Energy Efficiency Assessment for Buildings Based on the Generative Adversarial Network Structure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Infrared Measures
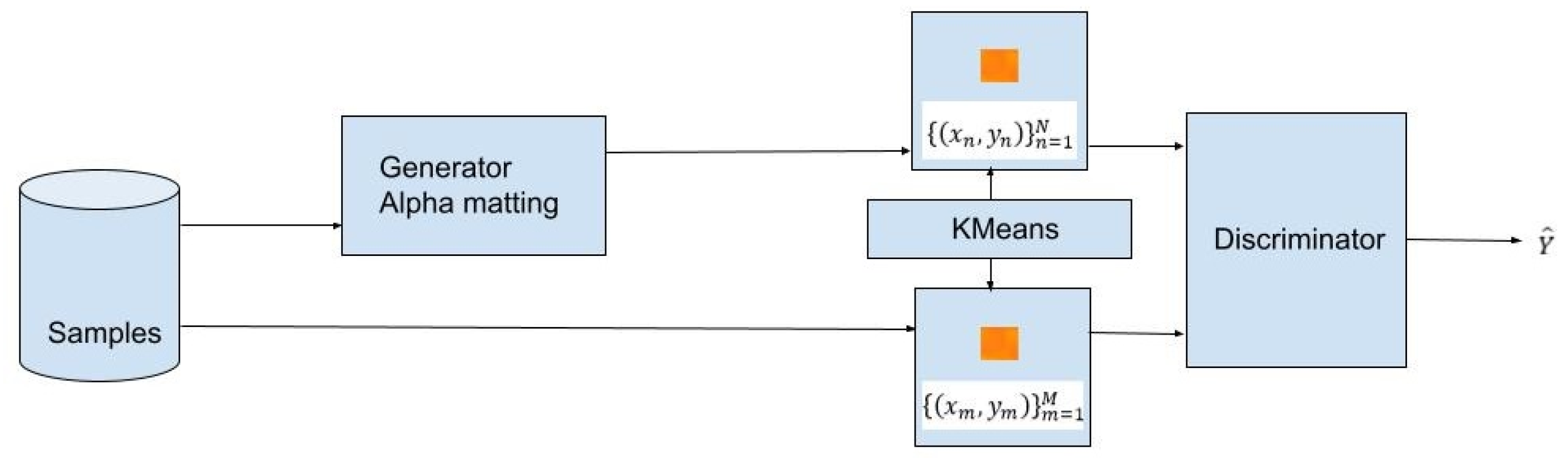
