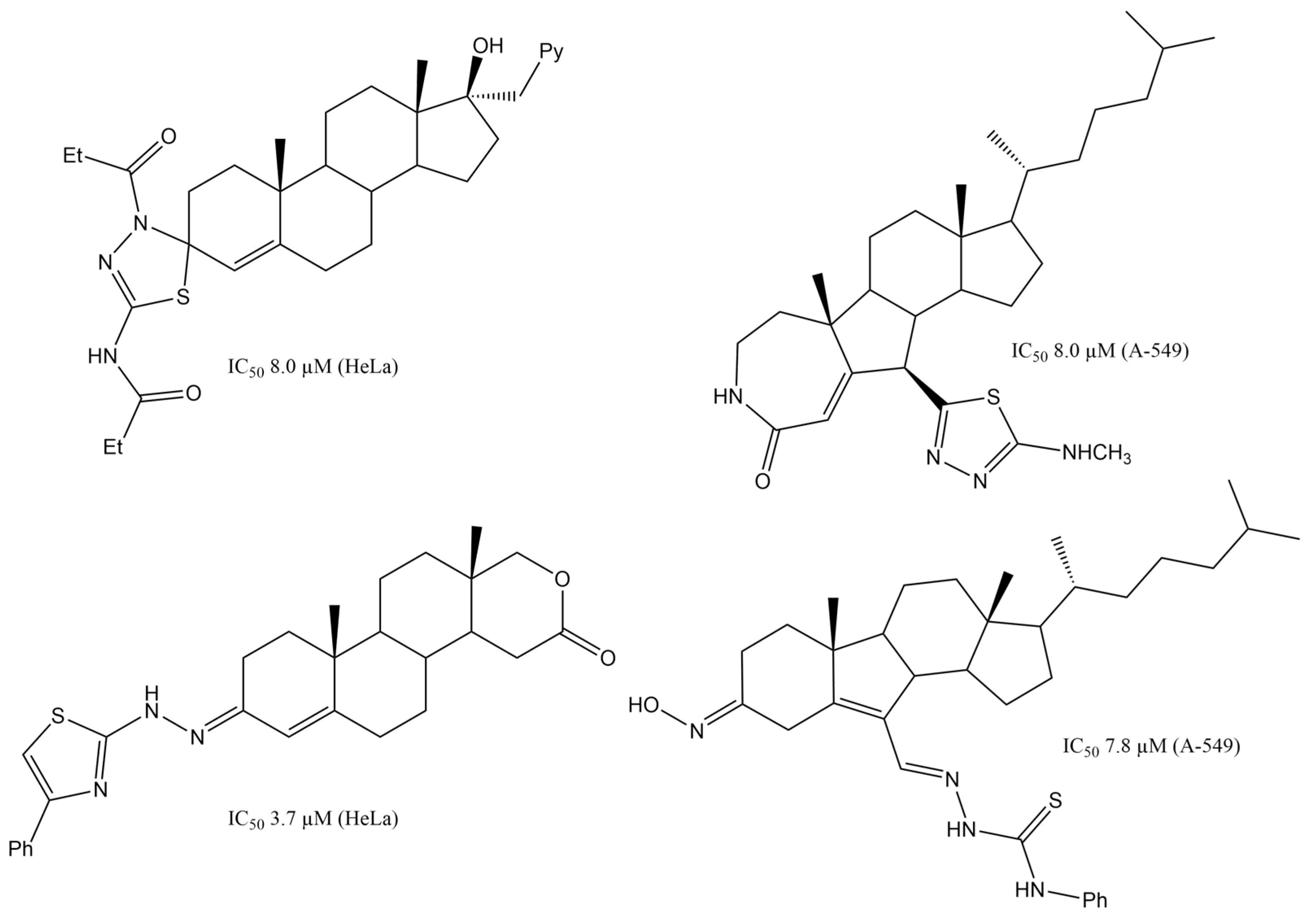
All the solvents used were of analytical grade (Aldrich or J. T. Baker). The progress of the reactions was monitored by analytical TLC performed on silica gel plates (Silica gel 60 F254, E. Merck, Darmstadt, Germany), using hexane/ethyl acetate (7:3) as the mobile phase. Spots were visualized under UV light (254 nm) and by charring with 10% vanillin in EtOH containing 1% H2SO4. Chromatographic columns were carried out on silica gel DavisilTM grade 633 (200–425 mesh, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). NMR was recorded on a Bruker AscendTM 500 MHz instrument (Bruker BioSpin GmbH, Rheinstetten, Germany). Chemical shifts are stated in ppm (δ) and referred to the 1H signal or the central 13C triplet signal (δ = 7.26 and 77.16) for CDCl3 or the signal of TMS (δ = 0) as the internal standard. Coupling constants (J) are expressed in Hertz (Hz). The assignments of 1H and 13C signals were confirmed by 2D NMR homonuclear and heteronuclear experiments (COSY, HSQC, and HMBC). Melting points were measured by the open capillary tube method on a Melt-temp apparatus (Electrothermal, Essex, UK) and were not corrected. IR spectra were recorded on an Agilent Cary 360 FTIR spectrometer (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) and are reported in cm−1. High-resolution mass spectra (HRMS) were obtained only for compounds 21 and 22 using a JMS-700 MStation (JEOL Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) with fast atom bombardment (FAB) ionization.
2.3. Synthesis
Several alternative conditions were assayed throughout the synthetic sequence, including variations in acylating agents, solvents, and bases, but these proved suboptimal, leading to low yields or formation of side products. The optimized protocols adopted in this work were selected based on the systematic study reported in Méndez Delgado’s Master’s thesis [
27].
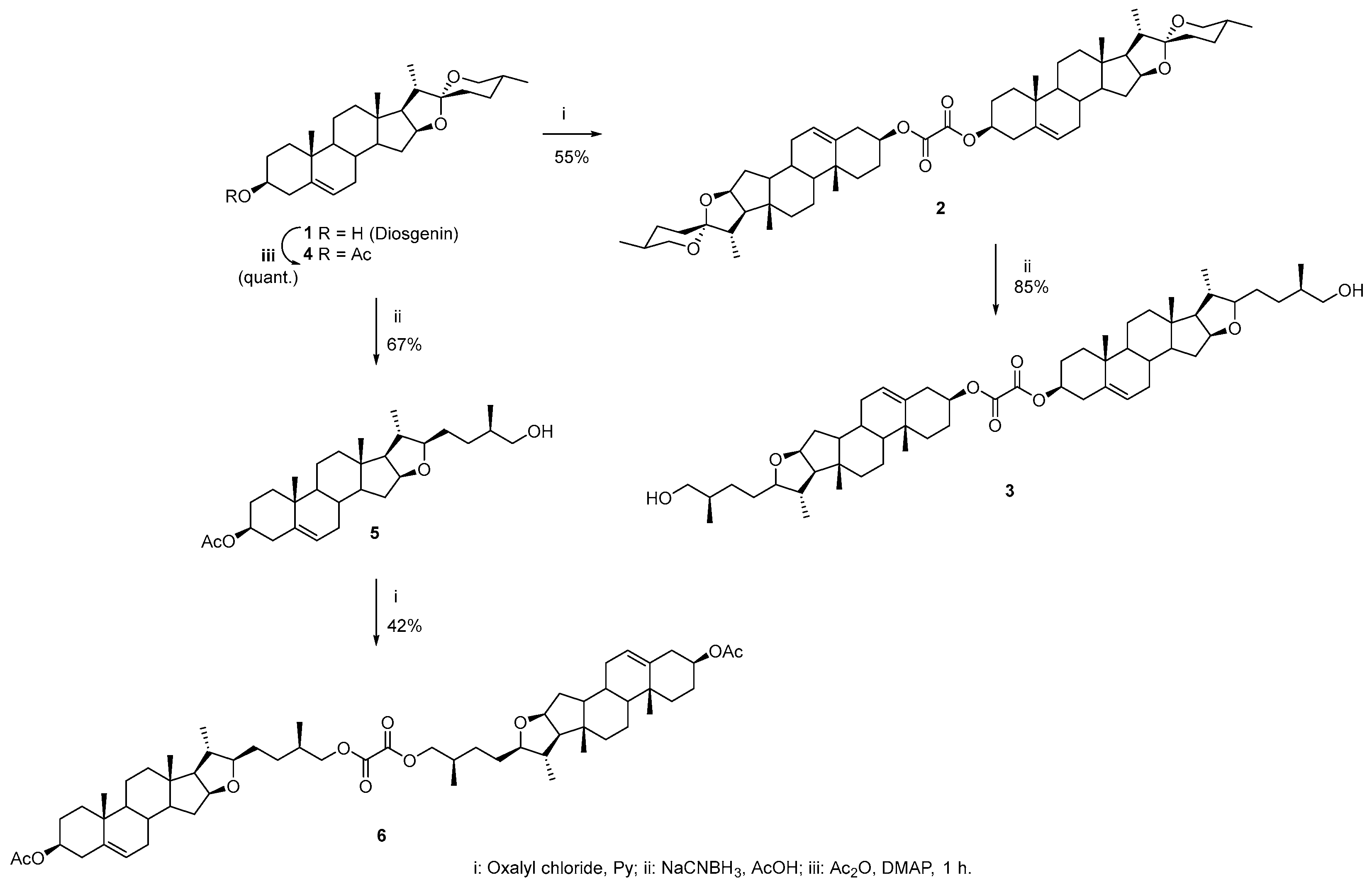
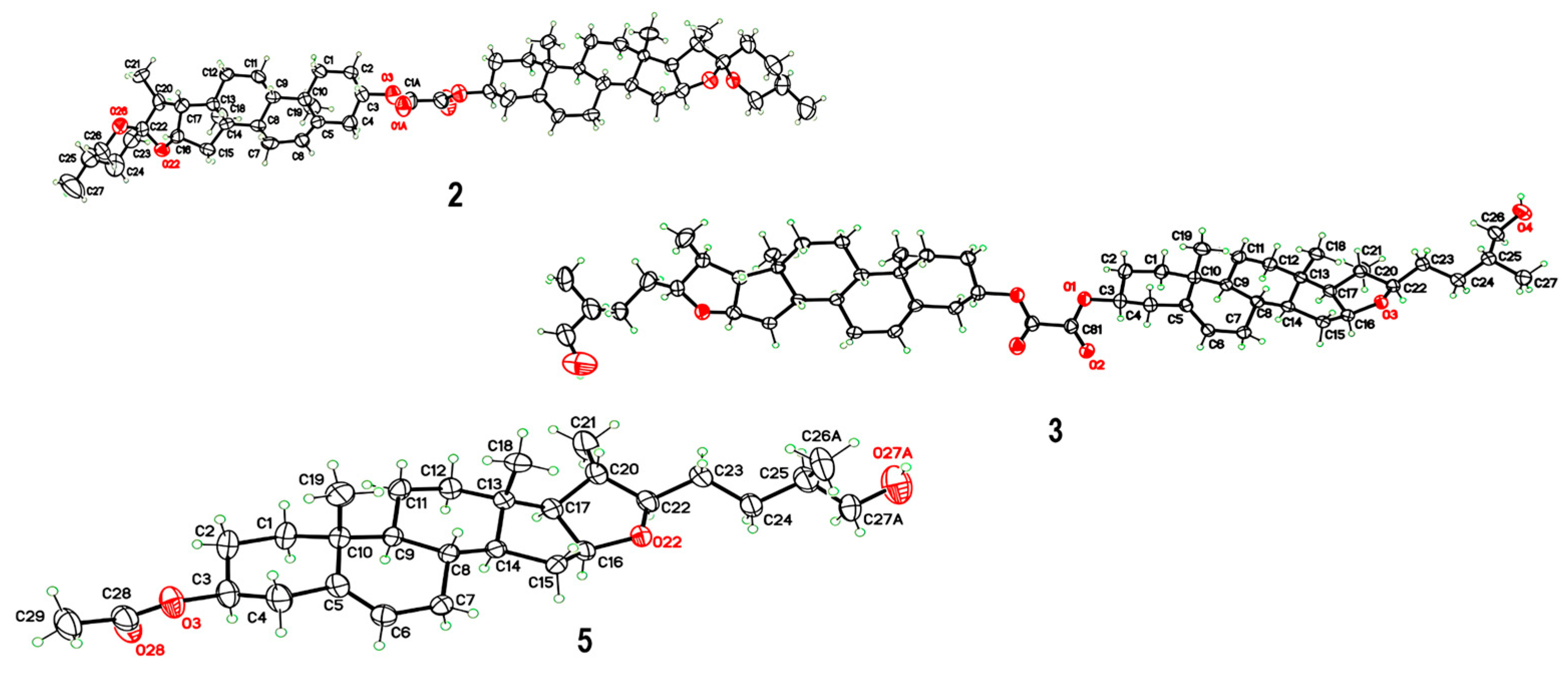
Oxalyl chloride (0.1 mL, 0.12 mmol, 1 eq.) was added to a solution of 1 (100 mg, 0.24 mmol, 2 eq.) in pyridine (5 mL). The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 18 h. The resulting mixture was poured into diluted cold 5% HCl and stirred for an extra 1 h. Ethyl acetate (3 × 15 mL) was added, and the mixture was extracted. The combined organic phase was washed with brine, distilled water, and dried over anhydrous MgSO4. The organic layer was filtered and evaporated under reduced pressure. The resulting crude product was purified by silica gel chromatography (eluent hexane/ethyl acetate 7:3) to give a white solid in 55%. A fraction was dissolved in CH2Cl2/Hex/MeOH/Et2O, and colorless crystals were obtained by slow evaporation of its solution at r.t.; mp 316–319 °C. IR : 2945, 1759, 1737, 1174 cm−1. Signals for the monomer unit 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 5.43–5.36 (m, 1H, H-6), 4.81–4.71 (m, 1H, H-3), 4.45–4.37 (m, 1H, H-16), 3.50–3.43 (m, 1H, H-26eq), 3.37 (t, J26ax-26eq = J26ax-25 = 10.9 Hz, 1H, H-26ax), 2.51–2.36 (m, 2H, H-4a, H-4b), 2.05–1.83 (m, 5H, H-7a, H-15a, H-2a, H-1a, H-20), 1.80–1.71 (m, 3H, H-2b, H-12a, H-17), 1.69–1.57 (m, 5H, H-8, H-23, H-24b, H-25), 1.56–1.41 (m, 4H, H-7b, H-11, H-24b), 1.32–1.24 (m, 1H, H-15b), 1.22–1.08 (m, 3H, H-1b, H-12b, H-14), 1.04 (s, 3H, H-19), 1.01–0.96 (m, 1H, H-9), 0.96 (d, 3H, J21-20 = 6.9 Hz, H-21), 0.84–0.74 (m, 6H, H-18, H-27). 13C-NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 157.7 (C=O oxalate), 139.2 (C-5), 123.2 (C-6), 109.4 (C-22), 80.9 (C-16), 77.2 (C-3), 67.0 (C-26), 62.2 (C-17), 56.5 (C-14), 50.0 (C-9), 41.7 (C-20), 40.4 (C-13), 39.8 (C-12), 37.7 (C-4), 36.9 (C-1), 36.8 (C-10), 32.2 (C-7), 32.0 (C-15), 31.5 (C-8), 31.5 (C-23), 30.4 (C-25), 28.9 (C-24), 27.4 (C-2), 20.9 (C-11), 19.4 (C-19), 17.3 (C-27), 16.4 (C-18), 14.7 (C-21).
