Intensive Speech Therapy for Hypokinetic Dysarthria in Parkinson’s Disease: Targeting the Five Subsystems of Speech Production with Clinical and Instrumental Evaluation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
- Patients with functional communicative intentionality;
- Patients with mild to severe dysarthria, according to the clinical evaluation of PRM physician;
- Severe hearing loss and/or hearing aid wearers;
- Inability to provide informed consent;
- Comorbidity with other neurological and/or vocal pathologies;
- Temporo-mandibular joint (TMJ) disorder;
- Myofascial pain syndrome;
- Demolitive/reconstructive surgical treatment for neoplasms of oral cavity and oropharynx;
- High risk of seizures.
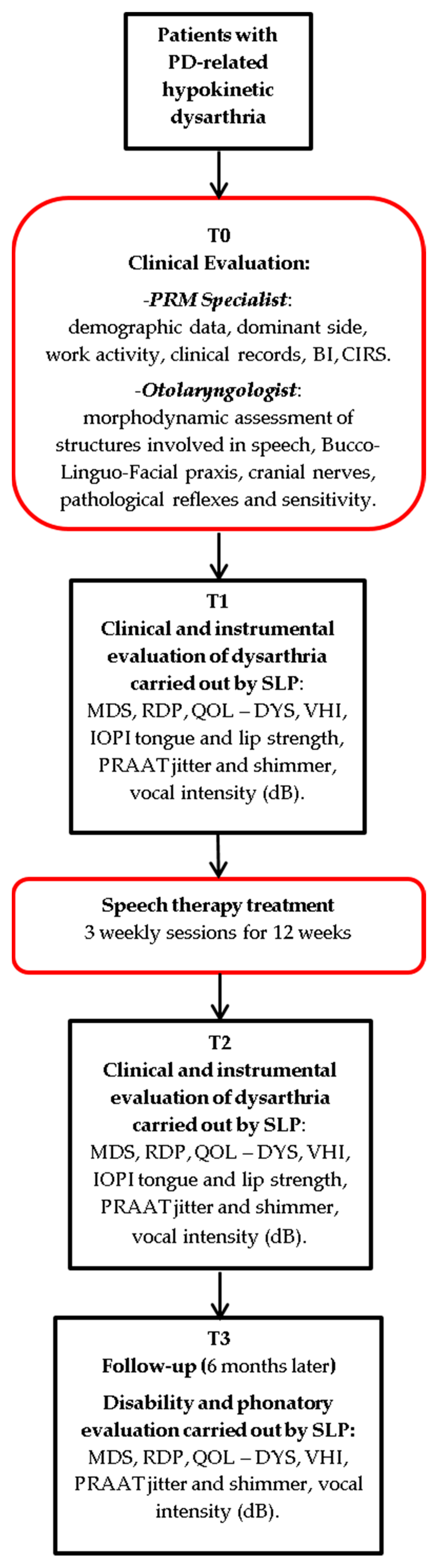
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Speech Therapy Treatment
2.4. Clinical Evaluation
2.5. Speech Therapist Assessment
- MDS—Unified Parkinson Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS) [32], to evaluate various aspects of Parkinson’s disease including non-motor and motor experiences of daily living and motor complications with ratings on a 5-point Likert scale (from 0 Normal to 4 Severe).
- Robertson Dysarthria Profile (RDP) [30], aims to identify the patient’s level of disability in the various aspects: breathing, phonation, facial musculature, diadochokinesis, reflexes, articulation, intelligibility, and prosody with ratings on a 4-point Likert scale (from 1 Poor to 4 Excellent). In this way, highlighting the individual’s difficulties in carrying out some activities, it was possible to outline a treatment framework aimed at recovering residual potential and therefore minimizing the associated disability.
- QOL—DYS: Dysarthria self-assessment questionnaire [33], which consist of 4 sections of 10 items each, with ratings on a 5-point Likert scale (from 0 Never to 4 Always).
