Intraclass Correlation in Paired Associative Stimulation and Metaplasticity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Review and Study Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Electromyographic Recording
2.4. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
2.4.1. “Hotspot” Identification and TMS Delivery
2.4.2. Resting Motor Threshold
2.4.3. Baseline Corticospinal Excitability
2.5. Paired Associative Stimulation
2.6. Post-PAS Assessment
2.7. Measures
2.8. Literature Review Details
2.9. Statistical Analyses
2.9.1. Effects of PAS25 on Overall Motor Excitability
2.9.2. Temporal Effects of PAS25 on Motor Excitability
2.9.3. Intraclass Correlation
3. Results
3.1. Effects of PAS on Motor Excitability
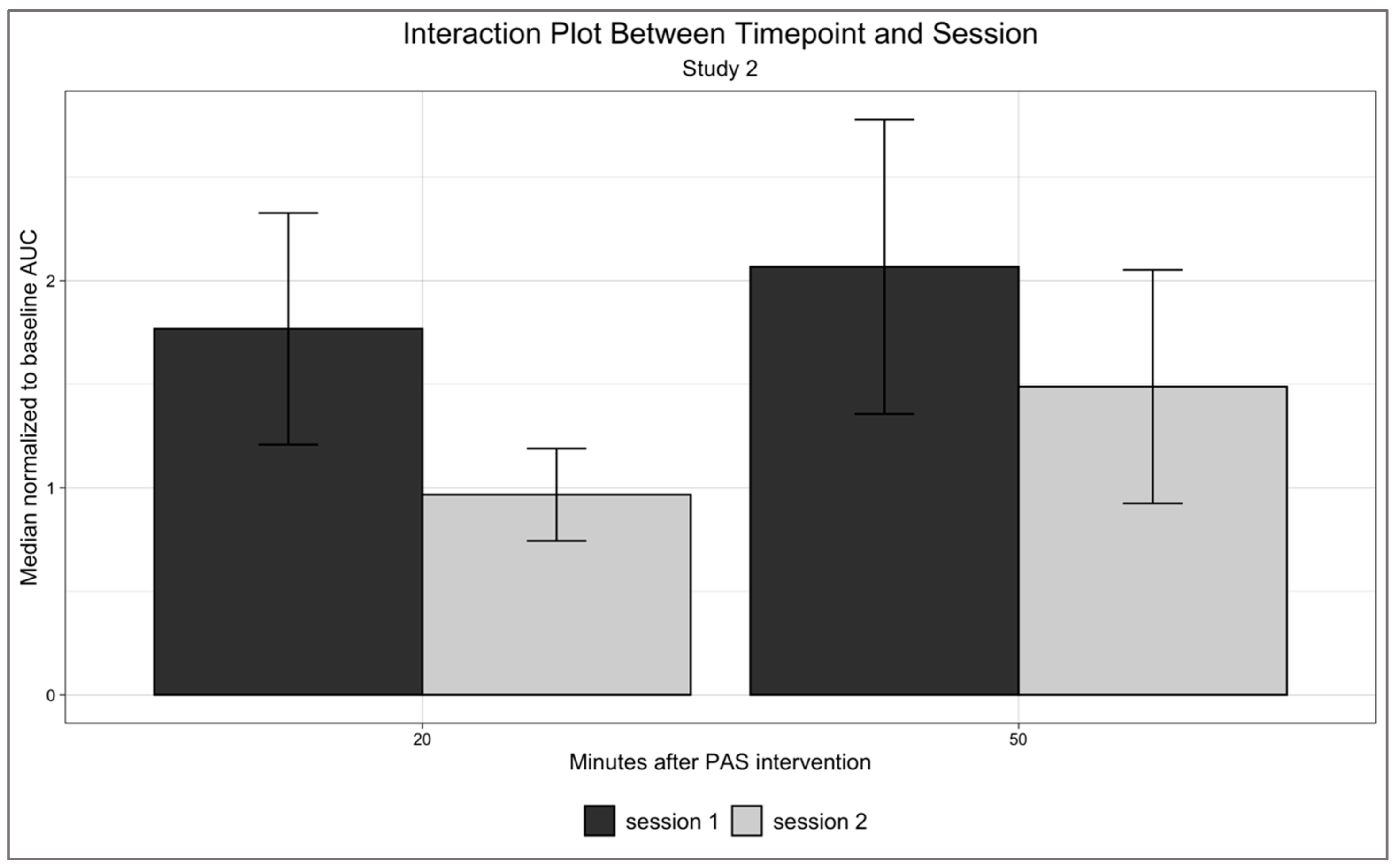
3.2. Temporal Effects of PAS25 on Motor Excitability
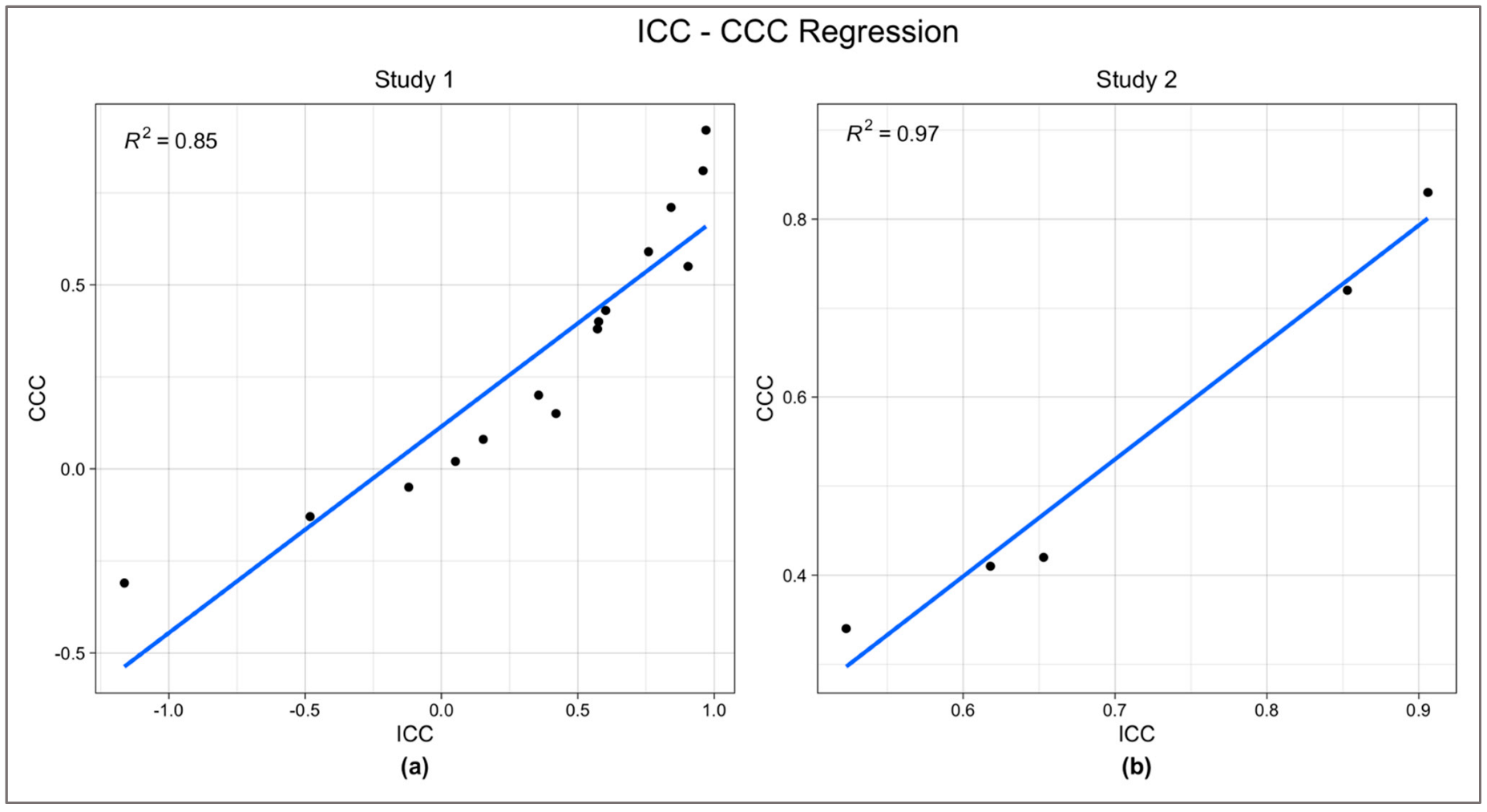
3.3. ICC-CCC Comparisons and Remaining ICC Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stefan, K.; Kunesch, E.; Benecke, R.; Cohen, L.G.; Classen, J. Mechanisms of Enhancement of Human Motor Cortex Excitability Induced by Interventional Paired Associative Stimulation. J. Physiol. 2002, 543, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverstein, J.; Cortes, M.; Tsagaris, K.Z.; Climent, A.; Gerber, L.M.; Oromendia, C.; Fonzetti, P.; Ratan, R.R.; Kitago, T.; Iacoboni, M.; et al. Paired Associative Stimulation as a Tool to Assess Plasticity Enhancers in Chronic Stroke. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.Q.; Dhaher, Y.Y. Contralesional Hemisphere Regulation of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation-Induced Kinetic Coupling in the Poststroke Lower Limb. Front. Neurol. 2017, 8, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stinear, J.W.; Hornby, T.G. Stimulation-Induced Changes in Lower Limb Corticomotor Excitability during Treadmill Walking in Humans: Stimulation-Induced Changes in Corticomotor Excitability. J. Physiol. 2005, 567, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodionov, A.; Savolainen, S.; Kirveskari, E.; Mäkelä, J.P.; Shulga, A. Restoration of Hand Function with Long-Term Paired Associative Stimulation after Chronic Incomplete Tetraplegia: A Case Study. Spinal Cord Ser. Cases 2019, 5, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bliss, T.V.P.; Cooke, S.F. Long-Term Potentiation and Long-Term Depression: A Clinical Perspective. Clinics 2011, 66, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Croarkin, P.E.; Ameis, S.H.; Sun, Y.; Blumberger, D.M.; Rajji, T.K.; Daskalakis, Z.J. Paired-Associative Stimulation-Induced Long-Term Potentiation-Like Motor Cortex Plasticity in Healthy Adolescents. Front. Psychiatry 2017, 8, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidali, G.; Roncoroni, C.; Bolognini, N. Modulating Frontal Networks’ Timing-Dependent-Like Plasticity with Paired Associative Stimulation Protocols: Recent Advances and Future Perspectives. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 658723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolters, A.; Sandbrink, F.; Schlottmann, A.; Kunesch, E.; Stefan, K.; Cohen, L.G.; Benecke, R.; Classen, J. A Temporally Asymmetric Hebbian Rule Governing Plasticity in the Human Motor Cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 2003, 89, 2339–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporale, N.; Dan, Y. Spike Timing-Dependent Plasticity: A Hebbian Learning Rule. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2008, 31, 25–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, K.; Kunesch, E.; Cohen, L.G.; Benecke, R.; Classen, J. Induction of Plasticity in the Human Motor Cortex by Paired Associative Stimulation. Brain 2000, 123, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Dahlhaus, F.; Lücke, C.; Lu, M.-K.; Arai, N.; Fuhl, A.; Herrmann, E.; Ziemann, U. Augmenting LTP-Like Plasticity in Human Motor Cortex by Spaced Paired Associative Stimulation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lazzaro, V.; Dileone, M.; Profice, P.; Pilato, F.; Oliviero, A.; Mazzone, P.; Di Iorio, R.; Capone, F.; Ranieri, F.; Florio, L.; et al. LTD-like Plasticity Induced by Paired Associative Stimulation: Direct Evidence in Humans. Exp. Brain Res. 2009, 194, 661–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamke, M.R.; Nydam, A.S.; Sale, M.V.; Mattingley, J.B. Associative Plasticity in the Human Motor Cortex Is Enhanced by Concurrently Targeting Separate Muscle Representations with Excitatory and Inhibitory Protocols. J. Neurophysiol. 2016, 115, 2191–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-Z.; Edwards, M.J.; Rounis, E.; Bhatia, K.P.; Rothwell, J.C. Theta Burst Stimulation of the Human Motor Cortex. Neuron 2005, 45, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallett, M. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation: A Primer. Neuron 2007, 55, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitsche, M.A.; Roth, A.; Kuo, M.-F.; Fischer, A.K.; Liebetanz, D.; Lang, N.; Tergau, F.; Paulus, W. Timing-Dependent Modulation of Associative Plasticity by General Network Excitability in the Human Motor Cortex. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 3807–3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strube, W.; Bunse, T.; Nitsche, M.A.; Palm, U.; Falkai, P.; Hasan, A. Differential Response to Anodal TDCS and PAS Is Indicative of Impaired Focal LTP-like Plasticity in Schizophrenia. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 311, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meder, A.; Liepelt-Scarfone, I.; Sulzer, P.; Berg, D.; Laske, C.; Preische, O.; Desideri, D.; Zipser, C.M.; Salvadore, G.; Tatikola, K.; et al. Motor Cortical Excitability and Paired-Associative Stimulation-Induced Plasticity in Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2021, 132, 2264–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirillo, J.; Lavender, A.P.; Ridding, M.C.; Semmler, J.G. Motor Cortex Plasticity Induced by Paired Associative Stimulation Is Enhanced in Physically Active Individuals: Motor Cortex Plasticity and Physical Activity. J. Physiol. 