To a solution of 2 (0.026 g, 0.03 mmol, 1 eq.) in CH2Cl2 (2 mL), AcOH (1 mL), and NaCNBH3 (0.02 g, 0.3 mmol, 10 eq.) were added. The reaction mixture was stirred for 3.5 h at r.t. After completion of the reaction monitored by TLC, cold water (30 mL) was added, and the mixture was extracted with CH2Cl2 (2 × 10 mL). The combined organic phase was washed with distilled water, dried over anhydrous MgSO4, filtered, and evaporated under reduced pressure. The resulting crude product was purified by column chromatography (eluent hexane/ethyl acetate 7:3) to afford a white solid in 85%. A fraction was dissolved in EtOH/CH2Cl2, and colorless crystals were obtained by slow evaporation of its solution at r.t. mp. 226–228 °C. IR : 3346, 2926, 1735, 1202 cm−1. Signals for monomer unit 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 5.42–5.37 (m, 1H, H-6), 4.81–4.72 (m, 1H, H-3), 4.30 (td, 1H, J16-15a = J16-17 = 7.7 Hz, J16-15b = 5.3 Hz, H-16), 3.49 (dd, 1H, J26a-26b = 10.6 Hz, J25-26a = 6.2 Hz, H-26a), 3.43 (dd, 1H, J25-26b = 6.1 Hz, H-26b), 3.32 (td, 1H, J22-20 = J22-23a = 8.2 Hz, J22-23b = 3.8 Hz, H-22), 2.52–2.43 (m, 1H, H-4a), 2.40 (ddd, 1H, J4b-4a = 13.3 Hz, J3-4b = 5.1 Hz, J4b-6 = 1.8 Hz, H-4b), 2.03–1.96 (m, 2H, H-7a, H-15a), 1.96–1.92 (m, 1H, H-2a), 1.89 (dt, 1H, J1a-1b = 13.5 Hz, J1a-2a = J1a-2b = 3.6 Hz, H-1a), 1.79–1.69 (m, 3H, H-2b, H-12a, H-20), 1.68–1.63 (m, 1H, H-25), 1.63–1.41 (m, 8H, H-8, H-11, H-15b, H-17, H-23, H-24a), 1.38–1.26 (m, 2H, H-7b, H-24b), 1.19–1.06 (m, 3H, H-1b, H-12b, H-14), 1.04 (s, 3H, H-19), 0.99 (d, 3H, J20-21 = 6.7 Hz, H-21), 0.97–0.92 (m, 1H, H-9), 0.90 (d, 3H, J27-25 = 6.7 Hz, H-27), 0.80 (s, 3H, H-18). 13C-NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 157.7 (C=O oxalate), 139.2 (C-5), 123.2 (C-6), 90.5 (C-22), 83.3 (C-16), 77.2 (C-3), 68.2 (C-26), 65.2 (C-17), 57.0 (C-14), 50.0 (C-9), 40.8 (C-13), 39.5 (C-12), 38.0 (C-20), 37.7 (C-4), 37.0 (C-1), 36.8 (C-10), 35.8 (C-25), 32.3 (C-7), 32.1 (C-15), 31.6 (C-8), 30.5 (C-23), 30.2 (C-24), 27.5 (C-2), 20.8 (C-11), 19.4 (C-19), 19.0 (C-21), 16.8 (C-27), 16.6 (C-18).
Oxalyl chloride (0.01 mL, 0.11 mmol, 1 eq.) was added to a solution of 5 (100 mg, 0.22 mmol, 2 eq.) in anhydrous pyridine (5 mL). The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 20 h under an argon atmosphere. The resulting mixture was poured into 30 mL of cold 5% HCl solution and stirred for an extra 1 h. Ethyl acetate was added, and the mixture was extracted (3 × 15 mL). The combined organic phase was washed with brine, distilled water, and dried over anhydrous MgSO4. The organic layer was filtered and evaporated under reduced pressure. The resulting crude product was purified by silica gel chromatography (eluent hexane/ethyl acetate 7:3) to give the product 6 as a white foam in 42%. IR : 2952, 1769, 1733, 1241 cm−1. Signals for monomer unit 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 5.40–5.33 (m, 1H, H-6), 4.64–4.53 (m, 1H, H-3), 4.29 (td, 1H, J15a-16 = J16-17 = 7.7 Hz, J15b-16 = 5.3 Hz, H-16), 4.18 (dd, 1H, J26a-26b = 10.7 Hz, J25-26a = 5.6 Hz, H-26a), 4.06 (dd, 1H, J25-26b = 7.1 Hz, H-26b), 3.30 (td, 1H, J20-22 = J22-23a = 8.1 Hz, J22-23b = 4.1 Hz, H-22), 2.35–2.28 (m, 2H, H-4), 2.03 (s, 3H, COCH3), 2.01–1.95 (m, 2H, H-7a, H-15a), 1.95–1.89 (m, 1H, H-25), 1.88–1.82 (m, 2H, H-1a, H-2a), 1.77–1.69 (m, 2H, H-12a, H-20,), 1.66–1.48 (m, 7H, H-2b, H-8, H-11a, H-15b, H-17, H-23), 1.47–1.37 (m, 3H, H-11b, H-24), 1.29 (td, 1H, J7a-7b = J7b-8 = 13.0 Hz, J6-7b = 5.3 Hz, H-7b), 1.16–1.05 (m, 3H, H-12b, H-1b, H-14), 1.03 (s, 3H, H-19), 0.99 (d, 3H, J20-21 = 4.7 Hz, H-21), 0.98 (d, 3H, J25-27 = 4.6 Hz, H-27), 0.96–0.90 (m, 1H, H-9), 0.79 (s, 3H, H-18). 13C-NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 170.7 (C=O acetate), 158.2 (C=O oxalate), 139.8 (C-5), 122.5 (C-6), 90.1 (C-22), 83.4 (C-16), 74.0 (C-3), 71.7 (C-26), 65.2 (C-17), 57.0 (C-14), 50.1 (C-9), 40.8 (C-13), 39.5 (C-12), 38.2 (C-4), 38.1 (C-20), 37.1 (C-1), 36.8 (C-10), 32.8 (C-25), 32.3 (C-7), 32.1 (C-15), 31.7 (C-8), 30.9 (C-23), 30.4 (C-24), 27.9 (C-2), 21.6 (COCH3), 20.8 (C-11), 19.5 (C-19), 19.0 (C-21), 16.8 (C-27), 16.6 (C-18).
