Effect of Different Irrigation Managements on Infiltration Equations and Their Coefficients
Abstract
1. Introduction
- To use soil columns to measure cumulative infiltration under various irrigation treatments;
- To calculate the soil hydraulic parameters and infiltration in various initial soil moistures and water heads with the HYDRUS-1D model;
- To determine the coefficients of the infiltration equations and identify the most sensitive infiltration equations and their coefficients relative to different initial soil moistures and water heads.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Methodology
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Irrigation Management
- Intermittent (Mi): Irrigation is performed when the soil moisture reaches 70% of field capacity (FC) (management of conventional). By the weighing procedure, the soil moisture was calculated.
- Daily (Md): To avoid an excessive buildup of solutes in the soil columns, the soil was irrigated daily with a fraction of leaching (LF) of 0.15 (management of ideal).
2.4. Laboratory Experiments
2.5. Simulation of Infiltration Process and Sensitivity Analysis
2.6. Infiltration Equations
2.7. Sensitivity Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Experimental Columns
3.2. Simulation and Sensitivity Analysis of 1D Infiltration
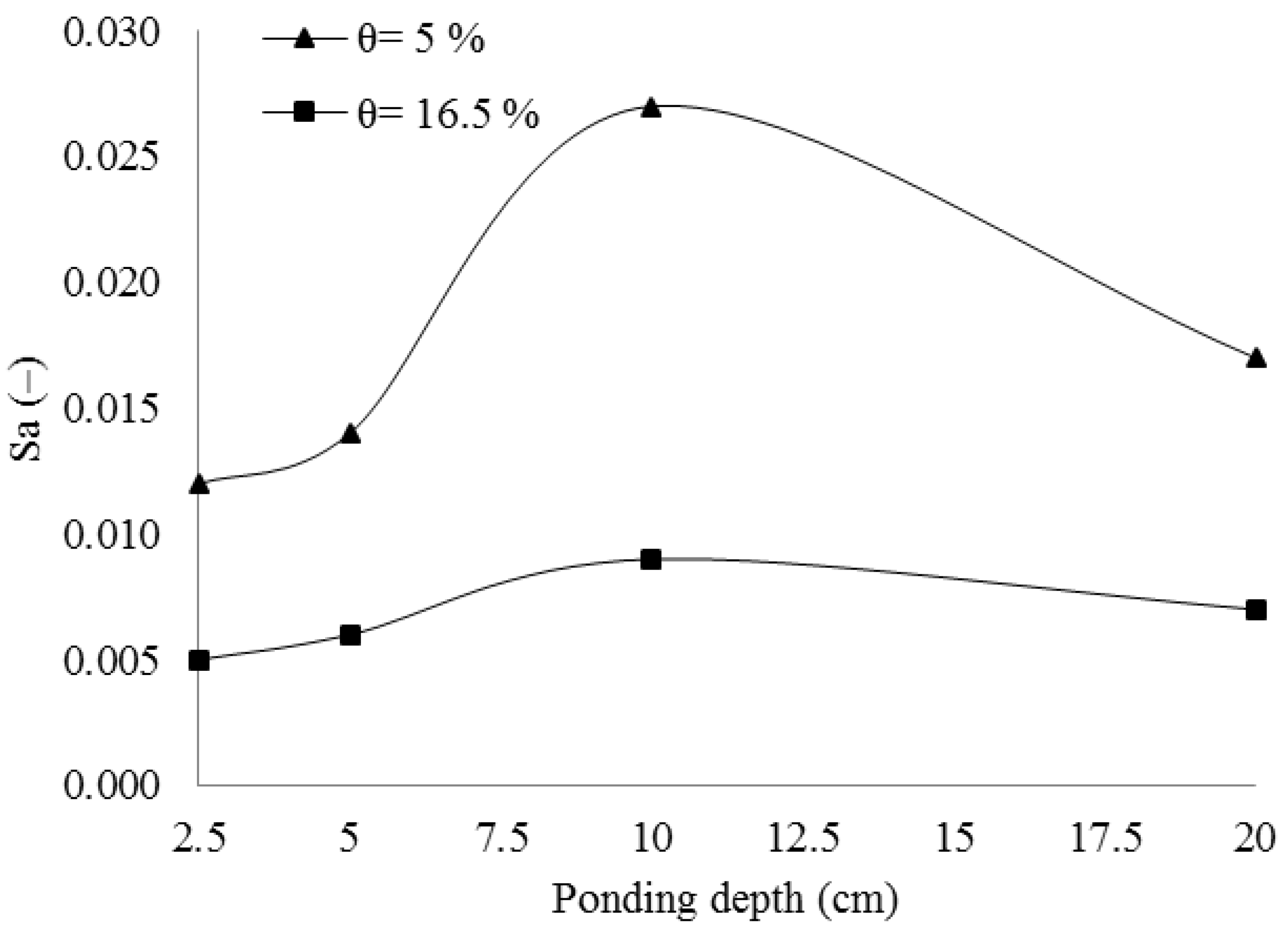
3.2.1. Sensitivity Analysis of Infiltration Equations Coefficients
3.2.2. Sensitivity Analysis of Infiltration Equations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Glossary
| Abbreviation | Definition |
| A | Kostiakov–Lewis empirical coefficient |
| a | Kostiakov empirical coefficient |
| B | Kostiakov–Lewis empirical coefficient |
| b | Kostiakov empirical coefficient |
| c | SCS empirical coefficient |
| d | SCS empirical coefficient |
| H | Ponding depth |
| ϴ | Initial soil moisture |
| ECe | Electrical conductivity of the saturated extract |
| FC | Field capacity |
| f0 | Final infiltration capacity (Kostiakov–Lewis) |
| fi | Initial infiltration capacity |
| ff | Final infiltration capacity (Horton) |
| Ib | The beginning of period |
| Im | The middle of period |
| Ie | The end of period |
| k | Decay time constant |
| Ks | Saturated hydraulic |
| ks | Hydraulic conductivity transition zone |
| l | Soil water retention function |
| LF | Leaching fraction |
| Mi | Intermittent irrigation |
| Md | Daily irrigation |
| n | Shape parameter |
| Qg | Low saline–sodic water quality |
| Qm | Medium saline–sodic water quality |
| Qh | High saline–sodic water quality |
| RMSE | Root-mean-square error |
| S | Soil absorption coefficient |
| Sr | Relative sensitivity indicator |
| Sa | Absolute sensitivity indicator |
| SARe | Sodium adsorption ratio |
| t | Time |
| Z | Cumulative infiltration |
| α | Scaling parameter |
| θr | Residual soil water content |
| θs | Saturated moisture |
References
