Energy Dissipation Technologies in Seismic Retrofitting: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
- The search stage, which required finding the articles published in the proposed scope and removing irrelevant papers by careful filtering;
- The inspection stage, which involved conducting a deep study of the selected papers in order to find the core ideas proposed by the authors and employing bibliometric tools;
- The discussion stage, in which the outputs of the previous stages were synthesized and final outputs were presented.
3. Energy-Dissipating Devices Used for Seismic Retrofitting
3.1. Friction Dampers
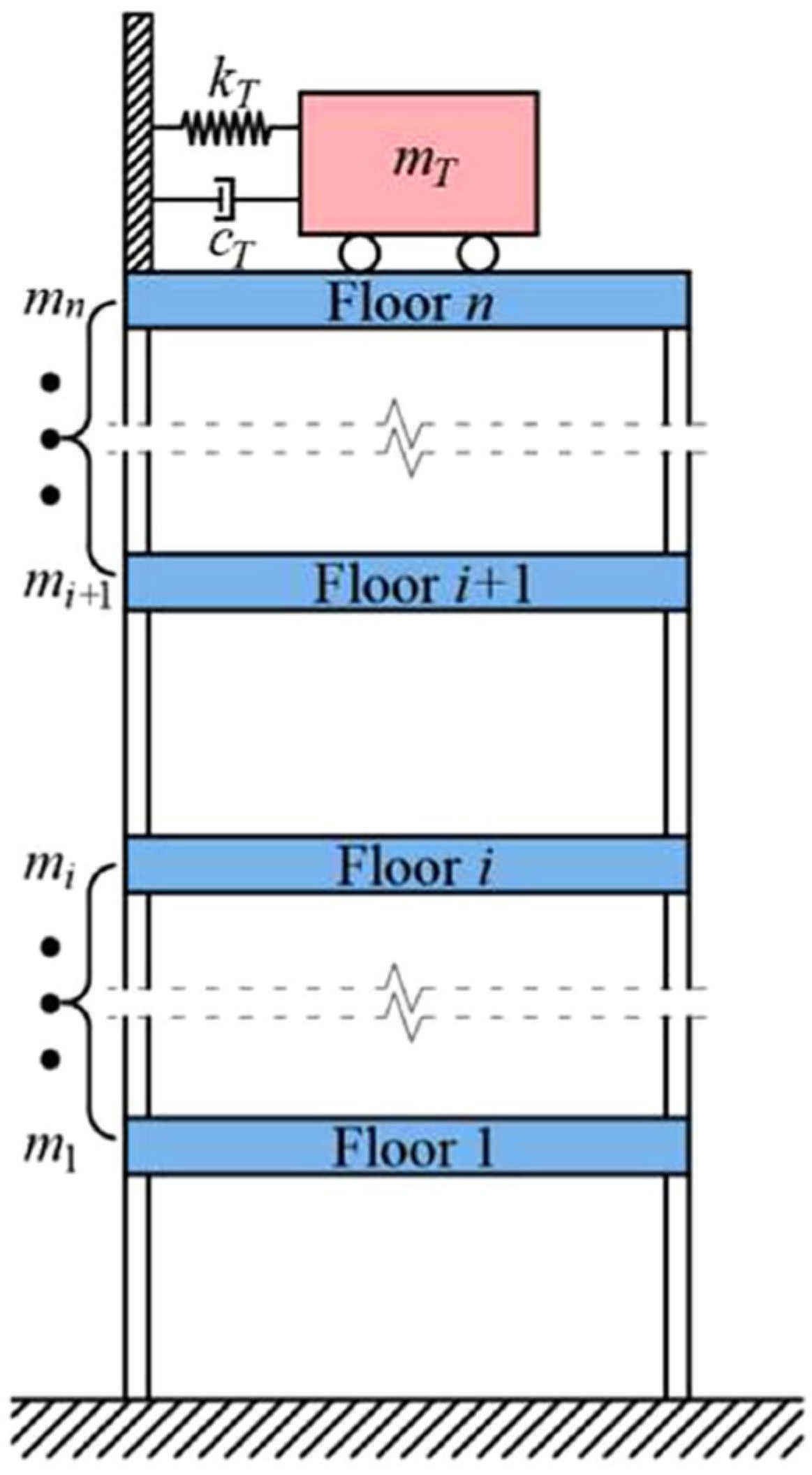
3.2. Tuned Mass Dampers
3.3. Viscous Dampers
3.4. Hysteretic Dampers
3.5. Viscoelastic Dampers
4. Brief Discussion on the Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Device
5. Future Developments and Research Gaps
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Titirla, M.D. A State-of-the-Art Review of Passive Energy Dissipation Systems in Steel Braces. Buildings 2023, 13, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javidan, M.M.; Ahmad, R.N.; Chun, S.; Kim, J. Seismic retrofit of framed structures using a steel frame with springs and friction dampers. Structures 2024, 64, 106555. [Google Scholar]
- Muho, E.V.; Kalapodis, N.A.; Papagiannopoulos, G.A.; Beskos, D.E. The MDOF equivalent linear system and its applications in seismic analysis and design of framed structures. Resilient Cities Struct. 2024, 3, 107–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.R.; Xu, Z.D.; He, Z.H.; Xu, Y.; Huang, X.H.; He, J.X.; Yang, Y. Dynamic performance and cross-level damage criteria of strengthened reinforced concrete frames with VE energy dissipation braces. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2024, 31, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Hu, X.; Chen, Q.; Yang, K.; Liao, C.; Zhang, R. Negative stiffness-enhanced seismic damping technology for an over-track complex with concrete-encased steel columns. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 73, 106722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorace, S.; Bidoli, N.; Terenzi, G. Glazed-level dissipative brace incorporation in a gym building. Structures 2024, 68, 107184. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, C.; Xie, Y. Seismic fragility of using friction dampers to retrofit non-ductile reinforced concrete shear wall buildings in western Canada. In Canadian Society of Civil Engineering Annual Conference; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 275–289. [Google Scholar]
- El-Feky, M.H.; Eraky, A.; Elsisi, A.A.; Purcz, P.; Demjan, I.; Katunský, D.; Sharabash, A.M. Optimal hysteresis of shape memory alloys for eliminating seismic pounding and unseating of movement joint systems. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 19, e02219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, A.; Maida, Y.; Koichi, K.; Javidan, M.M. Development and experimental verification of self-centering disc slit damper for buildings. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2023, 201, 107759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.H.; Luo, R.; Li, G.; Zhai, Z.J. Efficient optimal seismic design method of passive energy dissipation systems based on the inelasticity-separated finite element method. Earthq. Eng. Resil. 2023, 2, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprile, A.; Grossi, E.; Zerbin, M. A novel friction damper for seismic retrofit of precast rc structures with poor connections. In International Symposium of the International Federation for Structural Concrete at University of Stuttgart, Germany; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 1384–1394. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Shen, H.; Zhang, Z.; Qian, H. Mechanical behaviors of a buckling-plate self-centering friction damper. Buildings 2023, 13, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terenzi, G. Novel design procedure for steel hysteretic dampers in seismic retrofit of frame structures. Eng. Struct. 2023, 284, 115969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saingam, P. Response Control on Seismic Retrofit of Low-Rise RC Frame Using Viscous Damper. In International Conference on Civil Engineering, Singapore; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 38–48. [Google Scholar]
- Javidan, M.M.; Assefa, J.D.; Kim, J. December. Seismic retrofit of low-rise structures using rotational viscoelastic dampers. Structures 2023, 58, 105403. [Google Scholar]
- Grossi, E.; Aprile, A.; Zerbin, M. Tribological investigation on metal mating surfaces to explore real use conditions of a novel friction damper for seismic applications. Eng. Struct. 2023, 278, 115473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossi, E.; Zerbin, M.; Aprile, A.; De Risi, R.; De Luca, F. Conceptual study of an innovative friction damper for the seismic retrofit of precast RC structures with poor connections. Structures 2024, 67, 106960. [Google Scholar]
- Grossi, E.; Aprile, A.; Zerbin, M.; Livieri, P. Preliminary experimental tests of a novel friction damper for seismic retrofit of RC precast structures. Eng. Struct. 2024, 305, 117718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruschi, E.; Quaglini, V.; Zoccolini, L. Seismic upgrade of steel frame buildings by using damped braces. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharagoz, M.M.; Noureldin, M.; Kim, J. Machine learning-based design of a seismic retrofit frame with spring-rotational friction dampers. Eng. Struct. 2023, 292, 116053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharagoz, M.M.; Chun, S.; Noureldin, M.; Kim, J. Performance-based seismic design of a spring-friction damper retrofit system installed in a steel frame. Steel Compos. Struct. 2024, 51, 173–183. [Google Scholar]
- Melatti, V.; D’Ayala, D. Methodology for the assessment and refinement of friction-based dissipative devices. Eng. Struct. 2021, 229, 111666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, M.; Eldin, M.N. Optimal distribution of steel plate slit dampers for seismic retrofit of structures. Steel Compos. Struct 2017, 25, 473–484. [Google Scholar]
- Shimose, K.; Kaneda, T.; Nishitani, M.; Ishii, K. Seismic Retrofit using the Largest Viscous Damper in Japan. In Proceedings of the IABSE Symposium: Long Span Bridges, Istanbul, Turkey, 26–28 April 2023; pp. 760–767. [Google Scholar]
- Javidan, M.M.; Kim, J. Seismic retrofit of soft-first-story structures using rotational friction dampers. J. Struct. Eng. 2019, 145, 04019162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Liu, X.; Bai, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Pu, J.; Zhou, C. A novel dual self-centering friction damper for seismic responses control of steel frame. Buildings 2024, 14, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, X.; Simpson, B.G.; Xiao, J. Experimental testing of GCr15 bearing steel with different surface treatments as passive friction energy-dissipative shims. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 408, 133628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suk, R.; Demir, A.; Altintas, G.; Altiok, T.Y. Proposal for a novel technological damper system (TDS) for the retrofit of reinforced concrete frame structures. Structures 2024, 60, 105878. [Google Scholar]
- Bruschi, E.; Quaglini, V. Modelling of a Novel Lead Damper and Application to an Existing RC Structure. In Eurasian Conference on OpenSees; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 52–62. [Google Scholar]