2009, 587, 5831–5842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fratello, F.; Veniero, D.; Curcio, G.; Ferrara, M.; Marzano, C.; Moroni, F.; Pellicciari, M.; Bertini, M.; Rossini, P.; Degennaro, L. Modulation of Corticospinal Excitability by Paired Associative Stimulation: Reproducibility of Effects and Intraindividual Reliability. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2006, 117, 2667–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sale, M.V.; Ridding, M.C.; Nordstrom, M.A. Factors Influencing the Magnitude and Reproducibility of Corticomotor Excitability Changes Induced by Paired Associative Stimulation. Exp. Brain Res. 2007, 181, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickins, D.S.E.; Kamke, M.R.; Sale, M.V. Corticospinal Plasticity in Bilateral Primary Motor Cortices Induced by Paired Associative Stimulation to the Dominant Hemisphere Does Not Differ between Young and Older Adults. Neural Plast. 2017, 2017, 8319049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaulieu, L.-D.; Flamand, V.H.; Massé-Alarie, H.; Schneider, C. Reliability and Minimal Detectable Change of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Outcomes in Healthy Adults: A Systematic Review. Brain Stimulat. 2017, 10, 196–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Ngo, J.P.; Deblieck, C.; Edwards, D.J.; Dobkin, B.; Wu, A.D.; Iacoboni, M. Individual Level Reliability of PAS-Induced Neural Plasticity. bioRxiv 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayka, M.A.; Corcos, D.M.; Leurgans, S.E.; Vaillancourt, D.E. Three-Dimensional Locations and Boundaries of Motor and Premotor Cortices as Defined by Functional Brain Imaging: A Meta-Analysis. NeuroImage 2006, 31, 1453–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borckardt, J.J.; Nahas, Z.; Koola, J.; George, M.S. Estimating Resting Motor Thresholds in Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Research and Practice: A Computer Simulation Evaluation of Best Methods. J. ECT 2006, 22, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.M.; Creelman, C.D. PEST: Efficient Estimates on Probability Functions. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1967, 41, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ah Sen, C.B.; Fassett, H.J.; El-Sayes, J.; Turco, C.V.; Hameer, M.M.; Nelson, A.J. Active and Resting Motor Threshold Are Efficiently Obtained with Adaptive Threshold Hunting. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayaka, T.; Zoghi, M.; Farrell, M.; Egan, G.; Jaberzadeh, S. Comparison of Rossini-Rothwell and Adaptive Threshold-Hunting Methods on the Stability of TMS Induced Motor Evoked Potentials Amplitudes. J. Neurosci. Res. 2018, 96, 1758–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, K.; Wycislo, M.; Classen, J. Modulation of Associative Human Motor Cortical Plasticity by Attention. J. Neurophysiol. 2004, 92, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Player, M.J.; Taylor, J.L.; Alonzo, A.; Loo, C.K. Paired Associative Stimulation Increases Motor Cortex Excitability More Effectively than Theta-Burst Stimulation. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2012, 123, 2220–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM Corporation. IBM SPSS Statistics for Macintosh 2019; IBM: Armonk, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Massey, F.J. The Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test for Goodness of Fit. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1951, 46, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, G.E.P.; Cox, D.R. An Analysis of Transformations. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1964, 26, 211–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, T.K.; Li, M.Y. A Guideline of Selecting and Reporting Intraclass Correlation Coefficients for Reliability Research. J. Chiropr. Med. 2016, 15, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perinetti, G. StaTips Part IV: Selection, Interpretation and Reporting of the Intraclass Correlation Coefficient. South Eur. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Res. 2018, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobak, C.A.; Barr, P.J.; O’Malley, A.J. Estimation of an Inter-Rater Intra-Class Correlation Coefficient That Overcomes Common Assumption Violations in the Assessment of Health Measurement Scales. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2018, 18, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, T.S.; Chinchilli, V.M.; Carrasco, J.L. A Repeated Measures Concordance Correlation Coefficient. Stat. Med. 2007, 26, 3095–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, S.; Bastero-Caballero, R.F.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, R.; Murphy, D.K.; Hardas, B.; Koch, G. Performance of Intraclass Correlation Coefficient (ICC) as a Reliability Index under Various Distributions in Scale Reliability Studies. Stat. Med. 2018, 37, 2734–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-C.; Barnhart, H.X. Comparison of ICC and CCC for Assessing Agreement for Data without and with Replications. Comput. Stat. Data Anal. 2008, 53, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerwin, L.J.; Keller, C.J.; Wu, W.; Narayan, M.; Etkin, A. Test-Retest Reliability of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation EEG Evoked Potentials. Brain Stimulat. 2018, 11, 536–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.I.