- Chari, M.M.; Poozan, M.T.; Afrasiab, P. Modeling infiltration in surface irrigation with minimum measurement (study of USDA–NRCS intake families). Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2021, 7, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadi, A.; Shayannejad, M.; Ebrahimian, H.; Ghorbani-Dashtaki, S. Simulation modeling of border irrigation performance under different soil texture classes and land uses. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 8, 1135–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravejalahkami, B. Methods of infiltration estimation for furrow irrigation. Irrig. Drain. 2019, 69, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, F.; Zolfaghari, A.A.; Yazdani, M.R.; Sadeghipour, A. Spatial analysis of infiltration in agricultural lands in arid areas of Iran. Catena 2018, 170, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Seuntjens, P.; Shahidi, R.; Joris, I.; Boënne, W.; Al-Barri, B.; Cornelis, W. The relevance of in-situ and laboratory characterization of sandy soil hydraulic properties for soil water simulations. J. Hydrol. 2016, 534, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emdad, M.R.; Raine, S.R.; Smith, R.J.; Fardad, H. Effect of water quality on soil structure and infiltration under furrow irrigation. Irrig. Sci. 2004, 23, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Choudhary, O.P.; Ghuman, B.S.; Josan, A.S.; Bajwa, M.S. Effect of alternating irrigation with sodic and non-sodic waters on soil properties and sunflower yield. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 85, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feki, M.; Ravazzani, G.; Ceppi, A.; Milleo, G.; Mancini, M. Impact of infiltration process modeling on soil water content simulations for irrigation management. Water 2018, 10, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, D.; Abbasi, F.; Feyen, J. Sensitivity analysis of soil hydraulic properties on subsurface water flow in furrows. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2006, 132, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, M.; Mustafa, M.A.; Letey, J. Effect of mixed Na/Ca solutions on swelling, dispersion and transient water flow in unsaturated montmorillonitic soils. Geoderma 1992, 52, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Darby, A.M.; Mustafa, M.A.; Al-Omran, A.M. Effect of water quality on infiltration of loamy sand soil treated with three gel-conditioners. Soil Technol. 1990, 3, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sepaskhah, A.R.; Afshar-Chamanabad, H. SW-Soil and Water: Determination of Infiltration Rate for Every-other Furrow Irrigation. Biosyst. Eng. 2002, 82, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, M.K.; Lal, R.; Owens, L.B.; Unkefer, P. Land use and management impacts on structure and infiltration characteristics of soils in the North Appalachian region of Ohio. Soil Sci. 2003, 168, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagadu, J.S.; Nimbalkar, P.T. Infiltration studies of different soils under different soil conditions and comparison of infiltration models with field data. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Technol. 2012, 3, 154–157. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, E.R. Comparison of Infiltration Equations and Their Field Validation with Rainfall Simulation. Master’s Thesis, Faculty of the Graduate School of the University of Maryland, College Park, MD, USA, 2006; 185p. [Google Scholar]
- Javadi, A.; Mashal, M.; Ebrahimian, H. Sensitivity Analysis of Different Infiltration Equations and Their Coefficients under Various Initial Soil Moisture and Ponding Depth. Iran. J. Water Soil 2014, 28, 899–908. (In Persian) [Google Scholar]