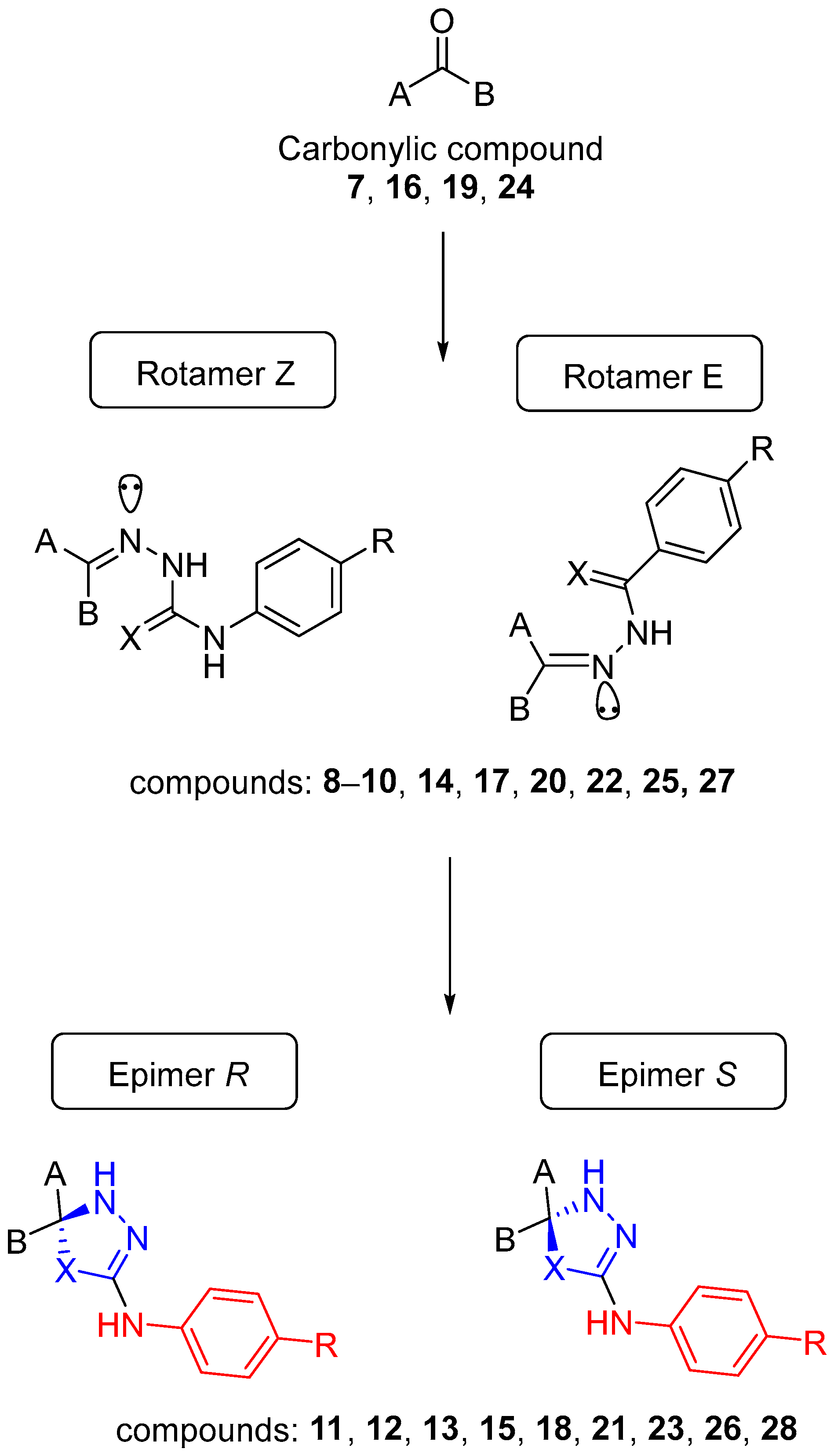
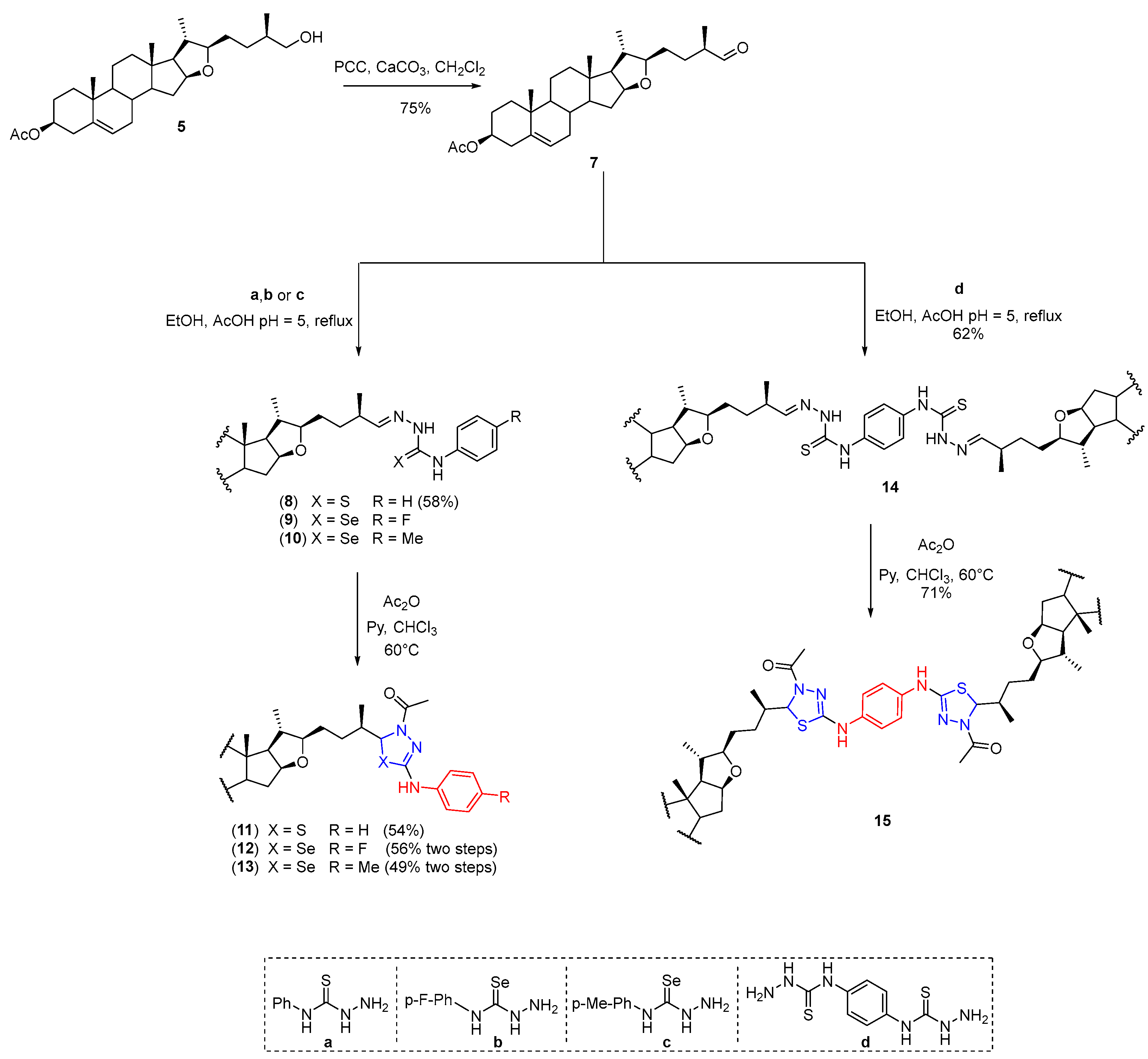
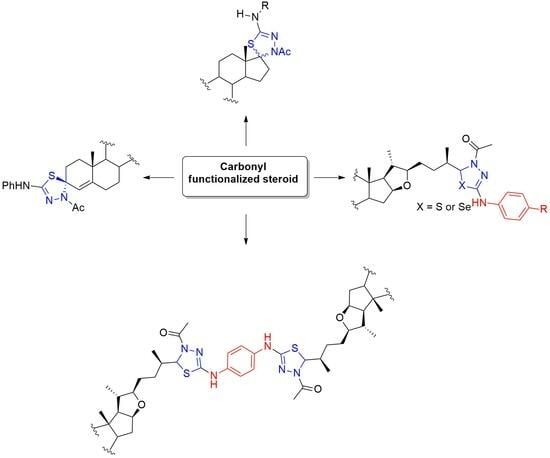
2.4. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Steroidal Thio and Selenosemicarbazones (8–10, 14, 17, 20, 22, 25, and 27)
AcOH was added to a solution of carbonyl compound 7, 16, 19, or 24 (1 eq.) in ethanol until pH reached 5. After that, thiosemicarbazide (TSC) or a–d (1.2 eq.) was added and the mixture was stirred and refluxed until the reaction was completed as detected by TLC. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure, and the residue was purified by column chromatography on silica gel to give the thiosemicarbazone intermediates. Selenosemicarbazones 9 and 10 and thiosemicarbazones 20 and 25 were not isolated in pure form, so they were used without any further purification for the next step.
