A High-Quality Random Number Generator Using Multistage Ring Oscillators and Fast Fourier Transform-Based Noise Extraction
Abstract
1. Introduction
- •
- A novel approach to generate true random numbers using a noise-based XOR combination of different multistage ring oscillators (MROs) with varying geometries and startup voltages (3, 5, and 7 stages). This approach helps mask potential periodicities or biases which existed in individual MRO outputs, leading to a more robust and unpredictable random number sequence.
- •
- Evaluation and validation of the level of randomness in TRNG implementations using the guidelines outlined in the NIST 800-22 standard recommendation. This ensures that the generated random numbers are suitable for cryptographic applications by passing a battery of tests designed to detect non-randomness.
- •
- Demonstrate that the combination of 3-, 5-, and 7-stage MROs with distinct geometries and startup voltages achieves the optimal balance between randomness and throughput. This finding provides valuable insights for designing MRO-based TRNGs for specific applications.
2. Multistage Ring Oscillator-Based TRNG Design and Implementation
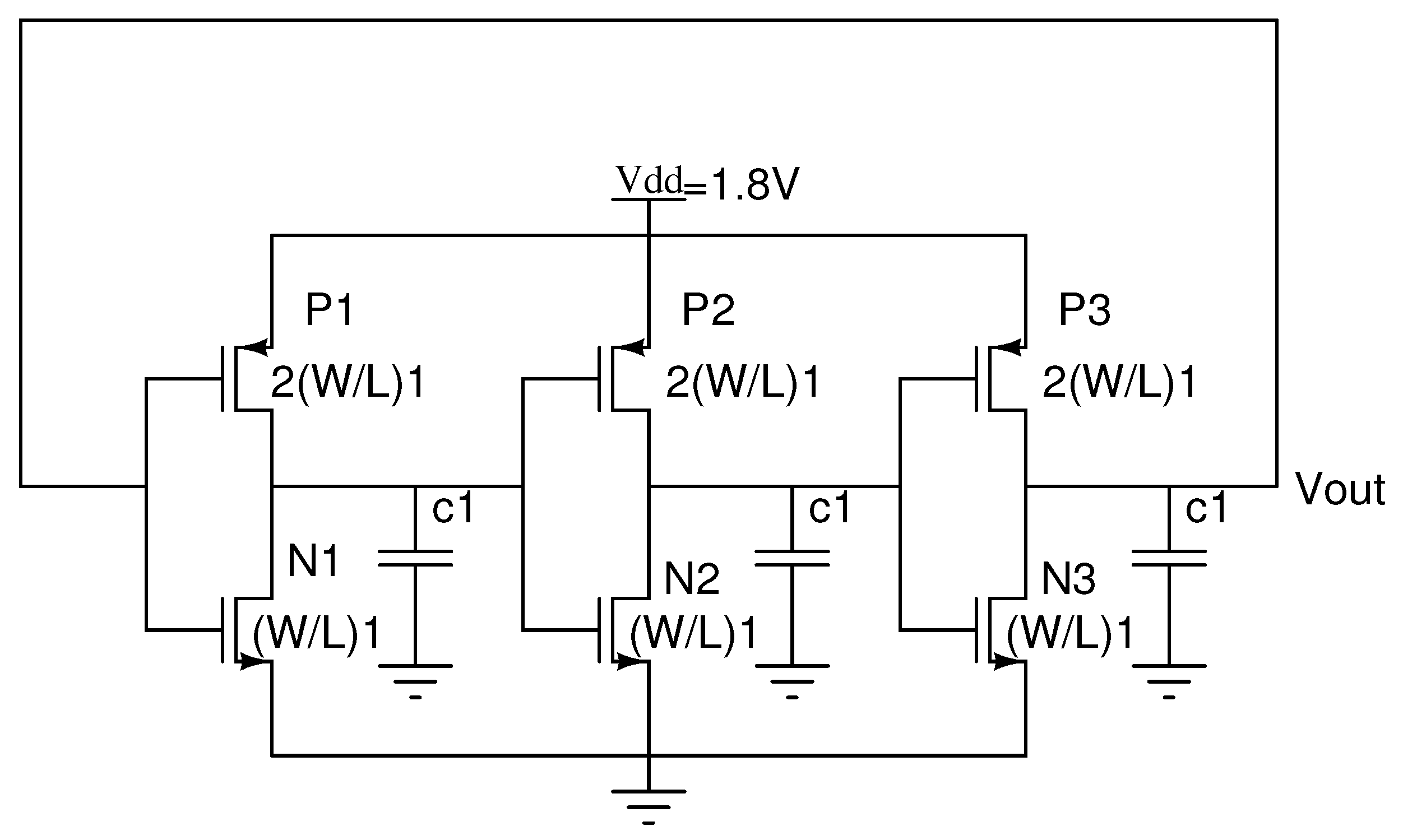
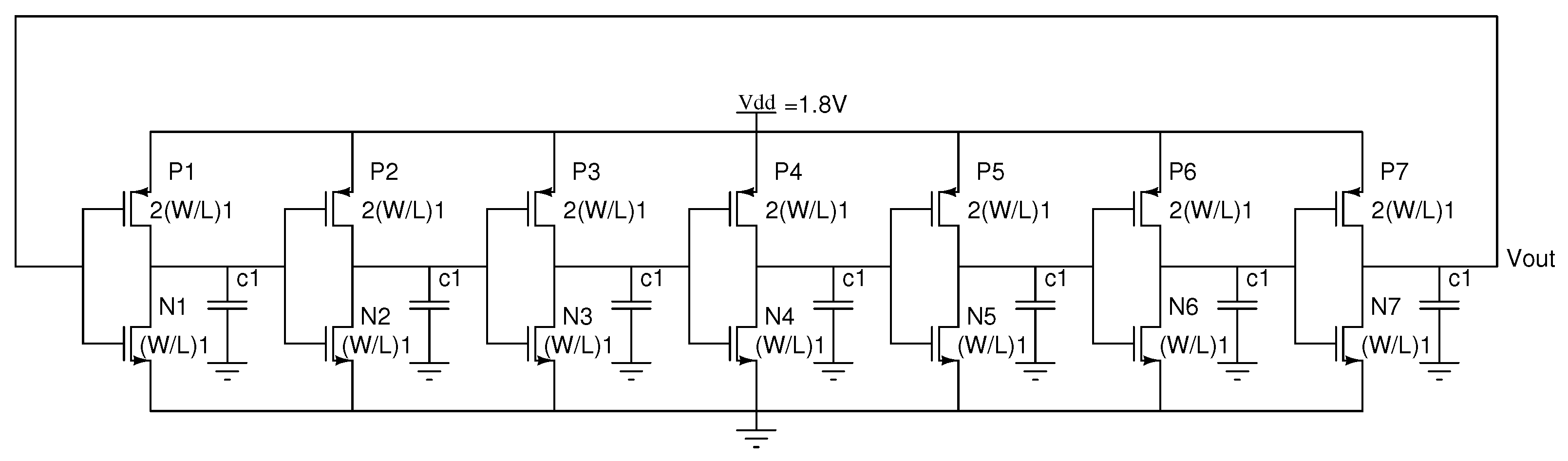
2.1. Three-Stage Ring Oscillator