- Hoyos, E.M.; Cavalcante, A.L.B. Sensitivity Analysis of One-Dimensional Infiltration Models. Electron. J. Geotech. Eng. 2015, 20, 4313–4324. [Google Scholar]
- Sepah Vand, A.; Sihag, P.; Singh, B.; Zand, M. Comparative evaluation of infiltration models. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2018, 22, 4173–4184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machiwal, D.; Jha, M.K.; Mal, B.C. Modelling infiltration and quantifying spatial soil variability in a wasteland of Kharagpur, India. Biosyst. Eng. 2006, 95, 569–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgarzadeh, H.; Mosaddeghi, M.R.; Dexter, A.R.; Mahboubi, A.A.; Neyshabouri, M.R. Determination of soil available water for plants: Consistency between laboratory and field measurements. Geoderma 2014, 226–227, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, T.B.; Goncalves, M.C.; Martins, J.C.; Van Genuchten, M.T.; Pires, F.P. Estimation of soil hydraulic properties from numerical inversion of tension disk infiltrometer data. Vadose Zone J. 2006, 5, 684–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashayekhi, P.; Ghorbani-Dashtaki, S.; Mosaddeghi, M.R.; Shirani, H.; Nodoushan, A.R. Different scenarios for inverse estimation of soil hydraulic parameters from double-ring infiltrometer data using HYDRUS-2D/3D. Int. Agrophys. 2016, 30, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Lu, Y.; Guo, X.; Li, H.; Sai, J.; Liu, X. Application of HYDRUS-1D model for research on irrigation infiltration characteristics in arid oasis of northwest China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šimůnek, J.; van Genuchten, M.T.; Šejna, M. The HYDRUS-1D software package for simulating the one-dimensional movement of water, heat, and multiple solutes in variably-saturated media. In Technical Manual; Version 4.17; Department of Environmental Sciences, University of California at Riverside: Riverside, CA, USA, 2013; 342p. [Google Scholar]
- Van Genuchten, M.T. A closed-form equation for predicting the hydraulic conductivity of unsaturated soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadi, A.; Mostafazadeh-Fard, B.; Shayannejad, M.; Ebrahimian, H. Effect of Initial Soil Water Content on Output Parameters of Sirmod Software under Types of Different Irrigation Management. Irrig. Drain. 2019, 68, 740–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostiakov, A.N. On the dynamics of the coefficient of water percolation in soils and the necessity of studying it from the dynamic point of view for the purposes of amelioration. Trans. Sixth Comm. Int. Soc. Soil Sci. 1932, 1, 7–21. [Google Scholar]
- Mezencev, V.J. Theory of formation of the surface runoff. Meteorologiaigidrologia 1948, 3, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Horton, R.E. An approach toward a physical interpretation of infiltration-capacity. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1941, 5, 399–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, J.R. The theory of infiltration: 1. The infiltration equation and its solution. Soil Sci. 1957, 83, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natural Resources and Conservation Service. National Engineering Handbook; Section 15, Border Irrigation; National Technical Information Service: Washington, DC, UAS, 1974; Chapter 4. [Google Scholar]
