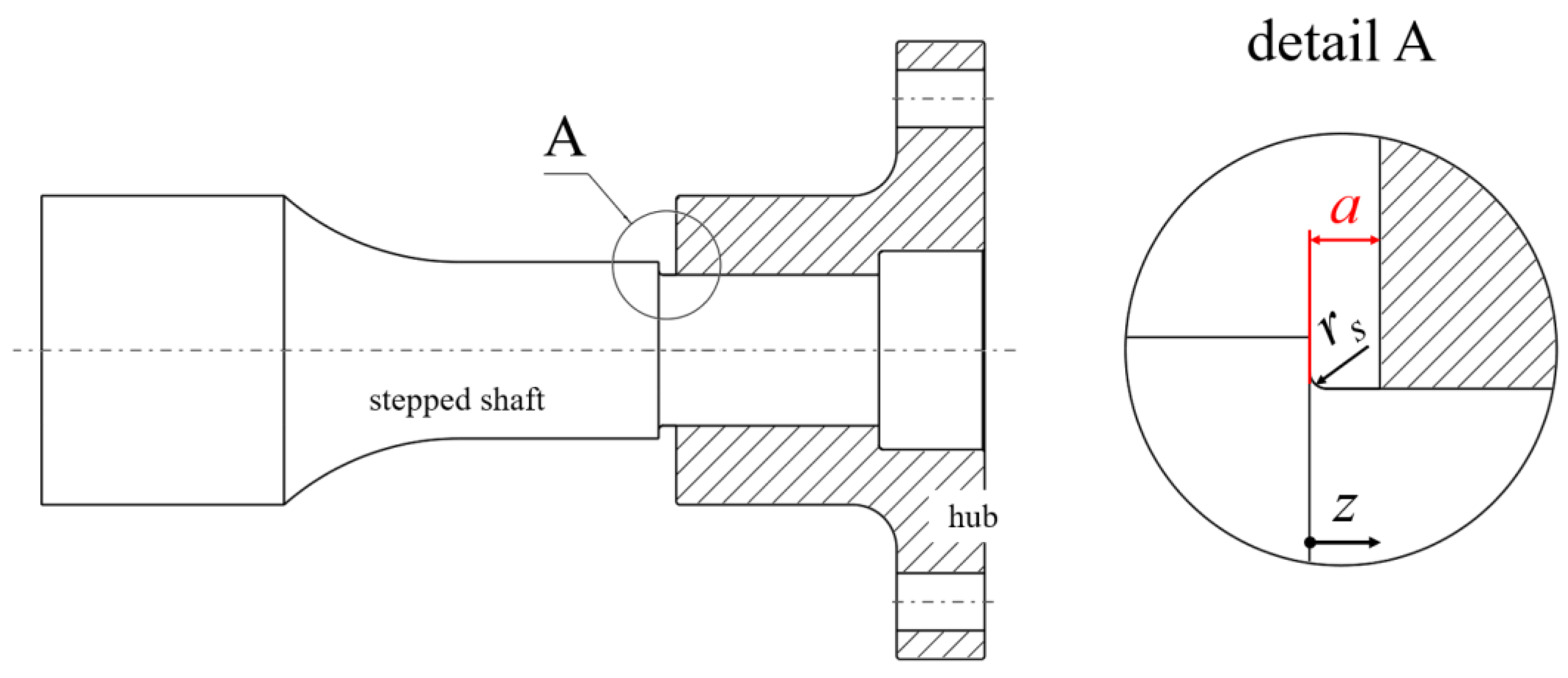
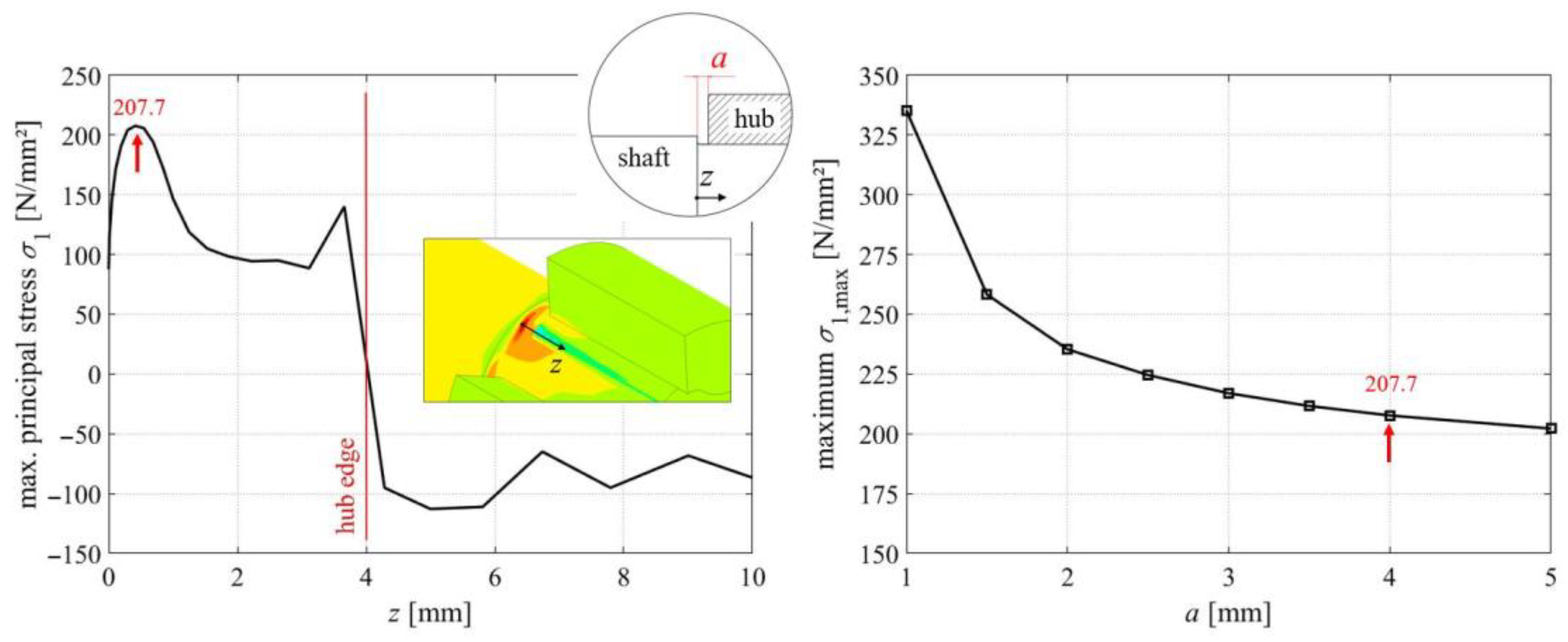
3.3. Superimposed Influence of the Hub Edge and the Shaft Shoulder
4. Experimental Investigations
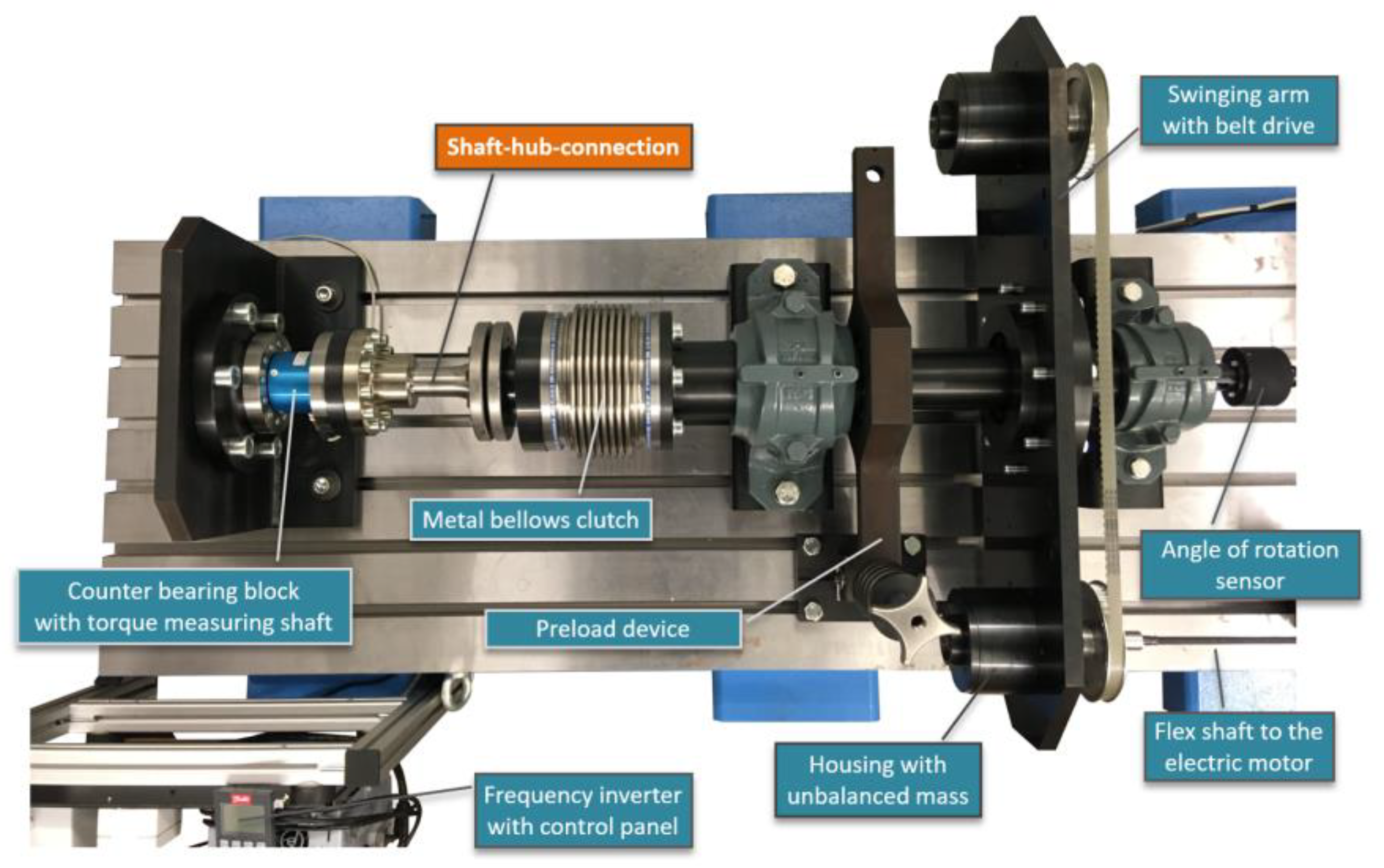
4.1. Test Bench and Test Parameters
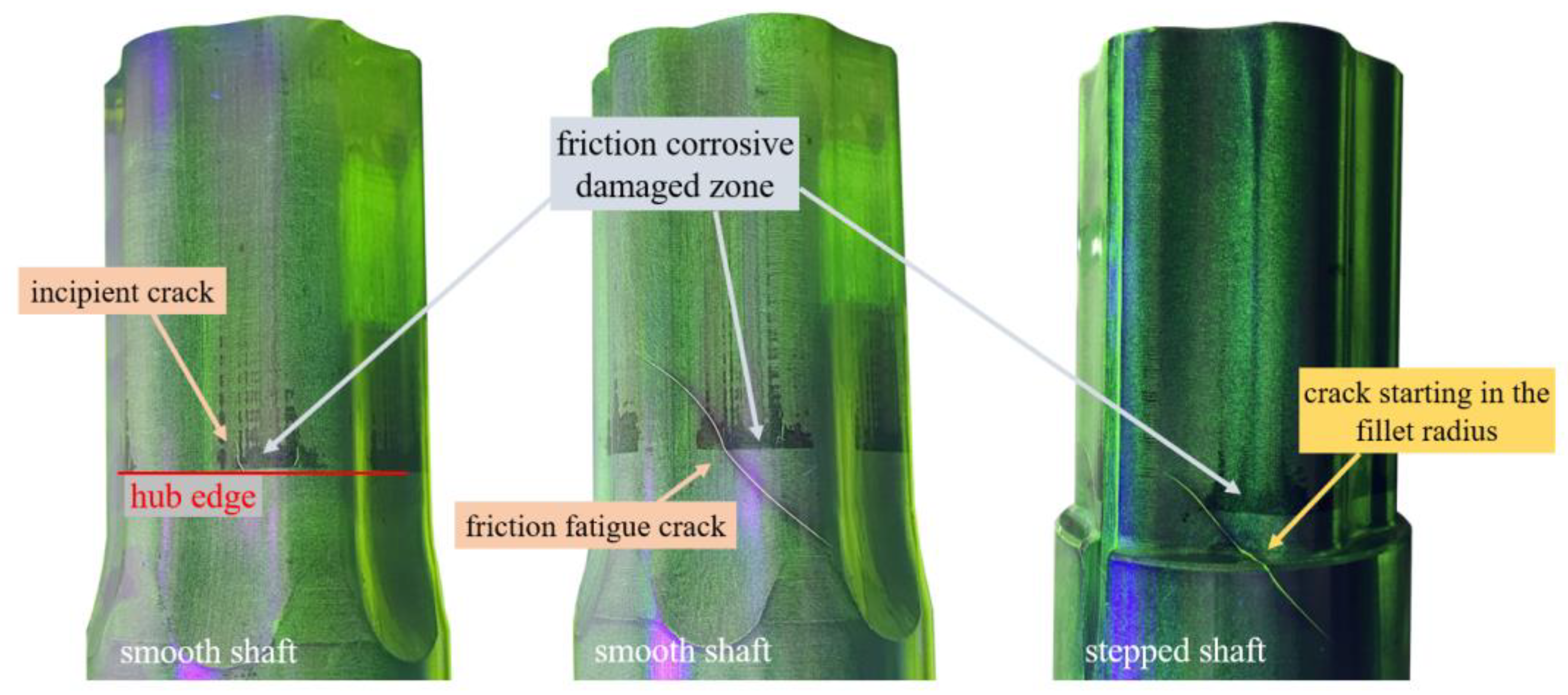
4.2. Influence of a Shaft Shoulder on the Dynamic Transmission Capacity
4.3. Interference between the Shaft and Hub
5. Epitrochoidal and Hypotrochoidal Connections with the Stepped Shaft
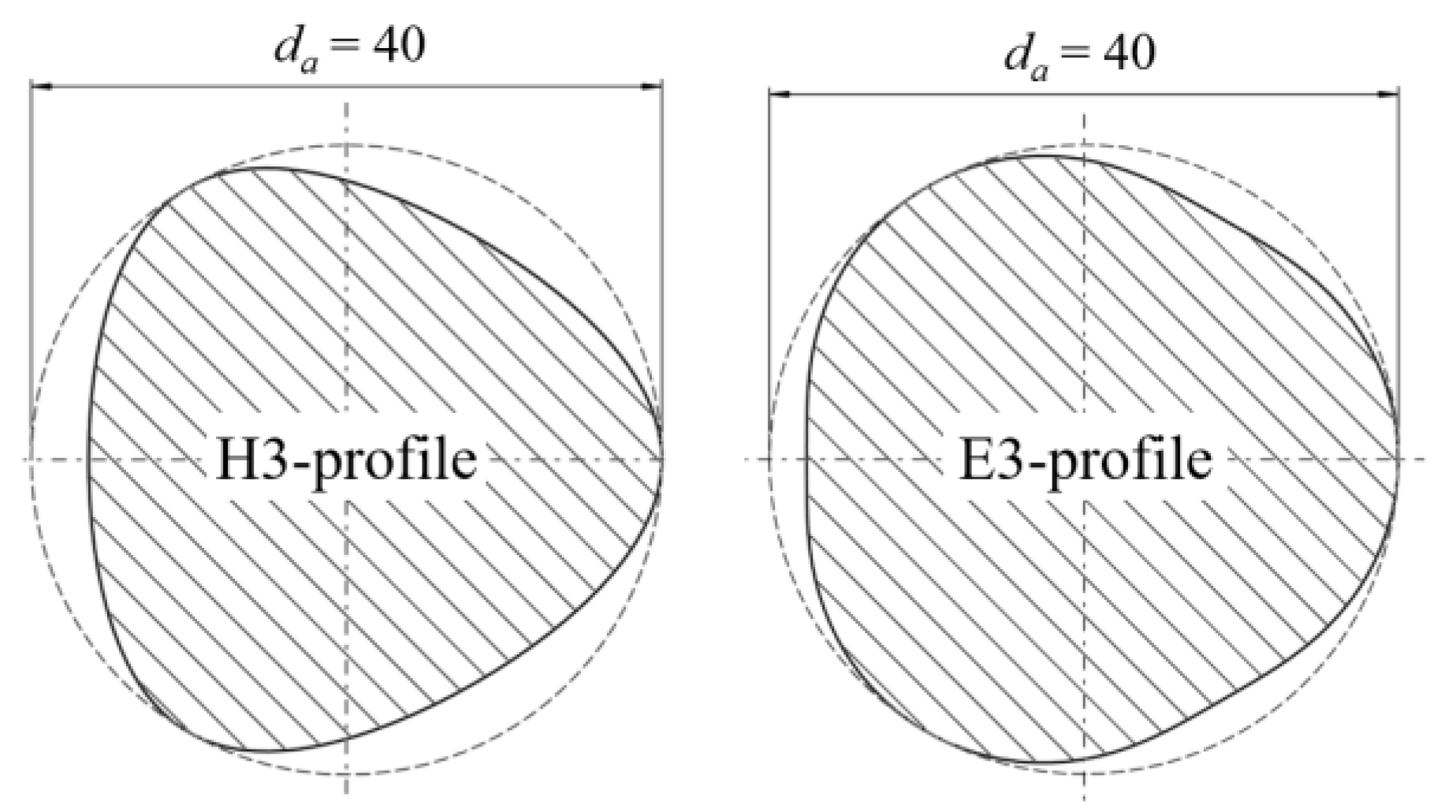
5.1. Geometry of Specimen
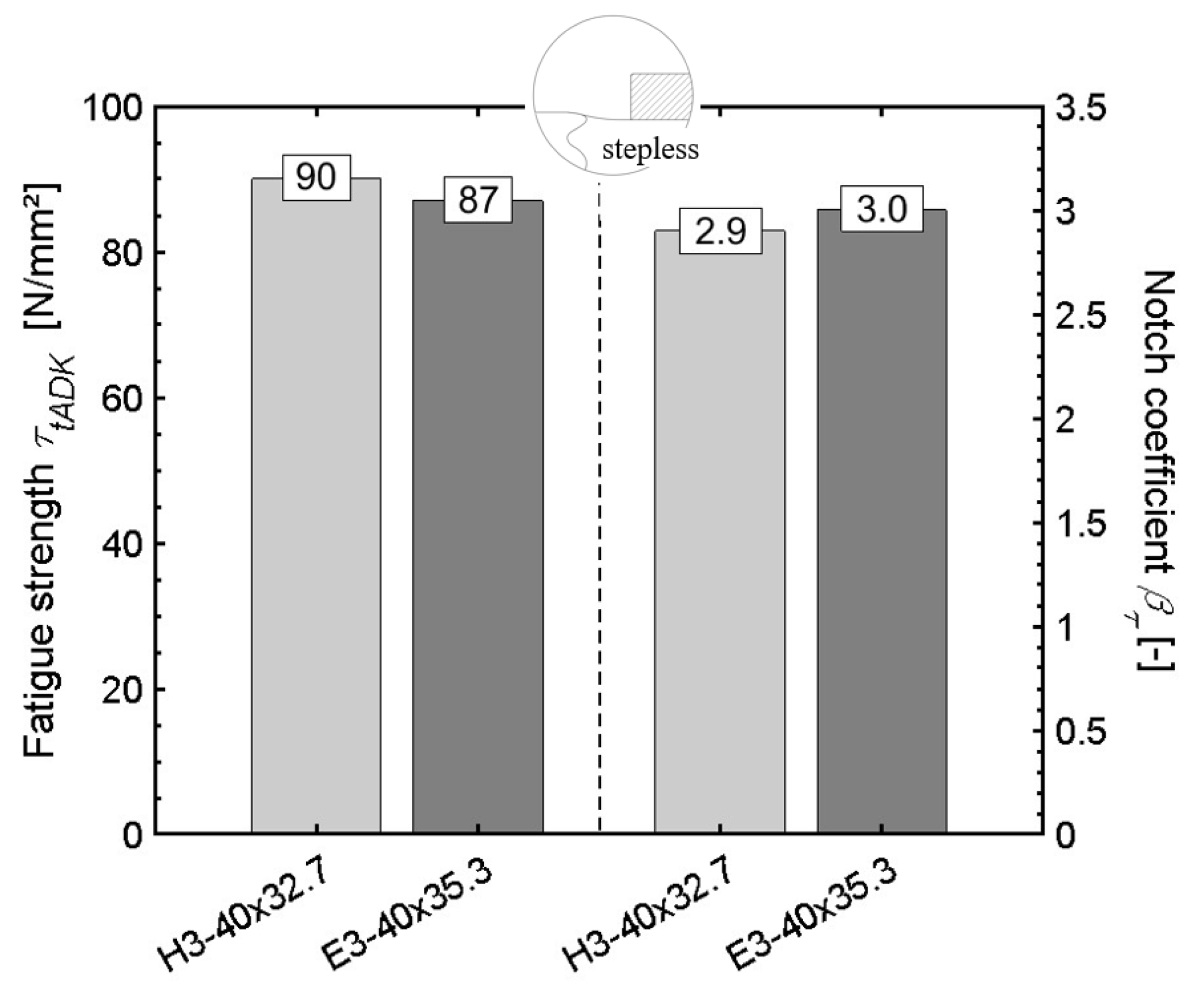
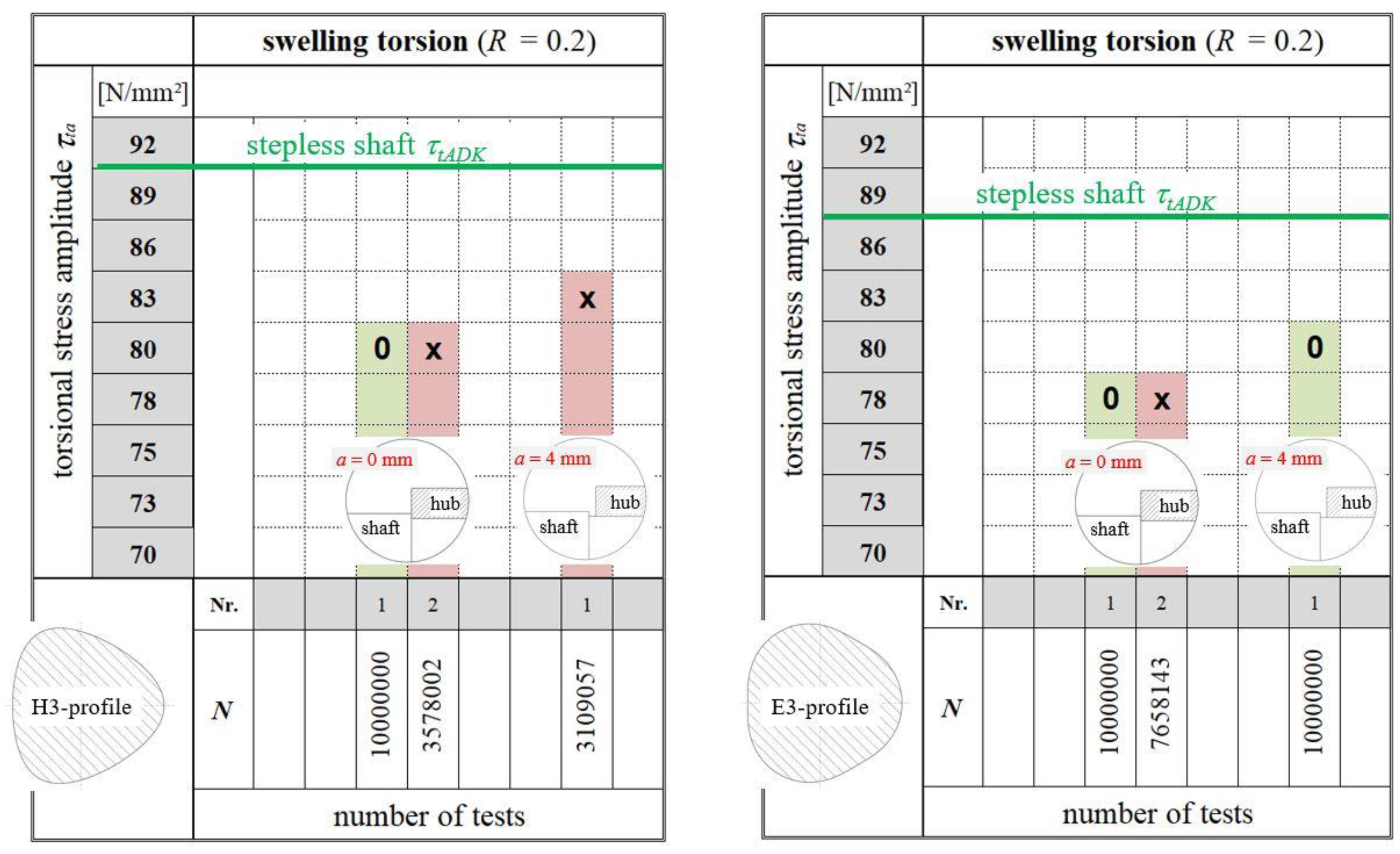
5.2. Dynamic Strength under Swelling Torsion
6. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Distance of the hub edge to the shaft shoulder; | |
| A | Surface area; |
| Tip diameter; | |
| Outer diameter of the hub; | |
