Chemical Interaction between the Sr4Al6O12SO4 Ceramic Substrate and Al–Si Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of Study Samples
2.2. Static Inmersion Test
2.3. Wettability Test
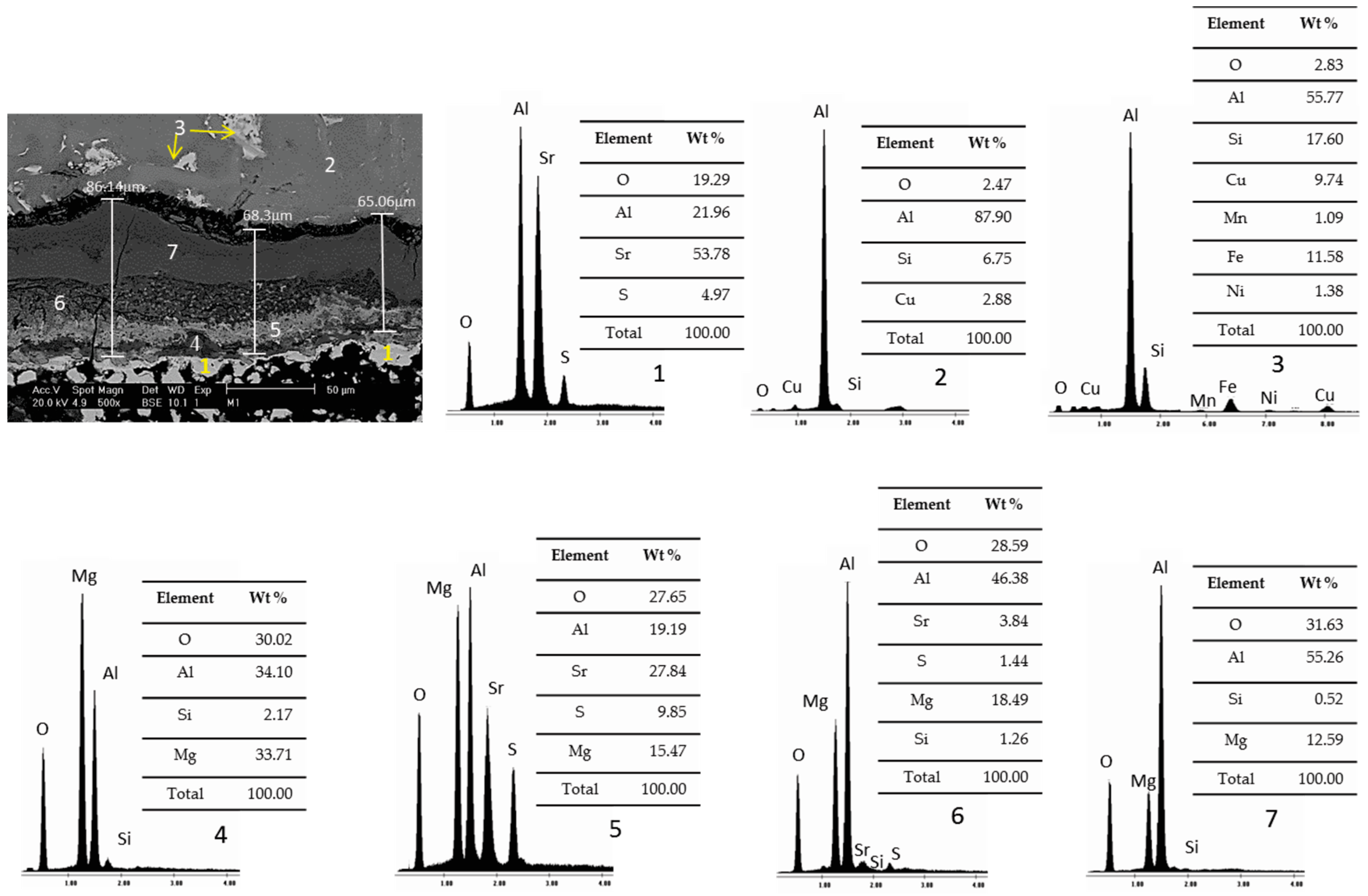
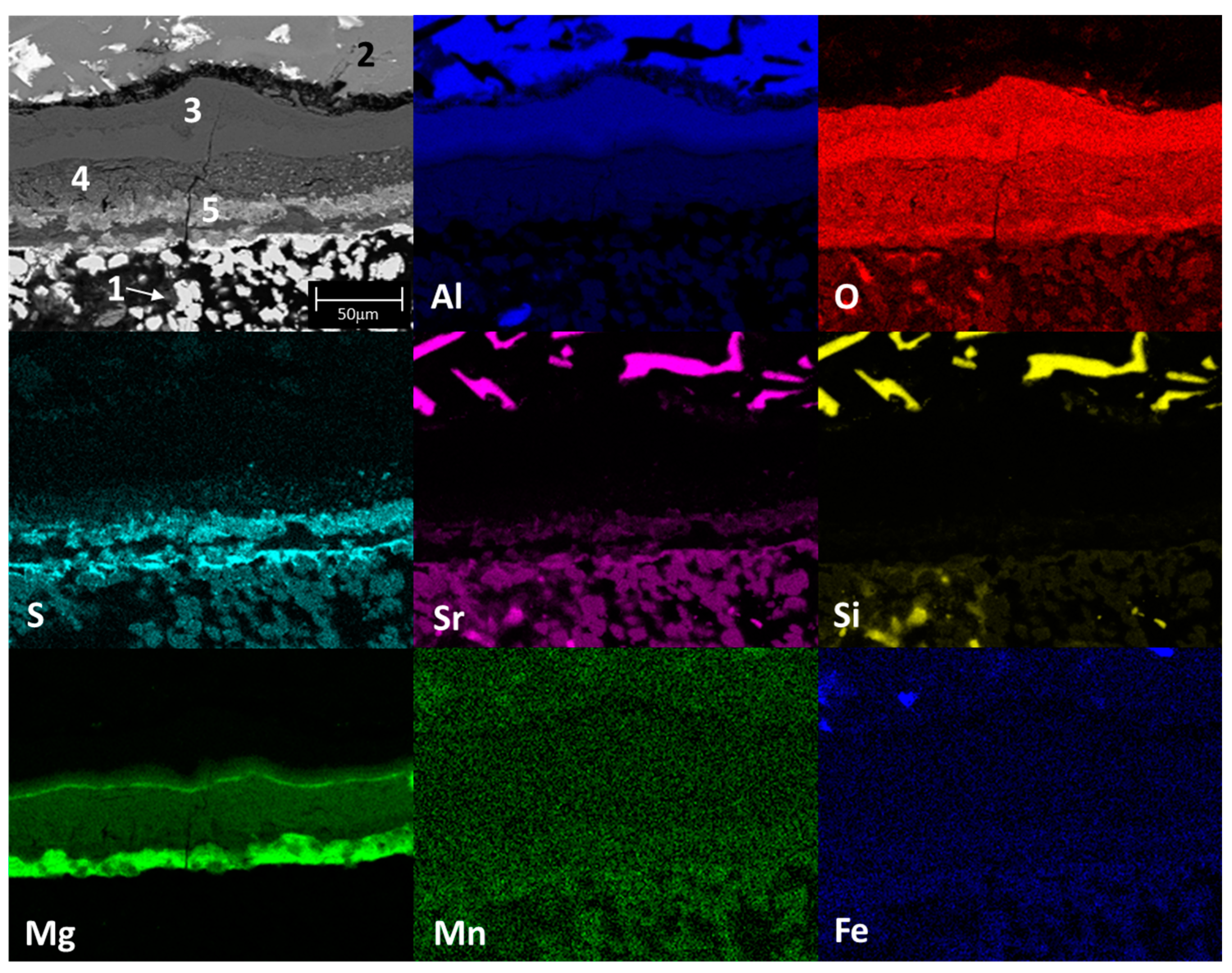
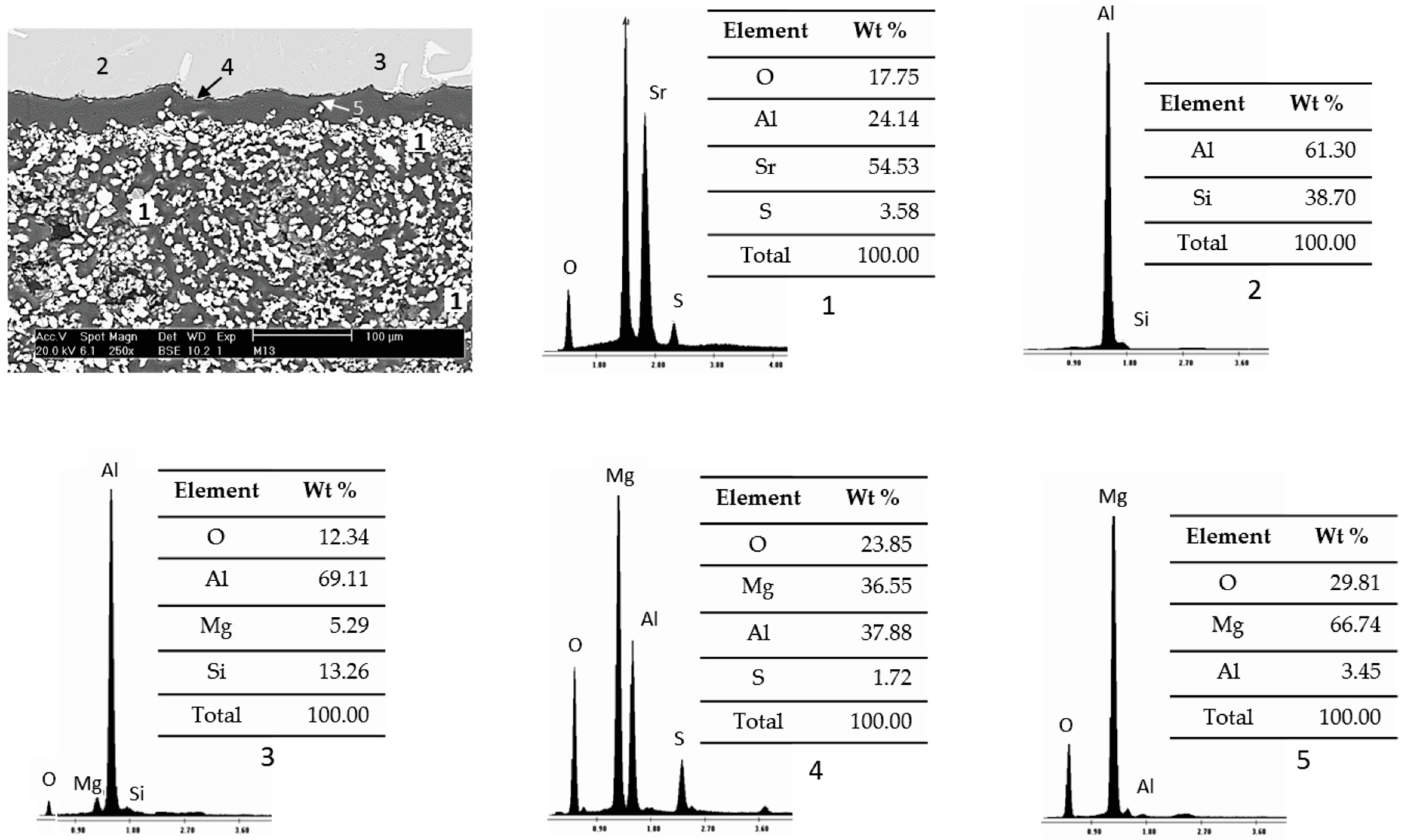
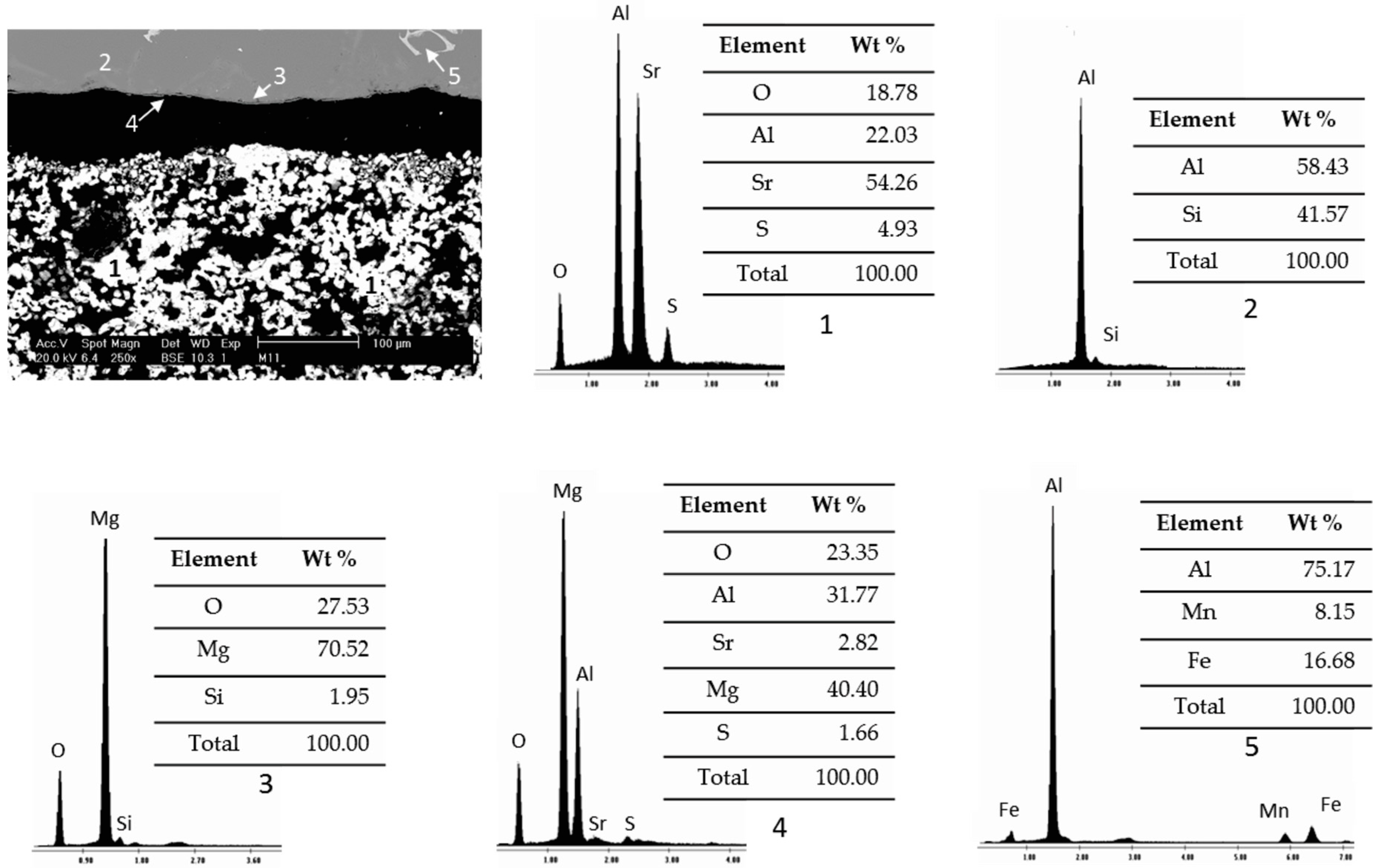
3. Results
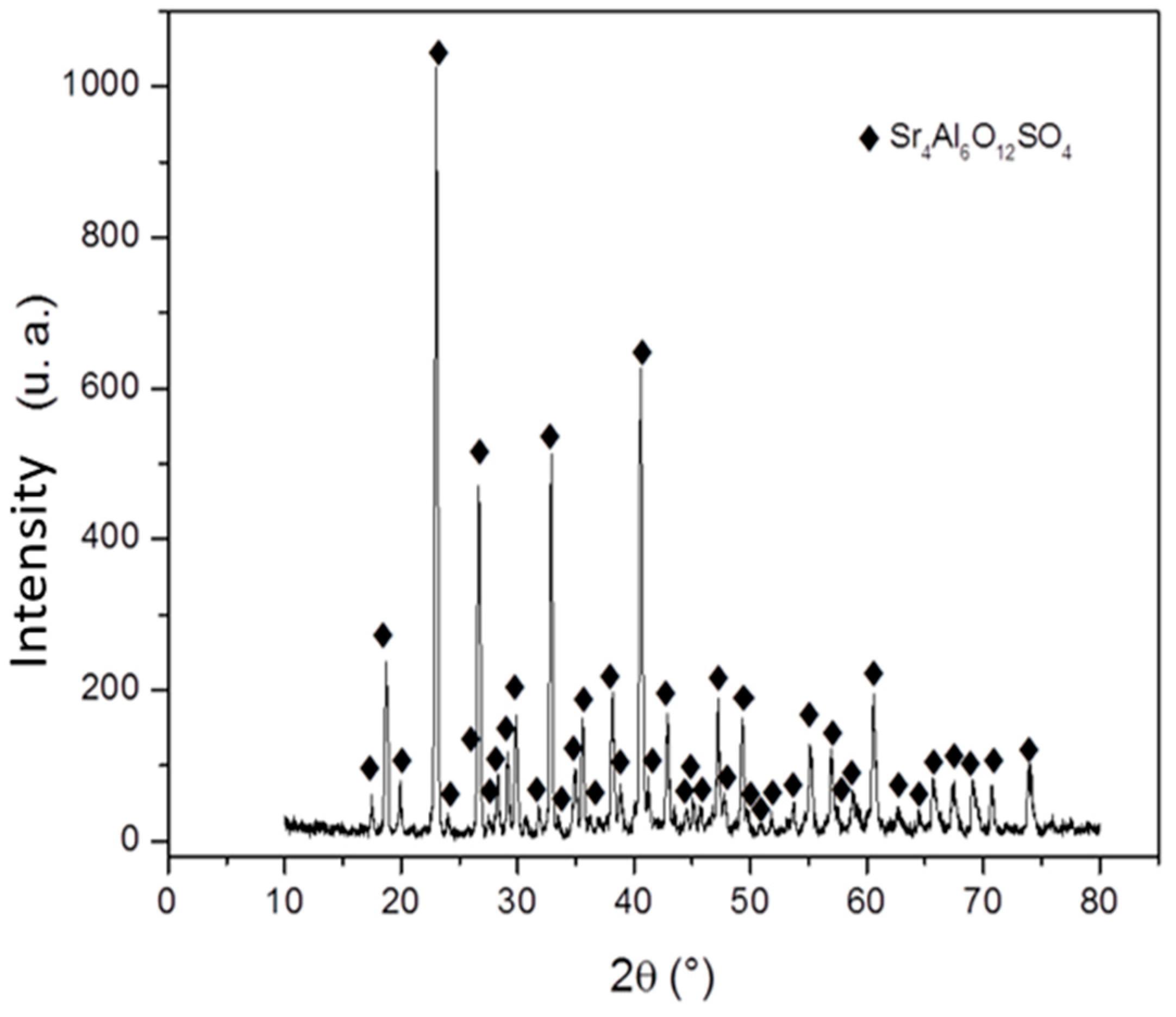
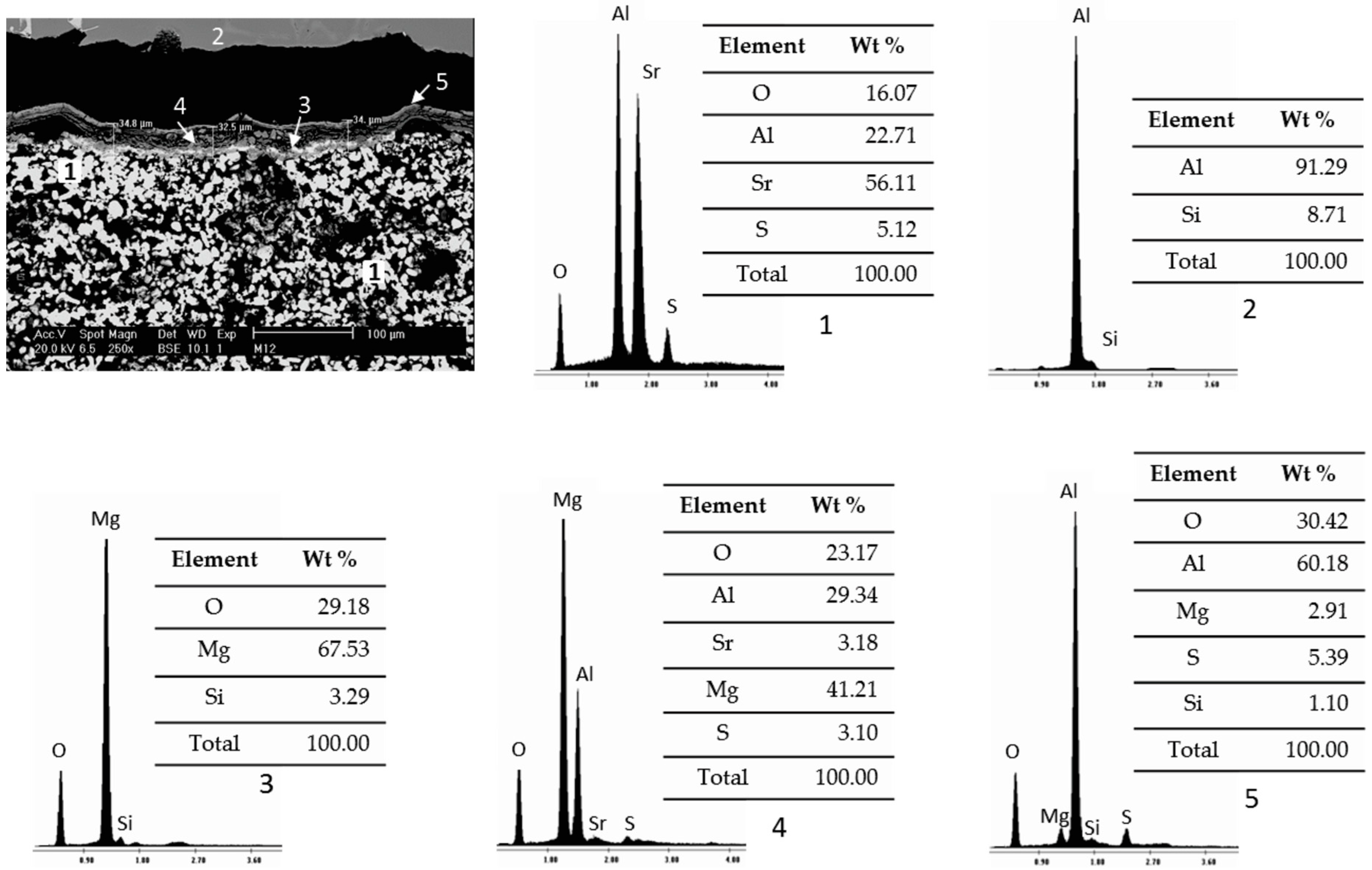
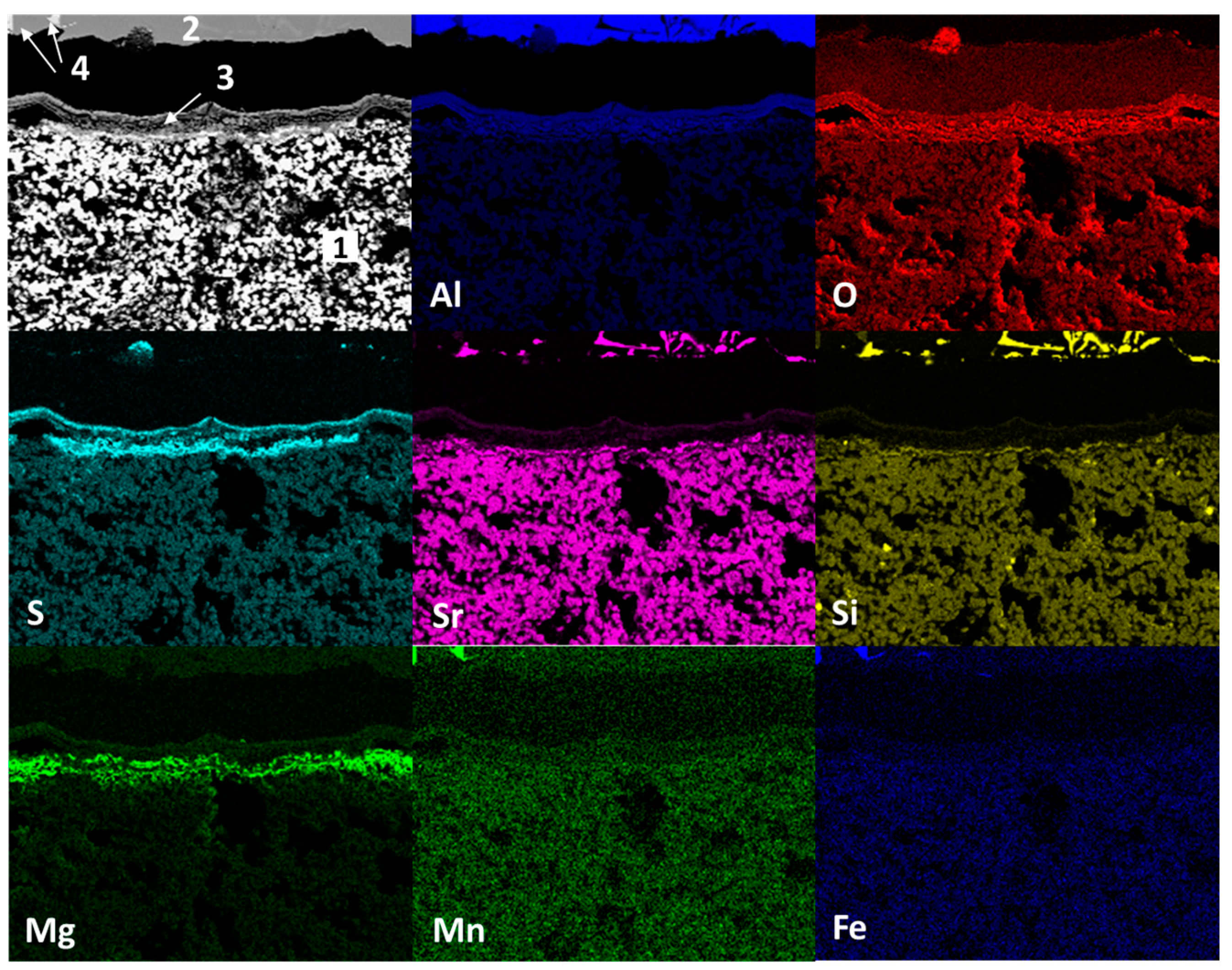
3.1. Characterization of Materials
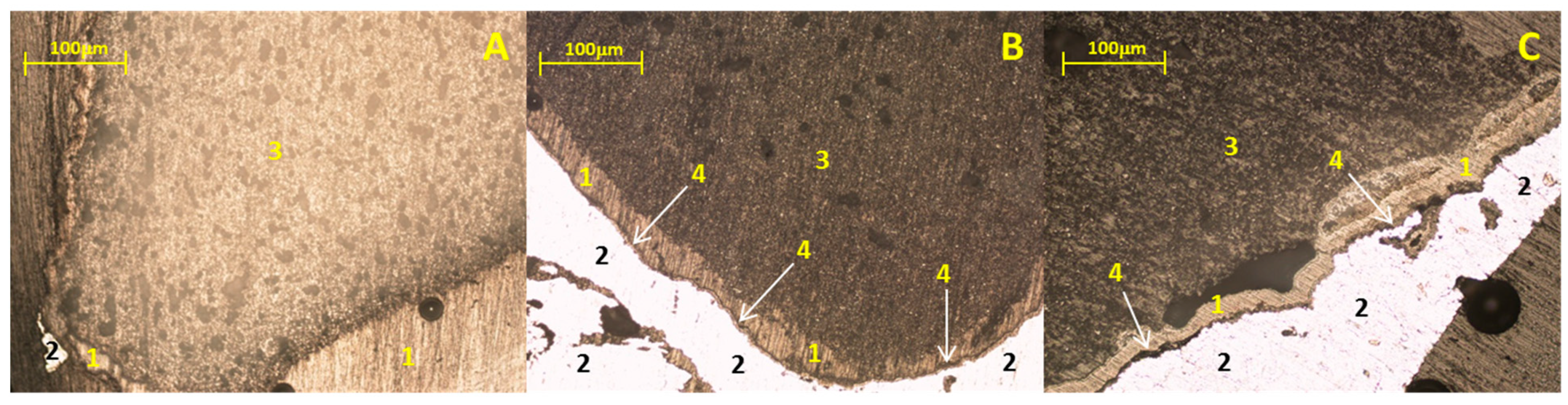
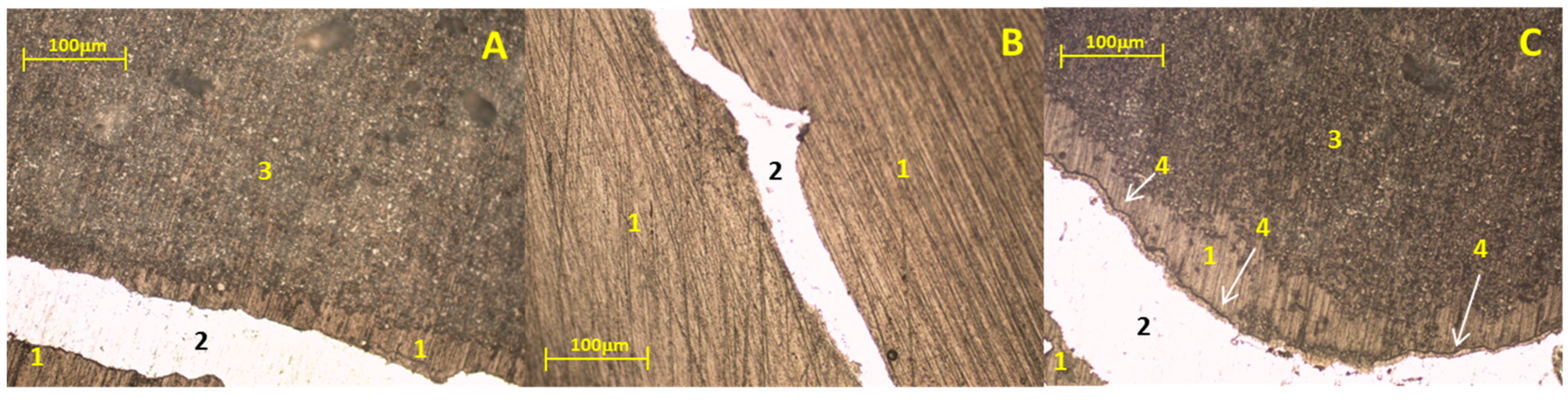
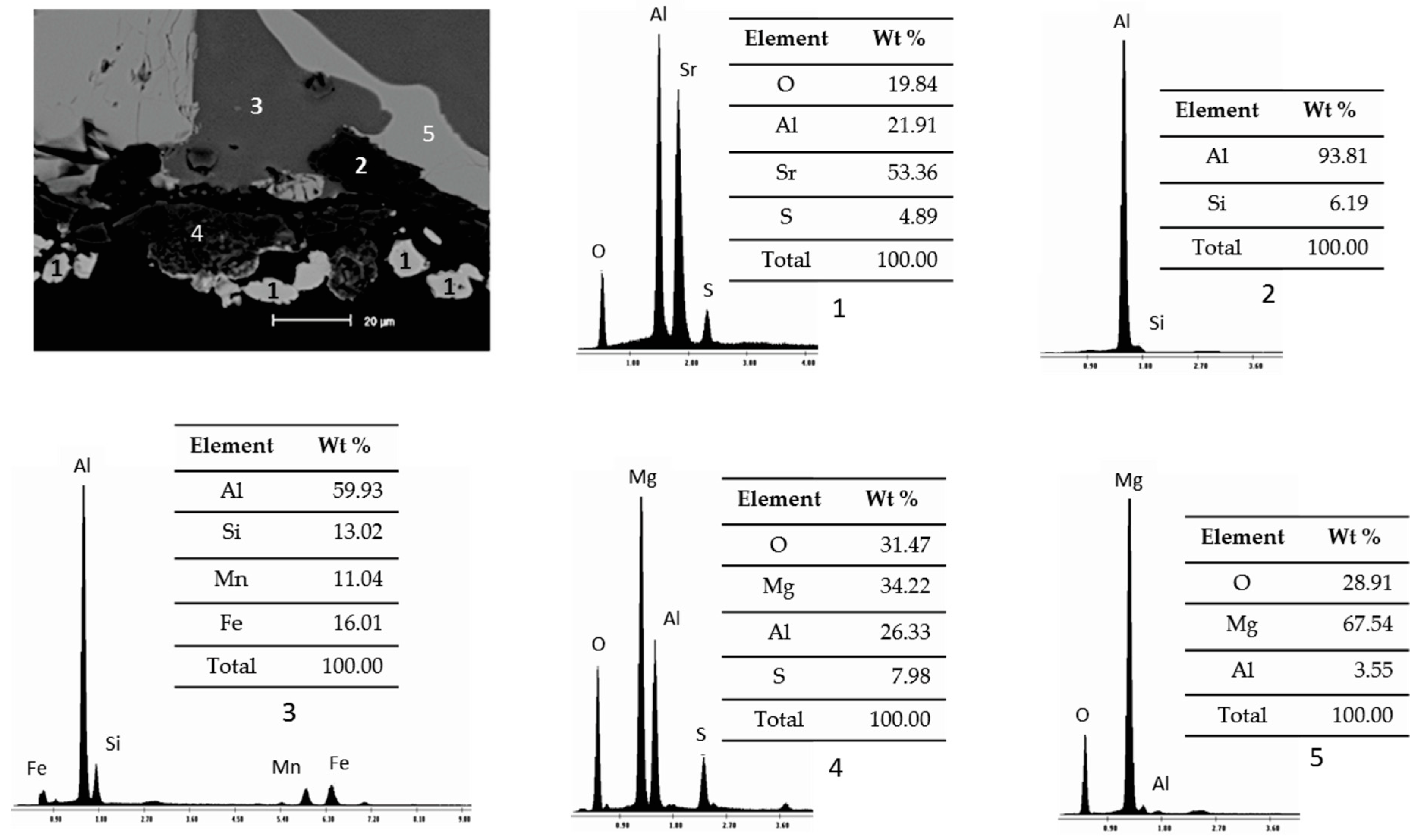
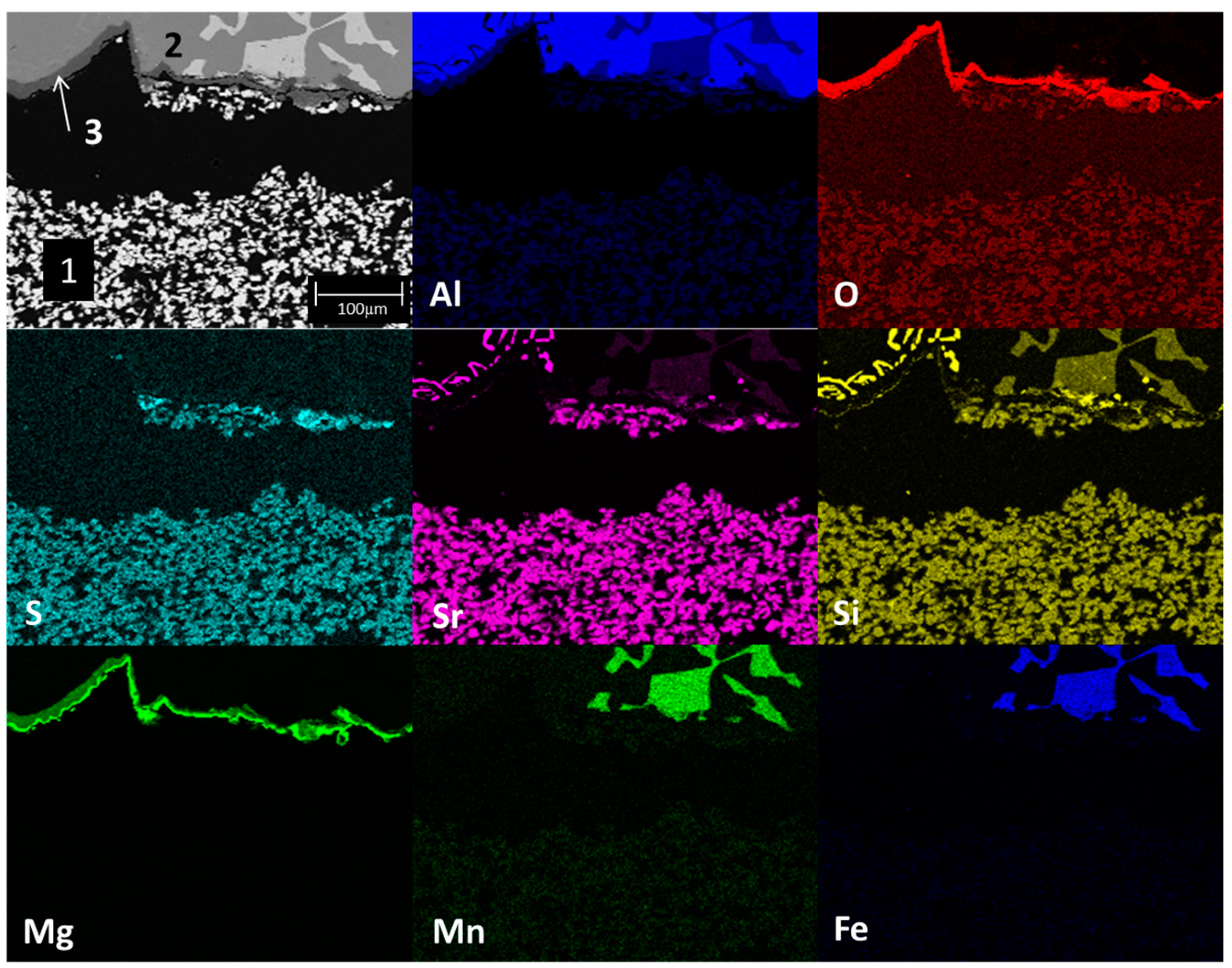
3.2. Static Immersion Test Results
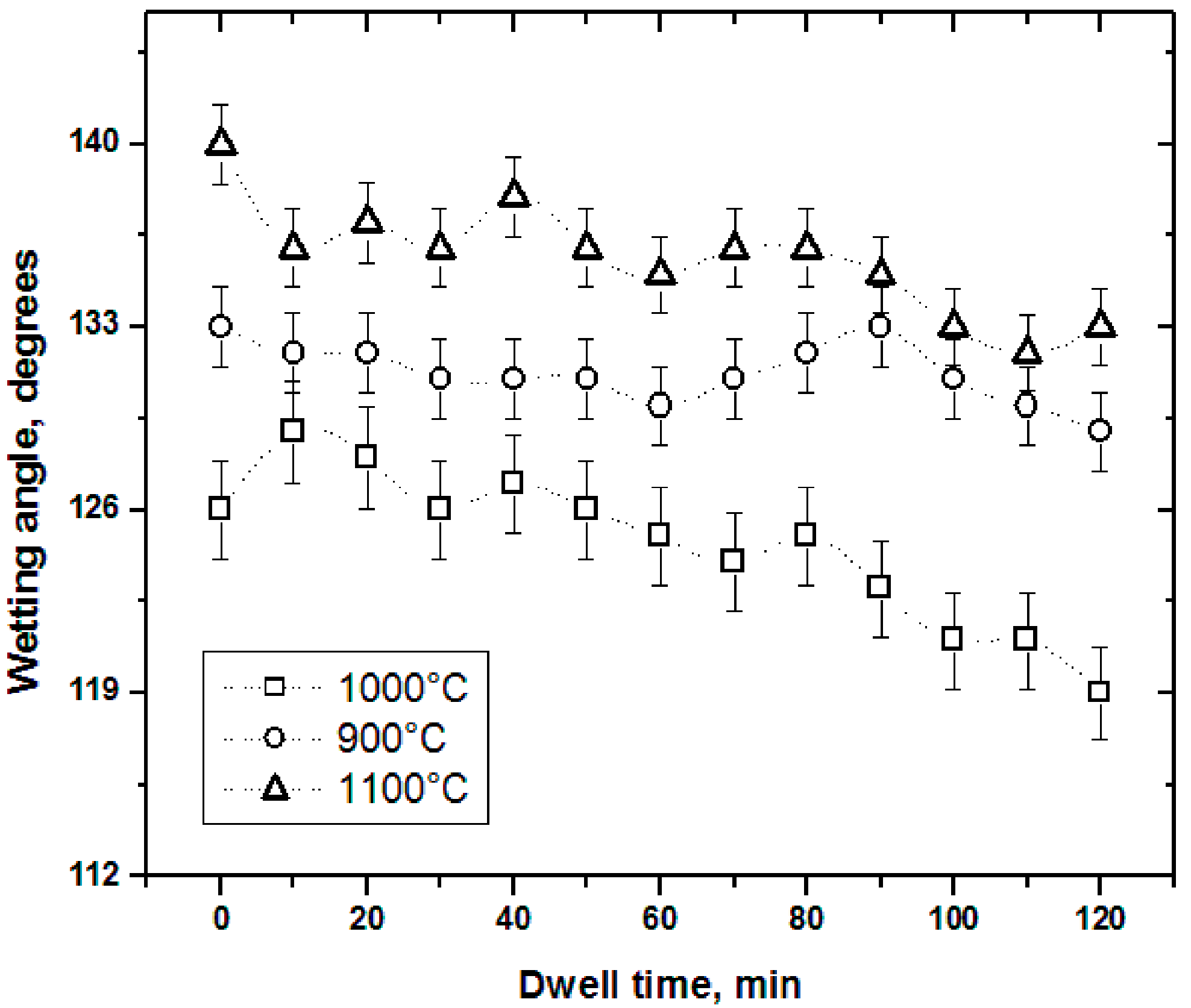
3.3. Wettability Test Results
4. Conclusions
- ○
- In general, when carrying out the static immersion tests, the performance of the Sr4Al6O12SO4 ceramic substrate can be highlighted since, despite the extreme conditions (1000 °C for 100 h) to which it was subjected, the corrosion layer on the samples was less than 100 µm, which makes the compound resistant to corrosion due to the alloys used;
- ○