- Javadi, A.; Mostafazadeh-Fard, B.; Shayannejad, M.; Mosaddeghi, M.R.; Ebrahimian, H. Soil physical and chemical properties and drain water quality as affected by irrigation and leaching managements. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2019, 65, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolfaghari, A.A.; Mirzaee, S.; Gorji, M. Comparison of different models for estimating cumulative infiltration. Int. J. Soil Sci. 2012, 7, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.; Fedler, C.B.; Borrelli, J. Field evaluation of infiltration models in lawn soils. Irrig. Sci. 2011, 29, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sy, N.L. Modelling the infiltration process with a multi-layer perceptron artificial neural network. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2006, 51, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.D.; Dobrowolski, J.P.; West, N.E. Microbiotic crust influence on unsaturated hydraulic conductivity. Arid Soil Res. Rehabil. 1999, 13, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, A.; Singh, R. Development of a portable rainfall simulator infiltrometer for infiltration, runoff and erosion studies. Agric. Water Manag. 1992, 22, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lei, T.W.; Zhao, J.; Yuan, C.P.; Fan, Y.T.; Qu, L.Q. Effects of rainfall intensity and antecedent soil water content on soil infiltrability under rainfall conditions using the run off-on-out method. J. Hydrol. 2011, 396, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ghazal, A.A. Effect of Ripping and Water Head on Infiltration Rate of Soils in Saudi Arabia. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2002, 5, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamedov, A.I.; Levy, G.J. Clay dispersivity and aggregate stability effects on seal formation and erosion in effluent-irrigated soils. Soil Sci. 2001, 166, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoades, J.D. The Use of Saline Waters for Crop Production; No. 628.167 F3; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1992. [Google Scholar]

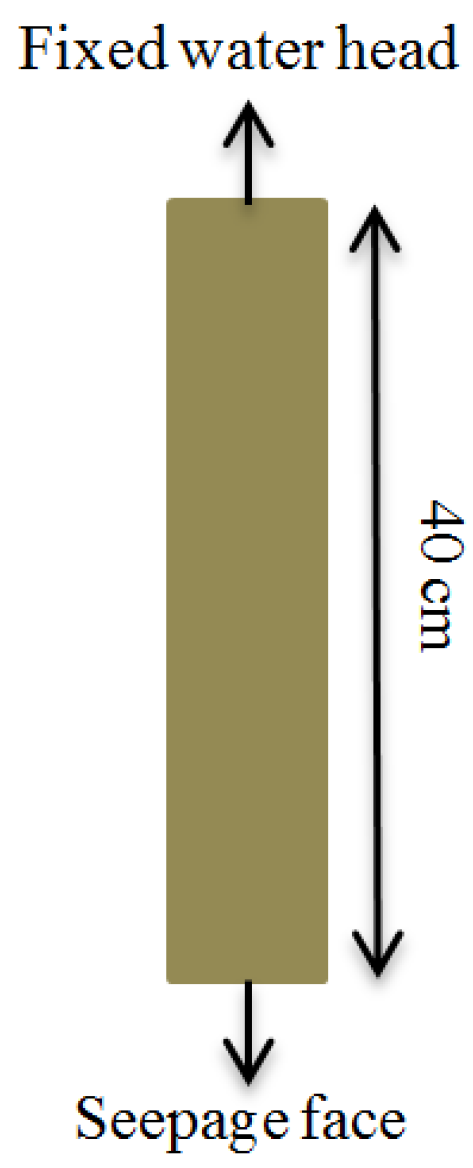
| Description | Treatment |
|---|---|
| Low saline–sodic (Qg; SAR = 0.77 (meq L−1)−0.5 and EC = 0.6 dS m−1) | Irrigation water quality (Q) |
| Medium saline–sodic (Qm; SAR = 11.30 (meq L−1)−0.5 and EC = 3.0 dS m−1) | |
| High saline–sodic (Qh; SAR = 21.38 (meq L−1)−0.5 and EC = 6.0 dS m−1) | |
| Intermittent (Mi) | Management of irrigation (M) |
| Daily (Md) | |
| The end of period (100 days, Ib) | Period of the irrigation (I) |
| The middle of period (45 days, Im) | |
| The beginning of period (8 days, Ib) |
| Value | Soil Properties |
|---|---|
| 55 | Sand (kg 100 kg−1) |
| 15 | Clay (kg 100 kg−1) |
| 30 | Silt (kg 100 kg−1) |
| 1.60 | Bulk density (g/cm3) |
| 0.094 | Hydraulic conductivity (cm/min) |
| 0.65 | Sodium adsorption ratio; SARe ((meq·L−1)−0.5) |
| 0.72 | Electrical conductivity of the saturated extract; ECe (dS/m) |
| 7.37 | pH |
| Irrigation Management | Irrigation Period | θFC (m3m−3) | Irrigation (mm/Event) | Mean of Irrigation Interval (Day) | Amount of Irrigation Events | Period of Irrigation (Days) | Leaching Fraction with Irrigation (%) | Infiltration Experiment Time (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mi | Ib | 0.153 | 18.1 | 8 | 1 | 8 | - | 16 |