- Javidan, M.M.; Ali, A.; Kim, J. A steel hysteretic damper for seismic design and retrofit of precast portal frames. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 57, 104958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloisio, A.; Boggian, F.; Tomasi, R. Design of a novel seismic retrofitting system for RC structures based on asymmetric friction connections and CLT panels. Eng. Struct. 2022, 254, 113807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jeong, J. Seismic retrofit of asymmetric structures using steel plate slit dampers. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2016, 120, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Chiu, I.C.; Yu, C.H.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Chang, K.C. Experimental beyond design and residual performances of full-scale viscoelastic dampers and their empirical modeling. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2019, 48, 1093–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, M.; Pampanin, S.; Rodgers, G.W. SLaMA-Based Retrofit of RC Frame Buildings Using Alternative Bracing Systems. J. Struct. Eng. 2024, 150, 04024154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirca, L.; Morales, J.D.; Guo, G.L.; Chen, L. Optimal design of friction dampers for multistorey buildings. In Proceedings of the 9th US National and 10th Canadian Conference on Earthquake Engineering: Reaching Beyond Borders, Toronto, Canada, 25–29 July 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Sirinipitakul, T.; Suwannatrai, R.; Hlaing, H.H.; Saingam, P. Reduction of Damage Concentration in Seismic Retrofitted RC Building with Friction Dampers. In Proceedings of the 9th World Congress on Civil, Structural, and Environmental Engineering (CSEE 2024), London, UK, 14–16 April 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Saingam, P.; Sangswang, N.; Sansombat, P. Energy-dissipation in Seismic Retrofit RC Building with Friction Dampers. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Resources and Environment Sciences, Hong Kong, China, 6 September 2023; Volume 422, p. 03004. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, D.H.; Oh, S.H.; Park, B.J.; Choi, S.M. Experimental investigation on retrofitting effects of circular steel rod damper systems on non-seismic detailed reinforced concrete frames. Structures 2024, 65, 106642. [Google Scholar]
- Titirla, M.D. Using friction-yielding damper CAR1 to seismic retrofit a two-story RC building: Numerical application. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.; Haroon, M.; Lee, J.; Shin, K.; Lee, H. Shaking table tests and numerical simulations on RC frames retrofitted with friction-damped brace. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 82, 108277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Ebadi-Jamkhaneh, M. Seismic upgrading of existing steel buildings built on soft soil using passive damping systems. Buildings 2023, 13, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraioli, M.; Di Lauro, G.; Crisci, P.; Laezza, G.; Lavino, A.; Bellantoni, C. Seismic retrofit of a RC building using metallic yielding dampers: A case study. Procedia Struct. Integr. 2023, 44, 982–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noureldin, M.; Adane, M.; Kim, J. Seismic fragility of structures with energy dissipation devices for mainshock-aftershock events. Earthq. Struct 2021, 21, 219–230. [Google Scholar]
- Naeem, A.; Kim, J. Seismic retrofit of structures using rotational friction dampers with restoring force. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2020, 23, 3525–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saingam, P.; Matsuzaki, R.; Nishikawa, K.; Sitler, B.; Terazawa, Y.; Takeuchi, T. Experimental dynamic characterization of friction brace dampers and application to the seismic retrofit of RC buildings. Eng. Struct. 2021, 242, 112545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jara, J.M.; García-Calzada, C.; Olmos, B.A.; Martínez, G. Seismic response and reliability index of RC weak story buildings on soft soils of Mexico city. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 50, 104199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noureldin, M.; Memon, S.A.; Gharagoz, M.; Kim, J. Performance-based seismic retrofit of RC structures using concentric braced frames equipped with friction dampers and disc springs. Eng. Struct. 2021, 243, 112555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldin, M.N.; Dereje, A.J.; Kim, J. Seismic retrofit of RC buildings using self-centering PC frames with friction-dampers. Eng. Struct. 2020, 208, 109925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Dong, H.; Wang, X.; He, M. Experimental and numerical investigations into seismic performance of timber-steel hybrid structure with supplemental dampers. Eng. Struct. 2017, 151, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshti Aval, S.B.; Kouhestani, H.S.; Mottaghi, L. Effectiveness of two conventional methods for seismic retrofit of steel and RC moment resisting frames based on damage control criteria. Earthq. Eng. Eng. Vib. 2017, 16, 537–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khader, S.A.; Naish, D.; Lanning, J. Experimental evaluation and development of a self-centering friction damping brace. In Proceedings of the Structures Congress 2017, Denver, CO, USA, 6–8 April 2017; pp. 382–391. [Google Scholar]
- Tabeshpour, M.R.; Ebrahimian, H. Seismic retrofit of existing structures using friction dampers. Asian J. Civ. Eng. 2010, 11, 509–520. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Choi, H.; Min, K.W. Use of rotational friction dampers to enhance seismic and progressive collapse resisting capacity of structures. Struct. Des. Tall Spec. Build. 2011, 20, 515–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahraei, S.M.; Moradi, A.; Moradi, M. Using pall friction dampers for seismic retrofit of a 4-story steel building in Iran. In Proceedings of the Topics in Dynamics of Civil Structures, Volume 4: Proceedings of the 31st IMAC, A Conference on Structural Dynamics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 101–107. [Google Scholar]
- Narita, K.; Terazawa, Y.; Maehara, K.; Matsuoka, Y.; Matsui, R.; Takeuchi, T. Dynamic loading tests and response evaluation of steel roof bearings with friction dampers. J. Struct. Constr. Eng. (Trans. AIJ) 2015, 80, 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tafakori, E.; Banazadeh, M.; Jalali, S.A.; Tehranizadeh, M. Risk-based optimal retrofit of a tall steel building by using friction dampers. Struct. Des. Tall Spec. Build. 2013, 22, 700–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalieri, F.; Bellotti, D.; Caruso, M.; Nascimbene, R. Comparative evaluation of seismic performance and environmental impact of traditional and dissipation-based retrofitting solutions for precast structures. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 79, 107918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar, P.M.; Zahrai, S.M. Seismic retrofit of steel buildings using external resistant RC walls and friction dampers. Struct. Eng. Mech. 2020, 76, 823–837. [Google Scholar]
- Mottier, P.; Tremblay, R.; Rogers, C. Shake table test of a two-story steel building seismically retrofitted using gravity-controlled rocking braced frame system. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 50, 1576–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, K.H.; Han, S.W.; Lee, C.S. Seismic retrofit design method using friction damping systems for old low-and mid-rise regular reinforced concrete buildings. Eng. Struct. 2017, 146, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldin, M.N.; Kim, J.; Kim, J. Optimum distribution of steel slit-friction hybrid dampers based on life cycle cost. Steel Compos. Struct. 2018, 27, 633–646. [Google Scholar]
- Caprili, S.; Mattei, F.; Salvatore, W. Seismic performance of steel braced frames equipped with dissipative replaceable components. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 95, 110246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kang, H.; Kim, J. Seismic performance of steel plate slit-friction hybrid dampers. J. Constr. 2017, 136, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atam, E. Friction damper-based passive vibration control assessment for seismically-excited buildings through comparison with active control: A case study. IEEE Access 2018, 7, 4664–4675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, F.; Rezazadeh, H.; Afshar, M.A. Adaptive control of rotationally non-linear asymmetric structures under seismic loads. Struct. Eng. Mech. Int. J. 2018, 65, 721–730. [Google Scholar]
