Influence of MW Irradiation on the Reaction Between (2R,7R,11S,16S)-1,8,10,17-tetraazapentacyclo[8.8.1.1.8,170.2,70.11,16]icosane and p-Substituted Phenols
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Methods and Materials
2.2. General Procedure: Reaction Between Aminal and p-Substituted Phenols
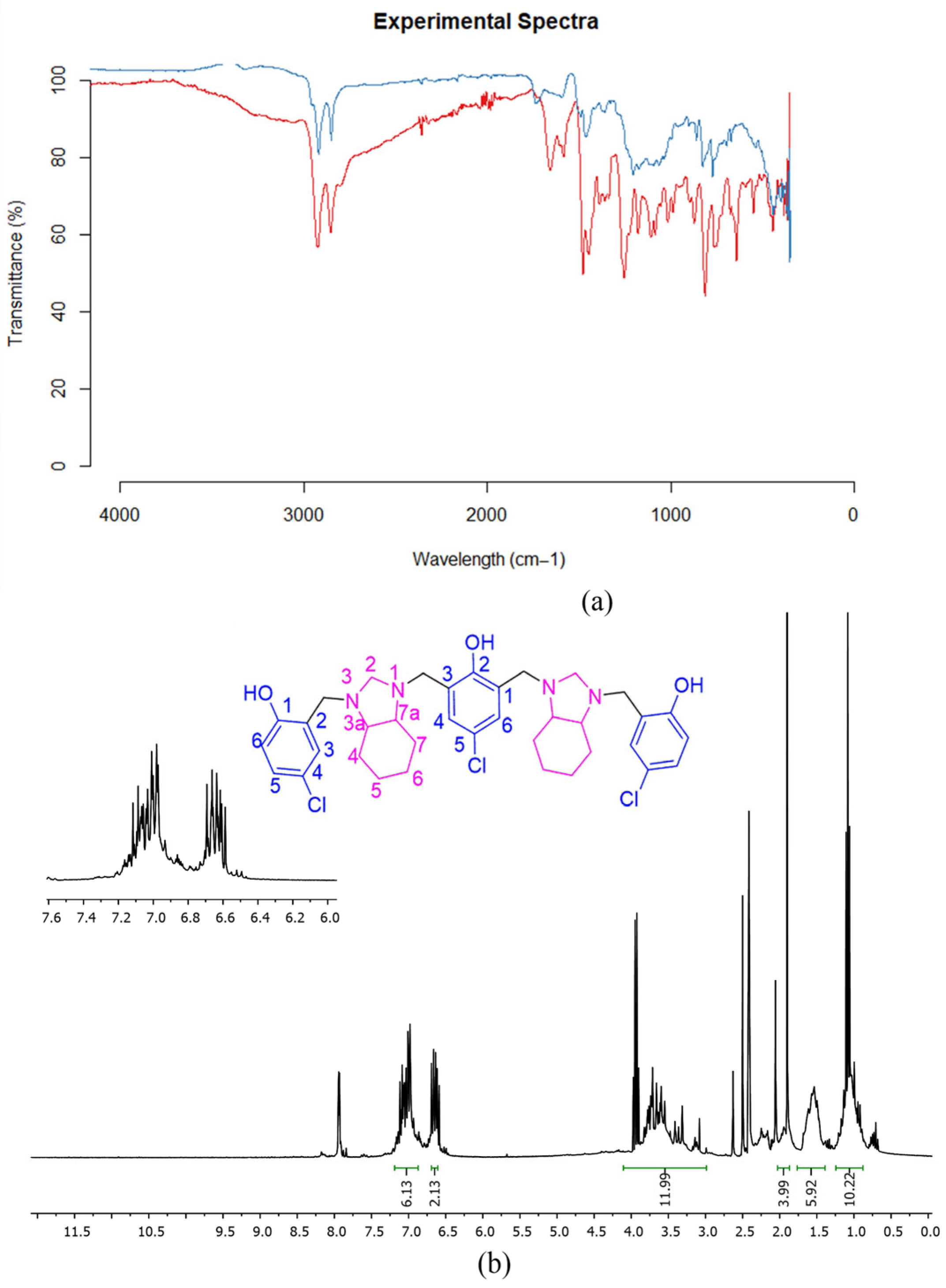
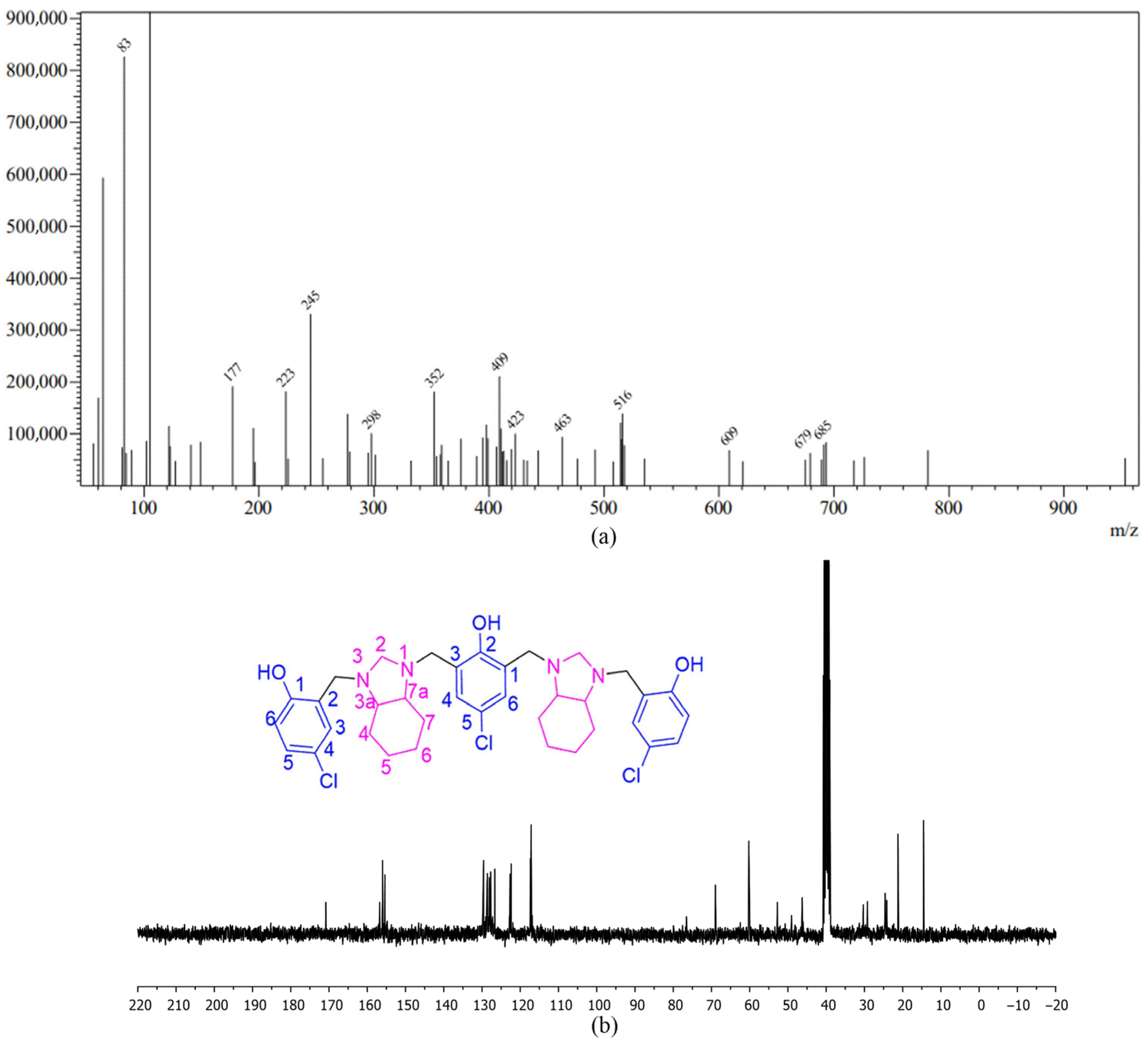
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bala, S.; Sharma, N.; Kajal, A.; Kamboj, S.; Saini, V. Mannich Bases: An Important Pharmacophore in Present Scenario. Int. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 2014, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, G. Mannich Bases in Medicinal Chemistry and Drug Design. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 89, 743–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janowska, S.; Andrzejczuk, S.; Gawryś, P.; Wujec, M. Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activity of New Mannich Bases with Piperazine Moiety. Molecules 2023, 28, 5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raju, S.K.; Settu, A.; Thiyagarajan, A.; Rama, D. Synthetic Applications of Biologically Important Mannich Bases: An Updated Review. Open Access Res. J. Biol. Pharm. 2023, 7, 001–015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietze, R.; Chaudhari, M. Advanced Benzoxazine Chemistries Provide Improved Performance in a Broad Range of Applications. In Handbook of Benzoxazine Resins; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sheng, W.; Yang, R.; Liu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, K. Synthesis of Bio-diamine Derived Main-chain Type Benzoxazine Resins with Low Surface Free Energy. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2023, 140, e53578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gungor, F.S. Investigating Oxazine Exchange Reactions for Thermally Curable Naphthoxazine Synthesis. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 196, 112285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appasamy, S.; Shanmugam, K.; Krishnasamy, B.; Arumugam, H.; Muthukaruppan, A. Hybrid Benzoxazines from Natural Bio-Phenolics for Enhanced Thermal Stability and Hydrophobicity: A Study on Vermiculite Reinforced Composites with Low Dielectric Constant. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2024, 29, 226–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berrouane, A.; Derradji, M.; Khiari, K.; Mehelli, O.; Habes, A.; Abdous, S.; Amri, B.; Kadi, M.E.A.; Liu, W. Sustainable Synthesis of a Novel Bio-Based Low Temperature Curable Benzoxazine Monomer from Quercetin: Synthesis, Curing Reaction and Thermal Properties. High Perform. Polym. 2024, 36, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinnamuthu, R.; Madesh, P.; Arumugam, H.; Krishnasamy, B.; Govindraj, L.; Jaganathan, M.; Muthukaruppan, A. Synthesis and Characterization of New Quinolinyl Phenol Based Polybenzoxazine: Thermal Stability, Hydrophobicity and Corrosion Resistant Properties. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2023, 28, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madesh, P.; Arumugam, H.; Krishnasamy, B.; Muthukaruppan, A. Synthesis of Sustainable Curcumin Based Photo-Crosslinkable Benzoxazines: Thermal, Hydrophobic and Anti-Corrosion Properties. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1296, 136902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madesh, P.; Ramachandran, S.; Krishnasamy, B.; Muthukaruppan, A. Synthesis of a New Type of Bisphenol-BC-Based Benzoxazines from Sustainable Bio-Phenol for Hydrophobic, Dielectric and Corrosion-Resistant Applications. J. Macromol. Sci. Part A 2024, 61, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, X.-L.; Fei, P.; Wang, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Lv, R. Large Free Volume Biobased Benzoxazine Resin: Synthesis and Characterization, Dielectric Properties, Thermal and Mechanical Properties. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 198, 112420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, R.; Sheng, W.; Zhang, K. A Study of Ortho-Phthalimide Functional Benzoxazine Resins with Additional Cross-Linkable Group. Polym. Bull. 2024, 81, 5403–5420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikesell, L.D.; Livinghouse, T. Base-Catalyzed Phenol-Mannich Condensation of Preformed Cesium Iminodiacetate. The Direct Synthesis of Calcein Blue AM and Related Acyloxymethyl Esters. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 88, 12064–12068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wile, B.M.; Griffith, C.L.; Johnson, A.R. Crystal Structure of Bis(3,5-Dichloro-2-Hydroxybenzyl)(2-Methoxyethyl)Amine. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. E Crystallogr. Commun. 