| Im | 0.146 | 17.3 | 9 | 5 | 45 | - | 56 | |
| Ie | 0.151 | 17.9 | 10 | 10 | 100 | - | 114 | |
| Md | Ib | 0.153 | 2 to 3.1 | 1 | 8 | 8 | 15 | 16 |
| Im | 0.146 | 2 to 3.1 | 1 | 45 | 45 | 15 | 56 | |
| Ie | 0.151 | 2 to 3.1 | 1 | 100 | 100 | 15 | 114 |
| FC | Drain Water | Infiltration | Hydraulic Parameters | Treatment | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RMSE (%) | RMSE (cm) | RMSE (cm) | Ks (cm min−1) | n (-) | α (cm−1) | θs (-) | |
| 0.18 | 0.17 | 0.26 | 0.108 | 1.89 | 0.0119 | 0.200 | Qg.Mi.Ib |
| 0.06 | 0.13 | 0.19 | 0.097 | 1.48 | 0.0145 | 0.184 | Qm.Mi.Ib |
| 0.01 | 0.55 | 0.18 | 0.102 | 1.46 | 0.0178 | 0.210 | Qh. Mi.Ib |
| 0.17 | 0.13 | 0.18 | 0.055 | 1.89 | 0.0035 | 0.171 | Qg.Md.Ib |
| 0.08 | 0.03 | 0.09 | 0.071 | 1.30 | 0.0220 | 0.203 | Qm.Md.Ib |
| 0.29 | 0.33 | 0.19 | 0.046 | 1.27 | 0.0020 | 0.164 | Qh.Md.Ib |
| 1.01 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.019 | 1.54 | 0.0005 | 0.157 | Qg.Mi.Im |
| 0.44 | 0.06 | 0.17 | 0.027 | 1.28 | 0.0459 | 0.170 | Qm.Mi.Im |
| 0.63 | 0.06 | 0.21 | 0.022 | 1.16 | 0.0498 | 0.161 | Qh.Mi.Im |
| 0.79 | 3.72 | 1.61 | 0.183 | 2.25 | 0.0128 | 0.242 | Qg.Md.Im |
| 0.75 | 2.86 | 1.10 | 0.199 | 2.10 | 0.0153 | 0.250 | Qm.Md.Im |
| 0.73 | 2.17 | 1.06 | 0.198 | 2.37 | 0.0123 | 0.233 | Qh.Md.Im |
| 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 0.042 | 1.19 | 0.0644 | 0.179 | Qg.Mi.Ie |
| 0.26 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.026 | 1.17 | 0.0760 | 0.179 | Qm.Mi.Ie |
| 0.29 | 0.25 | 0.24 | 0.029 | 1.19 | 0.0780 | 0.174 | Qh.Mi.Ie |
| 0.21 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.018 | 1.29 | 0.0422 | 0.182 | Qg.Md.Ie |
| 0.67 | 0.73 | 0.46 | 0.094 | 1.79 | 0.0060 | 0.207 | Qm.Md.Ie |
| 0.01 | 0.48 | 0.40 | 0.120 | 1.63 | 0.0066 | 0.209 | Qh.Md.Ie |
| Boundary | θr (cm3cm−3) | θs (cm3cm−3) | α (cm−1) | n (-) | Ks (cm min−1) | l (-) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | 0.0456 | 0.34 | 0.0441 | 1.45 | 0.029 | 0.5 |
| Maximum | - | 0.46 | 0.145 | 2.68 | 1 | - |
| Minimum | - | 0.15 | 0.0001 | 1.09 | 0.005 | - |
| Cumulative Infiltration (cm, at 100 min) | SARe (meq·L−1)−0.5 | ECe (dS m−1) | Treatments |
|---|---|---|---|
| 13.7 | 0.72 | 1.05 | Qg.Mi.Ib |
| 12.3 | 2.61 | 1.27 | Qm.Mi.Ib |
| 12.8 | 2.29 | 1.96 | Qh.Mi.Ib |
| 8.3 | 1.74 | 1.21 | Qg.Md.Ib |
| 9.3 | 2.22 | 1.74 | Qm.Md.Ib |
| 7.6 | 4.64 | 1.88 | Qh.Md.Ib |
| 4.6 | 1.77 | 1.32 | Qg.Mi.Im |
| 4.1 | 3.77 | 2.63 | Qm.Mi.Im |
| 4.2 | 6.21 | 4.88 | Qh.Mi.Im |
| 23.6 | 1.99 | 1.08 | Qg.Md.Im |
| 25.5 | 5.93 | 3.42 | Qm.Md.Im |
| 25.3 | 5.65 | 4.58 | Qh.Md.Im |
| 5.7 | 1.33 | 1.32 | Qg.Mi.Ie |
| 3.7 | 6.06 | 3.44 | Qm.Mi.Ie |
| 4.2 | 10.36 | 6.35 | Qh.Mi.Ie |
| 3.0 | 1.81 | 1.35 | Qg.Md.Ie |
| 13.4 | 7.37 | 4.78 | Qm.Md.Ie |
| 16.2 | 14.42 | 8.12 | Qh.Md.Ie |
| Infiltration Equation Coefficients | Treatment | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCS | Philip | Horton | Kostiakov–Lewis | Kostiakov | ||||||||
| d | c | S | ff | fi | k | f0 | B | A | b | a | ||
| 0.810 | 0.315 | 0.081 | 0.588 | 0.123 | 0.637 | 0.275 | 0.108 | 0.925 | 0.275 | 0.458 | 0.740 | Qg.Mi.Ib |