- Voice Handicap Index (VHI) [34], to assess dysphonia-related quality of life. This index addresses the impact of vocal issues on daily activities, the psychological impact, and the perception of vocal emission characteristics, with ratings on a 5-point severity scale (0–4).
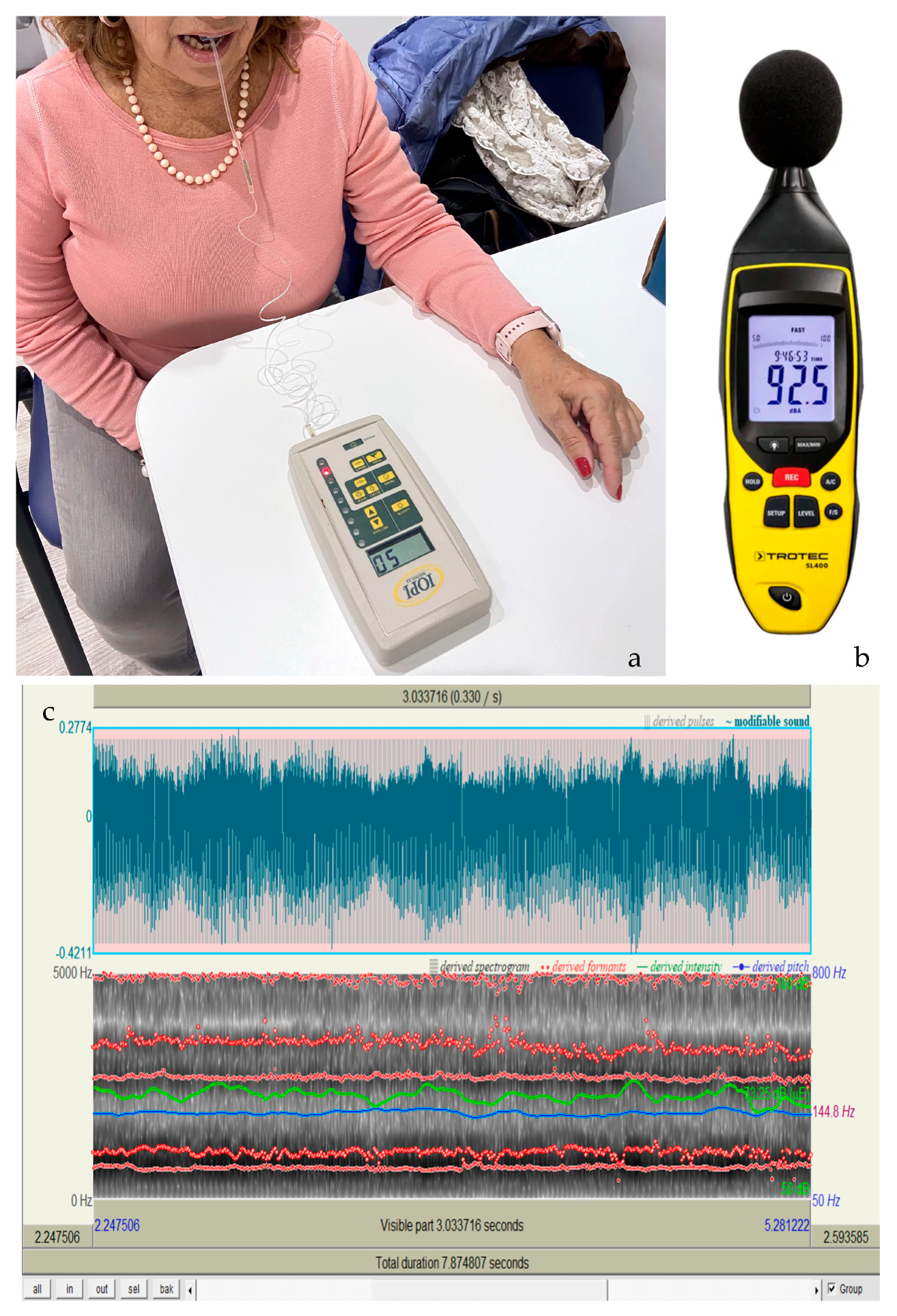
2.6. Instrumental Assessment
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Darley, F.L.; Aronson, A.E.; Brown, J.R. Differential diagnostic patterns of dysarthria. J. Speech Hear. Res. 1969, 12, 246–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utianski, R.L.; Clark, H.M.; Duffy, J.R.; Botha, H.; Whitwell, J.L.; Josephs, K.A. Communication Limitations in Patients with Progressive Apraxia of Speech and Aphasia. Am. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2020, 29, 1976–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapir, S.; Ramig, L.O.; Fox, C.M. Intensive voice treatment in Parkinson’s disease: Lee Silverman Voice Treatment. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2011, 11, 815–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruoppolo, G.; Amitrano, A. Disartria Possiamo Fare di Più? Omega: Milano, Italy, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, V.; Alerić, Z.; Jancić, E.; Miholović, V. Voice quality in Parkinson’s disease in the Croatian language speakers. Coll. Antropol. 2011, 35 (Suppl. S2), 209–212. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Duffy Joseph, R. Motor Speech Disorders—Substrates, Differential Diagnosis, Management, 4th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jagadeesan, A.J.; Murugesan, R.; Vimala Devi, S.; Meera, M.; Madhumala, G.; Vishwanathan Padmaja, M.; Ramesh, A.; Banerjee, A.; Sushmitha, S.; Khokhlov, A.N.; et al. Current trends in etiology, prognosis and therapeutic aspects of Parkinson’s disease: A review. Acta Biomed. 2017, 88, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Herd, C.P.; Tomlinson, C.L.; Deane, K.H.; Brady, M.C.; Smith, C.H.; Sackley, C.M.; Clarke, C.E. Speech and language therapy versus placebo or no intervention for speech problems in Parkinson’s disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 2012, CD002812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Amitrano, A.; Genovese, E.; Ruoppolo, G.; Schindler, A. Manuale di Foniatria e Logopedia; SEU: Roma, Italy, 2012; pp. 294–297. [Google Scholar]
- Chiaramonte, R.; Bonfiglio, M. Acoustic analysis of voice in Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review of voice disability and meta-analysis of studies. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 70, 393–405, (In Spanish, English). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaza, E.; Busanello-Stella, A.R. Tongue strength and clinical correlations in Parkinson’s disease. J. Oral Rehabil. 