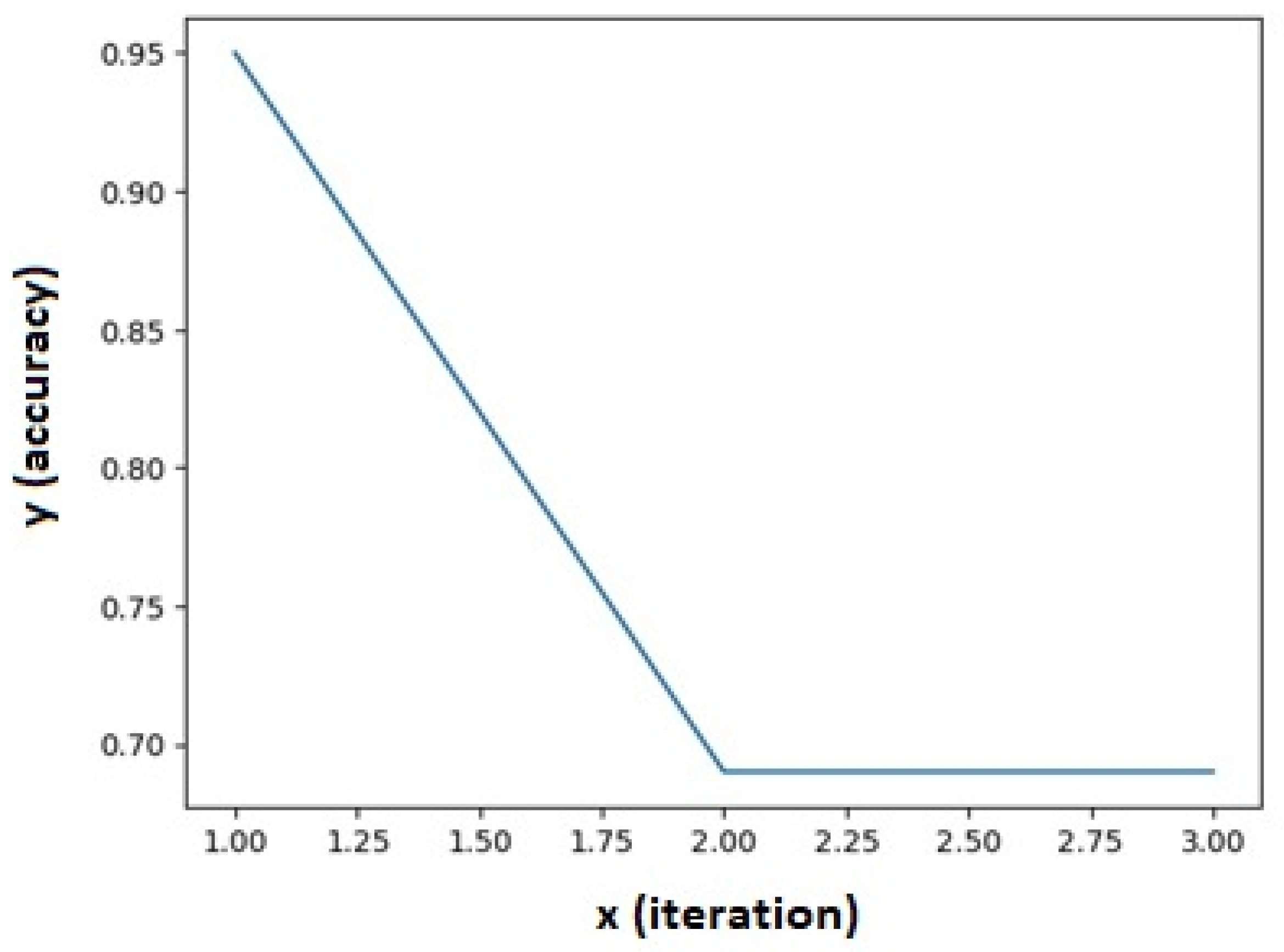
2.2. Adapted GAN Mechanism
3. Results
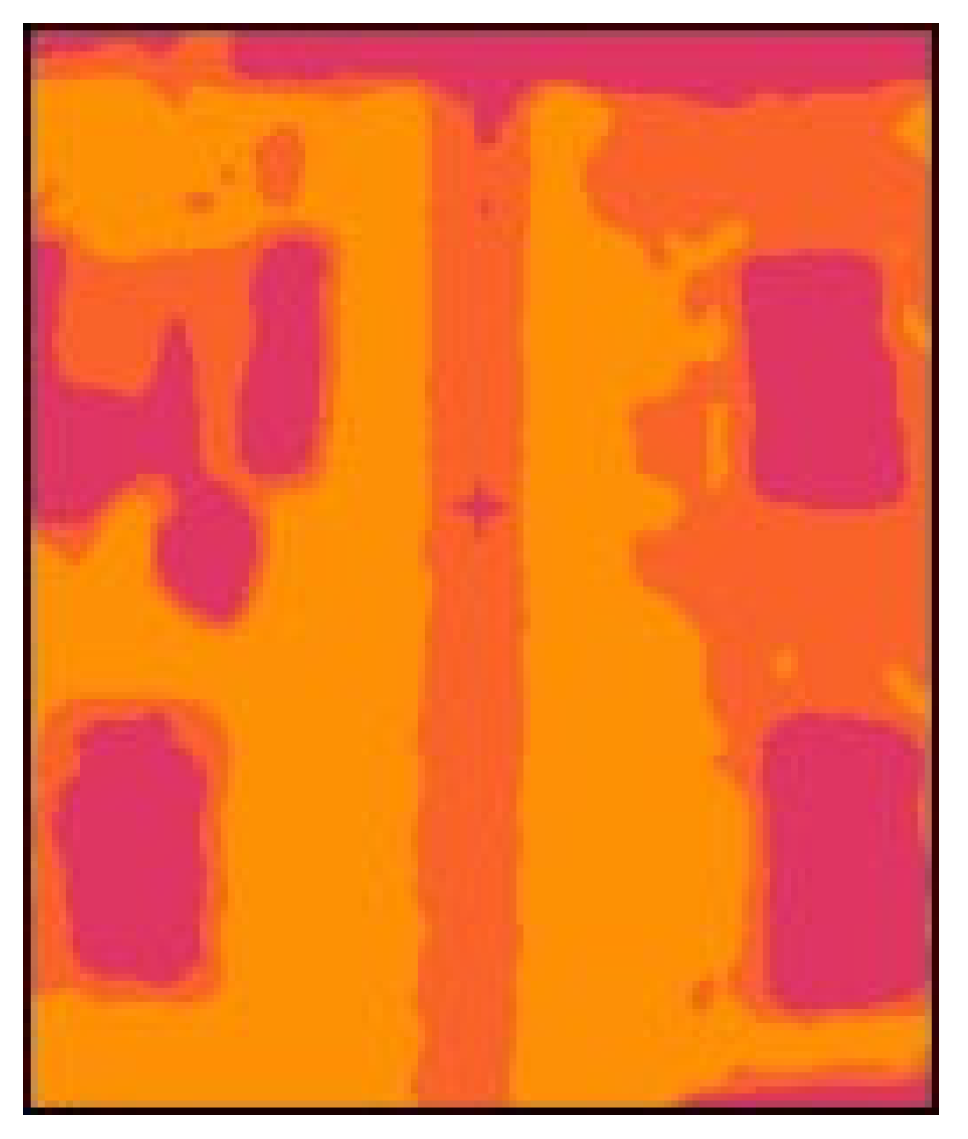
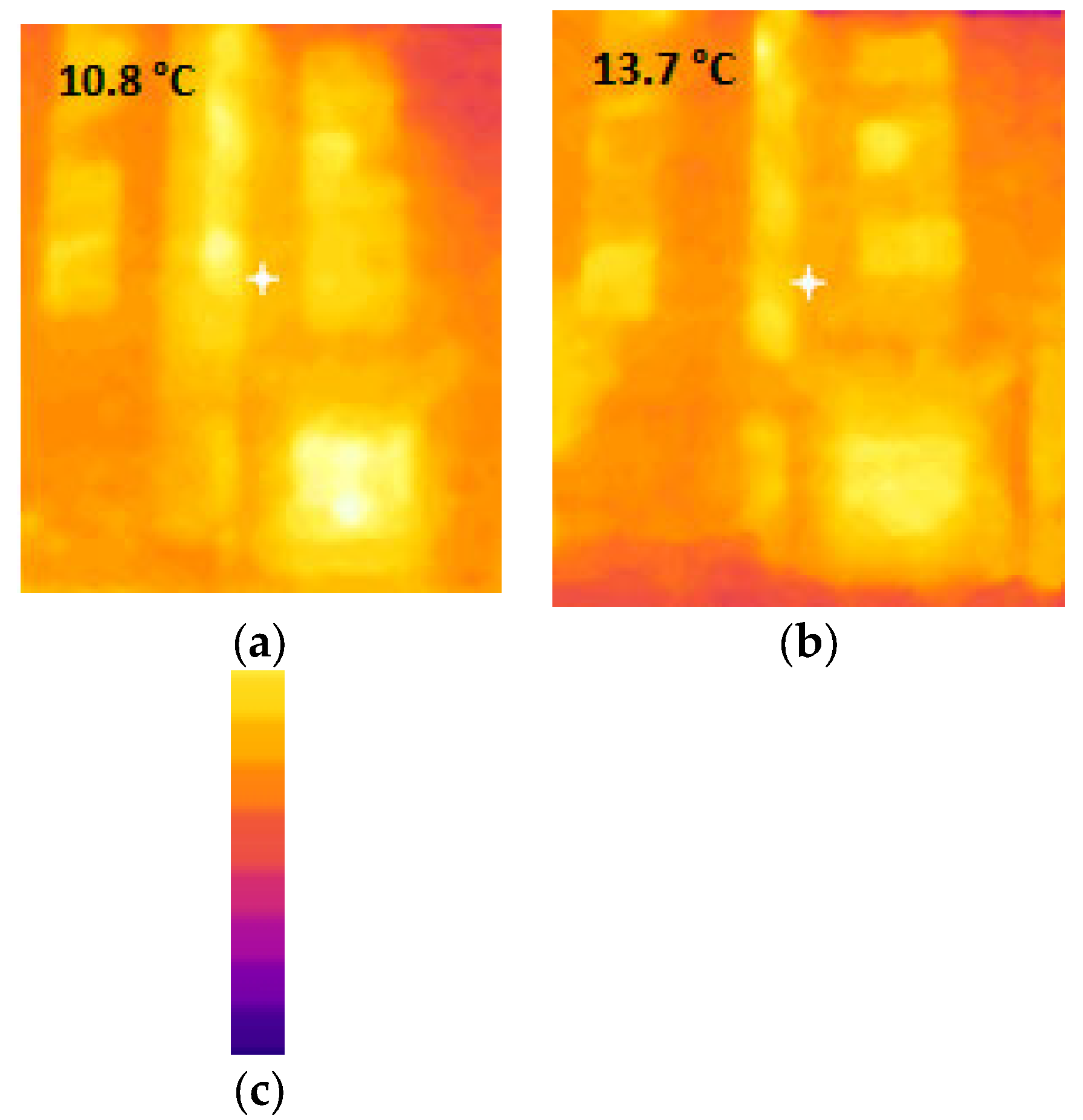
3.1. IRT Measurements
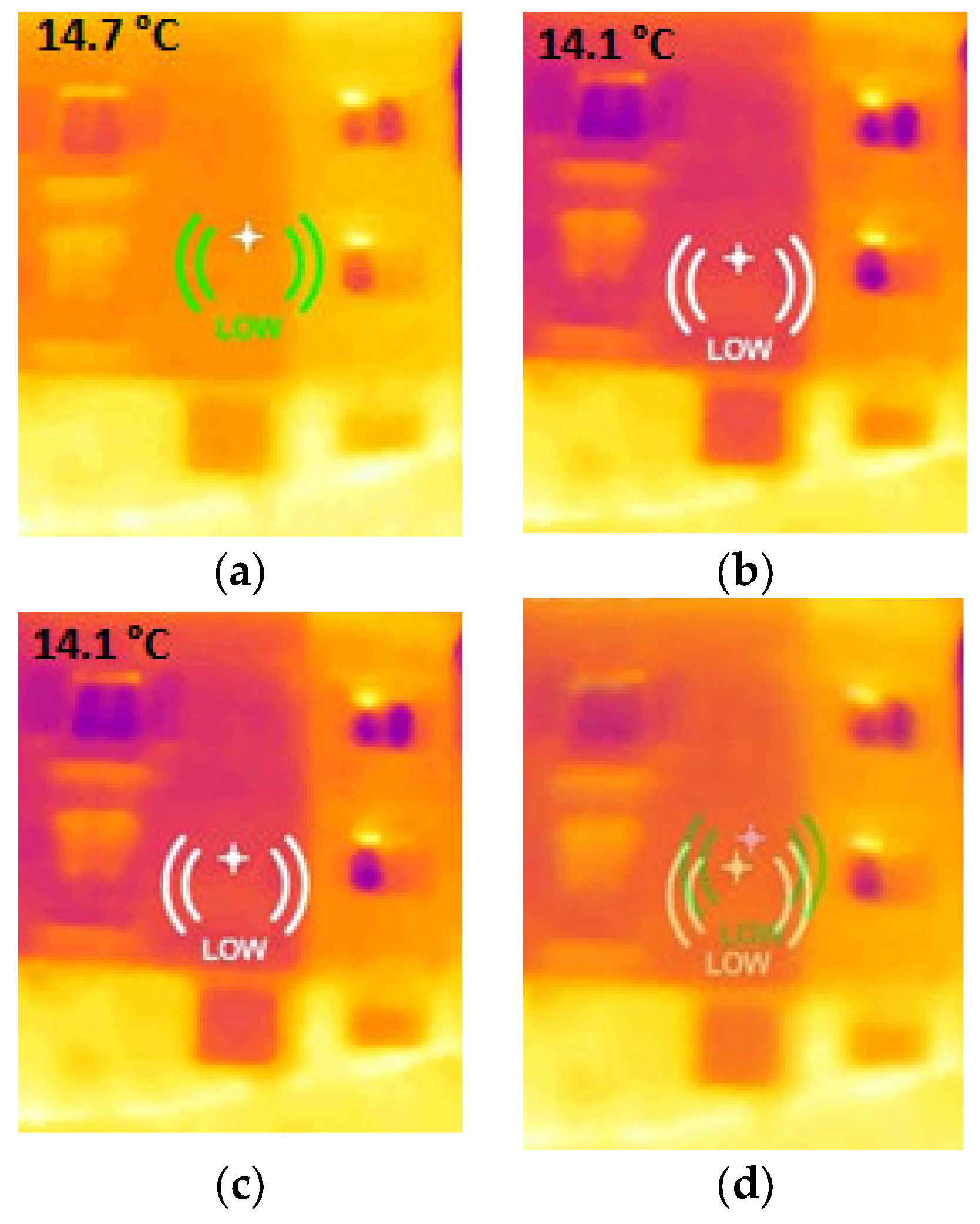