- There are diffusion phenomena of chemical elements between the ceramic substrate and the aluminum alloy, which are a function of temperature;
- ○
- Furthermore, reported reaction products mainly contain alumina (Al2O3), magnesium oxide (MgO), and spinel (MgAl2O4). These compounds form a surface layer protecting the sample from chemical attack by liquid aluminum;
- ○
- These results suggest the use of the ceramic substrate Sr4Al6O12SO4 in the refractory industry, possibly as an additive to commercial refractory ceramics;
- ○
- For future work, carrying out the same study with the aluminum–magnesium alloy and as an additive in commercial refractory ceramics is considered prudent.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reddy, P.S.; Reddy, N.G.; Serjun, V.Z.; Mohanty, B.; Das, S.K.; Reddy, K.R.; Rao, B.H. Properties and Assessment of Applications of Red Mud (Bauxite Residue): Current Status and Research Needs. Waste. Biomass. Valori. 2020, 12, 1185–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujaczki, É.; Feigl, V.; Molnár, M.; Cusack, P.; Cutin, T.; Courtney, R.; O’Donoghue, L.; Davris, P.; Hugi, C.; Evangelou, M.W.H.; et al. Re-using bauxite residues: Benefits beyond (critical raw) material recovery. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2018, 93, 2498–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.S.; Suri, N.M.; Kant, S. Applications of bauxite residue: A mini-review. Waste Manag. Res. 2017, 35, 999–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, K. The History, Challenges, and New Developments in the Management and Use of Bauxite Residue. J. Sustain. Metall. 2016, 2, 316–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.E.H.; Haynes, R.J. Bauxite Processing Residue: A critical Review of its Formation, Properties, Storage, and Revegetation. Crit. Rev. Env. Sci. Technol. 2011, 41, 271–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.; Agathopoulos, S.; Ferreira, J.M. Reactions at the interface between Al2O3-SiO2 ceramics with additives of alkaline -earth oxides and liquid Al-Si alloy. J. Mater. Res. 2002, 17, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, E.T.; Mackenzie, D.S. Handbook of Aluminum: Alloy Production and Materials Manufacturing, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; pp. 1–115. [Google Scholar]
- Rahaman, M.N. Ceramic Fabrication Processes: An Introductory Overview Processing and Sintering, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2003; pp. 1–48. [Google Scholar]