2023, 50, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinho, P.; Monteiro, L.; Soares, M.F.P.; Tourinho, L.; Melo, A.; Nóbrega, A.C. Impact of levodopa treatment in the voice pattern of Parkinson’s disease patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. CoDAS 2018, 30, e20170200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechien, J.R.; Delsaut, B.; Abderrakib, A.; Huet, K.; Delvaux, V.; Piccaluga, M.; Khalife, M.; Harmegnies, B.; Saussez, S.; Blecic, S. Orofacial Strength and Voice Quality as Outcome of Levodopa Challenge Test in Parkinson Disease. Laryngoscope 2020, 130, E896–E903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, A.K.; Bradshaw, J.L.; Iansek, R.; Alfredson, R. Speech volume regulation in Parkinson’s disease: Effects of implicit cues and explicit instructions. Neuropsychologia 1999, 37, 1453–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapir, S.; Ramig, L.O.; Spielman, J.L.; Fox, C. Formant centralization ratio: A proposal for a new acoustic measure of dysarthric speech. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2010, 53, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Constantinescu, G.; Theodoros, D.; Russell, T.; Ward, E.; Wilson, S.; Wootton, R. Treating disordered speech and voice in Parkinson’s disease online: A randomized controlled non-inferiority trial. Int. J. Lang. Commun. Disord. 2011, 46, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaza, E.; Ruviaro Busanello-Stella, A. Effects of a tongue training program in Parkinson’s disease: Analysis of electrical activity and strength of suprahyoid muscles. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2022, 63, 102642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchese, M.R.; Proietti, I.; Longobardi, Y.; Mari, G.; Ausili Cefaro, C.; D’Alatri, L. Multidimensional voice assessment after Lee Silverman Voice Therapy (LSVT®) in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2022, 42, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Vigueras, N.; Prados-Román, E.; Valenza, M.C.; Granados-Santiago, M.; Cabrera-Martos, I.; Rodríguez-Torres, J.; Torres-Sánchez, I. Speech and language therapy treatment on hypokinetic dysarthria in Parkinson disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Rehabil. 2021, 35, 639–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krekeler, B.N.; Hopkins, A.; Tabangin, M.E.; Altaye, M.; Roberts, R.; Saadi, R.; Martin-Harris, B.; Rogus-Pulia, N. Criterion (Concurrent) Validity and Clinical Utility of the Tongueometer Device. Am. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2024, 33, 1763–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.; Gildeh, N.; Holmes, C. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment: Validity and utility in a memory clinic setting. Can. J. Psychiatry 2007, 52, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirani, A.; Tulipani, C.; Neri, M. Italian Translation of MoCA Test and of Its Instructions. 2006. Available online: http://www.mocatest.org (accessed on 15 October 2024).