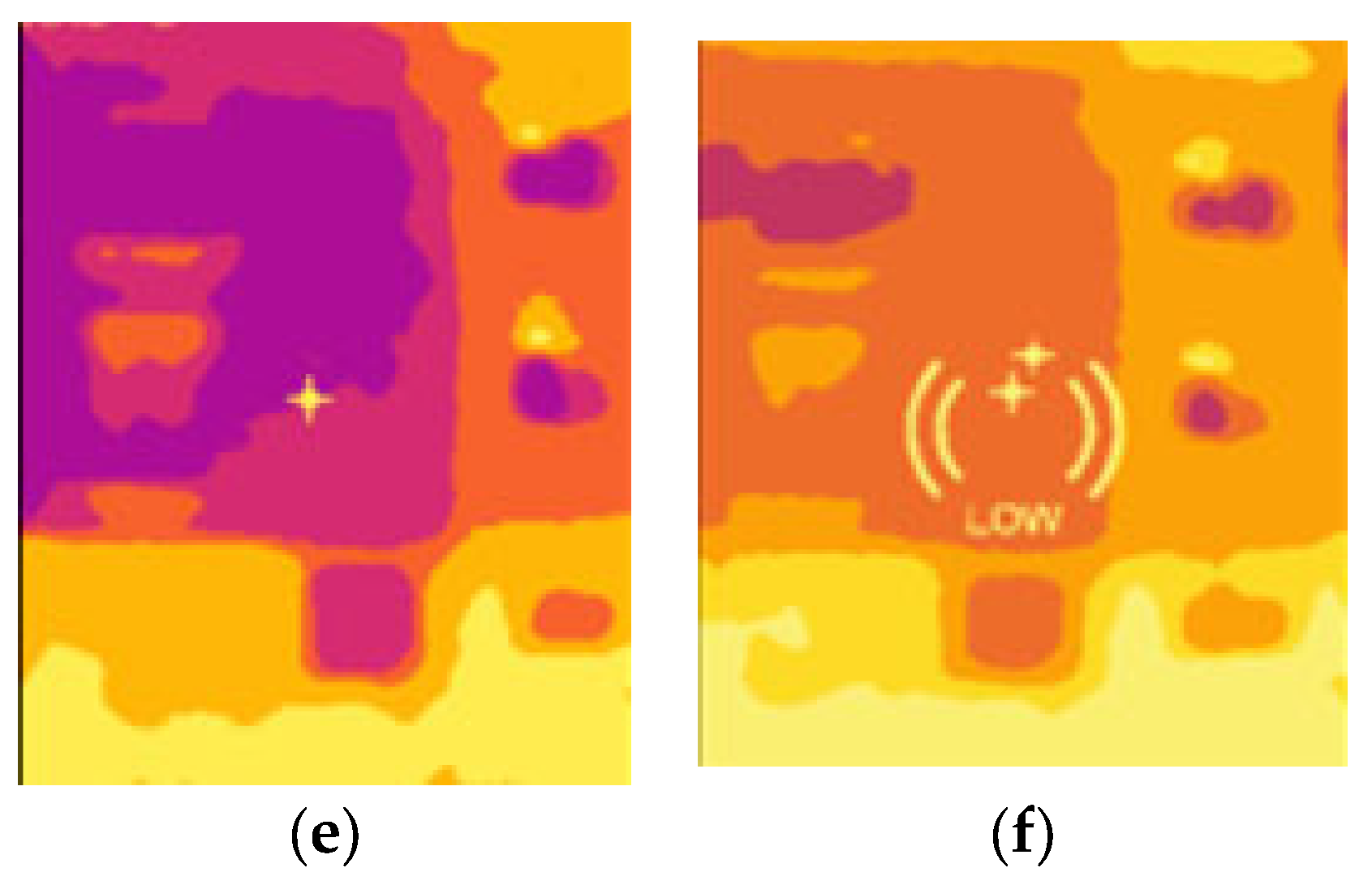
3.2. Heat Loss Localization
4. Discussion and Future Work Scope
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leggiero, M.; Andrew, B.; Elliott, R.; Indergaard, J.; Sharma, J.B.; Vogel, T. Radiative heat loss estimation of building enelopes based on 3D thermographic models utilizing small unmanned aerial systems (sUAS). Energy Build. 2021, 244, 110957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heckel, M. Unter Strom. VDE Dialog, 1 April 2023. Available online: https://dialog.vde.com/de/vde-dialog-ausgaben/all-electric-society/unter-strom(accessed on 3 August 2023).