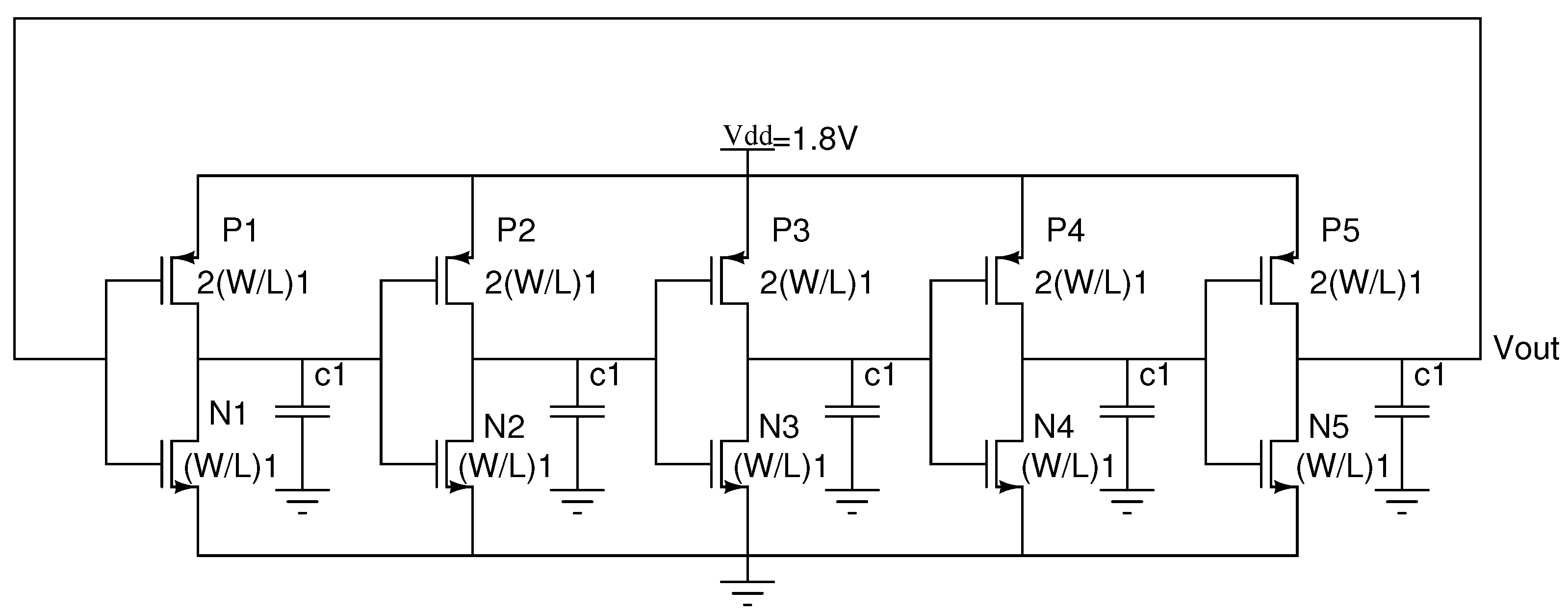
2.2. Five-Stage Ring Oscillator
2.3. Seven-Stage Ring Oscillator
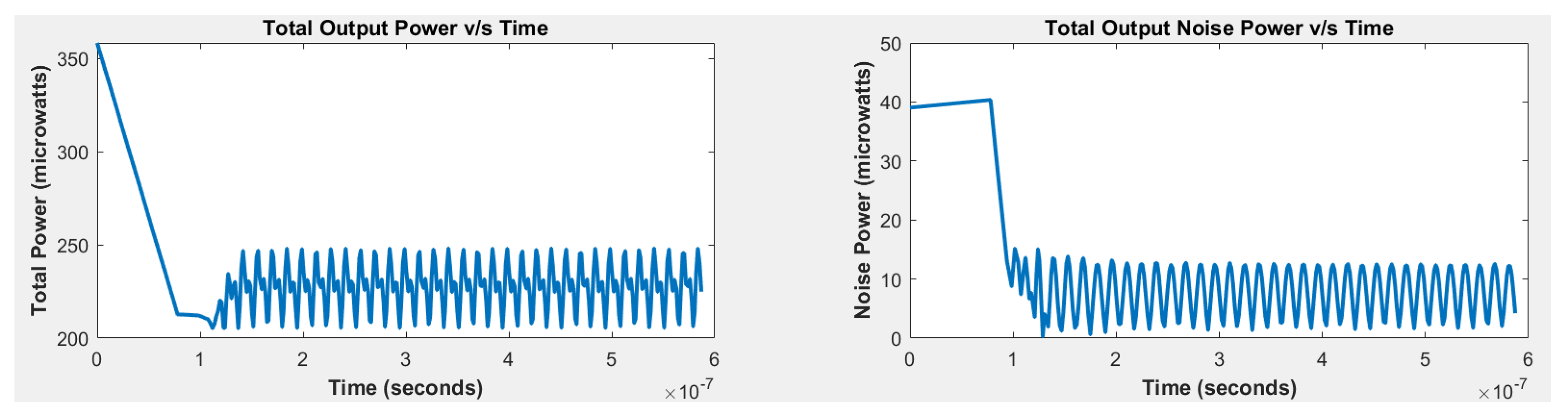
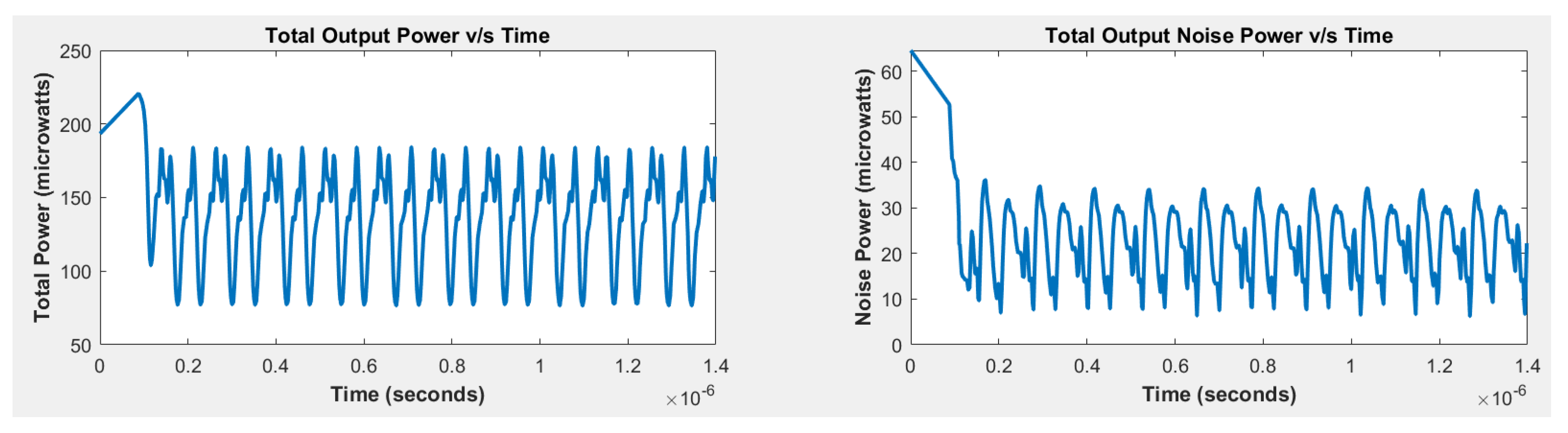
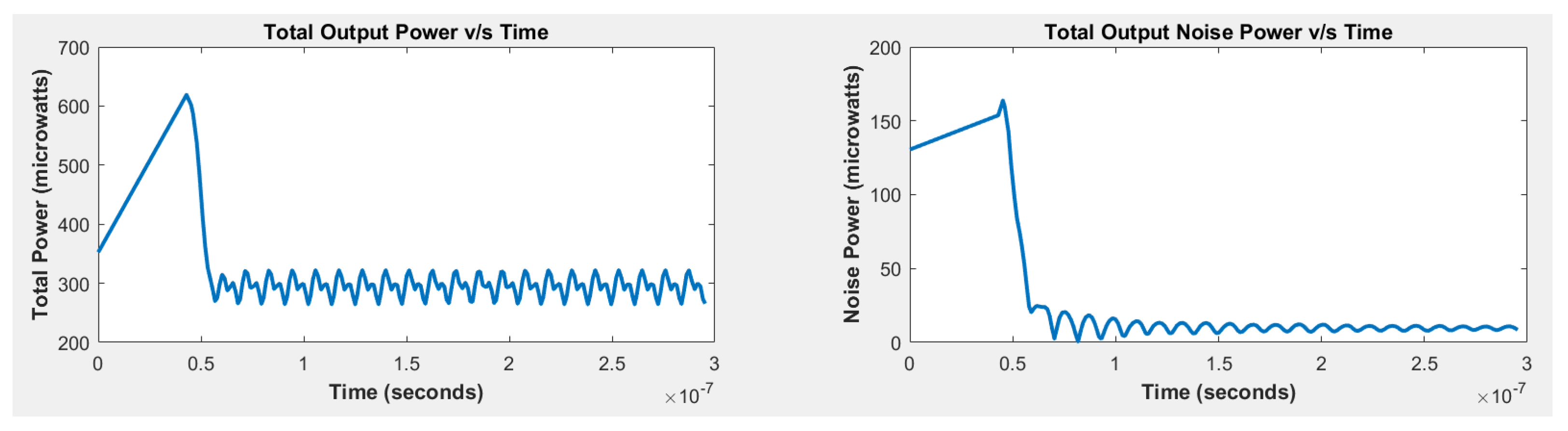
2.4. FFT-Based Noise Extractor
2.5. Post-Processing
2.6. Entropy and Probability Calculator
2.7. NIST-800 Statistical Randomness Tests
- Frequency (Monobit) Test;
- Block Frequency;
- Cumulative Sums;
- Runs;
- Longest Runs;
- Binary Matrix Rank;
- Non-Overlapping;
- Overlapping;
- Universal Statistical;
- Approximate Entropy;
- Random Excursions;
- Random Excursions Variant;
- Serial;
- Linear Complexity;
- Discrete Fourier Transform (Spectral) Test.
3. TRNG: Randomness Statistical Assessment and Entropy Source Validation
3.1. Comparitive Study of Entropy and Probability Numbers
- The entropy of the three-stage ring oscillator deviates significantly from the ideal values for two, three, and four bits. Therefore, three-stage ring oscillator alone is not an ideal candidate for the true random number generator. Therefore, there is no need to run NIST-800 tests for this case.
- The five-stage ring oscillator exhibits a substantial difference from the ideal entropy for two, three, and four bits. Therefore, five-stage ring oscillator alone is not an ideal candidate for the true random number generator. Therefore, there is no need to run NIST-800 tests for this case.
- The seven-stage ring oscillator, while closer to the ideal values, still falls short for three and four bits. Therefore, seven-stage ring oscillator alone is not an ideal candidate for the true random number generator. Therefore, there is no need to run NIST-800 tests for this case.
- The XOR operation of the three-, five-, and seven-stage ring oscillators achieves the ideal entropy values for all four bits. Therefore, this combination is an ideal choice for the true random number generator (TRNG). Thus, NIST-800 tests will be run for this case.