- Bernetti, A.; Ruggiero, M.; Ruiu, P.; Napoli, M.; D’Urzo, R.; Mancuso, A.; Mariani, F.; Tota, L.; Agostini, F.; Mangone, M.; et al. Analysis and Report of the Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine Evaluation Activity in Patients Admitted to Acute Care Setting: An Observational Retrospective Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 6039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Mahoney, F.I.; Barthel, D.W. Functional Evaluation: The Barthel Index. Md. State Med. J. 1965, 14, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Castiglia, S.F.; Galeoto, G. The culturally adapted Italian version of the Barthel Index (IcaBI): Assessment of structural validity, inter-rater reliability and responsiveness to clinically relevant improvements in patients admitted to inpatient rehabilitation centers. Funct. Neurol. 2017, 22, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, S.; Ford, A.B. Studies of illness in the aged. The index of adl: A standardized measure of biological and psychosocial function. JAMA 1963, 185, 914–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linn, B.S.; Linn, M.W. Cumulative illness rating scale. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1968, 16, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoehn, M.M.; Yahr, M.D. Parkinsonism: Onset, progression, and mortality. Neurology 1967, 17, 427–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Factor, S.A.; Weiner, W.J. Parkinson’s Disease: Diagnosis and Clinical Management; Demos Medical: New York City, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Fussi, F.; Cantagallo, A.; Bertozzini, L. Profilo di Valutazione Della Disartria: Adattamento Italiano del Test di Robertson, Raccolta di Dati Normativi e Linee di Trattamento; Omega: Palm Springs, CA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, S. The efficacy of oro-facial and articulation exercises in dysarthria following stroke. Int. J. Lang. Commun. Disord. 2001, 36, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, C.G.; Tilley, B.C.; Shaftman, S.R.; Stebbins, G.T.; Fahn, S.; Martinez-Martin, P.; Poewe, W.; Sampaio, C.; Stern, M.B.; Dodel, R.; et al. Movement Disorder Society-sponsored revision of the Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS): Scale presentation and clinimetric testing results. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 2129–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piacentini, V.; Zuin, A.; Cattaneo, D.; Schindler, A. Reliability and validity of an instrument to measure quality of life in the dysarthric speaker. Folia Phoniatr. Logop. 2011, 63, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forti, S.; Amico, M.; Zambarbieri, A.; Ciabatta, A.; Assi, C.; Pignataro, L.; Cantarella, G. Validation of the Italian Voice Handicap Index-10. J. Voice 2014, 28, 263.e17–263.e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtis, J.A.; Mocchetti, V.; Rameau, A. Concurrent Validity of the IOPI and Tongueometer Orofacial Strength Measurement Devices. Laryngoscope 2023, 133, 3123–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorris, C.; Ricci Maccarini, A.; Vanoni, F.; Poggioli, M.; Vaschetto, R.; Garzaro, M.; Aluffi Valletti, P. Acoustic Analysis of Normal Voice Patterns in Italian Adults by Using Praat. J. Voice 2020, 34, 961.e9–961.