- Kaliyannan, G.V.; Rathanasamy, R.; Gunasekaran, R.; Anbupalani, M.S.; Moganapriya, C.; Palaniappan, S.K. Doping of Carbon Nanostructures for Energy Application. Defect Eng. Carbon Nanostruct. 2022, 20, 83–109. [Google Scholar]
- Chinnasamy, V.; Palaniappan, S.K.; Raj, M.K.A.; Rajendran, M.; Cho, H. Thermal Energy Storage and Its Applications. In Materials for Solar Energy Conversion: Materials, Methods and Applications, 1st ed.; Scrivener Publishing LLC: Beverly, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ghahramani, A.; Xu, Q.; Min, S.; Wang, A.; Zhang, H.; He, Y.; Merritt, A.; Levinson, R. Inrared-Fused Vision-Based Thermoregulation Performance Estimation for Personal Thermal Comfort-Driven HVAC System Controls. Buildings 2022, 12, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, M.; Huynh, N.K.; Schiavon, S.; Selkowitz, S. Using support vector machine to desk illuminance sensor blockage for closed-loop daylight harvesting. Energy Build. 2022, 274, 112443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Lee, D. Smart Sensors Enable Smart Air Conditioning Control. Sensors 2014, 14, 11179–11203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Israr, A.; Abro, G.E.M.; Khan, M.S.A.; Fahran, M.; Zulkifi, S.A.B.M. Internet of Things (IoT)-Enabled Unmanned Aerial Vehicles for the Inspection of Construction Sites: A Vision and Future Directions. Math. Probl. Eng. 2021, 2021, 9931112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lulu, T.; Zidong, W.; Weibo, L.; Yuhua, C.; Fuad, F.A.; Xiaohui, L. A New GAN-Based Approach to Data Augmentation and Image Segmentation for Crack Detection in Thermal Imaging Tests. Cogn. Comput. 2021, 13, 1263–1273. [Google Scholar]
- Batchuluun, G.; Kang, J.K.; Nguyen, N.T.; Pham, P.D.; Arsalan, M.; Park, K.R. Deep Learning-Based Thermal Image Reconstruction and Object Detection. IEEE Access 2022, 9, 5951–5971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nand, K.Y.; Satish, K.S.; Shiv, R.D. TVA-GAN: Attention Guided Generative Adversarial Network For Thermal To Visible Image Transformations. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 1–27, 1433–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizginov, V.A.; Kniaz, V.V.; Fomin, N.A. A method for synthesizing thermal images using GAN multilayered approach. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2021, 44, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkaya, I.B.; Fazil, A.; Ugur, H. Self-training Guided Adversarial Domain Adaptation For Thermal Imagery. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Baasch, G.M.; Rousseau, G.; Evins, R. A Conditional Generative Adversarial Network for Energy Use in Multiple Buildings Using Scarce Data. Energy AI 2021, 5, 100087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, D.; Zhao, X.; Lu, W.; Li, P.; Shi, X.; Fukuda, H. A Deep Learning Approach toward Energy-Effective Residential Building Floor Plan Generation. Sustainability 2022, 14, 8074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Chen, M.; Volk, R.; Soibelman, L. An Approach to Semantically Segmenting Building Components and Outdoor Scenes Based on Multichannel Aerial Imagery Datasets. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daffara, C.; Muradore, R.; Piccinelli, N.; Gaburro, N.; Tullio de Rubeis, T.R.; Ambrosini, D. A Cost-Effective System for Aerial 3D Thermography of Buildings. J. Imaging 2022, 6, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benz, A.; Taraben, J.; Debus, P.; Habte, B.; Oppermann, L.; Hallermann, N.; Voelker, C.; Rodehosrst, V.; Morgenthal, G. Framework for a UAS-based assessment of energy performance of buildings. Energy Build. 2021, 250, 111266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokaides, P.A.; Kalogirou, S.A. Application of infrared thermography for the determination of the overall heat transfer coefficient (U-Value) in building envelopes. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 4358–4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minkina, W.; Klecha, D. Atmospheric transmission coefficient modelling in the infrared for thermovision measurements. J. Sens. Sens. Syst. 2016, 5, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funmilola, A.; Oke, O.A.; Adedeji, T.O.; Alade, O.M.; Adewusi, E.A. Fuzzy k-c-means Clustering Algorithm for Medical Image Segmentation. J. Inf. Eng. Appl. 2012, 2, 21–32. [Google Scholar]
