Effect of Na Doping on the Electrochemical Performance of Li1.2Ni0.13Co0.13Mn0.54O2 Cathode for Lithium-Ion Batteries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
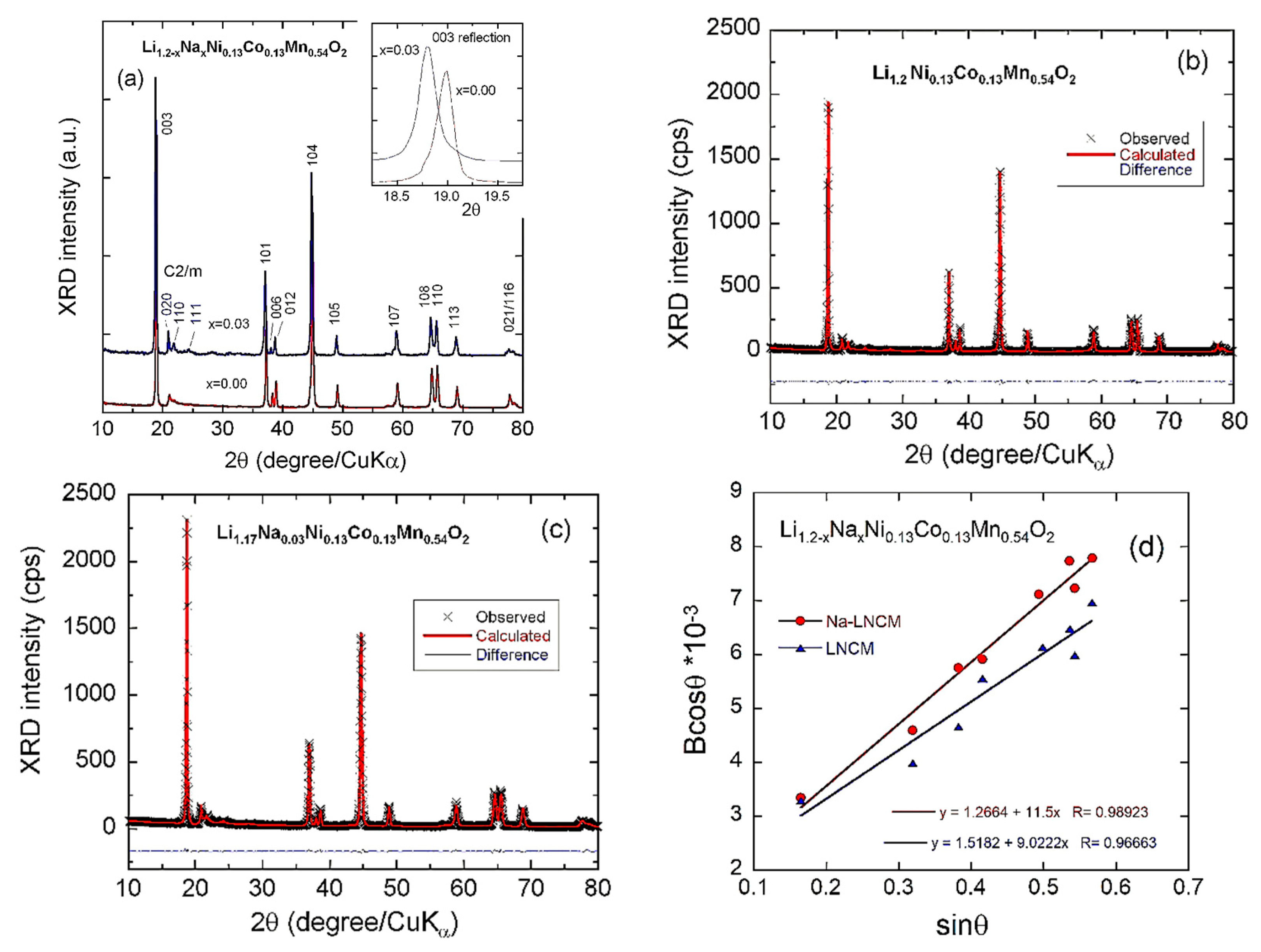
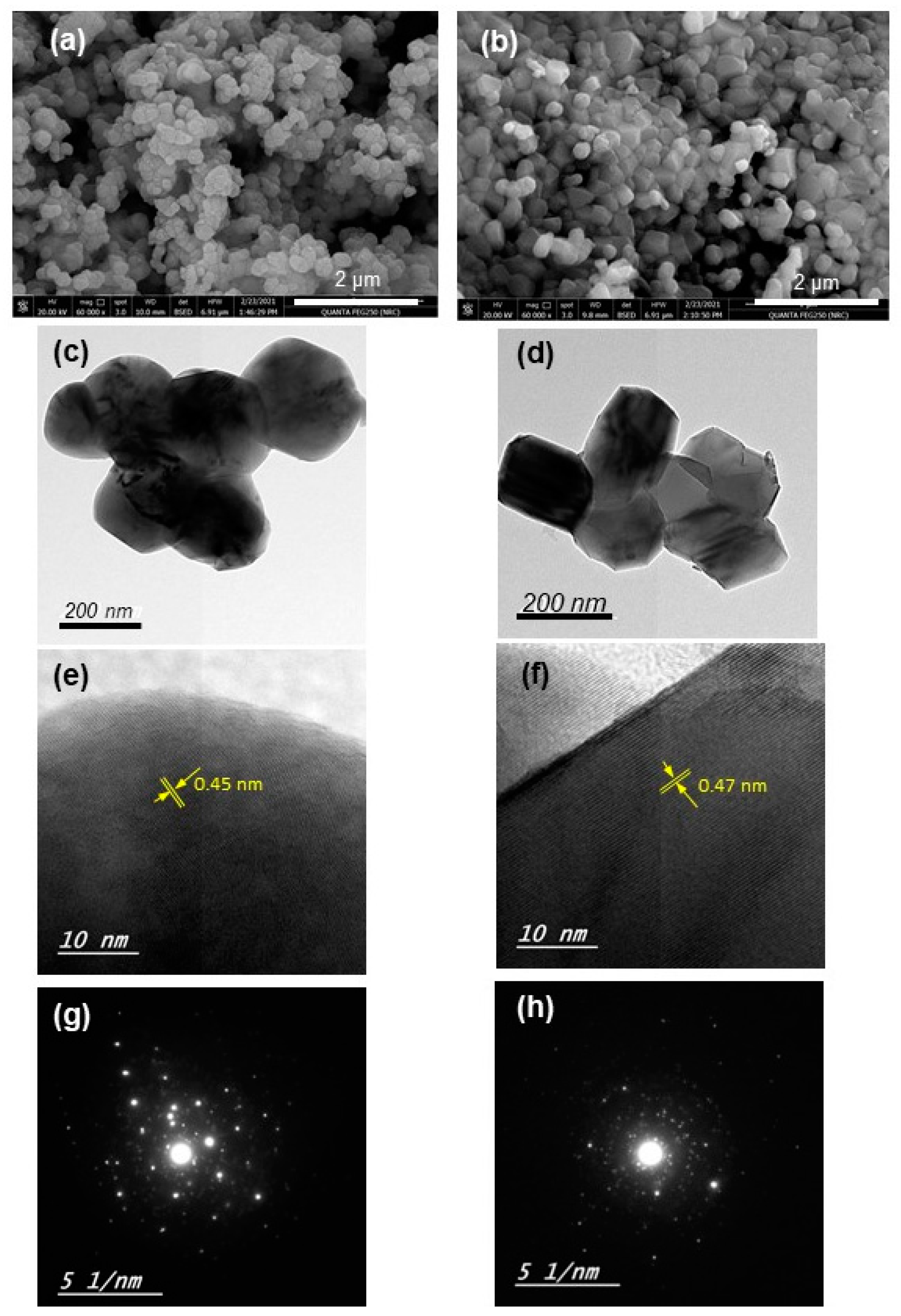
3.1. Structural Properties
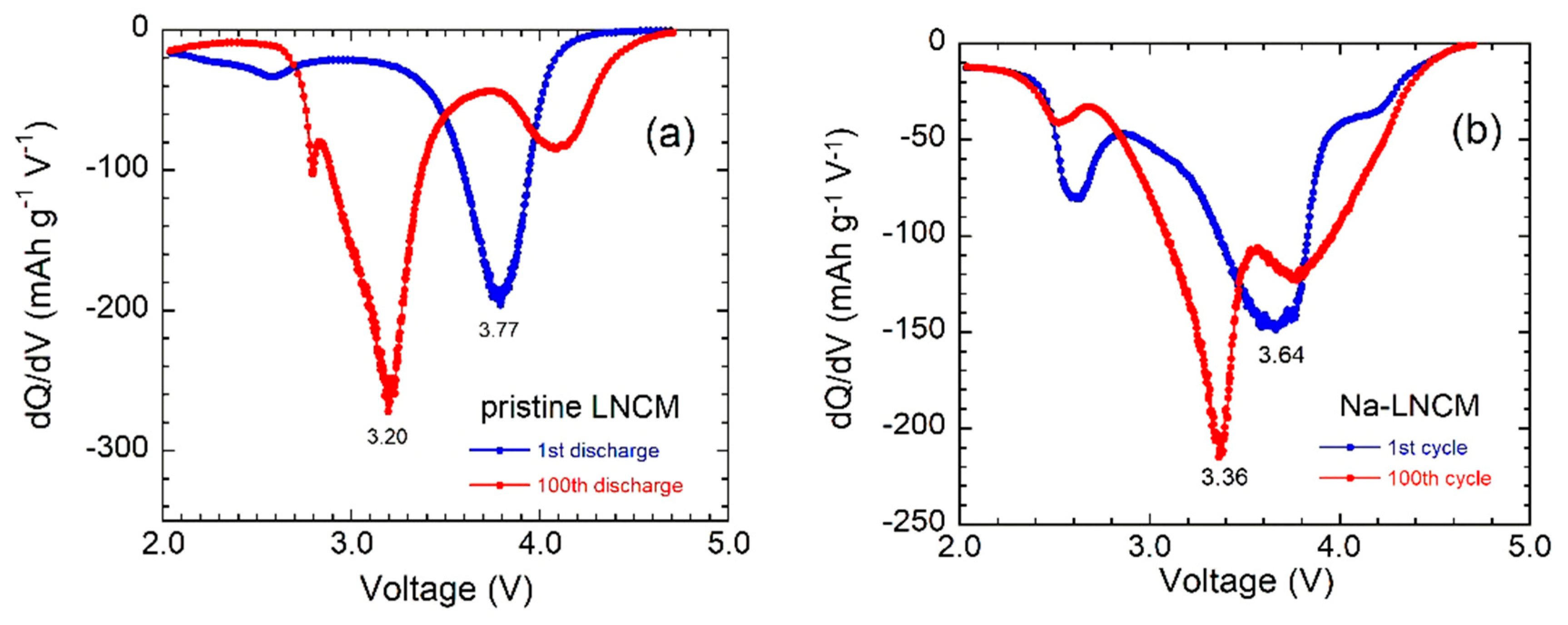
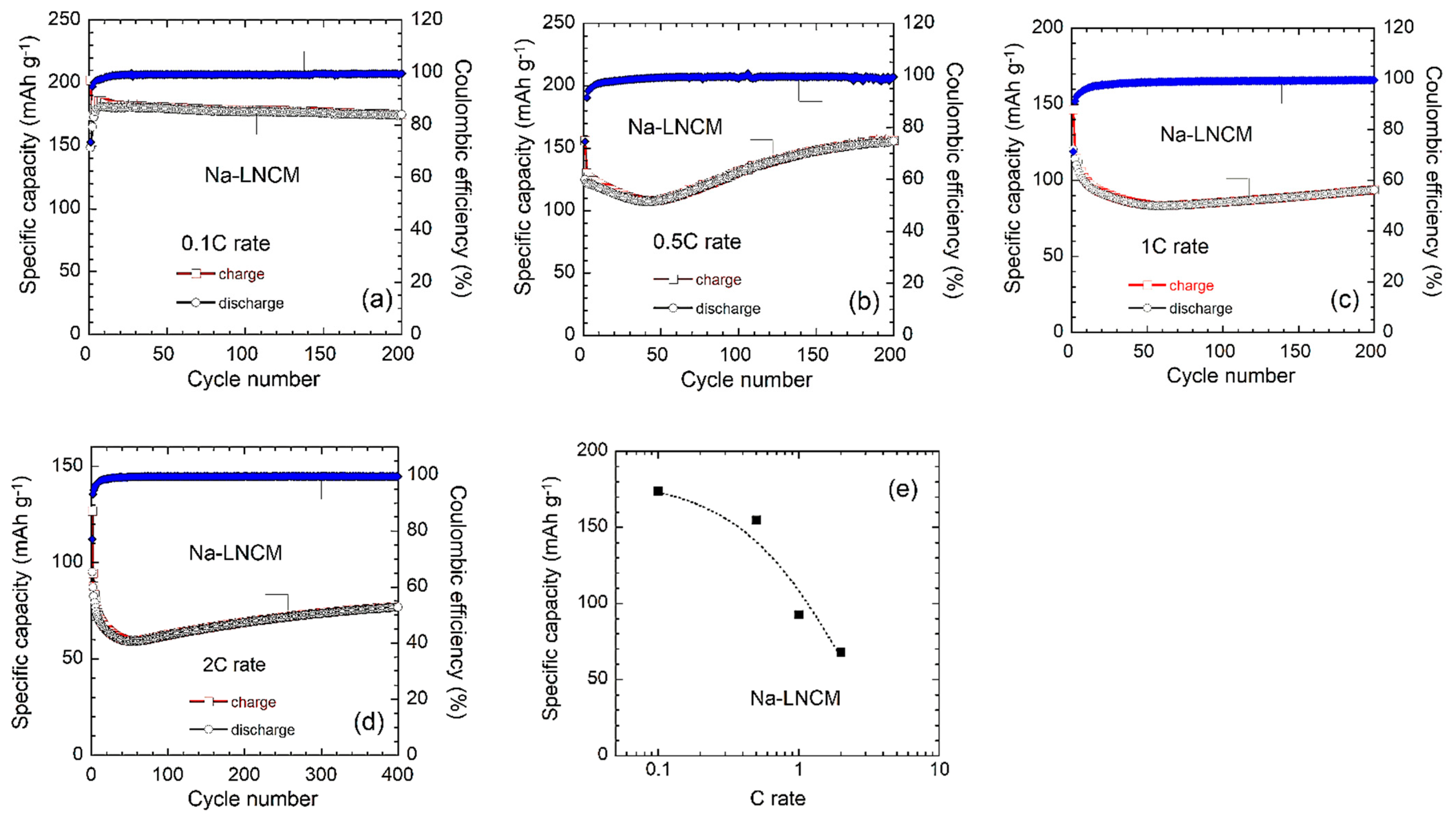
3.2. Electrochemical Properties
3.3. Transport Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manthiram, A.; Knight, J.C.; Myung, S.-T.; Oh, S.-M.; Sun, Y.-K. Nickel-rich and lithium-rich layered oxide cathodes. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1501010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; Reeja-Jayan, B.; Manthiram, A. Carbon-coated high capacity layered Li[Li0.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13]O2 cathodes. Electrochem. Commun. 2010, 12, 750–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Guo, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Chen, N.; Gui, W. Improving rate capability and decelerating voltage decay of Li-rich layered oxide cathodes by chromium doping. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2018, 43, 11109–11119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hy, S.; Felix, F.; Rick, J.; Su, W.-N.; Hwang, B.J. Direct in situ observation of Li2O evolution on Li-rich high-capacity cathode material Li[NixLi(1–2x)/3Mn(2–x)/3]O2 (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.5). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, J.T.; Wang, S.; Ji, R.; Xia, Q.; Ding, Z. Surface structural transition induced by gradient polyanion-doping in Li-rich layered oxides: Implications for enhanced electrochemical performance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 4760–4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Ghany, A.; El-Tawil, R.S.; Hashem, A.M.; Mauger, A.; Julien, C.M. Improved electrochemical performance of LiNi0.5Mn0.5O2 by Li-enrichment and AlF3 coating. Materialia 2019, 5, 100207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, C.; Wu, B.; Wu, F. High-rate layered lithium-rich cathode nanomaterials for lithium-ion batteries synthesized with the assist of carbon spheres templates. J. Power Sources 2016, 331, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Ghany, A.E.; Hashem, A.M.; Mauger, A.; Julien, C.M. Effects of chelators on the structure and electrochemical properties of Li-rich Li1.2Ni0.13Co0.13Mn0.54O2 cathode materials. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2020, 24, 3157–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Wang, X.; Fu, Y.; Wang, L.; Cai, M.; Liu, M.; Lu, B.; Wang, G.; Wang, D.; Ren, Q.; et al. Effect of magnesium doping on properties of lithium-rich layered oxide cathodes based on a one-step co-precipitation strategy. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 4941–4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, Z.; Guo, H.; Li, X.; He, Z.; Li, T. Synthesis and electrochemical characterization of Zn-doped Li-rich layered Li[Li0.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13]O2 cathode material. Ceramics. Int. A 2015, 41, 11396–11401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Lim, J.; Yoon, J.; Park, K.S.; Gim, J.; Song, J.; Park, H.; Im, D.; Park, M.; Ahn, D.; et al. The effects of Mo doping on 0.3Li[Li0.33Mn0.67]O2·0.7Li[Ni0.5Co0.2Mn0.3]O2 cathode material. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 3053–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Huang, T.; Yu, A. Fe doped Li1.2Mn0.6−x/2Ni0.2−x/2FexO2 (x ≤ 0.1) as cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 133, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dianat, A.; Seriani, N.; Bobeth, M.; Cuniberti, G. Effects of Al-doping on the properties of Li-Mn-Ni-O cathode materials for Li-ion batteries: An ab initio study. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 9273–9280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Fan, L.Z. Effects of fluorine substitution on the electrochemical performance of layered Li-excess nickel manganese oxides cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 113, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Xu, M.; Liu, J.; Huang, Q.; Chen, L.; Wang, P. Understanding the enhanced kinetics of gradient-chemical-doped lithium-rich cathode material. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 20519–20526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.N.; Seo, J.Y.; Jung, D.S.; Ahn, W.; Song, H.S.; Yeon, S.H.; Park, S.B. Rate capability for Na-doped Li1.167Ni0.18Mn0.548Co0.105O2 cathode material and characterization of Li-ion diffusion using galvanostatic intermittent titration technique. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 623, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Guo, X.; Zhong, Y.; Hua, W.; Shen, C.; Chou, S.; Yang, X. Host structural stabilization of Li1.232Mn0.615Ni0.154O2 through K-doping attempt: Toward superior electrochemical performances. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 188, 336–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.H.; Shin, S.S.; Sun, Y.K. The effects of Na doping on performance of layered Li1.1−xNax(Ni0.2Co0.3Mn0.4)O2 materials for lithium secondary batteries. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2006, 95, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, B.; Wang, J.; Xia, Y.; Liu, Y.; Qin, L.; Yao, X.; Liu, Z. Effects of Na+ contents on electrochemical properties of Li1.2Co0.13Ni0.13Mn0.54O2 cathode materials. J. Power Sources 2013, 240, 530–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Yuan, D.; Qian, J.; Ai, X.; Yang, H.; Cao, Y. Enhanced high-rate capability and cycling stability of Na-stabilized layered Li1.2[Co0.13Ni0.13Mn0.54]O2 cathode material. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 11397–11403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, K.A.; Deng, Z.; Allard, L.F.; Manthiram, A.; Ferreira, P.J. Atomic structure of a lithium-rich layered oxide material for lithium-ion batteries: Evidence of a solid solution. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 3614–3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Fan, X.; Zhou, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, Q.; Ma, L.; Yang, C.; Hu, E.; Yang, X.Q.; Wang, C. Structure and interface design enable stable Li-rich cathode. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 8918–8927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, C.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, M.; Qiu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Zhou, D.; Yun, L.; Li, C.; Gu, Q.; et al. Structural insights into composition design of Li-rich layered cathode materials for high-energy rechargeable battery. Mater. Today 2021, 51, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Ishikawa, R.; So, Y.G.; Shibata, N.; Kudo, T.; Zhou, H.; Ikuhara, Y. Direct atomic-resolution observation of two phases in the Li1.2Mn0.567Ni0.166Co0.067O2 cathode material for lithium-ion batteries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 5969–5973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ates, M.N.; Jia, Q.; Shah, A.; Busnaina, A.; Mukerjee, S.; Abraham, K.M. Mitigation of layered to spinel conversion of a Li-rich layered metal oxide cathode material for Li-ion batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, A290–A301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hashem, A.M.; Abdel-Ghany, A.E.; Scheuermann, M.; Indris, S.; Ehrenberg, H.; Mauger, A.; Julien, C.M. Doped nanoscale NMC333 as cathode materials for Li-ion batteries. Materials 2019, 12, 2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Liu, M.; Wang, X.; Yu, R.; Wang, G.; Ren, Q.; Yang, X. Facile synthesis and performance of Na-doped porous lithium-rich cathodes for lithium-ion batteries. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 57310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jiang, W.J.; Mauger, A.; Lu, Q.; Gendron, F.; Julien, C.M. Minimization of the cation mixing in Li1+x (NMC)1−x O2 as cathode material. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 1292–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilican, S. Effect of Na doping on the microstructures and optical properties of ZnO nanorods. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 553, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Qiao, Y.; Guo, S.