3.2. NIST-800 Statistical Randomness Tests
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FPGA | Field Programmable Gate Arrays |
| VCO | Variable Controlled Oscillator |
| TRNG | True Random Number Generator |
| FFT | Fast Fourier Transform |
| NIST | National Institute of Standards and Technology |
| RO | Ring Oscillator |
| ROs | Ring Oscillators |
| MRO | Multistage Ring Oscillator |
| PUF | Physical Unclonable Function |
| SV1 | Start Up Voltage 1 |
| SV2 | Start Up Voltage 2 |
| SV3 | Start Up Voltage 3 |
| G1 | Geometry 1 |
| G2 | Geometry 2 |
| G3 | Geometry 3 |
References
- Rostami, M.; Koushanfar, F.; Karri, R. A primer on hardware security: Models, methods, and metrics. Proc. IEEE 2014, 102, 1283–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannipieri, P.; Di Matteo, S.; Baldanzi, L.; Crocetti, L.; Belli, J.; Fanucci, L.; Saponara, S. True random number generator based on Fibonacci-Galois ring oscillators for FPGA. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrilla, L.; García, A.; Castillo, E.; López-Villanueva, J.A.; Meyer-Baese, U. Revisiting Multiple Ring Oscillator-Based True Random Generators to Achieve Compact Implementations on FPGAs for Cryptographic Applications. Cryptography 2023, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şarkışla, M.A.; Ergün, S. An area efficient true random number generator based on modified ring oscillators. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Asia Pacific Conference on Circuits and Systems (APCCAS), Chengdu, China, 26–30 October 2018; IEEE: Piscataway Township, NJ, USA; pp. 274–278. [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann, P. Software Generation of Practically Strong Random Numbers. In Proceedings of the Usenix Security Symposium, San Antonio, TX, USA, 26–29 January 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, T.; Peng, Q.; Bian, J.; Yao, L.; Huang, Z.; Yan, A.; Wen, X. MRCO: A Multi-ring Convergence Oscillator-based High-Efficiency True Random Number Generator. In Proceedings of the 2022 Asian Hardware Oriented Security and Trust Symposium (AsianHOST), Singapore, 14–16 December 2022; IEEE: Piscataway Township, NJ, USA; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.; Shin, Y.; Yoo, H. Analysis of Ring-Oscillator-based True Random Number Generator on FPGAs. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Electronics, Information, and Communication (ICEIC), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 31 January–3 February 2021; IEEE: Piscataway Township, NJ, USA; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Sivaraman, R.; Rajagopalan, S.; Amirtharajan, R. FPGA based generic RO TRNG architecture for image confusion. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2020, 79, 13841–13868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaraman, R.; Sridevi, A.; Rajagopalan, S.; Janakiraman, S.; Rengarajan, A. Design and analysis of ring oscillator influenced beat frequency detection for true random number generation on fpga. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Computer Communication and Informatics (ICCCI), Coimbatore, India, 23–25 January 2019; IEEE: Piscataway Township, NJ, USA; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Bakiri, M.; Guyeux, C.; Couchot, J.F.; Oudjida, A.K. Survey on hardware implementation of random number generators on FPGA: Theory and experimental analyses. Comput. Sci. Rev. 2018, 27, 135–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syafalni, I.; Jonatan, G.; Sutisna, N.; Mulyawan, R.; Adiono, T. Efficient homomorphic encryption accelerator with integrated PRNG using low-cost FPGA. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 7753–7771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Gun Choi, B.; Kang, T.; Park, K.; Kwon, Y.; Kim, J. Efficient hardware implementation and analysis of true random-number generator based on beta source. ETRI J. 2020, 42, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petura, O.; Mureddu, U.; Bochard, N.; Fischer, V.; Bossuet, L. A survey of AIS-20/31 compliant TRNG cores suitable for FPGA devices. In Proceedings of the 2016 26th international conference on field programmable logic and applications (FPL), Lausanne, Switzerland, 29 August–2 September 2016; IEEE: Piscataway Township, NJ, USA; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, J.; Yi, M.; Cao, D.; Yao, L.; Wang, X.; Liang, H.; Huang, Z.; Qi, H.; Ni, T.; Lu, Y. Design of true random number generator based on multi-stage feedback ring oscillator. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Ii: Express Briefs 2021, 69, 1752–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zheng, W.; Zheng, Y.; Chang, C.H. A new energy-efficient and high throughput two-phase multi-bit per cycle ring oscillator-based true random number generator. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Regul. Pap. 2021, 69, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Muñoz, L.F.; Sánchez-Solano, S.; Martínez-Rodríguez, M.C.; Brox, P. True Random Number Generation Capability of a Ring Oscillator PUF for Reconfigurable Devices. Electronics 2022, 11, 4028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaraman, R.; Rajagopalan, S.; Sridevi, A.; Rayappan, J.; Annamalai, M.P.V.; Rengarajan, A. Metastability-induced TRNG architecture on FPGA. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Electr. Eng. 2020, 44, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidi, A.A. Phase noise and jitter in CMOS ring oscillators. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2006, 41, 1803–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manku, T. Microwave CMOS-device physics and design. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 1999, 34, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, B. CMOS technology characterization for analog and RF design. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 1999, 34, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafarkhah, E.; Maymandi-Nejad, M.; Zare, M. Single-ended ring oscillators: Analysis and design. IET Circuits Devices Syst. 2020, 14, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, R.; Suprotik, A.N.K.; Uddin, S.Z.; Amin, M.T. Design and analysis of 3 stage ring oscillator based on MOS capacitance for wireless applications. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Communication Engineering (ECCE), Cox’s Bazar, Bangladesh, 16–18 February 2017; IEEE: Piscataway Township, NJ, USA; pp. 723–727. [Google Scholar]
- Rezayee, A.; Martin, K. A three-stage coupled ring oscillator with quadrature outputs. In Proceedings of the ISCAS 2001. The 2001 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (Cat. No. 01CH37196), Sydney, NSW, Australia, 6–9 May 2001; IEEE: Piscataway Township, NJ, USA; Volume 1, pp. 484–487. [Google Scholar]
- Bounchaleun, A. An Elementary Introduction To Fast Fourier Transform Algorithms. 2019. Available online: https://math.uchicago.edu/~may/REU2019/REUPapers/Bounchaleun.pdf (accessed on 30 December 2023).
- Yoshizawa, T.; Hirobayashi, S.; Misawa, T. Noise reduction for periodic signals using high-resolution frequency analysis. EURASIP J. Audio Speech Music. Process. 2011, 2011, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikos, A.; Nastou, P.E.; Petroudis, G.; Stamatiou, Y.C. Random Number Generators: Principles and Applications. Cryptography 2023, 7, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Liu, W.; Qin, L.; Liu, B.; Chen, S.; Ye, J.; Xia, X.; Wang, C. Entropy Sources Based on Silicon Chips: True Random Number Generator and Physical Unclonable Function. Entropy 2022, 24, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Ma, Y.; Lin, J.; Zhuang, J.; Jing, J. More powerful and reliable second-level statistical randomness tests for NIST SP 800-22. In Proceedings of the Advances in Cryptology–ASIACRYPT 2016: 22nd International Conference on the Theory and Application of Cryptology and Information Security, Hanoi, Vietnam, 4–8 December 2016; Proceedings, Part I 22. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 307–329. [Google Scholar]