| Root diameter; | |
| Eccentricity; | |
| Main eccentricity; | |
| Single eccentricity; | |
| FE | Finite element |
| FEA | Finite element analysis |
| l | Arc length; |
| Joining length; | |
| Torsional moment; | |
| n | Number of corners; |
| N | Number of load cycles; |
| Limit number of load cycles; | |
| Diameter ratio; | |
| Nominal radius; | |
| Fillet radius; | |
| R | Stress ratio (min/max); |
| s | Running coordinate; |
| t | Parameter angle; |
| Displacement in the spatial direction; | |
| U | Interference fit; |
| x | Cartesian coordinate; |
| y | Cartesian coordinate; |
| Notch coefficient; | |
| µ | Coefficient of friction; |
| Contact normal stress; | |
| Von Mises stress; | |
| Maximum principal stress; | |
| Torsional stress amplitude; | |
| Fatigue strength. |
References
- Ziaei, M. Optimale Welle-Nabe-Verbindung mit Mehrfachzyklischen Profilen, 5; VDI-Fachtagung “Welle-Nabe-Verbindungen”: Nürtingen, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ziaei, M.; Selzer, M. Entwicklung Kontinuierlicher Unrunder Innen- und Außenkonturen für Formschlüssige Welle-Nabe-Verbindungen und Ermittlung Analytischer Lösungsansätze; Forschungsvorhaben DFG-ZI1161-1/2, Abschlussbericht; Westsächsische Hochschule Zwickau: Zwickau, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- DIN 5480:2006-03. Involute Splines Based on Reference Diameters—Part 1: Generalities. Beuth-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2006.
- DIN 6885-1:1968-08. Drive Type Fastenings without Taper Action; Parallel Keys, Keyways, Deep Pattern. Beuth-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1968.