The title compound 8 was prepared from 7 and a according to the general procedure to give a yellowish solid in 58% yield. mp 82–84 °C. IR : 3318, 2947, 1731, 1545, 1245 cm−1. 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 10.08 (s, 1H, NNH), 9.10 (s, 1H, PhNH), 7.66–7.54 (m, 2H, Ar), 7.41–7.32 (m, 2H, Ar), 7.24 (d, 1H, J25′-26′ = 5.8 Hz, H-26′), 7.23–7.15 (m, 1H, Ar), 5.37–5.33 (m, 1H, H-6′), 4.63–4.53 (m, 1H, H-3′), 4.27 (td, 1H, J15′a-16′ = J16′-17′ = 7.7 Hz, J15′b-16′ = 5.3 Hz, H-16′), 3.37–3.23 (m, 1H, H-22′), 2.48–2.38 (m, 1H, H-25′), 2.35–2.25 (m, 2H, H-4′), 2.02 (s, 3H, COCH3), 1.98–1.89 (m, 2H, H-15′a, H-7′a), 1.88–1.80 (m, 2H, H-2′a, H-1′a), 1.76–1.66 (m, 2H, H-20′, H-12′a), 1.64–1.46 (m, 9H, H-2′b, H-8′, H-11′a, H-15′b, H-17′, H-23′, H-24′), 1.45–1.38 (m, 1H, H-11′b), 1.23 (td, 1H, J7′a-7′b = J7′b-8′ = 13.0 Hz, J6′-7′b = 5.2 Hz, H-7′b), 1.15–1.08 (m, 5H, H-1′b, H-12′b, H-27′), 1.07–1.02 (m, 1H, H-14′), 1.00 (s, 3H, H-19′), 0.97 (d, 3H, J20′-21′ = 6.7 Hz, H-21′), 0.94–0.88 (m, 1H, H-9′), 0.76 (s, 3H, H-18′). 13C-NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 175.8 (C=S), 170.6 (CH3CO), 151.6 (C-26′), 139.7 (C-5′), 138.0 (Ar), 128.7 (Ar), 126.1 (Ar), 124.7 (Ar), 122.4 (C-6′), 90.0 (C-22′), 83.3 (C-16′), 73.9 (C-3′), 65.0 (C-17′), 56.9 (C-14′), 50.0 (C-9′), 40.7 (C-13′), 39.4 (C-12′), 38.1 (C-4′), 37.8 (C-20′), 37.0 (C-1′), 36.9 (C-25′), 36.7 (C-10′), 32.2 (C-7′), 32.0 (C-15′), 31.6 (C-8′), 31.2 (C-24′), 30.8 (C-23′), 27.8 (C-2′), 21.5 (COCH3), 20.7 (C-11′), 19.4 (C-19′), 18.9 (C-21′), 17.8 (C-27′), 16.5 (C-18′).
(22’’R,25’’R)-N,N′-1,4-Phenylenebis[2-(3’’β-acetoxyfurost-5’’-en-26’’-ylidene)hidrazinecarbotiamide] (14).
The title compound 14 was prepared from 7 and d according to the general procedure to give a beige foam in 62% yield. IR : 2941, 1730, 1517, 1241, 1032 cm−1. 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 10.24 (s, 1H, NNH), 9.09 (s, 1H, PhNH), 7.62 (s, 2H, Ar), 7.24 (d, J25″-26″ = 6.0 Hz, 1H, H-26″), 5.37–5.32 (m, 1H, H-6″), 4.62–4.52 (m, 1H, H-3″), 4.32–4.24 (m, 1H, H-16″), 3.34–3.25 (m, 1H, H-22″), 2.46–2.36 (m, 1H, H-25″), 2.33–2.26 (m, 2H, H-4″), 2.02 (s, 3H, COCH3), 1.99–1.90 (m, 2H, H-15″a, H-7″a), 1.87–1.79 (m, 2H, H-1″a, H-2″a), 1.76–1.66 (m, 2H, H-20″, H-12″a), 1.64–1.49 (m, 8H, H-2″b, H-8″, H-15″b, H-17″, H-23″, H-24″), 1.49–1.45 (m, 1H, H-11″a), 1.44–1.38 (m, 1H, H-11″b), 1.29–1.20 (m, 1H, H-7′b), 1.14–1.07 (m, 5H, H-1b, H-12′b, H-27″), 1.07–1.02 (m, 1H, H-14″), 1.00 (s, 3H, H-19′), 0.97 (d, 3H, J20″-21″ = 6.7 Hz, H-21″), 0.93–0.88 (m, 1H, H-9″), 0.77 (s, 3H, H-18″). 13C-NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 175.5 (C=S), 170.7 (CH3CO), 151.8 (C-26″), 139.6 (C-5″), 135.6 (Ar), 124.9 (Ar), 122.4 (C-6″), 89.9 (C-22″), 83.3 (C-16″), 73.9 (C-3″), 64.9 (C-17″), 56.8 (C-14″), 49.9 (C-9″), 40.7 (C-13″), 39.4 (C-12″), 38.1 (C-4″), 37.8 (C-20″), 37.1 (C-1″), 37.0 (C-25″), 36.7 (C-10″), 32.2 (C-7″), 32.0 (C-15″), 31.5 (C-8″), 31.3 (C-24″), 31.0 (C-23″), 27.7 (C-2″), 21.6 (COCH3), 20.6 (C-11″), 19.4 (C-19″), 18.9 (C-21″), 17.9 (C-27″), 16.6 (C-18″).
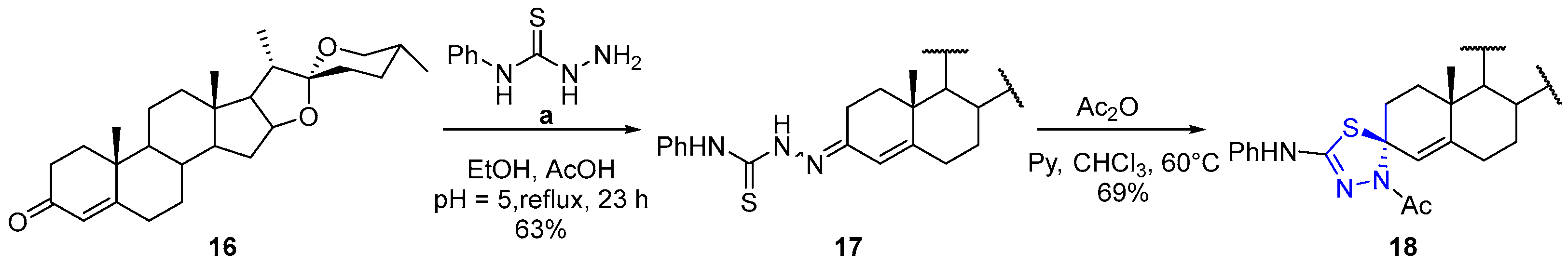
The title compound 17 was prepared from 16 and a in 18 mL of EtOH according to the general procedure. White foam was obtained in 63% yield, after the reaction was refluxed for 23 h. Column chromatography (9:1 hexane/ethyl acetate). Rotamer ratio = 7:3. A fraction was dissolved in CH2Cl2/EtOH/MeOH, and colorless crystals were obtained by slow evaporation of its solution at room temperature. mp = 164–166 °C. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3,) major isomer δ: 9.38–9.23 (m, 1H, PhNH), 8.66 (s, 1H, NH), 7.73–7.59 (m, 2H, Ar), 7.42–7.31 (m, 2H, Ar), 7.23–7.17 (m, 1H, Ar), 5.86 (s, 1H, H-4′), 4.45–4.34 (m, 1H, H-16′), 3.49–3.44 (m, 1H, H-26′equatorial (eq)), 3.36 (t, 1H, J26′ax-26′eq = J25′-26′ax = 10.9 Hz, H-26′axial (ax)), 2.61 (ddd, 1H, J2′a-2′b = 16.6 Hz, J1′a-2′a = 5.0 Hz, J1′b-2′a = 2.7 Hz, H-2′a), 2.48–2.14 (m, 3H, H-2′b, H-6′), 2.07–1.97 (m, 2H, H-1′a, H-15′a,), 1.89–1.85 (m, 1H, H-20′), 1.83–1.72 (m, 3H, H-11′a, H-12′a, H-17′), 1.71–1.56 (m, 5H, H-8′, H-23′, H-24′a, H-25′), 1.55–1.37 (m, 4H, H-1′b, H-7′, H-24′b), 1.35–1.26 (m, 1H, H-15′b), 1.21–1.04 (m, 3H, H-11′b, H-12′b, H-14′), 1.10 (s, 3H, H-19′), 0.97 (d, 3H, J20′-21′ = 7.0 Hz, H-21′), 0.91–0.85 (m, 1H, H-9′), 0.84–0.72 (m, 6H, H-18′, H-27′). Minor isomer δ: 8.86 (s, 1H, NH), 6.09 (s, 1H, H-4′), 1.95–1.91 (m, 1H, H-1′a). 13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3) major isomer δ: 175.5 (C=S), 158.7 (C-5′), 149.6 (C-3′), 138.2 (Ar), 128.8 (Ar), 125.9 (Ar), 124.0 (Ar), 120.3 (C-4′), 109.4 (C-22′), 80.7 (C-16′), 67.0 (C-26′), 62.1 (C-17′), 55.9 (C-14′), 53.6 (C-9′), 41.7 (C-20′), 40.4 (C-13′), 39.8 (C-12′), 38.1 (C-10′), 35.4 (C-8′), 34.6 (C-1′), 32.6 (C-6′), 32.3 (C-11′), 31.8 (C-15′), 31.4 (C-23′), 30.4 (C-25′), 28.9 (C-24′), 21.2 (C-7), 20.8 (C-2′), 17.9 (C-19′), 17.2 (C-27′), 16.5 (C-18′), 14.6 (C-21′), minor isomer δ: 175.7 (C=S), 164.1 (C-5′), 148.6 (C-3′), 138.2 (Ar), 128.7 (Ar), 125.8 (Ar), 124.1 (Ar), 110.2 (C-4′), 109.4 (C-22′), 62.1 (C-17′), 55.7 (C-14′), 54.1 (C-9′), 40.5 (C-13′), 39.7 (C-12′), 39.5 (C-10′), 36.4 (C-1′), 35.4 (C-8′), 33.5, 32.9, 27.8, 21.0, 18.2 (C-19′).