| 0.832 | 0.202 | 0.055 | 0.453 | 0.089 | 1.076 | 0.724 | 0.100 | 0.765 | 0.265 | 0.354 | 0.725 | Qm.Mi.Ib |
| 0.876 | 0.183 | 0.070 | 0.405 | 0.100 | 1.306 | 0.994 | 0.106 | 0.727 | 0.275 | 0.315 | 0.770 | Qh.Mi.Ib |
| 0.628 | 0.498 | 0.017 | 0.810 | 0.078 | 3.191 | 1.287 | 0.060 | 1.365 | 0.163 | 0.782 | 0.546 | Qg.Md.Ib |
| 0.791 | 0.204 | 0.038 | 0.471 | 0.073 | 0.790 | 0.500 | 0.077 | 0.650 | 0.221 | 0.381 | 0.673 | Qm.Md.Ib |
| 0.746 | 0.278 | 0.037 | 0.573 | 0.080 | 2.584 | 1.463 | 0.057 | 1.289 | 0.122 | 0.479 | 0.645 | Qh.Md.Ib |
| 0.632 | 0.167 | 0.022 | 0.206 | 0.027 | 1.295 | 0.993 | 0.021 | 1.257 | 0.150 | 0.510 | 0.430 | Qg.Mi.Im |
| 0.963 | 0.060 | 0.032 | 0.251 | 0.050 | 0.603 | 0.731 | 0.033 | 0.168 | 0.331 | 0.196 | 0.729 | Qm.Mi.Im |
| 1.365 | 0.006 | 0.028 | 0.089 | 0.034 | 0.117 | 0.296 | 0.024 | 0.049 | 0.652 | 0.076 | 0.841 | Qh.Mi.Im |
| 0.606 | 1.359 | 0.060 | 1.735 | 0.190 | 3.359 | 0.604 | 0.165 | 3.435 | 0.167 | 1.565 | 0.585 | Qg.Md.Im |
| 0.526 | 1.738 | 0.058 | 1.675 | 0.158 | 4.560 | 0.746 | 0.183 | 4.302 | 0.119 | 2.035 | 0.502 | Qm.Md.Im |
| 0.610 | 1.301 | 0.061 | 1.677 | 0.186 | 3.064 | 0.566 | 0.189 | 2.724 | 0.190 | 1.503 | 0.589 | Qh.Md.Im |
| 0.975 | 0.059 | 0.034 | 0.246 | 0.052 | 0.987 | 1.273 | 0.049 | 0.529 | 0.090 | 0.191 | 0.740 | Qg.Mi.Ie |
| 1.281 | 0.010 | 0.029 | 0.107 | 0.037 | 0.333 | 0.917 | 0.033 | 0.287 | 0.089 | 0.088 | 0.827 | Qm.Mi.Ie |
| 1.068 | 0.033 | 0.032 | 0.186 | 0.046 | 0.408 | 0.645 | 0.039 | 0.120 | 0.133 | 0.145 | 0.769 | Qh.Mi.Ie |
| 0.922 | 0.050 | 0.014 | 0.267 | 0.034 | 0.783 | 0.936 | 0.022 | 0.415 | 0.128 | 0.229 | 0.622 | Qg.Md.Ie |
| 0.666 | 0.497 | 0.034 | 0.817 | 0.095 | 1.858 | 0.717 | 0.091 | 1.327 | 0.257 | 0.721 | 0.600 | Qm.Md.Ie |
| 0.716 | 0.450 | 0.053 | 0.771 | 0.111 | 1.401 | 0.551 | 0.121 | 1.169 | 0.268 | 0.636 | 0.653 | Qh.Md.Ie |
| RMSE (cm) | Treatment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCS | Philip | Horton | Kostiakov–Lewis | Kostiakov | |
| 0.148 | 0.175 | 0.035 | 0.079 | 0.236 | Qg.Mi.Ib |
| 0.096 | 0.106 | 0.031 | 0.053 | 0.176 | Qm.Mi.Ib |
| 0.099 | 0.108 | 0.040 | 0.057 | 0.183 | Qh.Mi.Ib |
| 0.153 | 0.238 | 0.03 | 0.104 | 0.219 | Qg.Md.Ib |
| 0.071 | 0.064 | 0.044 | 0.035 | 0.118 | Qm.Md.Ib |
| 0.118 | 0.181 | 0.033 | 0.089 | 0.166 | Qh.Md.Ib |
| 0.128 | 0.296 | 0.057 | 0.107 | 0.131 | Qg.Mi.Im |
| 0.075 | 0.029 | 0.022 | 0.012 | 0.055 | Qm.Mi.Im |
| 0.108 | 0.017 | 0.026 | 0.009 | 0.045 | Qh.Mi.Im |
| 0.555 | 0.507 | 0.026 | 0.138 | 0.677 | Qg.Md.Im |
| 0.606 | 0.546 | 0.028 | 0.151 | 0.726 | Qm.Md.Im |
| 0.448 | 0.345 | 0.217 | 0.269 | 0.474 | Qh.Md.Im |
| 0.080 | 0.041 | 0.032 | 0.022 | 0.086 | Qg.Mi.Ie |
| 0.098 | 0.019 | 0.028 | 0.010 | 0.051 | Qm.Mi.Ie |
| 0.090 | 0.023 | 0.029 | 0.012 | 0.056 | Qh.Mi.Ie |
| 0.100 | 0.017 | 0.033 | 0.006 | 0.041 | Qg.Md.Ie |
| 0.272 | 0.283 | 0.032 | 0.115 | 0.379 | Qm.Md.Ie |
| 0.284 | 0.285 | 0.029 | 0.105 | 0.404 | Qh.Md.Ie |
| Infiltration Equation Coefficients | Sensitivity Indicator | Treatment | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCS | Philip | Horton | Kostiakov–Lewis | Kostiakov | ||||||||||
| d | c | S | ff | fi | k | f0 | B | A | b | a | ||||
| 0.51 | −2.01 | 0.42 | −1.26 | 0.00 | −0.13 | 1.40 | 0.89 | −1.11 | −0.82 | 0.39 | −0.70 | H = c ϴ ↑ | MSr (-) | QgMi |