- DIN 3689-1:2021-11. Shaft to Collar Connection—Hypotrochoidal H-Profiles—Part 1: Geometry and Dimensions. Beuth-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2021.
- Vetter, S.; Leidich, E.; Ziaei, M.; Herrmann, M.; Hasse, A. Durability of hypotrochoidal shaft-hub connections under rotating bending with static torsion. Procedia Struct. Integr. 2019, 17, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuber, H. Kerbspannungslehre: Theorie der Spannungskonzentration Genaue Berechnung der Festigkeit; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, R.E. Stress Concentration Factors, 2nd ed.; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- DIN 32711-1:2009-03. Shaft to Collar Connection—Polygon Profil P3G—Part 1: Generalities and Geometry. Beuth-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2009.
- Reinholz, R. Tragfähigkeit von P3G-Welle-Nabe-Verbindungen bei Dauerschwingbeanspruchung. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität, Berlin, Germany, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Göttlicher, C. Entwicklung einer Verbesserten Festigkeitsberechnung für P3G-Polygon-Welle-Nabe-Verbindungen bei Torsion und Kombinierter Biege und Torsionsbeanspruchung. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Hochschule Darmstadt, Darmstadt, Germany, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Großmann, C. Fretting Fatigue of Shape-Optimised Polygon-Shaft-Hub Connections. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität, Berlin, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Daryusi, A. Beitrag zur Ermittlung der Kerbwirkung an Zahnwellen mit freiem und gebundenem Auslauf. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität, Dresden, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Sommer, S.; Ziaei, M.; Kunert, J. Einflüsse des Wellenabsatzes auf das Tragverhalten der Welle-Nabe-Verbindung mit M04-Profil unter reiner Torsion. In VDI-Fachtagung “Welle-Nabe-Verbindungen” Dimensionierung—Fertigung—Anwendung und Trends; VDI Verlag: Düsseldorf, Germany, 2022; ISBN 978-3-18-092408-3. [Google Scholar]
- Ziaei, M. Bending Stresses and Deformations in Prismatic Profiled Shafts With Noncircular Contours Based on Higher Hybrid Trochoids. Appl. Mech. 2022, 3, 1063–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hück, M. Ein verbessertes Verfahren für die Auswertung von Treppenstufenversuchen. Mater. Werkst. 1983, 14, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marc 2022 Manual; MSC Software Corporation: Newport Beach, CA, USA, 2022; Volume B, (Element Library).