- Rezazadeh, H.; Amini, F.; Dogani Aghcheghloo, P.; Khansefid, A. Effects of geometrical nonlinearity on the performance of bidirectional tuned mass dampers. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 50, 3220–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezazadeh, H.; Amini, F.; Afshar, M.A. Effect of inertia nonlinearity on dynamic response of an asymmetric building equipped with tuned mass dampers. Earthq. Eng. Eng. Vib. 2020, 19, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezazadeh, H.; Jafarzadeh, V.; Atabakhsh, S.; Aghcheghloo, P.D. A novel passive nonlinear two-DOF internal resonance-based tuned mass damper. Mech. Syst. Signal Process 2023, 204, 110788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yu, T.; Yang, Z.; Chen, S.; Hua, X.; Yang, O. Optimum design of pendulum tuned mass dampers considering control performance degradation from damper connection. J. Struct. Eng. 2023, 149, 04023163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzon, L.; Frappa, G.; Pauletta, M. Effectiveness of tuned mass damper in reducing damage caused by strong earthquake in a medium-rise building. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 6815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Balendra, T. Passive control of bilinear hysteretic structures by tuned mass damper for narrow band seismic motions. Eng. Struct. 2013, 54, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrazzo, P.R.; Montuori, R.; Nastri, E.; Benzoni, G. Advanced seismic retrofitting with high-mass-ratio Tuned mass dampers. Soil. Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2024, 179, 108544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.G.; Pantelides, C.P.; Reaveley, L.D. Nonlinear rooftop tuned mass damper frame for the seismic retrofit of buildings. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2015, 44, 299–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, T.; Kurino, H.; Yaguchi, T.; Kano, N. Control effect of large tuned mass damper used for seismic retrofitting of existing high-rise building. Jpn. Archit. Rev. 2019, 2, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, K.; Kanebako, Y.; Tarumi, Y.; Ito, M.; Motoyui, S.; Kitaoka, T. Seismic retrofitting technique of existing mid-rise SRC buildings with newly-added stories utilizing mass damper effect. J. Struct. Constr. Eng. (Trans. AIJ) 2016, 726, 1243–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ji, X.; Jia, R.; Wang, L.; Wang, M.; Wu, X. Seismic design and performance assessment of a retrofitted building with tuned viscous mass dampers (TVMD). Eng. Struct. 2024, 305, 117688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.H.; Chen, C.C.; Chen, T.W.; Shiao, S.Y.; Jiang, C.R.; Yeh, F.Y. Enhancement of structural seismic performance of low-rise buildings using displacement-dependent tuned mass damper. Structures 2022, 37, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Sun, J.; Qiu, H. Experimental study on seismic upgrading of RC frames using innovative brace system with two-stage characteristic. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2022, 22, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, P.; Nishitani, A. Optimum design and application of non-traditional tuned mass damper toward seismic response control with experimental test verification. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2015, 44, 2199–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idels, O.; Lavan, O. Performance-based seismic retrofitting of frame structures using negative stiffness devices and fluid viscous dampers via optimization. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 50, 3116–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrotzki, P.; Siepe, D.; Bottoni, F. Modern systems for wind and seismic induced vibrations. In World Conference on Seismic Isolation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 895–902. [Google Scholar]
- He, H.; Hao, L.; Zhong, J.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, Z.; Xiang, Y. Investigation on a substructure-TVMD (SSTVMD) system for seismic response control of civil structures. Structures 2024, 69, 107517. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Yuan, B. Effect of Soil-Structure interaction on energy dissipation and shock absorption of swing column control devizce. Structures 2023, 57, 105227. [Google Scholar]
- Basili, M.; Busato, F.; De Angelis, M. Integrated seismic and energetic rehabilitation of existing buildings based on the tuned mass damper concept. Results Eng. 2024, 24, 103552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiella, D.; Argenziano, M.; Esposito, F.; Brandonisio, G.; Fraldi, M.; Mele, E. Effectiveness of isolated vertical extension of masonry buildings as nonconventional TMD. Soil. Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2023, 165, 107675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvi, J.; Rizzi, E.; Rustighi, E.; Ferguson, N.S. Optimum tuning of passive tuned mass dampers for the mitigation of pulse-like responses. J. Vib. Acoust. 2018, 140, 061014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Lu, L.Y.; Lin, G.L.; Yang, T.W. Vibration control of seismic structures using semi-active friction multiple tuned mass dampers. Eng. Struct. 2010, 32, 3404–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Marzano, G.; Sasaki, Y.; Kurata, M.; Skalomenos, K. Force redistribution of steel moment-resisting frame retrofitted with a minimal disturbance arm damper. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2018, 114, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, S.A.; Esfandiyari, R.; Zahrai, S.M. Experimental study on two full scale Iranian viscous dampers. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Steel & Structures, Xiamen, China, 29–30 December 2018; pp. 11–12. [Google Scholar]
- Chalarca, B.; Filiatrault, A.; Perrone, D. Expected seismic response and annual seismic loss of viscously damped braced steel frames. Eng. Struct. 2024, 303, 117569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Domenico, D.; Gandelli, E.; Gioitta, A. Displacement-based design procedure for the seismic retrofit of existing buildings with self-centering dissipative braces. Structures 2024, 62, 106174. [Google Scholar]
- Rajeswaran, G.; Wijeyewickrema, A.C. An alternative design method for the seismic retrofit of RC moment resisting frame buildings with viscous dampers. J. Earthq. Eng. 2022, 26, 240–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Xue, J.; Sui, Y.; Wu, Z. Smart retrofitting of irregular steel joints in traditional Chinese buildings by viscous dampers. Eng. Struct. 2021, 228, 111526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, L.; Molari, A.; Diotallevi, P.P. Comparison of different distributions of viscous damper properties in asymmetric-plan frames. Earthq. Struct. 2020, 18, 233–248. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, I.Y.; Ryu, J.; Oh, J.; Ryu, D.; Ko, H.J. Experimental investigation on displacement amplification mechanism of steel wire rope-pulley damping systems with viscous damper. Eng. Struct. 2021, 248, 113206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logotheti, V.E.; Kafetzi, T.C.; Papagiannopoulos, G.A.; Karabalis, D.L. On the use of interstorey velocity for the seismic retrofit of steel frames with viscous dampers. Soil. Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 129, 105312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Zhang, R.; Weng, D.; Ge, Q.; Wang, C.; Islam, M.M. Design method of structural retrofitting using viscous dampers based on elastic–plastic response reduction curve. Eng. Struct. 2020, 208, 109917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bañuelos-García, F.H.; Ayala, G.; López, S. A displacement-based seismic design procedure for buildings with fluid viscous dampers. Earthq. Struct. 2020, 18, 609. [Google Scholar]