- López-Perales, J.F.; Contreras, J.E.; Vázquez-Rodríguez, F.J.; Gómez-Rodríguez, C.; Díaz-Tato, L.; Banda-Muñoz, F.; Rodríguez, E.A. Partial replacement of a traditional raw material by blast furnace slag in developing a sustainable conventional refractory castable of improved physical-mechanical properties. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 306, 127266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, H.; Yu, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J. Synthesis and characterization of reaction-bonded calciun aluminium-titanate-bauxite-Sic composite refractories in a reducing atmosphere. Ceram. Int. 2018, 44, 15338–15345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurkov, A.L.; Pikhutin, I.A. Corrosion of aluminosilicate refractories by molten aluminum and melts based upon it in melting and casting units. Ref. Ind. Ceram. 2009, 50, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.L.; Reis, M.A.; Ferreira, L.L.H.C.; Nakachima, P.M. Brazilian refractory grade bauxite: A new alternative to refractories makers and users. Ceramic 2019, 65, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.P.; Pelissari, P.I.B.G.B.; de Oliveira, B.S.; Leiva, D.R.; de Mello, R.F.; Pandolfelli, V.C. Materials selection of furnace linings with multi-component refractory ceramics based on an evolutionary screening procedure. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 4113–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verran, G.O.; Kurzawa, U. An experimental study of aluminum can recycling using fusion in induction furnace. Res. Conserv. Recyc. 2008, 52, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonadia, P.; Valenzuela, F.A.O.; Bittencourt, L.R.; Pandolfelli, V.C. Aluminosilicates refractories for aluminum cell linings. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2005, 84, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, R.E. Refractories, Structure and Properties of, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 8079–8087. [Google Scholar]
- Sangghaleh, A.; Mohammad, H. An investigation on the wetting of polycrystalline alumina by aluminium. J. Mat. Proc. Technol. 2008, 197, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaire, C.; Desclaux, P. Effect of Alkalies and of a reducing atmosphere on the corrosion of refractories by molten aluminum. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1991, 74, 2781–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra, M.N.; Almanza, J.M.; Cortés, D.A.; Escobedo, J.C.; Torres, J. The effect of SrSO4 and BaSO4 on the corrosion and wetting by molten aluminum alloys of mullite ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2010, 36, 1205–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adabifiroozjaei, E.; Koshy, P.; Sorrell, C. Effects of AlPO4 addition on the corrosion resistance of andalusite-based low-cement castables with molten Al-alloy. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 33, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra, M.N.; Almanza, J.M.; Cortés, D.A.; Escobedo, J.C.; Pech, M.; Martínez, J. Effect of the addition of alkaline earth sulfates to mullite ceramics on the corrosion and wetting by Al-Mg alloy. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 35, 2189–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adabifiroozjaei, E.; Koshy, P.; Pardehkhorram, R.; Rastkerdar, E.; Sorrell, C. Interfacial reactions between BaAl2Si2O8 and molten Al alloy at 850 °C. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 98, 3299–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, J.A.; Ríos, E.; Rocha, E.; Almanza, J.M.; Torres, J.; Refugio, E. Kinetics of formation and crystal structure determination of Sr4Al6O12SO4. Mater. Res. 2016, 19, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storoshenko, M.S.; Umanskyi, O.P.; Terentiev, O.; Krasovkyy, V.P.; Martzenyuk, I.S.; Gubin, Y. Contact interaction of chromium diboride with iron-based self-fluxing alloy. Powder Metall. Met. Ceram. 2023, 61, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaoyan, C.; Zhihui, L.; Yanjie, Z.; Chengkang, Q.; Shurong, L.; Fei, L. Wetting and interfacial phenomena between a Ni-based superalloy and silica-based ceramic cores with ZrSiO4 additions. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2671, 012025. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, J.A.; Rocha, E.; Torres, J.; Almanza, J.M. Synthesis by solid state reaction of the Sr4Al6O12SO4 compound. J. Ceram. Process. Res. 2011, 12, 310–313. [Google Scholar]
- Sangghaleh, A.; Halali, M. Effect of magnesium addition on the wetting of alumina by aluminium. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 8202–8206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Aluminum Alloy | Si | Fe | Cu | Mn | Mg | Cr | Ni | Zn | Ti | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al–Si | 7.420 | 0.717 | 2.630 | 0.437 | 0.454 | 0.050 | 0.041 | 0.637 | 0.158 | 87.456 