-K. A Concordance Correlation Coefficient to Evaluate Reproducibility. Biometrics 1989, 45, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller-Dahlhaus, J.F.M.; Orekhov, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ziemann, U. Interindividual Variability and Age-Dependency of Motor Cortical Plasticity Induced by Paired Associative Stimulation. Exp. Brain Res. 2008, 187, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tecchio, F.; Zappasodi, F.; Pasqualetti, P.; Gennaro, L.D.; Pellicciari, M.C.; Ercolani, M.; Squitti, R.; Rossini, P.M. Age Dependence of Primary Motor Cortex Plasticity Induced by Paired Associative Stimulation. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008, 119, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conde, V.; Vollmann, H.; Sehm, B.; Taubert, M.; Villringer, A.; Ragert, P. Cortical Thickness in Primary Sensorimotor Cortex Influences the Effectiveness of Paired Associative Stimulation. NeuroImage 2012, 60, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- List, J.; Kübke, J.C.; Lindenberg, R.; Külzow, N.; Kerti, L.; Witte, V.; Flöel, A. Relationship between Excitability, Plasticity and Thickness of the Motor Cortex in Older Adults. NeuroImage 2013, 83, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleim, J.A.; Chan, S.; Pringle, E.; Schallert, K.; Procaccio, V.; Jimenez, R.; Cramer, S.C. BDNF Val66met Polymorphism Is Associated with Modified Experience-Dependent Plasticity in Human Motor Cortex. Nat. Neurosci. 2006, 9, 735–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheeran, B.; Talelli, P.; Mori, F.; Koch, G.; Suppa, A.; Edwards, M.; Houlden, H.; Bhatia, K.; Greenwood, R.; Rothwell, J.C. A Common Polymorphism in the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Gene (BDNF) Modulates Human Cortical Plasticity and the Response to RTMS: BNDF Polymorphism Modulates Response to RTMS. J. Physiol. 2008, 586, 5717–5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Missitzi, J.; Gentner, R.; Geladas, N.; Politis, P.; Karandreas, N.; Classen, J.; Klissouras, V. Plasticity in Human Motor Cortex Is in Part Genetically Determined: Genetic Variation of Plasticity in Human Motor Cortex. J. Physiol. 2011, 589, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwen, B.S.; Chattarji, S. Molecular Mechanisms of Neuroplasticity and Pharmacological Implications: The Example of Tianeptine. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2004, 14, S497–S502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Jing, L.; Toledo-Salas, J.-C.; Xu, L. Rapid-Onset Antidepressant Efficacy of Glutamatergic System Modulators: The Neural Plasticity Hypothesis of Depression. Neurosci. Bull. 2015, 31, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chollet, F.; Tardy, J.; Albucher, J.-F.; Raposo, N.; Acket, B.; Sattler, V.; Pariente, J.; Loubinoux, I. Monoaminergic Drugs for Motor Recovery after Ischemic Stroke. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2014, 57, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundman, M.H.; Lim, K.; Ton That, V.; Mizell, J.