The title compound 22 was prepared using estrone 19 and a in 20 mL of EtOH according to the general procedure. White foam was obtained in 84% yield, after the reaction was refluxed for 6 h and stirred at room temperature for an additional 12 h. Column chromatography (9:1 hexane/ethyl acetate). 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 9.25 (s, 1H, PhNH), 8.63 (s, 1H, NNH), 7.67–7.59 (m, 2H, Ar), 7.45–7.37 (m, 2H, Ar), 7.27–7.23 (m, 1H, Ar), 7.15 (d, 1H, J1′-2′ = 8.6 Hz, H-1′), 6.69 (dd, 1H, Hz, J2′-4′ = 3.0 Hz, H-2′), 6.62 (d, 1H, H-4′), 6.57 (brs, 1H, OH-3′), 2.91–2.77 (m, 2H, H-6′), 2.47 (dd, 1H, J16′a-16′b = 18.2 Hz, J15′a-16′a = 8.8 Hz, J15′b-16′a = 0 Hz, H-16a), 2.41–2.36 (m, 1H, H-11′a), 2.35–2.20 (m, 2H, H-9′, H-16′b), 2.10–2.05 (m, 1H, H-12′a), 2.04–1.97 (m, 1H, H-15′a), 1.97–1.90 (m, 1H, H-7′a), 1.62–1.48 (m, 4H, H-8′, H-11′b, H-12′b, H-15′b), 1.45–1.34 (m, 2H, H-7′b, H-14′), 0.92 (s, 3H, H-18′). 13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 175.71 (C=S), 167.5 (C-17′), 153.7 (C-3′), 137.9 (Ar), 137.7 (Ar), 131.7 (C-10′), 128.8 (Ar), 126.5 (C-1′), 126.2 (Ar), 124.7 (Ar), 115.4 (C-4′), 112.9 (C-2′), 52.2 (C-14′), 45.1 (C-13′), 43.9 (C-9′), 38.0 (C-8′), 33.9 (C-12′), 29.5 (C-6′), 27.1 (C-7′), 26.4 (C-16′), 26.1 (C-11′), 23.2 (C-15′), 17.1 (C-18′). HRFAB-MS m/z calcd. for C25H30N3OS [M + H]+: 420.2110, found: 420.2116.
The 3-hydroxyl group of trans-androsterone
25 was acylated under standard conditions [
28]. The resulting 3-OAc trans-androsterone (3.3 mmol) was then treated with thiosemicarbazide
a (3.97 mmol) in 50 mL of ethanol, following the general procedure. After refluxing for 6 h, the reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for an additional 3 days. The crude product was isolated as a white foam in 46% yield. Purification by column chromatography (hexane/ethyl acetate, 9:1) afforded a fraction that was recrystallized by slow evaporation from a CH
2Cl
2/hexane/ethyl acetate solution at room temperature, yielding colorless crystals. mp = 216–219 °C. IR
: 3357, 3286, 2929, 1731, 1535, 1243, 1178 cm
−1.
1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl
3) δ: 9.21 (s, 1H, PhNH), 8.32 (s, 1H, NNH), 7.68–7.60 (m, 2H, Ar), 7.41–7.33 (m, 2H, Ar), 7.23–7.18 (m, 1H, Ar), 4.74–4.61 (m, 1H, H-3′), 2.44 (dd, 1H, J16′a-16′b = 18.2 Hz,
J15′a-16′a = 8.6 Hz,
J15′b-16′a = 0 Hz, H-16′a), 2.27 (dt, 1H,
J15′a-16′b =
J15′b-16′b = 8.7 Hz, H-16′b), 2.01 (s, 3H, OAc-3), 1.97–1.89 (m, 2H, H-12′a, H-15′a,), 1.86–1.79 (m, 1H, H-2′a), 1.76–1.70 (m, 2H, H-1′a, H-7′a), 1.69–1.59 (m, 2H, H-4′a, H-11′a,) 1.56–1.43 (m, 3H, H-2′b,H-8′, H-15′b), 1.39–1.24 (m, 5H, H-4′b, H-6′, H-11′b, H-12′b), 1.23–1.14 (m, 2H, H-5′, H-14′), 1.09–0.93 (m, 2H, H-1′b, H-7′b), 0.90 (s, 3H, H-18′), 0.85 (s, 3H, H-19′), 0.78–0.70 (m, 1H, H-9′).
13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl
3) δ: 176.12 (C=S), 170.8 (C=O), 166.8 (C=N), 138.1 (Ar), 128.8 (Ar), 126.0 (Ar), 124.3 (Ar), 73.59 (C-3′), 54.4 (C-9′), 53.5 (C-14′), 45.0 (C-13′), 44.7 (C-5′), 36.8 (C-1′), 35.7 (C-10′), 35.0 (C-8′), 34.1 (C-4′), 34.0 (C-12′), 31.4 (C-7′), 28.4 (C-6′), 27.5 (C-2′), 26.4 (C-16′), 23.5 (C-15′), 21.6 (COCH
3), 20.7 (C-11′), 17.2 (C-18′), 12.3 (C-19′).
2.5. General Method for the Intramolecular Cyclization by Base-Catalyzed Acetylation Conditions
Dry pyridine (4 equivalents) and acetic anhydride (4 equivalents) were added to a solution of thio- or selenosemicarbazone compounds 8–10, 14, 17, 22, or 27 (1 equivalent) in dry chloroform. The reaction mixture was stirred and refluxed until the reaction was completed as detected by TLC. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure, and the residue was purified by column chromatography on silica gel to give the desired compounds.
(5RS,22′R,25′R)-4-Acetyl-2-phenylamino-5-[27′-nor-3′β-acetoxyfurost-5′-en-25′-yl]-4,5-dihydro-1,3,4-thiadiazole (11).
The title compound 11 was prepared from 8 according to the general method to give a white solid in 54%. Isomer ratio = 7:3. A fraction was dissolved in CH2Cl2, and colorless crystals were obtained by slow evaporation of its solution at room temperature. m.p.: 175 °C (dec.). IR : 3269, 2943, 1729, 1595, 1444, 1237, 1029 cm−1. 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) major isomer δ: 7.43–7.37 (m, 2H, Ar), 7.33–7.26 (m, 2H, Ar), 7.08 (s, 1H, NH), 7.04–7.00 (m, 1H, Ar), 6.16 (d, 1H, J5-25′ = 4.1 Hz, H-5), 5.37–5.32 (m, 1H, H-6′), 4.63–4.54 (m, 1H, H-3′), 4.32–4.21 (m, 1H, H-16′), 3.32–3.23 (m, 1H, H-22′), 2.39–2.24 (m, 6H, NCOCH3, H-4′, H-25′), 2.02 (s, 3H, OCOCH3), 2.00–1.89 (m, 2H, H-7′a, H-15′a), 1.88–1.80 (m, 2H, H-1′a, H-2′a), 1.74–1.64 (m, 2H, H-12′a, H-20′), 1.63–1.43 (m, 7H, H-2′b, H-8′, H-11′a, H-15′b, H-17′, H-23′), 1.42–1.37 (m, 1H, H-11′b), 1.36–1.29 (m, 2H, H-24′), 1.29–1.25 (m, 1H, H-7′b), 1.16–1.04 (m, 3H, H-1′b, H-12′b, H-14′), 1.01 (s, 3H, H-19′), 0.98–0.92 (m, 4H, H-9′, H-21′), 0.90 (d, 3H, J25′-26′ = 6.7 Hz, H-26′), 0.76 (s, 3H, H-18′). Minor isomer δ: 7.04–7.00 (m, 1H, NH), 6.10 (d, 1H, J5-25′ = 4.8 Hz, H-5), 2.19–2.13 (m, 1H, H-25′). 13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3) major isomer δ: 170.8 (OC=O), 168.8 (NC=O), 149.1 (C=N), 140.0 (Ar), 139.7 (C-5′), 129.2 (Ar), 122.9 (Ar), 122.5 (C-6′), 118.3 (Ar), 90.2 (C-22′), 83.4 (C-16′), 74.0 (C-3′), 73.3 (C-5), 65.1 (C-17′), 57.0 (C-14′), 50.0 (C-9′), 40.8 (C-13′), 39.5 (C-12′), 38.2 (C-4′), 38.0 (C-20′), 37.7 (C-25′), 37.1 (C-1′), 36.8 (C-10′), 32.3 (C-7′), 32.1 (C-15′), 31.6 (C-8′), 31.1 (C-23′), 29.9 (C-24′), 27.8 (C-2′), 22.6 (NCOCH3), 21.6 (OCOCH3), 20.7 (C-11′), 19.4 (C-19′), 19.0 (C-21′), 16.6 (C-18′), 12.6 (C-26′). Minor isomer δ: 171.4 (OC=O), 169.2 (NC=O), 149.4 (C=N), 129.2 (Ar), 122.8 (Ar), 118.2 (Ar), 90.0 (C-22′), 83.3 (C-16′), 73.2 (C-5), 65.0 (C-17′), 38.9 (C-25′), 36.8 (C-10′), 31.0 (C-23′), 27.3 (C-24′), 18.9 (C-21′), 16.5 (C-18′), 15.7 (C-27′).
(5RS,22′R,25′R)-4-Acetyl-2-p-fluorophenylamino-5-[27′-nor-3′β-acetoxyfurost-5′-en-25′-yl]-4,5-dihydro-[1,3,4]selenadiazole (12).
The title compound 12 was prepared from 9 according to the general method to give a beige solid (56% yield from 7). Isomer ratio = 7:3. mp: 222 °C (dec.). IR : 3281, 2952, 1728, 1595, 1506, 1241, 1030 cm−1. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3, major isomer δ: 7.41–7.31 (m, 2H, Ar), 7.20–7.13 (m, 1H, NH), 7.04–6.94 (m, 2H, Ar), 6.50 (d, 1H, J5-25′ = 4.5 Hz, H-5), 5.40–5.32 (m, 1H, H-6′), 4.65–4.54 (m, 1H, H-3′), 4.32–4.21 (m, 1H, H-16′), 3.33–3.21 (m, 1H, H-22′), 2.38–2.27 (m, 5H, NCOCH3, H-4′), 2.24–2.18 (m, 1H, H-25′), 2.03 (s, 3H, OCOCH3), 2.00–1.89 (m, 2H, H-7′a, H-15′a), 1.87–1.81 (m, 2H, H-1′a, H-2′a), 1.74–1.65 (m, 2H, H-12′a, H-20′), 1.64–1.46 (m, 7H, H-2′b, H-8′, H-11′a, H-15′b, H-17′, H-23′), 1.44–1.34 (m, 1H, H-11′b), 1.34–1.20 (m, 3H, H-7′b, H-24′), 1.15–1.04 (m, 3H, H-1′b, H-12′b, H-14′), 1.02 (s, 3H, H-19′), 0.98–0.91 (m, 4H, H-9′, H-21′), 0.90–0.86 (m, 3H, H-26), 0.77 (s, 3H, H-18), minor diastereomer δ: 6.44 (d, 1H, J5-25′ = 5.3 Hz, H-5), 2.14–2.09 (m, 1H, H-25). 13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3) major isomer δ: 170.8 (OC=O), 169.0 (NC=O), 158.7 (d, 1JC, F = 242.5 Hz, Ar), 145.4 (C=N), 139.8 (C-5′),136.6 (Ar), 122.5 (C-6′), 120.2 (d, 3JC,F = 7.7 Hz, Ar), 115.9 (d, 2JC,F = 22.6 Hz, Ar), 90.3 (C-22′), 83.4 (C-16′), 74.1 (C-3′), 73.7 (C-5), 65.0 (C-17′), 57.0 (C-14′), 50.1 (C-9′), 40.8 (C-13′), 39.5 (C-12′), 38.2 (C-25′), 38.2 (C-4′), 38.0 (C-20′), 37.1 (C-1′), 36.8 (C-10′), 32.3 (C-7′), 32.1 (C-15′), 31.6 (C-8′), 31.1 (C-23′), 30.8 (C-24′), 27.8 (C-2′), 23.1 (NCOCH3), 21.6 (OCOCH3), 20.7 (C-11′), 19.5 (C-19′), 19.0 (C-21′), 16.6 (C-18′), 13.8 (C-26′), minor isomer δ: 169.4 (NC=O), 158.6 (d, 2JC,F = 242.9 Hz, Ar), 145.9 (C=N), 139.7 (C-5′), 120.0 (d, 3JC,F = 7.8 Hz, Ar), 115.8 (d, 2JC,F = 22.4 Hz, Ar), 73.3 (C-5), 39.3 (C-25′), 30.9 (C-23′), 28.3 (C-24′), 18.9 (C-21′), 14.0 (C-26′).