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, Y.; He, P.; Ishida, M.; Zhou, H. Direct visualization of the reversible O2−/O− redox process in Li-rich cathode materials. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1705197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Liu, P.; Qu, B.; Zheng, Z.; Zheng, H.; Deng, P.; Li, P.; Li, S.; Huang, H.; Wang, L.; et al. Uniform Na+ doping-induced defects in Li- and Mn-rich cathodes for high-performance lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1802114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Ning, D.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, Q.; Gu, L.; Gao, R.; Zhang, J.; Franz, A.; Schumacher, G.; Liu, X. Improving the electrochemical performances of Li-rich Li1.2Ni0.13Co0.13Mn0.54O2 through a cooperative doping of Na+ and PO4 with Na3PO4. J. Power Sources 2018, 375, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, S.H.; Johnson, C.S.; Vaughey, J.T.; Amine, K.; Thackeray, M.M. The effects of acid treatment on the electrochemical properties of 0.5Li2MnO3·0.5LiNi0.44Co0.25Mn0.31O2 electrodes in lithium cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2006, 153, A1186–A1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.K.; Li, M.J.; Yoon, C.S.; Hassoun, J.; Amine, K.; Scrosati, B. The role of AlF3 coatings in improving electrochemical cycling of Li-enriched nickel-manganese oxide electrodes for Li-ion batteries. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1192–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, K.; Yang, F.; Hu, G.R.; Peng, Z.D.; Cao, Y.B.; Ryn, K. Sodium additive to improve rate performance of Li[Li0.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13]O2 LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2 material for Li-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2013, 244, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Mu, K.; Cao, Y.; Xu, L.; Du, K.; Hu, G. Enhanced electrochemical performance of layered Li-rich cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries via aluminum and boron dual-doping. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 4184–4192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schipper, F.; Nayak, P.K.; Erickson, E.M.; Amalraj, S.F.; Srur-Lavi, O.; Penki, T.R.; Talianker, M.; Grinblat, J.; Sclar, H.; Breuer, O.; et al. Studies of cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries: Recent progress and new challenges. Inorganics 2017, 5, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, W.; Wang, S.; Knapp, M.; Leake, S.J.; Senyshyn, A.; Richter, C.; Yavuz, M.; Binder, J.R.; Grey, C.P.; Ehrenberg, H.; et al. Structural insights into the formation and voltage degradation of lithium- and manganese-rich layered oxides. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Gu, M.; Genc, A.; Xiao, J.; Xu, P.; Chen, X.; Zhu, Z.; Zhao, W.; Pullan, L.; Wang, C.; et al. Mitigating voltage fade in cathode materials by improving the atomic level uniformity of elemental distribution. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 2628–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, D.; Xu, B.; Chi, M.; Meng, Y.S. Uncovering the roles of oxygen vacancies in cation migration in lithium excess layered oxides. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 14665–14668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Genevois, C.; Koga, H.; Croguennec, L.; Ménétrier, M.; Delmas, C.; Weill, F. Insight into the atomic structure of cycled lithium-rich layered oxide Li1.20Mn0.54Co0.13Ni0.13O2 using HAADF STEM and electron nanodiffraction. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Cho, W.; Zhang, X.; Oshima, Y.; Choi, J.W. A stable lithium-rich surface structure for lithium-rich layered cathode materials. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keppeler, M.; Srinivasan, M. Interfacial phenomena/capacities beyond conversion reaction occurring in nano-sized transition-metal-oxide-based negative electrodes in lithium-ion batteries: A review. ChemElectroChem 2017, 4, 2727–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.M.; Hu, X.L.; Luo, W.; Huang, Y.H. Porous carbon-modified MnO disks prepared by a microwave-polyol process and their superior lithium-ion storage properties. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 19190–19195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Hu, X.; Sun, Y.; Huang, Y. Controlled synthesis of mesoporous MnO/C networks by microwave irradiation and their enhanced lithium-storage properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 1997–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.K.; Song, B.H.; Lai, M.O.; Lu, L. Electrochemical property of LiMn2O4 in over-discharge conditions. Funct. Mater. Lett. 2012, 5, 1250028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, D.; Wu, H.-H.; Fan, X.; Dou, A.; Zhang, Q.; Su, M. Improved cycling stability of Na-doped cathode materials Li1.2Ni0.2Mn0.6O2 via a facile synthesis. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 13045–13055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Tao, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, B.; Su, M. Effects of raw materials on the electrochemical performance of Na-doped Li-rich cathode materials Li[Li0.2Ni0.2Mn0.6]O2. Ionics 2019, 25, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Sheng, H.; Wu, X.; Fu, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, C.; Holze, R.; Wu, Y. Improving electrochemical properties by sodium doping for lithium-rich layered oxides. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2020, 3, 8953–8959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, F.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.J.; Wan, Y.; Hou, B.R. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy analysis for oxygen reduction reaction in 3.5% NaCl solution. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2009, 13, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, W.B.; Zhang, J.B.; Zheng, Z.; Liu, W.Y.; Peng, X.H.; Guo, X.D.; Zhong, B.H.; Wang, Y.J.; Wang, X.L. Na-doped Ni-rich LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2 cathode material with both high rate capability and high tap density for lithium ion batteries. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 14824–14832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Yang, Z.; Liang, J.; Lu, D.; Liang, C.; Guan, X.; Gao, A.; Chen, H. Understanding the role of Na-doping on Ni-rich layered oxide LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 689, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.J.; Wang, Z.X.; Jing, Q.; Gao, H.J.; Li, X.H.; Yang, Z.H. Investigation on the effect of Na doping on structure and Li-ion kinetics of layered LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 cathode material. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 192, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; Qi, X.; Li, L.; Li, W.; Xu, L.; Xie, Y.; Lai, X.; Hu, G.; Peng, Z.; Cao, Y.; et al. Sodium doping to enhance electrochemical performance of overlithiated oxide cathode materials for Li-ion batteries via Li/Na ion-exchange method. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 27141–27149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Shan, W.; Hou, X.; Lam, K.; Zhao, X.; Liu, X.; Wu, Y. Study of spherical Li1.2NaxMn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13O2 cathode based on dual Li+/Na+ transport system for Li-ion batteries. Solid State Ion. 2020, 350, 115326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, D.L.; Lee, J. Na-doped layered LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 with improved rate capability and cycling stability. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2018, 22, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhai, X.; Huang, H.; Zhou, J.; Li, X.; He, Y.; Guo, Z. Suppression of structural phase transformation of Li-rich Mn-based layered cathode materials with Na ion substitution strategy. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 349, 136402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, R.-P.; Shi, J.-L.; Xiao, D.-D.; Zhang, X.-D.; Yin, Y.-X.; Zhai, Y.-B.; Gu, L.; Guo, Y.-G. Enhancing the kinetics of Li-rich cathode materials through the pinning effects of gradient surface Na+ doping. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 6, 1501914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Mauger, A.; Lu, Q.; Groult, H.; Perrigaud, L.; Gendron, F.; Julien, C.M. Synthesis and characterization of LiNi1/3Mn1/3Co1/3O2 by wet-chemical method. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 6440–6449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaju, K.M.; Subba-Rao, G.V.; Chowdari, B.V.R. EIS and GITT studies on oxide cathodes, O2-Li2/3x(Co0.15Mn0.85)O2 (x= 0 and 1/3). Electrochim. Acta 2003, 48, 2691–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiderska-Mocek, A.; Lewandovski, A. Kinetics of Li-ion transfer reaction at LiMn2O4, LiCoO2, and LiFePO4 cathodes. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2017, 21, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, J.; He, X.; Gao, J.; Li, J.; Wan, C.; Juang, C. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) study of LiNi1/3Mn1/3Co1/3O2 for Li-ion batteries. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 345–353. [Google Scholar]
- Heubner, C.; Schneider, M.; Michaelis, A. Investigation of charge transfer kinetics of Li-intercalation in LiFePO4. J. Power Sources 2015, 288, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, R.; Belharouak, I. Part-II: Exchange current density and ionic diffusivity studies on the ordered and disordered spinel LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode. J. Power Sources 2017, 348, 218–325. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.-K.; Myung, S.-T.; Park, B.-C.; Yashiro, H. Improvement of the electrochemical properties of Li[Ni0.5Mn0.5]O2 by AlF3 coating. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2008, 155, A705–A710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Sample | LNCM | Na-LNCM |
|---|---|---|
| Lattice parameters | ||
| a (Å) | 2.849 (7) | 2.850 (2) |
| c (Å) | 14.214 (1) | 14.242 (5) |
| c/a | 4.987 (9) | 4.997 (1) |
| V (Å3) | 99.92 | 100.18 |
| I(003)/I(104) | 1.33 | 1.49 |
| Lc (nm) | 38.4 | 49.2 |
| ε × 10−3 (rd) | 2.26 | 2.86 |
| Reliability factors | ||
| Rp (%) | 8.27 | 8.98 |
| Rwp (%) | 11.3 | 12.18 |
| RF | 1.75 | 3.22 |
| χ2 | 1.26 | 1.81 |
| Ni2+ in Li layer | 2.85 | 1.68 |
| S(MO2)a(Å) | 2.102 | 2.109 |
| I(LiO2)b(Å) | 2.629 | 2.638 |
| Nominal Formula | Composition | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Na | Ni | Co | Mn | |
| Li1.2Ni0.13Co0.13Mn0.54O2 | 0.000 | 0.127 | 0.135 | 0.538 |
| Li1.17Na0.03Ni0.13Co0.13Mn0.54O2 | 0.032 | 0.126 | 0.127 | 0.547 |
| Sample | SBET | LBET | LTEM |
|---|---|---|---|
| (m2 g−1) | (nm) | (nm) | |
| LNCM | 7.28 | 181 | 180 |
| Na-LNCM | 6.67 | 198 | 200 |
| Pristine Material | Synthesis | Particle Size (nm) | Specific Capacity (mAh g−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2 | coprecipitation | 100–400 | 210 @ C/5 (10) | [50] |
| LiNi0.5Co0.2Mn0.3O2 (a) | coprecipitation | 500 | 150 @ C/5 (50) | [51] |
| Li1.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13O2 | solid-state reaction | 500 | 170 @ 2C (5) | [52] |