| 0.01 | 0.14 | 0.24 | 0.07 | 0.17 | 0.20 | 0.17 | 0.47 | −0.13 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 0.05 | H ↑ ϴ = c | ||
| 0.51 | 2.02 | 0.42 | 1.27 | 0.02 | 0.14 | 1.41 | 0.90 | 1.12 | 0.83 | 0.40 | 1.47 | H = c ϴ ↑ | MSa (-) | |
| 0.04 | 0.17 | 0.25 | 0.08 | 0.17 | 0.21 | 0.18 | 0.48 | 0.16 | 0.16 | 0.04 | 0.11 | H ↑ ϴ = c | ||
| 2 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 7 | 5 | 4 | 1 | 6 | Rank | ||
| 0.32 | −1.69 | 0.36 | −1.28 | −0.05 | −0.22 | 1.13 | 0.30 | −0.95 | −0.69 | 0.25 | −1.13 | H = c ϴ ↑ | MSr (-) | QmMi |
| −0.05 | 0.44 | 0.11 | 0.20 | 0.16 | 0.31 | 0.18 | 0.17 | −0.15 | 0.30 | −0.01 | 0.22 | H ↑ ϴ = c | ||
| 0.32 | 1.69 | 0.37 | 1.28 | 0.05 | 0.22 | 1.16 | 0.33 | 0.98 | 0.70 | 0.26 | 1.14 | H = c ϴ ↑ | MSa (-) | |
| 0.06 | 0.44 | 0.13 | 0.21 | 0.16 | 0.31 | 0.22 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.30 | 0.03 | 0.22 | H ↑ ϴ = c | ||
| 3 | 9 | 4 | 8 | 2 | 6 | 8 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 1 | 8 | Rank | ||
| 0.33 | −1.78 | 0.38 | −1.31 | −0.05 | −0.23 | 1.21 | 0.34 | −0.96 | −0.69 | 0.26 | −1.18 | H = c ϴ ↑ | MSr (-) | QhMi |
| −0.06 | 0.51 | 0.12 | 0.20 | 0.16 | 0.30 | 0.17 | 0.17 | −0.16 | 0.31 | −0.01 | 0.21 | H ↑ ϴ = c | ||
| 0.34 | 1.79 | 0.38 | 1.32 | 0.05 | 0.24 | 1.22 | 0.34 | 0.99 | 0.70 | 0.27 | 1.19 | H = c ϴ ↑ | MSa (-) | |
| 0.07 | 0.52 | 0.13 | 0.21 | 0.16 | 0.32 | 0.24 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.31 | 0.03 | 0.22 | H ↑ ϴ = c | ||
| 3 | 10 | 4 | 8 | 2 | 6 | 9 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 1 | 7 | Rank | ||
| 0.48 | −2.07 | 1.20 | −1.32 | −0.05 | −0.31 | 1.06 | 0.32 | −1.21 | −1.00 | 0.39 | −1.46 | H = c ϴ ↑ | MSr (-) | QgMd |
| −0.01 | 0.24 | 0.23 | 0.09 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.07 | 0.16 | −0.07 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.08 | H ↑ ϴ = c | ||
| 0.49 | 2.08 | 1.20 | 1.32 | 0.05 | 0.32 | 1.13 | 0.36 | 1.26 | 1.00 | 0.40 | 1.47 | H = c ϴ ↑ | MSa (-) | |
| 0.07 | 0.30 | 0.45 | 0.11 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.19 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.14 | H ↑ ϴ = c | ||
| 2 | 9 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 7 | Rank | ||
| 0.33 | −1.46 | 0.58 | −1.36 | 0.00 | −0.16 | 1.25 | 0.19 | −1.33 | −0.96 | 0.31 | −1.26 | H = c ϴ ↑ | MSr (-) | QmMd |
| 0.02 | 0.08 | 0.25 | 0.03 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.20 | −0.14 | 0.09 | 0.03 | 0.03 | H ↑ ϴ = c | ||
| 0.33 | 1.46 | 0.59 | 1.37 | 0.01 | 0.17 | 1.26 | 0.19 | 1.34 | 0.96 | 0.31 | 1.26 | H = c ϴ ↑ | MSa (-) | |
| 0.03 | 0.12 | 0.26 | 0.06 | 0.17 | 0.16 | 0.15 | 0.20 | 0.15 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.09 | H ↑ ϴ = c | ||
| 1 | 8 | 8 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 6 | 7 | 4 | 1 | 5 | Rank | ||
| 0.48 | −1.89 | 1.52 | −1.42 | 0.00 | −0.15 | 1.41 | 0.78 | −1.30 | −0.89 | 0.42 | −1.57 | H = c ϴ ↑ | MSr (-) | QhMd |
| 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.25 | 0.00 | 0.13 | 0.09 | 0.11 | 0.23 | −0.09 | 0.03 | 0.04 | −0.02 | H ↑ ϴ = c | ||
| 0.48 | 1.89 | 1.52 | 1.43 | 0.00 | 0.16 | 1.42 | 0.79 | 1.31 | 0.90 | 0.43 | 1.58 | H = c ϴ ↑ | MSa (-) | |
| 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.48 | 0.02 | 0.13 | 0.10 | 0.11 | 0.39 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.04 | H ↑ ϴ = c | ||