-M.; Ugonna, C.; Rodriguez, R.; Chen, N.-K.; Fuglevand, A.J.; Liu, Y.; Wilson, R.C.; et al. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Reveals Diminished Homoeostatic Metaplasticity in Cognitively Impaired Adults. Brain Commun. 2020, 2, fcaa203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, A.C.; Sack, A.T. How to Design Optimal Accelerated RTMS Protocols Capable of Promoting Therapeutically Beneficial Metaplasticity. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 599918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantone, M.; Lanza, G.; Ranieri, F.; Opie, G.M.; Terranova, C. Editorial: Non-Invasive Brain Stimulation in the Study and Modulation of Metaplasticity in Neurological Disorders. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 721906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suppa, A.; Asci, F.; Guerra, A. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation as a Tool to Induce and Explore Plasticity in Humans. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 184, pp. 73–89. ISBN 978-0-12-819410-2. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, W.C.; Mason-Parker, S.E.; Bear, M.F.; Webb, S.; Tate, W.P. Heterosynaptic Metaplasticity in the Hippocampus in Vivo: A BCM-like Modifiable Threshold for LTP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 10924–10929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Combination * | ICCs Obtained | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Between sessions | Study 1 | S1 vs. S2 vs. S3 vs. S4 vs. S5 | 1 |
| Study 2 | S1 vs. S2 | 1 | |
| Across timepoints for each session | Study 1 | S1 (0 min vs. 10 min vs. 20 min vs. 30 min vs. 40 min vs. 50 min vs. 60 min), … S5 (0 min vs. 10 min vs. 20 min vs. 30 min vs. 40 min vs. 50 min vs. 60 min) | 5 |
| Study 2 | S1 (20 min vs. 50 min), S2 (20 min vs. 50 min) | 2 | |
| Across sessions for each timepoint | Study 1 | 0 min (S1 vs. S2 vs. S3 vs. S4 vs. S5), … 60 min (S1 vs. S2 vs. S3 vs. S4 vs. S5). | 7 |
| Study 2 | 20 min (S1 vs. S2), 50 min (S1 vs. S2) | 2 |
| Combination | CCC Obtained | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Between sessions | Study 1 | S1 vs. S2, S1 vs. S3, S1 vs. S4, S1 vs. S5, S2 vs. S3… | 10 |
| Study 2 | S1 vs. S2 | 1 | |
| Across timepoints within each session | Study 1 | S1 (G1 vs. G2), S2 (G1 vs. G2), … S5 (G1 vs. G2) | 5 |
| Study 2 | S1 (20 min vs. 50 min), S2 (20 min vs. 50 min) | 2 | |
| Across sessions for each timepoint | Study 2 | 20 min (S1 vs. S2), 50 min (S1 vs. S2) | 2 |
| ICC (95% CI) | CCC (95% CI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Across timepoints within each session (G1 vs. G2) | S1 | 0.84 (0.21–0.97) | 0.71 (0.12–0.93) |
| S2 | 0.96 (0.79–0.99) | 0.81 (0.49–0.94) | |
| S3 | 0.58 (−1.12–0.92) | 0.48 (0.35–0.84) | |
| S4 | 0.97 (0.85–1.00) | 0.92 (0.67–0.98) | |