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez-García, J.A.; Calles-Arriaga, C.A.; López-García, R.D.; Castillo-Robles, J.A.; Rocha-Rangel, E. Chemical Interaction between the Sr4Al6O12SO4 Ceramic Substrate and Al–Si Alloys. Eng 2024, 5, 461-476. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5010025
Rodríguez-García JA, Calles-Arriaga CA, López-García RD, Castillo-Robles JA, Rocha-Rangel E. Chemical Interaction between the Sr4Al6O12SO4 Ceramic Substrate and Al–Si Alloys. Eng. 2024; 5(1):461-476. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5010025
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez-García, José Amparo, Carlos Adrián Calles-Arriaga, Ricardo Daniel López-García, José Adalberto Castillo-Robles, and Enrique Rocha-Rangel. 2024. "Chemical Interaction between the Sr4Al6O12SO4 Ceramic Substrate and Al–Si Alloys" Eng 5, no. 1: 461-476. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5010025
APA StyleRodríguez-García, J. A., Calles-Arriaga, C. A., López-García, R. D., Castillo-Robles, J. A., & Rocha-Rangel, E. (2024). Chemical Interaction between the Sr4Al6O12SO4 Ceramic Substrate and Al–Si Alloys. Eng, 5(1), 461-476. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5010025