- Sulak, F.; Uğuz, M.; Kocak, O.; Doğanaksoy, A. On the independence of statistical randomness tests included in the NIST test suite. Turk. J. Electr. Eng. Comput. Sci. 2017, 25, 3673–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | 3-Stage | 5-Stage | 7-Stage | XOR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P(0) | 48.9800 | 50.0319 | 53.0404 | 49.9856 |
| P(1) | 51.0200 | 49.9681 | 46.9596 | 50.0144 |
| H(A) | 0.9997 | 1.0000 | 0.9973 | 1.0000 |
| P(00) | 17.0464 | 21.7931 | 28.8902 | 24.9983 |
| P(01) | 31.9336 | 28.2388 | 24.1502 | 24.9872 |
| P(10) | 31.9336 | 28.2388 | 24.1502 | 24.9872 |
| P(11) | 19.0864 | 21.7292 | 22.8094 | 25.0272 |
| H(B) | 1.9429 | 1.9879 | 1.9940 | 2.0000 |
| P(000) | 5.4355 | 6.9194 | 17.1509 | 12.4973 |
| P(001) | 11.6109 | 14.8737 | 11.7393 | 12.5011 |
| P(010) | 20.0756 | 15.9456 | 13.6319 | 12.4656 |
| P(011) | 11.8580 | 12.2932 | 10.5184 | 12.5217 |
| P(100) | 11.6109 | 14.8737 | 11.7393 | 12.5011 |
| P(101) | 20.3227 | 13.3651 | 12.4109 | 12.4861 |
| P(110) | 11.8580 | 12.2932 | 10.5184 | 12.5217 |
| P(111) | 7.2284 | 9.4360 | 12.2910 | 12.5055 |
| H(C) | 2.8855 | 2.9597 | 2.9826 | 3.0000 |
| P(0000) | 0.6112 | 1.3428 | 6.8250 | 6.1881 |
| P(0001) | 4.8243 | 5.5766 | 10.3258 | 6.3092 |
| P(0010) | 7.0283 | 6.8265 | 3.9519 | 6.1957 |
| P(0011) | 4.5826 | 8.0472 | 7.7874 | 6.3054 |
| P(0100) | 6.2776 | 7.4559 | 7.8502 | 6.1887 |
| P(0101) | 13.7981 | 8.4897 | 5.7816 | 6.2769 |
| P(0110) | 6.1326 | 5.4613 | 1.1004 | 6.2261 |
| P(0111) | 5.7253 | 6.8320 | 9.4180 | 6.2956 |
| P(1000) | 4.8243 | 5.5766 | 10.3258 | 6.3092 |
| P(1001) | 6.7866 | 9.2971 | 1.4135 | 6.1919 |
| P(1010) | 13.0473 | 9.1191 | 9.6800 | 6.2698 |
| P(1011) | 7.2753 | 4.2460 | 2.7310 | 6.2163 |
| P(1100) | 5.3334 | 7.4178 | 3.8891 | 6.3124 |
| P(1101) | 6.5246 | 4.8754 | 6.6293 | 6.2093 |
| P(1110) | 5.7253 | 6.8320 | 9.4180 | 6.2956 |
| P(1111) | 1.5031 | 2.6041 | 2.8730 | 6.2099 |
| H(D) | 3.7998 | 3.8994 | 3.7950 | 4.0000 |
| Test Name | p-Value | Pass Rate | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 0.066882 | 10/10 | Passed |
| Block Frequency | 0.350485 | 10/10 | Passed |
| Cumulative Sums | 0.066882 | 10/10 | Passed |
| Runs | 0.122325 | 9/10 | Passed |
| Longest Run | 0.534146 | 10/10 | Passed |
| Binary Matrix Rank | 0.350485 | 9/10 | Passed |
| Non-Overlapping | 0.739918 | 10/10 | Passed |
| Overlapping | 0.534146 | 9/10 | Passed |
| Universal Statistical | 0.534146 | 10/10 | Passed |
| Approximate Entropy | 0.350485 | 10/10 | Passed |
| Random Excursions | 0.911413 | 10/10 | Passed |
| Random Excursions Variant | 0.534146 | 10/10 | Passed |
| Serial | 0.122325 | 10/10 | Passed |
| Linear Complexity | 0.350485 | 10/10 | Passed |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, V.; Hasan, M.S.; Azeemuddin, S. A High-Quality Random Number Generator Using Multistage Ring Oscillators and Fast Fourier Transform-Based Noise Extraction. Eng 2024, 5, 433-446. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5010023
Singh V, Hasan MS, Azeemuddin S. A High-Quality Random Number Generator Using Multistage Ring Oscillators and Fast Fourier Transform-Based Noise Extraction. Eng. 2024; 5(1):433-446. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5010023
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Vatanpreet, Md Sakib Hasan, and Syed Azeemuddin. 2024. "A High-Quality Random Number Generator Using Multistage Ring Oscillators and Fast Fourier Transform-Based Noise Extraction" Eng 5, no. 1: 433-446. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5010023
APA StyleSingh, V., Hasan, M. S., & Azeemuddin, S. (2024). A High-Quality Random Number Generator Using Multistage Ring Oscillators and Fast Fourier Transform-Based Noise Extraction. Eng, 5(1), 433-446. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng5010023