- Kashiwabara, K.; Kazama, K.; Marumo, Y. Performance Evaluation of Image Registration for Map Images. J. Robot. Mechatron. Jpn. 2022, 35, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeliski, R. Computer Vision: Algorithms and Applications; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, I.; Tanasković, M.; Stanković, M. IR Building Analysis with Extraction of Elements Usiong Image Segmentation and RetinaNet. Buildings 2023, 13, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


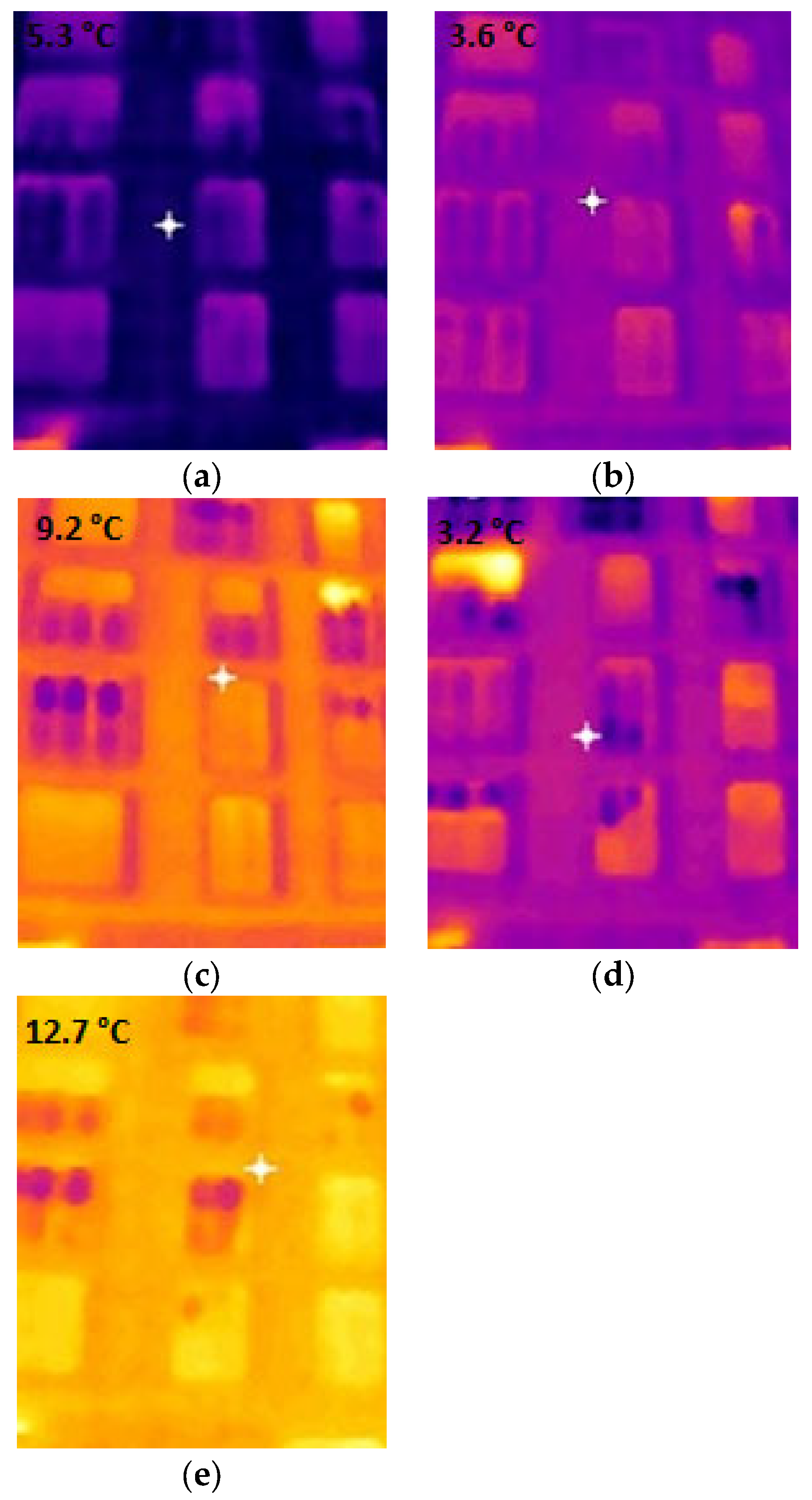
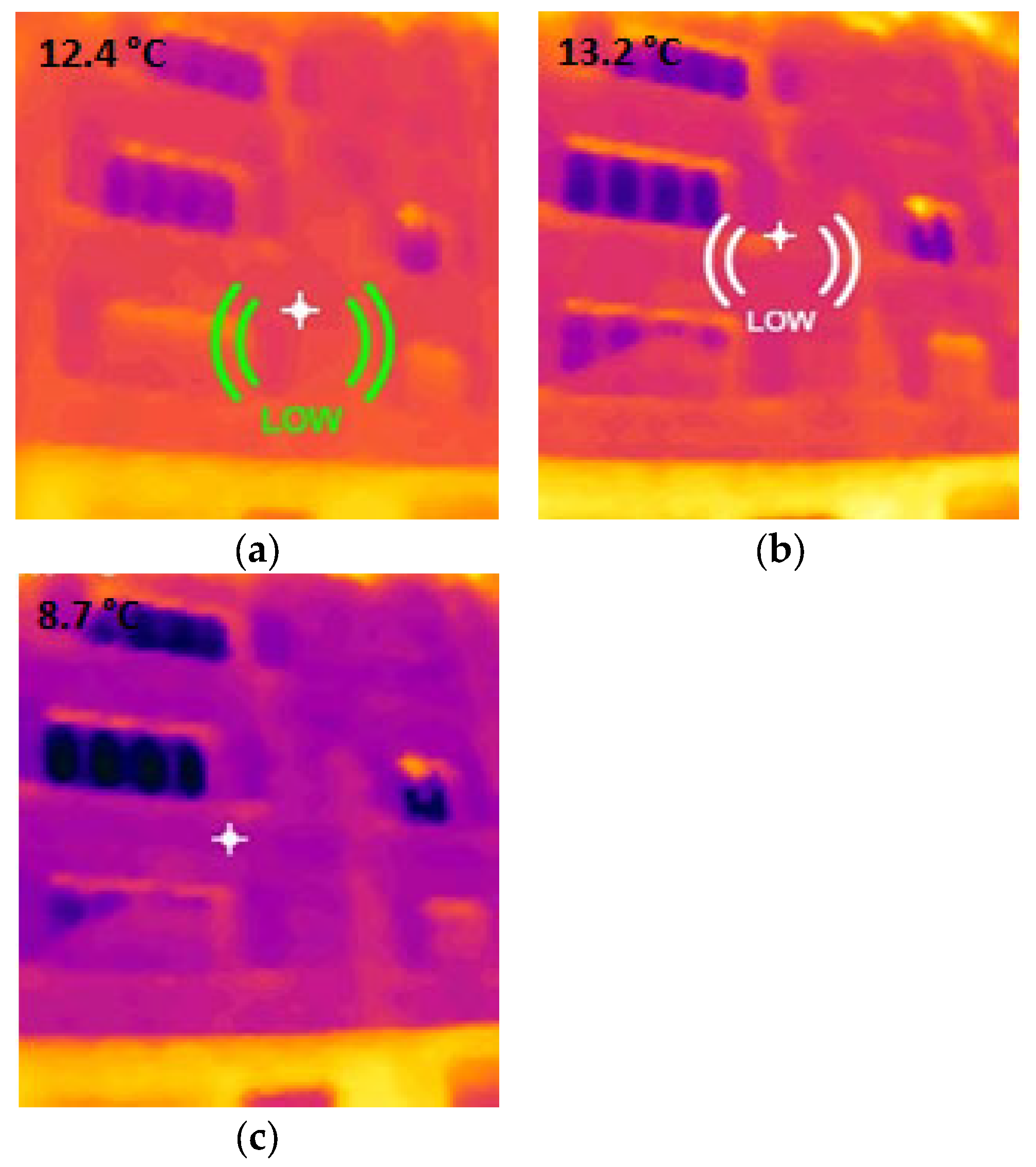
| 31 March 8 °C Humidity 76% Wind 26 km/h | Metal | Marble | Plastic | Brick | Block |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Emitted energy (W/) | 385.4 | 387.5 | 382.7 | 356.1 | 340.7 |
| Reflected energy (W/) | 3.8 | 3.7 | 3.8 | 19 | 46.8 |
| Atmospheric energy (W/) | 4.4 | 4.4 | 4.4 | 4.4 | 4.4 |
| Total radiated energy (W/) | 388.95 | 390.9 | 386.3 | 375 | 387.25 |
| Percentage emitted energy (%) | 99 | 99 | 99 | 95 | 88 |
| 1 April 8 °C Humidity 76% Wind 26 km/h | Metal | Plastic | Brick |
|---|---|---|---|
| Emitted energy (W/) | 371 | 363.9 | 336.1 |
| Reflected energy (W/) | 3.7 | 3.7 | 24.7 |
| Atmospheric energy (W/) | 4.3 | 4.3 | 4.3 |
| Total Radiated energy (W/) | 375.2 | 367.5 | 360.8 |
| Percentage emitted energy (%) | 99 | 99 | 93 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Walter, I.; Tanasković, M.; Stanković, M. Energy Efficiency Assessment for Buildings Based on the Generative Adversarial Network Structure. Eng 2023, 4, 2178-2190. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng4030125
Walter I, Tanasković M, Stanković M. Energy Efficiency Assessment for Buildings Based on the Generative Adversarial Network Structure. Eng. 2023; 4(3):2178-2190. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng4030125
Chicago/Turabian StyleWalter, Ivana, Marko Tanasković, and Miloš Stanković. 2023. "Energy Efficiency Assessment for Buildings Based on the Generative Adversarial Network Structure" Eng 4, no. 3: 2178-2190. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng4030125
APA StyleWalter, I., Tanasković, M., & Stanković, M. (2023). Energy Efficiency Assessment for Buildings Based on the Generative Adversarial Network Structure. Eng, 4(3), 2178-2190. https://doi.org/10.3390/eng4030125