2023, 79, 782–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohain, M.; Malefo, M.S.; Kunyane, P.; Scholtz, C.; Baruah, S.; Zitha, A.; Klashorst, G.v.d.; Malan, H. Process Development for the Manufacture of the Antimalarial Amodiaquine Dihydrochloride Dihydrate. Org. Process Res. Dev. 2024, 28, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ding, N.; Du, X.; Gao, D.; Puglia, D.; Wang, F.; Yang, X.; Xu, F.; Yang, W. Grafting Vitamin B onto Lignin to Produce Highly Bioactive Materials for Wound Dressing Hydrogels. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 14854–14865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammadbayli, E.H.; Jafarov, I.A.; Astanova, A.D.; Shakhmammadova, A.G.; Habibova, A.G. Synthesis and Properties of Aminomethoxy Derivatives of 1-(Benzylsulfanyl)Octan-2-Ol. Russ. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 59, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, A.; Quevedo, R. Solvent-Free Mannich-Type Reaction of Tetraazatricyclododecane (TATD) with Phenols. Tetrahedron Lett. 2013, 54, 1416–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, A.; Nerio, L.S.; Quevedo, R. Synthesis of Macrocyclic and Linear Benzylimidazolidine Oligomers from Solvent Free Aromatic Mannich-Type Reaction. Tetrahedron Lett. 2015, 56, 6059–6062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiroga, D.; Ríos-Motta, J.; Rivera, A. Synthesis of Diastereomeric 2,6-Bis{[3-(2-Hydroxy-5-Substitutedbenzyl)Octahydro-1H-Benzimidazol-1-Yl]Methyl}-4-Substituted Phenols (R = Me, OMe) by Mannich-Type Tandem Reactions. Molbank 2024, 2024, M1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martina, K.; Cravotto, G.; Varma, R.S. Impact of Microwaves on Organic Synthesis and Strategies toward Flow Processes and Scaling Up. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 13857–13872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabalka, G.W.; Wang, L.; Pagni, R.M. A Microwave-Enhanced, Solventless Mannich Condensation on CuI-Doped Alumina. Synlett 2001, 2001, 0676–0678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, A.; Farhangian, H.; Mohsenzadeh, F.; Naimi-Jamal, M.R. Microwave Assisted Mannich Reaction of Terminal Alkynes on Alumina. Monatshefte Chem./Chem. Mon. 2002, 133, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Liu, T.; Chen, J.; Ying, H.; Hu, Y. Microwave-Assisted Mannich Reaction of 2-Hydroxy-Chalcones. Synth. Commun. 