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fava, G.; Oliveira, G.; Baglione, M.; Pimpinella, M.; Spitzer, J.B. The Use of Sound Level Meter Apps in the Clinical Setting. Am J. Speech. Lang. Pathol. 2016, 25, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azadi, H.; Akbarzadeh-T, M.R.; Shoeibi, A.; Kobravi, H.R. Evaluating the Effect of Parkinson’s Disease on Jitter and Shimmer Speech Features. Adv. Biomed. Res. 2021, 10, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Pu, T.; Huang, M.; Kong, X.; Wang, M.; Chen, X.; Feng, X.; Wei, C.; Weng, X.; Xu, F. Lee Silverman Voice Treatment to Improve Speech in Parkinson’s Disease: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis. Park. Dis. 2021, 2021, 3366870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ballard, K.J.; Solomon, N.P.; Robin, D.A.; Moon, J.B.; Folkins, J.W. Nonspeech assessment of the speech production mechanism. In Clinical Management of Sensorimotor Speech Disorders, 2nd ed.; McNeil, M.R., Ed.; Thieme: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 30–45. [Google Scholar]
- Ackermann, H.; Hage, S.R.; Ziegler, W. Brain mechanisms of acoustic communication in humans and nonhuman primates: An evolutionary perspective. Behav. Brain Sci. 2014, 37, 529–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| System | Exercise Description | Duration | Dose/Intensity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Respiratory | •Establish optimal conditions for breathing through relaxation and body posture | 1′ | 3 repetitions |
| •Decrease the inhalation time and lengthen the exhalation time with non-verbal exercises | 2′ | 5 repetitions | |
| Phonatory (for pneumo-phonic coordination) | •Exhalation–phonation coordination | 1.5′ | 5 repetitions |
| •Production of long vowels | 2.5′ | 5–10–15 * repetitions | |
| •Production of long vowels with pitch and volume variations | 2.5′ | 5–10–15 * repetitions | |
| Phonatory (for glottic occlusion) | •Hold the inhaled air as long as possible | 1′ | 3 repetitions |
| •Pushing exercise | 5′ | 5–10–15 * repetitions | |
| •Harsh vowels attacks | 5′ | 5–10–15 * repetitions | |
| Resonance | •Velar stimulation (ice stimulation, veil massage) | 1.5′ | 3 repetitions |
| •Production of prolonged vowels | 1′ | 5 repetitions | |
| Articulatory | •Hyperarticulation | 5′ | 3 repetitions |
| •Articulatory exercises on single phonemes or syllables | 5′ | 5–10–15 * repetitions | |
| •Verbal and non-verbal functional oral motor exercises | 5′ | 5–10–15 * repetitions | |
| •Learning or articulatory positions | 1′ | 3 repetitions | |
| •Speed control techniques | 5′ | 5 repetitions | |
| Prosodic | •Reading of affirmative, negative, interrogative, and exclamatory sentences | 5′ | 3 repetitions |
| •Vocalization with variable pitch and volume | 5′ | 5–10–15 * repetitions | |
| •Reading of sentences with variable emphasis | 5′ | 5–10–15 * repetitions |
| Characteristics | T1 | T2 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Barthel Index | 71.4 ± 3.6 | 92.7 ± 5.4 | <0.001 1 |