- DIN 509:2022-12. Technical Product Documentation—Relief Grooves—Types Dimensions and Tolerances. Beuth-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2022.
- DIN 743-1:2012-12. Calculation of Load Capacity of Shafts and Axles—Part 1: General. Beuth-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2012.
- Ziaei, M. Torsionsspannungen in prismatischen, unrunden Profilwellen mit trochoidischen Konturen. Forsch. Im Ingenieurwesen 2021, 85, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaei, M. Gegenüberstellung von K- und H-Profil-Welle-Nabe-Verbindungen, Übertragungsverhalten der epi- und hypotrochoidischen Profile für die Lastfälle Torsion und Biegung, VDI-Fachtagung “Welle-Nabe-Verbindungen” Dimensionierung—Fertigung—Anwendung und Trends; VDI Verlag: Düsseldorf, Germany, 2022; ISBN 978-3-18-092408-3. [Google Scholar]


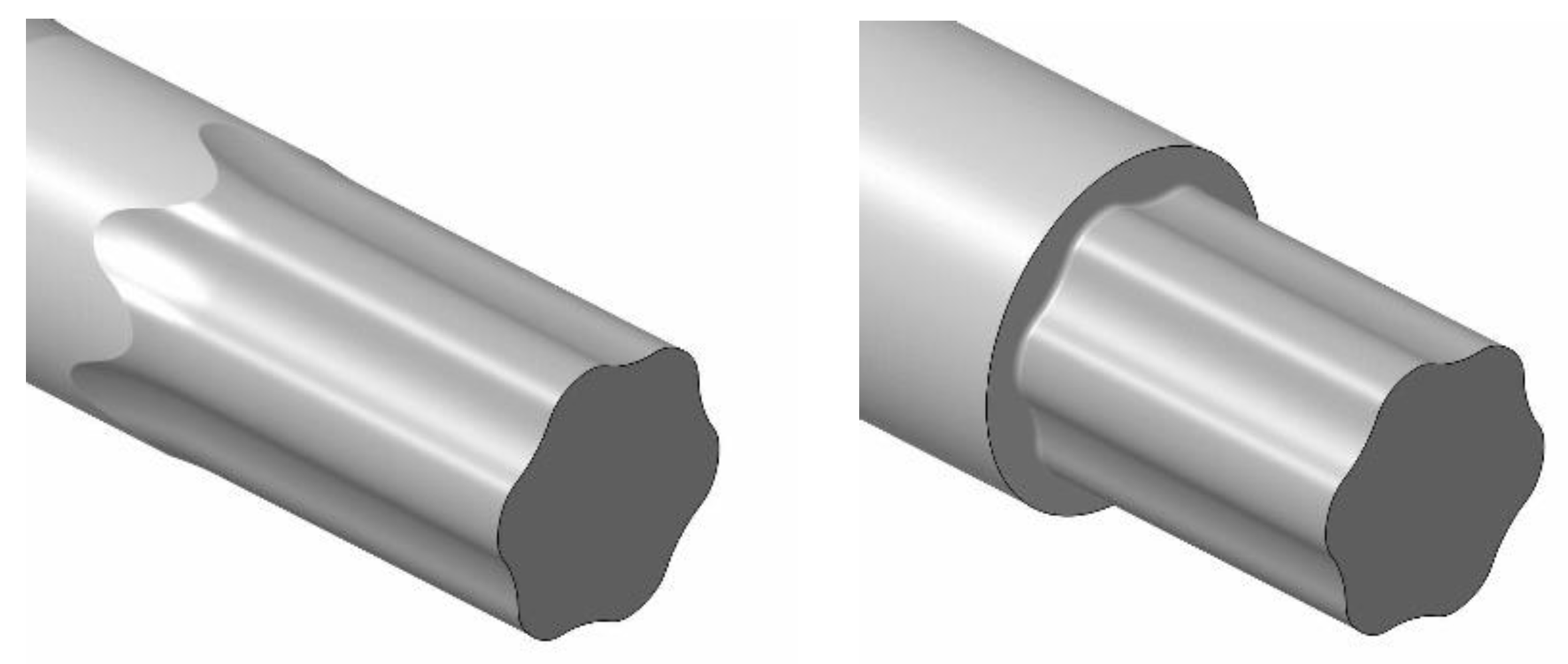


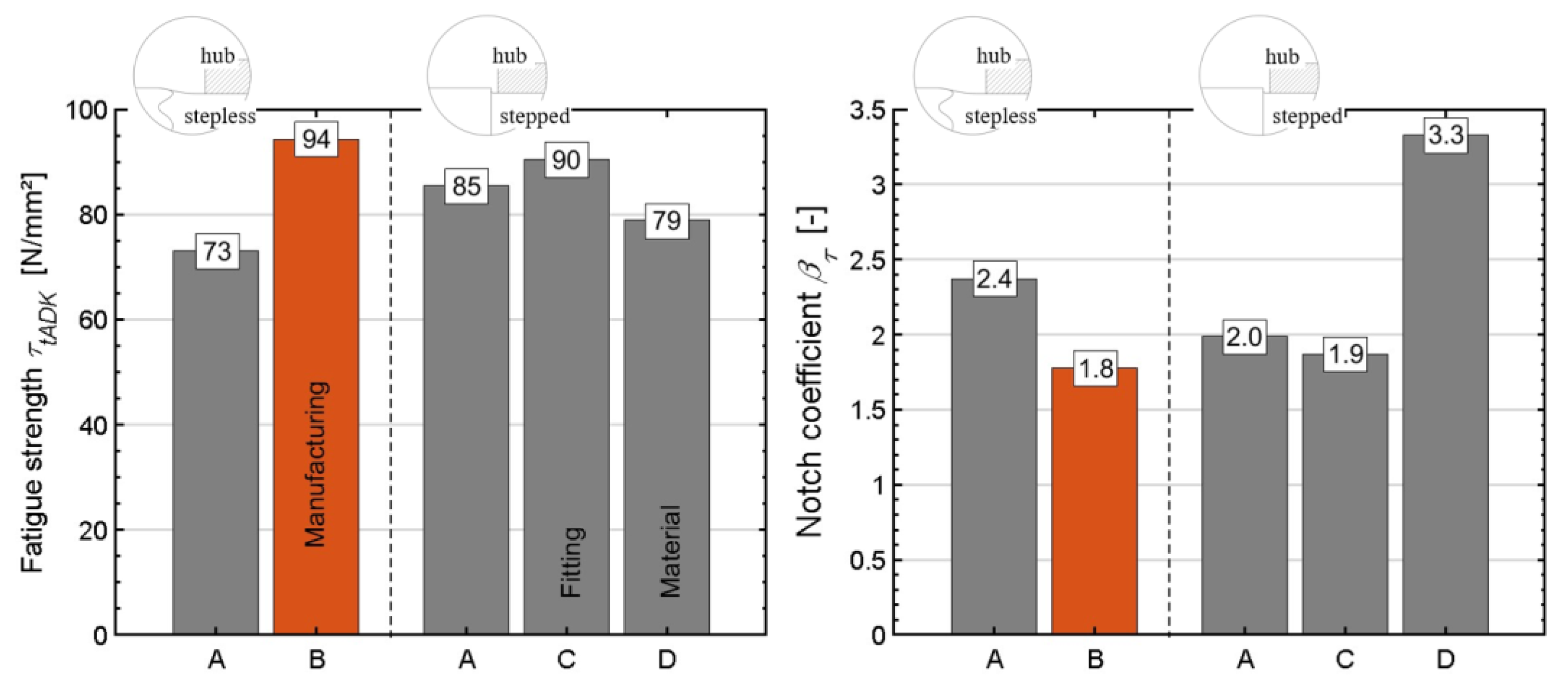
| Labelling | Material of the Shaft | Manufacturing Process Used to Create the Shaft | Fitting |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | C45R+N | Oscillating non-circular turning | Clearance fit |
| B | C45R+N | Hobbing | Clearance fit |
| C | C45R+N | Oscillating non-circular turning | Interference fit |
| D | 42CrMoS4+QT | Oscillating non-circular turning | Clearance fit |
| Profile Type | H-Profile | E-Profile |