(5RS,22′R,25′R)-4-Acetyl-2-p-metylphenylamino-5-[27′-nor-3′β-acetoxyfurost-5′-en-25′-yl]-4,5-dihydro-[1,3,4]selenadiazole (13).
Compound
5 was acylated under standard conditions [
29], then proceeded according to the general method to give a yellowish solid (49% two steps). Isomer ratio: 1:1. mp: 231 °C (dec.). IR
: 3284, 2934, 1731, 1661, 1601, 1245, 1034 cm
−1.
1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl
3) δ: 7.29–7.25 (m, 2H, Ar), 7.24–7.20 (m, 2H, Ar), 7.14–7.09 (m, 2H, Ar), 7.09–7.03 (m, 2H, Ar), 6.52, 6.12 (d each, 1H each,
J5-25′ = 4.7 Hz,
J5-25′ = 4.0 Hz, H-5′), 5.40–5.33 (m, 2H, H-6′), 4.64–4.54 (m, 2H, H-3′), 4.32–4.24 (m, 2H, H-16′), 3.32–3.23 (m, 2H, H-22′), 2.41 (s, 3H, PhCH
3), 2.36–2.30 (m, 5H, H-4′, PhCH
3), 2.29 (s, 3H, NCOCH
3), 2.25–2.15 (m, 2H, H-25′), 2.03 (s, 3H, OCOCH
3), 2.02–1.97 (m, 4H, H-7′a, H-15′a), 1.96 (s, 3H, OCOCH
3), 1.90 (s, 3H, NCOCH
3), 1.88–1.82 (m, 4H, H-1′a, H-2′a), 1.74–1.68 (m, 4H, H-1′a, H-20′), 1.63–1.44 (m, 16H, H-2′b, H-8′, H-11′, H-15′b, H-17′, H-23′), 1.26–1.23 (m, 4H, H-24′), 1.13–1.05 (m, 3H, H-1′b, H-12′b, H-14′), 1.03 (s, 6H, H-19), 0.98 (d, 6H,
J20′-21′ = 6.8 Hz, H-21′), 0.95–0.91 (m, 2H, H-9′), 0.90, 0.82 (d each, 3H each,
J25′-26′ = 6.7 Hz,
J25′-26′ = 6.5 Hz, H-26′), 0.78 (s, 6H, H-18′).
13C-NMR (126 MHz, CDCl
3) δ: 170.9 (OC=O), 170.7 (OC=O), 170.0 (NC=O), 168.9 (NC=O), 145.7 (C=N), 145.1 (C=N), 139.8 (C-5′), 139.3 (Ar), 137.8 (Ar), 137.4 (Ar), 133.1 (Ar), 130.6 (Ar), 129.8 (Ar), 128.0 (Ar), 122.6 and 122.5 (C-6′), 119.1 (Ar), 90.2 and 90.1 (C-22′), 83.4 (C-16′), 74.0 (C-3′), 73.7 and 69.6 (C-5), 65.3 and 65.2 (C-17′), 57.0 (C-14′), 50.1 (C-9′), 40.8 (C-13′), 39.5 (C-12′), 38.2 (C-4′), 38.0 (C-20′), 37.9 (C-25′), 37.1 (C-1′), 36.8 (C-10′), 36.7 (C-25′), 32.3 (C-7′), 32.1 (C-15′), 31.7 (C-8′), 30.9 and 29.9 (C-24′), 30.7 (C-23′), 27.9 (C-2′), 23.8 and 21.6 (OCOCH
3), 23.0 and 22.5 (NCOCH
3), 21.4 and 20.9 (PhCH
3), 20.8 (C-11′), 19.5 (C-19′), 19.1 (C-21′), 16.6 (C-18′), 14.0 and 13.4 (C-26′).
(5″RS)-N, N′-bis-(4″-Acetyl-5″-(27‴-nor-3‴β-acetoxy-(22‴R,25‴R)-furost-5‴-en-25‴-yl)-4″,5″-dihydro-[1″,3″,4″]thiadiazol-2″-yl)-p-phenylendiamine (15).
The title compound 15 was prepared from 14 according to the general method to give a white foam in 71%. Isomer ratio: 7:3. IR : 3279, 2947, 1728, 1597, 1511, 1247, 1032 cm−1. 1H-NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) major isomer δ: 7.38–7.27 (m, 4H, Ar), 6.20–6.12 (m, 1H, H-5″), 5.38–5.30 (m, 2H, H-6), 4.64–4.52 (m, 2H, H-3‴), 4.33–4.20 (m, 2H, H-16‴), 3.33–3.20 (m, 2H, H-22‴), 2.34–2.26 (m, 12H, NCOCH3, H-4‴, H-25‴), 2.03 (s, 6H, OCOCH3), 2.00–1.89 (m, 4H, H-7‴a, H-15‴a), 1.85–1.78 (m, 4H, H-2‴a, H-1‴a), 1.75–1.67 (m, 4H, H-20‴, H-12‴a), 1.63–1.45 (m, 14H, H-17‴, H-23‴, H-2‴b, H-8‴, H-15‴b, H-11‴a), 1.43–1.36 (m, 2H, H-11‴b), 1.35–1.29 (m, 2H, H-24‴a), 1.28–1.22 (m, 4H, H-7‴b, H-24‴b), 1.14–1.03 (m, 6H, H-1‴b, H-12‴b, H-14‴), 1.02–0.98 (m, 6H, H-19‴), 0.97–0.93 (m, 6H, H-21‴), 0.92–0.85 (m, 8H, H-9‴, H-26‴), 0.77 (s, 3H, H-18‴), minor isomer δ: 6.08 (d, 1H, J = 4.6 Hz, H-5″), 0.75 (s, 3H, H-18‴). 13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3) major isomer δ: 170.8 (OC=O), 168.5 (NC=O), 149.3 (C=N), 139.6 (C-5), 135.2 (Ar), 122.4 (C-6‴), 119.2 (Ar), 90.2 (C-22‴), 83.3 (C-16‴), 74.0 (C-3‴), 73.2 (C-5″), 64.8 (C-17‴), 56.8 (C-14‴), 49.9 (C-9‴), 40.7 (C-13‴), 39.3 (C-12‴), 38.1 (C-4‴), 37.9 (C-20‴), 37.6 (C-25‴), 37.0 (C-1‴), 36.7 (C-10‴), 32.2 (C-7‴), 32.0 (C-15‴), 31.5 (C-8‴), 31.0 (C-23‴), 29.8 (C-24‴), 27.7 (C-2‴), 22.6 (NCOCH3), 21.6 (OCOCH3), 20.6 (C-11‴), 19.4 (C-19‴), 18.9 (C-21‴), 16.5 (C-18‴), 12.4 (C-26‴), minor isomer δ: 168.6 (NC=O), 135.0 (Ar), 119.0 (Ar), 90.4 (C-22‴), 73.1 (C-5″), 64.7 (C-17‴), 38.6 (C-25‴), 36.7 (C-10‴), 29.9 (C-24‴), 22.8 (NCOCH3), 19.3 (C-19‴), 18.8 (C-21‴), 15.6 (C-26‴).
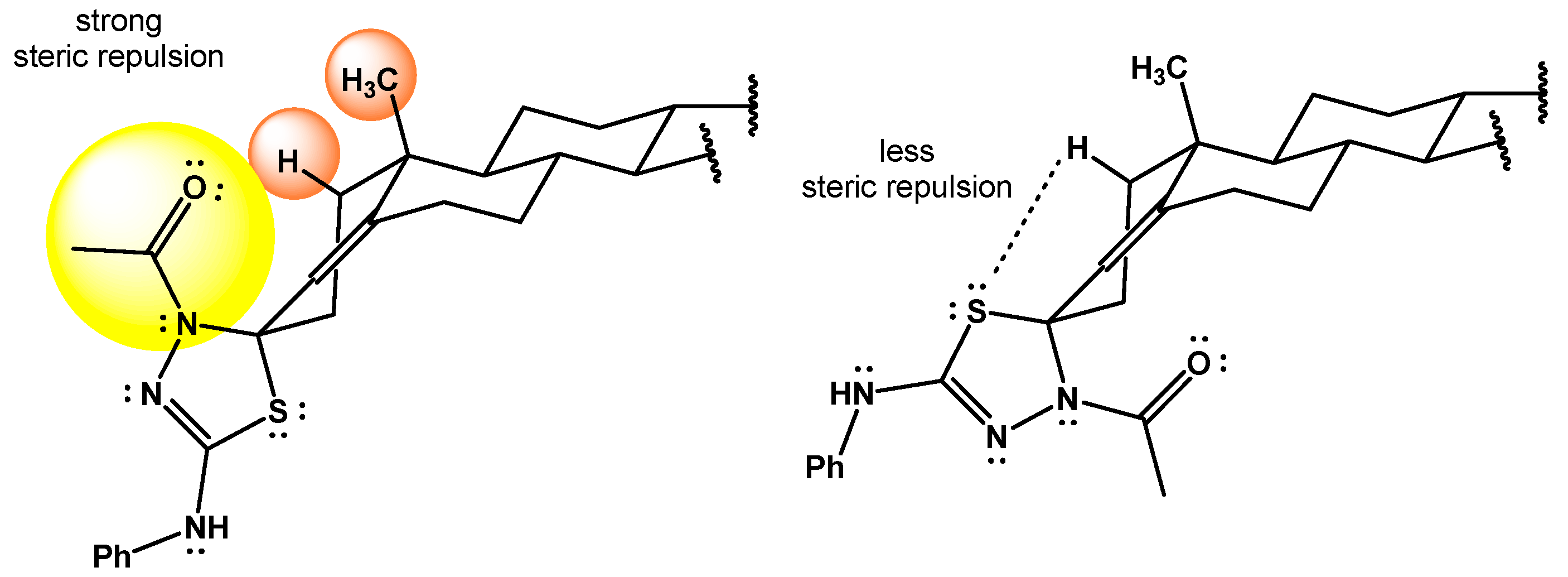
(3′ξ-22′R,25′R)-4-Acetyl-2-phenylamino-spiro[spirost-4′-en-3′,5-[1,3,4]-thiadiazoline] (18).