- Jara, J.M.; Hernández, E.J.; Olmos, B.A.; Martínez, G. Building damages during the September 19, 2017 earthquake in Mexico City and seismic retrofitting of existing first soft-story buildings. Eng. Struct. 2020, 209, 109977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, S.; Ghobadi, M.S. Seismic resilient bracing structure equipped with hybrid device at base. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 138, 106256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, F.; Asgarkhani, N.; Lasowicz, N.; Jankowski, R. Development and experimental validation of a novel double-stage yield steel slit damper-buckling restrained brace. Eng. Struct. 2024, 315, 118427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollini, N.; Lavan, O.; Amir, O. Optimization-based minimum-cost seismic retrofitting of hysteretic frames with nonlinear fluid viscous dampers. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2018, 47, 2985–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollini, N. Fail-safe optimization of viscous dampers for seismic retrofitting. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2020, 49, 1599–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidiha, H.R.; Yakhchalian, M.; Mohebi, B. Advanced scalar intensity measures for collapse capacity prediction of steel moment resisting frames with fluid viscous dampers. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2018, 109, 102–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollini, N.; Lavan, O.; Amir, O. Minimum-cost optimization of nonlinear fluid viscous dampers and their supporting members for seismic retrofitting. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2017, 46, 1941–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhu, L.H.; Li, H.N. Displacement-based seismic design for buildings installed hysteretic dampers with hardening post-yielding stiffness. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2019, 22, 3420–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidiha, H.R.; Yakhchalian, M. New vector-valued intensity measure for predicting the collapse capacity of steel moment resisting frames with viscous dampers. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2019, 125, 105625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Mahin, S.A. Seismic retrofit of a high-rise steel moment-resisting frame using fluid viscous dampers. Struct. Des. Tall Spec. Build. 2017, 26, e1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Gobbo, G.M.; Blakeborough, A.; Williams, M.S. Improving total-building seismic performance using linear fluid viscous dampers. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2018, 16, 4249–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, L.; Conti, F.; Diotallevi, P.P. Effectiveness of different distributions of viscous damping coefficients for the seismic retrofit of regular and irregular RC frames. Eng. Struct. 2015, 100, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Shin, H. Seismic loss assessment of a structure retrofitted with slit-friction hybrid dampers. Eng. Struct. 2017, 130, 336–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahmani, M.; Zahrai, S.M. Proposed Methodology and Comprehensive Design Process for Seismic Rehabilitation of Steel Structures with Supplemental Viscous Dampers. Civ. Eng. Infrastruct. J. 2023, 56, 79–103. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, R.; Lu, Z.; Guo, M.; Guo, L. Capacity Spectrum-Based Retrofitting Method and Quick Design for Viscously Damped Structures by Utilizing the Concept of Uniform Damping Ratio. Buildings 2023, 13, 1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Domenico, D.; Hajirasouliha, I. Multi-level performance-based design optimisation of steel frames with nonlinear viscous dampers. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2021, 19, 5015–5049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terenzi, G.; Costoli, I.; Sorace, S. Activation control extension of a design method of fluid viscous dissipative bracing systems. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 18, 4017–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahmani, M.; Zahrai, S.M. Application of a comprehensive seismic retrofit procedure for steel buildings using nonlinear viscous dampers. Int. J. Civ. Eng. 2019, 17, 1261–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Xu, J.; Xu, W.; Di, Z. Seismic upgrade of existing buildings with fluid viscous dampers: Design methodologies and case study. J. Perform. Constr. Facil. 2015, 29, 04014175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Mahin, S.A. High-performance computer-aided optimization of viscous dampers for improving the seismic performance of a tall building. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2018, 113, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollini, N.; Lavan, O.; Amir, O. Towards realistic minimum-cost optimization of viscous fluid dampers for seismic retrofitting. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2016, 14, 971–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, D.G.; Zhang, C.; Lu, X.L.; Zeng, S.; Zhang, S.M. A simplified design procedure for seismic retrofit of earthquake-damaged RC frames with viscous dampers. Struct. Eng. Mech. 2012, 44, 611–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavent-Climent, A. An energy-based method for seismic retrofit of existing frames using hysteretic dampers. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2011, 31, 1385–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.W.W.; Christopoulos, C. Performance spectra based method for the seismic design of structures equipped with passive supplemental damping systems. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2013, 42, 935–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Lu, X.; Weng, D.; Zhang, R. A practical design method for reinforced concrete structures with viscous dampers. Eng. Struct. 2012, 39, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.Y.; Patil, R.D. A review on seismic analysis of a multi-storied steel building provided with different types of damper and base isolation. Asian J. Civ. Eng. 2024, 25, 3277–3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.Y.; Patil, R.D. Effect of seismic provision on behaviour of steel and composite slab building analyzed using ETABs software. Asian J. Civ. Eng. 2024, 25, 5435–5442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldız, M.G.; Tüzün, C.; Tanırcan, G. Design of seismic retrofitting using viscous dampers: A case study from a school building. In World Conference on Seismic Isolation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 253–266. [Google Scholar]
- Sorace, S.; Costoli, I.; Terenzi, G. Seis mic assessment and dissipative bracing retrofit-based protection of infills and partitions in RC structures. Eng. Struct. 2023, 281, 115781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.C.; Wang, S.J.; Hwang, J.S. Seismic retrofit of existing critical structures using externally connected viscous dampers. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. 2022, 22, 2250144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miani, M.; Di Marco, C.; Frappa, G.; Pauletta, M. Effects of dissipative systems on the seismic behavior of irregular buildings—Two case studies. Buildings 2020, 10, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, J.; Ahmad, N.; Rizwan, M.; Javed, S.; Alam, B. Response modification factor of RC frames strengthened with RC haunches. Shock Vib. 2020, 2020, 3835015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonda, D.; Pollini, A.; Cossu, M. Seismic retrofit of an industrial building using damping devices. Struct. Eng. Int. 2020, 30, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettinga, D. Retrofit of reinforced concrete moment frames in NZ using dual supplemental damping. Struct. Eng. International 2020, 30, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, A.; Kim, J. Seismic performance evaluation of a spring viscous damper cable system. Eng. Struct. 2018, 176, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terenzi, G.; Bazzani, C.; Costoli, I.; Sorace, S.; Spinelli, P. Seismic assessment and retrofit design of a school building in Florence. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 603, 032003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazaveh, N.K.; Rodgers, G.W.; Pampanin, S.; Chase, J.G. Damping reduction factors and code-based design equation for structures using semi-active viscous dampers. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2016, 45, 2533–2550. [Google Scholar]