| RDP | 153.4 ± 34.8 | 202.6 ± 23.4 | <0.001 2 |
| IOPI Tongue | 35.9 ± 7.6 | 45.2 ± 7.2 | <0.001 2 |
| IOPI Lip Right | 23.7 ± 7.1 | 28.0 ± 7.1 | <0.001 2 |
| IOPI Lip Left | 25.2 ± 7.4 | 29.1 ± 7.4 | <0.001 2 |
| Vocal Intensity (dB) | 53.5 ± 7.2 | 74.6 ± 6.6 | <0.001 2 |
| IOPI Tongue Resistance | 7.8 ± 2.3 | 13.1 ± 3.9 | <0.001 2 |
| Characteristics | T1 | T2 | T3 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VHI | 42.4 ± 18.4 | 26.1 ± 17.0 | 34.0 ± 20.5 | <0.001 1 |
| QoL–Dys | 76.4 ± 35.8 | 47.7 ± 28.4 | 47.5 ± 27.7 | <0.001 1 |
| PRAAT JITT | 2.4 ± 1.4 | 1.4 ± 1.0 | 1.7 ± 0.9 | 0.021 2 |
| PRAAT SHIM | 18.0 ± 0.6 | 14.4 ± 2.1 | 16.9 ± 1.2 | <0.001 1 |
| MPT | 10.8 ± 3.2 | 16.2 ± 5.0 | 13.1 ± 4.7 | <0.001 2 |
| Variables | IOPI Tongue (p) | IOPI Lip Right (p) | IOPI Lip Left (p) | IOPI Tongue Resistance (p) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.196 (0.300) | −0.169 (0.371) | 0.102 (0.591) | −0.460 (0.010) + |
| Years onset | −0.117 (0.537) | 0.048 (0.799) | −0.005 (0.978) | −0.281 (0.133) |
| CIRS | −0.023 (0.902) | −0.347 (0.060) | 0.177 (0.350) | −0.467 (0.009) + |
| RDP | −0.076 (0.691) | −0.282 (0.131) | 0.001 (0.996) | 0.078 (0.683) |
| QoL-Dys score | 0.038 (0.842) | 0.325 (0.080) | 0.025 (0.895) | 0.206 (0.275) |
| PRAAT score | −0.223 (0.237) | −0.135 (0.477) | 0.118 (0.536) | −0.071 (0.709) |
| VHI score | 0.262 (0.162) | −0.248 (0.186) | −0.009 (0.996) | −0.101 (0.595) |
| Vocal Intensity (dB) | 0.178 (0.346) | −0.085 (0.656) | 0.134 (0.481) | −0.168 (0.376) |
| MoCA | 0.116 (0.542) | 0.508 (0.004) + | −0.120 (0.528) | −0.032 (0.869) |
| Barthel Index | −0.091 (0.346) | −0.005 (0.978) | 0.094 (0.622) | −0.059 (0.755) |
| MDS-UPDRS | 0.053 (0.782) | −0.359 (0.051) | 0.073 (0.700) | −0.465 (0.010) + |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gison, A.; Ruggiero, M.; Tufarelli, D.; Proietti, S.; Moscariello, D.; Valente, M. Intensive Speech Therapy for Hypokinetic Dysarthria in Parkinson’s Disease: Targeting the Five Subsystems of Speech Production with Clinical and Instrumental Evaluation. NeuroSci 2025, 6, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6010007
Gison A, Ruggiero M, Tufarelli D, Proietti S, Moscariello D, Valente M. Intensive Speech Therapy for Hypokinetic Dysarthria in Parkinson’s Disease: Targeting the Five Subsystems of Speech Production with Clinical and Instrumental Evaluation. NeuroSci. 2025; 6(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleGison, Annalisa, Marco Ruggiero, Davide Tufarelli, Stefania Proietti, Daniela Moscariello, and Marianna Valente. 2025. "Intensive Speech Therapy for Hypokinetic Dysarthria in Parkinson’s Disease: Targeting the Five Subsystems of Speech Production with Clinical and Instrumental Evaluation" NeuroSci 6, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6010007
APA StyleGison, A., Ruggiero, M., Tufarelli, D., Proietti, S., Moscariello, D., & Valente, M. (2025). Intensive Speech Therapy for Hypokinetic Dysarthria in Parkinson’s Disease: Targeting the Five Subsystems of Speech Production with Clinical and Instrumental Evaluation. NeuroSci, 6(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci6010007