| Li1.2Co0.13Ni0.13Mn0.54O2 | polymer-pyrolysis | 100–150 | 190 @ C/3 (100) | [20] |
| LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 | HT solid reaction | 50–80 | 150 @C/10 (100) | [35] |
| Li1.2Ni0.246Mn0.462Co0.062O2 | hydrothermal | 400–600 | 180 @1C (100) | [53] |
| Li1.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13O2 | Li/Na ion exchange | 15 µm (d) | 180 @1C (100) | [54] |
| Li1.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13O2 (b) | coprecipitation | 200–400 | 120 @1C (100) | [55] |
| LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 | solid-state reaction | 300 | 161 @ C/10 (100) | [56] |
| Li1.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13O2 | coprecipitation | 500 | 210 @ C/10 (5) | [35] |
| Li1.167Ni0.18Mn0.548Co0.105O2 (c) | spray pyrolysis | 1 µm (d) | 180 @ C/2 (50) | [16] |
| Li1.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13O2 (c) | HT solid reaction | 200–400 | 217 @ 1C (100) | [57] |
| Li1.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13O2 (e) | molten salt | 18.6 µm (d) | 230 @ C/5 (100) | [58] |
| Li1.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13O2 | sol-gel | 200 | 180 @ C/10 (100) | this work |
| Li1.2Mn0.54Ni0.13Co0.13O2 | sol-gel | 200 | 50 @ 2C (400) | this work |
| Sample | RΩ | Rct | CPEct | σw | DLi | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Ω) | (Ω) | T | p | (Ω s−1/2) | (cm2 s−1) | |
| LNMC | 3.2 | 933 | 3.8 × 10−5 | 39.2 | 41.3 | 3.4 × 10−11 |
| Na-NMC | 2.9 | 298 | 5.1 × 10−6 | 25.7 | 24.6 | 10.7 × 10−11 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hashem, A.M.; Abdel-Ghany, A.E.; El-Tawil, R.S.; Mauger, A.; Julien, C.M. Effect of Na Doping on the Electrochemical Performance of Li1.2Ni0.13Co0.13Mn0.54O2 Cathode for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Sustain. Chem. 2022, 3, 131-148. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem3020010
Hashem AM, Abdel-Ghany AE, El-Tawil RS, Mauger A, Julien CM. Effect of Na Doping on the Electrochemical Performance of Li1.2Ni0.13Co0.13Mn0.54O2 Cathode for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Sustainable Chemistry. 2022; 3(2):131-148. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem3020010
Chicago/Turabian StyleHashem, Ahmed M., Ashraf E. Abdel-Ghany, Rasha S. El-Tawil, Alain Mauger, and Christian M. Julien. 2022. "Effect of Na Doping on the Electrochemical Performance of Li1.2Ni0.13Co0.13Mn0.54O2 Cathode for Lithium-Ion Batteries" Sustainable Chemistry 3, no. 2: 131-148. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem3020010
APA StyleHashem, A. M., Abdel-Ghany, A. E., El-Tawil, R. S., Mauger, A., & Julien, C. M. (2022). Effect of Na Doping on the Electrochemical Performance of Li1.2Ni0.13Co0.13Mn0.54O2 Cathode for Lithium-Ion Batteries. Sustainable Chemistry, 3(2), 131-148. https://doi.org/10.3390/suschem3020010