- Barbagallo, F.; Bosco, M.; Marino, E.M.; Rossi, P.P. Seismic retrofitting of braced frame buildings by RC rocking walls and viscous dampers. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2018, 47, 2682–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, J. Retrofit existing frame structures to increase their economy and sustainability in high seismic hazard regions. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, K.; Yang, S. Mechanical performance analysis of a piezoelectric ceramic friction damper and research of its semi-active control strategy. Structures 2021, 33, 1510–1531. [Google Scholar]
- Naeem, A.; Kim, J. Seismic retrofit of a framed structure using damped cable systems. Steel Compos. Struct 2018, 29, 287–299. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Bao, L.; Xue, B. An energy-dissipating approach for adjacent retrofitted structures. Struct. Des. Tall Spec. Build. 2018, 27, e1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.S.; Mahin, S. High-Performance Computer-Aided Optimization of Viscous Dampers for Improving the Seismic Performance of a Tall Steel Building. Key Eng. Mater. 2018, 763, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terenzi, G.; Bazzani, C.; Costoli, I.; Sorace, S.; Spinelli, P. Advanced seismic retrofit of a mixed R/C-Steel structure. Buildings 2019, 9, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorace, S.; Terenzi, G.; Fadi, F. Shaking table and numerical seismic performance evaluation of a fluid viscous-dissipative bracing system. Earthq. Spectra 2012, 28, 1619–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougteb, Y.; Ray, T. Choice between series and parallel connections of hysteretic system and viscous damper for seismic protection of structures. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2018, 47, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorace, S.; Terenzi, G. Motion control-based seismic retrofit solutions for a R/C school building designed with earlier Technical Standards. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2014, 12, 2723–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavan, O.; Amir, O. Simultaneous topology and sizing optimization of viscous dampers in seismic retrofitting of 3D irregular frame structures. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2014, 43, 1325–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, F.; Mohebi, B.; Jankowski, R. Predicting the seismic collapse capacity of adjacent SMRFs retrofitted with fluid viscous dampers in pounding condition. Mech. Syst. Signal Process 2021, 161, 107939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubaldi, E.; Barbato, M.; Ghazizadeh, S. A probabilistic performance-based risk assessment approach for seismic pounding with efficient application to linear systems. Struct. Saf. 2012, 36, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tubaldi, E.; Gioiella, L.; Scozzese, F.; Ragni, L.; Dall’Asta, A. A design method for viscous dampers connecting adjacent structures. Front. Built Environ. 2020, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavia, A.; Scozzese, F.; Petrucci, E.; Zona, A. Seismic upgrading of a historical masonry bell tower through an internal dissipative steel structure. Buildings 2021, 11, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, F.; Ding, J.; Wu, H.; Cai, X.; Yang, J. Optimization Analysis of Hysteretic Dampers Design Parameters on Seismic Performance of a Novel Self-Centering Prefabricated Concrete Frame. J. Earthq. Eng. 2023, 27, 3228–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, A.; Koichi, K.; Lee, J. Seismic Performance Evaluation of Reinforced Concrete Building Structure Retrofitted with Self-Centering Disc-Slit Damper and Conventional Steel Slit Damper. Buildings 2024, 14, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Salvatore, C.; Magliulo, G.; Caterino, N. Innovative hysteretic device for seismic retrofit of single-story RC precast buildings. Eng. Struct. 2024, 313, 118261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javidan, M.M.; Kim, J. A rotational friction damper-brace for seismic design of resilient framed structures. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 51, 104248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruschi, E.; Quaglini, V. Assessment of a novel hysteretic friction damper for the seismic retrofit of reinforced concrete frame structures. In Structures; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 46, pp. 793–811. [Google Scholar]
- Javidan, M.M.; Kim, J. Steel hysteretic column dampers for seismic retrofit of soft-first-story structures. Steel Compos. Struct 2020, 37, 259–272. [Google Scholar]
- Javidan, M.M.; Chun, S.; Kim, J. Experimental study on steel hysteretic column dampers for seismic retrofit of structures. Steel Compos. Struct. 2021, 40, 495–509. [Google Scholar]
- Terenzi, G.; Costoli, I.; Sorace, S.; Spinelli, P. Verification of an energy-based design procedure for seismic retrofit of a school building. Procedia Struct. Integr. 2018, 11, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruschi, E.; Quaglini, V.; Calvi, P.M. A simplified design procedure to improve the seismic performance of RC framed buildings with hysteretic damped braces. In International Symposium, New Metropolitan Perspectives; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 2173–2182. [Google Scholar]
- Gandelli, E.; Chernyshov, S.; Distl, J.; Dubini, P.; Weber, F.; Taras, A. Novel adaptive hysteretic damper for enhanced seismic protection of braced buildings. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2021, 141, 106522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmat Rabi, R.; Bianco, V.; Monti, G. Energy-based method to design hysteretic bracings for the seismic rehabilitation of low-to-medium rise RC frames. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2022, 20, 587–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Domenico, D.; Facconi, L.; Gandelli, E.; Gioitta, A.; Longo, P.; Maugeri, N. Seismic protection of substandard rc frames through self-centering dissipative braces. In Proceedings of the Compdyn 2023, The 9th ECCOMAS Thematic Conference on Computational Methods in Structural Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, Athens, Grece, 12–14 June 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Bruschi, E.; Quaglini, V. Reliability analysis of two archetype RC buildings with hysteretic dampers. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2024, 176, 108290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Koetaka, Y.; Chen, Z.P.; Zhu, S.; Alam, M.S. Hybrid self-centering braces with NiTi-SMA U-shaped and frequency-dependent viscoelastic dampers for structural and nonstructural damage control. Eng. Struct. 2024, 308, 117920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare, A.; Lamarucciola, N.; Ponzo, F.C. Multi-stripe dynamic analysis of existing rc buildings seismically retrofitted by base isolation or dissipative bracing systems conforming to italian code. In World Conference on Seismic Isolation; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 267–276. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.N.; Zhu, L.H. Dynamic analysis of structures installed hysteretic dampers with hardening post-yielding stiffness using connection element method. J. Comb. Optim. 2024, 45, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraioli, M.; Laurenza, B.; Lavino, A.; Frattolillo, C.; De Matteis, G. Seismic retrofit of a steel-reinforced concrete hospital building using continuous energy-dissipative steel columns. Steel Compos. Struct. 2023, 47, 467–488. [Google Scholar]