The title compound 18 was prepared from 17 (26 mg, 0.043 mmol), pyridine (14 mL, 0.17 mmol), and Ac2O (16 mL, 0.17 mmol) for 2 h according to the general method to give a colorless oil in 69%. IR : 3193, 2923, 2852, 1598, 1560, 1051 cm−1. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 7.37–7.27 (m, 4H, Ar), 7.09–6.98 (m, 1H, Ar), 6.44–6.28 (m, 1H, NH), 5.59 (s, 1H, H-4′), 4.42–4.36 (m, 1H, H-16′), 3.50–3.44 (m, 1H, H-26′a), 3.37 (t, 1H, J26′a-26′b = J25′-26′b = 11.0 Hz, H-26′b), 2.85 (td, 1H, J2′a-2′b = J1′a-2a’ = 13.8 Hz, J1′b-2′a = 2.6 Hz, H-2′a), 2.31–2.20 (m, 4H, NAc, H-6′a), 2.15–2.03 (m, 2H, H-2′b, H-6′b), 2.01–1.95 (m, 1H, H-15′a), 1.91–1.83 (m, 2H, H-1′a, H-20′), 1.79–1.70 (m, 3H, H-17′, H-7′a, H-12′a), 1.68–1.56 (m, 5H, H-8′, H-23′a, H-23′b, H-24′a, H-25′), 1.52–1.32 (m, 4H, H-1′b, H-11′a, H-11′b, H-24′b,), 1.30–1.26 (m, 1H, H-15′b), 1.17–1.04 (m, 5H, H-12′b, H-14′, H-19′), 0.96 (d, 3H, J20′-21′ = 7.0 Hz, H-21′), 0.90–0.86 (m, 1H, H-7′b), 0.80–0.77 (m, 6H, H-18′, H-27′), 0.76–0.69 (m, 1H, H-9′). 13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 168.4 (C=O), 146.6 (C-5′), 145.8 (C=N), 139.8 (Ar), 129.3 (Ar), 123.0 (Ar), 120.0 (C-4′), 118.4 (Ar), 109.5 (C-22′), 83.8 (C-3′), 80.9 (C-16′), 67.0 (C-26′), 62.2 (C-17′), 56.0 (C-14′), 54.4 (C-9′), 41.7 (C-20′), 40.6 (C-13′), 40.0 (C-12′), 37.2 (C-10′), 35.9 (C-1′), 35.5 (C-8′), 32.6 (C-7′), 32.0 (C-6′), 31.8 (C-15′), 31.5 (C-2′, C-23′), 30.4 (C-25′), 28.9 (C-24′), 24.4 (COCH3), 21.1 (C-11′), 17.9 (C-19′), 17.3 (C-27′), 16.5 (C-18′), 14.6 (C-21′).
(17′RS)-4-Acetyl-2-acetylamino-spiro-[3′-acetoxyestra-1′,3′,5′(10′)-trien-17′,5-[1,3,4]-thiadiazoline] (21).
The title compound 21 was prepared from the condensation of 19 (150 mg, 0.55 mmol) and TSC (61 mg, 0.67 mmol) in 20 mL of EtOH for 15 h reflux and 2 d at r.t. to give the intermediate 20. The whole resulting crude 20 was dissolved in Ac2O (3 mL), stirred, and heated at 100 °C for 3 h. After completion of the reaction, the mixture was allowed to reach r.t., and cold water was added, and the precipitate was filtered. The collected solid was dried under reduced pressure to give a residue, which was purified by silica gel chromatography to give an isomeric mixture as white foam (91%). Column chromatography (85:15 hexane/ethyl acetate). Isomer ratio: 1:1. IR : 3224, 3164, 2929, 2863, 1762, 1607, 1369, 1206 cm−1. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 10.35–9.90 (m, 1H, NH), 7.19 and 7.14 (d each, 1H each, J1′-2′ = 8.5 Hz, J1′-2′ = 8.2 Hz, H-1′), 6.84–6.78 (m, 2H, H-2′), 6.78–6.74 (m, 2H, H-4′), 4.48–4.36 (m, 1H, H-16′a), 3.09 (ddd, 1H, J16′a-16′b = 14.2 Hz, J16′a-15′a = 8.6 Hz, J16′a-15′b = 4.9 Hz, H-16′a), 2.90–2.76 (m, 4H, H-6′), 2.34–2.29 (m, 1H, H-16′b), 2.29–2.05 (m, 24H, OAc, NAc, NHAc, H-11′a, H-9′, H-16′b, H-15′a), 1.99 (td, 1H, J12′a-12′b = J12′a -11′a = 12.7 Hz, J12′a -11′b = 4.2 Hz, H-12′a), 1.93–1.84 (m, 3H, H-7′a, H-14′), 1.83–1.73 (m, 1H, H-15′a), 1.65–1.59 (m, 1H, H-12′a), 1.59–1.53 (m, 1H, H-12′b), 1.50–1.26 (m, 10H, H-7′b, H-8′, H-11′b, H-12′b, H-14′, H-15′b,), 0.94 (s, 3H, H-18′), 0.85 (s, 3H, H-18′). 13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3) δ: 171.5 and 171.0 (NC=O), 170.0 × 2 (OC=O), 169.4 × 2 (NHC=O), 148.3 × 2 (C-3), 148.1 and 147.8 (C=N), 138.1 and 138.0 (C-5), 137.5 and 137.4 (C-10), 126.2 and 126.1 (C-1), 121.5 and 121.4 (C-4), 118.6 and 118.5 (C-2), 92.6 and 91.7 (C-17), 52.8 and 51.9 (C-13), 49.3 and 46.2 (C-14), 43.2 × 2 (C-9), 39.4 and 38.6 (C-8), 31.8 and 31.6 (C-12), 30.6 and 29.8 (C-16), 29.4 and 29.3 (C-6), 27.5 and 27.0 (C-7), 25.9 × 2 (C-11), 24.9 and 24.8 (NCOCH3), 24.6 and 22.9 (C-15), 23.1 and 23.0 (NHCOCH3), 21.1 × 2 (OCOCH3), 15.1 and 14.8 (C-18). HRFAB-MS m/z calcd. for C25H32N3O4S [M + H]+: 470.2114, found: 470.2147.
(17RS)-4-Acetyl-2-phenylamino-spiro-[3′-acetoxyestra-1′,3′,5′(10′)-trien-17′,5-[1,3,4]-thiadiazoline] (23).
The title compound 23 was prepared from 22 (100 mg, 0.24 mmol), pyridine (96 mL, 1.19 mmol), and Ac2O (112 mL, 1.19 mmol) for 11.5 h according to the general method to give a yellowish foam in 71% yield. Isomer ratio: 3:2. IR : 3278, 3200, 2921, 2852, 1763, 1595, 1376, 1206 cm−1. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) major isomer δ: 7.44–7.38 (m, 2H, Ar), 7.34–7.29 (m, 2H, Ar), 7.22 (d, 1H, J1′-2′ = 8.6 Hz, H-1′), 7.06–7.02 (m, 1H, Ar), 6.82 (dd, 1H, J2′-4′ = 2.4 Hz, H-2′), 6.76 (d, 1H, H-4′), 3.21 (ddd, 1H, J16′a-16′b = 14.9 Hz, J16′a-15′a = 9.1 Hz, J16′a-15′b = 4.5 Hz, H-16′a), 2.91–2.76 (m, 2H, H-6′), 2.40–2.32 (m, 4H, NAc, H-16′b), 2.32–2.25 (m, 4H, H-11′a, OAc), 2.24–2.15 (m, 2H, H-9′, H-15′a), 1.99–1.87 (m, 2H, H-7′a, H-14′), 1.68 (dt, 1H, J12a-12b = 12.1 Hz, J12a -11a = J12a -11b = 3.3 Hz, H-12′a), 1.55–1.38 (m, 4H, H-7′b, H-8, H-11′b, H-12′b), 1.34–1.28 (m, 1H, H-15′b), 0.88 (s, 3H, H-18). Minor isomer δ: 7.22 (d, 1H, J1′-2′ = 8.5 Hz, H-1′), 6.78 (d, 1H, J2′-4′ = 2.4 Hz, H-4′), 4.63 (ddd, 1H, J16′a-16′b = 15.3 Hz, J15a’-16a’ = 11.7 Hz, J15′b-16′a = 3.4 Hz, H-16′a), 2.24–2.15 (m, 1H, H-16′b), 1.99–1.87 (m, 2H, H-7′a, H-12′), 1.83–1.79 (m, 1H, H-15a’), 1.78–1.74 (m, 1H, H-12′), 1.55–1.38 (m, 2H, H-14′, H-15′b), 1.34–1.28 (m, 1H, H-7′b), 1.03 (s, 3H, H-18′). 13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3) major isomer δ: 170.3 (NC=O), 170.1 (OC=O), 148.8 (C=N), 148.4 (C-3′), 140.0 (Ar), 138.5 (Ar), 138.0 (Ar), 129.2 (Ar), 126.4 (C-1′), 122.8 (ArC), 121.6 (C-4′), 118.6 (C-2′), 118.3 (Ar), 94.4 (C-17′), 53.0 (C-13′), 49.0 (C-14′), 43.3 (C-9′), 39.9 (C-8′), 32.4 (C-12′), 30.1 (C-16′), 29.6 (C-6′), 27.5 (C-7′), 26.3 (C-11′), 25.5 (NCOCH3), 24.7 (C-15′), 21.3 (OCOCH3), 15.6 (C-18′), Minor isomer δ: 170.7 (NC=O), 148.9 (C=N), 148.5 (C-3′), 138.2 (Ar), 137.6 (Ar), 126.5 (C-1′), 121.6 (C-4′), 118.7 (C-2′), 118.2 (Ar), 95.8 (C-17′), 52.3 (C-13′), 47.0 (C-14′), 43.7 (C-9′), 38.8 (C-8′), 32.3 (C-12′), 29.5 (C-6′), 29.5 (C-16′), 27.3 (C-7′), 26.1 (C-11′), 25.7 (NCOCH3), 23.2 (C-15′), 15.2 (C-18′).