|---|---|---|
| Nominal profile radius r | 18.181 mm | 18.824 mm |
| Eccentricity e | 1.818 mm | 1.177 mm |
| Number of corners n | 3 | 3 |
| Tip diameter da | 40.00 mm | 40.00 mm |
| Root diameter di | 32.73 mm | 35.29 mm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ziaei, M.; Selzer, M.; Sommer, H. Influence of a Shaft Shoulder on the Torsional Load-Bearing Behaviour of Trochoidal Profile Contours as Positive Shaft–Hub Connections. Eng 2024, 5, 834-850. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5020045
Ziaei M, Selzer M, Sommer H. Influence of a Shaft Shoulder on the Torsional Load-Bearing Behaviour of Trochoidal Profile Contours as Positive Shaft–Hub Connections. Eng. 2024; 5(2):834-850. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5020045
Chicago/Turabian StyleZiaei, Masoud, Marcus Selzer, and Heiko Sommer. 2024. "Influence of a Shaft Shoulder on the Torsional Load-Bearing Behaviour of Trochoidal Profile Contours as Positive Shaft–Hub Connections" Eng 5, no. 2: 834-850. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5020045
APA StyleZiaei, M., Selzer, M., & Sommer, H. (2024). Influence of a Shaft Shoulder on the Torsional Load-Bearing Behaviour of Trochoidal Profile Contours as Positive Shaft–Hub Connections. Eng, 5(2), 834-850. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5020045