| S5 | 0.90 (0.52–0.98) | 0.55 (0.09–0.82) | |
| Between sessions | S1 vs. S2 | 0.051 (−3.74–0.81) | 0.02 (−0.5–0.53) |
| S1 vs. S3 | 0.36 (−2.18–0.871) | 0.2 (−0.47–0.73) | |
| S1 vs. S4 | 0.57 (−1.14–0.91) | 0.38 (−0.19–0.76) | |
| S1 vs. S5 | 0.60 (−0.99–0.92) | 0.43 (−0.08–0.76) | |
| S2 vs. S3 | 0.42 (−1.90–0.88) | 0.15 (−0.25–0.5) | |
| S2 vs. S4 | 0.76 (−0.20–0.95) | 0.59 (0.01–0.87) | |
| S2 vs. S5 | −0.48 (−6.40–0.70) | −0.13 (−0.45–0.21) | |
| S3 vs. S4 | −0.12 (−4.60–0.78) | −0.05 (0.47–0.39) | |
| S3 vs. S5 | −1.16 (−9.80–0.57) | −0.31 (−0.72–0.28) | |
| S4 vs. S5 | 0.15 (−3.23–0.83) | 0.08 (−0.23–0.38) |
| ICC (95% CI) | CCC (95% CI) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Across timepoints within each session | S1 | 0.91 (0.53–0.98) | 0.83 (0.37–0.96) |
| S2 | 0.86 (0.27–0.97) | 0.72 (0.32–0.9) | |
| Across sessions for each timepoint | 20 min | 0.65 (−0.73–0.93) | 0.42 (−0.14–0.74) |
| 50 min | 0.52 (−1.38–0.90) | 0.34 (−0.39–0.81) | |
| Between sessions | S1 vs. S2 | 0.62 (−0.91–0.92) | 0.41 (−0.14–0.78) |
| ICC (95% CI) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Across timepoints within each session | S1 | 0.86 (0.63–0.97) |
| S2 | 0.96 (0.88–0.99) | |
| S3 | 0.84 (0.57–0.96) | |
| S4 | 0.97 (0.93–0.99) | |
| S5 | 0.70 (0.21–0.93) | |
| Across sessions for each timepoint | 0 min | 0.22 (−1.18–0.82) |
| 10 min | 0.33 (−0.87–0.85) | |
| 20 min | 0.45 (−0.54–0.87) | |
| 30 min | 0.72 (0.21–0.94) | |
| 40 min | 0.04 (−1.66–0.78) | |
| 50 min | 0.66 (0.05–0.92) | |
| 60 min | 0.67 (0.07–0.90) | |
| Between sessions | S1 vs. S2 vs. S3 vs. S4 vs. S5 | 0.58 (−0.18–0.90) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schapira, G.; Chang, J.; Kim, Y.; Ngo, J.P.; Deblieck, C.; Bianco, V.; Edwards, D.J.; Dobkin, B.H.; Wu, A.D.; Iacoboni, M. Intraclass Correlation in Paired Associative Stimulation and Metaplasticity. NeuroSci 2022, 3, 589-603. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci3040042
Schapira G, Chang J, Kim Y, Ngo JP, Deblieck C, Bianco V, Edwards DJ, Dobkin BH, Wu AD, Iacoboni M. Intraclass Correlation in Paired Associative Stimulation and Metaplasticity. NeuroSci. 2022; 3(4):589-603. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci3040042
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchapira, Giuditta, Justin Chang, Yeun Kim, Jacqueline P. Ngo, Choi Deblieck, Valentina Bianco, Dylan J. Edwards, Bruce H. Dobkin, Allan D. Wu, and Marco Iacoboni. 2022. "Intraclass Correlation in Paired Associative Stimulation and Metaplasticity" NeuroSci 3, no. 4: 589-603. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci3040042
APA StyleSchapira, G., Chang, J., Kim, Y., Ngo, J. P., Deblieck, C., Bianco, V., Edwards, D. J., Dobkin, B. H., Wu, A. D., & Iacoboni, M. (2022). Intraclass Correlation in Paired Associative Stimulation and Metaplasticity. NeuroSci, 3(4), 589-603. https://doi.org/10.3390/neurosci3040042