2009, 39, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadhich, P.; Das, B.; Dhara, S. Microwave Assisted Rapid Synthesis of N-Methylene Phosphonic Chitosan via Mannich-Type Reaction. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 133, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljohani, G.; Said, M.A.; Lentz, D.; Basar, N.; Albar, A.; Alraqa, S.Y.; Ali, A.A.-S. Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Mono- and Disubstituted 4-Hydroxyacetophenone Derivatives via Mannich Reaction: Synthesis, XRD and HS-Analysis. Molecules 2019, 24, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glister, J.F.; Vaughan, K.; Biradha, K.; Zaworotko, M.J. (2S,7R,11S,16R)-1,8,10,17-Tetraazapentacyclo [8.8.1.18,17.02,7.011,16]Icosane and Its Enantiomer. Synthesis, NMR Analysis and X-Ray Crystal Structure. J. Mol. Struct. 2005, 749, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, A.; Quiroga, D.; Ríos-Motta, J.; Carda, J.; Peris, G. Synthesis, Characterization and X-Ray Crystal Structure of the Di-Mannich Base 2,2′-(3aR,7aR/3aS,7aS)-Hexahydro-1H-Benzo[d]Imidazole-1,3(2H)-Diyl)Bis(Methylene)Bis(4-Methylphenol). J. Chem. Crystallogr. 2009, 39, 827–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daza, Q.E.D. Estudios de La Reacción de Los Aminales (2R,7R,11S,16S)-y (2S,7R,11S,16R)-1,8,10,17-Tetrazapentaciclo[8.8.1.1.8,170.2,7011,16]Eicosano Con Nucleófilos y Electrófilos. Ph.D. Thesis, Universidad Militar Nueva Granada, Bogotá, Colombia, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Rivera, A.; Quiroga, D.; Ríos-Motta, J.; Eigner, V.; Dušek, M. Single-Step Synthesis of a New Series of Meso Di-Mannich Bases from the Cyclic Aminal (2S,7R,11S,16R)-1,8,10,17-Tetraazapentacyclo[8.8.1.1.8,170.2,7011,16]Icosane and p-Substituted Phenols. Chem. Cent. J. 2013, 7, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzezinski, B.; Radziejewski, P.; Rabold, A.; Zundel, G. Hydrogen Bonds and Hydrogen-Bonded Systems in Mannich Bases of 2,2′-Biphenol: An FTIR Study of the Proton Polarizability and Fermi Resonance Effects as a Function of Temperature. J. Mol. Struct. 1995, 355, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzezinski, B.; Wojciechowski, G.; Urjasz, H.; Zundel, G. FT-IR Study of the Proton Polarizability of Hydrogen Bonds and of the Hydrogen-Bonded Systems in a Di-Mannich Base of 5,5′-Dimethoxy-2,2′-Biphenol. J. Mol. Struct. 