- Sorace, S.; Terenzi, G.; Frangipane, A. Incorporation of dissipative connections for seismic retrofit of reinforced concrete prefab structures. Ing. Sismica 2019, 36, 55–65. [Google Scholar]
- Ferraioli, M.; Concilio, A.; Molitierno, C. Seismic performance of a reinforced concrete building retrofitted with self-centering shape memory alloy braces. Earthq. Eng. Eng. Vib. 2022, 21, 785–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javidan, M.M.; Nasab, M.E.; Kim, J. Full-scale tests of two-story RC frames retrofitted with steel plate multi-slit dampers. Steel Compos. Struct 2021, 39, 645–664. [Google Scholar]
- Nuzzo, I.; Losanno, D.; Caterino, N.; Serino, G.; Rotondo, L.M.B. Experimental and analytical characterization of steel shear links for seismic energy dissipation. Eng. Struct. 2018, 172, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, J. Development of box-shaped steel slit dampers for seismic retrofit of building structures. Eng. Struct. 2017, 150, 934–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavent-Climent, A.; Mota-Páez, S. Earthquake retrofitting of R/C frames with soft first story using hysteretic dampers: Energy-based design method and evaluation. Eng. Struct. 2017, 137, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terenzi, G.; Sorace, S.; Fuso, E. Stiffening effects-controlling sizing procedure of ADAS dampers in seismic retrofit of frame structures. Front. Built Environ. 2023, 9, 1114349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dereje, A.J.; Javidan, M.M.; Ahn, T.S.; Kim, J. Experimental and analytical study of a seismic energy dissipation device made of butterfly-shaped steel plates and viscoelastic pads. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 82, 108251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruschi, E.; Quaglini, V.; Calvi, P.M. A simplified design procedure for seismic upgrade of frame structures equipped with hysteretic dampers. Eng. Struct. 2022, 251, 113504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javidana, M.M.; Kim, J. Steel hexagonal damper-brace system for efficient seismic protection of structures. Steel Compos. Struct. 2022, 45, 683–695. [Google Scholar]
- Nuzzo, I.; Losanno, D.; Caterino, N. Seismic design and retrofit of frame structures with hysteretic dampers: A simplified displacement-based procedure. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2019, 17, 2787–2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazza, F. A simplified retrofitting method based on seismic damage of a SDOF system equivalent to a damped braced building. Eng. Struct. 2019, 200, 109712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavent-Climent, A.; Oliver-Saiz, E.; Donaire-Ávila, J. Seismic retrofitting of RC frames combining metallic dampers and limited strengthening with FRP/SRP applying energy-based methods. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2024, 177, 108432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.W.W.; Christopoulos, C. Mitigation of the seismic response of structures with vertical stiffness and strength irregularity using supplemental dampers. In Seismic Behaviour and Design of Irregular and Complex Civil Structures; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 309–322. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Shu, G. Optimal placement of metallic dampers for seismic upgrading of multistory buildings based on a cost-effectiveness criterion using genetic algorithm. Struct. Des. Tall Spec. Build. 2019, 28, e1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraioli, M.; Lavino, A. A displacement-based design method for seismic retrofit of rc buildings using dissipative braces. Math. Probl. Eng. 2018, 2018, 5364564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolakis, G.; Dargush, G.F. Optimal seismic design of moment-resisting steel frames with hysteretic passive devices. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2010, 39, 355–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazza, F.; Mazza, M. Seismic retrofitting of gravity-loads designed rc framed buildings combining CFRP and hysteretic damped braces. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2019, 17, 3423–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, F.; Piscini, A.; Salvatore, W. Seismic behavior of an industrial steel structure retrofitted with self-centering hysteretic dampers. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2017, 139, 157–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatanshenas, A.; Rohanimanesh, M.S.; Mohammadiha, E. Investigating the performance of viscoelastic dampers (ved) under nearfield earthquakes with directivity feature. Civ. Environ. Eng. Rep. 2018, 14, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javidan1a, M.M.; Naeem, A.; Kim, J. Seismic retrofit of structures using added steel column friction dampers. Steel Compos. Struct 2023, 49, 257–270. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.R.; Xu, Z.D.; Shi, Q.; Li, Q.Q.; He, Z.H.; Cheng, Y. Seismic performance and material-level damage evolution of retrofitted RC framed structures by high-performance AVED under different shear-span ratio. J. Build. Eng. 2023, 63, 105495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasab, M.S.E.; Chun, S.; Kim, J. Soil-structure interaction effect on seismic retrofit of a soft first-story structure. Structures 2021, 32, 1553–1564. [Google Scholar]
- Nasab, M.S.E.; Kim, J. Fuzzy analysis of a viscoelastic damper in seismic retrofit of structures. Eng. Struct. 2022, 250, 113473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, R.; Yang, K.; Chen, Q.; Weng, D. Seismic resilient design and negative stiffness-assisted nonlinear isolation system for adjacent non-coaxial buildings linked by corridors. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2023, 175, 108227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.R.; Xu, Z.D.; Zhu, L.; Shi, Q.; Li, Q.Q.; He, J.X.; Cheng, Y. Experimental study and multi-scale refinement model of high damping acrylic polymer matrix VEDs for civil structural seismic retrofit. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2024, 53, 2908–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javidan, M.M.; Ahmad, R.N.; Park, S.; Kim, J. Seismic retrofit of structures using steel frames with viscoelastic hinges. Structures 2024, 64, 106585. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.R.; Xu, Z.D.; Li, Q.Q.; Zhu, C.; He, Z.H. Design parameters and material-scale damage evolution of seismic upgraded RC frames by viscoelastic haunch bracing-dampers. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2021, 50, 1476–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir Pour, M.J. Seismic Damage Assessment of Steel Buildings considering Viscoelastic Dampers in Near-Field Earthquake. Shock. Vib. 2022, 2022, 2905960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Liu, M.; Li, J.; Tan, P.; Wu, D. Multi-performance oriented seismic design of viscoelastic dampers for structural retrofitting. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 86, 108657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Aguaguiña, M.; Beskos, D.E.; Gong, S. A displacement-based seismic design method for building structures with nonlinear viscoelastic dampers. Bull. Earthq. Eng. 2021, 19, 4535–4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvin Darabad, Y.; Hassanpour Yasaghi, A.; Khodaei, B.; Zarei, R. Distribution of seismic damage in steel buildings component equipped by viscoelastic dampers against far-field earthquake. Shock Vib. 2021, 2021, 8291173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasab, M.S.E.; Guo, Y.Q.; Kim, J. Seismic retrofit of a soft first-story building using viscoelastic dampers considering inherent uncertainties. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 47, 103866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasab, M.S.E.; Kim, J.; Ahn, T.S. Seismic performance evaluation of a steel slit damper for retrofit of structures on soft soil. Steel Compos. Struct. 2024, 51, 93–101. [Google Scholar]