The title compound 26 was prepared from 24 (240 mg, 0.70 mmol), and TSC (76 mg, 0.84 mmol) in 25 mL of EtOH for 4 h reflux and 4 d at r.t to give the intermediate 25. The resulting crude 25 was dissolved in Ac2O (5 mL), stirred, and heated at 90 °C for 2 h. After completion of the reaction, the mixture was allowed to reach r.t., cold water was added, and the precipitate was filtered. The collected solid was dried under reduced pressure to give a residue, which was purified by silica gel chromatography to give the isomeric mixture as a white foam in 89% yield. Isomer ratio: 8:2. Column chromatography (8:2 hexane/ethyl acetate). IR : 3158, 2927, 2851, 1732, 1610, 1376, 1237 cm−1. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) major isomer δ: 9.69–9.35 (m, 1H, NH), 4.69–4.57 (m, 1H, H-3′), 3.00 (ddd, 1H, J16′a-16′b = 15.1 Hz, J16′a-15′a = 9.3 Hz, J16′a-15b = 4.9 Hz, H-16′a), 2.21 (ddd, 1H, J16′b-15′a = 11.3 Hz, J16′b-15′b = 3.7 Hz, H-16′b), 2.18–2.14 (m, 6H, 2xNAc), 1.99 (s, 3H, OAc), 1.96–1.91 (m, 1H, H-15′a), 1.80–1.73 (m, 1H, H-2′a), 1.70–1.59 (m, 3H, H-1′a, H-7′a, H-14′), 1.58–1.48 (m, 2H, H-4′a, H-11′a), 1.47–1.38 (m, 2H, H-2′b, H-12′a), 1.38–1.27 (m, 2H, H-4′b, H-8′), 1.26–1.03 (m, 6H, H-5′, H-6′, H-11′b, H-12′b, H-15′b), 1.00–0.88 (m, 2H, H-1′, H-7′b), 0.78 (s, 3H, H-18′), 0.77 (s, 3H, H-19′), 0.66–0.55 (m, 1H, H-9′), minor isomer δ: 9.88–9.75 (m, 1H, NH), 4.33 (ddd, 1H, J16′a-16′b = 15.1 Hz, J16′a-15′a = 11.7 Hz, J16′a-15′b = 3.4 Hz, H-16′a), 2.08–2.03 (m, 1H, H-16′b), 1.26–1.03 (m, 1H, H-14′), 0.85 (s, 3H, H-18′). 13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3) major isomer δ: 171.0 (OC=O), 170.8 (NC=O), 169.1 (NHC=O), 147.6 (C=N), 92.1 (C-17′), 73.7 (C-3′), 53.5 (C-9′), 52.8 (C-13′), 50.1 (C-14′), 44.6 (C-5′), 36.7 (C-1′), 36.7 (C-8′), 35.5 (C-10′), 33.9 (C-4′), 31.9 (C-12′, C-7′), 30.8 (C-16′), 28.5 (C-6′), 27.4 (C-2′), 25.0 (C-15′), 24.9 (NCOCH3), 23.3 (NCOCH3), 21.5 (OCOCH3), 20.9 (C-11′), 15.1 (C-18′), 12.2 (C-19′). Minor isomer δ: 170.0 (NC=O), 169.3 (NHC=O), 147.8 (C=N), 93.0 (C-17′), 51.9 (C-13′), 47.1 (C-14′), 44.5 (C-5′), 35.8 (C-8′), 35.5 (C-10′), 31.6 (C-12′), 29.9 (C-16′), 28.4 (C-6′), 24.0 (NCOCH3), 15.2 (C-18′), 12.3 (C-19′).
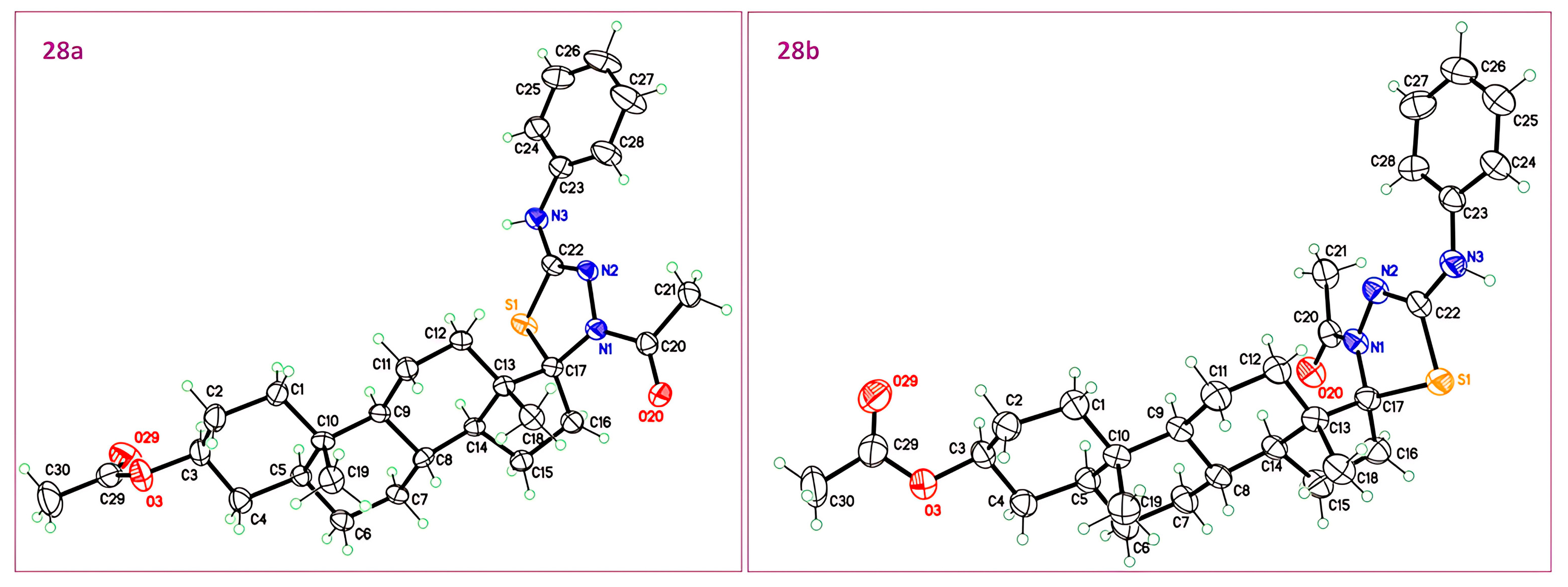
The mixture of epimers 28a and 28b was prepared from 27 (100 mg, 0.24 mmol), pyridine (78 mL, 0.96 mmol), and Ac2O (90 mL, 0.96 mmol) for 24 h according to the general method to give a yellowish solid in 60%. Two fractions were dissolved in two different solvent systems, hexane/ethyl acetate and hexane/ethyl acetate/Et2O/pyridine, and in both cases, colorless crystals were obtained by slow evaporation of their solution at r.t. without separation of the isomers. Isomer ratio: 6:4. IR : 3277, 2932, 2855, 1732, 1596, 1379, 1240 cm−1. 1H NMR (500 MHz, CDCl3) major isomer δ: 7.40–7.34 (m, 2H, Ar), 7.34–7.28 (m, 2H, Ar), 7.07–7.00 (m, 1H, Ar), 6.39–6.31 (m, 1H, NH), 4.71–4.61 (m, 1H, H-3), 3.13 (ddd, 1H, J16′a-16′b = 15.0 Hz, J16′a-15′a = 9.3 Hz, J16′a-15′b = 4.7 Hz, H-16′a), 2.33 (s, 3H, NAc), 2.27 (ddd, 1H, J16′b-15′a = 11.2 Hz, J16′b-15′b = 3.6 Hz, H-16′b), 2.08–2.03 (m, 1H, H-15′), 2.01 (s, 3H, OAc), 1.83–1.76 (m, 1H, H-2′a), 1.74–1.65 (m, 4H, H-1′a, H-7′a, H-14′, H-15′), 1.61–1.31 (m, 6H, H-2′b, H-4′, H-8′, H-11′a, H-12′a), 1.31–1.10 (m, 6H, H-5′, H-6′, H-11′b, H-12′b, H-15′), 1.07–0.97 (m, 2H, H-1′b, H-7′b), 0.82 (s, 3H, H-18′), 0.80 (s, 3H, H-19′), 0.70–0.60 (m, 1H, H-9′). Minor isomer δ: 4.54 (ddd, 1H, J16′a-16′b = 15.4 Hz, J16′a-15′a = 11.9 Hz, J16′a-15′b = 3.2 Hz, H16′a), 2.34 (s, 3H, NAc), 2.15–2.09 (m, 1H, H-16′b), 2.02 (s, 3H, OAc), 1.74–1.65 (m, 1H, H-7′a), 1.61–1.31 (m, 1H, H-15′), 1.31–1.10 (m, 1H, H-14′), 0.96 (s, 3H, H-18′), 0.93–0.87 (m, 1H, H-7′b), 0.81 (s, 3H, H-19′). 13C NMR (126 MHz, CDCl3) major isomer δ: 170.9 (OC=O), 170.1 (NC=O), 148.5 (C=N), 139.8 (Ar), 129.3 (Ar), 123.0 (Ar), 118.3 (Ar), 94.9 (C-17′), 73.8 (C-3′), 53.4 (C-9′), 52.9 (C-13′), 49.8 (C-14′), 44.6 (C-5′), 37.0 (C-8′), 36.8 (C-1′), 35.6 (C-10′), 34.1 (C-4′), 32.4 (C-12′), 31.9 (C-7′), 30.1 (C-16′), 28.6 (C-6′), 27.5 (C-2′), 25.5 (NCOCH3), 25.0 (C-15′), 21.6 (OCOCH3), 21.1 (C-11′), 15.7 (C-18′), 12.3 (C-19′). Minor diastereomer δ: 171.0 (OC=O), 170.6 (NC=O), 148.8 (C=N), 139.8 (Ar), 129.3 (Ar), 123.0 (Ar), 118.2 (Ar), 96.4 (C-17′), 73.8 (C-3′), 54.0 (C-9′), 52.2 (C-13′), 47.9 (C-14′), 44.7 (C-5′), 36.9 (C-1′), 36.0 (C-8′), 35.6 (C-10′), 34.1 (C-4′), 32.3 (C-12′), 31.8 (C-7′), 29.4 (C-16′), 28.5 (C-6′), 25.7 (NCOCH3), 23.4 (C-15′), 20.9 (C-11′), 15.2 (C-18′), 12.4 (C-19′).