1998, 470, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koll, A.; Melikova, S.M.; Karpfen, A.; Wolschann, P. Spectroscopic and Structural Consequences of Intramolecular Hydrogen Bond Formation in Ortho -Dimethylaminomethylphenol. J. Mol. Struct. 2001, 559, 127–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
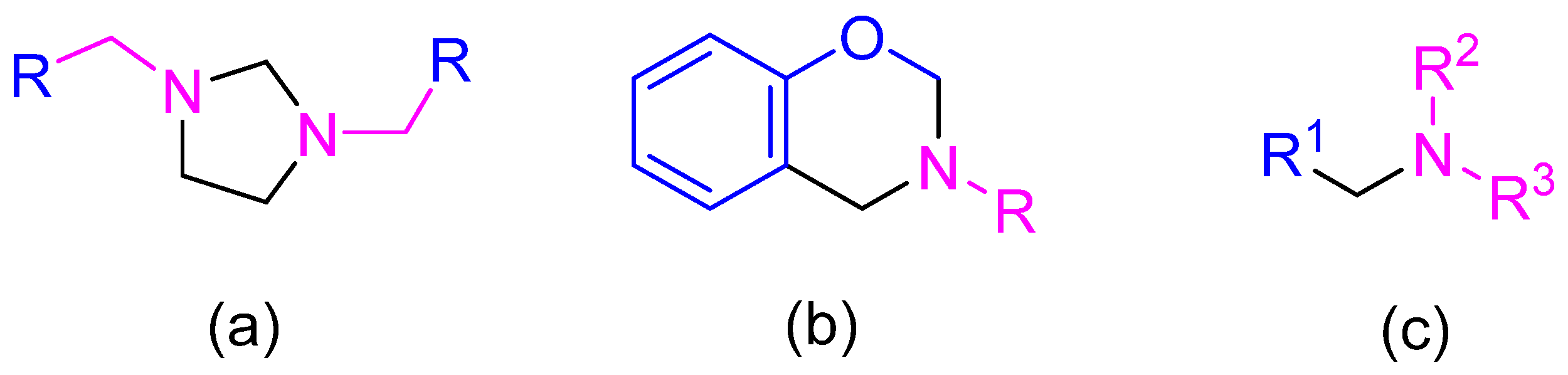


| R | Reflux Protocol [31] | MW-Assisted Protocol | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T = 80 °C | T = 100 °C | T = 120 °C | ||||||
| % Yield for Compound 1 | % Yield for Compound 2 | % Yield for Compound 1 | % Yield for Compound 2 | % Yield for Compound 1 | % Yield for Compound 2 | % Yield for Compound 1 | % Yield for Compound 2 | |
| Me | 45 | 15 | 44 ± 1 | 16 ± 1 | 33 ± 1 | 27 ±1 | 15 ± 4 | 19 ± 1 |
| OMe | 34 | 15 | 36 ± 4 | 15 ± 9 | 27 ± 2 | 24 ±1 | 17 ± 1 | 18 ± 2 |
| Cl | 30 | 17 | 31 ± 2 | 18 ± 1 | 24 ± 1 | 21 ±1 | 11 ± 2 | 14 ± 1 |
| COOMe | 20 | 15 | 22 ± 4 | 15 ± 2 | 17 ± 1 | 21 ±2 | 11 ± 1 | 11 ± 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quiroga, D.; Ríos-Motta, J.; Rivera, A. Influence of MW Irradiation on the Reaction Between (2R,7R,11S,16S)-1,8,10,17-tetraazapentacyclo[8.8.1.1.8,170.2,70.11,16]icosane and p-Substituted Phenols. Organics 2025, 6, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/org6040044
Quiroga D, Ríos-Motta J, Rivera A. Influence of MW Irradiation on the Reaction Between (2R,7R,11S,16S)-1,8,10,17-tetraazapentacyclo[8.8.1.1.8,170.2,70.11,16]icosane and p-Substituted Phenols. Organics. 2025; 6(4):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/org6040044
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuiroga, Diego, Jaime Ríos-Motta, and Augusto Rivera. 2025. "Influence of MW Irradiation on the Reaction Between (2R,7R,11S,16S)-1,8,10,17-tetraazapentacyclo[8.8.1.1.8,170.2,70.11,16]icosane and p-Substituted Phenols" Organics 6, no. 4: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/org6040044
APA StyleQuiroga, D., Ríos-Motta, J., & Rivera, A. (2025). Influence of MW Irradiation on the Reaction Between (2R,7R,11S,16S)-1,8,10,17-tetraazapentacyclo[8.8.1.1.8,170.2,70.11,16]icosane and p-Substituted Phenols. Organics, 6(4), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/org6040044