- Nasab, M.S.E.; Kim, J. Seismic retrofit of structures using hybrid steel slit–viscoelastic dampers. J. Struct. Eng. 2020, 146, 04020238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Huang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, W. Experimental and numerical investigation on seismic performance of retrofitted RC frame with sector lead viscoelastic damper. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 44, 103218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshti, M.; Asadi, P. Optimal seismic retrofit of fractional viscoelastic dampers for minimum life-cycle cost of retrofitted steel frames. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2020, 61, 2021–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Zhang, L.; Pan, C.; Zhang, R.; Chen, T. Uniform damping ratio-based design method for seismic retrofitting of elastoplastic RC structures using viscoelastic dampers. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2020, 128, 105866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaldo, P.; De Iuliis, M. Optimal integrated seismic design of structural and viscoelastic bracing-damper systems. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2014, 43, 1809–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.R.; Xu, Z.D.; Li, Q.Q.; Xu, Y.S.; Chen, Z.H. Seismic behavior and damage evolution for retrofitted RC frames using haunch viscoelastic damping braces. Eng. Struct. 2019, 199, 109583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.D.; Wang, D.X.; Shi, C.F. Model, tests and application design for viscoelastic dampers. J. Vib. Control 2011, 17, 1359–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, J.E.; Hur, M.W.; Choi, H.H.; Lee, S.H. Development of a multiaction hybrid damper for passive energy dissipation. Shock Vib. 2018, 2018, 5630746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaisee, S.; Yue, F.; Ooi, Y.H. A state-of-the-art review on passive friction dampers and their applications. Eng. Struct. 2021, 235, 112022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Housner, G.; Bergman, L.A.; Caughey, T.K.; Chassiakos, A.G.; Claus, R.O.; Masri, S.F.; Skelton, R.E.; Soong, T.T.; Spencer, B.F.; Yao, J.T. Structural control: Past, present, and future. J. Eng. Mech. 1997, 123, 897–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.C.; Tseng, W.H.; Huang, C.H.; Tsuang, S.; Chang, L.M.; Chen, Y.H. A novel steel lever viscoelastic wall with amplified damper force-friction for wind and seismic resistance. Eng. Struct. 2020, 210, 110362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Hu, S.; Yang, M.; Zhang, Y. Metallic yielding dampers and fluid viscous dampers for vibration control in civil engineering: A review. Int. J. Struct. Stab. Dyn. 2022, 22, 2230006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halperin, I.; Ribakov, Y.; Agranovich, G. Optimal viscous dampers gains for structures subjected to earthquakes. Struct. Control Health Monit 2016, 23, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, A.; Su, Y.; Xu, G.; Ben, S. Viscoelastic dampers for civil engineering structures: A systematic review of constructions, materials, and applications. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 96, 110597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djerouni, S.; Elias, S.; Abdeddaim, M.; Rupakhety, R. Multi-tuned mass damper inerter (MTMDI) system for earthquake-induced vibration control of buildings. Eng. Struct. 2025, 322, 119139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, Q.; Xue, Y.; Jiang, Y. Nonlinear damping baffle-isolated tuned liquid damper for vibration control. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2025, 190, 109213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Koetaka, Y.; Sun, F.F.; Liu, C.; Nagarajaiah, S.; Ashida, Y.; Du, X.L. Dynamic Test of Negative Stiffness Damped Outrigger with Damping Amplification. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2025, 54, 1141–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A. Response control of multi-storied adjacent buildings using double-compliant liquid dampers-inerter subjected to seismic excitations. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2025, 191, 109276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.G.; Kim, J.Y.; Jung, J.S.; Lee, K.S. Seismic protection provided by a new diamond-shaped bracing system with a horizontally layered friction damper. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 92, 109709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Hao, H.; Meng, D.; Yang, M. Theoretical and numerical study of the thermo-mechanical coupling effect on the fluid viscous damper. J. Sound Vib. 2025, 597, 118846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lie, W.; Zhu, B.; Shi, F.; Zhou, Y. Temperature-Dependent Probabilistic Seismic Assessment of Moment-Resisting Frame with Frequency-independent Viscoelastic Dampers. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 104, 112227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaz, R.D.; Malik, U.J.; Shah, M.U.; Usman, M.; Najam, F.A. Enhancing seismic resilience of existing reinforced concrete building using non-linear viscous dampers: A comparative study. Actuators 2023, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Wang, B.; Chen, P.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, Z. Adaptive seismic isolation system combining gap dampers for pounding mitigation in base-isolated structures. Eng. Struct. 2025, 322, 119079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ye, K.; Hu, L. Enhancing base-isolation structures by optimized configurable friction isolator-tuned inerter damper system. Eng. Struct. 2025, 329, 119818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, H. Performance-based seismic design and vulnerability assessment of concrete frame retrofitted by metallic dampers. Structures 2023, 57, 105073. [Google Scholar]
- Ozer, E.; Inel, M. The Effect of Single and Combined Use of Base Isolator and Fluid Viscous Damper on Seismic Performance in a Conventional RC Building with Torsional Irregularity. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 101, 111898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.; Mesny, L.; Chesné, S. Sliding Mode Control for Hybrid Mass Dampers: Experimental analysis on robustness. J. Sound Vib. 2024, 575, 118241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Hao, L.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, Z.; Xiang, Y.; Li, Y. Equivalent damping ratio oriented investigation on tuned negative stiffness inerter damper for seismic application. J. Sound Vib. 2024, 589, 118538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djerouni, S.; Bekdaş, G.; Nigdeli, S.M. Optimization and performance assessment of Multi-Tuned Mass Dampers (MTMD) to mitigate seismic pounding of adjacent buildings via a novel hybrid algorithm. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 103, 112168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lie, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Hong, J.; Chen, Z. Potential use of rotational metallic dampers for seismic enhancement of infilled RC frames with open first story. Eng. Struct. 2025, 322, 119080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latosh, F.; Al-Sakkaf, A.; Bagchi, A. Feasibility Study on the Effect of FRP Shear Reinforcements on the Behaviour of FRP-Reinforced Concrete Deep Beams. CivilEng 2023, 4, 522–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algamati, M.; Al-Sakkaf, A.; Mohammed Abdelkader, E.; Bagchi, A. Studying and Analyzing the Seismic Performance of Concrete Moment-Resisting Frame Buildings. CivilEng 2023, 4, 34–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algamati, M.; Al-Sakkaf, A.; Bagchi, A. Seismic Retrofitting of Reinforced Concrete Structures: A Comparative. Eur. J. Adv. Eng. Technol. 2025, 12, 10–19. [Google Scholar]