| 2 | 9 | 10 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 3 | 1 | 5 | Rank | ||
| 2 | 10 | 9 | 6 | 3 | 4 | 8 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 7 | Final ranking | ||
| Infiltration Equations | Sensitivity Indicator | Treatment | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCS | Philip | Horton | Kostiakov–Lewis | Kostiakov | |||
| −0.290 | −0.348 | −0.306 | −0.300 | −0.305 | H = c, ϴ ↑ | MSr(-) | QgMi |
| 0.136 | 0.138 | 0.139 | 0.139 | 0.137 | ϴ = c, H ↑ | ||
| 0.290 | 0.348 | 0.306 | 0.300 | 0.305 | H = c, ϴ ↑ | MSa(-) | |
| 0.136 | 0.138 | 0.139 | 0.139 | 0.137 | ϴ = c, H ↑ | ||
| 1 | 4 | 5 | 3 | 2 | Rank | ||
| −0.179 | −0.194 | −0.200 | −0.192 | −0.188 | H = c, ϴ ↑ | MSr(-) | QmMi |
| 0.163 | 0.167 | 0.168 | 0.168 | 0.167 | ϴ = c, H ↑ | ||
| 0.179 | 0.194 | 0.200 | 0.192 | 0.188 | H = c, ϴ ↑ | MSa(-) | |
| 0.163 | 0.167 | 0.168 | 0.168 | 0.167 | ϴ = c, H ↑ | ||
| 1 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 2 | Rank | ||
| −0.185 | −0.199 | −0.206 | −0.197 | −0.191 | H = c, ϴ ↑ | MSr(-) | QhMi |
| 0.161 | 0.167 | 0.167 | 0.168 | 0.168 | ϴ = c, H ↑ | ||
| 0.185 | 0.199 | 0.206 | 0.197 | 0.191 | H = c, ϴ ↑ | MSa(-) | |
| 0.161 | 0.167 | 0.167 | 0.168 | 0.168 | ϴ = c, H ↑ | ||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | Rank | ||
| −0.239 | −0.264 | −0.270 | −0.259 | −0.251 | H = c, ϴ ↑ | MSr(-) | QgMd |
| 0.149 | 0.148 | 0.150 | 0.151 | 0.152 | ϴ = c, H ↑ | ||
| 0.239 | 0.264 | 0.270 | 0.259 | 0.251 | H = c, ϴ ↑ | MSa(-) | |
| 0.149 | 0.148 | 0.150 | 0.151 | 0.152 | ϴ = c, H ↑ | ||
| 1 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 3 | Rank | ||
| −0.140 | −0.150 | −0.165 | −0.158 | −0.143 | H = c, ϴ ↑ | MSr(-) | QmMd |
| 0.152 | 0.153 | 0.151 | 0.152 | 0.153 | ϴ = c, H ↑ | ||
| 0.140 | 0.150 | 0.165 | 0.158 | 0.143 | H = c, ϴ ↑ | MSa(-) | |
| 0.152 | 0.153 | 0.151 | 0.152 | 0.153 | ϴ = c, H ↑ | ||
| 1 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | Rank | ||
| −0.247 | -0−264 | −0.268 | −0.256 | −0.254 | H = c, ϴ ↑ | MSr(-) | QhMd |
| 0.106 | 0.105 | 0.107 | 0.107 | 0.107 | ϴ = c, H ↑ | ||
| 0.247 | 0.264 | 0.268 | 0.256 | 0.254 | H = c, ϴ ↑ | MSa(-) | |
| 0.106 | 0.105 | 0.107 | 0.107 | 0.107 | ϴ = c, H ↑ | ||
| 1 | 2 | 5 | 4 | 3 | Rank | ||
| 1 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 2 | Final ranking | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Javadi, A.; Ostad-Ali-Askari, K. Effect of Different Irrigation Managements on Infiltration Equations and Their Coefficients. CivilEng 2023, 4, 949-965. https://doi.org/10.3390/civileng4030051
Javadi A, Ostad-Ali-Askari K. Effect of Different Irrigation Managements on Infiltration Equations and Their Coefficients. CivilEng. 2023; 4(3):949-965. https://doi.org/10.3390/civileng4030051
Chicago/Turabian StyleJavadi, Ali, and Kaveh Ostad-Ali-Askari. 2023. "Effect of Different Irrigation Managements on Infiltration Equations and Their Coefficients" CivilEng 4, no. 3: 949-965. https://doi.org/10.3390/civileng4030051
APA StyleJavadi, A., & Ostad-Ali-Askari, K. (2023). Effect of Different Irrigation Managements on Infiltration Equations and Their Coefficients. CivilEng, 4(3), 949-965. https://doi.org/10.3390/civileng4030051