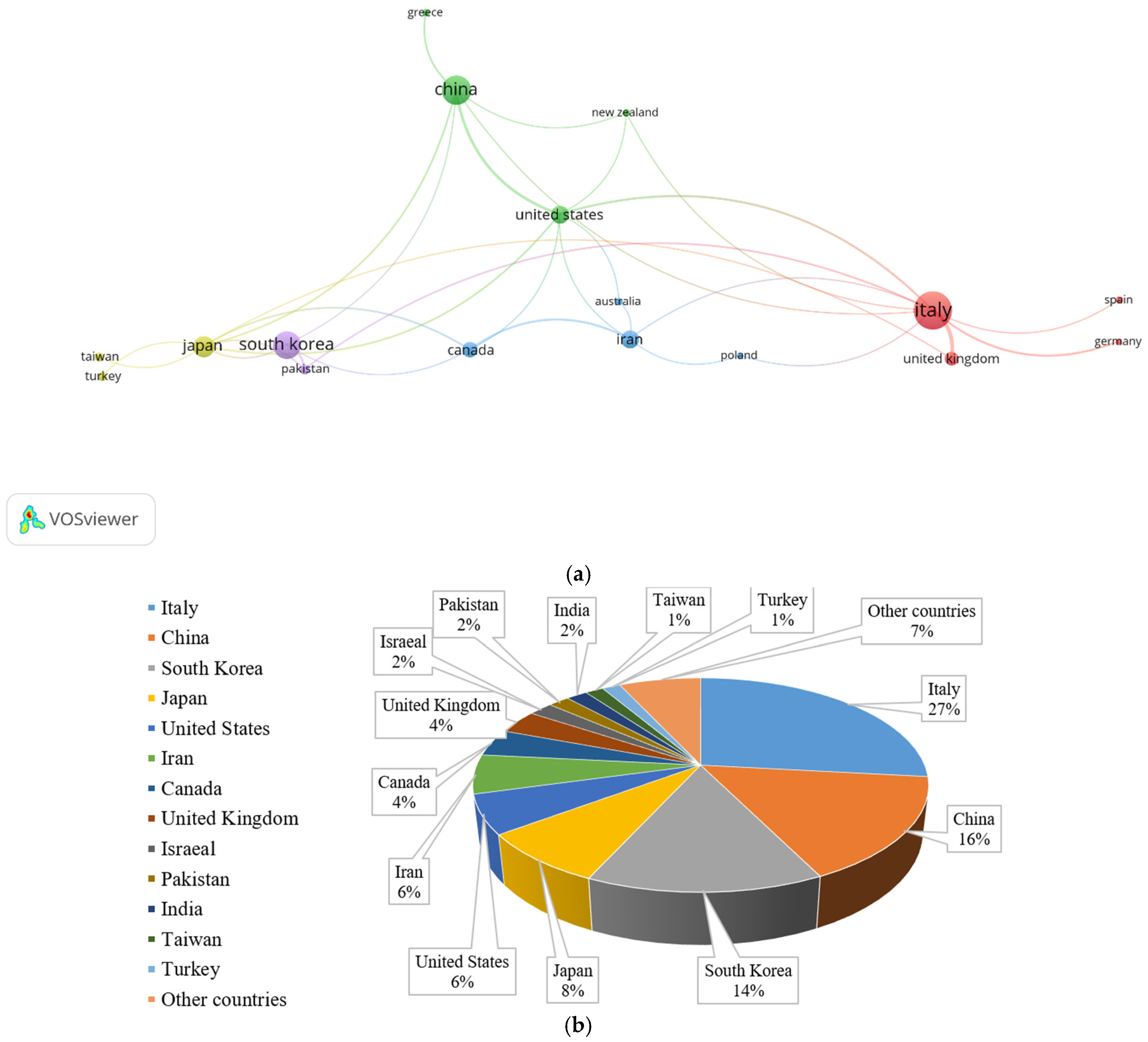

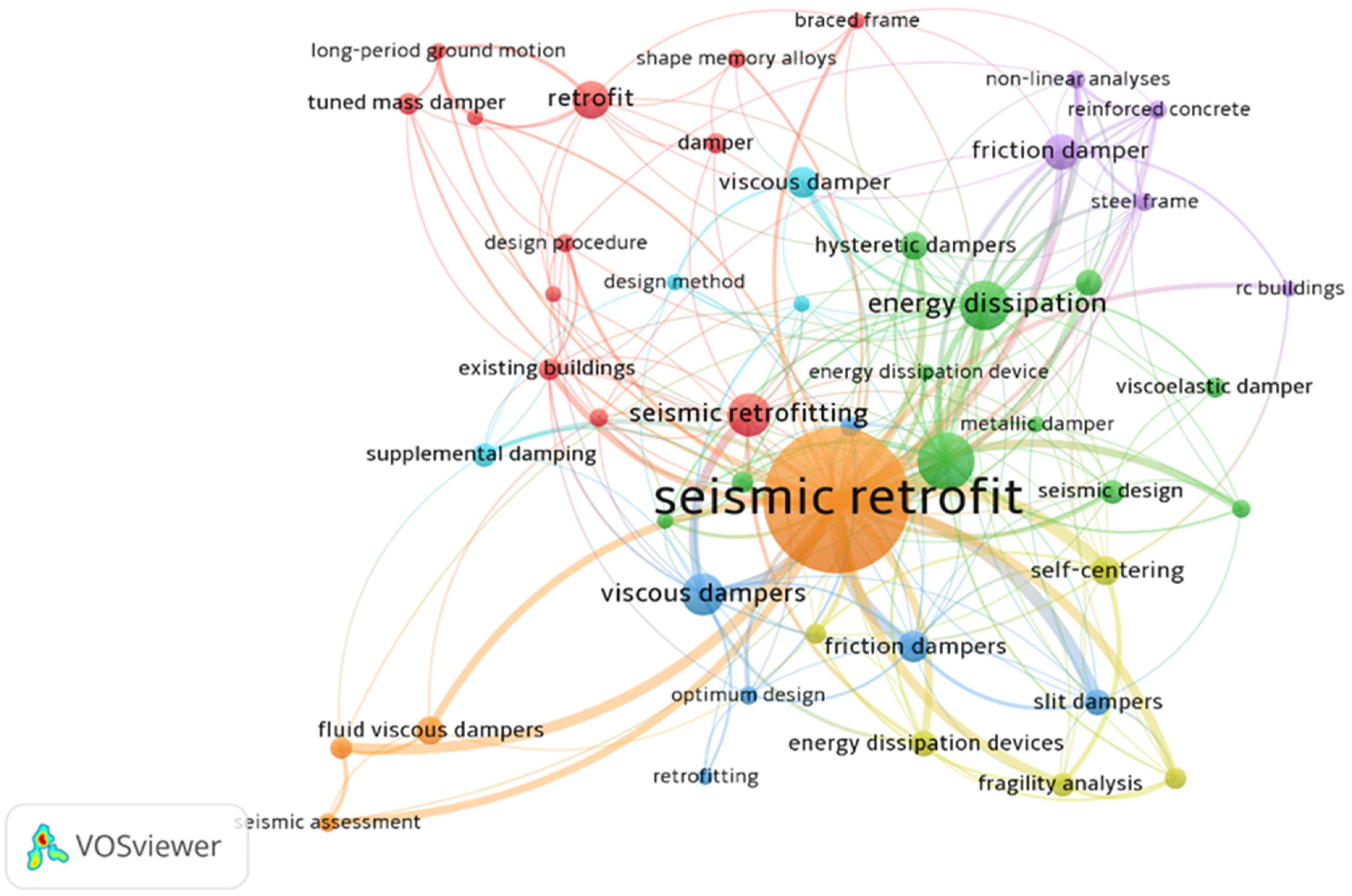
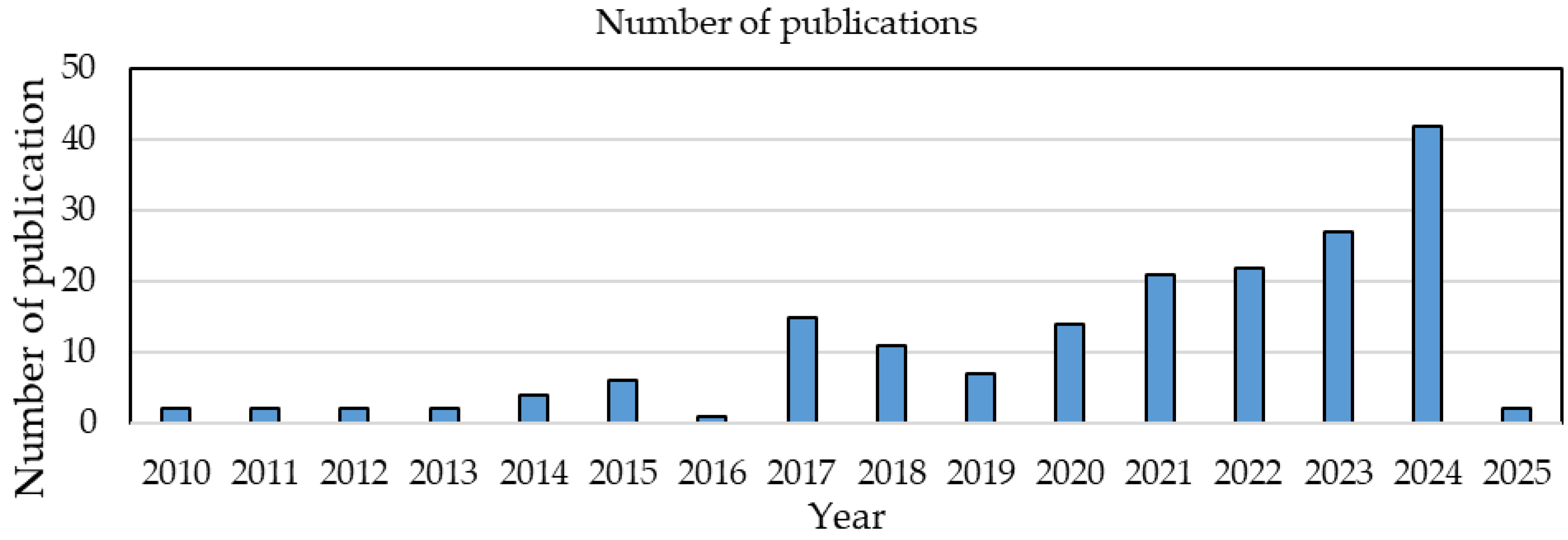
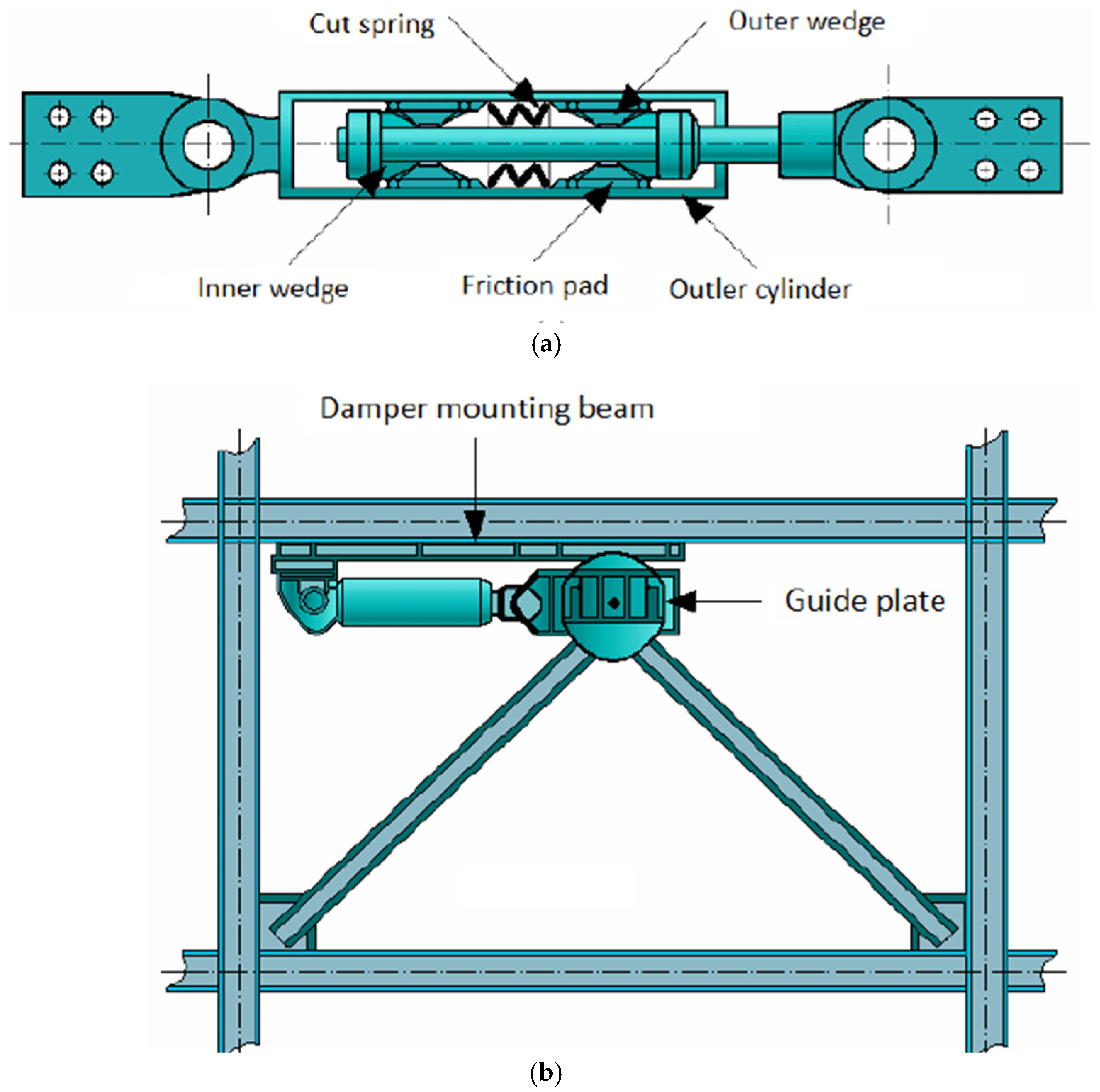



| Author Name | Number of Publication |
|---|---|
| Kim, Jinkoo | 43 |
| Javadian, Mohammad Mehdi | 15 |
| Terenzi, Gloria | 15 |
| Sorace, Stefano | 13 |
| Quaglini, Virginio | 9 |
| Bruschi, Eleonora | 8 |
| Ferraioli, Massimiliano | 8 |
| Naeem, Asad | 7 |
| Chun, Seungho | 6 |
| Nasab, Mohammad Seddiq Eskandari | 6 |
| Noureldin, Mohamad | 6 |
| Xu, Zhao-Dong | 6 |
| Zhang, Ruifu | 6 |
| Institution | Number of Publication |
|---|---|
| Department of Civil and Architectural Engineering, Sungkyunkwan University | 31 |
| Department of civil and environmental engineering, University of Florence | 11 |
| Department of Disaster Mitigation for Structures, Tongji University | 6 |
| School of Civil Engineering, Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology | 6 |
| Polytechnic Department of Engineering and Architecture, University of Udine | 5 |
| Politecnico di Milano, Department of Architecture, Built Environment and Construction Engineering | 4 |
| General Goal | Related Papers |
|---|---|
| Presenting and developing new friction damping devices | Javidan et al. [2], Aprile et al. [11], Wang et al. [12], Qu et al. [26], Li et al. [27], Grossi et al. [16], Grossi et al. [17], Grossi et al. [18], Suk et al. [28], Bruschi et al. [19], Melatti et al. [22], Bruschi et al. [29], Javidan et al. [30], Aloisio et al. [31], Javidan et al. [25], Kim and Jinkoo [32], Wang et al. [33] |
| Developing design method | Gharagoz et al. [20], Gharagoz et al. [21], Rad et al. [34], Tirca et al. [35] |
| Case and feasibility study | Sirinipitakul et al. [36], Saingam et al. [37], Shin et al. [38], Javidan et al. [15], Titirla and Magdalini [39], Woo et al. [40], Ahmadi et al. [41], Ferraioli et al. [42], Noureldin et al. [43], Naeem & Kim [44], Saingam et al. [45], Jara et al. [46], Noureldin et al. [47], Eldin et al. [48], Li et al. [49], Beheshti et al. [50], Khader et al. [51], Tabeshpour and Ebrahimian [52], Kim et al. [53], Zahraei et al. [54], Narita et al. [55], Tafakori et al. [56] |
| Comparative study | Cavalieri et al. [57], Afshar & Zahari [58], Mottier et al. [59], Moon et al. [60] |
| Optimization and arrangement of dampers | Eldin et al. [61], Kim et al. [23] |
| Evaluating the performance of retrofitted buildings | Caprili et al. [62], Lee et al. [63] |
| Loss assessment study | Kim et al. [23] |
| General Goal | Related Papers |
|---|---|
| Case study | Mazzon et al. [70], Nawrotzki et al. [81], Marrazzo et al. [72], He et al. [82], Zheng et al. [83], Basili et al. [84], Faiella et al. [85], Nakai [74], Kaneko et al. [75], Idels et al. [80] |
| Design method | Ji et al. [76], Lee et al. [77], Xiang & Nishitani [79], Salvi et al. [86] |
| New dissipating device | Johnson et al. [73] |
| Comparative study | Lin et al. [87] |
| Feasibility study | Zhang et al. [88] |
| General Goal | Related Papers |
|---|---|
| Presenting and developing new viscous damping devices | Jung et al. [95], Salehi & Ghobadi [100], Kim and Shin [111] |
| Developing design method | Bahmani and Zahrai [112], Hu et al. [113], De Domenico & Hajirasouliha [114], Rajeswaran & Wijeyewickrema [92], Terenzi et al. [115], Shen et al. [97], Bañuelos-García et al. [98], Pollini [103], Bahmani et al. [116], Guo et al. [117], Wang et al. [118], Pollini et al. [105], Pollini et al. [119], Weng et al. [120], Benavent-Climent and Amadeo [121], Guo et al. [122], Zhou et al. [123] |
| Case and feasibility study | Sorace et al. [6], Saingam and Panumas [37], Patil et al. [124,125], Yıldız et al. [126], Sorace et al. [127], Lin et al. [128], Qi et al. [93], Jara et al. [46], Miani et al. [129], Logotheti et al. [96], Akbar et al. [130], Sonda et al. [131], Jara et al. [99], Pettinga and Didier [132], Naeem et al. [133], Terenzi et al. [134], Hazaveh et al. [135], Barbagallo et al. [136], Li et al. [137], Wang et al. [138], Naeem & Kim [139], Zhao et al. [140], Wang & Mahin [141], Terenzi et al. [142], Sorace et al. [143] |
| Comparative study | Bougteb et al. [144], Sorace & Terenzi [145], |
| Optimization and arrangement of dampers | Landi et al. [94], Landi et al. [110], Lavan & Amir [146] |
| Evaluating the performance of retrofitted buildings | |
| Predictive and loss assessment study | Chalarca et al. [90], Kazemi et al. [147], Jamshidiha et al. [104], Jamshidihaand Yakhchalian [107], Del Gobbo et al. [109], Tubaldi et al. [148], Tubaldi et al. [149] |
| General Goal | Related Papers |
|---|---|
| Experimental verification | Naeem et al. [9] |
| Case study | Wang et al. [24], Hu et al. [164], Bruschi et al. [163], Di Cesare et al. [165], Ma et al. [166], Ferraioli et al. [167], Naeem et al. [152], Sorace et al. [168], Ahmadi et al. [41], Ferraioli et al. [169], Javidan et al. [170], Nuzzo et al. [171], Lee & Kim [172], Benavent-Climent et al. [173] |
| Introducing and developing new device | Terenzi and Gloria [174], Dereje et al. [175], Di Salvatore et al. [153], Javidan et al. [30], Bruschi et al. [176], Javidan et al. [177], Gandelli et al. [160], Javidan et al. [154], Nuzzo et al. [178], Mazza and Fabio [179], Benavent-Climent et al. [180], Guo & Christopoulos [181] |
| Presenting new design method | Bruschi et al. [19], Bruschi et al. [29], Javidan et al. [177], Rahmat Rabi et al. [161], Bruschi et al. [176], Pollini et al. [119], Li & Shu [182], Ferraioli & Lavinon [183] |
| Optimization and arrangement of dampers | Apostolakis & G. F. Dargush [184] |
| General Goal | Related Paper |
|---|---|
| Presenting and developing new viscous damping devices | Dong et al. [193], Hu et al. [164], Dereje et al. [175], Dong et al. [189], Dong et al. [4], Javidan et al. [2], Nasab et al. [200], Nasab et al. [201], Nasab et al. [202], Zhang et al. [203], Wang et al. [33] |
| Developing design method | Hao et al. [197], Beheshti et al. [204], Zhou et al. [198], Dong et al. [195], Xie et al. [205], Castaldo et al. [206] |
| Case and feasibility study | Javidan et al. [188], Parvin Darabad et al. [199], Nasab et al. [200], Nasab et al. [190], Dong et al. [207], Xu et al. [208] |
| Comparative study | |
| Optimization and arrangement of dampers | |
| Evaluating the performance of retrofitted buildings | |
| Predictive and Loss assessment study | Bashir Pour and Mohammad Javad [196] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Algamati, M.; Al-Sakkaf, A.; Bagchi, A. Energy Dissipation Technologies in Seismic Retrofitting: A Review. CivilEng 2025, 6, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/civileng6020023
Algamati M, Al-Sakkaf A, Bagchi A. Energy Dissipation Technologies in Seismic Retrofitting: A Review. CivilEng. 2025; 6(2):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/civileng6020023
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlgamati, Mohamed, Abobakr Al-Sakkaf, and Ashutosh Bagchi. 2025. "Energy Dissipation Technologies in Seismic Retrofitting: A Review" CivilEng 6, no. 2: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/civileng6020023
APA StyleAlgamati, M., Al-Sakkaf, A., & Bagchi, A. (2025). Energy Dissipation Technologies in Seismic Retrofitting: A Review. CivilEng, 6(2), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/civileng6020023








